

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 79-92.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.00079 cstr: 32111.14.2021.00079
收稿日期:2020-05-14
出版日期:2021-01-15
发布日期:2020-11-23
GUO Ying1, GONG Xianmin2, WANG Dahua1( )
)
Received:2020-05-14
Online:2021-01-15
Published:2020-11-23
摘要:
采用信息加工视角, 在划分不同信息来源的基础上分析编码、存储(巩固)、再激活/再巩固和提取的一系列加工过程如何导致错误记忆形成, 由此总结出错误记忆产生的三个可能原因:(1)因缺乏针对目标事物特异性细节的记忆表征而侧重于编码和提取目标和非目标事物共享的抽象记忆表征, 使被试更倾向于依赖抽象表征对缺失的目标细节进行重构, 引发错误记忆; (2)目标事物启动了对应图式, 导致与图式相关的非目标事物记忆表征得到增强, 引发错误记忆; (3)误导信息干扰了再度激活状态下目标事物的记忆表征, 妨碍其进行准确的记忆再巩固, 从而引发错误记忆。未来研究可进一步探讨目标事物特异性细节的表征区域、不同类型的图式表征促进非目标事物记忆表征的具体机制以及提取阶段的图式复现对错误记忆形成的影响等问题。
中图分类号:
郭滢, 龚先旻, 王大华. (2021). 错误记忆产生的认知与神经机制:信息加工视角. 心理科学进展 , 29(1), 79-92.
GUO Ying, GONG Xianmin, WANG Dahua. (2021). The cognitive and neural mechanisms underlying false memory: An information processing perspective. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(1), 79-92.
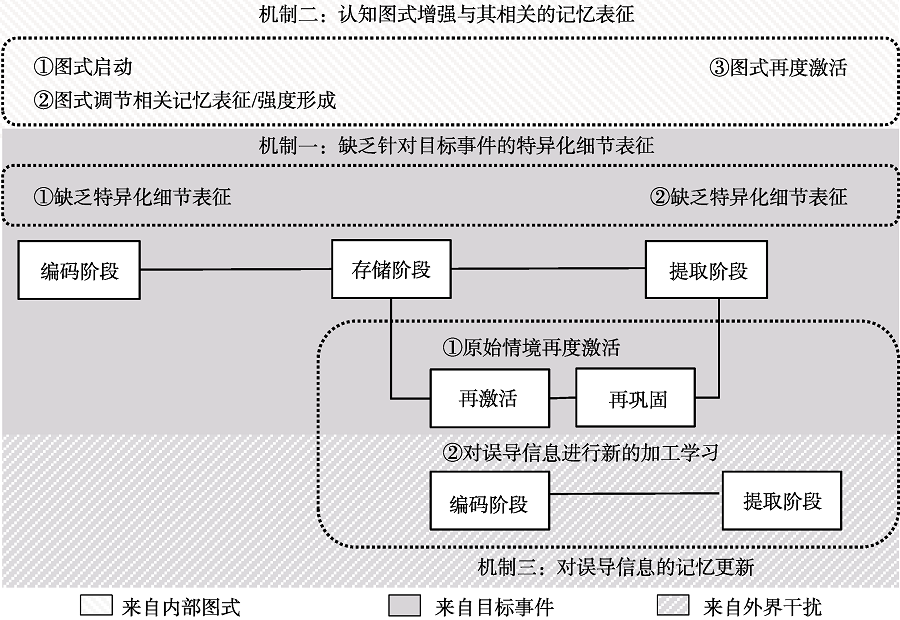
图1 信息加工视角下错误记忆产生机制的示意图 注:各灰色背景框代表不同的信息来源(来自目标事件、内部图式和外界干扰); 各白色方框代表不同的信息加工过程(编码、存储、再激活/再巩固和提取); 各虚线方框代表错误记忆产生的可能机制, 每条机制着重描述某一来源信息的各加工过程, 由①②③代表, 且它的发生阶段与下方的白色方框相对应。三条机制相互独立, 又彼此联系1(1 三种机制之间既相互独立, 又彼此联系。其中, 独立体现在:每条机制都对应着不同的信息来源, 并与不同种类的错误记忆形成有关, 比如机制2可以用来解释关联性错误记忆的形成, 而机制3可以用来解释植入性错误记忆的形成。联系体现在:正确记忆形成相关的机制1与错误记忆形成相关的机制2和机制3通常共同发生。不论是关联性错误记忆, 还是植入性错误记忆都缺乏针对目标事件的特异化细节表征。另外, 机制1与机制2、机制1与机制3间还存在相互影响的可能。如机制2中图式对特异性细节的抑制作用(如van der Linden et al., 2017)以及机制3中误导信息与特异性细节间的相互竞争(如Okado & Stark, 2005)。), 共同导致错误记忆的发生。有必要进行说明的是, 机制3虽着重描述对外界干扰的信息加工, 但同样涉及对目标事件的信息加工, 因此代表机制3的虚线方框同时呈现在两种灰色背景框之上。
| [1] | 陈红, 郭春彦, 杨海波. (2015). 延迟间隔和提取条件对短时错误记忆的影响. 心理与行为研究, 13(1), 37-43. |
| [2] | 江荣焕, 李晓东. (2015). 错误记忆的发展性逆转: 为什么越长大越易“错”? 心理科学进展, 23(8), 1371-1379. |
| [3] | 雷威, 杨志, 詹旻野, 李红, 翁旭初. (2010). 利用脑成像多体素模式分析解码认知的神经表征: 原理和应用. 心理科学进展, 18(12), 1934-1941. |
| [4] | 刘振亮, 刘田田, 韩佳慧, 沐守宽. (2015). 错误记忆的可植入性. 心理科学进展, 23(5), 806-814. |
