

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 70-82.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.00070 cstr: 32110.14.2024.00070
收稿日期:2023-03-15
发布日期:2023-11-23
出版日期:2024-01-25
通讯作者:
伍新春, E-mail: xcwu@bnu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHAO Ying1, WU Xinchun2( ), CHEN Hongjun2, SUN Peng2, WANG Haolan2
), CHEN Hongjun2, SUN Peng2, WANG Haolan2
Received:2023-03-15
Online:2023-11-23
Published:2024-01-25
摘要:
对416名二(低)、四(中)、六(高)年级(学段)的汉语儿童进行半年追踪, 检验了语素意识与快速命名对两类阅读能力(理解与流畅性)的影响机制。结果表明, 对于低学段的儿童而言, 语素意识与快速命名通过字词识别准确性影响半年后的阅读能力, 且字词识别流畅性在快速命名影响阅读流畅性的过程中发挥中介作用。对于中、高学段的儿童而言, 语素意识与快速命名对半年后阅读理解的间接影响均不显著; 字词识别准确性在语素意识影响阅读流畅性的过程中发挥中介作用, 而字词识别流畅性的作用仅体现在中学段; 快速命名通过字词识别准确性和字词识别流畅性影响到阅读流畅性。结果揭示了在小学不同学段, 阅读理解与阅读流畅性的影响机制存在一定的共享性与特异性。
中图分类号:
赵英, 伍新春, 陈红君, 孙鹏, 王淏蘭. (2024). 语素意识与快速命名对汉语儿童阅读能力的影响:跨学段的中介效应分析. 心理学报, 56(1), 70-82.
ZHAO Ying, WU Xinchun, CHEN Hongjun, SUN Peng, WANG Haolan. (2024). Mechanisms underlying the effects of morphological awareness and rapid automatized naming (RAN) on the reading abilities of Chinese Children: An analysis of mediating effects across different stages. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(1), 70-82.
| 人口学 信息 | 低学段 (二年级) | 中学段 (四年级) | 高学段 (六年级) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人数 | 总 | 130 | 134 | 152 |
| 男 | 63 | 67 | 89 | |
| 女 | 67 | 67 | 63 | |
| 年龄(岁) | M | 7.70 | 9.65 | 11.61 |
| SD | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
表1 各学段汉语儿童的基本人口学信息
| 人口学 信息 | 低学段 (二年级) | 中学段 (四年级) | 高学段 (六年级) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人数 | 总 | 130 | 134 | 152 |
| 男 | 63 | 67 | 89 | |
| 女 | 67 | 67 | 63 | |
| 年龄(岁) | M | 7.70 | 9.65 | 11.61 |
| SD | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏度 | 峰度 | 偏度 | 峰度 | 偏度 | 峰度 | |
| 一般认知能力 | -0.56 | -0.04 | -0.82 | 0.40 | -0.42 | -0.33 |
| T1工作记忆 | 0.61 | 0.20 | 0.52 | -0.19 | 0.85 | -0.05 |
| T1语音意识 | -0.82 | -0.38 | -1.74 | 3.35 | -1.77 | 3.10 |
| T1正字法意识 | -1.15 | 2.04 | -1.34 | 2.35 | -1.43 | 2.31 |
| T1语素意识 | -0.04 | -0.37 | -0.59 | 0.73 | -1.00 | 0.90 |
| T1快速命名 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 1.54 | 4.94 | 0.61 | 0.04 |
| T1字词识别准确性 | -0.36 | -0.50 | -1.27 | 2.23 | -0.99 | 0.48 |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.60 | 1.49 | -0.15 | -0.07 | 0.75 | 1.99 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.67 | 0.82 | -0.34 | -0.24 | -0.46 | 0.52 |
| T2阅读理解 | -1.16 | 1.69 | -1.00 | 0.77 | -1.13 | 1.32 |
| T2阅读流畅性 | 0.31 | 0.22 | -0.15 | -0.21 | 0.56 | 1.58 |
表2 低、中、高三个学段各个变量的偏度和峰度
| 变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏度 | 峰度 | 偏度 | 峰度 | 偏度 | 峰度 | |
| 一般认知能力 | -0.56 | -0.04 | -0.82 | 0.40 | -0.42 | -0.33 |
| T1工作记忆 | 0.61 | 0.20 | 0.52 | -0.19 | 0.85 | -0.05 |
| T1语音意识 | -0.82 | -0.38 | -1.74 | 3.35 | -1.77 | 3.10 |
| T1正字法意识 | -1.15 | 2.04 | -1.34 | 2.35 | -1.43 | 2.31 |
| T1语素意识 | -0.04 | -0.37 | -0.59 | 0.73 | -1.00 | 0.90 |
| T1快速命名 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 1.54 | 4.94 | 0.61 | 0.04 |
| T1字词识别准确性 | -0.36 | -0.50 | -1.27 | 2.23 | -0.99 | 0.48 |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.60 | 1.49 | -0.15 | -0.07 | 0.75 | 1.99 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.67 | 0.82 | -0.34 | -0.24 | -0.46 | 0.52 |
| T2阅读理解 | -1.16 | 1.69 | -1.00 | 0.77 | -1.13 | 1.32 |
| T2阅读流畅性 | 0.31 | 0.22 | -0.15 | -0.21 | 0.56 | 1.58 |
| 变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | F | η2p | 事后比较 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | ||||
