

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 12-25.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00012 cstr: 32110.14.2020.00012
收稿日期:2018-09-21
发布日期:2019-11-21
出版日期:2020-01-25
基金资助:
SUN Yan( ), BO Siyu, LV Jiaojiao
), BO Siyu, LV Jiaojiao
Received:2018-09-21
Online:2019-11-21
Published:2020-01-25
摘要:
本文旨在对认知重评和表达抑制两种常用情绪调节策略的自发脑网络特征及认知神经活动进行深入探讨。研究采集36名在校大学生的静息态和任务态脑电数据, 经过源定位和图论分析发现节点效率与两种情绪调节显著相关的脑区, 以及脑区之间的功能连接。研究结果表明, 在使用认知重评进行情绪调节时会激活前额叶皮质、前扣带回、顶叶、海马旁回和枕叶等多个脑区, 在使用表达抑制进行情绪调节时会激活前额叶皮质、顶叶、海马旁回、枕叶、颞叶和脑岛等多个脑区。因此, 这些脑区的节点效率或功能连接强度可能成为评估个体使用认知重评和表达抑制调节情绪效果的指标。
中图分类号:
孙岩, 薄思雨, 吕娇娇. (2020). 认知重评和表达抑制情绪调节策略的脑网络分析:来自EEG和ERP的证据. 心理学报, 52(1), 12-25.
SUN Yan, BO Siyu, LV Jiaojiao. (2020). Brain network analysis of cognitive reappraisal and expressive inhibition strategies: Evidence from EEG and ERP. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(1), 12-25.
| 情绪调节策略 | 脑区 | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 顶叶(中央后回)-额叶(额下回/额中回) (1R-46R) | 0.63*** | 0.00049 |
| ES | 海马旁回-额下回/额中回/脑岛(35L-47R) | 0.61*** | 0.00012 |
| 海马旁回-顶叶(顶下回) (37L-40L) | 0.60*** | 0.00014 | |
| 额下回/额中回/脑岛-海马旁回(47L-36R) | 0.56*** | 0.00046 | |
| 海马旁回-额下回/额中回/脑岛(28L-47R) | 0.55*** | 0.00063 | |
| 额下回/额中回/脑岛-海马旁回(47L-35R) | 0.54*** | 0.00082 |
表1 theta频带下相位滞后同步与CR和ES评分相关显著的功能连接脑区
| 情绪调节策略 | 脑区 | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 顶叶(中央后回)-额叶(额下回/额中回) (1R-46R) | 0.63*** | 0.00049 |
| ES | 海马旁回-额下回/额中回/脑岛(35L-47R) | 0.61*** | 0.00012 |
| 海马旁回-顶叶(顶下回) (37L-40L) | 0.60*** | 0.00014 | |
| 额下回/额中回/脑岛-海马旁回(47L-36R) | 0.56*** | 0.00046 | |
| 海马旁回-额下回/额中回/脑岛(28L-47R) | 0.55*** | 0.00063 | |
| 额下回/额中回/脑岛-海马旁回(47L-35R) | 0.54*** | 0.00082 |
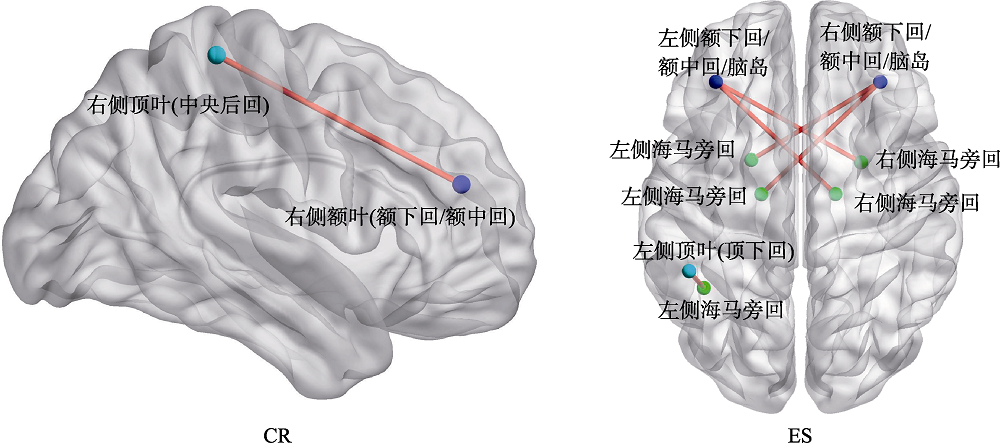
图2 theta频带下相位滞后同步与CR和ES心理估计变量(即情绪调节两个分量表评分)相关显著的功能连接脑区(p < 0.001, Bonferroni校正)。左图表示在theta频带下EEG信号与被试的CR得分相关显著的功能连接脑区; 右图表示在该频带下EEG信号与被试的ES得分相关显著的功能连接脑区。红色线表示连接的两个布鲁德曼脑区之间功能上的同步性与情绪调节得分呈显著正相关。
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 前额中央后回(4R) | -0.51** | 0.0016 | 额下回/额中回/脑岛(47R) | 0.36* | 0.034 |
| 顶叶中央后回(3R) | -0.43* | 0.010 | 前额叶皮层(6L) | -0.34* | 0.044 |
| 前扣带回(25L) | -0.35* | 0.041 | 内侧前额叶皮层(11R) | -0.34* | 0.049 |
表2 theta频带下节点效率与CR和ES评分相关显著的脑区
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 前额中央后回(4R) | -0.51** | 0.0016 | 额下回/额中回/脑岛(47R) | 0.36* | 0.034 |
| 顶叶中央后回(3R) | -0.43* | 0.010 | 前额叶皮层(6L) | -0.34* | 0.044 |
| 前扣带回(25L) | -0.35* | 0.041 | 内侧前额叶皮层(11R) | -0.34* | 0.049 |
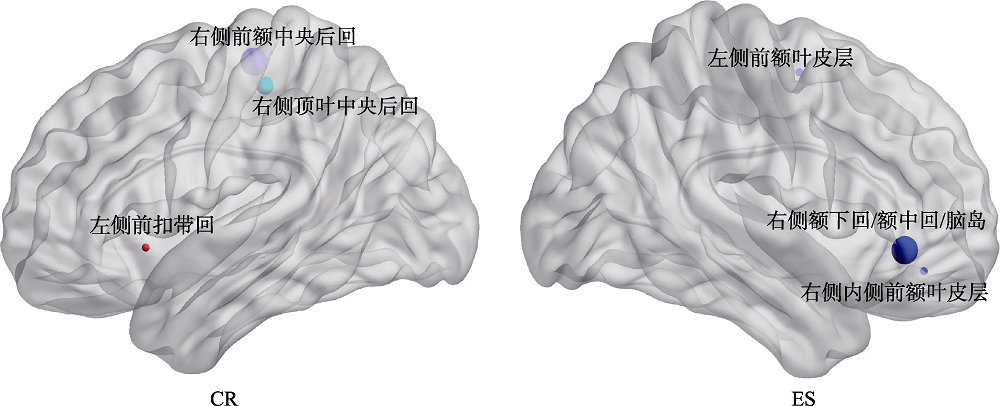
图3 theta频带下节点效率与CR和ES心理估计变量(即情绪调节两个分量表评分)相关显著的脑区(p < 0.05, Bonferroni校正)。左图表示theta频带下节点效率与被试的CR得分相关显著的脑区, 右图表示theta频带下节点效率与被试的ES得分相关显著的脑区。图中圆点位置表示对应的布鲁德曼脑区, 圆点大小表示相关的显著性程度, 越大表示两者相关越显著。
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 颞下回(20L)-额上回(8R) | 0.66*** | 0.000016 | |||