| [5] | 王密, 耿海燕. (2010). 从关联性记忆错觉的毕生发展看记忆的适应性特质. 科学通报, 55(4), 307-315. |
| [6] |
Addis, D. R., & McAndrews, M. P. (2006). Prefrontal and hippocampal contributions to the generation and binding of semantic associations during successful encoding. Neuroimage, 33(4), 1194-1206.
URL pmid: 17023179 |
| [7] |
Aminoff, E., Schacter, D. L., & Bar, M. (2008). The cortical underpinnings of context-based memory distortion. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(12), 2226-2237.
URL pmid: 18457503 |
| [8] |
Baldassano, C., Chen, J., Zadbood, A., Pillow, J. W., Hasson, U., & Norman, K. A. (2017). Discovering event structure in continuous narrative perception and memory. Neuron, 95(3), 709-721.
URL pmid: 28772125 |
| [9] |
Baldassano, C., Hasson, U., & Norman, K. A. (2018). Representation of real-world event schemas during narrative perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 38(45), 9689-9699.
URL pmid: 30249790 |
| [10] | Baym, C. L., & Gonsalves, B. D. (2010). Comparison of neural activity that leads to true memories, false memories, and forgetting: An fMRI study of the misinformation effect. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 10(3), 339-348. |
| [11] |
Berkers, R. M. W. J., van der Linden, M., de Almeida, R. F., Müller, N. C. J., Bovy, L., Dresler, M., ... Fernández, G. (2017). Transient medial prefrontal perturbation reduces false memory formation. Cortex, 88, 42-52.
URL pmid: 28068640 |
| [12] |
Binder, J. R., & Desai, R. H. (2011). The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(11), 527-536.
URL pmid: 22001867 |
| [13] |
Bonasia, K., Sekeres, M. J., Gilboa, A., Grady, C. L., Winocur, G., & Moscovitch, M. (2018). Prior knowledge modulates the neural substrates of encoding and retrieving naturalistic events at short and long delays. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 153, 26-39.
