

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 342-363.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2024.00342 cstr: 32111.14.2024.00342
车强燕1, 孙韵琳1, 靳佳1, 朱春燕1,2,3,4, 汪凯1,2,3,4,5, 叶榕1,2,4, 余凤琼1,2,4( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-20
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
余凤琼, E-mail: yufengqin1@163.com基金资助:
CHE Qiangyan1, SUN Yunlin1, JIN Jia1, ZHU Chunyan1,2,3,4, WANG Kai1,2,3,4,5, YE Rong1,2,4, YU Fengqiong1,2,4( )
)
Received:2023-06-20
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2023-11-23
摘要:
积极情绪的增强对抑郁症患者的临床症状改善和社会功能恢复具有重要意义。近年来神经反馈技术的发展为调控抑郁症积极情绪提供了有效的手段。传统积极情绪干预方法主观性强、治疗效果局限、缺乏可量化的客观评价指标, 基于客观生理和影像指标的神经反馈技术在增强抑郁症积极情绪中具有重要的应用价值。神经反馈通过可视化方式将实时的大脑活动反馈给被试, 让其能够使用特定的策略针对性地调控情绪相关脑区, 客观定量地评价积极情绪的改善。现有的研究在实验范式、参数设置和个体疗效上存在较大异质性。通过回顾和总结神经反馈增强积极情绪的实验设计、研究的影响因素和基于神经影像标记物的目标靶点, 强调了神经反馈实验设计和结果报告标准的重要性, 探索性地提出了基于奖赏环路的潜在干预靶点及优化方案。有望为临床抑郁症积极情绪恢复提供可操作性的参考方案, 为未来神经反馈技术在抑郁症临床症状治愈和社会功能康复中的转化应用和普及奠定基础。
中图分类号:
车强燕, 孙韵琳, 靳佳, 朱春燕, 汪凯, 叶榕, 余凤琼. (2024). 神经反馈增强积极情绪在抑郁症治疗中的应用. 心理科学进展 , 32(2), 342-363.
CHE Qiangyan, SUN Yunlin, JIN Jia, ZHU Chunyan, WANG Kai, YE Rong, YU Fengqiong. (2024). The application of neurofeedback for positive emotion enhancement in depression treatment. Advances in Psychological Science, 32(2), 342-363.
| 研究 | 分组及样本量 (EG/CG) | 效应量 (effect size) | 调节能力 报告 | 目标 靶点 | 反馈呈现 方式 | 指导策略 | 服药 情况 | 实验 设计 | 训练次数 | 效果评价 | 随访 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosenfeld et al. ( | EG: 5人(4名女性, 1名男性); CG: 无 | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 被试自己的任何策略 | 部分服药 | 非随机、非盲 | 每周1次, 每次50分钟, 共8~19次 | FAA评分与积极情绪变化之间有很强的正相关 | 无 | ||
| Baehr et al. ( | EG: 2人、女性(个案研究) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 放松训练 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 1人34次; 1人36次 | 2人都能够自主上调FAA, 同时MMPI得分降低; 患者情感状态改善 | 无 | ||
| Earnest ( | EG: 1名青少年(个案研究) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 无 | 否 | 非随机、非盲 | 一周2次, 每次55分钟, 共67次 | 能够自主上调FAA, 抑郁症状改善 | 无 | ||
| Nazarian ( | 共19名抑郁症患者参与, 只有7人完成所有训练, EG和CG组人数未报告; | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、听觉 | 无 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 36次 | FAA无显著改变, 抑郁症状和情绪未改善 | 有 | ||
| Choi et al. ( | EG: 12名 CG: 12/11名(单纯心理治疗对照) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、视听觉 | 无 | 否 | 随机对照、非盲 | 10次 | 抑郁症状改善 | 有 | ||
| Peeters et al. ( | EG: 9名 | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、视觉 | 无 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 平均26.78次 | FAA显著改变, 抑郁症状改善 | 无 | ||
| Wang et al. ( | EG: 7名 CG:7名(无神经反馈的药物治疗对照组) | 未报告 | 有 | FAA | 未报告 | 无 | 是 | 随机、非盲 | 6次 | EG患者焦虑和抑郁改善 | 无 | ||
| Linden et al. ( | EG: 8名 CG:8名(无神经反馈的积极心理意象对照组) | Cohen’s d = 1.5 | 无 | ↑与积极情绪有关脑区 | 连续的、视觉 | 观看情绪性图片 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 4次 | EG的患者在症状评分上改善了约30% (在17项HDRS中约为4分), CG完全没有改善 | 无 | ||
| Young et al. ( | EG: 14/13 CG: 7/6(无关脑区的假神经反馈 | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、双盲 | 1次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动。焦虑评分明显下降, 快乐评分明显增加。情绪改善。 | 无 | ||
| Yuan et al. ( | EG: 14名 HC: 27名 CG: 13名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、双盲 | 1次 | EG患者情绪环路低连接性被逆转, 并持续发生积极变化。 | 有 | ||
| Zotev et al. ( | EG: 13名 CG: 11名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、单盲 | 2次 | 抑郁症状改善和FAA的变化相关, 积极情绪增加 | 无 | ||
| Young et al. ( | EG: 19/18 CG: 17/15(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1.03 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | 抑郁症状显著降低, 情绪改善 | 有 | ||
| Mehler et al. ( | EG:21/16 CG:22 /16(高级视觉皮层的假神经反馈) | Hedges' g = 1.46 | 无 | ↑与积极情绪有关脑区 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极的心理想象 | 是 | 随机、单盲 | 5次 | 抑郁症状改善持续到随访(第18周), 自我效能感评分增加。 | 有 | ||
| Zotev et al. ( | EG:16名 CG: 8名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑LrACC和LA环路、前额叶的α和高β偏侧化) | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、单盲 | 1次 | 抑郁症状和情绪显著改善, EG参与者的LA和LrACC之间功能连接显著增强。 | 无 | ||
| Ahrweiler et al. ( | EG: 34名 HC: 19名 | 未报告 | 无 | ↑杏仁核海马复合体 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 1次 | 参与杏仁核−海马复合体的情绪调节可以引起自我和情绪处理区域的神经可塑性, 与抑郁和反刍症状的改善有关 | 无 | ||
| Compère, Siegle, Lazzaro, et al. ( | EG: 16名 CG: 22名(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动, 抑郁症状改善。 | 有 | ||
| Compère, Siegle, Riley, et al. ( | EG:16名 CG: 19名(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1.04 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 是 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动, 同时神经反馈促进了CBT的治疗效果, 积极情绪的增加更加显著 | 有 | |||
表1 神经反馈增强抑郁症积极情绪的应用研究汇总
| 研究 | 分组及样本量 (EG/CG) | 效应量 (effect size) | 调节能力 报告 | 目标 靶点 | 反馈呈现 方式 | 指导策略 | 服药 情况 | 实验 设计 | 训练次数 | 效果评价 | 随访 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosenfeld et al. ( | EG: 5人(4名女性, 1名男性); CG: 无 | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 被试自己的任何策略 | 部分服药 | 非随机、非盲 | 每周1次, 每次50分钟, 共8~19次 | FAA评分与积极情绪变化之间有很强的正相关 | 无 | ||
| Baehr et al. ( | EG: 2人、女性(个案研究) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 放松训练 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 1人34次; 1人36次 | 2人都能够自主上调FAA, 同时MMPI得分降低; 患者情感状态改善 | 无 | ||
| Earnest ( | EG: 1名青少年(个案研究) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 无 | 无 | 否 | 非随机、非盲 | 一周2次, 每次55分钟, 共67次 | 能够自主上调FAA, 抑郁症状改善 | 无 | ||
| Nazarian ( | 共19名抑郁症患者参与, 只有7人完成所有训练, EG和CG组人数未报告; | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、听觉 | 无 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 36次 | FAA无显著改变, 抑郁症状和情绪未改善 | 有 | ||
| Choi et al. ( | EG: 12名 CG: 12/11名(单纯心理治疗对照) | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、视听觉 | 无 | 否 | 随机对照、非盲 | 10次 | 抑郁症状改善 | 有 | ||
| Peeters et al. ( | EG: 9名 | 未报告 | 无 | FAA | 连续的、视觉 | 无 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 平均26.78次 | FAA显著改变, 抑郁症状改善 | 无 | ||
| Wang et al. ( | EG: 7名 CG:7名(无神经反馈的药物治疗对照组) | 未报告 | 有 | FAA | 未报告 | 无 | 是 | 随机、非盲 | 6次 | EG患者焦虑和抑郁改善 | 无 | ||
| Linden et al. ( | EG: 8名 CG:8名(无神经反馈的积极心理意象对照组) | Cohen’s d = 1.5 | 无 | ↑与积极情绪有关脑区 | 连续的、视觉 | 观看情绪性图片 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 4次 | EG的患者在症状评分上改善了约30% (在17项HDRS中约为4分), CG完全没有改善 | 无 | ||
