

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (8): 1061-1075.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.01061 cstr: 32110.14.2024.01061
刘梦颖1, 蒋婧怡1, 杨依琳1, 江波3, 黄建平1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-05
发布日期:2024-06-17
出版日期:2024-08-25
通讯作者:
黄建平, E-mail: jphuang@suda.edu.cn基金资助:
LIU Mengying1, JIANG Jingyi1, YANG Yilin1, JIANG Bo3, HUANG Jianping1,2( )
)
Received:2023-09-05
Online:2024-06-17
Published:2024-08-25
摘要:
前人研究发现食物摆盘的美感水平会影响个体的食物选择, 但未有研究进一步探讨相同美感、不同审美特征对健康饮食决策的影响机制。本研究招募被试34名, 采用基于价值的食物决策范式, 使用2 (审美特征:古典美, 表现美) × 2 (食物热量:高, 低)被试内设计, 通过分离计算模型参数与脑电指标来检验不同审美特征差异化的审美价值, 以及审美价值对热量影响的调节效应及其认知神经基础。结果显示:(1)古典美(vs. 表现美)审美价值更高, 食物选择率和漂移率(v)更高、N400振幅更低; (2)审美价值调节热量价值, 但热量价值的突显性高于审美, 热量信息的神经处理时间更早(240~320 ms); (3)审美价值的调节效应发生在决策证据积累过程中, 影响漂移率(v)以及中央顶叶正波(CPP)。本研究在理论层面揭示了健康饮食决策中审美价值的调节效应及认知神经基础, 同时在实践应用方面为助推健康饮食选择提供了食物摆盘的审美设计指导。
中图分类号:
刘梦颖, 蒋婧怡, 杨依琳, 江波, 黄建平. (2024). 古典美还是表现美:摆盘美学影响健康饮食决策的计算与神经机制. 心理学报, 56(8), 1061-1075.
LIU Mengying, JIANG Jingyi, YANG Yilin, JIANG Bo, HUANG Jianping. (2024). Classical or expressive aesthetics: Computational and neural mechanisms by which plating aesthetics influence healthy eating decisions. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(8), 1061-1075.
| 模型 | DIC |
|---|---|
| 热量◊审美特征 | 13623 |
| 热量 | 13652 |
| 审美特征 | 14015 |
| 无 | 14197 |
表1 四个HDDM的DIC值
| 模型 | DIC |
|---|---|
| 热量◊审美特征 | 13623 |
| 热量 | 13652 |
| 审美特征 | 14015 |
| 无 | 14197 |
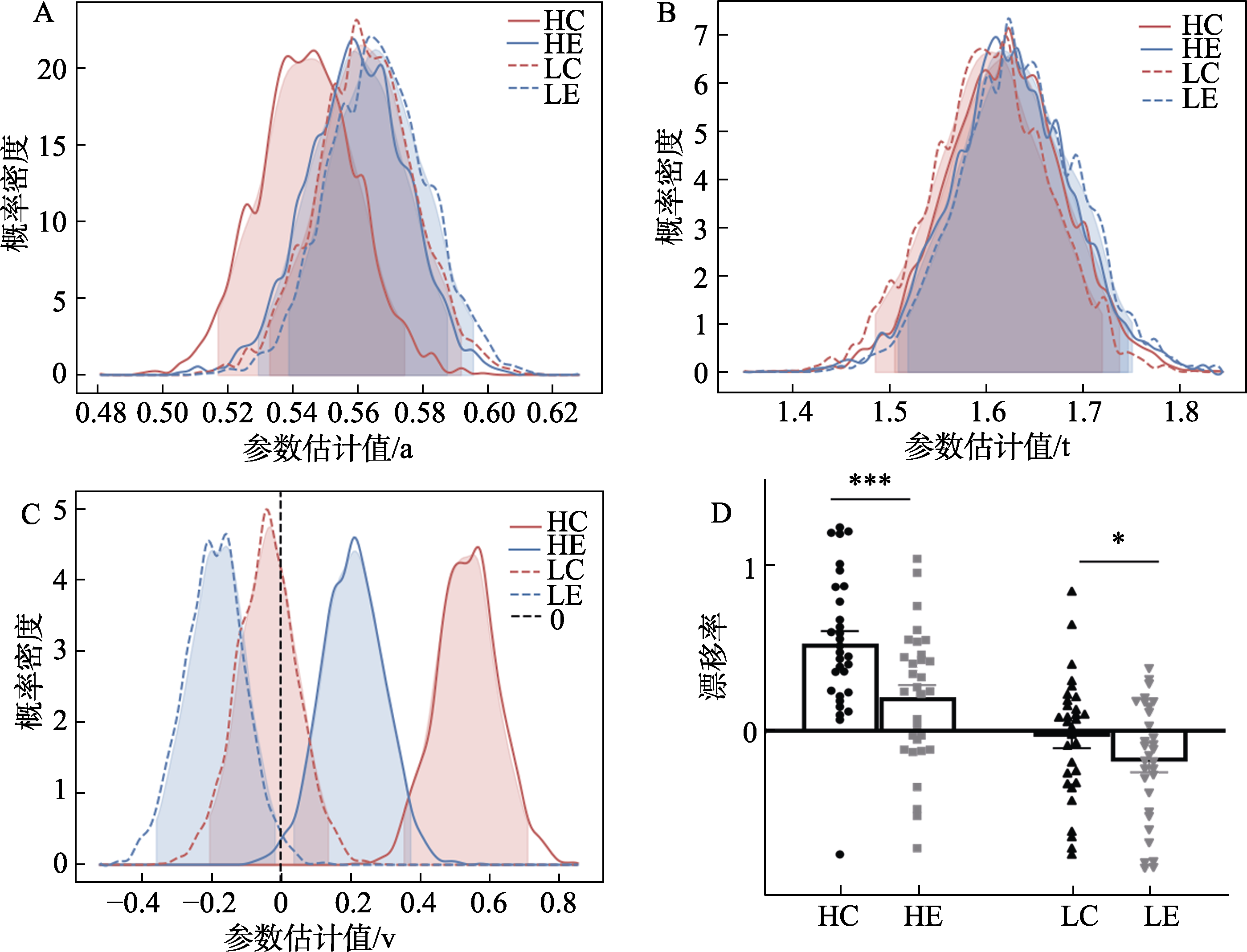
图6 决策参数估计的后验分布A) 决策阈值a; B) 非决策时间t; C) 漂移率v; D) 不同条件下漂移率v的平均数和数据分布, 误差棒反映标准误SE。 注: HC为高热量古典美摆盘; HE为高热量表现美; LC为低热量古典美; LE为低热量表现美, 误差棒为SE, ***为p < 0.001, **为p < 0.01
| 变量 | 配对 | P (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 热量 | P (HC > LC) | 100 |
| P (HE > LE) | 99.86 | |
| 审美 | P (HC > HE) | 99.56 |
| P (LC > LE) | 89.08 | |
| 热量×审美 | P (HC > LE) | 100 |
| P (HE > LC) | 97.28 | |
| 方向 | P (HE > 0) | 98.88 |
| P (HC > 0) | 100 | |
| P (LE < 0) | 98.36 | |
| P (LC < 0) | 65.66 |
表2 后验分布概率差异比较
| 变量 | 配对 | P (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 热量 | P (HC > LC) | 100 |
| P (HE > LE) | 99.86 | |
| 审美 | P (HC > HE) | 99.56 |
| P (LC > LE) | 89.08 | |
| 热量×审美 | P (HC > LE) | 100 |
| P (HE > LC) | 97.28 | |
| 方向 | P (HE > 0) | 98.88 |
| P (HC > 0) | 100 | |
| P (LE < 0) | 98.36 | |
| P (LC < 0) | 65.66 |
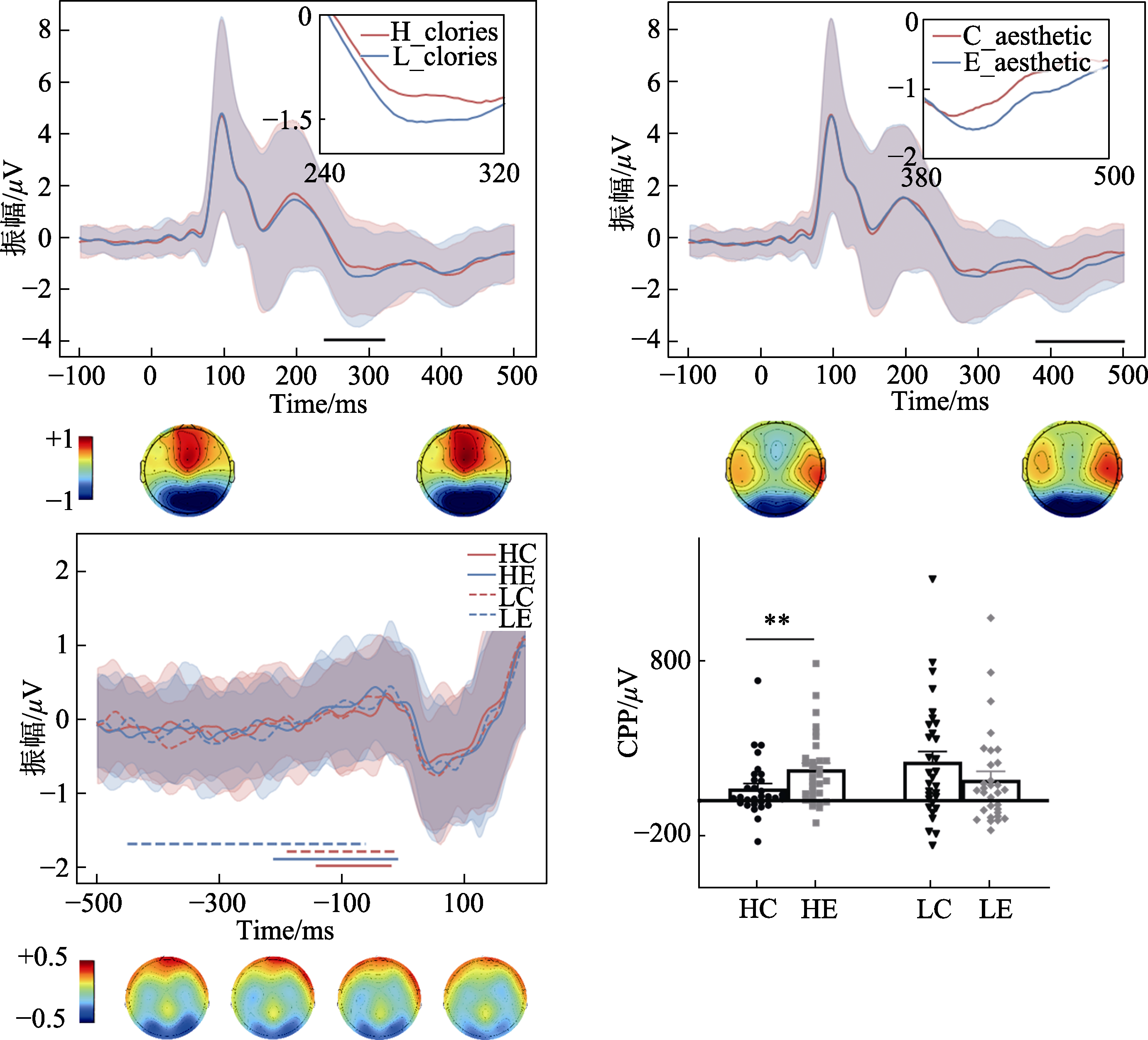
图7 刺激锁时与反应锁时ERP波形图与不同条件在CPP上的描述性统计。 A)刺激锁时枕叶皮层电极团的N300成分波形图及其对应地形图, 图下横线代表N300时间窗, 图右上方为局部放大的N300时间窗波形图; B) 刺激锁时枕叶皮层电极团的N400成分波形图及其对应地形图, 图下横线代表N400时间窗, 图右上方为局部放大的N400时间窗波形图; C) 反应锁时Pz点波形图, 波形图下横线代表不同条件信号积累加速的时间窗; D)各条件在CPP上的均值。注:HC为高热量古典美; HE为高热量表现美; LC为低热量古典美; LE为低热量表现美, 误差棒为SE, **为p < 0.01
| 古典美 | 表现美 | t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 美感 | 美感 | −1.69 | 29 | 0.102 | −0.342 | 0.0326 | −0.31 |
| 古典美感 | 古典美感 | 3.76 | 29 | <0 .001 | 0.225 | 0.7617 | 0.687 |
| 表现美感 | 表现美感 | −13.7 | 29 | < 0.001 | −1.888 | −1.3974 | −2.5 |
附表1 美学维度操纵检验