URL pmid: 29269085 |
| [14] |
Bower, G. H., Black, J. B., & Turner, T. J. (1979). Scripts in memory for text. Cognitive Psychology, 11(2), 177-220.
doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(79)90009-4 URL |
| [15] |
Bowman, C. R., & Dennis, N. A. (2016). The neural basis of recollection rejection: Increases in hippocampal-prefrontal connectivity in the absence of a shared recall-to-reject and target recollection network. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 28(8), 1194-1209.
URL pmid: 27054401 |
| [16] |
Brainerd, C. J., & Reyna, V. F. (1993). Memory independence and memory interference in cognitive development. Psychological Review, 100(1), 42-67.
URL pmid: 8426881 |
| [17] |
Brainerd, C. J., & Reyna, V. F. (2002). Fuzzy-trace theory and false memory. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 11(5), 164-169.
doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.00192 URL |
| [18] |
Bridge, D. J., & Voss, J. L. (2014). Hippocampal binding of novel information with dominant memory traces can support both memory stability and change. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(6), 2203-2213.
URL pmid: 24501360 |
| [19] |
Cabeza, R., Rao, S. M., Wagner, A. D., Mayer, A. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2001). Can medial temporal lobe regions distinguish true from false? An event-related functional MRI study of veridical and illusory recognition memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(8), 4805-4810.
URL pmid: 11287664 |
| [20] |
Chadwick, M. J., Anjum, R. S., Kumaran, D., Schacter, D. L., Spiers, H. J., & Hassabis, D. (2016). Semantic representations in the temporal pole predict false memories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(36), 10180-10185.
URL pmid: 27551087 |
| [21] |
Chen, J., Leong, Y. C., Honey, C. J., Yong, C. H., Norman, K. A., & Hasson, U. (2017). Shared memories reveal shared structure in neural activity across individuals. Nature Neuroscience, 20(1), 115-125.
doi: 10.1038/nn.4450 URL pmid: 27918531 |
| [22] |
Chen, J., Olsen, R. K., Preston, A. R., Glover, G. H., & Wagner, A. D. (2011). Associative retrieval processes in the human medial temporal lobe: Hippocampal retrieval success and CA1 mismatch detection. Learning & Memory, 18(8), 523-528.
URL pmid: 21775513 |
| [23] |
Cooper, R. A., & Ritchey, M. (2020). Progression from feature-specific brain activity to hippocampal binding during episodic encoding. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(8), 1701-1709.
URL pmid: 31826947 |
| [24] |
Davis, T., & Poldrack, R. A. (2013). Measuring neural representations with fMRI: practices and pitfalls. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1296(1), 108-134.
doi: 10.1111/nyas.12156 URL |
| [25] | Dennis, N. A., Bowman, C. R., & Turney, I. C. (2015). Functional neuroimaging of false memories. In D. R. Addis, M. Barense & A. Duarte (Eds.), The Wiley Handbook on the Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory (pp. 150-171). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. |
| [26] |
Dennis, N. A., Kim, H., & Cabeza, R. (2008). Age-related differences in brain activity during true and false memory retrieval. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 20(8), 1390-1402.
URL pmid: 18303982 |
| [27] |
Doss, M. K., Picart, J. K., & Gallo, D. A. (2018). The dark side of context: Context reinstatement can distort memory. Psychological Science, 29(6), 914-925.
URL pmid: 29671680 |
| [28] | Friedman, A. (1979). Framing pictures: the role of knowledge in automatized encoding and memory for gist. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 108(3), 316-355. |
| [29] | Gallo, D. A. (2006). Processes that cause false memory. In H. L. Roediger & J. R. Pomerantz (Eds.), Associative illusions of memory: False memory research in DRM and related tasks (pp. 39-73). New York, NY: Psychology Press. |
| [30] |
Garoff-Eaton, R. J., Kensinger, E. A., & Schacter, D. L. (2007). The neural correlates of conceptual and perceptual false recognition. Learning & Memory, 14(10), 684-692.
