

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 572-587.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00572 cstr: 32110.14.2023.00572
李为1, 边子茗1, 陈曦梅1, 王俊杰1, 罗一君1, 刘永1,2, 宋诗情1, 高笑1,2, 陈红1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-15
发布日期:2022-12-30
出版日期:2023-04-25
通讯作者:
陈红, E-mail: chenhg@swu.edu.cn作者简介:李为和边子茗为共同第一作者。
基金资助:
LI Wei1, BIAN Ziming1, CHEN Ximei1, WANG Junjie1, LUO Yijun1, LIU Yong1,2, SONG Shiqing1, GAO Xiao1,2, CHEN Hong1,2( )
)
Received:2022-03-15
Online:2022-12-30
Published:2023-04-25
摘要:
首次采用多模态数据结合机器学习的方法考察了78名学龄儿童(女性39名, 平均年龄10.18岁)应激的神经关联。结果表明, 儿童应激水平与内侧眶额叶、脑岛、颞上回和辅助运动区的灰质体积呈显著正相关; 而与脑岛和顶下小叶之间的功能连接强度呈显著负相关。这表明涉及情绪加工的前额叶−边缘−颞叶脑区可能在儿童应激的个体差异中起着关键作用, 而负责整合内外部信息(如, 积极的自我评价和外部消极刺激)的脑岛与顶下小叶之间功能同步性的增加与儿童应激的降低有密切关联。基于结构网络的预测分析显示, 感觉运动、额顶、突显、视觉和小脑网络对儿童应激水平具有较好的预测能力。研究不仅丰富了儿童应激神经基础的实证证据, 而且对儿童应激的早期预防策略和干预手段具有启示意义。
中图分类号:
李为, 边子茗, 陈曦梅, 王俊杰, 罗一君, 刘永, 宋诗情, 高笑, 陈红. (2023). 9~12岁儿童应激与额颞区的关联: 来自多模态脑影像的证据. 心理学报, 55(4), 572-587.
LI Wei, BIAN Ziming, CHEN Ximei, WANG Junjie, LUO Yijun, LIU Yong, SONG Shiqing, GAO Xiao, CHEN Hong. (2023). The relationship between frontotemporal regions and early life stress in children aged 9 to 12: Evidence from multimodal fMRI. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(4), 572-587.
| 变量 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 范围 | 偏度 | 峰度 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.性别(sex): 男/女 | 39/39 | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 2.年龄(age) | 10.18 | 1.02 | 9~12 | 0.39 | -0.95 | — | ||||
| 3.颅内总体积(TIV, mm3) | 1461.64 | 116.38 | 1199.41~1751.50 | 0.44 | 0.30 | -0.13 | — | |||
| 4.头动(mean FD, mm) | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.05~0.38 | 1.11 | 0.58 | -0.25* | 0.18 | — | ||
| 5.应激原始分数(stress) | 26.35 | 22.96 | 1~105 | 1.57 | 2.43 | -0.04 | 0.07 | 0.04 | — | |
| 6.应激转换分数(stress_sqrt) | 4.69 | 2.10 | 1~10.25 | 0.61 | 0.08 | -0.04 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.97** | — |
| 7.消极情绪 | 15.13 | 3.89 | 10~29 | 1.10 | 1.52 | -0.18 | 0.06 | 0.26* | 0.29** | 0.34** |
表1 描述性统计与相关分析结果(N=78)
| 变量 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 范围 | 偏度 | 峰度 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.性别(sex): 男/女 | 39/39 | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 2.年龄(age) | 10.18 | 1.02 | 9~12 | 0.39 | -0.95 | — | ||||
| 3.颅内总体积(TIV, mm3) | 1461.64 | 116.38 | 1199.41~1751.50 | 0.44 | 0.30 | -0.13 | — | |||
| 4.头动(mean FD, mm) | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.05~0.38 | 1.11 | 0.58 | -0.25* | 0.18 | — | ||
| 5.应激原始分数(stress) | 26.35 | 22.96 | 1~105 | 1.57 | 2.43 | -0.04 | 0.07 | 0.04 | — | |
| 6.应激转换分数(stress_sqrt) | 4.69 | 2.10 | 1~10.25 | 0.61 | 0.08 | -0.04 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.97** | — |
| 7.消极情绪 | 15.13 | 3.89 | 10~29 | 1.10 | 1.52 | -0.18 | 0.06 | 0.26* | 0.29** | 0.34** |
| 脑区 | 半球 | MNI坐标 | 体素 量 | t值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| 与灰质体积相关的脑区 | ||||||
| 内侧眶额叶(mOFC) | 左 | −1.5 | 55.5 | −19.5 | 807 | 4.59 |
| 脑岛(Insular) | 右 | 46.5 | 4.5 | −9 | 968 | 4.46 |
| 颞上回(STG) | 左 | −64.5 | −6 | −4.5 | 739 | 4.43 |
| 辅助运动区(SMA) | 右 | 9 | 16.5 | 61.5 | 918 | 3.97 |
| 与静息功能连接相关的脑区 | ||||||
| 脑岛−顶下小叶 (Insular-IPL) | 左 | −36 | −57 | 45 | 333 | −4.37 |
表2 儿童应激与灰质体积和静息功能连接相关分析结果
| 脑区 | 半球 | MNI坐标 | 体素 量 | t值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| 与灰质体积相关的脑区 | ||||||
| 内侧眶额叶(mOFC) | 左 | −1.5 | 55.5 | −19.5 | 807 | 4.59 |
| 脑岛(Insular) | 右 | 46.5 | 4.5 | −9 | 968 | 4.46 |
| 颞上回(STG) | 左 | −64.5 | −6 | −4.5 | 739 | 4.43 |
| 辅助运动区(SMA) | 右 | 9 | 16.5 | 61.5 | 918 | 3.97 |
| 与静息功能连接相关的脑区 | ||||||
| 脑岛−顶下小叶 (Insular-IPL) | 左 | −36 | −57 | 45 | 333 | −4.37 |
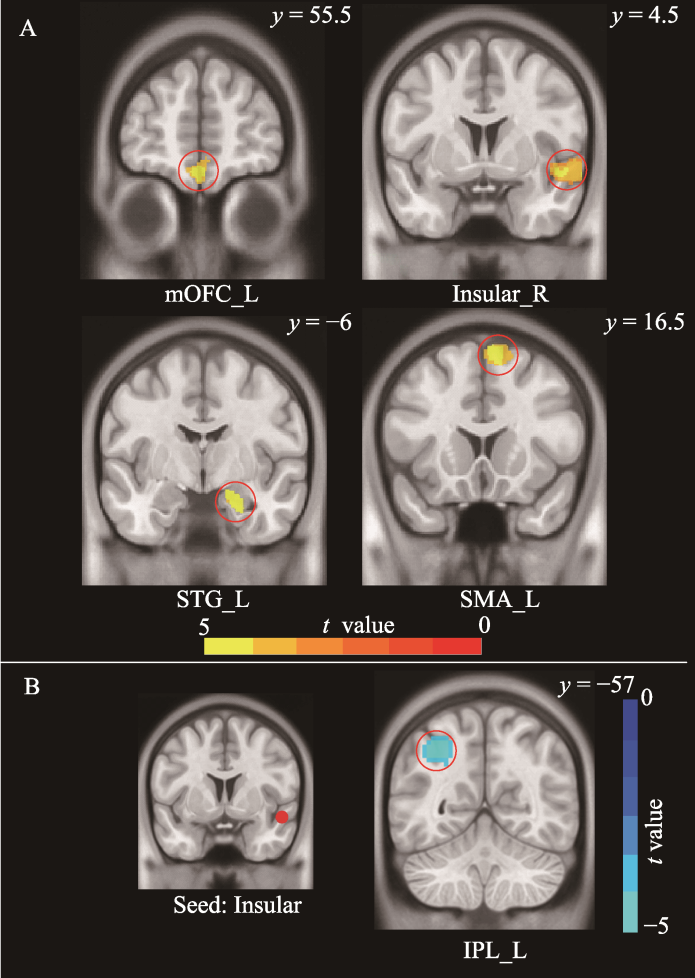
图2 (A)儿童应激相关的灰质体积结果; (B)儿童应激相关的静息功能连接结果 注: 采用体素水平p < 0.005, 团块水平p < 0.05的GRF多重比较矫正。mOFC=内侧眶额叶(medial orbitofrontal cortex); Insular=脑岛; STG=颞上回(superior temporal gyrus); SMA=辅助运动区(supplementary motor area); IPL=顶下小叶(inferior parietal lobule); L=Left hemisphere; R=Right hemisphere。
