

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 56-69.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.00056 cstr: 32111.14.2021.00056
王葛彤1,2, 席洁1,2( ), 陈霓虹3,4(
), 陈霓虹3,4( ), 黄昌兵1,2
), 黄昌兵1,2
收稿日期:2020-03-18
出版日期:2021-01-15
发布日期:2020-11-23
基金资助:
WANG Getong1,2, XI Jie1,2( ), CHEN Nihong3,4(
), CHEN Nihong3,4( ), HUANG Changbing1,2
), HUANG Changbing1,2
Received:2020-03-18
Online:2021-01-15
Published:2020-11-23
摘要:
双眼瞳距使得空间某物体在左右眼视网膜的成像存在微小位置差异, 这种差异被称为双眼视差(binocular disparity), 是立体视知觉的重要信息来源。对双眼视差的心理物理学研究始于18世纪初, 迄今已有接近两百年的历史。近年来, 双眼视差研究主要集中在两方面。其一是用电生理、脑成像技术考察双眼视差在视觉背、腹侧通路的模块化表征, 其脑区表征反映出视觉系统的层级式、平行式加工规律。其二是应用知觉学习范式研究双眼视差的可塑性。未来研究应综合脑成像和神经调控技术考察双眼视差的神经机制及其学习效应, 包括双眼视差与多种深度线索间的信息整合和交互作用。应用方向上, 可结合虚拟现实等技术优化训练范式, 实现立体视力的康复和增强。
中图分类号:
王葛彤, 席洁, 陈霓虹, 黄昌兵. (2021). 双眼视差的神经机制与知觉学习效应. 心理科学进展 , 29(1), 56-69.
WANG Getong, XI Jie, CHEN Nihong, HUANG Changbing. (2021). Binocular disparity: Neural mechanisms and perceptual learning. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(1), 56-69.
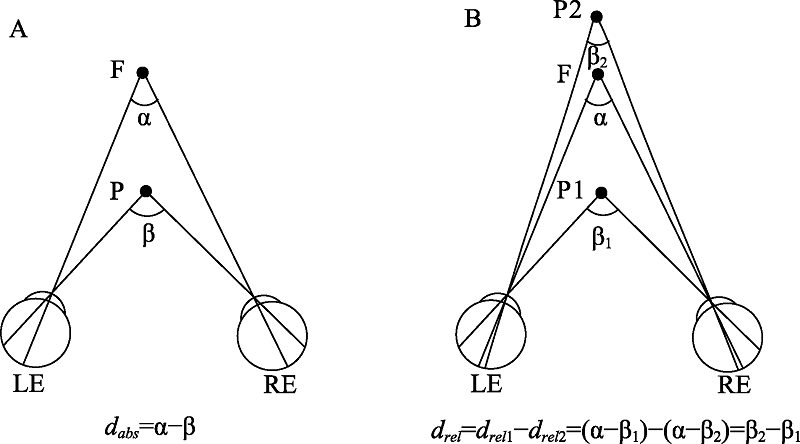
图2 双眼视差示意图。双眼视差是空间中某一物体P在左眼(LE)和右眼(RE)视网膜上成像的水平差异。A为绝对视差示意图, F为注视点, 双眼视线在注视点F处夹角为α, 在物体P处夹角为β, 绝对视差dabs为(α-β), 其大小与注视点F的位置有关; B为相对视差示意图, F为注视点, 双眼视线在注视点F处夹角为α, 在物体P1和P2处夹角分别为β1和β2, 两物体之间的相对视差drel等于两者绝对视差的差值, 其值为(β2-β1), 其大小与注视点F的位置无关。

图4 双眼视差的神经表征。箭头表示信息传递方向。图中白底标示脑区主要加工绝对视差, 橙底标示脑区主要加工相对视差。绿框标示现有研究发现的人类大脑皮层激活区域, 蓝框标示现有研究发现的猴大脑皮层激活区域, 红框标示人和猴共有的激活区域。MT+: middle temporal complex, 颞中回; VIPS: ventral IPS area, 顶内沟腹侧区; CIP: caudal intraparietal area, 顶内沟后部; DIPSM: the dorsal IPS medial area, 背侧顶内沟内侧区域; LIP: lateral intraparietal area, 顶内沟外侧区; DIPSA: the dorsal IPS anterior area, 背侧顶内沟前部; AIP: anterior intraparietal area, 顶内沟前部; PIP: posterior intraparietal area, 顶内沟后侧区; MIP: medial intraparietal area, 顶内沟内侧区; TE: the superior temporal sulcus, 颞上沟; TEO: temporal-occipital area。
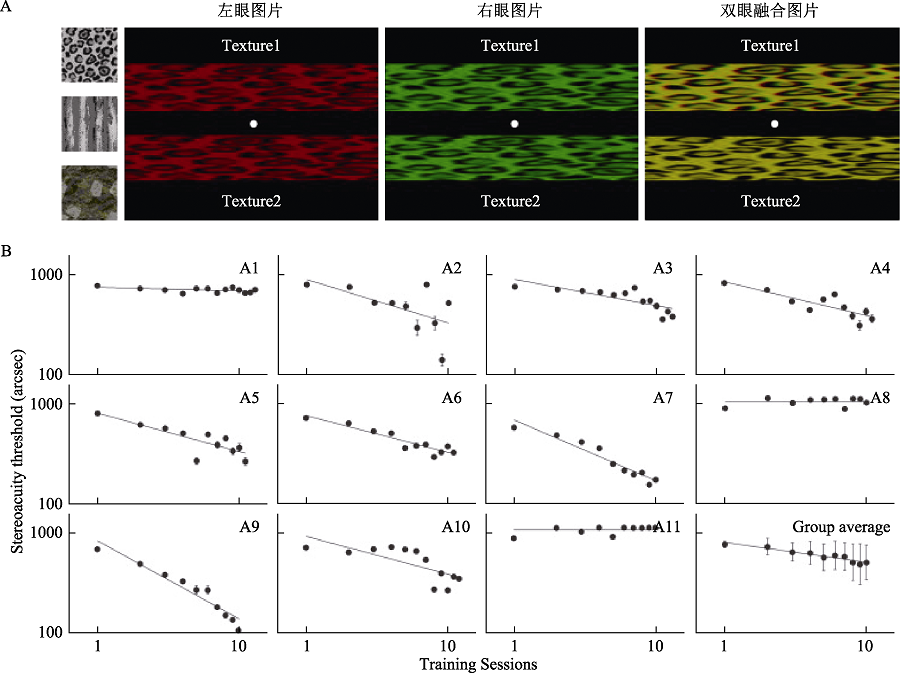
图5 立体视训练(Xi et al., 2014)。A为训练使用的刺激, 第一行为刺激的三种纹理, 第二行以其中一种纹理图案为例, 从左至右依次为刺激的左眼、右眼及双眼融合后图片, 被试在实验中需佩戴红绿眼镜; B为11名弱视被试单人及平均学习曲线, 横坐标为训练次数, 纵坐标为立体视阈值, 研究发现训练后11名弱视被试中的9人立体视阈值显著降低。
| [1] | 侯川. (1995). 立体视觉的发生机理与检测. 中国斜视与小儿眼科杂志, 3, 141-144. |
| [2] | 颜少明. (2006). 立体视觉检查图 (第3版). 北京: 人民卫生出版社. |
| [3] | Alexander, J. A. (1979). A new clinical test of stereopsis: Theoretical evaluation. The Australian Journal of Optometry, 62(5), 191-193. |