| Young et al. ( | EG: 14/13 CG: 7/6(无关脑区的假神经反馈 | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、双盲 | 1次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动。焦虑评分明显下降, 快乐评分明显增加。情绪改善。 | 无 | ||
| Yuan et al. ( | EG: 14名 HC: 27名 CG: 13名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、双盲 | 1次 | EG患者情绪环路低连接性被逆转, 并持续发生积极变化。 | 有 | ||
| Zotev et al. ( | EG: 13名 CG: 11名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、单盲 | 2次 | 抑郁症状改善和FAA的变化相关, 积极情绪增加 | 无 | ||
| Young et al. ( | EG: 19/18 CG: 17/15(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1.03 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | 抑郁症状显著降低, 情绪改善 | 有 | ||
| Mehler et al. ( | EG:21/16 CG:22 /16(高级视觉皮层的假神经反馈) | Hedges' g = 1.46 | 无 | ↑与积极情绪有关脑区 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极的心理想象 | 是 | 随机、单盲 | 5次 | 抑郁症状改善持续到随访(第18周), 自我效能感评分增加。 | 有 | ||
| Zotev et al. ( | EG:16名 CG: 8名(无关脑区的假神经反馈) | 未报告 | 无 | ↑LrACC和LA环路、前额叶的α和高β偏侧化) | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 非随机、单盲 | 1次 | 抑郁症状和情绪显著改善, EG参与者的LA和LrACC之间功能连接显著增强。 | 无 | ||
| Ahrweiler et al. ( | EG: 34名 HC: 19名 | 未报告 | 无 | ↑杏仁核海马复合体 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 是 | 非随机、非盲 | 1次 | 参与杏仁核−海马复合体的情绪调节可以引起自我和情绪处理区域的神经可塑性, 与抑郁和反刍症状的改善有关 | 无 | ||
| Compère, Siegle, Lazzaro, et al. ( | EG: 16名 CG: 22名(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1 | 无 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 否 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动, 抑郁症状改善。 | 有 | ||
| Compère, Siegle, Riley, et al. ( | EG:16名 CG: 19名(无关脑区假神经反馈) | Cohen’s d = 1.04 | ↑左侧杏仁核 | 连续的、视觉 | 积极自传体回忆 | 是 | 随机、双盲 | 2次 | EG能够上调杏仁核的活动, 同时神经反馈促进了CBT的治疗效果, 积极情绪的增加更加显著 | 有 | |||
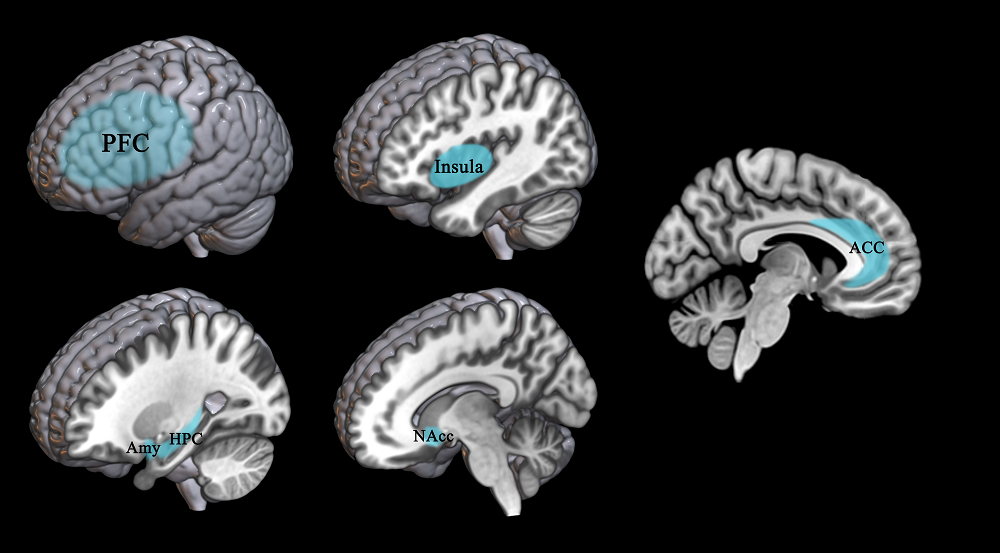
图2 增强积极情绪神经反馈靶点的单一脑区示意图 注: 根据大脑的偏侧化理论, 左半球与积极情绪相关, 右半球与消极情绪相关, 因此本图主要以呈现左侧的相关脑区为主。PFC = prefrontal cortex, HPC = Hippocampus, Amy = Amygdala, ACC = anterior cingulate cortex, NAcc = nucleus accumbens
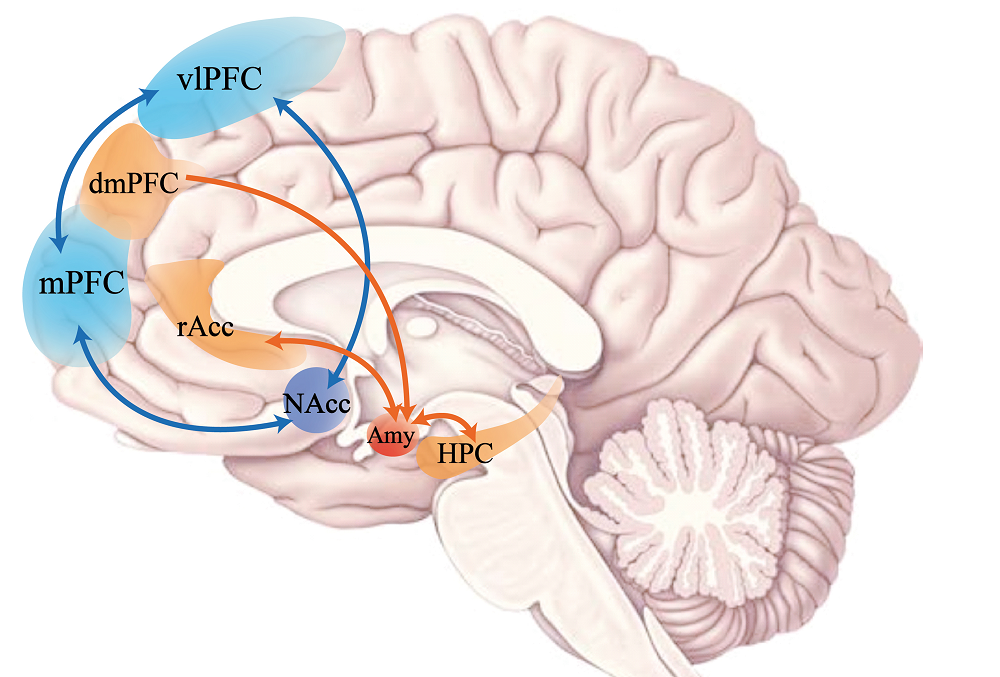
图3 杏仁核与其他情绪加工脑区连接的脑环路神经反馈靶点及潜在环路靶点 注:图3为与积极情绪脑区相关的的4个神经反馈训练的脑环路靶点, 其中包括LA-LrACC环路、AMY-HIPP环路、dmPFC-双侧Amy环路以及vlPFC-mPFC-NAcc环路。其中vlPFC-mPFC-NAcc环路为基于奖赏加工提出的神经反馈的潜在靶点。LA-LrACC环路、AMY-HIPP环路以及vlPFC- mPFC-NAcc环路的神经反馈调节机制都是基于两个脑区的功能连接, 如图所示双向箭头代表功能连接, 而dmPFC-双侧Amy环路为自上而下的有效连接, 图中箭头为单向。LA = left amygdala, LrACC = left rostral anterior cingulate cortex, dmPFC = dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, AMY = amygdala, L = left, R = right
| [1] |
刘雷, 周仁来. (2015). 一个测量抑郁症的重要神经指标:静息额叶脑电活动的不对称性. 心理科学进展, 23(6), 1000-1008.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2015.01000 |
| [2] | 张晶, 周仁来. (2010). 额叶EEG偏侧化: 情绪调节能力的指标. 心理科学进展, 18(11), 1679-1683. |
| [3] | Ahrweiler, N., Santana-Gonzalez, C., Zhang, N., Quandt, G., Ashtiani, N., Liu, G. M.,... Quevedo, K. (2022). Neural activity associated with symptoms change in depressed adolescents following self-processing neurofeedback. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1128. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12091128 |
| [4] |
Alkoby, O., Abu-Rmileh, A., Shriki, O., & Todder, D. (2018). Can we predict who will respond to neurofeedback? A review of the inefficacy problem and existing predictors for successful eeg neurofeedback learning. Neuroscience, 378, 155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.12.050
pmid: 28069531 |
| [5] | Amadei, E. A., Johnson, Z. V., Kwon, Y. J., Shpiner, A. C., Saravanan, V., Mays, W. D.,... Liu, R. C. (2017). Dynamic corticostriatal activity biases social bonding in monogamous female prairie voles. Nature, 546(7657), 297-301. doi: 10.1038/nature22381 |
| [6] | Anderson, A. K., & Phelps, E. A. (2001). Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events. Nature, 411(6835), 305-309. doi: 10.1038/35077083 |
| [7] | Arditte Hall, K. A., de Raedt, R., Timpano, K. R., & Joormann, J. (2018). Positive memory enhancement training for individuals with major depressive disorder. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 47(2), 155-168. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2017.1364291 |
| [8] | Arns, M., Batail, J. M., Bioulac, S., Congedo, M., Daudet, C., Drapier, D.,... Vialatte, F. (2017). Neurofeedback: One of today's techniques in psychiatry? Neurofeedback en psychiatrie: Une technique du présent? L’Encéphale, 43(2), 135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.11.003 |
| [9] | Baas, D., Aleman, A., & Kahn, R. S. (2004). Lateralization of amygdala activation: A systematic review of functional neuroimaging studies. Brain Research Reviews, 45(2), 96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.02.004 |
| [10] | Baehr, E., Rosenfeld, J. P., & Baehr, R. (1997). The clinical use of an alpha asymmetry protocol in the neurofeedback treatment of depression. Journal of Neurotherapy, 2(3), 10-23. doi: 10.1300/J184v02n03_02 |
| [11] | Banks, S. J., Eddy, K. T., Angstadt, M., Nathan, P. J., & Phan, K. L. (2007). Amygdala - frontal connectivity during emotion regulation. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 2(4), 303-312. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsm029 |
| [12] | Barreiros, A. R., Almeida, I., Baía, B. C., & Castelo-Branco, M. (2019). Amygdala modulation during emotion regulation training with fMRI-based neurofeedback. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 24. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00089 |
| [13] | Batail, J. M., Bioulac, S., Cabestaing, F., Daudet, C., Drapier, D., Fouillen, M.,... Vialatte, F. (2019). EEG neurofeedback research: A fertile ground for psychiatry? L’Encephale, 45(3), 245-255. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2019.02.001 |
| [14] |
Belzung, C., Willner, P., & Philippot, P. (2015). Depression: From psychopathology to pathophysiology. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 30, 24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2014.08.013
pmid: 25218233 |
| [15] |
