

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 182-198.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00182
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Guangrong1, LI Danyang1, REN Zhihong1( ), YAN Yupeng1, WU Xinchun2, ZHU Xu1, YU Lixia3, XIA Mian1, LI Fenglan4, WEI Hui1,5, ZHANG Yan1,6, ZHAO Chunxiao1, ZHANG Lin1
), YAN Yupeng1, WU Xinchun2, ZHU Xu1, YU Lixia3, XIA Mian1, LI Fenglan4, WEI Hui1,5, ZHANG Yan1,6, ZHAO Chunxiao1, ZHANG Lin1
Received:2020-05-21
Published:2021-02-25
Online:2020-12-29
Contact:
REN Zhihong
E-mail:ren@ccnu.edu.cn
Supported by:JIANG Guangrong, LI Danyang, REN Zhihong, YAN Yupeng, WU Xinchun, ZHU Xu, YU Lixia, XIA Mian, LI Fenglan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin. (2021). The status quo and characteristics of Chinese mental health literacy. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(2), 182-198.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00182
| Variable | Number of participants | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Place of residence | ||
| Urban | 2563 | 28.9% |
| Rural | 6287 | 70.9% |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 4010 | 45.2% |
| Female | 4827 | 54.4% |
| Age | ||
| 18 ~ 35 | 2668 | 30.1% |
| 36 ~ 59 | 4816 | 54.3% |
| ≥ 60 | 1358 | 15.3% |
| Education level | ||
| ≤ Junior secondary | 2939 | 33.1% |
| Technical or high school | 2490 | 28.1% |
| College or university degree | 2744 | 30.9% |
| ≥ Master degree | 604 | 6.8% |
| Per capita disposable annual income of households | ||
| ≤ ¥ 5, 500 | 2847 | 32.1% |
| ¥ 5, 501 ~ 13, 000 | 1776 | 20.0% |
| ¥ 13, 001 ~ 21, 000 | 869 | 9.8% |
| ¥ 21, 001 ~ 32, 000 | 892 | 10.1% |
| ¥ 32, 001 ~ 60, 000 | 1179 | 13.3% |
| > ¥ 60, 000 | 1256 | 14.2% |
Table 1 Sample distributions of urban and rural, gender, age, education level and per capita disposable annual income of households
| Variable | Number of participants | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Place of residence | ||
| Urban | 2563 | 28.9% |
| Rural | 6287 | 70.9% |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 4010 | 45.2% |
| Female | 4827 | 54.4% |
| Age | ||
| 18 ~ 35 | 2668 | 30.1% |
| 36 ~ 59 | 4816 | 54.3% |
| ≥ 60 | 1358 | 15.3% |
| Education level | ||
| ≤ Junior secondary | 2939 | 33.1% |
| Technical or high school | 2490 | 28.1% |
| College or university degree | 2744 | 30.9% |
| ≥ Master degree | 604 | 6.8% |
| Per capita disposable annual income of households | ||
| ≤ ¥ 5, 500 | 2847 | 32.1% |
| ¥ 5, 501 ~ 13, 000 | 1776 | 20.0% |
| ¥ 13, 001 ~ 21, 000 | 869 | 9.8% |
| ¥ 21, 001 ~ 32, 000 | 892 | 10.1% |
| ¥ 32, 001 ~ 60, 000 | 1179 | 13.3% |
| > ¥ 60, 000 | 1256 | 14.2% |
| Variable | Data type | Effective sample size | Valus range | Value means |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per-capita GDP level | Categorize | 8866 | 1~3 | Low = 1, Medium = 2, High = 3 |
| Geographical distribution | Categorize | 8866 | 1~3 | Western = 1, Central = 2, Eastern = 3 |
| Place of residence | Categorize | 8850 | 1、2 | Urban = 1, Rural = 2 |
| Gender | Categorize | 8837 | 1、2 | Male = 1, Female = 2 |
| Age | Categorize | 8842 | 1~3 | Youth = 1, Middle-aged = 2, Older = 3 |
| Education level | Rank | 8777 | 1~4 | The higher the score, the higher the education level. |
| Per capita disposable annual income of households | Rank | 8819 | 1~6 | The higher the score, the higher the income level. |
| Occupational hierarchy | Rank | 8605 | 1~10 | The higher the score, the higher the occupational hierarchy. |
| Socio-economic status | Interval | 8489 | -1.49~2.36 | The higher the score, the higher the socio-economic status. |
| Professional identity | Categorize | 8762 | 0、1 | Professionals = 1, Non-professionals = 0 |
| Contact frequency | Rank | 8828 | 1~7 | The higher the score, the higher the frequency of contacting with the psychiatric patients. |
| Familiarity | Rank | 8837 | 1~7 | The higher the score, the more familiar with mental health professional services |
Table 2 Basic information about city characteristics, demographic characteristics, and mental health experience
| Variable | Data type | Effective sample size | Valus range | Value means |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per-capita GDP level | Categorize | 8866 | 1~3 | Low = 1, Medium = 2, High = 3 |
| Geographical distribution | Categorize | 8866 | 1~3 | Western = 1, Central = 2, Eastern = 3 |
| Place of residence | Categorize | 8850 | 1、2 | Urban = 1, Rural = 2 |
| Gender | Categorize | 8837 | 1、2 | Male = 1, Female = 2 |
| Age | Categorize | 8842 | 1~3 | Youth = 1, Middle-aged = 2, Older = 3 |
| Education level | Rank | 8777 | 1~4 | The higher the score, the higher the education level. |
| Per capita disposable annual income of households | Rank | 8819 | 1~6 | The higher the score, the higher the income level. |
| Occupational hierarchy | Rank | 8605 | 1~10 | The higher the score, the higher the occupational hierarchy. |
| Socio-economic status | Interval | 8489 | -1.49~2.36 | The higher the score, the higher the socio-economic status. |
| Professional identity | Categorize | 8762 | 0、1 | Professionals = 1, Non-professionals = 0 |
| Contact frequency | Rank | 8828 | 1~7 | The higher the score, the higher the frequency of contacting with the psychiatric patients. |
| Familiarity | Rank | 8837 | 1~7 | The higher the score, the more familiar with mental health professional services |