| [4] | Allouni, A. K., Thomas, O., Solomon, S. G., Krug, K., & Parker, A. J. (2005). Local and global binocular matching in V2 of the awake macaque. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts, 510, 8. |
| [5] |
Andersen, R. A., & Buneo, C. A. (2002). Intentional maps in posterior parietal cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 25(1), 189-220.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142922 URL |
| [6] |
Anzai, A., Chowdhury, S. A., & DeAngelis, G. C. (2011). Coding of stereoscopic depth information in visual areas V3 and V3A. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(28), 10270-10282.
URL pmid: 21753004 |
| [7] |
Anzai, A., & DeAngelis, G. C. (2010). Neural computations underlying depth perception. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 20(3), 367-375.
URL pmid: 20451369 |
| [8] | Astle, A. T., McGraw, P. V., & Webb, B. S. (2011). Recovery of stereo acuity in adults with amblyopia. BMJ Case Reports, 7-10. |
| [9] |
Backus, B. T., Fleet, D. J., Parker, A. J., & Heeger, D. J. (2001). Human cortical activity correlates with stereoscopic depth perception. Journal of Neurophysiology, 86(4), 2054-2068.
URL pmid: 11600661 |
| [10] |
Ban, H., Preston, T. J., Meeson, A., & Welchman, A. E. (2012). The integration of motion and disparity cues to depth in dorsal visual cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 15(4), 636-643.
doi: 10.1038/nn.3046 URL |
| [11] |
Barlow, H. B., Blakemore, C., & Pettigrew, J. D. (1967). The neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. The Journal of Physiology, 193(2), 327-342.
URL pmid: 6065881 |
| [12] |
Bohr, I., & Read, J. C. A. (2013). Stereoacuity with Frisby and revised FD2 stereo tests. PLoS One, 8(12), e82999.
URL pmid: 24349416 |
| [13] | Born, R. T., & Bradley, D. C. (2005). Structure and function of visual area MT. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 28(1), 157-189. |
| [14] |
Bosten, J. M., Goodbourn, P. T., Lawrance-Owen, A. J., Bargary, G., Hogg, R. E., & Mollon, J. D. (2015). A population study of binocular function. Vision Research, 110, 34-50.
URL pmid: 25771401 |
| [15] |
Bradshaw, M. F., & Glennerster, A. (2006). Stereoscopic acuity and observation distance. Spatial Vision, 19(1), 21-36.
URL pmid: 16411481 |
| [16] |
Bredfeldt, C. E., & Cumming, B. G. (2006). A simple account of cyclopean edge responses in macaque V2. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(29), 7581-7596.