Blackwell, S. E., Browning, M., Mathews, A., Pictet, A., Welch, J., Davies, J.,... Holmes, E. A. (2015). Positive imagery-based cognitive bias modification as a web-based treatment tool for depressed adults: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Psychological Science, 3(1), 91-111. doi: 10.1177/2167702614560746
pmid: 25984421 |
| [16] | Brush, C. J., Burani, K., Schmidt, K. M., Santopetro, N. J., & Hajcak, G. (2021). The impact of a single session of aerobic exercise on positive emotional reactivity in depression: Insight into individual differences from the late positive potential. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 144, 103914. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2021.103914 |
| [17] |
Bu, J. J., Young, K. D., Hong, W., Ma, R., Song, H. W., Wang, Y.,... Zhang, X. C. (2019). Effect of deactivation of activity patterns related to smoking cue reactivity on nicotine addiction. Brain, 142(6), 1827-1841. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz114
pmid: 31135053 |
| [18] |
Burkhardt, G., Kumpf, U., Crispin, A., Goerigk, S., Andre, E., Plewnia, C.,... Padberg, F. (2023). Transcranial direct current stimulation as an additional treatment to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in adults with major depressive disorder in Germany (DepressionDC): A triple-blind, randomised, sham-controlled, multicentre trial. The Lancet, 402(10401), 545-554. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00640-2
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00640-2 URL |
| [19] | Chen, K., Barnes-Horowitz, N., Treanor, M., Sun, M., Young, K. S., & Craske, M. G. (2020). Virtual reality reward training for anhedonia: A pilot study. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 613617. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.613617 |
| [20] | Cheon, E.-J., Koo, B.-H., & Choi, J.-H. (2016). The efficacy of neurofeedback in patients with major depressive disorder: An open labeled prospective study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 41(1), 103-110. doi: 10.1007/s10484-015-9315-8 |
| [21] |
Choi, S. W., Chi, S. E., Chung, S. Y., Kim, J. W., Ahn, C. Y., & Kim, H. T. (2011). Is alpha wave neurofeedback effective with randomized clinical trials in depression? A pilot study. Neuropsychobiology, 63(1), 43-51. doi: 10.1159/000322290
pmid: 21063132 |
| [22] | Compère, L., Siegle, G. J., Lazzaro, S., Strege, M., Canovali, G., Barb, S.,... Young, K. (2023). Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback training of amygdala upregulation increases affective flexibility in depression. Journal of Psychiatry Neuroscience, 48(3), E232-E239. doi: 10.1503/jpn.220208 |
| [23] |
Compère, L., Siegle, G. J., Riley, E., Lazzaro, S., Strege, M., Pacoe, E.,... Young, K. (2023). Enhanced efficacy of CBT following augmentation with amygdala rtfMRI neurofeedback in depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 339, 495-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.07.063
pmid: 37459978 |
| [24] |
Cook, I. A., O'Hara, R., Uijtdehaage, S. H., Mandelkern, M., & Leuchter, A. F. (1998). Assessing the accuracy of topographic EEG mapping for determining local brain function. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 107(6), 408-414. doi: 10.1016/s0013-4694(98)00092-3
pmid: 9922086 |
| [25] |
Craske, M. G., Meuret, A. E., Ritz, T., Treanor, M., & Dour, H. J. (2016). Treatment for anhedonia: A neuroscience driven approach. Depression and Anxiety, 33(10), 927-938. doi: 10.1002/da.22490
pmid: 27699943 |
| [26] |
Critchley, H. D. (2005). Neural mechanisms of autonomic, affective, and cognitive integration. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 493(1), 154-166. doi: 10.1002/cne.20749
pmid: 16254997 |
| [27] | Cusin, C., & Dougherty, D. D. (2012). Somatic therapies for treatment-resistant depression: ECT, TMS, VNS, DBS. Biology of Mood & Anxiety Disorders, 2, 14. doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-2-14 |
| [28] | Cuthbert, B. N., & Insel, T. R. (2013). Toward the future of psychiatric diagnosis: The seven pillars of RDoC. BMC Medicine, 11, 126. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-126 |
| [29] |
Dalgleish, T., & Werner-Seidler, A. (2014). Disruptions in autobiographical memory processing in depression and the emergence of memory therapeutics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 18(11), 596-604. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2014.06.010
pmid: 25060510 |
| [30] |
Davidson, R. J. (1992). Anterior cerebral asymmetry and the nature of emotion. Brain and Cognition, 20(1), 125-151. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(92)90065-t
pmid: 1389117 |
| [31] |
Daws, R. E., Timmermann, C., Giribaldi, B., Sexton, J. D., Wall, M. B., Erritzoe, D.,... Carhart-Harris, R. (2022). Increased global integration in the brain after psilocybin therapy for depression. Nature Medicine, 28(4), 844-851. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01744-z
pmid: 35411074 |
| [32] |
de Schotten, M. T., & Forkel, S. J. (2022). The emergent properties of the connected brain. Science, 378(6619), 505-510. doi: 10.1126/science.abq2591
pmid: 36378968 |
| [33] |
Dillon, D. G., & Pizzagalli, D. A. (2018). Mechanisms of memory disruption in depression. Trends in Neurosciences, 41(3), 137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2017.12.006
pmid: 29331265 |
| [34] |
Dimidjian, S., Barrera, M., Martell, C., Muñoz, R. F., & Lewinsohn, P. M. (2011). The origins and current status of behavioral activation treatments for depression. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 1-38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104535
pmid: 21275642 |
| [35] | Doré, B. P., Rodrik, O., Boccagno, C., Hubbard, A., Weber, J., Stanley, B.,... Ochsner, K. N. (2018). Negative autobiographical memory in depression reflects elevated amygdala-hippocampal reactivity and hippocampally associated emotion regulation. Biological Psychiatry- Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 3(4), 358-366. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2018.01.002 |