| 情绪 | 应激原始分数 | 应激转换分数 | mOFC灰质体积 | Insular灰质体积 | STG灰质体积 | SMA灰质体积 | Insular-IPL功能连接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 消极情绪总分 | 0.29** | 0.34** | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.211 | 0.25* | 0.01 |
| 害怕的 | -0.02 | 0.05 | 0.03 | -0.04 | -0.03 | 0.02 | -0.01 |
| 羞耻的 | 0.19 | 0.20 | -0.02 | -0.16 | -0.06 | 0.02 | -0.11 |
| 痛苦的 | 0.31** | 0.31** | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.07 |
| 有罪恶感的 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.01 | -0.05 |
| 敌意的 | 0.27* | 0.30** | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.24* | -0.02 |
| 易怒的 | 0.26* | 0.25* | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.32** | 0.34** | 0.10 |
| 神经过敏的 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.04 |
| 紧张的 | 0.03 | 0.10 | -0.05 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.03 | -0.03 |
| 受惊吓的 | 0.12 | 0.16 | -0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.08 |
| 难过不安的 | 0.19 | 0.23* | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.10 | -0.10 |
附表1 消极情绪与应激水平和脑指标相关分析的结果(N=78)
| 情绪 | 应激原始分数 | 应激转换分数 | mOFC灰质体积 | Insular灰质体积 | STG灰质体积 | SMA灰质体积 | Insular-IPL功能连接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 消极情绪总分 | 0.29** | 0.34** | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.211 | 0.25* | 0.01 |
| 害怕的 | -0.02 | 0.05 | 0.03 | -0.04 | -0.03 | 0.02 | -0.01 |
| 羞耻的 | 0.19 | 0.20 | -0.02 | -0.16 | -0.06 | 0.02 | -0.11 |
| 痛苦的 | 0.31** | 0.31** | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.07 |
| 有罪恶感的 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.01 | -0.05 |
| 敌意的 | 0.27* | 0.30** | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.24* | -0.02 |
| 易怒的 | 0.26* | 0.25* | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.32** | 0.34** | 0.10 |
| 神经过敏的 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.04 |
| 紧张的 | 0.03 | 0.10 | -0.05 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.03 | -0.03 |
| 受惊吓的 | 0.12 | 0.16 | -0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.08 |
| 难过不安的 | 0.19 | 0.23* | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.10 | -0.10 |

图3 (A)预测儿童应激水平的正、负网络; (B)机器学习预测结果; (C)置换检验 注: 圈图: 脑区以解剖顺序呈现, 连线长度代表连接脑区的距离; 脑图: 节点大小代表节点对模型的贡献度; 矩阵图: 数字代表网络内或网络间连接的数量。特征选择阈值p < 0.01, 预测模型显著性采用2000次置换检验p < 0.05。
| 脑区 | 节点 | 半球 | 绝对权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 颞叶 | 颞极 | 右 | 0.007 |
| 颞下回 | 右 | 0.012 | |
| 颞下回 | 右 | 0.007 | |
| 颞极 | 左 | 0.010 | |
| 颞下回 | 左 | 0.012 | |
| 梭状回 | 左 | 0.018 | |
| 运动区 | 辅助运动区 | 右 | 0.006 |
| 中央后回 | 右 | 0.040 | |
| 额上回 | 右 | 0.007 | |
| 颞上回 | 右 | 0.008 | |
| 颞上回 | 右 | 0.010 | |
| 前额叶 | 眶额叶 | 右 | 0.008 |
| 额下三角回 | 左 | 0.008 | |
| 额下三角回 | 左 | 0.004 | |
| 顶叶 | 角回 | 右 | 0.006 |
| 顶上回 | 左 | 0.041 | |
| 颞中回 | 左 | 0.007 | |
| 枕叶 | 舌回 | 右 | 0.007 |
| 舌回 | 右 | 0.008 | |
| 边缘 | 中部扣带回 | 左 | 0.011 |
| 亚皮层 | 丘脑 | 右 | 0.004 |
| 小脑 | 小脑上部 | 右 | 0.019 |
| 小脑蚓体 | 右 | 0.004 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.011 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.006 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.011 | |
| 小脑上部 | 左 | 0.050 |
附表2 预测儿童应激水平贡献率前10%的脑区
| 脑区 | 节点 | 半球 | 绝对权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 颞叶 | 颞极 | 右 | 0.007 |
| 颞下回 | 右 | 0.012 | |
| 颞下回 | 右 | 0.007 | |
| 颞极 | 左 | 0.010 | |
| 颞下回 | 左 | 0.012 | |
| 梭状回 | 左 | 0.018 | |
| 运动区 | 辅助运动区 | 右 | 0.006 |
| 中央后回 | 右 | 0.040 | |
| 额上回 | 右 | 0.007 | |
| 颞上回 | 右 | 0.008 | |
| 颞上回 | 右 | 0.010 | |
| 前额叶 | 眶额叶 | 右 | 0.008 |
| 额下三角回 | 左 | 0.008 | |
| 额下三角回 | 左 | 0.004 | |
| 顶叶 | 角回 | 右 | 0.006 |
| 顶上回 | 左 | 0.041 | |
| 颞中回 | 左 | 0.007 | |
| 枕叶 | 舌回 | 右 | 0.007 |
| 舌回 | 右 | 0.008 | |
| 边缘 | 中部扣带回 | 左 | 0.011 |
| 亚皮层 | 丘脑 | 右 | 0.004 |
| 小脑 | 小脑上部 | 右 | 0.019 |
| 小脑蚓体 | 右 | 0.004 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.011 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.006 | |
| 小脑下部 | 左 | 0.011 | |
| 小脑上部 | 左 | 0.050 |
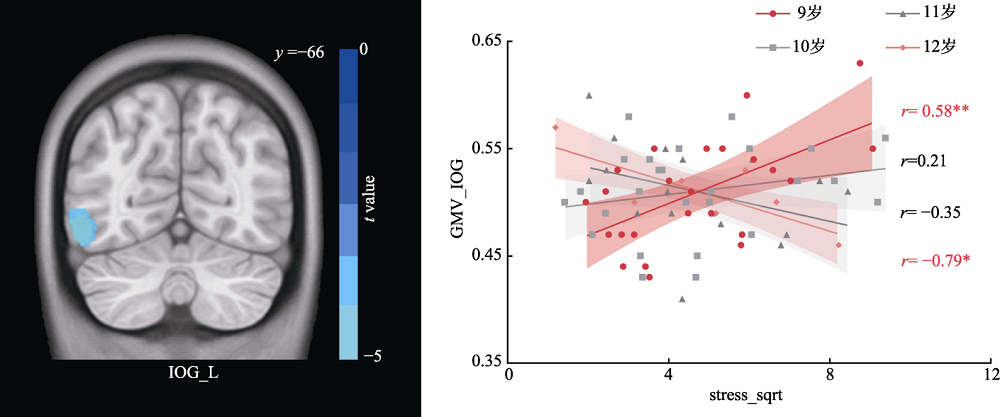
图4 儿童应激神经基础的年龄特征 注: 采用体素水平p < 0.005, 团块水平p < 0.05的GRF多重比较矫正。GMV=灰质体积(gray matter volume); IOG=inferior occipital gyrus; L=left hemisphere; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01。
| [1] |