| 海马旁回(37L)-海马旁回(37R) | -0.72*** | 0.0000014 | 海马旁回(35L)-海马旁回(36L) | 0.64*** | 0.000036 |
| 顶上回(5L)-海马旁回(34L) | 0.63*** | 0.000057 | |||
| 额内侧回\额上回\额下回(10L)-内侧 前额叶皮层(11R) | -0.60*** | 0.00015 | 海马旁回(36L)-额上回(8R) | 0.57*** | 0.00034 |
| 中央后回(3R)-额上回(8R) | 0.57*** | 0.00038 | |||
| 顶上回(5L)-海马旁回(28L) | 0.56*** | 0.00043 | |||
| 额上回(8L)-颞下回(20L) | 0.55*** | 0.00060 | |||
表3 LPP波幅和theta频带下相位滞后同步相关显著的脑区
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 颞下回(20L)-额上回(8R) | 0.66*** | 0.000016 | |||
| 海马旁回(37L)-海马旁回(37R) | -0.72*** | 0.0000014 | 海马旁回(35L)-海马旁回(36L) | 0.64*** | 0.000036 |
| 顶上回(5L)-海马旁回(34L) | 0.63*** | 0.000057 | |||
| 额内侧回\额上回\额下回(10L)-内侧 前额叶皮层(11R) | -0.60*** | 0.00015 | 海马旁回(36L)-额上回(8R) | 0.57*** | 0.00034 |
| 中央后回(3R)-额上回(8R) | 0.57*** | 0.00038 | |||
| 顶上回(5L)-海马旁回(28L) | 0.56*** | 0.00043 | |||
| 额上回(8L)-颞下回(20L) | 0.55*** | 0.00060 | |||
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 顶叶中央后回(1L) | 0.44** | 0.0088 | 额上回(8R) | 0.37* | 0.031 |
| 海马旁回(37L) | -0.41* | 0.013 | |||
| 枕下回(17L) | -0.35* | 0.040 | 枕下回(17L) | -0.34* | 0.043 |
表4 LPP波幅和theta频带下节点效率相关显著的脑区
| CR | ES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑区 | r | p | 脑区 | r | p |
| 顶叶中央后回(1L) | 0.44** | 0.0088 | 额上回(8R) | 0.37* | 0.031 |
| 海马旁回(37L) | -0.41* | 0.013 | |||
| 枕下回(17L) | -0.35* | 0.040 | 枕下回(17L) | -0.34* | 0.043 |

图5 LPP波幅和theta频带下相位滞后同步相关显著的脑区(p < 0.001, Bonferroni校正)。左图表示在theta频带下EEG信号与被试的CR条件下LPP波幅相关显著的功能连接脑区; 右图表示在该频带下EEG信号与被试的ES条件下LPP波幅相关显著的功能连接脑区。红色线表示连接的两个布鲁德曼脑区之间功能上的同步性与情绪调节得分呈显著正相关。蓝色线表示连接的两个布鲁德曼脑区之间功能上的同步性与情绪调节得分呈显著负相关。
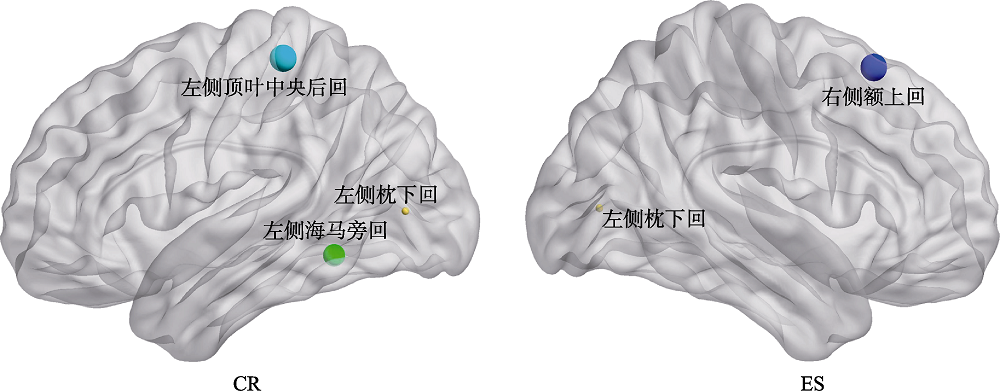
图6 LPP波幅和theta频带下节点效率相关显著的脑区(p < 0.05, Bonferroni校正)。左图表示theta频带下节点效率与被试的CR条件下LPP波幅相关显著的脑区, 右图表示theta频带下节点效率与被试的ES条件下LPP波幅相关显著的脑区。图中圆点位置表示对应的布鲁德曼脑区, 圆点大小表示相关的显著性程度, 越大表示两者相关越显著。
| [1] | Alizadeh A., Fatemizadeh E., & Deevband M. R . ( 2014, November) Investigation of Brain Default Network's activation in autism spectrum disorders Using Group Independent Component Analysis. 21st Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME 2014), Biomedical Engineering Faculty, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic), Tehran, Iran. |
| [2] |
Amrhein C., Mühlberger A., Pauli P., & Wiedemann G . ( 2004). Modulation of event-related brain potentials during affective picture processing: A complement to startle reflex and skin conductance response? International Journal of Psychophysiology, 54( 3), 231-240.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2004.05.009 URL pmid: 15331214 |
| [3] |
Arnold A. E. G. F., Protzner A. B., Bray S., Levy R. M., & Iaria G . ( 2014). Neural network configuration and efficiency underlies individual differences in spatial orientation ability. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26( 2), 380-394.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00491 URL |