| [36] | Ducasse, D., Dubois, J., Jaussent, I., Azorin, J. M., Etain, B., Gard, S.,... Courtet, P. (2021). Association between anhedonia and suicidal events in patients with mood disorders: A 3-year prospective study. Depression and Anxiety, 38(1), 17-27. doi: 10.1002/da.23072 |
| [37] |
Duerden, E. G., Arsalidou, M., Lee, M., & Taylor, M. J. (2013). Lateralization of affective processing in the insula. Neuroimage, 78, 159-175. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.014
pmid: 23587690 |
| [38] |
Dunlop, K., Rizvi, S. J., Kennedy, S. H., Hassel, S., Strother, S. C., Harris, J. K.,... Downar, J. (2020). Clinical, behavioral, and neural measures of reward processing correlate with escitalopram response in depression: A canadian biomarker integration network in depression (CAN-BIND-1) report. Neuropsychopharmacology, 45(8), 1390-1397. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0688-x
pmid: 32349119 |
| [39] | Dunn, B. D., German, R. E., Khazanov, G., Xu, C. L., Hollon, S. D., & DeRubeis, R. J. (2020). Changes in positive and negative affect during pharmacological treatment and cognitive therapy for major depressive disorder: A secondary analysis of two randomized controlled trials. Clinical Psychological Science, 8(1), 36-51. doi: 10.1177/2167702619863427 |
| [40] | Dunn, B. D., Widnall, E., Reed, N., Owens, C., Campbell, J., & Kuyken, W. (2019). Bringing light into darkness: A multiple baseline mixed methods case series evaluation of Augmented Depression Therapy (ADepT). Behaviour Research and Therapy, 120, 103418. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2019.103418 |
| [41] | Earnest, C. (1999). Single case study of EEG asymmetry biofeedback for depression. Journal of Neurotherapy, 3(2), 28-35. doi: 10.1300/J184v03n02_04 |
| [42] | Escolano, C., Navarro-Gil, M., Garcia-Campayo, J., Congedo, M., de Ridder, D., & Minguez, J. (2014). A controlled study on the cognitive effect of alpha neurofeedback training in patients with major depressive disorder. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 12. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00296 |
| [43] | Everaert, J., Vrijsen, J. N., Martin-Willett, R., van de Kraats, L., & Joormann, J. (2022). A meta-analytic review of the relationship between explicit memory bias and depression: Depression features an explicit memory bias that persists beyond a depressive episode. Psychological Bulletin, 148(5-6), 435-463. doi: 10.1037/bul0000367 |
| [44] | Fede, S. J., Dean, S. F., Manuweera, T., & Momenan, R. (2020). A guide to literature informed decisions in the design of real time fMRI neurofeedback studies: A systematic review. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14, 17. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00060 |
| [45] |
Fernandez, E., Salem, D., Swift, J. K., & Ramtahal, N. (2015). Meta-analysis of dropout from cognitive behavioral therapy: Magnitude, timing, and moderators. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 83(6), 1108-1122. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000044
pmid: 26302248 |
| [46] |
Frank, D. W., Dewitt, M., Hudgens-Haney, M., Schaeffer, D. J., Ball, B. H., Schwarz, N. F.,... Sabatinelli, D. (2014). Emotion regulation: Quantitative meta-analysis of functional activation and deactivation. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 45, 202-211. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.06.010
pmid: 24984244 |
| [47] | Fruitet, J., Carpentier, A., Munos, R., & Clerc, M. (2013). Automatic motor task selection via a bandit algorithm for a brain-controlled button. Journal of Neural Engineering, 10(1), 8. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/1/016012 |
| [48] |
Gabbay, V., Johnson, A. R., Alonso, C. M., Evans, L. K., Babb, J. S., & Klein, R. G. (2015). Anhedonia, but not irritability, is associated with illness severity outcomes in adolescent major depression. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 25(3), 194-200. doi: 10.1089/cap.2014.0105
pmid: 25802984 |
| [49] |
Gong, Q. Y., & He, Y. (2015). Depression, neuroimaging and connectomics: A selective overview. Biological Psychiatry, 77(3), 223-235. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.08.009
pmid: 25444171 |
| [50] |
Goodwin, G. M., Price, J., de Bodinat, C., & Laredo, J. (2017). Emotional blunting with antidepressant treatments: A survey among depressed patients. Journal of Affective Disorders, 221, 31-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.05.048
pmid: 28628765 |
| [51] |
Greer, S. M., Trujillo, A. J., Glover, G. H., & Knutson, B. (2014). Control of nucleus accumbens activity with neurofeedback. Neuroimage, 96, 237-244. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.073
pmid: 24705203 |
| [52] |
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H.,... Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: Abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62(5), 429-437. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.020
pmid: 17210143 |
| [53] |
Hamilton, J. P., Etkin, A., Furman, D. J., Lemus, M. G., Johnson, R. F., & Gotlib, I. H. (2012). Functional neuroimaging of major depressive disorder: A meta- analysis and new integration of baseline activation and neural response data. American Journal of Psychiatry, 169(7), 693-703. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11071105
pmid: 22535198 |
| [54] | Hamilton, J. P., Glover, G. H., Bagarinao, E., Chang, C., Mackey, S., Sacchet, M. D., & Gotlib, I. H. (2016). Effects of salience-network-node neurofeedback training on affective biases in major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Research- Neuroimaging, 249, 91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.01.016 |
| [55] |