Agorastos, A., Pervanidou, P., Chrousos, G. P., & Kolaitis, G. (2018). Early life stress and trauma: Developmental neuroendocrine aspects of prolonged stress system dysregulation. Hormones, 17(4), 507-520.
doi: 10.1007/s42000-018-0065-x |
| [2] |
Albaugh, M. D., Nguyen, T. V., Ducharme, S., Collins, D. L., Botteron, K. N., D’Alberto, N., ... Brain Development Cooperative Group. (2017). Age-related volumetric change of limbic structures and subclinical anxious/depressed symptomatology in typically developing children and adolescents. Biological Psychology, 124, 133-140.
doi: S0301-0511(17)30029-7 pmid: 28185945 |
| [3] | Anderson, M. L. (2014). After phrenology: Neural reuse and the interactive brain. MIT Press. |
| [4] |
Ani, C., Reading, R., Lynn, R., Forlee, S., & Garralda, E. (2013). Incidence and 12-month outcome of non-transient childhood conversion disorder in the U.K. and Ireland. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 202(6), 413-418.
doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.112.116707 URL |
| [5] |
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry— the methods. Neuroimage, 11, 805-821.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2000.0582 pmid: 10860804 |
| [6] |
Aupperle, R. L., Allard, C. B., Grimes, E. M., Simmons, A. N., Flagan, T., Behrooznia, M., ... Stein, M. B. (2012). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex activation during emotional anticipation and neuropsychological performance in posttraumatic stress disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69(4), 360-371.
doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1539 pmid: 22474105 |
| [7] |
Aybek, S., Nicholson, T. R., Draganski, B., Daly, E., Murphy, D. G., David, A. S., & Kanaan, R. A. (2014). Grey matter changes in motor conversion disorder. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 85(2), 236-238.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-304158 URL |
| [8] |
Bai, S., Elavsky, S., Kishida, M., Dvořáková, K., & Greenberg, M. T. (2020). Effects of mindfulness training on daily stress response in college students: Ecological momentary assessment of a randomized controlled trial. Mindfulness, 11(6), 1433-1445.
doi: 10.1007/s12671-020-01358-x pmid: 33343764 |
| [9] | Bari, A., Niu, T., Langevin, J. P., & Fried, I. (2014). Limbic neuromodulation: Implications for addiction, posttraumatic stress disorder, and memory. Neurosurgery Clinics, 25(1), 137-145. |
| [10] |
Berens, A. E., Jensen, S., & Nelson, C. A. (2017). Biological embedding of childhood adversity: From physiological mechanisms to clinical implications. BMC Medicine, 15(1), 135.
doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0895-4 pmid: 28724431 |
| [11] |
Black, S. R., Lerner, M. D., Shirtcliff, E. A., & Klein, D. N. (2018). Patterns of neuroendocrine coupling in 9-year-old children: Effects of sex, body-mass index, and life stress. Biological Psychology, 132, 252-259.
doi: S0301-0511(17)30306-X pmid: 29155118 |
| [12] |
Blithikioti, C., Nuño, L., Guell, X., Pascual-Diaz, S., Gual, A., Balcells-Olivero, Μ., & Miquel, L. (2022). The cerebellum and psychological trauma: A systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Neurobiology of Stress, 17, 100429.
doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100429 URL |
| [13] |
Bonini, F., Burle, B., Liégeois-Chauvel, C., Régis, J., Chauvel, P., & Vidal, F. (2014). Action monitoring and medial frontal cortex: Leading role of supplementary motor area. Science, 343(6173), 888-891.
doi: 10.1126/science.1247412 pmid: 24558161 |
| [14] |
Brunet, E., Sarfati, Y., Hardy-Baylé, M. C., & Decety, J. (2000). A PET investigation of the attribution of intentions with a nonverbal task. Neuroimage, 11(2), 157-166.
pmid: 10679187 |
| [15] | Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network:Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Science, 1124, 1-38. |
| [16] |
Burghy, C. A., Stodola, D. E., Ruttle, P. L., Molloy, E. K., Armstrong, J. M., Oler, J. A., ... Birn, R. M. (2012). Developmental pathways to amygdala-prefrontal function and internalizing symptoms in adolescence. Nature Neuroscience, 15(12), 1736-1741.