URL pmid: 17911372 |
| [31] |
Garoff-Eaton, R. J., Slotnick, S. D., & Schacter, D. L. (2005). The neural origins of specific and general memory: The role of the fusiform cortex. Neuropsychologia, 43(6), 847-859.
URL pmid: 15716157 |
| [32] |
Gershman, S. J., Schapiro, A. C., Hupbach, A., & Norman, K. A. (2013). Neural context reinstatement predicts memory misattribution. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(20), 8590-8595.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0096-13.2013 URL |
| [33] |
Ghosh, V. E., & Gilboa, A. (2014). What is a memory schema? A historical perspective on current neuroscience literature. Neuropsychologia, 53, 104-114.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.11.010 URL |
| [34] |
Ghosh, V. E., Moscovitch, M., Colella, B. M., & Gilboa, A. (2014). Schema representation in patients with ventromedial PFC lesions. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(36), 12057-12070.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0740-14.2014 URL |
| [35] |
Gilboa, A., & Marlatte, H. (2017). Neurobiology of schemas and schema-mediated memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(8), 618-631.
URL pmid: 28551107 |
| [36] |
Gilboa, A., & Moscovitch, M. (2017). Ventromedial prefrontal cortex generates pre-stimulus theta coherence desynchronization: A schema instantiation hypothesis. Cortex, 87, 16-30.
URL pmid: 27890323 |
| [37] |
Gonsalves, B., & Paller, K. A. (2000). Neural events that underlie remembering something that never happened. Nature Neuroscience, 3(12), 1316-1321.
URL pmid: 11100153 |
| [38] |
Gordon, A. M., Rissman, J., Kiani, R., & Wagner, A. D. (2014). Cortical reinstatement mediates the relationship between content-specific encoding activity and subsequent recollection decisions. Cerebral Cortex, 24(12), 3350-3364.
URL pmid: 23921785 |
| [39] |
Guerin, S. A., Robbins, C. A., Gilmore, A. W., & Schacter, D. L. (2012a). Interactions between visual attention and episodic retrieval: dissociable contributions of parietal regions during gist-based false recognition. Neuron, 75(6), 1122-1134.
URL pmid: 22998879 |
| [40] |
Guerin, S. A., Robbins, C. A., Gilmore, A. W., & Schacter, D. L. (2012b). Retrieval failure contributes to gist-based false recognition. Journal of Memory and Language, 66(1), 68-78.
URL pmid: 22125357 |
| [41] |
Hannigan, S. L., & Reinitz, M. T. (2001). A demonstration and comparison of two types of inference-based memory errors. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 27(4), 931-940.
URL pmid: 11486926 |
| [42] | Hardt, O., Einarsson, E. Ö., & Nader, K. (2010). A bridge over troubled water: Reconsolidation as a link between cognitive and neuroscientific memory research traditions. Annual Review of Psychology, 61(1), 141-167. |
| [43] |
Hupbach, A., Gomez, R., & Nadel, L. (2009). Episodic memory reconsolidation: Updating or source confusion? Memory, 17(5), 502-510.
URL pmid: 19468955 |
| [44] |
Jacques, P. L. S., Olm, C., & Schacter, D. L. (2013). Neural mechanisms of reactivation-induced updating that enhance and distort memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(49), 19671-19678.
URL pmid: 24191059 |
| [45] | Johnson, M. K., Raye, C. L., Mitchell, K. J., & Ankudowich, E. (2012). The cognitive neuroscience of true and false memories. In R. F. Belli (Ed.). True and false recovered memories: Toward a reconsolidation of the debate (pp. 15-52). New York, NY: Springer. |
| [46] |
Jonker, T. R., Dimsdale-zucker, H., Ritchey, M., Clarke, A., & Ranganath, C. (2018). Neural reactivation in parietal cortex enhances memory for episodically linked information. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(43), 11084-11089.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1800006115 URL pmid: 30297400 |
| [47] |
Kensinger, E. A., & Schacter, D. L. (2006). Neural processes underlying memory attribution on a reality-monitoring task. Cerebral Cortex, 16(8), 1126-1133.
