

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (10): 1745-1761.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1745
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Huazhan1,2,3( ), LIU Pengyu1,2(
), LIU Pengyu1,2( ), ZHANG Li1,2
), ZHANG Li1,2
Received:2024-10-23
Published:2025-10-25
Online:2025-09-05
Contact:
YIN Huazhan,LIU Pengyu
E-mail:yhz1979@sina.com;Liupengyupsy@163.com
YIN Huazhan, LIU Pengyu, ZHANG Li. (2025). Preliminary development and evaluation of the Chinese self-conscious emotions nonverbal behavior expression stimulus set, and its application in research. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(10), 1745-1761.
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (71.9) | Frowning (0) | Eyebrows drooping (0.7) | Relaxed eyebrows (27.4) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (54.1) | Slightly squinted eyes (17.8) | No change in eye size (27.4) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (35.6) | Eyes looking straight ahead (60) | Eyes looking downward (3) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (0.7) | Corners of mouth raised (86.7) | Corners of mouth drooping (0.7) | Relaxed mouth (11.9) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (46.7) | Chin retracted (5.9) | Relaxed chin (45.2) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (65.9) | Slightly suppressed smile (8.9) | No smile (1.5) | Big smile (23) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (30.4) | Head upright (66.7) | Head lowered (1.5) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (0) | Body upright (41.5) | Body stretched (57.8) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (13.3) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (45.9) | Hands on hips (17.8) | Arms raised above head (8.9) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (3.7) | Hands touching the face (4.4) |
Table 1 Nonverbal behavior expression cues for pride and their ratios (%)
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (71.9) | Frowning (0) | Eyebrows drooping (0.7) | Relaxed eyebrows (27.4) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (54.1) | Slightly squinted eyes (17.8) | No change in eye size (27.4) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (35.6) | Eyes looking straight ahead (60) | Eyes looking downward (3) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (0.7) | Corners of mouth raised (86.7) | Corners of mouth drooping (0.7) | Relaxed mouth (11.9) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (46.7) | Chin retracted (5.9) | Relaxed chin (45.2) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (65.9) | Slightly suppressed smile (8.9) | No smile (1.5) | Big smile (23) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (30.4) | Head upright (66.7) | Head lowered (1.5) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (0) | Body upright (41.5) | Body stretched (57.8) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (13.3) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (45.9) | Hands on hips (17.8) | Arms raised above head (8.9) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (3.7) | Hands touching the face (4.4) |
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (1.5) | Frowning (35.6) | Eyebrows drooping (60) | Relaxed eyebrows (3) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (4.4) | Slightly squinted eyes (60.7) | No change in eye size (33.3) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (3) | Eyes looking straight ahead (5.2) | Eyes looking downward (91.1) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (69.6) | Corners of mouth raised (0.7) | Corners of mouth drooping (26.7) | Relaxed mouth (3) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (7.4) | Chin retracted (78.5) | Relaxed chin (11.9) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (2.2) | Slightly suppressed smile 28.9) | No smile (57.8) | Big smile (0) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (1.5) | Head upright (5.9) | Head lowered (92.6) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (75.6) | Body upright (18.5) | Body stretched (5.2) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (5.2) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (30.4) | Hands on hips (0.7) | Arms raised above head (1.5) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (27.4) | Hands touching the face (27.4) |
Table 2 Nonverbal behavior expression cues for shame and their ratios (%)
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (1.5) | Frowning (35.6) | Eyebrows drooping (60) | Relaxed eyebrows (3) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (4.4) | Slightly squinted eyes (60.7) | No change in eye size (33.3) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (3) | Eyes looking straight ahead (5.2) | Eyes looking downward (91.1) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (69.6) | Corners of mouth raised (0.7) | Corners of mouth drooping (26.7) | Relaxed mouth (3) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (7.4) | Chin retracted (78.5) | Relaxed chin (11.9) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (2.2) | Slightly suppressed smile 28.9) | No smile (57.8) | Big smile (0) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (1.5) | Head upright (5.9) | Head lowered (92.6) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (75.6) | Body upright (18.5) | Body stretched (5.2) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (5.2) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (30.4) | Hands on hips (0.7) | Arms raised above head (1.5) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (27.4) | Hands touching the face (27.4) |
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (23.7) | Frowning (39.3) | Eyebrows drooping (20) | Relaxed eyebrows (12.6) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (24.4) | Slightly squinted eyes (55.6) | No change in eye size (18.5) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (15.6) | Eyes looking straight ahead (10.4) | Eyes looking downward (65.9) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (71.1) | Corners of mouth raised (13.3) | Corners of mouth drooping (8.9) | Relaxed mouth (5.9) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (17) | Chin retracted (53.3) | Relaxed chin (25.9) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (11.1) | Slightly suppressed smile (69.6) | No smile (8.1) | Big smile (6.7) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (9.6) | Head upright (20.7) | Head lowered (66.7) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (41.5) | Body upright (42.2) | Body stretched (11.9) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (4.4) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (26.7) | Hands on hips (0) | Arms raised above head (4.4) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (17) | Hands touching the face (38.5) |
Table 3 Nonverbal behavior expression cues for embarrassment and their ratios (%)
| Body part | Nonverbal behavior expression cues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyebrows | Eyebrows raised (23.7) | Frowning (39.3) | Eyebrows drooping (20) | Relaxed eyebrows (12.6) | ||
| Eyes | Eyes wide open (24.4) | Slightly squinted eyes (55.6) | No change in eye size (18.5) | |||
| Eyes gaze direction | Eyes looking upward (15.6) | Eyes looking straight ahead (10.4) | Eyes looking downward (65.9) | |||
| Mouth | Mouth tightly closed (71.1) | Corners of mouth raised (13.3) | Corners of mouth drooping (8.9) | Relaxed mouth (5.9) | ||
| Chin | Chin pushed forward (17) | Chin retracted (53.3) | Relaxed chin (25.9) | |||
| Cheeks | Smile (11.1) | Slightly suppressed smile (69.6) | No smile (8.1) | Big smile (6.7) | ||
| Head | Head tilted backward (9.6) | Head upright (20.7) | Head lowered (66.7) | |||
| Torso | Body curled (41.5) | Body upright (42.2) | Body stretched (11.9) | |||
| Hands | Arms crossed in front of chest (4.4) | Arms hanging vertically by sides (26.7) | Hands on hips (0) | Arms raised above head (4.4) | Arms crossed and hanging downward (17) | Hands touching the face (38.5) |

Figure 1. Example of experimental materials. A?D represent the pictures of nonverbal behavior expressions for pride, embarrassment, shame, and neutral emotions, respectively. All pictures are fixed in position within the picture using horizontal and vertical reference lines.