| Variable | Scoring | Value range | M | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total score | —— | 0~60 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 22.50% |
| Knowledge and concepts about mental health | 0, 1 | 0~9 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 35.43% |
| Knowledge and concepts about mental illness | 0, 1 | 0~21 | 11.88 | 3.40 | 28.62% |
| Attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of oneself | Likert 5 | 5~25 | 19.80 | 2.81 | 14.19% |
| Attitudes and behaviorsregarding mental illness coping for oneself | Likert 5 | 8~40 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 13.40% |
| Attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of others | Likert 5 | 6~30 | 21.35 | 3.23 | 15.13% |
| Attitudes and behaviors regarding mental illness coping for others | Likert 5 | 11~55 | 36.86 | 4.73 | 12.83% |
Table 3 Summary of the descriptive characteristics about MHL (N = 8866)
| Variable | Scoring | Value range | M | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total score | —— | 0~60 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 22.50% |
| Knowledge and concepts about mental health | 0, 1 | 0~9 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 35.43% |
| Knowledge and concepts about mental illness | 0, 1 | 0~21 | 11.88 | 3.40 | 28.62% |
| Attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of oneself | Likert 5 | 5~25 | 19.80 | 2.81 | 14.19% |
| Attitudes and behaviorsregarding mental illness coping for oneself | Likert 5 | 8~40 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 13.40% |
| Attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of others | Likert 5 | 6~30 | 21.35 | 3.23 | 15.13% |
| Attitudes and behaviors regarding mental illness coping for others | Likert 5 | 11~55 | 36.86 | 4.73 | 12.83% |
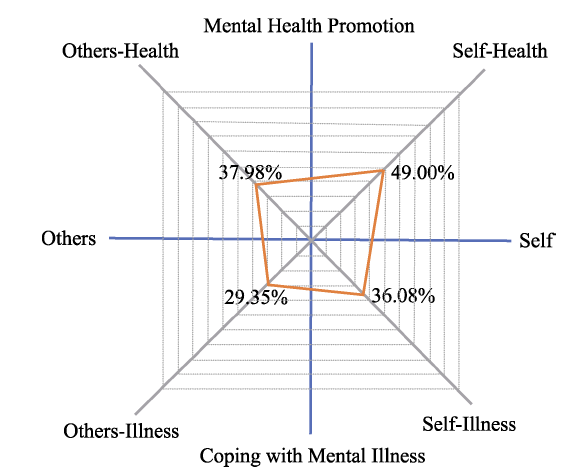
Figure 1. Structual characteristic of MHL among Chinese adults6(6The method of data transformation calculation is as follows: (1) others-health = the accuracy of knowledge and concepts about mental health * the accuracy of attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of others; (2) self-health = the accuracy of knowledge and concepts about mental health * the accuracy of attitudes and behaviors to promote mental health of oneself; (3) self-illness = the accuracy of knowledge and concepts about mental illness * the accuracy of attitudes and behaviors to cope with mental illness of oneself; (4) others-illness = the accuracy of knowledge and concepts about mental illness * the accuracy of attitudes and behaviors to cope with mental illness of others.).
| Variable | City | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing (n = 1033) | Wuhan (n = 1090) | Chengdu (n = 994) | Lishui (n = 900) | Kaifeng (n = 898) | Guilin (n = 1183) | Zhangye (n = 962) | Baoding (n = 931) | Linfen (n = 875) | ||||||
| Total | 38.39 (8.54) | 36.36 (7.87) | 35.48 (7.97) | 36.76 (8.02) | 36.26 (7.60) | 35.47 (7.82) | 34.44 (7.80) | 35.21 (8.12) | 33.62 (7.83) | 29.25 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | ||
| Sub 1 | 6.88 (1.99) | 6.09 (1.98) | 5.61 (2.08) | 5.78 (2.08) | 5.94 (1.88) | 5.71 (2.10) | 5.32 (2.10) | 5.98 (2.03) | 5.45 (2.06) | 50.08 | < 0.001 | 4.3% | ||
| Sub 2 | 13.54 (3.60) | 12.38 (3.20) | 11.58 (3.21) | 12.02 (3.26) | 11.97 (3.17) | 11.74 (3.31) | 10.98 (3.28) | 11.71 (3.44) | 10.78 (3.29) | 58.54 | < 0.001 | 5.0% | ||
| Sub 3 | 19.87 (2.70) | 19.75 (2.72) | 20.00 (2.76) | 20.21 (2.94) | 20.03 (2.80) | 19.77 (2.85) | 19.44 (2.88) | 19.53 (2.76) | 19.56 (2.82) | 7.78 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | ||
| Sub 4 | 29.13 (3.98) | 29.52 (4.00) | 30.01 (3.87) | 30.56 (4.07) | 29.82 (3.99) | 29.69 (3.95) | 29.83 (3.94) | 29.25 (3.74) | 29.58 (4.13) | 10.86 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | ||
| Sub 5 | 21.78 (3.23) | 21.48 (3.21) | 21.12 (3.12) | 21.78 (3.37) | 21.72 (3.19) | 21.27 (3.36) | 20.99 (3.13) | 21.23 (3.09) | 20.78 (3.17) | 11.80 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | ||
| Sub 6 | 37.40 (4.73) | 36.63 (4.59) | 36.85 (4.72) | 37.75 (4.96) | 36.94 (4.76) | 36.89 (4.70) | 36.91 (4.58) | 36.13 (4.35) | 36.18 (4.98) | 11.17 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | ||
| Variable | Per-capita GDP level | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Low (n = 2768) | Medium (n = 2981) | High (n = 3117) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 34.44 (7.94) | 36.10 (7.83) | 36.75 (8.22) | 64.17 | < 0.001 | 1.4% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.58 (2.08) | 5.80 (2.03) | 6.20 (2.08) | 67.36 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.16 (3.36) | 11.89 (3.26) | 12.51 (3.43) | 118.50 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.51 (2.82) | 19.98 (2.86) | 19.87 (2.73) | 22.18 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.56 (3.94) | 29.99 (4.01) | 29.55 (3.97) | 12.17 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.01 (3.13) | 21.56 (3.32) | 21.46 (3.20) | 23.86 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.41 (4.65) | 37.16 (4.81) | 36.96 (4.69) | 19.17 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | ||||||||