doi: 10.1038/nn.3257 pmid: 23143517 |
| [17] |
Calderon-Delgado, L., Barrera-Valencia, M., Noriega, I., Al-Khalil, K., Trejos-Castillo, E., Mosi, J., Chavez, B., Galvan, M., & O'Boyle, M. W. (2020). Implicit processing of emotional words by children with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: An fMRI investigation. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 20(1), 46-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2019.11.002 URL |
| [18] |
Calem, M., Bromis, K., McGuire, P., Morgan, C., & Kempton, M. J. (2017). Meta-analysis of associations between childhood adversity and hippocampus and amygdala volume in non-clinical and general population samples. Neuroimage: Clinical, 14, 471-479.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.02.016 URL |
| [19] |
Choi, J., Jeong, B., Polcari, A., Rohan, M. L., & Teicher, M. H. (2012). Reduced fractional anisotropy in the visual limbic pathway of young adults witnessing domestic violence in childhood. Neuroimage, 59(2), 1071-1079.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.033 pmid: 21985907 |
| [20] |
Cole, M. W., Reynolds, J. R., Power, J. D., Repovs, G., Anticevic, A., & Braver, T. S. (2013). Multi-task connectivity reveals flexible hubs for adaptive task control. Nature Neuroscience, 16(9), 1348-1355.
doi: 10.1038/nn.3470 pmid: 23892552 |
| [21] | Craig, A. D. (2009). How do you feel-now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Natrue Reviews: Neuroscience, 10(1), 59-70. |
| [22] |
Cwik, J. C., Vahle, N., Woud, M. L., Potthoff, D., Kessler, H., Sartory, G., & Seitz, R. J. (2020). Reduced gray matter volume in the left prefrontal, occipital, and temporal regions as predictors for posttraumatic stress disorder: A voxel-based morphometric study. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 270(5), 577-588.
doi: 10.1007/s00406-019-01011-2 pmid: 30937515 |
| [23] |
de Bellis, M. D., Keshavan, M. S., Frustaci, K., Shifflett, H., Iyengar, S., Beers, S. R., & Hall, J. (2002). Superior temporal gyrus volumes in maltreated children and adolescents with PTSD. Biological Psychiatry, 51(7), 544-552.
doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01374-9 pmid: 11950456 |
| [24] |
de Bellis, M. D., Keshavan, M. S., Shifflett, H., Iyengar, S., Dahl, R. E., Axelson, D. A., ... Ryan, N. D. (2002). Superior temporal gyrus volumes in pediatric generalized anxiety disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 51(7), 553-562.
pmid: 11950457 |
| [25] |
Demir-Lira, Ö. E., Voss, J. L., O'Neil, J. T., Briggs-Gowan, M. J., Wakschlag, L. S., & Booth, J. R. (2016). Early-life stress exposure associated with altered prefrontal resting-state fMRI connectivity in young children. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 107-114.
doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2016.02.003 pmid: 27010576 |
| [26] |
Etkin, A., & Wager, T. D. (2007). Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: A meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(10), 1476-1488.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07030504 pmid: 17898336 |
| [27] |
Feng, C., Yuan, J., Geng, H., Gu, R., Zhou, H., Wu, X., & Luo, Y. (2018). Individualized prediction of trait narcissism from whole-brain resting-state functional connectivity. Human Brain Mapping, 39(9), 3701-3712.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.24205 pmid: 29749072 |
| [28] |
Ferketich, A. K., Ferguson, J. P., & Binkley, P. F. (2005). Depressive symptoms and inflammation among heart failure patients. American Heart Journal, 150(1), 132-136.
pmid: 16084159 |
| [29] |
Funke, R., Eichler, A., Distler, J., Golub, Y., Kratz, O., & Moll, G. H. (2017). Stress system dysregulation in pediatric generalized anxiety disorder associated with comorbid depression. Stress and Health, 33(5), 518-529.
doi: 10.1002/smi.2736 pmid: 27982510 |
| [30] |
Grayson, D. S., & Fair, D. A. (2017). Development of large-scale functional networks from birth to adulthood: A guide to the neuroimaging literature. Neuroimage, 160, 15-31.
doi: S1053-8119(17)30102-7 pmid: 28161313 |
| [31] | Goetschius, L. G., Hein, T. C., McLanahan, S. S., Brooks- Gunn, J., McLoyd, V. C., Dotterer, H. L., ... Beltz, A. M. (2020). Association of childhood violence exposure with adolescent neural network density. JAMA Network Open, 3(9), e2017850. |
| [32] |
Gogtay, N., Giedd, J. N., Lusk, L., Hayashi, K. M., Greenstein, D., Vaituzis, A. C., ... Thompson, P. M. (2004). Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(21), 8174-8179.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402680101 pmid: 15148381 |
| [33] |
Gu, X., Hof, P. R., Friston, K. J., & Fan, J. (2013). Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 521(15), 3371-3388.
doi: 10.1002/cne.23368 pmid: 23749500 |
| [34] |
Hahm, S., Lotze, M., Domin, M., & Schmidt, S. (2019). The association of health-related quality of life and cerebral gray matter volume in the context of aging: A voxel-based morphometry study with a general population sample. Neuroimage, 191, 470-480.
doi: S1053-8119(19)30129-6 pmid: 30790673 |
| [35] |
Hamani, C., Davidson, B., Levitt, A., Meng, Y., Corchs, F., Abrahao, A., ... Lipsman, N. (2020). Patient with posttraumatic stress disorder successfully treated with deep brain stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex and uncinate fasciculus. Biological Psychiatry, 88(11), e57-e59.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.05.018 URL |
| [36] |
Hammen, C., Henry, R., & Daley, S. E. (2000). Depression and sensitization to stressors among young women as a function of childhood adversity. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(5), 782-787.
pmid: 11068964 |
| [37] |
Hart, H., Lim, L., Mehta, M. A., Simmons, A., Mirza, K., & Rubia, K. (2018). Altered fear processing in adolescents with a history of severe childhood maltreatment: An fMRI study. Psychological Medicine, 48(7), 1092-1101.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291716003585 pmid: 29429419 |
| [38] |
Haufe, S., Meinecke, F., Görgen, K., Dähne, S., Haynes, J. D., Blankertz, B., & Bießmann, F. (2014). On the interpretation of weight vectors of linear models in multivariate neuroimaging. Neuroimage, 87, 96-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.067 pmid: 24239590 |
| [39] |
Herringa, R. J., Birn, R. M., Ruttle, P. L., Burghy, C. A., Stodola, D. E., Davidson, R. J., & Essex, M. J. (2013). Childhood maltreatment is associated with altered fear circuitry and increased internalizing symptoms by late adolescence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(47), 19119-19124.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310766110 pmid: 24191026 |
| [40] | Holmes, S. E., Scheinost, D., DellaGioia, N., Davis, M. T., Matuskey, D., Pietrzak, R. H., ... Esterlis, I. (2018). Cerebellar and prefrontal cortical alterations in PTSD: Structural and functional evidence. Chronic Stress, 2, 2470547018786390. |
| [41] |
Horien, C., Noble, S., Finn, E. S., Shen, X., Scheinost, D., & Constable, R. T. (2018). Considering factors affecting the connectome-based identification process: Comment on Waller et al. Neuroimage, 169, 172-175.