| Emotion type | Hand actions | n (Number of pictures) | Mean recognition percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Total | 36 | 0.96 ± 0.04 |
| Shame | Arms crossed and hanging down (front) | 43 | 0.67 ± 0.09 |
| Arms crossed and hanging down (behind) | 29 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | |
| Arms hanging vertically by sides | 29 | 0.63 ± 0.06 | |
| Hand pulling the hem of clothes | 23 | 0.70 ± 0.08 | |
| Total | 124 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | |
| Pride | Arms raised above head | 26 | 0.78 ± 0.05 |
| Arms crossed in front of chest | 26 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | |
| Hands on hips | 25 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | |
| Raising above the head with one hand | 21 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | |
| Other | 9 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | |
| Total | 107 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | |
| Embarrassment | Left hand touching the face | 44 | 0.63 ± 0.11 |
| Right hand touching the face | 34 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | |
| Arms hanging vertically by sides | 5 | 0.45 ± 0.04 | |
| Scratching the head with one hand | 36 | 0.77 ± 0.08 | |
| Other | 3 | 0.54 ± 0.11 | |
| Total | 122 | 0.68 ± 0.13 |
Table 4 Mean recognition percentages of hand actions across the four categories of emotion pictures
| Emotion type | Hand actions | n (Number of pictures) | Mean recognition percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Total | 36 | 0.96 ± 0.04 |
| Shame | Arms crossed and hanging down (front) | 43 | 0.67 ± 0.09 |
| Arms crossed and hanging down (behind) | 29 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | |
| Arms hanging vertically by sides | 29 | 0.63 ± 0.06 | |
| Hand pulling the hem of clothes | 23 | 0.70 ± 0.08 | |
| Total | 124 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | |
| Pride | Arms raised above head | 26 | 0.78 ± 0.05 |
| Arms crossed in front of chest | 26 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | |
| Hands on hips | 25 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | |
| Raising above the head with one hand | 21 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | |
| Other | 9 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | |
| Total | 107 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | |
| Embarrassment | Left hand touching the face | 44 | 0.63 ± 0.11 |
| Right hand touching the face | 34 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | |
| Arms hanging vertically by sides | 5 | 0.45 ± 0.04 | |
| Scratching the head with one hand | 36 | 0.77 ± 0.08 | |
| Other | 3 | 0.54 ± 0.11 | |
| Total | 122 | 0.68 ± 0.13 |
| Emotion dimension | Neutral | Embarrassment | Shame | Pride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 4.94 ± 0.08 | 4.67 ± 0.70 | 2.95 ± 0.27 | 7.11 ± 0.65 |
| Arousal | 1.75 ± 0.12 | 5.70 ± 0.17 | 5.90 ± 0.27 | 6.66 ± 0.45 |
| Dominance | 4.83 ± 0.07 | 4.17 ± 0.42 | 3.24 ± 0.18 | 6.87 ± 0.41 |
Table 5 Descriptive statistics of dimensional ratings of self-conscious emotions pictures (M ± SD)
| Emotion dimension | Neutral | Embarrassment | Shame | Pride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 4.94 ± 0.08 | 4.67 ± 0.70 | 2.95 ± 0.27 | 7.11 ± 0.65 |
| Arousal | 1.75 ± 0.12 | 5.70 ± 0.17 | 5.90 ± 0.27 | 6.66 ± 0.45 |
| Dominance | 4.83 ± 0.07 | 4.17 ± 0.42 | 3.24 ± 0.18 | 6.87 ± 0.41 |
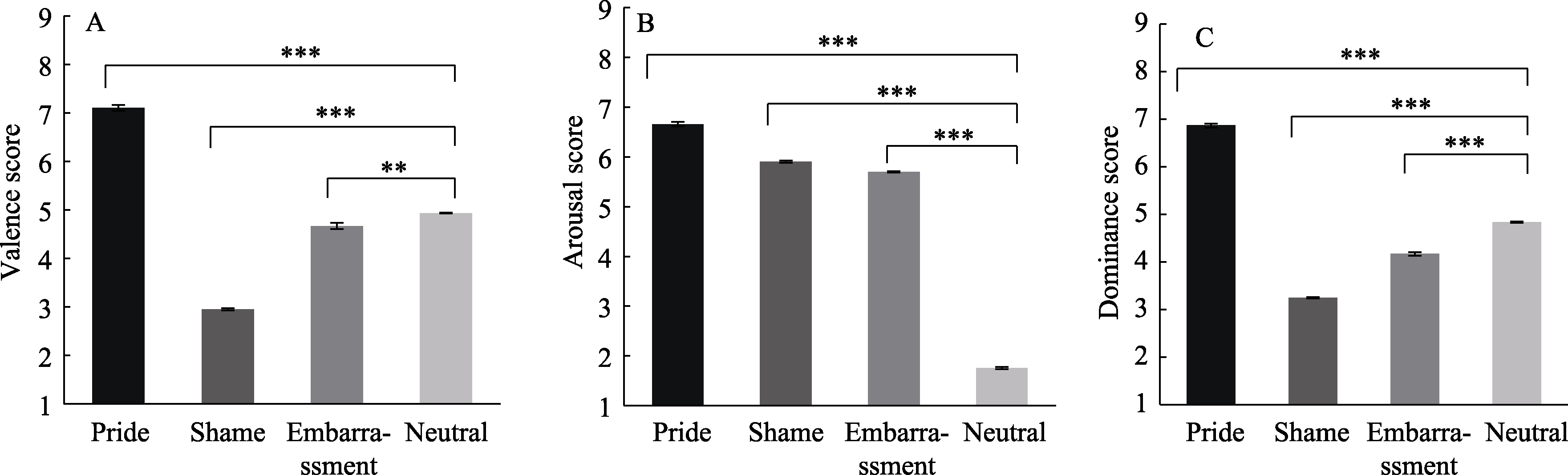
Figure 3. Comparison of valence (A), arousal (B), and dominance (C) score between three self-conscious emotion pictures and neutral pictures. The error bars indicate standard errors. **p <.01, ***p <.001.