| [4] |
Badre D., & Wagner A. D . ( 2004). Selection, integration, and conflict monitoring: Assessing the nature and generality of prefrontal cognitive control mechanisms. Neuron, 41( 3), 473-487.
doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00851-1 URL |
| [5] |
Balconi M., Grippa E., & Vanutelli M. E . ( 2015). What hemodynamic (FNIRs), electrophysiological (EEG) and autonomic integrated measures can tell us about emotional processing. Brain and Cognition, 95, 67-76.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2015.02.001 URL pmid: 25721430 |
| [6] |
Barch D., Braver T., Akbudak E., & Ollinger J . ( 2000). Anterior cingulate cortex and response conflict: Effects of response modality and processing domain. Neuroimage, 11( 5), S104-S104.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017635 URL pmid: 21408006 |
| [7] |
Batut A. C., Gounot D., Namer I. J., Hirsch E., Kehrli P., & Metz-Lutz M. N . ( 2006). Neural responses associated with positive and negative emotion processing in patients with left versus right temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 9( 3), 415-423.
doi: 10.21101/cejph.a5765 URL pmid: 31901191 |
| [8] |
Bradley M. M., & Lang P. J . ( 1994). Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 25( 1), 49-59.
doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(94)90063-9 URL pmid: 7962581 |
| [9] |
Braver T. S., Barch D. M., Gray J. R., Molfese D. L., & Snyder A . ( 2001). Anterior cingulate cortex and response conflict: Effects of frequency, inhibition and errors. Cerebral Cortex, 11( 9), 825-836.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/11.9.825 URL pmid: 11532888 |
| [10] |
Buchanan T. W., Tranel D., & Adolphs R . ( 2006). Memories for emotional autobiographical events following unilateral damage to medial temporal lobe. Brain, 129( 1), 115-127.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awh672 URL pmid: 16291807 |
| [11] |
Buhle J. T., Silvers J. A., Wager T. D., Lopez R., Onyemekwu C., Kober H., … Ochsner. K. N . ( 2014). Cognitive reappraisal of emotion: A meta-analysis of human neuroimaging studies. Cerebral Cortex, 24( 11), 2981-2990.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht154 URL |
| [12] |
Bush G., Luu P., & Posner M. I . ( 2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4( 6), 215-222.
doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01483-2 URL pmid: 10827444 |
| [13] |
Butler E. A., Egloff B., Wlhelm F. H., Smith N. C., Erickson E. A., & Gross J. J . ( 2003). The social consequences of expressive suppression. Emotion, 3( 1), 48-67.
doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.3.1.48 URL pmid: 12899316 |
| [14] |
Canuet L., Ishii R., Pascual-Marqui R. D., Iwase M., Kurimoto R., Aoki Y., … Takeda M . ( 2011). Resting-state EEG source localization and functional connectivity in schizophrenia-like psychosis of epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 6( 11), e27863.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027863 URL pmid: 22125634 |
| [15] |
Canuet L., Tellado I., Couceiro V., Fraile C., Fernandez- Novoa L., Ishii R., … Cacabelos R . ( 2012). Resting-state network disruption and APOE genotype in Alzheimer’s disease: A lagged functional connectivity study. PLOS ONE, 7( 9), e46289.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046289 URL pmid: 23050006 |
| [16] |
Cauda F., Costa T., Torta D. M., Sacco K., D'Agata F., & Duca S., … Vercelli A . ( 2012). Meta-analytic clustering of the insular cortex: Characterizing the meta-analytic connectivity of the insula when involved in active tasks. Neuroimage, 62( 1), 343-355.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.012 URL |
| [17] | Cheng L., Yuan J. J., He Y. Y., & Li H . ( 2009). Emotion regulation strategies: Cognitive reappraisal is more effective than expressive suppression. Advances in Psychological Science, 17( 4), 730-735. |
| [ 程利, 袁加锦, 何媛媛, 李红 . ( 2009). 情绪调节策略: 认知重评优于表达抑制. 心理科学进展, 17( 4), 730-735.] | |
| [18] | Cui X. J., Lu C. J., Guo Y. F., & Shi H. M .( 2012). The relationship between emotion regulation and depression of college students. China Journal of Health Psychology, 20( 3), 431-433. |
| [ 崔向军, 逯春洁, 郭永芳, 石贺敏 . ( 2012). 大学生情绪调节与抑郁的相关研究. 中国健康心理学杂志, 20( 3), 431-433.] | |
| [19] |
D’ Avanzato C., Joormann J., Siemer M., & Gotlib I. H . ( 2013). Emotion regulation in depression and anxiety: Examining diagnostic specificity and stability of strategy use. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 37( 5), 968-980.
doi: 10.1007/s10608-013-9537-0 URL |
| [20] | Deak A., Bodrogi B., Biro B., Perlaki G., Orsi G., & Bereczkei T . ( 2017). Machiavellian emotion regulation in a cognitive reappraisal task: An fMRI study. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 17( 3), 528-541. |
| [21] |
Dennis T. A . ( 2007). Interactions between emotion regulation strategies and affective style: Implications for trait anxiety versus depressed mood. Motivation and Emotion, 31( 3), 200-207.
doi: 10.1007/s11031-007-9069-6 URL |
| [22] |
Dennis T. A., & Hajcak G . ( 2009). The late positive potential: A neurophysiological marker for emotion regulation in children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50( 11), 1373-1383.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02168.x URL pmid: 19754501 |
| [23] |
Dolcos F., Labar K. S., & Cabeza R . ( 2004). Interaction between the amygdala and the medial temporal lobe memory system predicts better memory for emotional events. Neuron, 42( 5), 855-863.
doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00289-2 URL |
| [24] |
Dougal S., Phelps E. A., & Davachi L . ( 2007). The role of medial temporal lobe in item recognition and source recollection of emotional stimuli. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 7( 3), 233-242.
doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1050 URL pmid: 31899609 |
| [25] |
Drabant E. M., Mcrae K., Manuck S. B., Hariri A. R., & Gross J. J . ( 2008). Individual differences in typical reappraisal use predict amygdala and prefrontal responses. Biological Psychiatry, 65( 5), 367-373.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.09.007 URL pmid: 18930182 |
| [26] |
Duncan J., & Owen A. M ., ( 2000). Common regions of the human frontal lobe recruited by diverse cognitive demands. Trends in Neurosciences, 23( 10), 475-483.
doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01633-7 URL pmid: 11006464 |
| [27] |
Egner T., Etkin A., Gale S., & Hirsch J . ( 2008). Dissociable neural systems resolve conflict from emotional versus nonemotional distracters. Cerebral Cortex, 18( 6), 1475-1484.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm179 URL pmid: 17940084 |
| [28] |
Egner T., & Hirsch J . ( 2005). Cognitive control mechanisms resolve conflict through cortical amplification of task- relevant information. Nature Neuroscience, 8, 1784-1790.
doi: 10.1038/nn1594 URL pmid: 16286928 |
| [29] |
Ertl M., Hildebrandt M., Ourina K., Leicht G., & Mulert C . ( 2013). Emotion regulation by cognitive reappraisal - The role of frontal theta oscillations. NeuroImage, 81( 11), 412-421.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.044 URL pmid: 23689018 |
| [30] |
Etkin A., Egner T., Peraza D. M., Kandel E. R., & Hirsch J . ( 2006). Resolving emotional conflict: A role for the rostral anterior cingulate cortex in modulating activity in the amygdala. Neuron, 51( 6), 871-882.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.07.029 URL pmid: 16982430 |
| [31] |
Foti D., & Hajcak G . ( 2008). Deconstructing reappraisal: Descriptions preceding arousing pictures modulate the subsequent neural response. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20 ( 6), 977-988.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2008.20066 URL pmid: 18211235 |
| [32] |
Fraga González G., Van der Molen M., Žarić G., Bonte M., Tijms J., Blomert L., … Van der Molen M. W . ( 2016). Graph analysis of EEG resting state functional networks in dyslexic readers. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127( 9), 3165-3175.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2016.06.023 URL pmid: 27476025 |
| [33] |
Frank D. W., Dewitt M., Hudgens-Haney M., Schaeffer D. J., Ball B. H., Schwarz N. F., … Sabatinelli D . ( 2014). Emotion regulation: Quantitative meta-analysis of functional activation and deactivation. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 202-211.