| 古典美 | 表现美 | t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 美感 | 美感 | −1.69 | 29 | 0.102 | −0.342 | 0.0326 | −0.31 |
| 古典美感 | 古典美感 | 3.76 | 29 | <0 .001 | 0.225 | 0.7617 | 0.687 |
| 表现美感 | 表现美感 | −13.7 | 29 | < 0.001 | −1.888 | −1.3974 | −2.5 |
| 高热量 | 低热量 | t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 热量 | 热量 | 16.62 | 29 | <0 .001 | 1.51 | 1.9341 | 3.035 |
附表2 食物热量操纵检验
| 高热量 | 低热量 | t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 热量 | 热量 | 16.62 | 29 | <0 .001 | 1.51 | 1.9341 | 3.035 |
| t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| 比较 | 13.3 | 29 | < 0.001 | 1.59 | 2.18 | 2.42 |
附表3 不同摆盘的同种食物可被识别为相同食物的操纵检验
| t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval | 效应量Cohen's d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| 比较 | 13.3 | 29 | < 0.001 | 1.59 | 2.18 | 2.42 |
| [1] | Bara, I., Binney, R. J., Ward, R., & Ramsey, R. (2022). A generalised semantic cognition account of aesthetic experience. Neuropsychologia, 173, 108288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2022.108288 |
| [2] | Berthoud, H. -R. (2012). The neurobiology of food intake in an obesogenic environment. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 71(4), 478-487. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0029665112000602 |
| [3] |
Brown, S., Gao, X., Tisdelle, L., Eickhoff, S. B., & Liotti, M. (2011). Naturalizing aesthetics: Brain areas for aesthetic appraisal across sensory modalities. NeuroImage, 58(1), 250-258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.012
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.012 URL pmid: 21699987 |
| [4] | Cadario, R., & Chandon, P. (2020). Which healthy eating nudges work best? A meta-analysis of field experiments. Marketing Science, 39(3), 459-465. https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2018.1128 |
| [5] | Casey, T. W., & Poropat, A. (2014). Beauty is more than screen deep: Improving the web survey respondent experience through socially-present and aesthetically-pleasing user interfaces. Computers in Human Behavior, 30, 153-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.08.001 |
| [6] | Chang, S. -H., Chih, W. -H., Liou, D. -K., & Hwang, L. -R. (2014). The influence of web aesthetics on customers’ PAD. Computers in Human Behavior, 36, 168-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.03.050 |
| [7] |
Choi, E. A., Husić, M., Millan, E. Z., Gilchrist, S., Power, J. M., Bressel, P. J. -R., & McNally, G. P. (2022). A corticothalamic circuit trades off speed for safety during decision-making under motivational conflict. Journal of Neuroscience, 42(16), 3473-3483. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0088-22.2022
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0088-22.2022 URL pmid: 35273082 |
| [8] | Chonpracha, P., Ardoin, R., Gao, Y., Waimaleongoraek, P., Tuuri, G., & Prinyawiwatkul, W. (2020). Effects of intrinsic and extrinsic visual cues on consumer emotion and purchase intent: A case of ready-to-eat salad. Foods, 9(4), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040396 |