| Emotion type | Valence | Arousal | Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | 0.758 | 0.971 | 0.978 |
| Shame | 0.990 | 0.997 | 0.993 |
| Pride | 0.981 | 0.995 | 0.989 |
| Embarrassment | 0.981 | 0.997 | 0.987 |
Table 6 Cronbach’s α coefficients for each dimension across the four categories of emotion pictures
| Emotion type | Valence | Arousal | Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | 0.758 | 0.971 | 0.978 |
| Shame | 0.990 | 0.997 | 0.993 |
| Pride | 0.981 | 0.995 | 0.989 |
| Embarrassment | 0.981 | 0.997 | 0.987 |
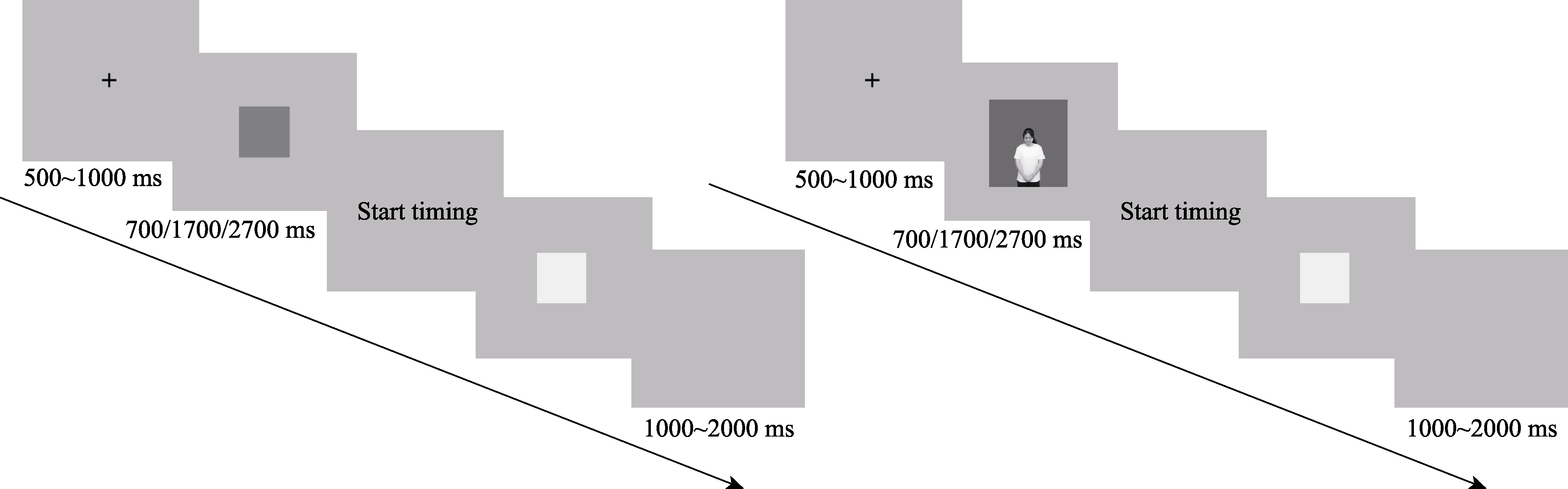
Figure 5. A single trial of the time reproduction task, the left side represents the practice phase, and the right side represents the formal experimental phase (using shame picture as an example)
| Emotion dimension | Neutral | Embarrassment | Shame | Pride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 4.83 ± 0.40 | 4.71 ± 1.07 | 3.08 ± 0.84 | 6.36 ± 0.58 |
| Arousal | 1.94 ± 0.75 | 4.70 ± 1.17 | 5.24 ± 1.11 | 5.79 ± 0.78 |
Table 7 Mean and standard deviation of valence and arousal ratings for self-conscious emotion pictures
| Emotion dimension | Neutral | Embarrassment | Shame | Pride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 4.83 ± 0.40 | 4.71 ± 1.07 | 3.08 ± 0.84 | 6.36 ± 0.58 |
| Arousal | 1.94 ± 0.75 | 4.70 ± 1.17 | 5.24 ± 1.11 | 5.79 ± 0.78 |
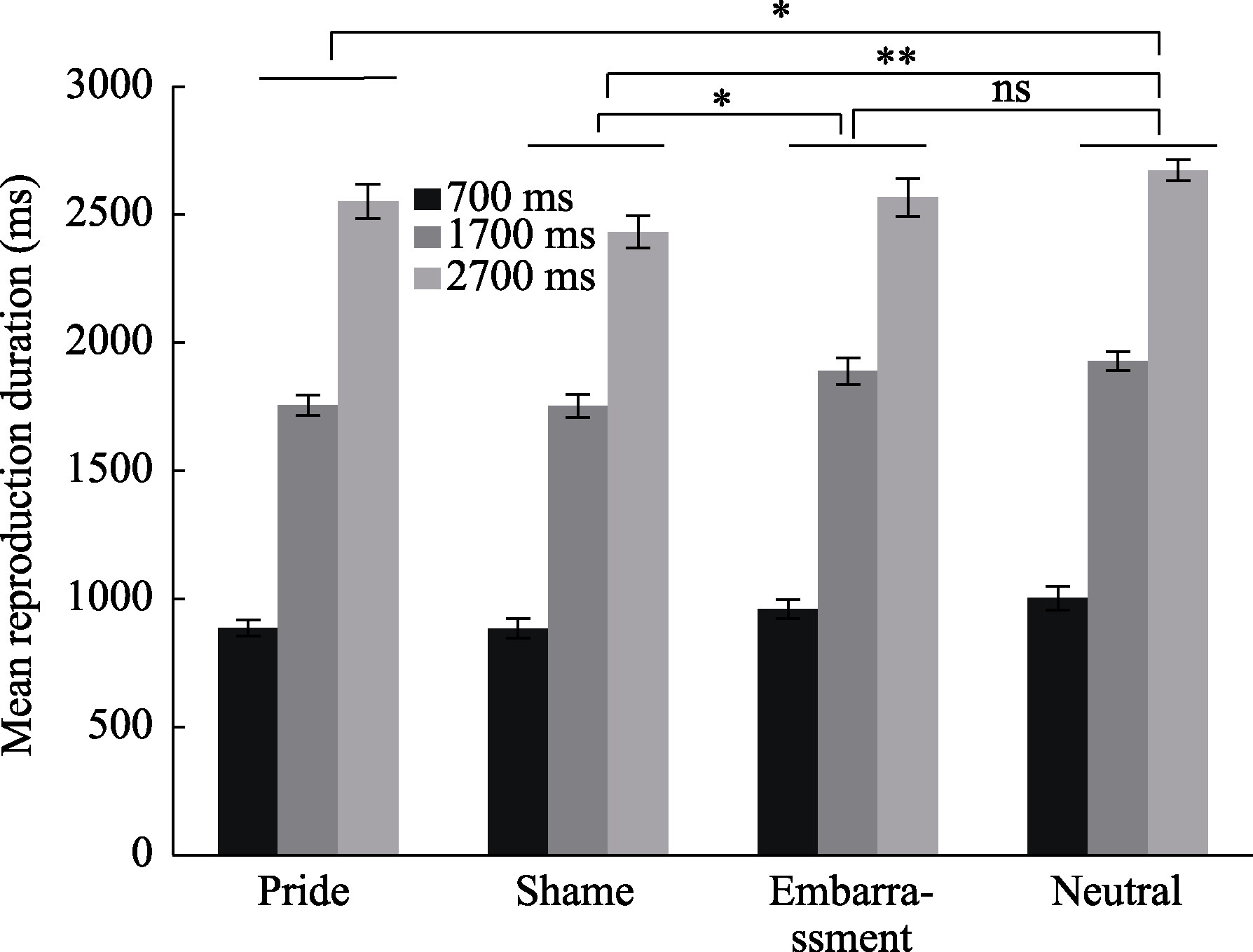
Figure 7. Mean reproduction duration under 700 ms, 1700 ms, and 2700 ms conditions for different emotions The error bars indicate standard errors. ns = nonsignificant. *p <.05, **p <.01.
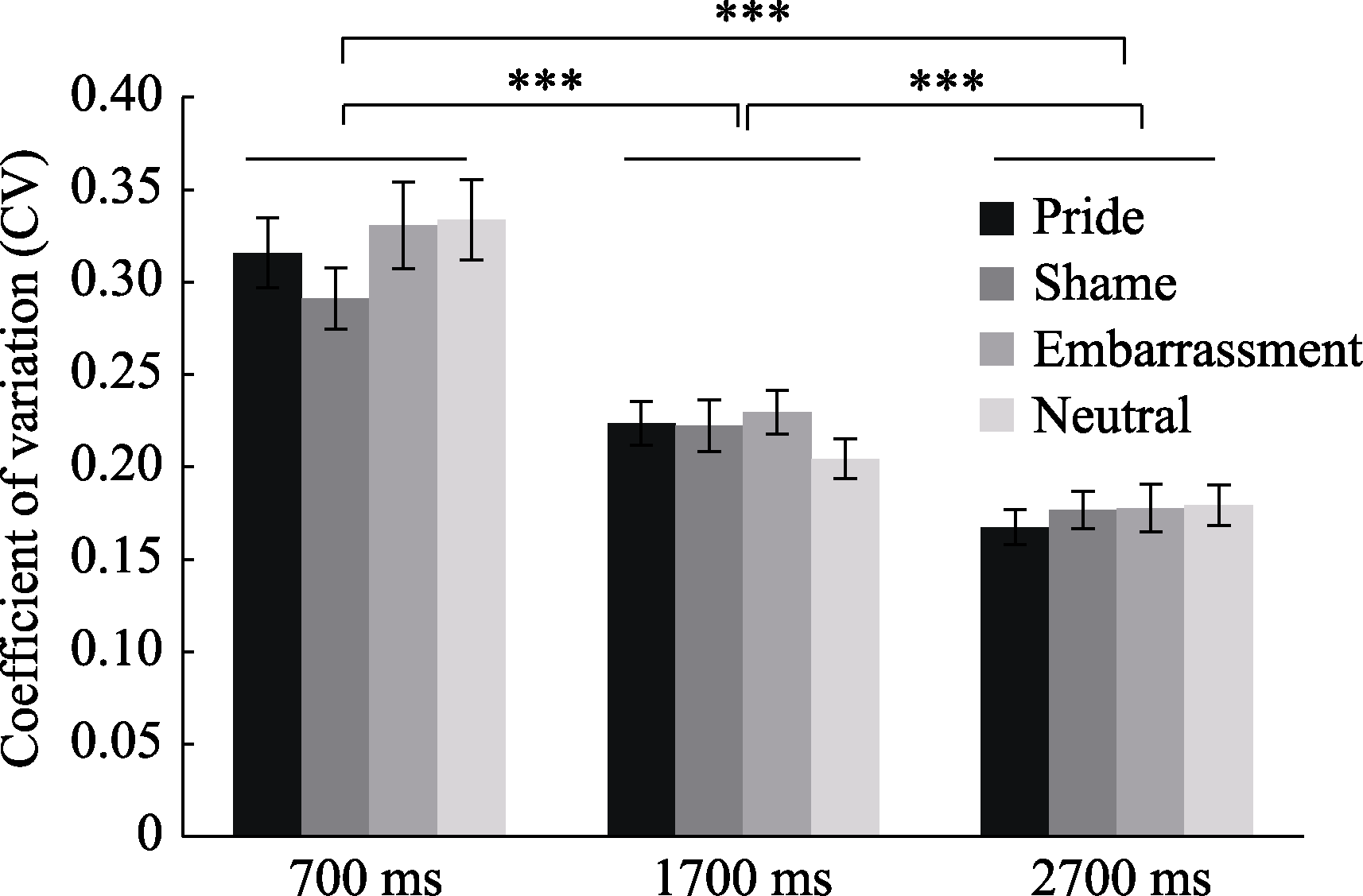
Figure 8. Mean coefficient of variation under 700 ms, 1700 ms, and 2700 ms conditions for different emotions The error bars indicate standard errors. ***p < 0.001.
| [1] | Angrilli A., Cherubini P., Pavese A., & Manfredini S. (1997). The influence of affective factors on time perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 59(6), 972-982. |