| Variable | Geographical distribution | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Western (n = 3139) | Central (n = 2863) | Eastern (n = 2864) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 35.16 (7.87) | 35.49 (7.87) | 36.85 (8.35) | 36.59 | < 0.001 | 0.8% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.56 (2.10) | 5.84 (1.99) | 6.24 (2.09) | 81.60 | < 0.001 | 1.8% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.45 (3.28) | 11.76 (3.29) | 12.47 (3.54) | 70.54 | < 0.001 | 1.6% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.74 (2.84) | 19.78 (2.78) | 19.86 (2.81) | 1.44 | 0.238 | —— | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.83 (3.92) | 29.63 (4.04) | 29.62 (3.98) | 2.83 | 0.059 | —— | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.14 (3.22) | 21.34 (3.22) | 21.60 (3.24) | 15.54 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.88 (4.67) | 36.59 (4.77) | 37.09 (4.73) | 8.17 | < 0.001 | 0.2% | ||||||||
| Variable | Place of residence | t | p | d | ||||||||||
| Urban (n = 6287) | Rural (n = 2563) | |||||||||||||
| Total | 36.53 (7.95) | 34.07 (8.05) | 13.19 | < 0.001 | 0.31 | |||||||||
| Sub 1 | 6.06 (2.05) | 5.41 (2.07) | 13.59 | < 0.001 | 0.32 | |||||||||
| Sub 2 | 12.30 (3.36) | 10.88 (3.25) | 18.44 | < 0.001 | 0.43 | |||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.98 (2.73) | 19.34 (2.95) | 9.44 | < 0.001 | 0.23 | |||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.68 (3.94) | 29.75 (4.08) | -0.78 | 0.434 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.49 (3.18) | 21.01 (3.32) | 6.40 | < 0.001 | 0.15 | |||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.93 (4.66) | 36.70 (4.88) | 2.03 | 0.043* | 0.05 | |||||||||
| Variable | Gender | t | p | d | ||||||||||
| Male (n = 4010) | Female (n = 4827) | |||||||||||||
| Total | 35.58 (8.20) | 36.01 (7.94) | -2.46 | 0.014* | -0.05 | |||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.83 (2.11) | 5.91 (2.05) | -1.84 | 0.066 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.92 (3.43) | 11.85 (3.37) | 0.90 | 0.369 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.66 (2.77) | 19.92 (2.84) | -4.31 | < 0.001 | -0.09 | |||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.35 (3.93) | 29.99 (4.00) | -7.55 | < 0.001 | -0.16 | |||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.25 (3.24) | 21.44 (3.22) | -2.89 | 0.004** | -0.06 | |||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.79 (4.74) | 36.91 (4.71) | -1.12 | 0.265 | —— | |||||||||
| Variable | Age | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Youth (n = 2668) | Middle-aged (n = 4816) | Older (n = 1358) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 35.87 (7.94) | 36.54 (7.98) | 33.16 (8.03) | 95.08 | < 0.001 | 2.1% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 6.00 (2.04) | 6.05 (2.02) | 4.99 (2.15) | 150.92 | < 0.001 | 3.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.85 (3.35) | 12.16 (3.40) | 10.96 (3.31) | 67.58 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 20.00 (2.84) | 20.01 (2.73) | 18.67 (2.75) | 133.51 | < 0.001 | 2.9% | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.78 (4.00) | 29.88 (3.98) | 28.94 (3.83) | 30.18 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.45 (3.24) | 21.53 (3.26) | 20.55 (2.97) | 50.63 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.83 (4.83) | 37.05 (4.78) | 36.23 (4.28) | 16.24 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | ||||||||
Table 4 Summary of variance analysis and t-test about MHL and its dimensions on city, per-capita GDP level, geographical distribution, place of residence, gender, and age
| Variable | City | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing (n = 1033) | Wuhan (n = 1090) | Chengdu (n = 994) | Lishui (n = 900) | Kaifeng (n = 898) | Guilin (n = 1183) | Zhangye (n = 962) | Baoding (n = 931) | Linfen (n = 875) | ||||||
| Total | 38.39 (8.54) | 36.36 (7.87) | 35.48 (7.97) | 36.76 (8.02) | 36.26 (7.60) | 35.47 (7.82) | 34.44 (7.80) | 35.21 (8.12) | 33.62 (7.83) | 29.25 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | ||
| Sub 1 | 6.88 (1.99) | 6.09 (1.98) | 5.61 (2.08) | 5.78 (2.08) | 5.94 (1.88) | 5.71 (2.10) | 5.32 (2.10) | 5.98 (2.03) | 5.45 (2.06) | 50.08 | < 0.001 | 4.3% | ||
| Sub 2 | 13.54 (3.60) | 12.38 (3.20) | 11.58 (3.21) | 12.02 (3.26) | 11.97 (3.17) | 11.74 (3.31) | 10.98 (3.28) | 11.71 (3.44) | 10.78 (3.29) | 58.54 | < 0.001 | 5.0% | ||
| Sub 3 | 19.87 (2.70) | 19.75 (2.72) | 20.00 (2.76) | 20.21 (2.94) | 20.03 (2.80) | 19.77 (2.85) | 19.44 (2.88) | 19.53 (2.76) | 19.56 (2.82) | 7.78 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | ||
| Sub 4 | 29.13 (3.98) | 29.52 (4.00) | 30.01 (3.87) | 30.56 (4.07) | 29.82 (3.99) | 29.69 (3.95) | 29.83 (3.94) | 29.25 (3.74) | 29.58 (4.13) | 10.86 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | ||
| Sub 5 | 21.78 (3.23) | 21.48 (3.21) | 21.12 (3.12) | 21.78 (3.37) | 21.72 (3.19) | 21.27 (3.36) | 20.99 (3.13) | 21.23 (3.09) | 20.78 (3.17) | 11.80 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | ||
| Sub 6 | 37.40 (4.73) | 36.63 (4.59) | 36.85 (4.72) | 37.75 (4.96) | 36.94 (4.76) | 36.89 (4.70) | 36.91 (4.58) | 36.13 (4.35) | 36.18 (4.98) | 11.17 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | ||