| 一般认知能力 | 39.45 | 6.91 | 42.74 | 6.71 | 45.19 | 7.44 | 23.25*** | 0.10 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1工作记忆 | 1.72 | 0.98 | 2.52 | 1.18 | 3.32 | 1.60 | 52.80*** | 0.20 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1语音意识 | 10.81 | 1.30 | 10.66 | 1.73 | 10.39 | 2.04 | 2.13 | 0.01 | — |
| T1正字法意识 | 36.94 | 5.43 | 38.10 | 5.65 | 37.58 | 6.21 | 1.32 | 0.01 | — |
| T1语素意识 | 25.70 | 9.44 | 34.36 | 9.17 | 35.18 | 10.08 | 40.44*** | 0.16 | 2 < 4 = 6 |
| T1快速命名 | 10.11 | 2.37 | 8.67 | 2.04 | 7.36 | 1.63 | 65.60*** | 0.24 | 2 > 4 > 6 |
| T1字词识别准确性 | 75.35 | 24.48 | 117.16 | 13.62 | 127.95 | 11.33 | 357.78*** | 0.63 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 72.79 | 16.97 | 87.79 | 15.87 | 102.87 | 21.33 | 94.13*** | 0.31 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1词汇知识 | 18.57 | 5.54 | 30.44 | 7.18 | 35.75 | 7.97 | 215.80*** | 0.51 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T2阅读理解_原始 | 32.35 | 4.64 | 30.72 | 4.57 | 31.17 | 4.73 | — | — | — |
| T2阅读理解_等值 | −0.63 | 0.97 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.86 | 51.82*** | 0.20 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T2阅读流畅性 | 177.87 | 46.52 | 222.57 | 40.71 | 279.35 | 62.34 | 138.89*** | 0.40 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
表3 三个学段儿童在各任务上得分的描述性统计和差异检验
| 变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | F | η2p | 事后比较 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | ||||
| 一般认知能力 | 39.45 | 6.91 | 42.74 | 6.71 | 45.19 | 7.44 | 23.25*** | 0.10 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1工作记忆 | 1.72 | 0.98 | 2.52 | 1.18 | 3.32 | 1.60 | 52.80*** | 0.20 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1语音意识 | 10.81 | 1.30 | 10.66 | 1.73 | 10.39 | 2.04 | 2.13 | 0.01 | — |
| T1正字法意识 | 36.94 | 5.43 | 38.10 | 5.65 | 37.58 | 6.21 | 1.32 | 0.01 | — |
| T1语素意识 | 25.70 | 9.44 | 34.36 | 9.17 | 35.18 | 10.08 | 40.44*** | 0.16 | 2 < 4 = 6 |
| T1快速命名 | 10.11 | 2.37 | 8.67 | 2.04 | 7.36 | 1.63 | 65.60*** | 0.24 | 2 > 4 > 6 |
| T1字词识别准确性 | 75.35 | 24.48 | 117.16 | 13.62 | 127.95 | 11.33 | 357.78*** | 0.63 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 72.79 | 16.97 | 87.79 | 15.87 | 102.87 | 21.33 | 94.13*** | 0.31 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T1词汇知识 | 18.57 | 5.54 | 30.44 | 7.18 | 35.75 | 7.97 | 215.80*** | 0.51 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T2阅读理解_原始 | 32.35 | 4.64 | 30.72 | 4.57 | 31.17 | 4.73 | — | — | — |
| T2阅读理解_等值 | −0.63 | 0.97 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.86 | 51.82*** | 0.20 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| T2阅读流畅性 | 177.87 | 46.52 | 222.57 | 40.71 | 279.35 | 62.34 | 138.89*** | 0.40 | 2 < 4 < 6 |
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.24** | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.11 | 0.04 | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.05 | 0.15 | -0.10 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.22* | 0.26** | 0.17 | -0.03 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.06 | -0.11 | -0.29** | -0.06 | -0.21* | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.17 | 0.20* | 0.18* | 0.05 | 0.39*** | -0.35*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.14 | 0.23** | 0.22* | -0.02 | 0.32*** | -0.63*** | 0.63*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.06 | -0.24** | 0.32*** | -0.11 | 0.29** | 0.24** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.40*** | 0.17 | 0.10 | -0.08 | 0.39*** | -0.13 | 0.61*** | 0.40*** | 0.27** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.11 | 0.20* | 0.11 | -0.06 | 0.36*** | -0.53*** | 0.69*** | 0.80*** | 0.34*** | 0.52*** |
表4 低学段儿童两个时间点各个变量之间的相关