doi: 10.1111/ejn.14671 URL pmid: 31901174 |
| [34] | Gan T., Luo Y. J., & Zhang Z. J . ( 2009). The Influence of Emotion on Time Perception. Journal of Psychological Science, 32( 4), 836-839. |
| [ 甘甜, 罗跃嘉, 张志杰 . ( 2009). 情绪对时间知觉的影响. 心理科学, 32( 4), 836-839.] | |
| [35] |
Garnefski N., & Kraaij V . ( 2007). The Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire: Psychometric features and prospective relationships with depression and anxiety in adults. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 23, 141-149.
doi: 10.1027/1015-5759.23.3.141 URL |
| [36] |
Giuliani N. R., Drabant E. M., Bhatnagar R., & Gross J. J . ( 2011a). Emotion regulation and brain plasticity: Expressive suppression use predicts anterior insula volume. Neuroimage, 58( 1), 10-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.028 URL pmid: 21704173 |
| [37] |
Giuliani N. R., Drabant E. M., & Gross J. J . ( 2011b). Anterior cingulate cortex volume and emotion regulation: Is bigger better? Biological Psychology, 86( 3), 379-382.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.11.010 URL pmid: 21138751 |
| [38] |
Goldin P. R., McRae K., Ramel W., & Gross J. J . ( 2008). The neural bases of emotion regulation: Reappraisal and suppression of negative emotion. Biological Psychiatry, 63( 6), 577-586.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.05.031 URL pmid: 17888411 |
| [39] |
Gross J. J . ( 1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: An integrative review. Review of General Psychology, 2( 3), 271-299.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00093 URL pmid: 26191007 |
| [40] |
Gross J. J . ( 2002). Emotion regulation: Affective, cognitive, and social consequences. Psychophysiology, 39( 3), 281-291.
doi: 10.1017/s0048577201393198 URL pmid: 12212647 |
| [41] |
Gross J. J . ( 2015). Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26( 1), 1-26.
doi: 10.1080/1047840X.2014.940781 URL |
| [42] |
Gross J. J., & John O.P . ( 2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85( 2), 348-362.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.85.2.348 URL pmid: 12916575 |
| [43] |
Gu H., Chen Q., Xing X., Zhao J., & Li X . ( 2019). Facial emotion recognition in deaf children: Evidence from event-related potentials and event-related spectral perturbation analysis. Neuroscience Letters, 703, 198-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.01.032 URL pmid: 30677434 |
| [44] |
Haga S. M., Kraft P., & Corby E. K . ( 2009). Emotion regulation: Antecedents and well-being outcomes of cognitive reappraisal and expressive suppression in cross-cultural samples. Journal of Happiness Studies, 10( 3), 271-291.
doi: 10.1007/s10902-007-9080-3 URL |
| [45] |
Hajcak G., & Nieuwenhuis S . ( 2006). Reappraisal modulates the electrocortical response to unpleasant pictures. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 6( 4), 291-297.
doi: 10.3758/cabn.6.4.291 URL pmid: 17458444 |
| [46] |
Hamann S., . ( 2001). Cognitive and neural mechanisms of emotional memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5( 9), 394-400.
doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01707-1 URL pmid: 11520704 |
| [47] |
Hermann A., Bieber A., Keck T., Vaitl D., & Stark R . ( 2014). Brain structural basis of cognitive reappraisal and expressive suppression. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 9( 9), 1435-1442.
doi: 10.1007/s10802-019-00607-5 URL pmid: 31900836 |
| [48] |
Hermann A., Leutgeb V., Scharmüller W., Vaitl D., & Stark R . ( 2013). Individual differences in cognitive reappraisal usage modulate the time course of brain activation during symptom provocation in specific phobia. Biology of Mood and Anxiety Disorders, 3( 1), 16.
doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-3-20 URL pmid: 24517388 |
| [49] |
Hofmann S. G., Heering S., Sawyer A. T., & Asnaani A . ( 2009). How to handle anxiety: The effects of reappraisal, acceptance, and suppression strategies on anxious arousal. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 47( 5), 389-394.
doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2009.02.010 URL |
| [50] |
Karamacoska D., Barry R. J., & Steiner G. Z . ( 2017). Resting state intrinsic EEG impacts on go stimulus-response processes. Psychophysiology, 54( 6), 894-903.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.12851 URL pmid: 28258583 |
| [51] |
Karamacoska D., Barry R. J., Steiner G. Z., Coleman E. P., & Wilson E. J . ( 2018). Intrinsic EEG and task-related changes in EEG affect go/nogo task performance. International Journal of Psychophysiology, S0167876017306864.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2018.01.015 URL pmid: 29409782 |
| [52] |
Krach S., Jansen A., Krug A., Markov V., Thimm M., Sheldrick A. J., … Kircher T . ( 2010). Comt genotype and its role on hippocampal-prefrontal regions in declarative memory. Neuroimage, 53( 3), 978-984.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.090 URL pmid: 20060911 |
| [53] |
Samuelson K. W . ( 2011). Post-traumatic stress disorder and declarative memory functioning: A review. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 13( 3), 346-351.