URL pmid: 16855086 |
| [17] |
Brookes, A., & Stevens, K. A. (1989). The analogy between stereo depth and brightness. Perception, 18(5), 601-614.
URL pmid: 2602086 |
| [18] |
Chang, D. H. F., Mevorach, C., Kourtzi, Z., & Welchman, A. E. (2014). Training transfers the limits on perception from parietal to ventral cortex. Current Biology, 24(20), 2445-2450.
URL pmid: 25283780 |
| [19] |
Chen, G., Lu, H. D., & Roe, A. W. (2008). A map for horizontal disparity in monkey V2. Neuron, 58(3), 442-450.
URL pmid: 18466753 |
| [20] |
Chino, Y. M., Smith, E. L., Hatta, S., & Cheng, H. (1997). Postnatal development of binocular disparity sensitivity in neurons of the primate visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 17(1), 296-307.
URL pmid: 8987756 |
| [21] |
Chopin, A., Bavelier, D., & Levi, D. M. (2019). The prevalence and diagnosis of 'stereoblindness' in adults less than 60 years of age: A best evidence synthesis. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 39(2), 66-85.
URL pmid: 30776852 |
| [22] |
Ciner, E. B., Scheiman, M. M., Schanel-Klitsch, E., & Weil, L. (1989). Stereopsis testing in 18- to 35-month-old children using operant preferential looking. Optometry & Vision Science, 66(11), 782-787.
URL pmid: 2616139 |
| [23] |
Cooper, J., Feldman, J., & Medlin, D. (1979). Comparing stereoscopic performance of children using the Titmus, TNO, and randot stereo tests. Journal of the American Optometric Association, 50(7), 821-825.
URL pmid: 500993 |
| [24] |
Cottereau, B. R., McKee, S. P., Ales, J. M., & Norcia, A. M. (2011). Disparity-tuned population responses from human visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(3), 954-965.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3795-10.2011 URL pmid: 21248120 |
| [25] | Cowey, A., & Porter, J. (1979). Brain damage and global stereopsis. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 204(1157), 399-407. |
| [26] |
Cowey, A., & Wilkinson, F. (1991). The role of the corpus callosum and extra striate visual areas in stereoacuity in macaque monkeys. Neuropsychologia, 29(6), 465-479.
URL pmid: 1944856 |
| [27] |
Cumming, B. G., & Parker, A. J. (1997). Responses of primary visual cortical neurons to binocular disparity without depth perception. Nature, 389(6648), 280-283.
URL pmid: 9305841 |
| [28] |
Cumming, B. G., & Parker, A. J. (1999). Binocular neurons in V1 of awake monkeys are selective for absolute, not relative, disparity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 19(13), 5602-5618.
URL pmid: 10377367 |
| [29] |
DeAngelis, G. C., & Newsome, W. T. (1999). Organization of disparity-selective neurons in macaque area MT. The Journal of Neuroscience, 19(4), 1398-1415.
URL pmid: 9952417 |
| [30] |
DiCarlo, J. J., Zoccolan, D., & Rust, N. C. (2013). How does the brain solve visual object recognition?. Neuron, 73(3), 415-434.
URL pmid: 22325196 |
| [31] |
Ding, J., & Levi, D. M. (2011). Recovery of stereopsis through perceptual learning in human adults with abnormal binocular vision. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(37), E733-E741.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105183108 URL |
| [32] |
Dodd, J. V., Krug, K., Cumming, B. G., & Parker, A. J. (2001). Perceptually bistable three-dimensional figures evoke high choice probabilities in cortical area MT. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21(13), 4809-4821.
URL pmid: 11425908 |
| [33] |
DöVencioğlu, D., Ban, H., Schofield, A. J., & Welchman, A. E. (2013). Perceptual integration for qualitatively different 3-D cues in the human brain. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(9), 1527-1541.
URL pmid: 23647559 |
| [34] |
Durand, J.-B., Nelissen, K., Joly, O., Wardak, C., Todd, J. T., Norman, J. F., ... Orban, G. A. (2007). Anterior regions of monkey parietal cortex process visual 3D shape. Neuron, 55(3), 493-505.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.040 URL |
| [35] |
Durand, J.-B., Peeters, R., Norman, J. F., Todd, J. T., & Orban, G. A. (2009). Parietal regions processing visual 3D shape extracted from disparity. NeuroImage, 46(4), 1114-1126.
URL pmid: 19303937 |
| [36] |
Erkelens, C. J., & Collewijn, H. (1985). Motion perception during dichoptic viewing of moving random-dot stereograms. Vision Research, 25(4), 583-588.
URL pmid: 4060612 |
| [37] | Feinberg, R., & Reuel, S. (1961). Device for testing visual acuity. US3011394A. |
| [38] |
Fendick, M., & Westheimer, G. (1983). Effects of practice and the separation of test targets on foveal and peripheral stereoacuity. Vision Research, 23(2), 145-150.