| [2] | Bai L., Ma H., Huang Y. X., & Luo Y. Y. (2005). The development of native Chinese affective picture system-A pretest in 46 college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 19(11), 4-7. |
| [3] | Beaupré M. G., Cheung N., & Hess U. (2000). The Montreal set of facial displays of emotion [Slides]. (Available from Ursula Hess, Department of Psychology, University of Quebec at Montreal, P.O. Box 8888, Station “Centre-ville,” Montreal, Quebec H3C 3P8.). |
| [4] | Bi X. Y. (2021). An ERP study of the effect of self-conscious emotion on executive function [Unpublished master's thesis]. Yunnan: Yunnan Normal University. |
| [5] |
Bi X. Y., Ma X., & Tao Y. (2022). The consistency of the influence of pride and shame on cognitive flexibility: Evidence from ERP. Neuroscience, 487, 1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.12.021 pmid: 35031399 |
| [6] | Buechner V. L., Maier M. A., Lichtenfeld S., & Elliot A. J. (2015). Emotion expression and color: Their joint influence on perceived attractiveness and social position. Current Psychology, 34(2), 422-433. |
| [7] | Buhusi C. V., & Meck W. H. (2009). Relative time sharing: New findings and an extension of the resource allocation model of temporal processing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1525), 1875-1885. |
| [8] |
Caldara R., Deiber M. P., Andrey C., Michel C. M., Thut G., & Hauert C. A. (2004). Actual and mental motor preparation and execution: A spatiotemporal ERP study. Experimental Brain Research, 159(3), 389-399.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-004-2101-0 pmid: 15480592 |
| [9] | Carretié L., Tapia M., López-Martín S., & Albert J. (2019). EmoMadrid: An emotional pictures database for affect research. Motivation and Emotion, 43(6), 929-939. |