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.24** | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.11 | 0.04 | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.05 | 0.15 | -0.10 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.22* | 0.26** | 0.17 | -0.03 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.06 | -0.11 | -0.29** | -0.06 | -0.21* | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.17 | 0.20* | 0.18* | 0.05 | 0.39*** | -0.35*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.14 | 0.23** | 0.22* | -0.02 | 0.32*** | -0.63*** | 0.63*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.06 | -0.24** | 0.32*** | -0.11 | 0.29** | 0.24** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.40*** | 0.17 | 0.10 | -0.08 | 0.39*** | -0.13 | 0.61*** | 0.40*** | 0.27** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.11 | 0.20* | 0.11 | -0.06 | 0.36*** | -0.53*** | 0.69*** | 0.80*** | 0.34*** | 0.52*** |
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.11 | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.31*** | 0.27** | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.08 | -0.07 | -0.08 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.19* | 0.22* | 0.30*** | 0.08 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.22* | -0.17 | -0.17 | 0.08 | -0.13 | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.37*** | 0.28** | 0.26** | -0.02 | 0.44*** | -0.44*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.26** | 0.16 | 0.26** | 0.002 | 0.30*** | -0.59*** | 0.45*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.21* | 0.22** | 0.14 | -0.08 | 0.34*** | -0.27** | 0.54*** | 0.28** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.45*** | 0.18* | 0.38*** | -0.08 | 0.41*** | -0.28** | 0.52*** | 0.40*** | 0.39*** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.39*** | 0.23** | 0.33*** | -0.09 | 0.34*** | -0.47*** | 0.58*** | 0.71*** | 0.36*** | 0.51*** |
表5 中学段儿童两个时间点各个变量之间的相关
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.11 | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.31*** | 0.27** | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.08 | -0.07 | -0.08 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.19* | 0.22* | 0.30*** | 0.08 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.22* | -0.17 | -0.17 | 0.08 | -0.13 | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.37*** | 0.28** | 0.26** | -0.02 | 0.44*** | -0.44*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.26** | 0.16 | 0.26** | 0.002 | 0.30*** | -0.59*** | 0.45*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.21* | 0.22** | 0.14 | -0.08 | 0.34*** | -0.27** | 0.54*** | 0.28** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.45*** | 0.18* | 0.38*** | -0.08 | 0.41*** | -0.28** | 0.52*** | 0.40*** | 0.39*** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.39*** | 0.23** | 0.33*** | -0.09 | 0.34*** | -0.47*** | 0.58*** | 0.71*** | 0.36*** | 0.51*** |
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.44*** | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.15 | 0.25** | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.15 | 0.08 | -0.14 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.37*** | 0.16* | 0.17* | 0.11 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.06 | -0.21* | -0.01 | 0.27** | -0.08 | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.37*** | 0.38*** | 0.29*** | -0.13 | 0.42*** | -0.35*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.19* | 0.30*** | 0.15 | -0.14 | 0.18* | -0.68*** | 0.38*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.39*** | 0.34*** | 0.25** | -0.04 | 0.45*** | -0.14 | 0.47*** | 0.32*** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.53*** | 0.45*** | 0.21** | -0.04 | 0.40*** | -0.15 | 0.48*** | 0.28*** | 0.47*** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.19* | 0.30** | 0.19* | -0.18* | 0.19* | -0.58*** | 0.49*** | 0.74*** | 0.24* | 0.36*** |