| [9] |
Cornil, Y., & Chandon, P. (2016). Pleasure as an ally of healthy eating? Contrasting visceral and Epicurean eating pleasure and their association with portion size preferences and wellbeing. Appetite, 104, 52-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2015.08.045
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2015.08.045 URL pmid: 26363419 |
| [10] | de Vries, R., Morquecho-Campos, P., de Vet, E., de Rijk, M., Postma, E., de Graaf, K., Engel, B., & Boesveldt, S. (2020). Human spatial memory implicitly prioritizes high-calorie foods. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72570-x |
| [11] |
Delorme, A., & Makeig, S. (2004). EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 134(1), 9-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009 URL pmid: 15102499 |
| [12] | Deng, L., & Poole, M. S. (2012). Aesthetic design of e-commerce web pages—webpage complexity, order and preference. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 11(4), 420-440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2012.06.004 |
| [13] | Domracheva, M., & Kulikova, S. (2020). EEG correlates of perceived food product similarity in a cross-modal taste-visual task. Food Quality and Preference, 85, 103980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2020.103980 |
| [14] |
Draschkow, D., Heikel, E., Võ, M. L. -H., Fiebach, C. J., & Sassenhagen, J. (2018). No evidence from MVPA for different processes underlying the N300 and N400 incongruity effects in object-scene processing. Neuropsychologia, 120, 9-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.09.016
doi: S0028-3932(18)30327-0 URL pmid: 30261162 |
| [15] | Forstmann, B. U., Ratcliff, R., & Wagenmakers, E. -J. (2016). Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: Advantages, applications, and extensions. Annual Review of Psychology, 67(1), 641-666. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033645 |
| [16] | Frömer, R., Nassar, M., Ehinger, B., & Shenhav, A. (2023). Common neural choice signals emerge artifactually amidst multiple distinct value signals. BioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.02.502393 |
| [17] | Garcia-Guerrero, S., O’Hora, D., Zgonnikov, A., & Scherbaum, S. (2023). The action dynamics of approach-avoidance conflict during decision-making. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 76(1), 160-179. https://doi.org/10.1177/17470218221087625 |
| [18] | Gelman, A., & Rubin, D. B. (1992). Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Statistical Science, 7(4), 457-472. https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177011136 |
| [19] | Grzywacz, N. M., & Aleem, H. (2022). Does amount of information support aesthetic values? Frontiers in Neuroscience, 16, 805658. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.805658 |