| Variable | Per-capita GDP level | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Low (n = 2768) | Medium (n = 2981) | High (n = 3117) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 34.44 (7.94) | 36.10 (7.83) | 36.75 (8.22) | 64.17 | < 0.001 | 1.4% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.58 (2.08) | 5.80 (2.03) | 6.20 (2.08) | 67.36 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.16 (3.36) | 11.89 (3.26) | 12.51 (3.43) | 118.50 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.51 (2.82) | 19.98 (2.86) | 19.87 (2.73) | 22.18 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.56 (3.94) | 29.99 (4.01) | 29.55 (3.97) | 12.17 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.01 (3.13) | 21.56 (3.32) | 21.46 (3.20) | 23.86 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.41 (4.65) | 37.16 (4.81) | 36.96 (4.69) | 19.17 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | ||||||||
| Variable | Geographical distribution | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Western (n = 3139) | Central (n = 2863) | Eastern (n = 2864) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 35.16 (7.87) | 35.49 (7.87) | 36.85 (8.35) | 36.59 | < 0.001 | 0.8% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.56 (2.10) | 5.84 (1.99) | 6.24 (2.09) | 81.60 | < 0.001 | 1.8% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.45 (3.28) | 11.76 (3.29) | 12.47 (3.54) | 70.54 | < 0.001 | 1.6% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.74 (2.84) | 19.78 (2.78) | 19.86 (2.81) | 1.44 | 0.238 | —— | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.83 (3.92) | 29.63 (4.04) | 29.62 (3.98) | 2.83 | 0.059 | —— | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.14 (3.22) | 21.34 (3.22) | 21.60 (3.24) | 15.54 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.88 (4.67) | 36.59 (4.77) | 37.09 (4.73) | 8.17 | < 0.001 | 0.2% | ||||||||
| Variable | Place of residence | t | p | d | ||||||||||
| Urban (n = 6287) | Rural (n = 2563) | |||||||||||||
| Total | 36.53 (7.95) | 34.07 (8.05) | 13.19 | < 0.001 | 0.31 | |||||||||
| Sub 1 | 6.06 (2.05) | 5.41 (2.07) | 13.59 | < 0.001 | 0.32 | |||||||||
| Sub 2 | 12.30 (3.36) | 10.88 (3.25) | 18.44 | < 0.001 | 0.43 | |||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.98 (2.73) | 19.34 (2.95) | 9.44 | < 0.001 | 0.23 | |||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.68 (3.94) | 29.75 (4.08) | -0.78 | 0.434 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.49 (3.18) | 21.01 (3.32) | 6.40 | < 0.001 | 0.15 | |||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.93 (4.66) | 36.70 (4.88) | 2.03 | 0.043* | 0.05 | |||||||||
| Variable | Gender | t | p | d | ||||||||||
| Male (n = 4010) | Female (n = 4827) | |||||||||||||
| Total | 35.58 (8.20) | 36.01 (7.94) | -2.46 | 0.014* | -0.05 | |||||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.83 (2.11) | 5.91 (2.05) | -1.84 | 0.066 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.92 (3.43) | 11.85 (3.37) | 0.90 | 0.369 | —— | |||||||||
| Sub 3 | 19.66 (2.77) | 19.92 (2.84) | -4.31 | < 0.001 | -0.09 | |||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.35 (3.93) | 29.99 (4.00) | -7.55 | < 0.001 | -0.16 | |||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.25 (3.24) | 21.44 (3.22) | -2.89 | 0.004** | -0.06 | |||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.79 (4.74) | 36.91 (4.71) | -1.12 | 0.265 | —— | |||||||||
| Variable | Age | F | p | η2 | ||||||||||
| Youth (n = 2668) | Middle-aged (n = 4816) | Older (n = 1358) | ||||||||||||
| Total | 35.87 (7.94) | 36.54 (7.98) | 33.16 (8.03) | 95.08 | < 0.001 | 2.1% | ||||||||
| Sub 1 | 6.00 (2.04) | 6.05 (2.02) | 4.99 (2.15) | 150.92 | < 0.001 | 3.3% | ||||||||
| Sub 2 | 11.85 (3.35) | 12.16 (3.40) | 10.96 (3.31) | 67.58 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | ||||||||
| Sub 3 | 20.00 (2.84) | 20.01 (2.73) | 18.67 (2.75) | 133.51 | < 0.001 | 2.9% | ||||||||
| Sub 4 | 29.78 (4.00) | 29.88 (3.98) | 28.94 (3.83) | 30.18 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | ||||||||
| Sub 5 | 21.45 (3.24) | 21.53 (3.26) | 20.55 (2.97) | 50.63 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | ||||||||
| Sub 6 | 36.83 (4.83) | 37.05 (4.78) | 36.23 (4.28) | 16.24 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | ||||||||
| Variable | M | SD | SES | Familiarity | Contact Frequency | Total | Sub 1 | Sub 2 | Sub 3 | Sub 4 | Sub 5 | Sub 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SES | 0.004 | 1.00 | 1 | |||||||||
| Familiarity | 2.22 | 1.56 | 0.145*** | 1 | ||||||||
| Contact Frequency | 1.59 | 1.16 | 0.065*** | 0.380*** | 1 | |||||||
| Total | 35.81 | 8.06 | 0.308*** | 0.207*** | 0.059*** | 1 | ||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 0.331*** | 0.113*** | 0.036** | 0.644*** | 1 | |||||
| Sub 2 | 11.88 | 3.39 | 0.377*** | 0.163*** | 0.080*** | 0.779*** | 0.584*** | 1 | ||||
| Sub 3 | 19.79 | 2.80 | 0.152*** | 0.160*** | -0.003 | 0.493*** | 0.145*** | 0.214*** | 1 | |||
| Sub 4 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 0.033** | 0.144*** | 0.002 | 0.536*** | 0.143*** | 0.186*** | 0.430*** | 1 | ||
| Sub 5 | 21.35 | 3.22 | 0.140*** | 0.137*** | 0.016 | 0.539*** | 0.193*** | 0.241*** | 0.407*** | 0.404*** | 1 | |
| Sub 6 | 36.86 | 4.72 | 0.086*** | 0.142 *** | 0.057*** | 0.573*** | 0.180*** | 0.236*** | 0.350*** | 0.472*** | 0.486*** | 1 |
Table 5 Means, standard deviations and bivariate correlations
| Variable | M | SD | SES | Familiarity | Contact Frequency | Total | Sub 1 | Sub 2 | Sub 3 | Sub 4 | Sub 5 | Sub 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SES | 0.004 | 1.00 | 1 | |||||||||
| Familiarity | 2.22 | 1.56 | 0.145*** | 1 | ||||||||
| Contact Frequency | 1.59 | 1.16 | 0.065*** | 0.380*** | 1 | |||||||
| Total | 35.81 | 8.06 | 0.308*** | 0.207*** | 0.059*** | 1 | ||||||