doi: S1053-8119(17)31069-8 pmid: 29253655 |
| [42] |
Howard, D., Patterson, K., Wise, R., Brown, W. D., Friston, K., Weiller, C., & Frackowiak, R. (1992). The cortical localization of the lexicons: Positron emission tomography evidence. Brain, 115(6), 1769-1782.
doi: 10.1093/brain/115.6.1769 URL |
| [43] |
Hsu, W. T., Rosenberg, M. D., Scheinost, D., Constable, R. T., & Chun, M. M. (2018). Resting-state functional connectivity predicts neuroticism and extraversion in novel individuals. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(2), 224-232.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy002 URL |
| [44] |
Hu, S., Pruessner, J. C., Coupé, P., & Collins, D. L. (2013). Volumetric analysis of medial temporal lobe structures in brain development from childhood to adolescence. Neuroimage, 74, 276-287.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.032 pmid: 23485848 |
| [45] |
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1998). Early exploration of the visual cortex. Neuron, 20(3), 401-412.
pmid: 9539118 |
| [46] |
Insel, T. R. (2009). Translating scientific opportunity into public health impact: A strategic plan for research on mental illness. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(2), 128-133.
doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2008.540 pmid: 19188534 |
| [47] |
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage, 17(2), 825-841.
doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(02)91132-8 pmid: 12377157 |
| [48] |
Jones, D. K., & Cercignani, M. (2010). Twenty‐five pitfalls in the analysis of diffusion MRI data. NMR in Biomedicine, 23(7), 803-820.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1543 URL |
| [49] | Kautz, M., Ered, A., Nielsen, J., Olino, T., & Alloy, L. (2021). The effect of early life stress during sensitive exposure periods on orbitofrontal cortex thickness. Biological Psychiatry, 89(9), S278-S279. |
| [50] |
Kong, X. Z., Wang, X., Huang, L., Pu, Y., Yang, Z., Dang, X., ... Liu, J. (2014). Measuring individual morphological relationship of cortical regions. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 237, 103-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.09.003 URL |
| [51] |
Kozlowska, K., Palmer, D. M., Brown, K. J., McLean, L., Scher, S., Gevirtz, R., ... Williams, L. M. (2015). Reduction of autonomic regulation in children and adolescents with conversion disorders. Psychosomatic Medicine, 77(4), 356-370.
doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000184 pmid: 25954919 |
| [52] |
Kozlowska, K., Griffiths, K. R., Foster, S. L., Linton, J., Williams, L. M., & Korgaonkar, M. S. (2017). Grey matter abnormalities in children and adolescents with functional neurological symptom disorder. Neuroimage: Clinical, 15, 306-314.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.04.028 URL |
| [53] |
Kribakaran, S., Danese, A., Bromis, K., Kempton, M. J., & Gee, D. G. (2020). Meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies in pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder and comparison with related conditions. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 5(1), 23-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.08.006 URL |
| [54] | Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal, and coping. Springer publishing company. |
| [55] | Li, L., Zhang, H., Hu, X., Suo, X., Lei, D., Wu, M., ... Gong, Q. (2017). Voxel-based morphometry-diffeomorphic anatomical registration through exponentiated lie algebra algorithm evaluation of brain structural of recent-onset pediatric post-traumatic stress disorder patients. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 51(3), 210-213. |
| [黎磊, 张华为, 胡新宇, 索学玲, 雷都, 吴敏,... 龚启勇. (2017). 基于体素的形态学测量与自建模板及微分同胚图像融合方法对近期发病的创伤后应激障碍儿童的脑结构研究. 中华放射学杂志, 51(3), 210-213.] | |
| [56] |
Lim, L., Hart, H., Mehta, M. A., Simmons, A., Mirza, K., & Rubia, K. (2015). Neural correlates of error processing in young people with a history of severe childhood abuse: An fMRI study. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 172(9), 892-900.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.14081042 URL |
| [57] |
Lim, L., Radua, J., & Rubia, K. (2014). Gray matter abnormalities in childhood maltreatment: A voxel-wise meta-analysis. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 171(8), 854-863.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13101427 URL |
| [58] |
Liu, Z., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., ... Yang, Z. (2021). Altered gray matter volume and structural co-variance in adolescents with social anxiety disorder: Evidence for a delayed and unsynchronized development of the fronto-limbic system. Psychological Medicine, 51(10), 1742-1751.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291720000495 URL |
| [59] | Liu, S. D., Liu, Q., Luo, Y., & Wen, Y. (2016). Development of the stressful life events for primary school students. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 30(10), 745-751. |
| [刘舒丹, 刘琴, 罗燕, 文一. (2016). 小学生应激性生活事件量表的编制. 中国心理卫生杂志, 30(10), 745-751.] | |
| [60] |
Lu, S., Gao, W., Wei, Z., Wang, D., Hu, S., Huang, M., ... Li, L. (2017). Intrinsic brain abnormalities in young healthy adults with childhood trauma: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study of regional homogeneity and functional connectivity. The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 51(6), 614-623.
doi: 10.1177/0004867416671415 pmid: 27694638 |
| [61] |
Maikovich, A. K., Koenen, K. C., & Jaffee, S. R. (2009). Posttraumatic stress symptoms and trajectories in child sexual abuse victims: An analysis of sex differences using the national survey of child and adolescent well-being. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(5), 727-737.
doi: 10.1007/s10802-009-9300-x pmid: 19221872 |
| [62] | Manoliu, A., Meng, C., Brandl, F., Doll, A., Tahmasian, M., Scherr, M., ... Sorg, C. (2014). Insular dysfunction within the salience network is associated with severity of symptoms and aberrant inter-network connectivity in major depressive disorder. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 930. |
| [63] |
Marusak, H. A., Etkin, A., & Thomason, M. E. (2015). Disrupted insula-based neural circuit organization and conflict interference in trauma-exposed youth. Neuroimage: Clinical, 8, 516-525.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.04.007 URL |
| [64] |
May, A., & Gaser, C. (2006). Magnetic resonance-based morphometry: A window into structural plasticity of the brain. Current Opinion in Neurology, 19(4), 407-411.