URL pmid: 22033732 |
| [54] |
Langer N., Pedroni A., Gianotti L. R. R., Hänggi J., Knoch D., & Jäncke L . ( 2012). Functional brain network efficiency predicts intelligence. Human Brain Mapping, 33( 6), 1393-1406.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.21297 URL |
| [55] |
Langner C. A., Epel E., Matthews K., Moskowitz J. T., & Adler N . ( 2012). Social hierarchy and depression: The role of emotion suppression. Journal of Psychology, 146( 4), 417-436.
doi: 10.1080/00223980.2011.652234 URL |
| [56] |
Langeslag S. J. E., Jansma B. M., Franken I. H. A., & Strien J. W. V . ( 2007). Event-related potential responses to love-related facial stimuli. Biological Psychology, 76( 1-2), 109-115.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.06.007 URL pmid: 17681417 |
| [57] |
Langeslag S. J. E., & van Strien J. W . ( 2017). Preferential processing of task-irrelevant beloved-related information and task performance: Two event-related potential studies. Neuropsychologia, S002839321730341X.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107328 URL pmid: 31887313 |
| [58] |
Lee T. W., Dolan R. J., & Critchley H. D . ( 2008). Controlling emotional expression: Behavioral and neural correlates of nonimitative emotional responses. Cerebral Cortex, 18( 1), 104-113.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm035 URL pmid: 17483530 |
| [59] |
Li X., Lu J., Li B., Li H., Jin L., & Qiu J . ( 2017). The role of ventromedial prefrontal cortex volume in the association of expressive suppression and externally oriented thinking. Journal of Affective Disorders, 222, 112-119.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.06.054 URL pmid: 28688264 |
| [60] | Li Z. Q., Wang L., Zhang H. C., & Liu H. C . ( 2010). Personality traits and subjective well-being: The mediating role of emotion regulation. Journal of Psychological Science, 33( 1), 165-167. |
| [ 李中权, 王力, 张厚粲, 柳恒超 . ( 2010). 人格特质与主观幸福感: 情绪调节的中介作用. 心理科学, 33( 1), 165-167.] | |
| [61] |
Liu X., Banich M. T., Jacobson B. L., & Tanabe J. L . ( 2004). Common and distinct neural substrates of attentional control in an integrated Simon and spatial Stroop task as assessed by event-related fMRI. Neuroimage, 22( 3), 1097-1106.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.02.033 URL |
| [62] |
Lou Y. X., Cai A. Y., Yang J. M., & Yuan J. J . ( 2014). The impact of introversion-extraversion on emotion regulations and the neurophysiological underpinnings. Advances in Psychological Science, 22( 12), 1855-1866.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.01855 URL |
| [ 娄熠雪, 蔡阿燕, 杨洁敏, 袁加锦 . ( 2014). 内-外倾人格对情绪调节的影响及神经机制. 心理科学进展, 22(12), 1855-1866.] | |
| [63] |
Makris N., Goldstein J. M., Kennedy D., Hodge S. M., Caviness V. S., & Faraone S. V., … Seidmancdfi L. J . ( 2006). Decreased volume of left and total anterior insular lobule in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 83( 2-3), 155-171.
doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2005.11.020 URL pmid: 16448806 |
| [64] |
Mcrae K., Hughes B., Chopra S., Gabrieli J. D. E., Gross J. J., & Ochsner K. N . ( 2010). The neural bases of distraction and reappraisal. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22( 2), 248-262.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21243 URL pmid: 19400679 |
| [65] |
Miller E. K., & Cohen J. D . ( 2001). An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 167-202.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.167 URL pmid: 11283309 |
| [66] |
Moore S. A., Zoellner L. A., & Mollenholt N . ( 2008). Are expressive suppression and cognitive reappraisal associated with stress-related symptoms?. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 46( 9), 993-1000.
doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.05.001 URL |
| [67] |
Moser J. S., Hajcak G., Bukay E., & Simons R. F . ( 2006). Intentional modulation of emotional responding to unpleasant pictures: An ERP study. Psychophysiology, 43( 3), 292-296.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00402.x URL pmid: 16805868 |
| [68] |
Nallasamy N., & Tsao D. Y . ( 2011). Functional connectivity in the brain: Effects of anesthesia. The Neuroscientist, 17( 1), 94-106.
doi: 10.1177/1073858410374126 URL pmid: 21343409 |
| [69] |
Nelson B. D., Fitzgerald D. A., Klumpp H., Shankman S. A., & Phan K. L . ( 2015). Prefrontal engagement by cognitive reappraisal of negative faces. Behavioural Brain Research, 279, 218-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.034 URL pmid: 25433095 |
| [70] |
Ochsner K. N., Bunge S. A., Gross J. J., & Gabrieli J. D. E . ( 2002). Rethinking feelings: An FMRI study of the cognitive regulation of emotion. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 14( 8), 1215-1229.
doi: 10.1162/089892902760807212 URL pmid: 12495527 |
| [71] |
Ochsner K. N., Hughes B., Robertson E. R., Cooper J. C., & Gabrieli J. D. E . ( 2009). Neural systems supporting the control of affective and cognitive conflicts. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21( 9), 1841-1854.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21129 URL pmid: 18823233 |
| [72] |
Ohira H., Nomura M., Ichikawa N., Isowa T., Iidaka T., Sato A., … Yamada J .( 2006). Association of neural and physiological responses during voluntary emotion suppression. NeuroImage, 29( 3), 721-733.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.048 URL pmid: 17239620 |
| [73] |
Ohmatsu S., Nakano H., Tominaga T., Terakawa Y., Murata T., & Morioka S . ( 2014). Activation of the serotonergic system by pedaling exercise changes anterior cingulate cortex activity and improves negative emotion. Behavioural Brain Research, 270, 112-117.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.04.017 URL |
| [74] |
Pagani M., Di Lorenzo G., Verardo A. R., Nicolais G., Monaco L., & Lauretti G., … Siracusano A . ( 2012). Neurobiological correlates of EMDR monitoring - An EEG study. PLOS ONE, 7( 9), e45753.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045753 URL pmid: 23049852 |
| [75] |
Pan J., Zhan L., Hu C. L., Yang J., Wang C., Gu L., … Wu X . ( 2018). Emotion regulation and complex brain networks: Association between expressive suppression and efficiency in the fronto-parietal network and default-mode network. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 70.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00070 URL pmid: 29662443 |
| [76] |
Pannu H. J., Morey R. A., Petty C. M., Srishti S., Smoski M. J., Gregory M. C., & Labar K. S . ( 2010). Staying cool when things get hot: Emotion regulation modulates neural mechanisms of memory encoding. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 4, 230.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2010.00230 URL pmid: 21212840 |
| [77] |
Pascual-Marqui R. D., Lehmann D., Koukkou M., Kochi K., Anderer P., Saletu B., … Kinoshita T . ( 2011) Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low resolution electromagnetic tomography. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 369, 3768-3784.