表6 高学段儿童两个时间点各个变量之间的相关
| 变量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 一般认知能力 | — | |||||||||
| 2. T1工作记忆 | 0.44*** | — | ||||||||
| 3. T1语音意识 | 0.15 | 0.25** | — | |||||||
| 4. T1正字法意识 | 0.15 | 0.08 | -0.14 | — | ||||||
| 5. T1语素意识 | 0.37*** | 0.16* | 0.17* | 0.11 | — | |||||
| 6. T1快速命名 | -0.06 | -0.21* | -0.01 | 0.27** | -0.08 | — | ||||
| 7. T1字词识别准确性 | 0.37*** | 0.38*** | 0.29*** | -0.13 | 0.42*** | -0.35*** | — | |||
| 8. T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.19* | 0.30*** | 0.15 | -0.14 | 0.18* | -0.68*** | 0.38*** | — | ||
| 9. T1词汇知识 | 0.39*** | 0.34*** | 0.25** | -0.04 | 0.45*** | -0.14 | 0.47*** | 0.32*** | — | |
| 10. T2阅读理解 | 0.53*** | 0.45*** | 0.21** | -0.04 | 0.40*** | -0.15 | 0.48*** | 0.28*** | 0.47*** | — |
| 11. T2阅读流畅性 | 0.19* | 0.30** | 0.19* | -0.18* | 0.19* | -0.58*** | 0.49*** | 0.74*** | 0.24* | 0.36*** |
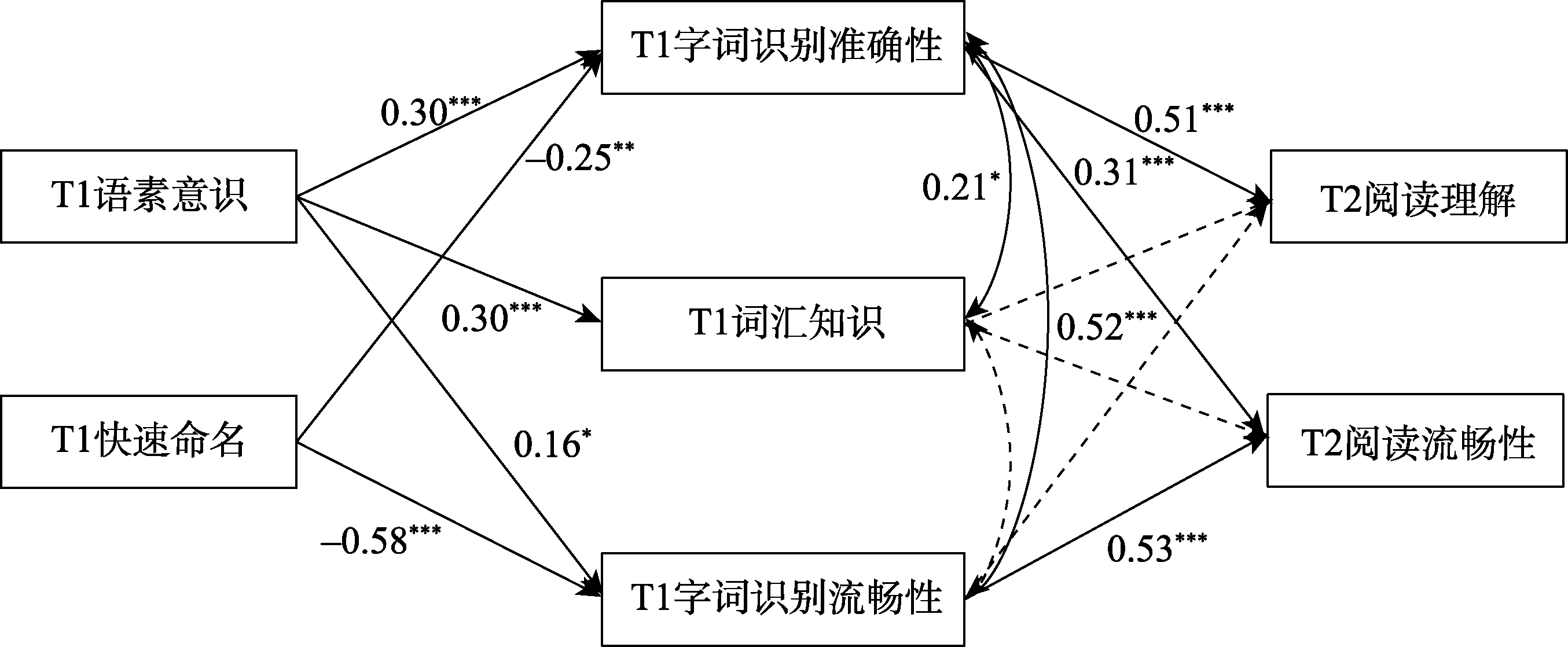
图1 低学段语素意识与快速命名对阅读能力影响的中介模型 注:T1快速命名对T1词汇知识的影响不进行估计。为了清晰呈现模型的标准化结果, 模型中其余的相关路径, 以及控制变量对中介变量和因变量的影响等均未画出; 自变量对因变量不显著的直接效应也未在图中呈现, 但在模型估计时均进行了估计。*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05。下同。
| 因 变 量 | 自变量 | 中介变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | ||||||
| 下限 | 上限 | 下限 | 上限 | 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| T2 阅 读 理 解 | T1语素意识 | T1字词识别准确性 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.07 | -0.01 | 0.15 | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.12 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.01 | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | -0.02 | 0.08 | 0.05 | -0.01 | 0.11 | ||
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.02 | -0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | -0.01 | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.03 | 0.04 | ||
| T1快速命名 | T1字词识别准确性 | -0.13 | -0.23 | -0.02 | -0.07 | -0.14 | 0.001 | -0.04 | -0.10 | 0.01 | |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | -0.06 | -0.17 | 0.06 | -0.08 | -0.17 | 0.002 | -0.05 | -0.20 | 0.10 | ||
| T2 阅 读 流 畅 性 | T1语素意识 | T1字词识别准确性 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.14 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.03 | -0.02 | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.04 | 0.05 | -0.04 | -0.09 | 0.01 | ||
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.08 | -0.003 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.05 | -0.05 | 0.14 | ||
| T1快速命名 | T1字词识别准确性 | -0.08 | -0.14 | -0.02 | -0.08 | -0.15 | -0.01 | -0.06 | -0.10 | -0.02 | |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | -0.31 | -0.43 | -0.18 | -0.28 | -0.39 | -0.17 | -0.40 | -0.52 | -0.27 | ||
表7 三个学段可能的间接路径的Bootstrap检验结果
| 因 变 量 | 自变量 | 中介变量 | 低学段 | 中学段 | 高学段 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | 标准化的估计值 | 95% CI | ||||||
| 下限 | 上限 | 下限 | 上限 | 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| T2 阅 读 理 解 | T1语素意识 | T1字词识别准确性 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.07 | -0.01 | 0.15 | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.12 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.01 | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | -0.02 | 0.08 | 0.05 | -0.01 | 0.11 | ||