| [10] | Chen J., Zhang Y., & Zhao G. (2021). The Qingdao preschooler facial expression set: Acquisition and validation of Chinese children’s facial emotion stimuli. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 554821. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.554821 |
| [11] |
Cheng J. T. (2020). Dominance, prestige, and the role of leveling in human social hierarchy and equality. Current Opinion in Psychology, 33, 238-244.
doi: S2352-250X(19)30183-6 pmid: 31794955 |
| [12] | Chung J. M., & Robins R. W. (2015). Exploring cultural differences in the recognition of the self-conscious emotions. PLOS ONE, 10(8), e136411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136411 |
| [13] | Coundouris S. P., Henry J. D., & Lehn A. C. (2022). Moving beyond basic emotions in Parkinson’s disease. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 61(3), 647-665. |
| [14] | Cui X., Tian Y., Zhang L., Chen Y., Bai Y., Li D.,... Yin H. (2022). The role of valence, arousal, stimulus type, and temporal paradigm in the effect of emotion on time perception: A meta- analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 30(1), 1-21. |
| [15] |
DaSilva E. B., Crager K., & Puce A. (2016). On dissociating the neural time course of the processing of positive emotions. Neuropsychologia, 83, 123-137.
doi: S0028-3932(15)30241-4 pmid: 26686550 |
| [16] |
de Gelder B. (2006). Towards the neurobiology of emotional body language. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(3), 242-249.
pmid: 16495945 |
| [17] | Dean Robbins B., & Parlavecchio H. (2006). The unwanted exposure of the self: A phenomenological study of embarrassment. The Humanistic Psychologist, 34(4), 321-345. |
| [18] | Droit-Volet S., Brunot S., & Niedenthal P. (2004). Brief report perception of the duration of emotional events. Cognition and Emotion, 18(6), 849-858. |
| [19] |
Droit-Volet S., Lamotte M., & Izaute M. (2015). The conscious awareness of time distortions regulates the effect of emotion on the perception of time. Consciousness and Cognition, 38, 155-164.
doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2015.02.021 pmid: 25890486 |
| [20] |
Faul F., Erdfelder E., Lang A.-G., & Buchner A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191.
doi: 10.3758/bf03193146 pmid: 17695343 |
| [21] | Feng X. H., & Zhang X. K. (2007). Self-conscious emotions: Advanced emotions of human. Advances in Psychological Science, 15(6), 878-884. |
| [22] | Fessler, D. (2007). From appeasement to conformity: Evolutionary and cultural perspectives on shame, competition, and cooperation. In J. L. Tracy, R. W. Robins, & J. P. Tangney (Eds.), The self-conscious emotions theory and research (pp. 174-193). Guilford Press. |
| [23] | Fraisse P. (1984). Perception and estimation of time. Annual Review of Psychology, 35(1), 1-36. |
| [24] |
Frank M. G., & Stennett J. (2001). The forced-choice paradigm and the perception of facial expressions of emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 80(1), 75-85.
pmid: 11195893 |
| [25] | Fredrickson B. L., & Branigan C. (2005). Positive emotions broaden the scope of attention and thought-action repertoires. Cognition & Emotion, 19(3), 313-332. |
| [26] | Gibbon J., Church R. M., & Meck W. H. (1984). Scalar timing in memory. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 423(1), 52-77. |
| [27] | Gil S., & Droit-Volet S. (2011a). “Time flies in the presence of angry faces”… depending on the temporal task used! Acta Psychologica, 136(3), 354-362. |
| [28] | Gil S., & Droit-Volet S. (2011b). Time perception in response to ashamed faces in children and adults. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 52(2), 138-145. |
| [29] | Gil S., & Droit-Volet S. (2012). Emotional time distortions: The fundamental role of arousal. Cognition and Emotion, 26(5), 847-862. |
| [30] | Giuliani N. R., Flournoy J. C., Ivie E. J., Von Hippel A., & Pfeifer J. H. (2017). Presentation and validation of the DuckEES child and adolescent dynamic facial expressions stimulus set. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research, 26, e1553. https://doi.org/10.1002/mpr.1553 |
| [31] | Gong X., Huang Y. X., Wang Y., & Luo Y. J. (2011). Revision of the Chinese facial affective picture system. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 25(1), 40-46. |
| [32] |
Grommet E. K., Droit-Volet S., Gil S., Hemmes N. S., Baker A. H., & Brown B. L. (2011). Time estimation of fear cues in human observers. Behavioural Processes, 86(1), 88-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2010.10.003 pmid: 20971168 |
| [33] |
Grommet E. K., Hemmes N. S., & Brown B. L. (2019). The role of clock and memory processes in the timing of fear cues by humans in the temporal bisection task. Behavioural Processes, 164, 217-229.
doi: S0376-6357(19)30006-3 pmid: 31102605 |
| [34] | Grondin S., Laflamme V., Bienvenue P., Labonté K., & Roy M. (2015). Sex effect in the temporal perception of faces expressing anger and shame. International Journal of Comparative Psychology, 28(1), 1-12. |
| [35] | Halmesvaara O., Harjunen V. J., Aulbach M. B., & Ravaja N. (2020). How bodily expressions of emotion after norm violation influence perceivers’ moral judgments and prevent social exclusion: A socio-functional approach to nonverbal shame display. PLOS ONE, 15(4), e232298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232298 |
| [36] |
Hastings M. E., Tangney J. P., & Stuewig J. (2008). Psychopathy and identification of facial expressions of emotion. Personality and Individual Differences, 44(7), 1474-1483.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2008.01.004 pmid: 21547246 |
| [37] | Huang X. T., Li B. Y., & Zhang Z. J. (2003). The research of the range-synthetic model of temporal cognition. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 29(2), 5-9. |
| [38] | Julle-Danière E. C. C. (2019). The expression, experience, and social consequences of guilt: A cross-cultural study [Unpublished doctorial dissertation]. University of Portsmouth. |
| [39] | Keltner, D., & Harker L. A. (1998). The forms and functions of the nonverbal signal of shame. In P. Gilbert, & B. Andrews (Eds.), Shame: Interpersonal behavior, psychopathology, and culture (pp. 78-98). Oxford: Oxford University Press. |
| [40] | Labroo A. A., & Rucker D. D. (2010). The orientation- matching hypothesis: An emotion-specificity approach to affect regulation. Journal of Marketing Research, 47(5), 955-966. |
| [41] |
Lake J. I., Labar K. S., & Meck W. H. (2016). Emotional modulation of interval timing and time perception. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 64, 403-420.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.003 pmid: 26972824 |
| [42] | Lang, P. J. (1980). Behavioral treatment and bio-behavioral assessment: Computer applications. In J. H. Johnson, J. B. Sidowski, & T. A. Willims (Eds.), Technology in mental health care delivery systems (pp. 119-137). Ablex. |
| [43] | Lang P. J., Bradley M. M., & Cuthbert B. N. (1997). International affective picture system (IAPS): Technical manual and affective ratings. NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention. |
| [44] | Langer J., Wapner S., & Werner H. (1961). The effect of danger upon the experience of time. The American Journal of Psychology, 74, 94-97. |
| [45] |
Lewis M., Sullivan M. W., Stanger C., & Weiss M. (1989). Self development and self-conscious emotions. Child Development, 60(1), 146-156.