doi: 10.1098/rsta.2011.0081 URL pmid: 21893527 |
| [78] |
Pei X., Wang J., Deng B., Wei X., & Yu H . ( 2014). Wlpvg approach to the analysis of eeg-based functional brain network under manual acupuncture. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 8( 5), 417-428.
doi: 10.1007/s11571-014-9297-x URL |
| [79] |
Phan K. L., Fitzgerald D. A., Nathan P. J., Moore G. J., Uhde T. W., & Tancer M. E . ( 2005). Neural substrates for voluntary suppression of negative affect: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Biological Psychiatry, 57( 3), 210-219.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.030 URL pmid: 15691521 |
| [80] |
Qian L., Xi C., Tom H., Duo X., Frederick C., & James B. R . ( 2014). Theta band activity in response to emotional expressions and its relationship with gamma band activity as revealed by MEG and advanced beamformer source imaging. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 940.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00940 URL pmid: 24550804 |
| [81] |
Scult M. A., Knodt A. R., Swartz J. R., Brigidi B. D., & Hariri A. R . ( 2017). Thinking and feeling: Individual differences in habitual emotion regulation and stress- related mood are associated with prefrontal executive control. Clinical Psychological Science, 5( 1), 150-157.
doi: 10.1177/2167702616654688 URL pmid: 28191365 |
| [82] |
Sheline Y. I., Price J. L., Yan Z., & Mintun M. A . ( 2010). Resting-state functional MRI in depression unmasks increased connectivity between networks via the dorsal nexus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107( 24), 11020-11025.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000446107 URL pmid: 20534464 |
| [83] |
Shigeto H., Ishiguro J., & Nittono H . ( 2011). Effects of visual stimulus complexity on event-related brain potentials and viewing duration in a free-viewing task. Neuroscience Letters, 497( 2), 85-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.04.035 URL pmid: 21540078 |
| [84] |
Stam C. J., Nolte G., & Daffertshofer A . ( 2007). Phase lag index: Assessment of functional connectivity from multichannel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Human Brain Mapping, 28( 11), 1178-1193.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.20346 URL pmid: 17266107 |
| [85] |
Szaflarski J. P., Allendorfer J. B., Heyse H., Mendoza L., Szaflarski B. A., & Cohen N . ( 2014). Functional mri of facial emotion processing in left temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 32, 92-99.
doi: 10.21101/cejph.a5765 URL pmid: 31901191 |
| [86] |
Urbain C., Sato J., Pang E. W., & Taylor M. J . ( 2017). The temporal and spatial brain dynamics of automatic emotion regulation in children. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 26, 62-68.
doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2017.05.004 URL pmid: 28527986 |
| [87] |
van den Heuvel M. P., Stam C. J., Kahn R. S., & Hulshoff Pol H. E . ( 2009). Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. Journal of Neuroscience, 29( 23), 7619-7624.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1443-09.2009 URL pmid: 19515930 |
| [88] |
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Hulshoff Pol, H. E . ( 2010). Exploring the brain network: A review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 20( 8), 519-534.
doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.03.008 URL |
| [89] |
Vanderhasselt M. A., Kuhn S., & De Raedt R . ( 2013). "Put on your poker face": Neural systems supporting the anticipation for expressive suppression and cognitive reappraisal. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8( 8), 903-910.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nss090 URL pmid: 22956675 |
| [90] |
van Diessen E., Numan T., van Dellen E., van der Kooi A.W., Boersma M., Hofman D., … Stam C. J . ( 2015). Opportunities and methodological challenges in EEG and MEG resting state functional brain network research. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126( 8), 1468-1481.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.11.018 URL pmid: 25511636 |
| [91] |
Varnum M. E. W., & Hampton R. S . ( 2016). Cultures differ in the ability to enhance affective neural responses. Social Neuroscience, 12( 5), 1-10.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2016.1209239 URL pmid: 27420406 |
| [92] |
Viviani R . ( 2014). Neural correlates of emotion regulation in the ventral prefrontal cortex and the encoding of subjective value and economic utility. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 5.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00187 URL pmid: 25691873 |
| [93] |
Wagner M., Fuchs M., & Kastner J . ( 2004). Evaluation of sLORETA in the presence of noise and multiple sources. Brain Topography, 16( 4), 277-280.
doi: 10.1023/B:BRAT.0000032865.58382.62 URL |
| [94] | Wang J. X., Wang C. M., Xie F., Chang M., & Zhang K . ( 2015). The effect of cognitive reappraisal and distraction in regulating negative emotion: ERPs study. Journal of Psychological Science, 38( 5), 1039-1044. |
| [ 王敬欣, 王春梅, 谢芳, 常敏, 张阔 . ( 2015). 负性情绪调节中认知重评和分心策略的作用: ERPs研究. 心理科学, 38( 5), 1039-1044.] | |
| [95] |
Wang J., Wang X., Xia M., Liao X., Evans A., & He Y . ( 2015). Gretna: A graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9.