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.02 | -0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | -0.01 | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.03 | 0.04 | ||
| T1快速命名 | T1字词识别准确性 | -0.13 | -0.23 | -0.02 | -0.07 | -0.14 | 0.001 | -0.04 | -0.10 | 0.01 | |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | -0.06 | -0.17 | 0.06 | -0.08 | -0.17 | 0.002 | -0.05 | -0.20 | 0.10 | ||
| T2 阅 读 流 畅 性 | T1语素意识 | T1字词识别准确性 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.14 |
| T1词汇知识 | 0.03 | -0.02 | 0.07 | 0.01 | -0.04 | 0.05 | -0.04 | -0.09 | 0.01 | ||
| T1字词识别流畅性 | 0.08 | -0.003 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.05 | -0.05 | 0.14 | ||
| T1快速命名 | T1字词识别准确性 | -0.08 | -0.14 | -0.02 | -0.08 | -0.15 | -0.01 | -0.06 | -0.10 | -0.02 | |
| T1字词识别流畅性 | -0.31 | -0.43 | -0.18 | -0.28 | -0.39 | -0.17 | -0.40 | -0.52 | -0.27 | ||
| [1] | Adams R. J., Wu M. L., & Wilson M. R. (2015). ACER ConQuest: Generalised item response modeling software [computer software] version 4. Australian Council for Educational Research. |
| [2] |
Altani A., Protopapas A., Katopodi K., & Georgiou G. K. (2020). From individual word recognition to word list and text reading fluency. Journal of Educational Psychology, 112(1), 22-39.
doi: 10.1037/edu0000359 URL |
| [3] |
Baker D. L., Biancarosa G., Park B. J., Bousselot T., Smith J., Baker S. K., … Tindal G. (2015). Validity of CBM measures of oral reading fluency and reading comprehension on high-stakes reading assessments in Grades 7 and 8. Reading and Writing, 28(1), 57-104.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-014-9505-4 URL |
| [4] |
Braze D., Katz L., Magnuson J. S., Mencl W. E., Tabor W., Van Dyke J. A., … Shankweiler D. (2016). Vocabulary does not complicate the simple view of reading. Reading and Writing, 29(3), 435-451.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-015-9608-6 URL |
| [5] | Chall J. S. (1983). Stages of reading development. McGraw-Hill. |
| [6] |
Chen H., Zhao Y., Wu X., Sun P., Feng J., Xie R., & Wang H. (2023). Effects of phonological awareness and morphological awareness on blind students’ reading comprehension. British Journal of Psychology, 114(2), 415-429.
doi: 10.1111/bjop.v114.2 URL |
| [7] |
Cheng Y., Wang J., & Wu X. (2018). The role of morphological awareness in Chinese children’s reading comprehension: The mediating effect of word reading fluency. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(4), 413-425.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2018.00413 URL |
| [ 程亚华, 王健, 伍新春. (2018). 小学低年级儿童汉语语素意识在阅读理解中的作用:字词阅读流畅性的中介效应. 心理学报, 50(4), 413-425.] | |
| [8] |
Cheng Y., Zhang J., Li H., Wu X., Liu H., Dong Q., … Sun P. (2017). Growth of compounding awareness predicts reading comprehension in young Chinese students: A longitudinal study from grade 1 to grade 2. Reading Research Quarterly, 52(1), 91-104.
doi: 10.1002/rrq.2017.52.issue-1 URL |
| [9] |
Cohen-Mimran R. (2009). The contribution of language skills to reading fluency: A comparison of two orthographies for Hebrew. Journal of Child Language, 36(3), 657-672.
doi: 10.1017/S0305000908009148 pmid: 19134231 |
| [10] |
Deacon S. H., Kieffer M. J., & Laroche A. (2014). The relation between morphological awareness and reading comprehension: Evidence from mediation and longitudinal models. Scientific Studies of Reading, 18(6), 432-451.
doi: 10.1080/10888438.2014.926907 URL |
| [11] |
Fuchs L. S., Fuchs D., Hosp M. K., & Jenkins J. R. (2001). Oral reading fluency as an indicator of reading competence: A theoretical, empirical, and historical analysis. Scientific Studies of Reading, 5(3), 239-256.