URL pmid: 16648457 |
| [48] |
Kim, G., Lewis-Peacock, J. A., Norman, K. A., & Turk-Browne, N. B. (2014). Pruning of memories by context-based prediction error. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(24), 8997-9002.
URL pmid: 24889631 |
| [49] |
Kim, H., & Cabeza, R. (2007). Differential contributions of prefrontal, medial temporal, and sensory-perceptual regions to true and false memory formation. Cerebral Cortex, 17(9), 2143-2150.
URL pmid: 17110592 |
| [50] |
Koen, J. D., & Rugg, M. D. (2016). Memory reactivation predicts resistance to retroactive interference: evidence from multivariate classification and pattern similarity analyses. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(15), 4389-4399.
URL pmid: 27076433 |
| [51] |
Kriegeskorte, N., Mur, M., & Bandettini, P. (2008). Representational similarity analysis-connecting the branches of systems neuroscience. Frontiers in systems neuroscience, 2, 4.
URL pmid: 19104670 |
| [52] |
Kubota, Y., Toichi, M., Shimizu, M., Mason, R. A., Findling, R. L., Yamamoto, K., & Calabrese, J. R. (2006). Prefrontal hemodynamic activity predicts false memory—A near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neuroimage, 31(4), 1783-1789.
URL pmid: 16545964 |
| [53] |
Kuhl, B. A., Bainbridge, W. A., & Chun, M. M. (2012). Neural reactivation reveals mechanisms for updating memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(10), 3453-3461.
URL pmid: 22399768 |
| [54] |
Kuhl, B. A., & Chun, M. M. (2014). Successful remembering elicits event-specific activity patterns in lateral parietal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(23), 8051-8060.
URL pmid: 24899726 |
| [55] |
Kuhl, B. A., Johnson, M. K., & Chun, M. M. (2013). Dissociable neural mechanisms for goal-directed versus incidental memory reactivation. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(41), 16099-16109.
URL pmid: 24107943 |
| [56] |
Kuhl, B. A., Rissman, J., Chun, M. M., & Wagner, A. D. (2011). Fidelity of neural reactivation reveals competition between memories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(14), 5903-5908.
URL pmid: 21436044 |
| [57] |
Kuhl, B. A., Shah, A. T., DuBrow, S., & Wagner, A. D. (2010). Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning. Nature neuroscience, 13(4), 501-506.
URL pmid: 20190745 |
| [58] |
Kurkela, K. A., & Dennis, N. A. (2016). Event-related fMRI studies of false memory: An Activation Likelihood Estimation meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia, 81, 149-167.
URL pmid: 26683385 |
| [59] |
LaRocque, K. F., Smith, M. E., Carr, V. A., Witthoft, N., Grill-Spector, K., & Wagner, A. D. (2013). Global similarity and pattern separation in the human medial temporal lobe predict subsequent memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(13), 5466-5474.
URL pmid: 23536062 |
| [60] |
Lee, H. M., Samide, R., Richter, F. R., & Kuhl, B. A. (2019). Decomposing parietal memory reactivation to predict consequences of remembering. Cerebral Cortex, 29(8), 3305-3318.
URL pmid: 30137255 |
| [61] |
Lee, J. L. C. (2009). Reconsolidation: maintaining memory relevance. Trends in Neurosciences, 32(8), 413-420.
doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2009.05.002 URL pmid: 19640595 |
| [62] |
McDermott, K. B., Gilmore, A. W., Nelson, S. M., Watson, J. M., & Ojemann, J. G. (2017). The parietal memory network activates similarly for true and associative false recognition elicited via the DRM procedure. Cortex, 87, 96-107.