Hamilton, J. P., Glover, G. H., Hsu, J. J., Johnson, R. F., & Gotlib, I. H. (2011). Modulation of subgenual anterior cingulate cortex activity with real-time neurofeedback. Human Brain Mapping, 32(1), 22-31. doi:10.1002/hbm.20997
pmid: 21157877 |
| [56] | Hammond, D. C. (2008). Neurofeedback treatment of depression with the roshi. Journal of Neurotherapy, 4(2), 45-56. doi: 10.1300/J184v04n02_06 |
| [57] |
Hasler, G., Drevets, W. C., Manji, H. K., & Charney, D. S. (2004). Discovering endophenotypes for major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology, 29(10), 1765-1781. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300506
pmid: 15213704 |
| [58] | Hellrung, L., Kirschner, M., Sulzer, J., Sladky, R., Scharnowski, F., Herdener, M., & Tobler, P. N. (2022). Analysis of individual differences in neurofeedback training illuminates successful self-regulation of the dopaminergic midbrain. Communications Biology, 5(1), 845. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03756-4 |
| [59] |
Holmes, E. A., Blackwell, S. E., Burnett Heyes, S., Renner, F., & Raes, F. (2016). Mental imagery in depression: Phenomenology, potential mechanisms, and treatment implications. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 12, 249-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-021815-092925
pmid: 26772205 |
| [60] |
Hu, R. K., Zuo, Y. N., Ly, T., Wang, J., Meera, P., Wu, Y. E., & Hong, W. Z. (2021). An amygdala-to-hypothalamus circuit for social reward. Nature Neuroscience, 24(6), 831-842. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00828-2
pmid: 33820999 |
| [61] |
Husain, M., & Roiser, J. P. (2018). Neuroscience of apathy and anhedonia: A transdiagnostic approach. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 19(8), 470-484. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0029-9
pmid: 29946157 |
| [62] |
Janicak, P. G., & Dokucu, M. E. (2015). Transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of major depression. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 11, 1549-1560. doi: 10.2147/ndt.S67477
pmid: 26170668 |
| [63] | Joormann, J., & Vanderlind, W. M. (2014). Emotion regulation in depression: The role of biased cognition and reduced cognitive control. Clinical Psychological Science, 2(4), 402-421. doi: 10.1177/2167702614536163 |
| [64] | Keller, M., Zweerings, J., Klasen, M., Zvyagintsev, M., Iglesias, J., Mendoza Quiñones, R., & Mathiak, K. (2021). fMRI neurofeedback-enhanced cognitive reappraisal training in depression: A double-blind comparison of left and right vlPFC regulation. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 715898. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.715898 |
| [65] |
Kim, S., & Birbaumer, N. (2014). Real-time functional MRI neurofeedback: A tool for psychiatry. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 27(5), 332-336. doi: 10.1097/yco.0000000000000087
pmid: 25023886 |
| [66] |
Klooster, D. C. W., de Louw, A. J. A., Aldenkamp, A. P., Besseling, R. M. H., Mestrom, R. M. C., Carrette, S.,... Boon, P. (2016). Technical aspects of neurostimulation: Focus on equipment, electric field modeling, and stimulation protocols. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 65, 113-141. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.02.016
pmid: 27021215 |
| [67] | Koller-Schlaud, K., Querbach, J., Behr, J., Ströhle, A., & Rentzsch, J. (2020). Test-retest reliability of frontal and parietal alpha asymmetry during presentation of emotional face stimuli in healthy subjects. Neuropsychobiology, 79(6), 428-436. doi: 10.1159/000505783 |
| [68] | Koush, Y., Meskaldji, D. E., Pichon, S., Rey, G., Rieger, S. W., Linden, D. E. J.,... Scharnowski, F. (2017). Learning control over emotion networks through connectivity-based neurofeedback. Cerebral Cortex, 27(2), 1193-1202. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv311 |
| [69] |
Koush, Y., Pichon, S., Eickhoff, S. B., van de Ville, D., Vuilleumier, P., & Scharnowski, F. (2019). Brain networks for engaging oneself in positive-social emotion regulation. Neuroimage, 189, 106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.12.049
pmid: 30594682 |
| [70] |
Kumar, P., Pisoni, A., Bondy, E., Kremens, R., Singleton, P., Pizzagalli, D., & Auerbach, R. P. (2019). Delineating the social valuation network in adolescents. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 14(11), 1159-1166. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsz086
pmid: 31680163 |
| [71] | Kuusinen, V., Peräkylä, J., Sun, L. H., Ogawa, K. H., & Hartikainen, K. M. (2021). Emotional modulation of frontal alpha asymmetry - a novel biomarker of mild traumatic brain injury. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 15, 13. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.699947 |
| [72] |
Lawrence, E. J., Su, L., Barker, G. J., Medford, N., Dalton, J., Williams, S. C. R.,... David, A. S. (2014). Self-regulation of the anterior insula: Reinforcement learning using real-time fMRI neurofeedback. Neuroimage, 88, 113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.069
pmid: 24231399 |
| [73] | Lee, B. T., Cho, S. W., Khang, H. S., Lee, B. C., Choi, I. G., Lyoo, I. K., & Ham, B. J. (2007). The neural substrates of affective processing toward positive and negative affective pictures in patients with major depressive disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 31(7), 1487-1492. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.06.030 |
| [74] | Li, K. S., Jiang, Y. H., Gong, Y. L., Zhao, W. H., Zhao, Z. Y., Liu, X. L.,... Becker, B. (2019). Functional near-infrared spectroscopy-informed neurofeedback: Regional-specific modulation of lateral orbitofrontal activation and cognitive flexibility. Neurophotonics, 6(2), 025011. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.6.2.025011 |
| [75] |
Linden, D. E. J. (2014). Neurofeedback and networks of depression. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 16(1), 103-112.