doi: 10.1207/S1532799XSSR0503_3 URL |
| [12] |
Geva E., & Farnia F. (2012). Developmental changes in the nature of language proficiency and reading fluency paint a more complex view of reading comprehension in ELL and EL1. Reading and Writing, 25(8), 1819-1845.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-011-9333-8 URL |
| [13] |
Hjetland H. N., Lervåg A., Lyster S. H., Hagtvet B. E., Hulme C., & Melby-Lervåg M. (2019). Pathways to reading comprehension: A longitudinal study from 4 to 9 years of age. Journal of Educational Psychology, 111(5), 751-763.
doi: 10.1037/edu0000321 |
| [14] |
Hoover W. A., & Gough P. B. (1990). The simple view of reading. Reading and Writing, 2(2), 127-160.
doi: 10.1007/BF00401799 URL |
| [15] | Hudson R. F., Pullen P. C., Lane H. B., & Torgesen J. K. (2009). The complex nature of reading fluency: A multidimensional view. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 25(1), 4-32. |
| [16] |
Jenkins J. R., Fuchs L. S., Van den Broek P., Espin C., & Deno S. L. (2003). Sources of individual differences in reading comprehension and reading fluency. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95(4), 719-729.
doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.95.4.719 URL |
| [17] |
Johnston T. C., & Kirby J. R. (2006). The contribution of naming speed to the simple view of reading. Reading and Writing, 19(4), 339-361.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-005-4644-2 URL |
| [18] |
Joshi R. M., Ji X. R., Breznitz Z., Amiel M., & Yulia A. (2015). Validation of the simple view of reading in Hebrew—A Semitic language. Scientific Studies of Reading, 19(3), 243-252.
doi: 10.1080/10888438.2015.1010117 URL |
| [19] |
Juul H., Poulsen M., & Elbro C. (2014). Separating speed from accuracy in beginning reading development. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106(4), 1096-1106.
doi: 10.1037/a0037100 URL |
| [20] |
Kieffer M. J., Biancarosa G., & Mancilla-martinez J. (2013). Roles of morphological awareness in the reading comprehension of Spanish-speaking language minority learners: Exploring partial mediation by vocabulary and reading fluency. Applied PsychoLinguistics, 34(4), 697-725.
doi: 10.1017/S0142716411000920 URL |
| [21] |
Kieffer M. J., & Lesaux N. K. (2012). Direct and indirect roles of morphological awareness in the English reading comprehension of native English, Spanish, Filipino, and Vietnamese speakers. Language Learning, 62(4), 1170-1204.
doi: 10.1111/lang.2012.62.issue-4 URL |
| [22] |
Kim Y. G. (2020). Hierarchical and dynamic relations of language and cognitive skills to reading comprehension: Testing the direct and indirect effects model of reading (DIER). Journal of Educational Psychology, 112(4), 667-694.
doi: 10.1037/edu0000407 URL |
| [23] |
Kim Y. G. (2015). Developmental, component-based model of reading fluency: An investigation of predictors of word-reading fluency, text-reading fluency, and reading comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 50(4), 459-481.
doi: 10.1002/rrq.2015.50.issue-4 URL |
| [24] |
Kim Y. G., Guo Q., Liu Y., Peng Y., & Yang L. (2020). Multiple pathways by which compounding morphological awareness is related to reading comprehension: Evidence from Chinese second graders. Reading Research Quarterly, 55(2), 193-212.
doi: 10.1002/rrq.v55.2 URL |
| [25] |
Kuo L., & Anderson R. C. (2006). Morphological awareness and learning to read: A cross-language perspective. Educational Psychologist, 41(3), 161-180.
doi: 10.1207/s15326985ep4103_3 URL |
| [26] |
Laberge D., & Samuels S. J. (1974). Toward a theory of automatic information processing in reading. Cognitive Psychology, 6(2), 293-323.
doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(74)90015-2 URL |
| [27] |
Li H., Shu H., Mcbridechang C., Liu H., & Peng H. (2012). Chinese children's character recognition: Visuo-orthographic, phonological processing and morphological skills. Journal of Research in Reading, 35(3), 287-307.
doi: 10.1111/jrir.2012.35.issue-3 URL |
| [28] | Li L., & Wu X. (2015). Effects of metalinguistic awareness on reading comprehension and the mediator role of reading fluency from grades 2 to 4. PloS One, 10(3), e114417. |
| [29] |
Liao C., Georgiou G. K., & Parrila R. (2008). Rapid naming speed and Chinese character recognition. Reading and Writing, 21(3), 231-253.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-007-9071-0 URL |
| [30] |
Liu P. D., & McBride-Chang C. (2010). What is morphological awareness? Tapping lexical compounding awareness in Chinese third graders. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(1), 62-73
doi: 10.1037/a0016933 URL |
| [31] |
Mcbride-Chang C., Tardif T., Cho J., Shu H., Fletcher P. C., Stokes S. F., … Leung K. (2008). What's in a word? Morphological awareness and vocabulary knowledge in three languages. Applied Psycholinguistics, 29(3), 437-462.