| [20] | Hagen, L. (2021). Pretty healthy food: How and when aesthetics enhance perceived healthiness. Journal of Marketing, 85(2), 129-145. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022242920944384 |
| [21] | Hajihosseini, A., & Hutcherson, C. A. (2021). Alpha oscillations and event-related potentials reflect distinct dynamics of attribute construction and evidence accumulation in dietary decision making. eLife, 10, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60874 |
| [22] | Hall, P. A. (2016). Executive-control processes in high-calorie food consumption. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 25(2), 91-98. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721415625049 |
| [23] |
Harris, A., Hare, T., & Rangel, A. (2013). Temporally dissociable mechanisms of self-control: Early attentional filtering versus late value modulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(48), 18917-18931. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5816-12.2013
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5816-12.2013 URL pmid: 24285897 |
| [24] | Hassenzahl, M., Diefenbach, S., & Göritz, A. (2010). Needs, affect, and interactive products—Facets of user experience. Interacting with Computers, 22(5), 353-362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intcom.2010.04.002 |
| [25] | Heiman, A., & Lowengart, O. (2014). Calorie information effects on consumers’ food choices: Sources of observed gender heterogeneity. Journal of Business Research, 67(5), 964-973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.08.002 |
| [26] | Hoffmann, R., & Krauss, K. (2004). A critical evaluation of literature on visual aesthetics for the web. In Proceedings of annual research conference of the South African institute of computer scientists and information technologists on IT research in developing countries. Stellenbosch, Western Cape, South Africa. |
| [27] | Huang, H. -W., Lee, C. -L., & Federmeier, K. D. (2010). Imagine that! ERPs provide evidence for distinct hemispheric contributions to the processing of concrete and abstract concepts. NeuroImage, 49(1), 1116-1123. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.031 |
| [28] | Jin, N. (Paul), Goh, B., Huffman, L., & Yuan, J. J. (2015). Predictors and outcomes of perceived image of restaurant innovativeness in fine-dining restaurants. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 24(5), 457-485. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2014.915781 |
| [29] | Krajbich, I., Hare, T., Bartling, B., Morishima, Y., & Fehr, E. (2015). A common mechanism underlying food choice and social decisions. PLOS Computational Biology, 11(10), e1004371. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004371 |
| [30] | Kutas, M., & Federmeier, K. (2011). Thirty years and counting: Finding meaning in the N400 component of the event- related brain potential (ERP). Annual Review of Psychology, 62, 621-647. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.093008.131123 |