doi: 10.1097/01.wco.0000236622.91495.21 pmid: 16914981 |
| [65] |
McEwen, B. S., Eiland, L., Hunter, R. G., & Miller, M. M. (2012). Stress and anxiety: Structural plasticity and epigenetic regulation as a consequence of stress. Neuropharmacology, 62(1), 3-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.014 pmid: 21807003 |
| [66] |
McEwen, B. S., Nasca, C., & Gray, J. D. (2016). Stress effects on neuronal structure: Hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41(1), 3-23.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.171 pmid: 26076834 |
| [67] |
McLaughlin, K. A., Conron, K. J., Koenen, K. C., & Gilman, S. E. (2010). Childhood adversity, adult stressful life events, and risk of past-year psychiatric disorder: A test of the stress sensitization hypothesis in a population-based sample of adults. Psychological Medicine, 40(10), 1647-1658.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291709992121 pmid: 20018126 |
| [68] |
McLaughlin, K. A., & Hatzenbuehler, M. L. (2009). Stressful life events, anxiety sensitivity, and internalizing symptoms in adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118(3), 659-669.
doi: 10.1037/a0016499 pmid: 19685962 |
| [69] |
McLaughlin, K. A., Sheridan, M. A., & Nelson, C. A. (2017). Neglect as a violation of species-expectant experience: Neurodevelopmental consequences. Biological Psychiatry, 82(7), 462-471.
doi: S0006-3223(17)31218-0 pmid: 28392082 |
| [70] | Mechelli, A., Price, C. J., Friston, K. J., Ashburner, J. (2005). Voxel-based morphometry of the human brain: Methods and applications. Current Medical Imaging, 1(2), 105-113. |
| [71] |
Mennes, M., Kelly, C., Zuo, X. N., Martino, A. D., Biswal, B. B., Castellanos, F. X., & Milham, M. P. (2010). Interindividual differences in resting-state functional connectivity predict task-induced BOLD activity. Neuroimage, 50(4), 1690-1701.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.002 URL |
| [72] |
Menon, V. (2011). Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: A unifying triple network model. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(10), 483-506.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003 pmid: 21908230 |
| [73] | Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q. (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: A network model of insula function. Brain Structure & Function, 214(5-6), 655-667. |
| [74] |
Morey, R. A., Petty, C. M., Xu, Y., Hayes, J. P., Wagner II, H. R., Lewis, D. V., ... McCarthy, G. (2009). A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. Neuroimage, 45(3), 855-866.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.12.033 pmid: 19162198 |
| [75] | Nelson, C. A., Scott, R. D., Bhutta, Z. A., Harris, N. B., Danese, A., & Samara, M. (2020). Adversity in childhood is linked to mental and physical health throughout life. British Medical Journal, 371, 3048. |
| [76] |
Noble, S., Spann, M. N., Tokoglu, F., Shen, X., Constable, R. T., & Scheinost, D. (2017). Influences on the test-retest reliability of functional connectivity MRI and its relationship with behavioral utility. Cerebral Cortex, 27(11), 5415-5429.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx230 URL |
| [77] |
O'Doherty,, J., Kringelbach,, M. L., Rolls,, E. T., Hornak,, J., & Andrews,, C. (2001). Abstract reward and punishment representations in the human orbitofrontal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 4(1), 95-102.
doi: 10.1038/82959 pmid: 11135651 |
| [78] |
Oliveri, M., Babiloni, C., Filippi, M. M., Caltagirone, C., Babiloni, F., Cicinelli, P., ... Rossini, P. M. (2003). Influence of the supplementary motor area on primary motor cortex excitability during movements triggered by neutral or emotionally unpleasant visual cues. Experimental Brain Research, 149(2), 214-221.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-002-1346-8 pmid: 12610690 |
| [79] |
Paquola, C., Bennett, M. R., Hatton, S. N., Hermens, D. F., & Lagopoulos, J. (2017). Utility of the cumulative stress and mismatch hypotheses in understanding the neurobiological impacts of childhood abuse and recent stress in youth with emerging mental disorder. Human Brain Mapping, 38(5), 2709-2721.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.23554 pmid: 28256777 |
| [80] |
Perino, M. T., Myers, M. J., Wheelock, M. D., Yu, Q., Harper, J. C., Manhart, M. F., ... Sylvester, C. M. (2021). Whole-brain resting-state functional connectivity patterns associated with pediatric anxiety and involuntary attention capture. Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science, 1(3), 229-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.05.007 pmid: 36033105 |
| [81] |
Phillips, M. L., Drevets, W. C., Rauch, S. L., & Lane, R. (2003). Neurobiology of emotion perception I: The neural basis of normal emotion perception. Biological Psychiatry, 54(5), 504-514.
doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00168-9 pmid: 12946879 |
| [82] |
Price, M., Legrand, A. C., Brier, Z. M., & Hébert-Dufresne, L. (2019). The symptoms at the center: Examining the comorbidity of posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and depression with network analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 109, 52-58.
doi: S0022-3956(18)30708-8 pmid: 30502492 |
| [83] |
Qin, S., Young, C. B., Duan, X., Chen, T., Supekar, K., & Menon, V. (2014). Amygdala subregional structure and intrinsic functional connectivity predicts individual differences in anxiety during early childhood. Biological Psychiatry, 75(11), 892-900.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.006 pmid: 24268662 |
| [84] |
Rabellino, D., Densmore, M., Théberge, J., McKinnon, M. C., & Lanius, R. A. (2018). The cerebellum after trauma: Resting-state functional connectivity of the cerebellum in posttraumatic stress disorder and its dissociative subtype. Human Brain Mapping, 39(8), 3354-3374.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.24081 pmid: 29667267 |
| [85] |
Ringwald, K. G., Meller, T., Schmitt, S., Andlauer, T., Stein, F., Brosch, K., … Kircher, T. (2021). Interaction of developmental factors and ordinary stressful life events on brain structure in adults. Neuroimage: Clinical, 30, 102683.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102683 URL |
| [86] |
Roger, C., Bénar, C. G., Vidal, F., Hasbroucq, T., & Burle, B. (2010). Rostral Cingulate Zone and correct response monitoring: ICA and source localization evidences for the unicity of correct- and error-negativities. Neuroimage, 51(1), 391-403.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.005 pmid: 20152906 |
| [87] |
Rolls, E. T. (2017). The orbitofrontal cortex and emotion in health and disease, including depression. Neuropsychologia, 128, 14-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.09.021 URL |
| [88] | Saedpanah, D., Salehi, S., & Moghaddam, L. F. (2016). The effect of emotion regulation training on occupational stress of critical care nurses. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 10(12), VC01-VC04. |
| [89] |
Saxbe, D., Khoddam, H., Piero, L. D., Stoycos, S. A., Gimbel, S. I., Margolin, G., & Kaplan, J. T. (2018). Community violence exposure in early adolescence: Longitudinal associations with hippocampal and amygdala volume and resting state connectivity. Developmental Science, 21(6), e12686.