doi: 10.1017/S014271640808020X URL |
| [32] |
Norton E. S., & Wolf M. (2012). Rapid automatized naming (RAN) and reading fluency: Implications for understanding and treatment of reading disabilities. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 427-452.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100431 pmid: 21838545 |
| [33] |
Pan J., McBride-Chang C., Shu H., Liu H., Zhang Y., & Li H. (2011). What is in the naming? A 5-year longitudinal study of early rapid naming and phonological sensitivity in relation to subsequent reading skills in both native Chinese and English as a second language. Journal of Educational Psychology, 103(4), 897-908.
doi: 10.1037/a0024344 URL |
| [34] |
Pan J., Song S., Su M., McBride C., Liu H., Zhang Y., … Shu H. (2016). On the relationship between phonological awareness, morphological awareness and Chinese literacy skills: Evidence from an 8-year longitudinal study. Developmental Science, 19(6), 982-991.
doi: 10.1111/desc.12356 pmid: 26537834 |
| [35] |
Peng P., Barnes M., Wang C., Wang W., Li S., Swanson H. L., … Tao S. (2018). A meta-analysis on the relation between reading and working memory. Psychological Bulletin, 144(1), 48-76.
doi: 10.1037/bul0000124 pmid: 29083201 |
| [36] | Perfetti C.A., Landi N., & Oakhill J. (2005). The acquisition of reading comprehension skill. In M. J. Snowling & C. Hulme(Eds.), The science of reading: A handbook (pp. 227-247). Blackwell. |
| [37] |
Ruan Y., Georgiou G. K., Song S., Li Y., & Shu H. (2018). Does writing system influence the associations between phonological awareness, morphological awareness, and reading? A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 110(2), 180-202.
doi: 10.1037/edu0000216 URL |
| [38] |
Shu H., Chen X., Anderson R. C., Wu N., & Xuan Y. (2003). Properties of school Chinese: Implications for learning to read. Child Development, 74(1), 27-47.
pmid: 12625434 |
| [39] |
Shu H., McBride-Chang C., Wu S., & Liu H. (2006). Understanding Chinese developmental dyslexia: Morphological awareness as a core cognitive construct. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(1), 122-133.
doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.98.1.122 URL |
| [40] |
Shu H., Peng H., & Mcbride-Chang C. (2008). Phonological awareness in young Chinese children. Developmental Science, 11(1), 171-181.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00654.x pmid: 18171377 |
| [41] |
Song S., Su M., Kang C., Liu H., Zhang Y., Mcbride- Chang C.,... Shu H. (2015). Tracing children's vocabulary development from preschool through the school-age years: An 8-year longitudinal study. Developmental Science, 18(1), 119-131.
doi: 10.1111/desc.12190 pmid: 24962559 |
| [42] |
Stanovich K. E. (1980). Toward an interactive-compensatory model of individual differences in the development of reading fluency. Reading Research Quarterly, 16(1), 32-71.
doi: 10.2307/747348 URL |
| [43] |
Verhoeven L., & Perfetti C. A. (2011). Morphological processing in reading acquisition: A cross-linguistic perspective. Applied Psycholinguistics, 32(3), 457-466.
doi: 10.1017/S0142716411000154 URL |
| [44] |
Wang Y., & McBride C. (2016). Character reading and word reading in Chinese: Unique correlates for Chinese kindergarteners. Applied Psycholinguistics, 37(2), 371-386.
doi: 10.1017/S014271641500003X URL |
| [45] |
Wang Z., Sabatini J., O'Reilly T., & Weeks J. (2019). Decoding and reading comprehension: A test of the decoding threshold hypothesis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 111(3), 387-401
doi: 10.1037/edu0000302 URL |
| [46] |
Wei W., Georgiou G. K., & Deng C. (2015). Examining the cross-lagged relationships between RAN and word reading in Chinese. Scientific Studies of Reading, 19(6), 446-455.
doi: 10.1080/10888438.2015.1077447 URL |
| [47] |
Yan M., Li Y., Sun X., Zhou X., Hui Y., & Li H. (2021). The roles of decoding and vocabulary in Chinese reading development: Evidence from a 3-year longitudinal study. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(1), 300-314.
doi: 10.1111/bjep.v91.1 URL |
| [48] |
Yu Y., Xie R., Wu X., Xia Y., Wang Z., & Nguyen T. P. (2023). The relationship between metalinguistic awareness and reading fluency in elementary school children: The mediating role of character recognition and vocabulary knowledge. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(6), 941-953.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00941 |
|
[ 喻艳玲, 谢瑞波, 伍新春, 夏月, 王振梁, 阮世芳. (2023). 小学低年级儿童元语言意识与阅读流畅性的关系:汉字识别和词汇知识的中介效应. 心理学报, 55(6), 941-953.]