pmid: 2702864 |
| [46] | Li W. L., & Qian M. Y. (1995). Revision of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory with sample of Chinese college students. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 31(1), 108-112. |
| [47] | Liu C., Lai W., Yu G., & Chen C. (2014). The individual and collective facets of pride in Chinese college students. Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 36(2), 176-189. |
| [48] | Lui M. A., Penney T. B., & Schirmer A. (2011). Emotion effects on timing: Attention versus pacemaker accounts. Plos One, 6(7), e21829. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021829 |
| [49] | Maire H., & Agnoletti M. F. (2020). Expressing embarrassment (or not): Which effects on produced impression on others and on attributed social value? European Review of Applied Psychology, 70(4), 100525. |
| [50] | Mauss I. B., & Robinson M. D. (2009). Measures of emotion: A review. Cognition and emotion, 23(2), 209-237. |
| [51] | Mercadante E., Witkower Z., & Tracy J. L. (2021). The psychological structure, social consequences, function, and expression of pride experiences. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 39, 130-135. |
| [52] |
Meuwissen A. S., Anderson J. E., & Zelazo P. D. (2017). The creation and validation of the developmental emotional faces stimulus set. Behavior Research Methods, 49(3), 960-966.
doi: 10.3758/s13428-016-0756-7 pmid: 27325165 |
| [53] | Mioni G., Grondin S., & Stablum F. (2021). Do I dislike what you dislike? Investigating the effect of disgust on time processing. Psychological Research, 85(7), 2742-2754. |
| [54] | Mioni G., Meligrana L., Grondin S., Perini F., Bartolomei L., & Stablum F. (2016). Effects of emotional facial expression on time perception in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 22(9), 890-899. |
| [55] | Mioni G., Stablum F., McClintock S. M., & Grondin S. (2014). Different methods for reproducing time, different results. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 76( 3), 675-681. |
| [56] |
Mioni G., Stablum F., Prunetti E., & Grondin S. (2016). Time perception in anxious and depressed patients: A comparison between time reproduction and time production tasks. Journal of Affective Disorders, 196, 154-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.02.047 pmid: 26922144 |
| [57] |
Niedenthal P. M. (2007). Embodying emotion. Science, 316(5827), 1002-1005.
doi: 10.1126/science.1136930 pmid: 17510358 |
| [58] | Niedenthal P. M., & Maringer M. (2009). Embodied emotion considered. Emotion Review, 1(2), 122-128. |
| [59] | Osgood C. E., Suci G. J., & Tannenbaum P. H. (1957). The measurement of meaning (No. 47). University of Illinois Press. |
| [60] | Piretti L., Pappaianni E., Lunardelli A., Zorzenon I., Ukmar M., Pesavento V.,... Grecucci A. (2020). The role of amygdala in self-conscious emotions in a patient with acquired bilateral damage. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 677. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00677 |
| [61] | Qian M. Y., Andrews B., Zhu R. C., & Wang A. M. (2000). The development of shame scale of Chinese college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 14(4), 217-221. |
| [62] | Rattat A., & Droit-Volet S. (2012). What is the best and easiest method of preventing counting in different temporal tasks? Behavior Research Methods, 44(1), 67-80. |
| [63] | Romani-Sponchiado A., Sanvicente-Vieira B., Mottin C., Hertzog-Fonini D., & Arteche A. (2015). Child emotions picture set (CEPS): Development of a database of children's emotional expressions. Psychology & Neuroscience, 8(4), 467-478. |
| [64] | Saito T., Motoki K., Nouchi R., Kawashima R., & Sugiura M. (2019). Does incidental pride increase competency evaluation of others who appear careless? Discrete positive emotions and impression formation. PLoS One, 14(8), e220883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220883 |
| [65] |
Schindler K., Van Gool L., & de Gelder B. (2008). Recognizing emotions expressed by body pose: A biologically inspired neural model. Neural Networks, 21(9), 1238-1246.
doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2008.05.003 pmid: 18585892 |
| [66] | Schmader T., & Lickel B. (2006). The approach and avoidance function of guilt and shame emotions: Comparing reactions to self- caused and other-caused wrongdoing. Motivation and Emotion, 30(1), 42-55. |
| [67] | Schmitz T. W., De Rosa E., & Anderson A. K. (2009). Opposing Influences of affective state valence on visual cortical encoding. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(22), 7199-7207. |
| [68] |
Shariff A. F., Tracy J. L., & Markusoff J. L. (2012). (Implicitly) Judging a book by its cover: The power of pride and shame expressions in shaping judgments of social status. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 38(9), 1178-1193.
doi: 10.1177/0146167212446834 pmid: 22611053 |
| [69] | Silver M., Sabini J., & Parrott W. G. (1987). Embarrassment: A dramaturgic account. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 17(1), 47-61. |
| [70] |
Simon-Thomas E. R., Godzik J., Castle E., Antonenko O., Ponz A., Kogan A., & Keltner D. J. (2012). An fMRI study of caring vs self-focus during induced compassion and pride. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 7(6), 635-648.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsr045 pmid: 21896494 |
| [71] | Takahashi H., Matsuura M., Koeda M., Yahata N., Suhara T., Kato M., & Okubo Y. (2008). Brain activations during judgments of positive self-conscious emotion and positive basic emotion: Pride and joy. Cerebral Cortex, 18(4), 898-903. |
| [72] |
Thoenes S., & Oberfeld D. (2017). Meta-analysis of time perception and temporal processing in schizophrenia: Differential effects on precision and accuracy. Clinical Psychology Review, 54, 44-64.
doi: S0272-7358(16)30270-7 pmid: 28391027 |
| [73] | Toso A., Fassihi A., Paz L., Pulecchi F., & Diamond M. E. (2021). A sensory integration account for time perception. Plos Computational Biology, 17(1), e1008668. |
| [74] |
Tracy J. L., & Matsumoto D. (2008). The spontaneous expression of pride and shame: Evidence for biologically innate nonverbal displays. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(33), 11655-11660.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802686105 pmid: 18695237 |
| [75] | Tracy J. L., & Robins R. W. (2004). Putting the self into self- conscious emotions: A theoretical model. Psychological Inquiry, 15(2), 103-125. |
| [76] |
Tracy J. L., & Robins R. W. (2007). The prototypical pride expression: Development of a nonverbal behavior coding system. Emotion, 7(4), 789-801.