URL pmid: 6868389 |
| [39] |
Finlay, D. C., Manning, M. L., Dunlop, D. P., & Dewis, S. A. M. (1989). Difficulties in the definition of 'stereoscotoma' using temporal detection of thresholds of dynamic random dot stereograms. Documenta Ophthalmologica, 72, 161-173.
URL pmid: 2582997 |
| [40] |
Fox, R., Patterson, R., & Francis, E. L. (1986). Stereoacuity in young children. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 27(4), 598-600.
URL pmid: 3957579 |
| [41] | Frisby, J. P., & Clatworthy, J. L. (1975). Learning to see complex random-dot stereograms. Perception, 4(2), 173-178. |
| [42] | Gallese, V., Murata, A., Kaseda, M., Niki, N., & Sakata, H. (1994). Deficit of hand preshaping after muscimol injection in monkey parietal cortex. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuropsychology, 5(12), 1525-1529. |
| [43] |
Gantz, L., Patel, S. S., Chung, S. T. L., & Harwerth, R. S. (2007). Mechanisms of perceptual learning of depth discrimination in random dot stereograms. Vision Research, 47(16), 2170-2178.
URL pmid: 17588634 |
| [44] |
Georgieva, S., Peeters, R., Kolster, H., Todd, J. T., & Orban, G. A. (2009). The processing of three-dimensional shape from disparity in the human brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(3), 727-742.
URL pmid: 19158299 |
| [45] |
Giaschi, D., Narasimhan, S., Solski, A., Harrison, E., & Wilcox, L. M. (2013). On the typical development of stereopsis: fine and coarse processing. Vision Research, 89, 65-71.
URL pmid: 23891704 |
| [46] |
Goncalves, N. R., Ban, H., Sánchez-Panchuelo, R. M., Francis, S. T., Schluppeck, D., & Welchman, A. E. (2015). 7 Tesla fMRI reveals systematic functional organization for binocular disparity in dorsal visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 35(7), 3056-3072.
URL pmid: 25698743 |
| [47] | Goodale, M. A., & Milner, A. D. (1992). Separate visual pathways for perception and action. Trends in Neuroscience, 15(1), 20-25. |
| [48] |
Grefkes, C., & Fink, G. R. (2005). The functional organization of the intraparietal sulcus in humans and monkeys. Journal of Anatomy, 207(1), 3-17.
URL pmid: 16011542 |
| [49] |
Haefner, R. M., & Cumming, B. G. (2008). Adaptation to natural binocular disparities in primate V1 explained by a generalized energy model. Neuron, 57(1), 147-158.
URL pmid: 18184571 |
| [50] |
Hegdé, J., & van Essen, D. C. (2005). Role of primate visual area V4 in the processing of 3-D shape characteristics defined by disparity. Journal of Neurophysiology, 94(4), 2856-2866.
URL pmid: 15987759 |
| [51] | Helmholtz, H. V. (1909). Handbuch der Physiologischen Optik. New York: Dover. |
| [52] |
Hess, R. F., Mansouri, B., & Thompson, B. (2010). A new binocular approach to the treatment of amblyopia in adults well beyond the critical period of visual development. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 28(6), 793-802.
URL pmid: 21209494 |
| [53] | Hess, R. F., Thompson, B., Black, J. M., Machara, G., Zhang, P., Bobier, W. R., & Cooperstock, J. (2012). An iPod treatment of amblyopia: An updated binocular approach. Optometry (St. Louis, Mo.), 83(2), 87-94. |
| [54] |
Hess, R. F., To, L., Zhou, J., Wang, G., & Cooperstock, J. R. (2015). Stereo vision: The haves and have-nots. i-Perception, 6(3), 2041669515593028.
URL pmid: 27433314 |
| [55] |
Hinkle, D. A., & Connor, C. E. (2002). Three-dimensional orientation tuning in macaque area V4. Nature Neuroscience, 5(7), 665-670.
URL pmid: 12068303 |
| [56] |
Howarth, P. A. (2008). The adverse health and safety effects of viewing visual images. Displays, 29(2), 45-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2007.09.012 URL |
| [57] | Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1962). Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. Journal of Physiology, 160(1), 106-154. |
| [58] |
Jameson, D., & Hurvich, L. M. (1959). Note on factors influencing the relation between stereoscopic acuity and observation distance. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 49(6), 639.
URL pmid: 13655159 |
| [59] |
Janssen, P., Vogels, R., Liu, Y., & Orban, G. A. (2003). At least at the level of inferior temporal cortex, the stereo correspondence problem is solved. Neuron, 37(4), 693-701.
URL pmid: 12597865 |
| [60] |
Janssen, P., Vogels, R., & Orban, G. A. (1999). Macaque inferior temporal neurons are selective for disparity-defined three-dimensional shapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(14), 8217-8222.
URL pmid: 10393975 |
| [61] |
Janssen, P., Vogels, R., & Orban, G. A. (2000a). Selectivity for 3D shape that reveals distinct areas within macaque inferior temporal cortex. Science, 288(5473), 2054-2056.
URL pmid: 10856221 |
| [62] |
Janssen, P., Vogels, R., & Orban, G. A. (2000b). Three-dimensional shape coding in inferior temporal cortex. Neuron, 27(2), 385-397.