| [31] |
Lauer, T., Cornelissen, T. H. W., Draschkow, D., Willenbockel, V., & Võ, M. L. -H. (2018). The role of scene summary statistics in object recognition. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 14666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32991-1
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32991-1 URL pmid: 30279431 |
| [32] |
Lauer, T., Schmidt, F., & Võ, M. L. -H. (2021). The role of contextual materials in object recognition. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 21988. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01406-z
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01406-z URL pmid: 34753999 |
| [33] | Lavie, T., & Tractinsky, N. (2004). Assessing dimensions of perceived visual aesthetics of web sites. International Journal of Human Computer Studies, 60(3), 269-298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2003.09.002 |
| [34] | Liu, M., Ji, S., Jiang, B., & Huang, J. (2023). Plating for health: A cross-cultural study of the influence of aesthetics characteristics on food evaluation. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 33, 100785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2023.100785 |
| [35] |
Michel, C., Velasco, C., Fraemohs, P., & Spence, C. (2015). Studying the impact of plating on ratings of the food served in a naturalistic dining context. Appetite, 90, 45-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2015.02.030
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2015.02.030 URL pmid: 25728885 |
| [36] | Michel, C., Velasco, C., Gatti, E., & Spence, C. (2014). A taste of Kandinsky: Assessing the influence of the artistic visual presentation of food on the dining experience. Flavour, 3(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/2044-7248-3-7 |
| [37] |
O'Connell, R. G., Dockree, P. M., & Kelly, S. P. (2012). A supramodal accumulation-to-bound signal that determines perceptual decisions in humans. Nature Neuroscience, 15(12), 1729-1735. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3248
doi: 10.1038/nn.3248 URL pmid: 23103963 |
| [38] | Olson, J. C., & Jacoby, J. (1972). Cue utilization in the quality perception process. ACR Special Volumes, 167-179. |
| [39] | Peng, Y., & Jemmott, J. B. (2018). Feast for the eyes: Effects of food perceptions and computer vision features on food photo popularity. International Journal of Communication, 12, 313-336. https://ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/6678 |
| [40] | Pombo, M., & Velasco, C. (2021). How aesthetic features convey the concept of brand premiumness. Psychology & Marketing, 38(9), 1475-1497. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21534 |
| [41] |
Popkin, B. M., Adair, L. S., & Ng, S. W. (2012). Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutrition Reviews, 70(1), 3-21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00456.x
doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00456.x URL pmid: 22221213 |
| [42] | Qi, D., Penn, J., Li, R., & Roe, B. E. (2022). Winning ugly: Profit maximizing marketing strategies for ugly foods. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 64, 102834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2021.102834 |
| [43] |
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The diffusion decision model: Theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873-922. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2008.12-06-420
doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.12-06-420 URL pmid: 18085991 |
| [44] | Ratcliff, R., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2002). Estimating parameters of the diffusion model: Approaches to dealing with contaminant reaction times and parameter variability. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(3), 438-481. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196302 |
| [45] |
Regenbogen, C., Johansson, E., Andersson, P., Olsson, M. J., & Lundström, J. N. (2016). Bayesian-based integration of multisensory naturalistic perithreshold stimuli. Neuropsychologia, 88, 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.12.017
doi: S0028-3932(15)30251-7 URL pmid: 26719235 |
| [46] | Robins, D., & Holmes, J. (2008). Aesthetics and credibility in web site design. Information Processing and Management, 44(1), 386-399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2007.02.003 |
| [47] | Spiegelhalter, D. J., Best, N. G., Carlin, B. P., & Van Der Linde, A. (2002). Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 64(4), 583-639. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00353 |
| [48] |
Steinemann, N. A., O’Connell, R. G., & Kelly, S. P. (2018). Decisions are expedited through multiple neural adjustments spanning the sensorimotor hierarchy. Nature Communications, 9(1), 3627. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06117-0
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06117-0 URL pmid: 30194305 |
| [49] | Thornhill, R., & Møller, A. P. (2007). Developmental stability, disease and medicine. Biological Reviews, 72(4), 497-548. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.1997.tb00022.x |
| [50] |
Truman, A., & Mudrik, L. (2018). Are incongruent objects harder to identify? The functional significance of the N300 component. Neuropsychologia, 117, 222-232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.06.004
doi: S0028-3932(18)30273-2 URL pmid: 29885960 |
| [51] |
Vandekerckhove, J., Tuerlinckx, F., & Lee, M. D. (2011). Hierarchical diffusion models for two-choice response times. Psychological Methods, 16(1), 44-62. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021765
doi: 10.1037/a0021765 URL pmid: 21299302 |
| [52] |