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00941 |
|
| [49] | Zhang H. C., & Wang X. P. (1989). Standardization research on Raven’s standard progressive matrices in China. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 21(2), 113-121. |
| [ 张厚粲, 王晓平. (1989). 瑞文标准推理测验在我国的修订. 心理学报, 21(2), 113-121.] | |
| [50] |
Zhao Y., Cheng Y., & Wu X. (2019). Contributions of morphological awareness and rapid automatized naming (RAN) to Chinese children’s reading comprehension versus reading fluency: Evidence from a longitudinal mediation model. Reading and Writing, 32(8), 2013-2036.
doi: 10.1007/s11145-019-09935-w |
| [51] |
Zhao Y., Cheng Y., Wu X., & Nguyen T. P. (2016). The reciprocal relationship between morphological awareness and vocabulary knowledge among Chinese children: A longitudinal study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(11), 1434-1444.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01434 |
| [ 赵英, 程亚华, 伍新春, 阮氏芳. (2016). 汉语儿童语素意识与词汇知识的双向关系:一项追踪研究. 心理学报, 48(11), 1434-1444.] | |
| [52] | Zhou T., Li Y., Li H., Xu Z., Zhang F., & Cheng Y. (2021). The relation between oral reading fluency and reading comprehension among Chinese children: A 3-year longitudinal study. Psychological Development and Education, 37(5), 691-700. |
| [ 周婷娜, 李宜逊, 李虹, 徐钟庚, 张锋, 程亚华. (2021). 汉语儿童口语流畅性与阅读理解的关系:一项三年追踪研究. 心理发展与教育, 37(5), 691-700.] | |
| [53] | Zhou X. L., & Marslen-Wilson W. (2000). Lexical representation of compound words: Cross-linguistic evidence. Psychologia, 43(1), 47-66. |
| [54] |
Ziegler J. C., Bertrand D., Tóth D., Csépe V., Reis A., Faísca L.,... Blomert L. (2010). Orthographic depth and its impact on universal predictors of reading a cross-language investigation. Psychological Science, 21(4), 551-559.
doi: 10.1177/0956797610363406 URL |
| [1] | 郭存, 谢瑞波, 喻艳玲, 夏月, 王振梁, 伍新春. 小学中高年级儿童复合语素意识、词语结构意识与词汇知识的关系:交叉滞后研究[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(11): 1488-1498. |
| [2] | 程亚华, 沈岚岚, 李宜逊, 伍新春, 李虹, 王铁群, 程芳. 家庭阅读环境对学龄儿童汉字识别、口语词汇知识与阅读理解的影响:一个发展级联模型[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(1): 83-92. |
| [3] | 程亚华, 冯瑶, 李宜逊, 马嘉琪, 沈岚岚, 张文建, 伍新春, 冯秋迪. 小学儿童口语词汇知识的发展轨迹及其对阅读能力的预测:一个潜变量增长模型[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(7): 1074-1086. |
| [4] | 喻艳玲, 谢瑞波, 伍新春, 夏月, 王振梁, 阮世芳. 小学低年级儿童元语言意识与阅读流畅性的关系:汉字识别和词汇知识的中介效应[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(6): 941-953. |
| [5] | 周怡彤, 谢瑞波, 伍新春, 阮世芳, 夏月, 喻艳玲, 王振梁. 小学低年级儿童语音意识和语素意识对阅读理解的影响:阅读流畅性的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(6): 930-940. |
| [6] | 夏月, 谢瑞波, 王振梁, 阮世芳, 伍新春. 小学低年级汉语儿童语素意识、汉字识别和词汇知识的发展关系——交叉滞后研究[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(8): 905-916. |
| [7] | 李利平, 伍新春, 程亚华. 小学低段汉字识别和听写的发展轨迹:语素意识的预测作用[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(5): 623-632. |
| [8] | 陈红君, 赵英, 伍新春, 孙鹏, 谢瑞波, 冯杰. 小学儿童词汇知识与阅读理解的关系:交叉滞后研究[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(8): 924-934. |
| [9] | 程亚华, 王健, 伍新春. 小学低年级儿童汉语语素意识在阅读理解中的 作用:字词阅读流畅性的中介效应[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(4): 413-425. |
| [10] | 程亚华, 伍新春, 刘红云, 李虹. 小学低年级儿童口语词汇知识的发展轨迹及其影响因素[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(2): 206-215. |
| [11] | 赵英;程亚华;伍新春;阮氏芳. 汉语儿童语素意识与词汇知识的双向关系:一项追踪研究[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(11): 1434-1444. |
| [12] | 李利平; 伍新春;周宁宁;程亚华; 阮氏芳. 汉语儿童读词者的认知特征及其影响因素[J]. 心理学报, 2016, 48(10): 1270-1281. |
| [13] | 刘文理,刘翔平,张婧乔. 汉语发展性阅读障碍亚类型的初步探讨[J]. 心理学报, 2006, 38(05): 681-693. |
| [14] | 王燕,林崇德,俞国良. 英语学习不良儿童语音能力与阅读理解的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2002, 34(03): 59-63. |
| [15] | 孟祥芝,周晓林,曾飚,孔瑞芬,庄捷. 动态视觉加工与儿童汉字阅读[J]. 心理学报, 2002, 34(01): 17-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||