| Sub 1 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 0.331*** | 0.113*** | 0.036** | 0.644*** | 1 | |||||
| Sub 2 | 11.88 | 3.39 | 0.377*** | 0.163*** | 0.080*** | 0.779*** | 0.584*** | 1 | ||||
| Sub 3 | 19.79 | 2.80 | 0.152*** | 0.160*** | -0.003 | 0.493*** | 0.145*** | 0.214*** | 1 | |||
| Sub 4 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 0.033** | 0.144*** | 0.002 | 0.536*** | 0.143*** | 0.186*** | 0.430*** | 1 | ||
| Sub 5 | 21.35 | 3.22 | 0.140*** | 0.137*** | 0.016 | 0.539*** | 0.193*** | 0.241*** | 0.407*** | 0.404*** | 1 | |
| Sub 6 | 36.86 | 4.72 | 0.086*** | 0.142 *** | 0.057*** | 0.573*** | 0.180*** | 0.236*** | 0.350*** | 0.472*** | 0.486*** | 1 |
| Predictor | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | |
| CC | 0.022*** | 0.029*** | 0.040*** | 0.005*** | 0.003*** | 0.009*** | 0.005*** | |||||||
| Medium GDP | 0.101 (0.026)*** | 0.014*** | 0.025 (0.026) | 0.014*** | 0.096 (0.025)*** | 0.025*** | 0.106 (0.026)*** | 0.005*** | 0.086 (0.027)** | 0.003*** | 0.126 (0.027)*** | 0.005*** | -0.037 (0.029) | 0.004*** |
| High GDP | 0.039 (0.028) | 0.041 (0.027) | 0.077 (0.027)** | 0.009 (0.028) | -0.016 (0.028) | 0.038 (0.029) | 0.074 (0.027)** | |||||||
| Central | 0.005 (0.025) | 0.008*** | 0.087 (0.025)*** | 0.015*** | 0.032 (0.024) | 0.015*** | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.058 (0.026)* | 0.004*** | -0.013 (0.027) | 0.002** |
| Eastern | 0.076 (0.026)** | 0.165 (0.025)*** | 0.126 (0.025)*** | —— | —— | 0.100 (0.027)*** | -0.072 (0.027)** | |||||||
| BDC | 0.026*** | 0.035*** | 0.030*** | 0.035*** | 0.012*** | 0.011*** | 0.003*** | |||||||
| Rural | 0.021 (0.026) | 0.009*** | 0.036 (0.026) | 0.009*** | -0.030 (0.026) | 0.018*** | -0.093 (0.027)** | 0.008*** | —— | —— | -0.009 (0.027) | 0.002*** | —— | —— |
| Female | 0.068 (0.021)** | 0.001* | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.089 (0.021)*** | 0.002*** | 0.159 (0.022)*** | 0.007*** | 0.059 (0.022)** | 0.001** | —— | —— |
| Youth | 0.146 (0.034)*** | 0.016*** | 0.289 (0.034)*** | 0.026*** | 0.052 (0.033) | 0.012*** | 0.394 (0.035)*** | 0.024*** | 0.166 (0.036)*** | 0.005*** | 0.190 (0.036)*** | 0.008*** | 0.063 (0.036) | 0.003*** |
| Middle-aged | 0.200 (0.032)*** | 0.309 (0.031)*** | 0.117 (0.031)*** | 0.368 (0.032)*** | 0.173 (0.033)*** | 0.188 (0.033)*** | 0.099 (0.033)** | |||||||
| SES | 0.268 (0.013)*** | 0.057*** | 0.288 (0.013)*** | 0.059*** | 0.328 (0.012)*** | 0.079*** | 0.092 (0.013)*** | 0.009*** | 0.009 (0.012) | 0.001* | 0.100 (0.013)*** | 0.009*** | 0.059 (0.012)*** | 0.005*** |
| MHB | 0.025*** | 0.003*** | 0.012*** | 0.017*** | 0.017*** | 0.012*** | 0.015*** | |||||||
| CF | -0.025 (0.011)* | 0.001*** | -0.014 (0.011) | 0.000 | 0.014 (0.011) | 0.003*** | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.006 (0.012) | 0.003*** |
| Familiarity | 0.167 (0.011)*** | 0.023*** | 0.063 (0.011)*** | 0.003*** | 0.103 (0.011)*** | 0.009*** | 0.130 (0.011)*** | 0.017*** | 0.134 (0.011)*** | 0.017*** | 0.111 (0.011)*** | 0.012*** | 0.123 (0.012)*** | 0.013*** |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.128 | 0.126 | 0.159 | 0.064 | 0.032 | 0.040 | 0.027 | |||||||
| F | 113.12*** | 122.238*** | 160.401 | 73.061*** | 40.951 | 36.328 | 27.194 | |||||||
| N | 8404 | 8428 | 8428 | 8419 | 8431 | 8419 | 8440 | |||||||
Table 6 Summary of hierarchical regression analyses for predictors of the MHL and its dimensions
| Predictor | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | B (SE) | ΔR2 | |
| CC | 0.022*** | 0.029*** | 0.040*** | 0.005*** | 0.003*** | 0.009*** | 0.005*** | |||||||
| Medium GDP | 0.101 (0.026)*** | 0.014*** | 0.025 (0.026) | 0.014*** | 0.096 (0.025)*** | 0.025*** | 0.106 (0.026)*** | 0.005*** | 0.086 (0.027)** | 0.003*** | 0.126 (0.027)*** | 0.005*** | -0.037 (0.029) | 0.004*** |
| High GDP | 0.039 (0.028) | 0.041 (0.027) | 0.077 (0.027)** | 0.009 (0.028) | -0.016 (0.028) | 0.038 (0.029) | 0.074 (0.027)** | |||||||
| Central | 0.005 (0.025) | 0.008*** | 0.087 (0.025)*** | 0.015*** | 0.032 (0.024) | 0.015*** | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.058 (0.026)* | 0.004*** | -0.013 (0.027) | 0.002** |
| Eastern | 0.076 (0.026)** | 0.165 (0.025)*** | 0.126 (0.025)*** | —— | —— | 0.100 (0.027)*** | -0.072 (0.027)** | |||||||
| BDC | 0.026*** | 0.035*** | 0.030*** | 0.035*** | 0.012*** | 0.011*** | 0.003*** | |||||||
| Rural | 0.021 (0.026) | 0.009*** | 0.036 (0.026) | 0.009*** | -0.030 (0.026) | 0.018*** | -0.093 (0.027)** | 0.008*** | —— | —— | -0.009 (0.027) | 0.002*** | —— | —— |
| Female | 0.068 (0.021)** | 0.001* | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.089 (0.021)*** | 0.002*** | 0.159 (0.022)*** | 0.007*** | 0.059 (0.022)** | 0.001** | —— | —— |
| Youth | 0.146 (0.034)*** | 0.016*** | 0.289 (0.034)*** | 0.026*** | 0.052 (0.033) | 0.012*** | 0.394 (0.035)*** | 0.024*** | 0.166 (0.036)*** | 0.005*** | 0.190 (0.036)*** | 0.008*** | 0.063 (0.036) | 0.003*** |
| Middle-aged | 0.200 (0.032)*** | 0.309 (0.031)*** | 0.117 (0.031)*** | 0.368 (0.032)*** | 0.173 (0.033)*** | 0.188 (0.033)*** | 0.099 (0.033)** | |||||||
| SES | 0.268 (0.013)*** | 0.057*** | 0.288 (0.013)*** | 0.059*** | 0.328 (0.012)*** | 0.079*** | 0.092 (0.013)*** | 0.009*** | 0.009 (0.012) | 0.001* | 0.100 (0.013)*** | 0.009*** | 0.059 (0.012)*** | 0.005*** |
| MHB | 0.025*** | 0.003*** | 0.012*** | 0.017*** | 0.017*** | 0.012*** | 0.015*** | |||||||