URL pmid: 10985357 |
| [63] | Julesz, B. (1960). Binocular depth perception of computer-generated patterns. Bell System Technical Journal, 39(5), 1125-1162. |
| [64] | Julesz, B. (1971). Foundations of cyclopean perception. Boston: MIT Press. |
| [65] | Julesz, B. (1978). Global stereopsis: Cooperative phenomena in stereoscopic depth perception. In R. Held, H. W. Leibowitz, & H. L. Teuber (Eds.), Perception: Vol. 8: Handbook of Sensory Physiology(p. 215). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [66] |
Julesz, B. (1986). Stereoscopic vision. Vision Research, 26(9), 1601-1612.
URL pmid: 3303677 |
| [67] |
Katsuyama, N., Yamashita, A., Sawada, K., Naganuma, T., Sakata, H., & Taira, M. (2010). Functional and histological properties of caudal intraparietal area of macaque monkey. Neuroscience, 167(1), 1-10.
URL pmid: 20096334 |
| [68] |
Leat, S. J., Pierre, J. S., Hasan-Abadi, S., & Faubert, J. (2001). The moving dynamic random dot stereosize test: Development, age norms, and comparison with the frisby, randot, and stereo smile tests. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus, 38(5), 284-294.
URL pmid: 11587177 |
| [69] |
Levi, D. M., Harwerth, R. S., & Smith, E. L. (1980). Binocular interactions in normal and anomalous binocular vision. Documenta Ophthalmologica, 49(2), 303-324.
URL pmid: 7438987 |
| [70] |
Liu, Y., Vogels, R., & Orban, G. A. (2004). Convergence of depth from texture and depth from disparity in macaque inferior temporal cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(15), 3795-3800.
URL pmid: 15084660 |
| [71] |
Long, N. R. (1982). Transfer of learning in transformed random-dot stereostimuli. Perception, 11(4), 409-414.
URL pmid: 7182800 |
| [72] |
Lu, Z.-L., Hua, T., Huang, C.-B., Zhou, Y., & Dosher, B. A. (2011). Visual perceptual learning. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 95(2), 145-151.
doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.09.010 URL pmid: 20870024 |
| [73] |
Manning, M. L., Finlay, D. C., Neill, R. A., & Frost, B. G. (1987). Detection threshold differences to crossed and uncrossed disparities. Vision Research, 27(9), 1683-1686.
URL pmid: 3445498 |
| [74] |
Marr, D. (1982). Vision. San Francisco: Freeman.
URL pmid: 32575705 |
| [75] |
Maruko, I., Zhang, B., Tao, X., Tong, J., Smith, E. L., & Chino, Y. M. (2008). Postnatal development of disparity sensitivity in visual area 2 (V2) of macaque monkeys. Journal of Neurophysiology, 100(5), 2486-2495.
URL pmid: 18753321 |
| [76] |
Mazziotti, R., Baroncelli, L., Ceglia, N., Chelini, G., Sala, G. D., Magnan, C., ... Pizzorusso, T. (2017). Mir-132/212 is required for maturation of binocular matching of orientation preference and depth perception. Nature Communication, 8, 15488.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms15488 URL |
| [77] |
McKee, S. P., Levi, D. M., & Movshon, J. A. (2003). The pattern of visual deficits in amblyopia. Journal of Vision, 3(5), 380-405.
URL pmid: 12875634 |
| [78] |
Mendola, J. D., Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., Liu, A. K., & Tootell, R. B. H. (1999). The representation of illusory and real contours in human cortical visual areas revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. The Journal of Neuroscience, 19(19), 8560-8572.
URL pmid: 10493756 |
| [79] |
Murata, A., Gallese, V., Luppino, G., Kaseda, M., & Sakata, H. (2000). Selectivity for the shape, size, and orientation of objects for grasping in neurons of monkey parietal area AIP. Journal of Neurophysiology, 83(5), 2580-2601.
URL pmid: 10805659 |
| [80] |
Neri, P., Bridge, H., & Heeger, D. J. (2004). Stereoscopic processing of absolute and relative disparity in human visual cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 92(3), 1880-1891.
URL pmid: 15331652 |
| [81] |
Neri, P., Parker, A. J., & Blakemore, C. (1999). Probing the human stereoscopic system with reverse correlation. Nature, 401, 695-698.
URL pmid: 10537107 |
| [82] |
Nguyenkim, J. D., & DeAngelis, G. C. (2003). Disparity-based coding of three-dimensional surface orientation by macaque middle temporal neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(18), 7117-7128.
URL pmid: 12904472 |
| [83] |
Nienborg, H., & Cumming, B. G. (2006). Macaque V2 neurons, but not V1 neurons, show choice-related activity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(37), 9567-9578.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2256-06.2006 URL |
| [84] |
Nikara, T., Bishop, P. O., & Pettigrew, J. D. (1968). Analysis of retinal correspondence by studying receptive fields of binocular single units in cat striate cortex. Experimental Brain Research, 6(4), 353-372.