URL pmid: 27745847 |
| [63] |
Moritz, S., Gläscher, J., Sommer, T., Büchel, C., & Braus, D. F. (2006). Neural correlates of memory confidence. Neuroimage, 33(4), 1188-1193.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.003 URL pmid: 17029986 |
| [64] |
Norman, K. A. (2010). How hippocampus and cortex contribute to recognition memory: revisiting the complementary learning systems model. Hippocampus, 20(11), 1217-1227.
URL pmid: 20857486 |
| [65] |
Nyberg, L., Habib, R., Mcintosh, A. R., & Tulving, E. (2000). Reactivation of encoding-related brain activity during memory retrieval. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11120-11124.
URL pmid: 11005878 |
| [66] |
Okado, Y., & Stark, C. E. L. (2005). Neural activity during encoding predicts false memories created by misinformation. Learning & Memory, 12(1), 3-11.
URL pmid: 15687227 |
| [67] |
Packard, P. A., Rodríguez-Fornells, A., Bunzeck, N., Nicolás, B., de Diego-Balaguer, R., & Fuentemilla, L. (2017). Semantic congruence accelerates the onset of the neural signals of successful memory encoding. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(2), 291-301.
URL pmid: 28077709 |
| [68] |
Patterson, K., Nestor, P. J., & Rogers, T. T. (2007). Where do you know what you know? The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(12), 976-987.
URL pmid: 18026167 |
| [69] |
Pidgeon, L. M., & Morcom, A. M. (2016). Cortical pattern separation and item-specific memory encoding. Neuropsychologia, 85, 256-271.
URL pmid: 27018483 |
| [70] |
Putnam, A. L., Sungkhasettee, V. W., & Roediger III, H. L. (2017). When misinformation improves memory: The effects of recollecting change. Psychological Science, 28(1), 36-46.
URL pmid: 27879321 |
| [71] |
Richter, F. R., Cooper, R., Bays, P. M., & Simons, J. S. (2016). Distinct neural mechanisms underlie the success, precision, and vividness of episodic memory. eLife, 5, e18260.
URL pmid: 28009253 |
| [72] |
Ritvo, V. J. H., Turk-Browne, N. B., & Norman, K. A. (2019). Nonmonotonic plasticity: How memory retrieval drives learning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(9), 726-742.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2019.06.007 URL pmid: 31358438 |
| [73] |
Schacter, D. L., Guerin, S. A., & Jacques, P. L. S. (2011). Memory distortion: An adaptive perspective. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(10), 467-474.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.004 URL pmid: 21908231 |
| [74] | Schacter, D. L., Norman, K. A., & Koutstaal, W. (1998). The cognitive neuroscience of constructive memory. Annual Review of Psychology, 49(1), 289-318. |
| [75] |
Sederberg, P. B., Gershman, S. J., Polyn, S. M., & Norman, K. A. (2011). Human memory reconsolidation can be explained using the temporal context model. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 18(3), 455-468.
doi: 10.3758/s13423-011-0086-9 URL pmid: 21512839 |
| [76] |
Sekeres, M. J., Bonasia, K., St-Laurent, M., Pishdadian, S., Winocur, G., Grady, C., & Moscovitch, M. (2016). Recovering and preventing loss of detailed memory: Differential rates of forgetting for detail types in episodic memory. Learning & Memory, 23(2), 72-82.
URL pmid: 26773100 |
| [77] |
Sinclair, A. H., & Barense, M. D. (2018). Surprise and destabilize: prediction error influences episodic memory reconsolidation. Learning & Memory, 25(8), 369-381.
doi: 10.1101/lm.046912.117 URL pmid: 30012882 |
| [78] |
Sinclair, A. H., & Barense, M. D. (2019). Prediction error and memory reactivation: How incomplete reminders drive reconsolidation. Trends in Neurosciences, 42(10), 727-739.