doi: 10.2147/NDT.S135426 URL pmid: 28652747 |
| [96] |
Wang J., Zuo X., & He Y . ( 2010). Graph-based network analysis of resting-state functional MRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4.
doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2010.00162 URL pmid: 21283555 |
| [97] |
Wang K., Huang H., Chen L., Hou X., Zhang Y., Yang J., … Qiu J . ( 2017). MRI correlates of interaction between gender and expressive suppression among the Chinese population. Neuroscience, 347, 76-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.01.042 URL pmid: 28188856 |
| [98] | Wang L., Liu H. C., Li Z. Q., & Du W .( 2007). Reliability and validity of emotion regulation questionnaire Chinese revised version. China Journal of Health Psychology, 15( 6), 503-505. |
| [ 王力, 柳恒超, 李中权, 杜卫 . ( 2007). 情绪调节问卷中文版的信效度研究. 中国健康心理学杂志, 15( 6), 503-505.] | |
| [99] | Wang Y. N., Zhou L. M., Qu C., & Luo Y. J . ( 2007). Implicitly processing of affective connotation of chinese words evidence from event-related brain potential. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 43( 4), 466-470. |
| [ 王一牛, 周立明, 曲琛, 罗跃嘉 . ( 2007). 感情色彩双字词内隐加工的ERP研究. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43( 4), 466-470.] | |
| [100] | Xing M., Tadayonnejad R., MacNamara A., Ajilore O., Phan K. L., Klumpp H., & Leow A . ( 2016). EEG based functional connectivity reflects cognitive load during emotion regulation. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. IEEE. |
| [101] |
Zhang W., Li X., Liu X., Duan X., Wang D., & Shen J . ( 2013). Distraction reduces theta synchronization in emotion regulation during adolescence. Neuroscience Letters, 550, 81-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.05.070 URL pmid: 23827226 |
| [102] |
Zhao L.Y., Tian J., Wang W., Qin W., Shi J., Li Q., … Lu L . ( 2012). The role of dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in the regulation of craving by reappraisal in smokers. PLOS ONE, 7( 8), e43598.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043598 URL pmid: 22928000 |
| [103] |
Zhou Y., Yu C., Zheng H., Liu Y., Song M., Qin W., … Jiang T . ( 2010). Increased neural resources recruitment in the intrinsic organization in major depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 121( 3), 220-230.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.05.029 URL pmid: 19541369 |
| [1] | 孙岩, 王艺锦, 侯沛雨, 冯雪, 兰帆. 抑郁倾向对自我关注重评和情境关注重评影响的脑网络研究[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(2): 232-246. |
| [2] | 姚雨佳, 颜之悦, 林慧慧, 陈静全, 宣雨阳. 人际距离和策略创造性对人际情绪调节的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(1): 125-134. |
| [3] | 童廷婷, 白幼玲, 冯廷勇. 情绪调节改善拖延行为的认知机制:任务厌恶中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(4): 458-468. |
| [4] | 俞梦霞, 宋宜颖, 刘嘉. 实地导航训练提高大脑功能连接模式稳定性[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(12): 1661-1675. |
| [5] | 肖程元, 赵世瑞, 袁加锦. 积极认知重评对负性信息传播的调控及多维证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(11): 1471-1487. |
| [6] | 王妹, 程思, 李宜伟, 李红, 张丹丹. 背外侧前额叶在安慰剂效应中的作用:社会情绪调节研究[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(7): 1063-1073. |
| [7] | 郭晓栋, 郑泓, 阮盾, 胡丁鼎, 王毅, 王艳郁, 陈楚侨. 认知和情感共情与负性情绪:情绪调节的作用机制[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(6): 892-904. |
| [8] | 谢慧, 林轩怡, 胡婉柔, 胡晓晴. 情绪调节促进负性社会反馈的遗忘:来自行为和脑电的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(6): 905-919. |
| [9] | 李彧, 位东涛, 邱江. 抑郁症的人格类型及其脑功能连接基础[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(5): 740-751. |
| [10] | 李为, 边子茗, 陈曦梅, 王俊杰, 罗一君, 刘永, 宋诗情, 高笑, 陈红. 9~12岁儿童应激与额颞区的关联: 来自多模态脑影像的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(4): 572-587. |
| [11] | 王小琴, 谈雅菲, 蒙杰, 刘源, 位东涛, 杨文静, 邱江. 情绪调节灵活性对负性情绪的影响:来自经验取样的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(2): 192-209. |
| [12] | 高可翔, 张岳瑶, 李思瑾, 袁加锦, 李红, 张丹丹. 腹内侧前额叶在内隐认知重评中的因果作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(2): 210-223. |
| [13] | 金花, 贾丽娜, 阴晓娟, 严世振, 魏士琳, 陈俊涛. 错误信息持续影响效应的神经基础[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(4): 343-354. |
| [14] | 刘宇平, 周冰涛, 杨波. 情绪如何引发暴力犯的攻击?基于情绪调节理论的解释[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(3): 270-280. |
| [15] | 张妮, 刘文, 刘方, 郭鑫. 8~12岁儿童抑郁与认知重评的关系:悲伤面孔注意偏向的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2022, 54(1): 25-39. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||