URL pmid: 5721765 |
| [85] |
Nongpiur, M. E, & Sharma, P. (2010). Horizontal Lang two-pencil test as a screening test for stereopsis and binocularity. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 58(4), 287-290.
URL pmid: 20534917 |
| [86] |
Ogle, K. N. (1952). Disparity limits of stereopsis. Archives of Ophthalmology, 48(1), 50-60.
URL pmid: 14932562 |
| [87] |
Ogle, K. N. (1958). Note on stereoscopic acuity and observation distance. Journal of the optical society of America, 48(11), 794-798.
URL pmid: 13588453 |
| [88] |
Ohzawa, I., DeAngelis, G. C., & Freeman, R. D. (1990). Stereoscopic depth discrimination in the visual cortex: Neurons ideally suited as disparity detectors. Science, 249(4972), 1037-1041.
URL pmid: 2396096 |
| [89] |
Ohzawa, I., DeAngelis, G. C., & Freeman, R. D. (1997). Encoding of binocular disparity by complex cells in the cat's visual cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 77(6), 2879-2909.
URL pmid: 9212245 |
| [90] | Orban, G. A. (2011). The extraction of 3D shape in the visual system of human and nonhuman primates. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 34(1), 361-388. |
| [91] |
O'Toole, A. J., & Kersten, D. J. (1992). Learning to see random-dot stereograms. Perception, 21(2), 227-243.
URL pmid: 1513672 |
| [92] | Panum, P. L. (1940). Physiological investigations concerning vision with two eyes (C. Hubscher, Trans.). Hanover, NH: Dartmouth Eye Institute. |
| [93] |
Patterson, R., & Fox, R. (1984). The effect of testing method on stereoanomaly. Vision Research, 24(5), 403-408.
URL pmid: 6740961 |
| [94] |
Poggio, G. F., & Fischer, B. (1977). Binocular interaction and depth sensitivity in striate and prestriate cortex of behaving rhesus monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology, 40(6), 1392-1405.
URL pmid: 411898 |
| [95] |
Poggio, G. F., Gonzalez, F., & Krause, F. (1988). Stereoscopic mechanisms in monkey visual cortex: Binocular correlation and disparity selectivity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 8(12), 4531-4550.
URL pmid: 3199191 |
| [96] |
Poggio, G. F., Motter, B. C., Squatrito, S., & Trotter, Y. (1985). Responses of neurons in visual cortex (V1 and V2) of the alert macaque to dynamic random-dot stereograms. Vision Research, 25(3), 397-406.
URL pmid: 4024459 |
| [97] |
Portela-Camino, J. A., Martín-González, S., Ruiz-Alcocer, J., Illarramendi-Mendicute, I., & Garrido-Mercado, R. (2018). A random dot computer video game improves stereopsis. Optometry and Vision Science, 95(6), 523-535.
URL pmid: 29787486 |
| [98] |
Ramachandran, V. S. (1976). Learning-like phenomena in stereopsis. Nature, 262(5567), 382-384.
URL pmid: 958387 |
| [99] |
Ramachandran, V. S., & Braddick, O. (1973). Orientation-specific learning in stereopsis. Perception, 2(3), 371-376.
URL pmid: 4794134 |
| [100] |
Richards, W. (1970). Stereopsis and stereoblindness. Experimental Brain Research, 10(4), 380-388.
URL pmid: 5422472 |
| [101] |
Richards, W. (1971). Anomalous stereoscopic depth perception. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 61(3), 410-414.
doi: 10.1364/josa.61.000410 URL pmid: 5542548 |
| [102] |
Rogers, B., & Graham, M. (1982). Similarities between motion parallax and stereopsis in human depth perception. Vision Research, 22(2), 261-270.
URL pmid: 7101762 |
| [103] |
Romano, P. E., Romano, J. A., & Puklin, J. E. (1975). Stereoacuity development in children with normal binocular single vision. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 79(6), 966-971.
doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90679-0 URL pmid: 1137000 |
| [104] |
Roy, J. P., Komatsu, H., & Wurtz, R. H. (1992). Disparity sensitivity of neurons in monkey extrastriate area MST. The Journal of Neuroscience, 12(7), 2478-2492.
URL pmid: 1613542 |
| [105] |
Sakata, H. (2003). The role of the parietal cortex in grasping. Advances in Neurology, 93, 121-139.
URL pmid: 12894405 |
| [106] |
Sakata, H., Taira, M., Murata, A., & Mine, S. (1995). Neural mechanisms of visual guidance of hand action in the parietal cortex of the monkey. Cerebral Cortex, 5(5), 429-438.
URL pmid: 8547789 |
| [107] | Sasieni, L. S. (1978). The frisby stereotest. Optician, 176, 7-10. |
| [108] |
Schmitt, C., Kromeier, M., Bach, M., & Kommerell, G. (2002). Interindividual variability of learning in stereoacuity. Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 240(9), 704-709.
doi: 10.1007/s00417-002-0458-y URL |
| [109] |
Schoemann, M. D., Lochmann, M., Paulus, J., & Michelson, G. (2017). Repetitive dynamic stereo test improved processing time in young athletes. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 35(4), 413-421.