URL pmid: 31506189 |
| [79] |
Slotnick, S. D., & Schacter, D. L. (2004). A sensory signature that distinguishes true from false memories. Nature Neuroscience, 7(6), 664-672.
URL pmid: 15156146 |
| [80] |
Sommer, T. (2017). The emergence of knowledge and how it supports the memory for novel related information. Cerebral Cortex, 27(3), 1906-1921.
URL pmid: 26908636 |
| [81] |
Spalding, K. N., Jones, S. H., Duff, M. C., Tranel, D., & Warren, D. E. (2015). Investigating the neural correlates of schemas: Ventromedial prefrontal cortex is necessary for normal schematic influence on memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(47), 15746-15751.
URL pmid: 26609165 |
| [82] |
Staresina, B. P., Henson, R. N. A., Nikolaus, K., & Arjen, A. (2012). Episodic reinstatement in the medial temporal lobe. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(50), 18150-18156.
URL pmid: 23238729 |
| [83] |
Stevenson, R. F., Reagh, Z. M., Chun, A. P., Murray, E. A., & Yassa, M. A. (2020). Pattern separation and source memory engage distinct hippocampal and neocortical regions during retrieval. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(4), 843-851.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0564-19.2019 URL pmid: 31748377 |
| [84] |
St-Laurent, M., Abdi, H., Bondad, A., & Buchsbaum, B. R. (2014). Memory reactivation in healthy aging: evidence of stimulus-specific dedifferentiation. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(12), 4175-4186.
URL pmid: 24647939 |
| [85] | Straube, B. (2012). An overview of the neuro-cognitive processes involved in the encoding, consolidation, and retrieval of true and false memories. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 8(1), 35-35. |
| [86] |
Sweegers, C. C. G., Coleman, G. A., van Poppel, E. A. M., Cox, R., & Talamini, L. M. (2015). Mental schemas hamper memory storage of goal-irrelevant information. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 629-629.
URL pmid: 26793093 |
| [87] |
van Buuren, M., Kroes, M. C. W., Wagner, I. C., Genzel, L., Morris, R. G. M., & Fernandez, G. (2014). Initial investigation of the effects of an experimentally learned schema on spatial associative memory in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(50), 16662-16670.
URL pmid: 25505319 |
| [88] |
van den Honert, R. N., McCarthy, G., & Johnson, M. K. (2016). Reactivation during encoding supports the later discrimination of similar episodic memories. Hippocampus, 26(9), 1168-1178.
URL pmid: 27082832 |
| [89] |
van der Linden, M., Berkers, R. M. W. J., Morris, R. G. M., & Fernández, G. (2017). Angular gyrus involvement at encoding and retrieval is associated with durable but less specific memories. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(39), 9474-9485.
URL pmid: 28871031 |
| [90] |
van Kesteren, M. T. R., Rijpkema, M., Ruiter, D. J., & Fernández, G. (2010). Retrieval of associative information congruent with prior knowledge is related to increased medial prefrontal activity and connectivity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(47), 15888-15894.
URL pmid: 21106827 |
| [91] |
Warren, D. E., Jones, S. H., Duff, M. C., & Tranel, D. (2014). False recall is reduced by damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex: implications for understanding the neural correlates of schematic memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(22), 7677-7682.
URL pmid: 24872571 |
| [92] |
Webb, C. E., Turney, I. C., & Dennis, N. A. (2016). What's the gist? The influence of schemas on the neural correlates underlying true and false memories. Neuropsychologia, 93, 61-75.
URL pmid: 27697593 |
| [93] |
Weinstein, Y., McDermott, K. B., & Chan, J. C. (2010). True and false memories in the DRM paradigm on a forced choice test. Memory, 18(4), 375-384.