| CF | -0.025 (0.011)* | 0.001*** | -0.014 (0.011) | 0.000 | 0.014 (0.011) | 0.003*** | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— | 0.006 (0.012) | 0.003*** |
| Familiarity | 0.167 (0.011)*** | 0.023*** | 0.063 (0.011)*** | 0.003*** | 0.103 (0.011)*** | 0.009*** | 0.130 (0.011)*** | 0.017*** | 0.134 (0.011)*** | 0.017*** | 0.111 (0.011)*** | 0.012*** | 0.123 (0.012)*** | 0.013*** |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.128 | 0.126 | 0.159 | 0.064 | 0.032 | 0.040 | 0.027 | |||||||
| F | 113.12*** | 122.238*** | 160.401 | 73.061*** | 40.951 | 36.328 | 27.194 | |||||||
| N | 8404 | 8428 | 8428 | 8419 | 8431 | 8419 | 8440 | |||||||
| Variable | Contact Frequency | t | p | d | Familiarity | t | p | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 7348) | High (n = 184) | Low (n = 5877) | High (n = 406) | |||||||
| Total | 35.55 (7.89) | 35.12 (9.05) | 0.634 | 0.527 | —— | 34.73 (7.92) | 37.68 (7.96) | -7.263 | < 0.001 | -0.37 |
| Sub 1 | 5.84 (2.06) | 5.66 (2.28) | 1.044 | 0.298 | —— | 5.72 (2.10) | 5.79 (2.08) | -0.662 | 0.508 | —— |
| Sub 2 | 11.74 (3.35) | 11.64 (3.71) | 0.389 | 0.697 | —— | 11.51 (3.39) | 12.07 (3.38) | -3.217 | 0.001** | -0.17 |
| Sub 3 | 19.80 (2.77) | 19.83 (3.20) | -0.126 | 0.900 | —— | 19.53 (2.80) | 20.99 (2.89) | -10.114 | < 0.001 | -0.51 |
| Sub 4 | 29.67 (3.94) | 29.46 (4.54) | 0.630 | 0.529 | —— | 29.36 (3.92) | 31.17 (4.38) | -8.073 | < 0.001 | -0.44 |
| Sub 5 | 21.33 (3.19) | 21.31 (3.65) | 0.063 | 0.950 | —— | 21.09 (3.14) | 22.17 (3.70) | -5.689 | < 0.001 | -0.31 |
| Sub 6 | 36.71 (4.68) | 36.97 (5.30) | -0.660 | 0.510 | —— | 36.41 (4.63) | 38.05 (5.30) | -6.066 | < 0.001 | -0.33 |
Table 7 T-test about MHL and its dimensions on contact frequency and familiarity
| Variable | Contact Frequency | t | p | d | Familiarity | t | p | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 7348) | High (n = 184) | Low (n = 5877) | High (n = 406) | |||||||
| Total | 35.55 (7.89) | 35.12 (9.05) | 0.634 | 0.527 | —— | 34.73 (7.92) | 37.68 (7.96) | -7.263 | < 0.001 | -0.37 |
| Sub 1 | 5.84 (2.06) | 5.66 (2.28) | 1.044 | 0.298 | —— | 5.72 (2.10) | 5.79 (2.08) | -0.662 | 0.508 | —— |
| Sub 2 | 11.74 (3.35) | 11.64 (3.71) | 0.389 | 0.697 | —— | 11.51 (3.39) | 12.07 (3.38) | -3.217 | 0.001** | -0.17 |
| Sub 3 | 19.80 (2.77) | 19.83 (3.20) | -0.126 | 0.900 | —— | 19.53 (2.80) | 20.99 (2.89) | -10.114 | < 0.001 | -0.51 |
| Sub 4 | 29.67 (3.94) | 29.46 (4.54) | 0.630 | 0.529 | —— | 29.36 (3.92) | 31.17 (4.38) | -8.073 | < 0.001 | -0.44 |
| Sub 5 | 21.33 (3.19) | 21.31 (3.65) | 0.063 | 0.950 | —— | 21.09 (3.14) | 22.17 (3.70) | -5.689 | < 0.001 | -0.31 |
| Sub 6 | 36.71 (4.68) | 36.97 (5.30) | -0.660 | 0.510 | —— | 36.41 (4.63) | 38.05 (5.30) | -6.066 | < 0.001 | -0.33 |
| [1] |
Aghukwa, C. N. (2010). Medical students' beliefs and attitudes toward mental illness: Effects of a psychiatric education. Academic Psychiatry, 34(1), 67-70.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ap.34.1.67 URL pmid: 20071734 |
| [2] | Andrews, G., Hall, W. D., Teesson, M., & Henderson, S. (1999). The mental health of Australians. In National Survey of Mental Health & Well-being Report No 2. Canberra: Mental Health Branch, Commonwealth Department of Aged Care. |
| [3] |
Angermeyer, M. C., & Dietrich, S . (2006). Public beliefs about and attitudes towards people with mental illness: A review of population studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 113(3), 163-179.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2005.00699.x URL pmid: 16466402 |
| [4] |
Angermeyer, M. C., Holzinger, A., & Matschinger, H. (2009). Mental health literacy and attitude towards people with mental illness: A trend analysis based on population surveys in the eastern part of Germany. European Psychiatry, 24(4), 225-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.06.010 URL pmid: 19361961 |
| [5] |
Angermeyer, M. C., & Matschinger, H . (2004). The stereotype of schizophrenia and its impact on discrimination against people with schizophrenia: Results from a representative survey in Germany. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 30(4), 1049-1061.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a007120 URL pmid: 15954207 |
| [6] |
Bjørnsen, H. N., Eilertsen, M.-E. B., Ringdal, R., Espnes, G. A., & Moksnes, U. K. (2017). Positive mental health literacy: Development and validation of a measure among Norwegian adolescents. BMC Public Health, 17(1), 717-726.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4733-6 URL pmid: 28923031 |
| [7] | Cao, S., Cao, R. X., Sun, X. Y., Guo, H. J., Li, X. N., & Xu, Q. (2016). Item Response Theory in the Application of ‘Residents Health Literacy Criterion-Referenced Test’. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 33(1), 31-34+38. |
| [8] | Chen, X. S. (1986). The progress of Psychiatry. In Qian, X. Z. (Ed.). Chinese yearbook of medical science (1985) (p. 167). Tianjin, China: Tianjin Science and Technology Press. |
| [9] | Chen, Z. Y., Wang, Y. X., Guo, F., Zhang, J., & Jiang, L. (2019). Survey on mental health literacy in China. In Fu X. L. & Zhang K. (Eds.), Report on national mental health development in China (2017-2018) (pp. 220-263). Beijing, China: Social Sciences Academic Press. |
| [10] | Cohen, J . (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. |
| [11] |
Cohen, J. (1992). Statistical power analysis. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 1(3), 98-101.
doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.ep10768783 URL |
| [12] |
Coles, M. E., Ravid, A., Gibb, B., George-Denn, D., Bronstein, L. R., & McLeod, S. (2016). Adolescent mental health literacy: Young people’s knowledge of depression and social anxiety disorder. Journal of Adolescent Health, 58(1), 57-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2015.09.017 URL |
| [13] |
Corrigan, P. W. (2002). Empowerment and serious mental illness: Treatment partnerships and community opportunities. Psychiatric Quarterly, 73(3), 217-228.
doi: 10.1023/A:1016040805432 URL |
| [14] |
Demyttenaere, K., Bruffaerts, R., Posada-Villa, J., Gasquet, I., Kovess, V., Lepine, J. P., …Brugha, T. S. (2004). Prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Journal of the American Medical Association, 291(21), 2581-2590.
doi: 10.1001/jama.291.21.2581 URL pmid: 15173149 |
| [15] |
Du, W. J., Zhou, J., & Li, H. B. (2013). The Item Parameters’ Estimation Accuracy of Two-Parameter Logistic Model. Acta Psychological Sinica, 45(10), 1179-1186.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2013.01179 URL |
| [16] |
Eckert, K. A., Kutek, S. M., Dunn, K. I., Air, T. M., & Goldney, R. D. (2010). Changes in depression-related mental health literacy in young men from rural and urban South Australia. Australian Journal of Rural Health, 18(4), 153-158.
doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1584.2010.01135.x URL |
| [17] | Fan, M. Y. (2011). Research on quality control of the data in web survey (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China. |
| [18] |
Farrer, L., Christensen, H., Leach, L., Griffiths, K. M., & Jorm, A. F. (2008). Age differences in mental health literacy. BMC Public Health, 8(1), 1-8.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-1 URL |
| [19] | Fu, W. Z. (2005). A Survey of the aware of knowledge about mental health rates among middle school students: 4007 Questionnaires Analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 12-13. |
| [20] |
Furnham, A., Annis, J., & Cleridou, K. (2014). Gender differences in the mental health literacy of young people. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 26(2), 283-292.
doi: 10.1515/ijamh-2013-0301 URL pmid: 23843570 |
| [21] |
Furnham, A., & Lousley, C . (2013). Mental health literacy and the anxiety disorders. Health, 5(3A), 521-531.
doi: 10.4236/health.2013.53A071 URL |
| [22] | Gao, W. J., & Li, Q . (2008). Primary research on the impact of mental health illness stigma social representations. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 14(4), 358-364. |
| [23] | Guimón, J., Fischer, W., & Sartorius, N. (1999). The Image of Madness: The Public Facing Mental Illness and Psychiatric Treatment (pp. 56-71). Basel: Karger Press. |
| [24] |
Gulliver, A., Griffiths, K. M., Christensen, H., & Brewer, J. (2012). A systematic review of help-seeking interventions for depression, anxiety and general psychological distress. BMC Psychiatry, 12(1), 81-92.
doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-81 URL |
| [25] | Guo, F., Huang, Z., & Chen, Z. Y. (2019). Survey on mental health in China. In Fu X. L. & Zhang K. (Eds.), Report on national mental health development in China (2017-2018) (pp. 001-055). Beijing, China: Social Sciences Academic Press. |
| [26] |
Have, M. T., de Graaf, R., Ormel, J., Vilagut, G., Kovess, V., Alonso, J., & the ESEMeD/MHEDEA 2000 Investigators. (2010). Are attitudes towards mental health help-seeking associated with service use? Results from the European study of epidemiology of mental disorders. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 45(2), 153-163.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-009-0050-4 URL |
| [27] |
Hengartner, M. P., Loch, A. A., Lawson, F. L., Guarniero, F. B., Wang, Y.-P., Rössler, W., & Gattaz, W. F. (2013). Public stigmatization of different mental disorders: A comprehensive attitude survey. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 22(3), 269-274.
doi: 10.1017/S2045796012000376 URL pmid: 22831815 |
| [28] |
Hollingshead, A. B., & Redlich, F. C. (1958). Social class and mental illness: a community study. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 29(1), 192-201.
doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1959.tb00180.x URL |
| [29] |
Holman, D. (2014). Exploring the relationship between social class, mental illness stigma and mental health literacy using British national survey data. Health, 19(4), 413-429.
doi: 10.1177/1363459314554316 URL pmid: 25323051 |
| [30] | Holzinger, A., Floris, F., Schomerus, G., Carta, M. G., & Angermeyer, M. C. (2012). Gender differences in public beliefs and attitudes about mental disorder in western countries: A systematic review of population studies. Epidemiology Psychiatric Science, 21(1), 73-85. |
| [31] |
Huang, Y. Q., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Z. R., Yu, X., Yan, J., .. Wu, Y. (2019). Prevalence of mental disorders in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(3), 211-224.
doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30511-X URL pmid: 30792114 |
| [32] | Jiang, G. R., & Xia, M . (2006). Psychological help-seeking: Current research and the phases-decision-making model. Advances in Psychological Science, 14(6), 888-894. |
| [33] | Jiang, G. R., Zhao, C. X., Wei, H., Yu, L. X., Li, D. Y., Lin, X. B., & Ren, Z. H. (2020). Mental health literacy: Connotation, measurement and new framework. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 232-238. |
| [34] |
Jorm, A. F. (2012). Mental health literacy: Empowering the community to take action for better mental health. American Psychologist, 67(3), 231-243.