pmid: 24733975 |
| [76] | Linden, D. E. J., Habes, I., Johnston, S. J., Linden, S., Tatineni, R., Subramanian, L.,... Goebel, R. (2012). Real-time self-regulation of emotion networks in patients with depression. Plos One, 7(6), e38115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038115 |
| [77] |
Linhartová, P., Látalová, A., Kóša, B., Kašpárek, T., Schmahl, C., & Paret, C. (2019). fMRI neurofeedback in emotion regulation: A literature review. Neuroimage, 193, 75-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.011
pmid: 30862532 |
| [78] | Luo, L., Wu, H. W., Xu, J. P., Chen, F. F., Wu, F. C., Wang, C., & Wang, J. J. (2021). Abnormal large-scale resting- state functional networks in drug-free major depressive disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 15(1), 96-106. doi: 10.1007/s11682-019-00236-y |
| [79] |
Martz, M. E., Trucco, E. M., Cope, L. M., Hardee, J. E., Jester, J. M., Zucker, R. A., & Heitzeg, M. M. (2016). Association of marijuana use with blunted nucleus accumbens response to reward anticipation. JAMA Psychiatry, 73(8), 838-844. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.1161
pmid: 27384542 |
| [80] |
Mathersul, D., Williams, L. M., Hopkinson, P. J., & Kemp, A. H. (2008). Investigating models of affect: Relationships among EEG alpha asymmetry, depression, and anxiety. Emotion, 8(4), 560-572. doi: 10.1037/a0012811
pmid: 18729586 |
| [81] |
McRae, K., & Gross, J. J. (2020). Emotion regulation. Emotion, 20(1), 1-9. doi: 10.1037/emo0000703
pmid: 31961170 |
| [82] |
Mehler, D. M. A., Sokunbi, M. O., Habes, I., Barawi, K., Subramanian, L., Range, M.,... Linden, D. E. J. (2018). Targeting the affective brain-a randomized controlled trial of real-time fMRI neurofeedback in patients with depression. Neuropsychopharmacology, 43(13), 2578-2585. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0126-5
pmid: 29967368 |
| [83] | Morawetz, C., Bode, S., Baudewig, J., Kirilina, E., & Heekeren, H. R. (2016). Changes in effective connectivity between dorsal and ventral prefrontal regions moderate emotion regulation. Cerebral Cortex, 26(5), 1923-1937. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv005 |
| [84] | Nawa, N. E., & Ando, H. (2019). Effective connectivity within the ventromedial prefrontal cortex-hippocampus- amygdala network during the elaboration of emotional autobiographical memories. Neuroimage, 189, 316-328. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.01.042 |
| [85] | Nazarian, M. (2005). An alternative treatment for depression using EEG biofeedback to alter frontal alpha asymmetry and improve mood (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). The University of Arizona, United States. |
| [86] |
Nutt, D., Demyttenaere, K., Janka, Z., Aarre, T., Bourin, M., Canonico, P. L.,... Stahl, S. (2007). The other face of depression, reduced positive affect: The role of catecholamines in causation and cure. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 21(5), 461-471. doi: 10.1177/0269881106069938
pmid: 17050654 |
| [87] |
Ochsner, K. N., Bunge, S. A., Gross, J. J., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2002). Rethinking feelings: An fMRI study of the cognitive regulation of emotion. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 14(8), 1215-1229. doi: 10.1162/08989290 2760807212
doi: 10.1162/089892902760807212 pmid: 12495527 |
| [88] |
Ochsner, K. N., & Gross, J. J. (2005). The cognitive control of emotion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(5), 242-249. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.03.010
pmid: 15866151 |
| [89] |
Ochsner, K. N., Ray, R. R., Hughes, B., McRae, K., Cooper, J. C., Weber, J.,... Gross, J. J. (2009). Bottom-up and top-down processes in emotion generation: Common and distinct neural mechanisms. Psychological Science, 20(11), 1322-1331. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02459.x
pmid: 19883494 |
| [90] | Ochsner, K. N., Silvers, J. A., & Buhle, J. T. (2012). Functional imaging studies of emotion regulation:A synthetic review and evolving model of the cognitive control of emotion. In A. Kingstone & M. B. Miller (Eds.), Year in Cognitive Neuroscience (Vol. 1251, pp. E1-E24). Oxford: Blackwell Science Publ. |
| [91] | Opel, N., Redlich, R., Grotegerd, D., Dohm, K., Zaremba, D., Meinert, S.,... Dannlowski, U. (2017). Prefrontal brain responsiveness to negative stimuli distinguishes familial risk for major depression from acute disorder. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 42(5), 343-352. doi: 10.1503/jpn.160198 |
| [92] |
Paret, C., & Hendler, T. (2020). Live from the "regulating brain": Harnessing the brain to change emotion. Emotion, 20(1), 126-131. doi: 10.1037/emo0000674
pmid: 31961191 |
| [93] | Peeters, F., Oehlen, M., Ronner, J., van Os, J., & Lousberg, R. (2014). Neurofeedback as a treatment for major depressive disorder-A pilot study. Plos One, 9(3), e91837. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091837 |
| [94] |
Pizzagalli, D. A. (2022). Toward a better understanding of the mechanisms and pathophysiology of anhedonia: Are we ready for translation? American Journal of Psychiatry, 179(7), 458-469. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20220423
pmid: 35775159 |
| [95] |
Quevedo, K., Harms, M., Sauder, M., Scott, H., Mohamed, S., Thomas, K. M.,... Smyda, G. (2018). The neurobiology of self face recognition among depressed adolescents. Journal of Affective Disorders, 229, 22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.12.023
pmid: 29304386 |
| [96] |
Ritchie, J. B., Kaplan, D. M., & Klein, C. (2019). Decoding the brain: Neural representation and the limits of multivariate pattern analysis in cognitive neuroscience. The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science, 70(2), 581-607. doi: 10.1093/bjps/axx023
pmid: 31086423 |
| [97] |
Ros, T., Enriquez-Geppert, S., Zotev, V., Young, K. D., Wood, G., Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.,... Thibault, R. T. (2020). Consensus on the reporting and experimental design of clinical and cognitive-behavioural neurofeedback studies (CRED-nf checklist). Brain, 143(6), 1674-1685. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa009
pmid: 32176800 |
| [98] |
Rosenfeld, J. P., Baehr, E., Baehr, R., Gotlib, I. H., & Ranganath, C. (1996). Preliminary evidence that daily changes in frontal alpha asymmetry correlate with changes in affect in therapy sessions. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 23(1-2), 137-141. doi: 10.1016/0167-8760(96)00037-2
pmid: 8880374 |
| [99] |
Roy, M., Shohamy, D., & Wager, T. D. (2012). Ventromedial prefrontal-subcortical systems and the generation of affective meaning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(3), 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2012.01.005
pmid: 22310704 |
| [100] | Sagud, M., Tudor, L., Šimunic, L., Jezernik, D., Madžarac, Z., Jakšić, N.,... Pivac, N. (2021). Physical and social anhedonia are associated with suicidality in major depression, but not in schizophrenia. Suicide & Life-Threatening Behavior, 51(3), 446-454. doi: 10.1111/sltb.12724 |
| [101] |
Sah, P., Faber, E. S. L., Lopez De Armentia, M., & Power, J. (2003). The amygdaloid complex: Anatomy and physiology. Physiological Reviews, 83(3), 803-834.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00002.2003 pmid: 12843409 |