URL pmid: 20408042 |
| [94] |
Wheeler, M. E., Petersen, S. E., & Buckner, R. L. (2000). Memory's echo: vivid remembering reactivates sensory-specific cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11125-11129.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.20.11125 URL pmid: 11005879 |
| [95] |
Wing, E. A., Geib, B. R., Wang, W. C., Monge, Z., Davis, S. W., & Cabeza, R. (2020). Cortical overlap and cortical-hippocampal interactions predict subsequent true and false memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(9), 1920-1930.
URL pmid: 31974208 |
| [96] |
Xiao, X. Q., Dong, Q., Gao, J. H., Men, W. W., Poldrack, R. A., & Xue, G. (2017). Transformed neural pattern reinstatement during episodic memory retrieval. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(11), 2986-2998.
URL pmid: 28202612 |
| [97] |
Yassa, M. A., Lacy, J. W., Stark, S. M., Albert, M. S., Gallagher, M., & Stark, C. E. L. (2011). Pattern separation deficits associated with increased hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus activity in nondemented older adults. Hippocampus, 21(9), 968-979.
URL pmid: 20865732 |
| [98] |
Ye, Z. F., Zhu, B., Zhuang, L. P., Lu, Z. L., Chen, C. S., & Xue, G. (2016). Neural global pattern similarity underlies true and false memories. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(25), 6792-6802.
URL pmid: 27335409 |
| [99] |
Zhu, B., Chen, C. S., Shao, X. H., Liu, W. Z., Ye, Z. F., Zhuang, L. P., ... Xue, G. (2019). Multiple interactive memory representations underlie the induction of false memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(9), 3466-3475.
URL pmid: 30765524 |
| [1] | 程晓荣, 仇式明, 定险峰, 范炤. 动作如何影响元认知?——基于认知模型和神经机制的探讨[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 425-438. |
| [2] | 巩芳颍, 孙逸梵, 贺琴, 石可, 刘伟, 陈宁. 教学互动中师生脑间同步性及其调节因素[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 452-464. |
| [3] | 夏熠, 张婕, 张火垠, 雷怡, 窦皓然. 焦虑个体趋避冲突失调的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 477-493. |
| [4] | 刘月月, 何文广. 书写认知老化发生机制及神经机理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(9): 1502-1513. |
| [5] | 雷怡, 梅颖, 王金霞, 袁子昕. 焦虑青少年无意识恐惧的神经机制及干预[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1221-1232. |
| [6] | 丁颖, 汪紫滢, 李卫东. 抑郁症疼痛加工的行为特点及神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1315-1327. |
| [7] | 曾庆贺, 崔晓宇, 唐为, 李娟. 记忆辨别力受老化影响的认知神经机制及其应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(7): 1138-1151. |
| [8] | 刘海宁, 董现玲, 刘海虹, 刘艳丽, 李现文. 老年遗忘型轻度认知障碍执行功能的神经机制及数字干预[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(6): 873-885. |
| [9] | 冯攀, 赵恒越, 姜雨矇, 张悦彤, 冯廷勇. 催产素影响条件化恐惧情绪加工的认知机制及神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(4): 557-567. |
| [10] | 岳佳莹, 刘欣怡, 张孟可, 陈旭. 母亲的依恋风格影响对婴儿敏感性的认知过程[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(4): 627-638. |
| [11] | 郑好, 陈荣荣, 买晓琴. 第三方惩罚行为的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(2): 398-412. |
| [12] | 孙丽君, 杨玉芳. 预期视角下音乐节拍结构的认知与神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(10): 1567-1577. |
| [13] | 曹晋菁, 仇式明, 定险峰, 程晓荣, 范炤. 意识的层级性和丰富性:解读意识的两条路径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(7): 1172-1185. |
| [14] | 王勇丽, 葛胜男, Lancy Lantin Huang, 万勤, 卢海丹. 言语想象的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(4): 608-621. |
| [15] | 孔祥祯, 张凤翔, 蒲艺. 空间导航的脑网络基础和调控机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(3): 330-337. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||