pmid: 18039048 |
| [77] |
Tracy J. L., Robins R. W., & Schriber R. A. (2009). Development of a FACS-verified set of basic and self-conscious emotion expressions. Emotion, 9(4), 554-559.
doi: 10.1037/a0015766 pmid: 19653779 |
| [78] |
van der Schalk J., Hawk S. T., Fischer A. H., & Doosje B.(2011). Moving faces, looking places: Validation of the Amsterdam Dynamic Facial Expression Set (ADFES). Emotion, 11(4), 907-920.
doi: 10.1037/a0023853 pmid: 21859206 |
| [79] | Wang Y., & Luo Y. J. (2005). Standardization and assessment of college students' facial expression of emotion. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 13(4), 396-398. |
| [80] | Wearden J. H., Parry A., & Stamp L. (2002). Is subjective shortening in human memory unique to time representations? Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 55(1), 1-25. |
| [81] |
Wicker B., Keysers C., Plailly J., Royet J., Gallese V., & Rizzolatti G. (2003). Both of us disgusted in my insula: The common neural basis of seeing and feeling disgust. Neuron, 40(3), 655-664.
doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00679-2 pmid: 14642287 |
| [82] |
Witkower Z., Mercadante E. J., & Tracy J. L. (2020). How affect shapes status: Distinct emotional experiences and expressions facilitate social hierarchy navigation. Current Opinion in Psychology, 33, 18-22.
doi: S2352-250X(19)30049-1 pmid: 31336192 |
| [83] | Yang L. Z., Jiang Y., & Zhang L. H. (2012). Development of a nonverbal behavior expression coding system for children’s pride. Psychological Development and Education, 28(3), 231-238. |
| [84] | Yang S., & Bai X. J. (2015). The recognition cues of self-conscious emotion for college students of different nationalities: Evidence from eye moments. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 13(3), 289-295. |
| [85] | Yin H. Z., Li D., Chen Y. Y., & Huang X. T. (2016). The characteristic of 1-6 s duration cognition segmentation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(9), 1119-1129. |
| [86] | Yin H. Z., Zhang L., & Li D. (2023). The Influence of Emotion on Time Perception: The Perspective of Non-Embodied Emotion View and Embodied Emotion View. Journal of Psychological Science, 46(2), 491-499. |
| [87] |
Yin H. Z., Zhang L., Liu P. Y., & Li D. (2023). How the dimension of negative emotional motivation influences time perception: The mediating role of attention control and attention bias. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(12), 1917-1931.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01917 |
| [1] | ZHOU Heng, WANG Ai-Jun, YUAN Xiang-Yong, JIANG Yi. Object category differences regulate the sensory dominance of the response level in an audiovisual cross-modal conflict [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(6): 1001-1012. |
| [2] | LI Bin, JIN Lai, CHEN Xiaoxi, YU Weinan, LI Aimei, DAI Xianchi. Order or disorder: The matching effect between display order and product attribute* [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(10): 1448-1461. |
| [3] | CHEN Peiqi, ZHANG Yinling, HU Xinmu, WANG Jing, MAI Xiaoqin. The effect of social value orientation on third-party altruistic behaviors in children aged 10-12 years: The role of emotion [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(8): 1255-1269. |
| [4] | ZHU Yanghao, LONG Lirong, LIU Wenxing. Can leader gratitude expression improve employee followership behavior? The role of emotional expression authenticity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(7): 1160-1175. |
| [5] | HUANG Xinjie, ZHANG Chi, WAN Huagen, ZHANG Lingcong. Effect of predictability of emotional valence on temporal binding [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(1): 36-44. |
| [6] | ZHOU Ping, XIAO Hua, LI Yonghui, DONG Xinwen. Sustained hyperarousal induced by acute stress in tryptophan-hydroxylase-2 genetic deficient male mice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(6): 604-612. |
| [7] | JIANG Hongyan, ZHANG Jing, SUN Peizhen, JIANG Xianjin. Emotional or rational? The impact of culturally-derived power on the preference for advertising appeals [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(6): 684-702. |
| [8] | FAN Wei, REN Mengmeng, ZHANG Wenjie, ZHONG Yiping. The impact of feedback on self-deception: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 481-496. |
| [9] | CHENG Rui, LU Kelong, HAO Ning. The effect of anger on malevolent creativity and strategies for its emotion regulation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(8): 847-860. |
| [10] | JIANG Guangrong, LI Danyang, REN Zhihong, YAN Yupeng, WU Xinchun, ZHU Xu, YU Lixia, XIA Mian, LI Fenglan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin. The status quo and characteristics of Chinese mental health literacy [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(2): 182-198. |
| [11] | LIN Rang, YANG Yimiao. Effect of ambivalent attitudes on post-decision self-evaluation: Two-stage moderation effect with a mediator [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(12): 1348-1360. |
| [12] | ZHENG Xutao, GUO Wenjiao, CHEN Man, JIN Jia, YIN Jun. Influence of the valence of social actions on attentional capture: Focus on helping and hindering actions [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(5): 584-596. |
| [13] | Xiaolei SONG, Xiaoqian JIA, Yuan ZHAO, Jingjing GUO. The underlying mechanism of emotions on co-representation in joint actions [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(3): 269-282. |
| [14] | ZHOU Aibao, XIE Pei, PAN Chaochao, TIAN Zhe, XIE Junwei, LIU Jiong. Looking for the lost self: Self-face recognition in schizophrenics [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(2): 184-196. |
| [15] | TANG Rixin, LI Jiajia, WANG Zhipeng. Valence, arousal and appraisal of emotion influence the hand movement [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(8): 890-902. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||