| [102] | Salamone, J. D., Yohn, S. E., López-Cruz, L., Miguel, N. S., & Correa, M. (2016). Activational and effort-related aspects of motivation: Neural mechanisms and implications for psychopathology. Brain, 139(5), 1325-1347. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww050 |
| [103] |
Sanislow, C. A., Ferrante, M., Pacheco, J., Rudorfer, M. V., & Morris, S. E. (2019). Advancing translational research using NIMH research domain criteria and computational methods. Neuron, 101(5), 779-782. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.024
pmid: 30844398 |
| [104] |
Santangelo, V., Cavallina, C., Colucci, P., Santori, A., Macri, S., McGaugh, J. L., & Campolongo, P. (2018). Enhanced brain activity associated with memory access in highly superior autobiographical memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(30), 7795-7800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1802730115
pmid: 29987025 |
| [105] |
Sarkheil, P., Zilverstand, A., Kilian-Hütten, N., Schneider, F., Goebel, R., & Mathiak, K. (2015). fMRI feedback enhances emotion regulation as evidenced by a reduced amygdala response. Behavioural Brain Research, 281, 326-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.027
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.027 URL pmid: 25461265 |
| [106] | Scheinost, D., Hsu, T. W., Avery, E. W., Hampson, M., Constable, R. T., Chun, M. M., & Rosenberg, M. D. (2020). Connectome-based neurofeedback: A pilot study to improve sustained attention. Neuroimage, 212, 116684. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116684 |
| [107] |
Schumacher, A., Villaruel, F. R., Ussling, A., Riaz, S., Lee, A. C. H., & Ito, R. (2018). Ventral hippocampal CA1 and CA3 differentially mediate learned approach-avoidance conflict processing. Current Biology, 28(8), 1318-1324. E4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.03.012
pmid: 29606418 |
| [108] |
Segrave, R. A., Cooper, N. R., Thomson, R. H., Croft, R. J., Sheppard, D. M., & Fitzgerald, P. B. (2011). Individualized alpha activity and frontal asymmetry in major depression. Clinical EEG and Neuroscience, 42(1), 45-52. doi: 10.1177/155005941104200110
pmid: 21309442 |
| [109] |
Sergerie, K., Chochol, C., & Armony, J. L. (2008). The role of the amygdala in emotional processing: A quantitative meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 32(4), 811-830. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.12.002
pmid: 18316124 |
| [110] |
Sherman, L. E., Payton, A. A., Hernandez, L. M., Greenfield, P. M., & Dapretto, M. (2016). The power of the like in adolescence: Effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychological Science, 27(7), 1027-1035. doi: 10.1177/0956797616645673
pmid: 27247125 |
| [111] |
Silk, J. S., Lee, K. H., Kerestes, R., Griffith, J. M., Dahl, R. E., & Ladouceur, C. D. (2017). "Loser" or "Popular"?: Neural response to social status words in adolescents with major depressive disorder. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 28, 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2017.09.005
pmid: 29028595 |
| [112] |
Sitaram, R., Ros, T., Stoeckel, L., Haller, S., Scharnowski, F., Lewis-Peacock, J.,... Sulzer, J. (2017). Closed-loop brain training: The science of neurofeedback. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 18(2), 86-100. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.164
pmid: 28003656 |
| [113] | Skottnik, L., & Linden, D. E. J. (2019). Mental imagery and brain regulation-new links between psychotherapy and neuroscience. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 14. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00779 |
| [114] |
Sosa, M., & Giocomo, L. M. (2021). Navigating for reward. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 22(8), 472-487. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00479-z
pmid: 34230644 |
| [115] |
Stewart, J. L., Coan, J. A., Towers, D. N., & Allen, J. J. B. (2011). Frontal EEG asymmetry during emotional challenge differentiates individuals with and without lifetime major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 129(1-3), 167-174. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2010.08.029
pmid: 20870293 |
| [116] |
Stewart, J. L., Towers, D. N., Coan, J. A., & Allen, J. J. B. (2011). The oft-neglected role of parietal EEG asymmetry and risk for major depressive disorder. Psychophysiology, 48(1), 82-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01035.x
pmid: 20525011 |
| [117] | Sun, L. H., Perakyla, J., & Hartikainen, K. M. (2017). Frontal alpha asymmetry, a potential biomarker for the effect of neuromodulation on brain's affective circuitry- preliminary evidence from a deep brain stimulation study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 9. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00584 |
| [118] |
Suslow, T., Konrad, C., Kugel, H., Rumstadt, D., Zwitserlood, P., Schöning, S.,... Dannlowski, U. (2010). Automatic mood-congruent amygdala responses to masked facial expressions in major depression. Biological Psychiatry, 67(2), 155-160. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.023
pmid: 19748075 |
| [119] | Szucs, D., & Ioannidis, J. P. A. (2017). Empirical assessment of published effect sizes and power in the recent cognitive neuroscience and psychology literature. Plos Biology, 15(3), e3001151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000797 |
| [120] | Taschereau-Dumouchel, V., Cushing, C. A., & Lau, H. (2022). Real-time functional MRI in the treatment of mental health disorders. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 18, 125-154. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-072220-014550 |
| [121] |
Tashjian, S. M., & Galván, A. (2018). The role of mesolimbic circuitry in buffering election-related distress. Journal of Neuroscience, 38(11), 2887-2898. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.2470-17.2018
pmid: 29431648 |
| [122] |
Taylor, C. T., Lyubomirsky, S., & Stein, M. B. (2017). Upregulating the positive affect system in anxiety and depression: Outcomes of a positive activity intervention. Depression and Anxiety, 34(3), 267-280. doi: 10.1002/da.22593
pmid: 28060463 |
| [123] |
Thibault, R. T., Lifshitz, M., & Raz, A. (2016). The self- regulating brain and neurofeedback: Experimental science and clinical promise. Cortex, 74, 247-261. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2015.10.024
pmid: 26706052 |
| [124] |
Thibault, R. T., Lifshitz, M., & Raz, A. (2017). Neurofeedback or neuroplacebo? Brain, 140(4), 862-864. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx033
pmid: 28375458 |
| [125] | Thibault, R. T., & Raz, A. (2016). Neurofeedback: The power of psychosocial therapeutics. Lancet Psychiatry, 3(11), E18-E18. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(16)30326-1 |
| [126] |
Thibodeau, R., Jorgensen, R. S., & Kim, S. (2006). Depression, anxiety, and resting frontal EEG asymmetry: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 115(4), 715-729. doi: 10.1037/0021-843x.115.4.715
pmid: 17100529 |
| [127] |