Voss, J. L., & Paller, K. A. (2006). Fluent conceptual processing and explicit memory for faces are electrophysiologically distinct. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(3), 926-933. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3931-05.2006
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3931-05.2006 URL pmid: 16421312 |
| [53] | Voss, J. L., & Paller, K. A. (2007). Neural correlates of conceptual implicit memory and their contamination of putative neural correlates of explicit memory. Learning & Memory, 14(4), 259-267. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.529807 |
| [54] |
Wiecki, T., Sofer, I., & Frank, M. (2013). HDDM: Hierarchical Bayesian estimation of the drift-diffusion model in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2013.00014
doi: 10.3389/fninf.2013.00014 URL pmid: 23935581 |
| [55] | Zheng, L., Miao, M., & Gan, Y. (2022). A systematic and meta-analytic review on the neural correlates of viewing high- and low-calorie foods among normal-weight adults. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 138, 104721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104721 |
| [1] | 谢晓玲, 潘文谊, 张纯纯, 林静远, 李红. 连续反馈影响主导感的心理与脑电机制[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(3): 380-397. |
| [2] | 石荣, 刘昌, 唐慧琳, 郝俊懿, 沈汪兵. 自发的善行:加工模式和情境紧急性影响亲社会行为[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(9): 1239-1251. |
| [3] | 吴小燕, 付洪宇, 张腾飞, 鲍东琪, 胡捷, 朱睿达, 封春亮, 古若雷, 刘超. 共赢促进合作的认知计算机制: 互惠中积极期望与社会奖赏的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(9): 1299-1312. |
| [4] | 张锋, 皮瑜, 李小保. 个体与集体时间自我评价:来自行为和ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(4): 447-457. |
| [5] | 王婷, 赵梁佛, 杨金朋, 张丹丹, 雷震. 分配意图与上行间接互惠:来自行为与ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(12): 1788-1799. |
| [6] | 吴珺, 李晚晨, 姚晓欢, 刘洁, 崔芳. 友善重要, 还是公平重要?亲社会性与公平性调节复杂道德判断[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(11): 1541-1555. |
| [7] | 胡月琴, 王理中, 陈钢, 甘怡群. CSF3R和行动控制对应激与健康饮食关系的调节作用:应激影响健康行为的个体化模型的初步证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(9): 1489-1500. |
| [8] | 张文芸, 卓诗维, 郑倩倩, 关颖琳, 彭微微. 自闭特质对疼痛共情的影响:疼痛负性情绪和认知的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(9): 1501-1517. |
| [9] | 钟毅平, 牛娜娜, 范伟, 任梦梦, 李梅. 动作自主性与社会距离对主动控制感的影响:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1932-1948. |
| [10] | 李梅, 李琎, 张冠斐, 钟毅平, 李红. 承诺水平与社会距离对信任投资的影响:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(11): 1859-1871. |
| [11] | 覃慧怡, 丁丽洪, 段威, 雷旭. 脑电的重测信度:在多项静息态和任务态实验中的对比[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(10): 1587-1596. |
| [12] | 占友龙, 肖啸, 谭千保, 李琎, 钟毅平. 声誉关注与社会距离对伤害困境中道德决策的影响:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(6): 613-627. |
| [13] | 李建花, 解佳佳, 庄锦英. 生理周期对情景记忆的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(5): 466-480. |
| [14] | 范伟, 任梦梦, 张文洁, 钟毅平. 反馈对自我欺骗的影响:来自ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(5): 481-496. |
| [15] | 罗文波, 齐正阳. 词汇具体性对情绪名词效价加工影响的ERP研究[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(2): 111-121. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||