doi: 10.1111/desc.2018.21.issue-6 URL |
| [90] |
Schlatter, S., Guillot, A., Schmidt, L., Mura, M., Trama, R., Di Rienzo, F., ... Debarnot, U. (2021). Combining proactive transcranial stimulation and cardiac biofeedback to substantially manage harmful stress effects. Brain Stimulation, 14(5), 1384-1392.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2021.08.019 pmid: 34438047 |
| [91] |
Serra-Blasco, M., Radua, J., Soriano-Mas, C., Gómez- Benlloch, A., Porta-Casteràs, D., Carulla-Roig, M., ... Cardoner, N. (2021). Structural brain correlates in major depression, anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder: A voxel-based morphometry meta-analysis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 129, 269-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.07.002 pmid: 34256069 |
| [92] |
Shen, X., Finn, E. S., Scheinost, D., Rosenberg, M. D., Chun, M. M., Papademetris, X., & Constable, R. T. (2017). Using connectome-based predictive modeling to predict individual behavior from brain connectivity. Nature Protocols, 12(3), 506-518.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.178 pmid: 28182017 |
| [93] |
Shen, X., Tokoglu, F., Papademetris, X., & Constable, R. T. (2013). Groupwise whole-brain parcellation from resting- state fMRI data for network node identification. Neuroimage, 82, 403-415.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.081 pmid: 23747961 |
| [94] |
Sheynin, J., Duval, E. R., Lokshina, Y., Scott, J. C., Angstadt, M., Kessler, D., ... Liberzon, I. (2020). Altered resting-state functional connectivity in adolescents is associated with PTSD symptoms and trauma exposure. Neuroimage: Clinical, 26, 102215.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102215 URL |
| [95] |
Shimada, K., Takiguchi, S., Mizushima, S., Fujisawa, T. X., Saito, D. N., Kosaka, H., ... Tomoda, A. (2015). Reduced visual cortex grey matter volume in children and adolescents with reactive attachment disorder. Neuroimage: Clinical, 9, 13-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.07.001 URL |
| [96] |
Shonkoff, J. P., Boyce, W. T., & McEwen, B. S. (2009). Neuroscience, molecular biology, and the childhood roots of health disparities: Building a new framework for health promotion and disease prevention. JAMA, 301(21), 2252-2259.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.754 pmid: 19491187 |
| [97] |
Simmons, A. N., Paulus, M. P., Thorp, S. R., Matthews, S. C., Norman, S. B., & Stein, M. B. (2008). Functional activation and neural networks in women with posttraumatic stress disorder related to intimate partner violence. Biological Psychiatry, 64(8), 681-690.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.05.027 pmid: 18639236 |
| [98] |
Smith, K. E., & Pollak, S. D. (2020). Early life stress and development: Potential mechanisms for adverse outcomes. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 12(1), 34.
doi: 10.1186/s11689-020-09337-y pmid: 33327939 |
| [99] |
Soares, J. M., Sampaio, A., Ferreira, L. M., Santos, N. C., Marques, P., Marques, F., ... Sousa, N. (2013). Stress impact on resting state brain networks. PLoS One, 8(6), e66500.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066500 URL |
| [100] |
Song, K. (2013). Asymptotic relative efficiency and exact variance stabilizing transformation for the generalized Gaussian distribution. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 59(7), 4389-4396.
doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2249182 URL |
| [101] |
Späti, J., Hänggi, J., Doerig, N., Ernst, J., Sambataro, F., Brakowski, J., ... Spinelli, S. (2015). Prefrontal thinning affects functional connectivity and regional homogeneity of the anterior cingulate cortex in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology, 40(7), 1640-1648.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.8 pmid: 25598428 |
| [102] |
Stevens, J. S., van Rooij, S., & Jovanovic, T. (2018). Developmental contributors to trauma response: The importance of sensitive periods, early environment, and sex differences. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences, 38, 1-22.
doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_38 pmid: 27830573 |
| [103] |
Strigo, I. A., Simmons, A. N., Matthews, S. C., Grimes, E. M., Allard, C. B., Reinhardt, L. E., ... Stein, M. B. (2010). Neural correlates of altered pain response in women with posttraumatic stress disorder from intimate partner violence. Biological Psychiatry, 68(5), 442-450.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.03.034 pmid: 20553750 |
| [104] |
Teicher, M. H., Samson, J. A., Anderson, C. M., & Ohashi, K. (2016). The effects of childhood maltreatment on brain structure, function and connectivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17(10), 652-666.
doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.111 pmid: 27640984 |
| [105] |
Thomason, M. E., Marusak, H. A., Tocco, M. A., Vila, A. M., McGarragle, O., & Rosenberg, D. R. (2015). Altered amygdala connectivity in urban youth exposed to trauma. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(11), 1460-1468.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv030 pmid: 25836993 |
| [106] | Tipping, M. E. (2001). Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 1, 211-244. |
| [107] |
Tomoda, A., Navalta, C. P., Polcari, A., Sadato, N., & Teicher, M. H. (2009). Childhood sexual abuse is associated with reduced gray matter volume in visual cortex of young women. Biological Psychiatry, 66(7), 642-648.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.04.021 pmid: 19560122 |
| [108] |
Tomoda, A., Sheu, Y. S., Rabi, K., Suzuki, H., Navalta, C. P., Polcari, A., & Teicher, M. H. (2011). Exposure to parental verbal abuse is associated with increased gray matter volume in superior temporal gyrus. Neuroimage, 54(suppl. 1), S280-S286.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.027 URL |
| [109] | Tomoda, A., Polcari, A., Anderson, C. M., & Teicher, M. H. (2012). Reduced visual cortex gray matter volume and thickness in young adults who witnessed domestic violence during childhood. PloS One, 7(12), e52528. |
| [110] |
Tong, D. D., Li, W. F., Lu, P., Yang, W. J., Yang, D., Zhang, Q. L., & Qiu, J. (2020). The neural basis of scientific innovation problem finding. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(11), 1253-1265.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.01253 URL |
| [童丹丹, 李文福, 禄鹏, 杨文静, 杨东, 张庆林, 邱江. (2020). 科学发明情境中问题提出的脑机制再探. 心理学报, 52(11), 1253-1265.] | |
| [111] |
Tooley, U. A., Bassett, D. S., & Mackey, A. P. (2021). Environmental influences on the pace of brain development. Nature Reviews: Neuroscience, 22(6), 372-384.
doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00457-5 |
| [112] |
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., ... Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273-289.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0978 pmid: 11771995 |
| [113] | Uddin, L.Q. (2017). Salience network of the human brain || Functions of the salience network (pp. 11-16). Academic Press. |
| [114] |
Vanaelst, B., Huybrechts, I., de Bourdeaudhuij, I., Bammann, K., Hadjigeorgiou, C., Eiben, G., ... de Henauw, S. (2012). Prevalence of negative life events and chronic adversities in European pre-and primary-school children: Results from the IDEFICS study. Archives of Public Health, 70(1), 1-11.
doi: 10.1186/0778-7367-70-1 URL |
| [115] |
Vuper, T. C., Philippi, C. L., & Bruce, S. E. (2021). Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the default mode and central executive networks following cognitive processing therapy for PTSD. Behavioural Brain Research, 409, 113312.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113312 pmid: 33895228 |
| [116] |
Wabnegger, A., Übel, S., & Schienle, A. (2018). Voxel-based morphometry of disgust sensitivity. Social Neuroscience, 13(2), 241-245.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2017.1288657 pmid: 28165888 |
| [117] |
Wallace, G. L., Richard, E., Peng, C. S., Knodt, A. R., & Hariri, A. R. (2020). Subclinical eating disorder traits are correlated with cortical thickness in regions associated with food reward and perception. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 14(2), 346-352.
doi: 10.1007/s11682-018-0007-x pmid: 30617787 |
| [118] |
Waller, L., Walter, H., Kruschwitz, J. D., Reuter, L., Müller, S., Erk, S., Veer, I. M. (2017). Evaluating the replicability, specificity, and generalizability of connectome fingerprints. Neuroimage, 158, 371-377.
doi: S1053-8119(17)30584-0 pmid: 28710040 |
| [119] | Wang, H., Jin, X., Zhang, Y., & Wang, J. (2016). Single‐subject morphological brain networks: Connectivity mapping, topological characterization and test-retest reliability. Brain and Behavior, 6(4), e00448. |
| [120] |
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063-1070.
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.54.6.1063 pmid: 3397865 |
| [121] |
Wu, J., Tong, H., Liu, Z., Tao, J., Chen, L., Chan, C., & Lee, T. (2021). Neurobiological effects of perceived stress are different between adolescents and middle-aged adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 15(2), 846-854.
doi: 10.1007/s11682-020-00294-7 |
| [122] | Xia, L., Wang, J. L., & He, Y. (2010). Human connectome: Structural and functional brain networks. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(16), 1565-1583. |
| [梁夏, 王金辉, 贺永. (2010). 人脑连接组研究: 脑结构网络和脑功能网络. 科学通报, 55(16), 1565-1583.] | |
| [123] |
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339-351.
doi: 10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4 URL |
| [124] | Yoo, C., Park, S., & Kim, M. J. (2022). Structural connectome- based prediction of trait anxiety. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 10.1007/s11682-022-00700-2. |
| [125] |
Yu, M., Linn, K. A., Shinohara, R. T., Oathes, D. J., Cook, P. A., Duprat, R., ... Sheline, Y. I. (2019). Childhood trauma history is linked to abnormal brain connectivity in major depression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(17), 8582-8590.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900801116 URL |
| [126] |
Zhou, F., Zhao, W., Qi, Z., Geng, Y., Yao, S., Kendrick, K. M., ... Becker, B. (2021). A distributed fMRI-based signature for the subjective experience of fear. Nature Communications, 12(1), 1-16.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20314-w |
| [127] |
Zhutovsky, P., Zantvoord, J. B., Ensink, J. B., op den Kelder, R., Lindauer, R. J., & van Wingen, G. A. (2021). Individual prediction of trauma-focused psychotherapy response in youth with posttraumatic stress disorder using resting-state functional connectivity. Neuroimage: Clinical, 32, 102898.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102898 URL |
| [128] |
Zuo, X. N., Di Martino, A., Kelly, C., Shehzad, Z. E., Gee, D. G., Klein, D. F., ... Milham, M. P. (2010). The oscillating brain: Complex and reliable. Neuroimage, 49(2), 1432-1445.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.037 URL |
| [1] | 韩宪国, 金国敏, 李丹, 刘世宏, 吴琴, 刘俊升, 陈欣银. 父母温暖与儿童晚期亲社会行为的关系: 集体取向的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(4): 614-630. |
| [2] | 崔一岑, 张易晓, 陈曦梅, 肖明岳, 刘永, 宋诗情, 高笑, 郭成, 陈红. 工具性喂养对9~12岁儿童挑食行为的影响:来自静息态功能磁共振的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(6): 731-744. |
| [3] | 徐静, 骆方, 马彦珍, 胡路明, 田雪涛. 开放式情境判断测验的自动化评分[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(6): 831-844. |
| [4] | 赵立, 郑怡, 赵均榜, 张芮, 方方, 傅根跃, 李康. 人工智能方法在探究小学生作业作弊行为及其关键预测因子中的应用[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(2): 239-254. |
| [5] | 郑远霞, 钟敏, 辛聪, 刘国雄, 朱莉琪. 学龄前儿童对道德承诺者的信任判断[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(12): 1761-1772. |
| [6] | 郭存, 谢瑞波, 喻艳玲, 夏月, 王振梁, 伍新春. 小学中高年级儿童复合语素意识、词语结构意识与词汇知识的关系:交叉滞后研究[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(11): 1488-1498. |
| [7] | 潘莱珂, 翟舒怡, 何洁. 亲子对话中父母教养行为与5~6岁儿童行为反应的动态关系[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(10): 1340-1350. |
| [8] | 陈永香, 裴斐斐, 黄佳丽. 语法和语义线索对儿童动词习得的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(1): 61-69. |
| [9] | 王阳, 温芳芳, 佐斌. 3~8岁儿童对群体认知的社会性线索偏好及发展特点[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(9): 1424-1440. |
| [10] | 胡月琴, 王理中, 陈钢, 甘怡群. CSF3R和行动控制对应激与健康饮食关系的调节作用:应激影响健康行为的个体化模型的初步证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(9): 1489-1500. |
| [11] | 范兴华, 方晓义, 赵纤, 陈锋菊. 留守儿童家庭处境不利累积风险与社会适应:压力的中介作用与心理社会资源的调节作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(8): 1270-1284. |
| [12] | 孟现鑫, 俞德霖, 陈怡静, 张玲, 傅小兰. 儿童期创伤与共情的关系:一项三水平元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(8): 1285-1300. |
| [13] | 祝孝亮, 赵鑫. 执行功能在不同年级儿童数学能力中的作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(5): 696-710. |
| [14] | 刘倩文, 王振宏. 亲子关系、感觉加工敏感性与COMT Val158Met多态性对学前儿童亲社会行为的交互影响[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(5): 711-725. |
| [15] | 李彧, 位东涛, 邱江. 抑郁症的人格类型及其脑功能连接基础[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(5): 740-751. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||