Trambaiolli, L. R., Kohl, S. H., Linden, D. E. J., & Mehler, D. M. A. (2021). Neurofeedback training in major depressive disorder: A systematic review of clinical efficacy, study quality and reporting practices. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 125, 33-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.015
pmid: 33587957 |
| [128] |
Treadway, M. T., & Zald, D. H. (2011). Reconsidering anhedonia in depression: Lessons from translational neuroscience. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(3), 537-555. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.06.006
pmid: 20603146 |
| [129] | Vanderlind, W. M., Millgram, Y., Baskin-Sommers, A. R., Clark, M. S., & Joormann, J. (2020). Understanding positive emotion deficits in depression: From emotion preferences to emotion regulation. Clinical Psychology Review, 76, 101826. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101826 |
| [130] |
Victor, T. A., Furey, M. L., Fromm, S. J., Ohman, A., & Drevets, W. C. (2010). Relationship between amygdala responses to masked faces and mood state and treatment in major depressive disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(11), 1128-1138. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.144
pmid: 21041614 |
| [131] | Wang, S.-Y., Lin, I. M., Peper, E., Chen, Y.-T., Tang, T.-C., Yeh, Y.-C.,... Chu, C.-C. (2016). The efficacy of neurofeedback among patients with major depressive disorder: Preliminary study. NeuroRegulation, 3(3), 127-134. doi: 10.15540/nr.3.3.127 |
| [132] |
Werner-Seidler, A., Banks, R., Dunn, B. D., & Moulds, M. L. (2013). An investigation of the relationship between positive affect regulation and depression. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 51(1), 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2012.11.001
pmid: 23178678 |
| [133] |
Young, K. D., Siegle, G. J., Bodurka, J., & Drevets, W. C. (2016). Amygdala activity during autobiographical memory recall in depressed and vulnerable individuals: Association with symptom severity and autobiographical overgenerality. American Journal of Psychiatry, 173(1), 78-89. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010119
pmid: 26541813 |
| [134] |
Young, K. D., Siegle, G. J., Zotev, V., Phillips, R., Misaki, M., Yuan, H.,... Bodurka, J. (2017). Randomized clinical trial of real-time fMRI amygdala neurofeedback for major depressive disorder: Effects on symptoms and autobiographical memory recall. American Journal of Psychiatry, 174(8), 748-755. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.16060637
pmid: 28407727 |
| [135] |
Young, K. D., Zotev, V., Phillips, R., Misaki, M., Drevets, W. C., & Bodurka, J. (2018). Amygdala real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback for major depressive disorder: A review. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 72(7), 466-481. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12665
pmid: 29687527 |
| [136] | Young, K. D., Zotev, V., Phillips, R., Misaki, M., Yuan, H., Drevets, W. C., & Bodurka, J. (2014). Real-time fMRI neurofeedback training of amygdala activity in patients with major depressive disorder. Plos One, 9(2), e88785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088785 |
| [137] |
Yuan, H., Young, K. D., Phillips, R., Zotev, V., Misaki, M., & Bodurka, J. (2014). Resting-state functional connectivity modulation and sustained changes after real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback training in depression. Brain Connectivity, 4(9), 690-701. doi: 10.1089/brain.2014.0262
pmid: 25329241 |
| [138] | Zheng, J., Anderson, K. L., Leal, S. L., Shestyuk, A., Gulsen, G., Mnatsakanyan, L.,... Lin, J. J. (2017). Amygdala- hippocampal dynamics during salient information processing. Nature Communications, 8, 14413. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14413 |
| [139] |
Zheng, L. J., Yang, G. F., Zhang, X. Y., Wang, Y. F., Liu, Y., Zheng, G.,... Han, Y. (2017). Altered amygdala and hippocampus effective connectivity in mild cognitive impairment patients with depression: A resting-state functional MR imaging study with granger causality analysis. Oncotarget, 8(15), 25021-25031. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15335
pmid: 28212570 |
| [140] | Zhu, Y. S., Gao, H., Tong, L., Li, Z. L., Wang, L. Y., Zhang, C.,... Yan, B. (2019). Emotion regulation of hippocampus using real-time fMRI neurofeedback in healthy human. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 14. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00242 |
| [141] | Zotev, V., Krueger, F., Phillips, R., Alvarez, R. P., Simmons, W. K., Bellgowan, P.,... Bodurka, J. (2011). Self- regulation of amygdala activation using real-time fMRI neurofeedback. Plos One, 6(9), e24522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024522 |
| [142] | Zotev, V., Mayeli, A., Misaki, M., & Bodurka, J. (2020). Emotion self-regulation training in major depressive disorder using simultaneous real-time fMRI and EEG neurofeedback. Neuroimage-Clinical, 27, 102331. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102331 |
| [143] | Zotev, V., Phillips, R., Young, K. D., Drevets, W. C., & Bodurka, J. (2013). Prefrontal control of the amygdala during real-time fMRI neurofeedback training of emotion regulation. Plos One, 8(11), e79184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079184 |
| [144] |
Zotev, V., Yuan, H., Misaki, M., Phillips, R., Young, K. D., Feldner, M. T., & Bodurka, J. (2016). Correlation between amygdala BOLD activity and frontal EEG asymmetry during real-time fMRI neurofeedback training in patients with depression. Neuroimage-Clinical, 11, 224-238. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.02.003
pmid: 26958462 |
| [1] | 潘运, 杨环瑜, 朱俊, 贾良智. 数量感知分组化策略的认知机制及神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(2): 191-201. |
| [2] | 温秀娟, 马毓璟, 谭斯祺, 李芸, 刘文华. 身体还是认知努力的损害?抑郁症努力奖赏动机评估及计算模型应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(1): 107-122. |
| [3] | 丁颖, 汪紫滢, 李卫东. 抑郁症疼痛加工的行为特点及神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1315-1327. |
| [4] | 吴朝毅, 王振. 抑郁症情绪失调的动态特征:情绪动力学的视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(2): 364-385. |
| [5] | 孙丽君, 杨玉芳. 预期视角下音乐节拍结构的认知与神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(10): 1567-1577. |
| [6] | 刘文华, 温秀娟, 陈灵, 杨瑞, 胡逸儒. 奖励期待和结果评估的脑电成分在精神疾病研究中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(5): 783-799. |
| [7] | 周广方, 金花. 精准功能磁共振成像揭示个体化脑功能网络组织[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(11): 2078-2091. |
| [8] | 张伟霞, 席敏, 阴甜甜, 王成, 司书宾. 基于网络分析的抑郁症产生与演变预测[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(11): 2129-2141. |
| [9] | 陈祥和, 李文秀, 刘波, 殷荣宾. 骨源性因子ucOCN在运动抗抑郁中的作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(2): 375-388. |
| [10] | 黄观澜, 周晓璐. 抑郁症患者的语言使用模式[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 838-848. |
| [11] | 叶超群, 林郁泓, 刘春雷. 创造力产生过程中的神经振荡机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 697-706. |
| [12] | 秦浩方, 黄蓉, 贾世伟. 反馈相关负波:一种抑郁症的生物标记物[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(3): 404-413. |
| [13] | 周爱保, 谢珮, 田喆, 潘超超. 情绪对饮食行为的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(11): 2013-2023. |
| [14] | 周璨, 周临舒, 蒋存梅. 音乐愉悦体验的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 123-130. |
| [15] | 高青林, 周媛. 计算模型视角下信任形成的心理和神经机制——基于信任博弈中投资者的角度[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 178-189. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||