URL pmid: 28671146 |
| [110] |
Scholl, B., Burge, J., & Priebe, N. J. (2013). Binocular integration and disparity selectivity in mouse primary visual cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 109(12), 3013-3024.
URL pmid: 23515794 |
| [111] |
Sereno, M. E., Trinath, T., Augath, M., & Logothetis, N. K. (2002). Three-dimensional shape representation in monkey cortex. Neuron, 33(4), 635-652.
URL pmid: 11856536 |
| [112] |
Simons, K. (1981). Stereoacuity norms in young children. Archives of Ophthalmology, 99(3), 439-445.
URL pmid: 7213162 |
| [113] |
Snyder, L. H., Batista, A. P., & Andersen, R. A. (1997). Coding of intention in the posterior parietal cortex. Nature (London), 386(6621), 167-170.
doi: 10.1038/386167a0 URL |
| [114] |
Solimini, A. G. (2013). Are there side effects to watching 3D movies? A prospective crossover observational study on visually induced motion sickness. PLoS ONE, 8(2), e56160.
URL pmid: 23418530 |
| [115] |
Sowden, P., Davies, I., Rose, D., & Kaye, M. (1996). Perceptual learning of stereoacuity. Perception, 25(9), 1043-1052.
URL pmid: 8983044 |
| [116] |
Srivastava, S., Orban, G. A., de Mazière, P. A., & Janssen, P. (2009). A distinct representation of three-dimensional shape in macaque anterior intraparietal area: Fast, metric, and coarse. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(34), 10613-10626.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6016-08.2009 URL pmid: 19710314 |
| [117] |
Taira, M., Mine, S., Georgopoulos, A. P., Murata, A., & Sakata, H. (1990). Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance of hand movement. Experimental Brain Research, 83(1), 29-36.
URL pmid: 2073947 |
| [118] |
Takemura, A., Inoue, Y., Kawano, K., Quaia, C., & Miles, F. A. (2001). Single-unit activity in cortical area MST associated with disparity-vergence eye movements: Evidence for population coding. Journal of Neurophysiology, 85(5), 2245-2266.
URL pmid: 11353039 |
| [119] |
Tanabe, S., Umeda, K., & Fujita, I. (2004). Rejection of false matches for binocular correspondence in macaque visual cortical area V4. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(37), 8170-8180.
URL pmid: 15371518 |
| [120] |
Tanabe, S., Yasuoka, S., & Fujita, I. (2008). Disparity-energy signals in perceived stereoscopic depth. Journal of Vision, 8(3), 1-10.
URL pmid: 18484820 |
| [121] |
Tanaka, H., Uka, T., Yoshiyama, K., Kato, M., & Fujita, I. (2001). Processing of shape defined by disparity in monkey inferior temporal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 85(2), 735-744.
URL pmid: 11160508 |
| [122] |
Thomas, O. M., Cumming, B. G., & Parker, A. J. (2002). A specialization for relative disparity in V2. Nature Neuroscience, 5(5), 472-478.
URL pmid: 11967544 |
| [123] |
Tomac, S., & Altay, Y. (2000). Near stereoacuity: Development in preschool children; Normative values and screening for binocular vision abnormalities; A study of 115 children. Binocular Vision Strabismus Quarterly, 15(3), 221-228.
URL pmid: 10960225 |
| [124] |
Tootell, R. B. H., & Nasr, S. (2017). Columnar segregation of magnocellular and parvocellular streams in human extrastriate cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(33), 8014-8032.
URL pmid: 28724749 |
| [125] |
Tsao, D. Y., Vanduffel, W., Sasaki, Y., Fize, D., Knutsen, T. A., Mandeville, J. B., ... Tootell, R. B. H. (2003). Stereopsis activates V3A and caudal intraparietal areas in macaques and humans. Neuron, 39(3), 555-568.
URL pmid: 12895427 |
| [126] |
Tsodyks, M., & Gilbert, C. (2004). Neural networks and perceptual learning. Nature, 431(7010), 775-781.
URL pmid: 15483598 |
| [127] |
Tsutsui, K. I., Jiang, M., Yara, K., Sakata, H., & Taira, M. (2001). Integration of perspective and disparity cues in surface-orientation-selective neurons of area CIP. Journal of Neurophysiology, 86(6), 2856-2867.
URL pmid: 11731542 |
| [128] |
Uka, T., & DeAngelis, G. C. (2006). Linking neural representation to function in stereoscopic depth perception: Roles of the middle temporal area in coarse versus fine disparity discrimination. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(25), 6791-6802.
URL pmid: 16793886 |
| [129] |
Uka, T., Tanaka, H., Yoshiyama, K., Kato, M., & Fujita, I. (2000). Disparity selectivity of neurons in monkey inferior temporal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 84(1), 120-132.
URL pmid: 10899190 |
| [130] |
Uka, T., Tanabe, S., Watanabe, M., & Fujita, I. (2005). Neural correlates of fine depth discrimination in monkey inferior temporal cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(46), 10796-10802.
URL pmid: 16291953 |
| [131] |
Ukai, K., & Howarth, P. A. (2008). Visual fatigue caused by viewing stereoscopic motion images: Background, theories, and observations. Displays, 29(2), 106-116.
doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2007.09.004 URL |
| [132] |
Umeda, K., Tanabe, S., & Fujita, I. (2007). Representation of stereoscopic depth based on relative disparity in macaque area V4. Journal of Neurophysiology, 98(1), 241-252.
doi: 10.1152/jn.01336.2006 URL pmid: 17507498 |
| [133] |
Verhoef, B.-E., Vogels, R., & Janssen, P. (2016). Binocular depth processing in the ventral visual pathway. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1697), 20150259.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0259 URL |
| [134] |
von der Heydt, R., Zhou, H., & Friedman, H. S. (2000). Representation of stereoscopic edges in monkey visual cortex. Vision Research, 40(15), 1955-1967.
URL pmid: 10828464 |
| [135] |
Watanabe, M., Tanaka, H., Uka, T., & Fujita, I. (2002). Disparity-selective neurons in area V4 of macaque monkeys. Journal of Neurophysiology, 87(4), 1960-1973.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00780.2000 URL pmid: 11929915 |
| [136] |
Westheimer, G. (1979). Cooperative neural processes involved in stereoscopic acuity. Experimental Brain Research, 36(3), 585-597.
URL pmid: 477784 |
| [137] | Wheatstone, C. (1838). On some remarkable, and hitherto unobserved, phenomena of binocular vision. Philosophical Transactions - Royal Society, 53, 371-394. |
| [138] |
Wilcox, L. M., & Allison, R. S. (2009). Coarse-fine dichotomies in human stereopsis. Vision Research, 49(22), 2653-2665.
URL pmid: 19520102 |
| [139] |
Wong, B. P. H., Woods, R. L., & Peli, E. (2002). Stereoacuity at distance and near. Optometry and Vision Science, 79(12), 771-778.
URL pmid: 12512685 |
| [140] |
Wright, L. A., & Wormald, R. P. (1992). Stereopsis and ageing. Eye, 6(5), 473-476.
doi: 10.1038/eye.1992.100 URL |
| [141] |
Xi, J., Jia, W.-L., Feng, L.-X., Lu, Z.-L., & Huang, C.-B. (2014). Perceptual learning improves stereoacuity in amblyopia. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 55(4), 2384-2391.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12627 URL pmid: 24508791 |
| [142] |
Yamane, Y., Carlson, E. T., Bowman, K. C., Wang, Z., & Connor, C. E. (2008). A neural code for three-dimensional object shape in macaque inferotemporal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 11(11), 1352-1360.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2202 URL pmid: 18836443 |
| [1] | 程晓荣, 仇式明, 定险峰, 范炤. 动作如何影响元认知?——基于认知模型和神经机制的探讨[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 425-438. |
| [2] | 巩芳颍, 孙逸梵, 贺琴, 石可, 刘伟, 陈宁. 教学互动中师生脑间同步性及其调节因素[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 452-464. |
| [3] | 夏熠, 张婕, 张火垠, 雷怡, 窦皓然. 焦虑个体趋避冲突失调的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 477-493. |
| [4] | 刘月月, 何文广. 书写认知老化发生机制及神经机理[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(9): 1502-1513. |
| [5] | 雷怡, 梅颖, 王金霞, 袁子昕. 焦虑青少年无意识恐惧的神经机制及干预[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1221-1232. |
| [6] | 丁颖, 汪紫滢, 李卫东. 抑郁症疼痛加工的行为特点及神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1315-1327. |
| [7] | 曾庆贺, 崔晓宇, 唐为, 李娟. 记忆辨别力受老化影响的认知神经机制及其应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(7): 1138-1151. |
| [8] | 刘海宁, 董现玲, 刘海虹, 刘艳丽, 李现文. 老年遗忘型轻度认知障碍执行功能的神经机制及数字干预[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(6): 873-885. |
| [9] | 冯攀, 赵恒越, 姜雨矇, 张悦彤, 冯廷勇. 催产素影响条件化恐惧情绪加工的认知机制及神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(4): 557-567. |
| [10] | 郑好, 陈荣荣, 买晓琴. 第三方惩罚行为的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(2): 398-412. |
| [11] | 孙丽君, 杨玉芳. 预期视角下音乐节拍结构的认知与神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(10): 1567-1577. |
| [12] | 叶健彤, 高洁, 邓芷晴, 陈娟. 视觉动作训练的视网膜位置特异性与迁移性[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 117-117. |
| [13] | 石宏桥, 丁悦, 宋炳辉, 李雅. 融景知觉学习及其特征特异性[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 126-126. |
| [14] | 韩郑祺, 李鸿戬, 俞洪波. 匹配刺激精准调控成年期动物视觉功能[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 127-127. |
| [15] | 曹晋菁, 仇式明, 定险峰, 程晓荣, 范炤. 意识的层级性和丰富性:解读意识的两条路径[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(7): 1172-1185. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||