doi: 10.1037/a0025957 URL |
| [35] |
Jorm, A. F., Korten, A. E., Jacomb, P. A., Christensen, H., Rodgers, B., & Pollitt, P. (1997). Mental health literacy: A survey of the public’s ability to recognise mental disorders and their beliefs about the effectiveness of treatment. The Medical journal of Australia, 166(4), 182-186.
doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1997.tb140071.x URL pmid: 9066546 |
| [36] |
Koyama, T., Tachimori, H., Sawamura, K., Koyama, A., Naganuma, Y., Makino, H., & Takeshima, T. (2009). Mental health literacy of autism spectrum disorders in the Japanese general population. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 44(8), 651-657.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-008-0485-z URL |
| [37] |
Kutcher, S., Wei, Y. F., & Coniglio, C. (2016). Mental health literacy: Past, present, and future. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 61(3), 154-158.
doi: 10.1177/0706743715616609 URL pmid: 27254090 |
| [38] |
Lee, S., Tsang, A. Huang, Y. Q., He, Y. L., Liu, Z. R., Zhang, M. Y., …Kessler, R. C. (2009). The epidemiology of depression in metropolitan China. Psychological Medicine, 39(5), 735-747.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291708004091 URL pmid: 18713484 |
| [39] |
Leiderman, E. A., Vazquez, G., Berizzo, C., Bonifacio, A., Bruscoli, N., Capria, J. I., … Milev, R. (2011). Public knowledge, beliefs and attitudes towards patients with schizophrenia: Buenos Aires. Social psychiatry and psychiatric epidemiology, 46(4), 281-290.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-010-0196-0 URL pmid: 20186530 |
| [40] |
Levav, I., Shemesh, A., Grinshpoon, A., Aisenberg, E., Shershevsky, Y., & Kohn, R.(2004). Mental health-related knowledge, attitudes and practices in two kibbutzim. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 39(9), 758-764.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-004-0811-z URL pmid: 15672298 |
| [41] | Li, F., Xiao, S. Y., Huang, Z. P., Shi, J. G., Cheng, Z. H., Luo, W. F., .. Zhou, L. (2009). Mental health literacy in three cities of China: A survey study. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 23(12), 883-887. |
| [42] | Li, F. L. (2015). The conception of mental illness in Chinese public: content, structure and measure (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China. |
| [43] | Li, L. H., Li, S. Y., Huang, L. H., & Mei, F. (2006). A survey of knowledge of mental health among the relatives of psychiatric patients. Journal of Nursing (China), 13(6), 19-21. |
| [44] | Liu, J. P., Zhang, Y. X., Yang, C., Huang, K. M., & Zhang, X. Q. (2017). The urban mental hygiene work and its suggestions: Base on the meta-analysis of urban citizen’s aware of knowledge about mental health rates from 2005 to 2015. China Journal of Health Psychology,(5), 666-670. |
| [45] | Liu, X., Yang, G., & Wang, F. Y. (2013). The structure of stigma of mental illness: IAT-based measurement. Journal of Gannan Normal University,(2), 92-94. |
| [46] |
Loureiro, L. M. J., Jorm, A. F., Oliveira, R. A., Mendes, A. M. O. C., dos Santos, J. C. P., Rodrigues, M. A., & Sousa, C. S. F. (2015). Mental health literacy about schizophrenia: A survey of Portuguese youth. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 9(3), 234-241.
doi: 10.1111/eip.12123 URL pmid: 24438429 |
| [47] | Lu, X. Y. (2002). An analysis of Strata and Classes of the contemporary China. Study and Practice,(3), 55-63. |
| [48] |
Madianos, M, G., Economou, M., Hatjiandreou, M., Papageorgiou, A., & Rogakou, E. (1999). Changes in public attitudes towards mental illness in the Athens area (1979/1980-1994). Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 99(1), 73-78.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1999.tb05387.x URL pmid: 10066010 |
| [49] |
Maunder, R. D., & White, F. A. (2019). Intergroup contact and mental health stigma: A comparative effectiveness meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 72, 101749.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101749 URL pmid: 31254936 |
| [50] | Mcleroy, K. R., Bibeau, D., Steckler, A., & Glanz, K. (1988). An ecological perspective on health promotion programs. Health Education and Behavior, 15(4), 351-377. |
| [51] | Meng, G. R., Yao, X. W., Zhu, Z. Q., & Zhang, M. Y. (2002). A survey of mental health awareness among Shanghai Citizen: 2697 Questionnaires Analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 14(z1), 56-57. |
| [52] |
Ming, Z. J., & Chen, Z. Y. (2020). Mental health literacy: Concept, measurement, intervention and factors. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(1), 1-12.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.00001 URL |
| [53] | Mojtabai, R. (2010). Mental illness stigma and willingness to seek mental health care in the European Union. Social psychiatry and psychiatric epidemiology, 45(7), 1741-1752. |
| [54] |
Morgan, A. J., Reavley, N. J., Ross, A., Too, L. S., & Jorm, A. F. (2018). Interventions to reduce stigma towards people with severe mental illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 103(5), 120-133.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.05.017 URL |
| [55] |
Morgan, A. J., Ross, A. & Reavley, N. J. (2018). Systematic review and meta-analysis of mental health first aid training: Effects on knowledge, stigma, and helping behaviour. Plos One, 13(5), e0197102.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197102 URL pmid: 29851974 |
| [56] |
Olfson, M., Blanco, C., & Marcus, S. C. (2016). Treatment of adult depression in the United States. JAMA Internal Medicine, 176(10), 1482-1491.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.5057 URL pmid: 27571438 |
| [57] |
Phillips, M. R. (2004). Suicide in China: Current status and suggestions for future work. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 25(4), 277-279.
URL pmid: 15231190 |
| [58] |
Piper, S. E., Bailey, P. E., Lam, L. T., & Kneebone, I. I. (2018). Predictors of mental health literacy in older people. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 79, 52-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.07.010 URL pmid: 30107312 |
| [59] | Rabkin, J. (1974). Public attitudes toward mental illness: A review of the literature. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1(10), 9-33. |
| [60] | Ren, C. R. (2010). Measurement methodology on social economic status index of students. Journal of Educational Studies, 6(5), 77-82. |
| [61] | Ren, Z. H., Zhao, C. X., Tian, F., Yan, Y. P., Li, D. Y., Zhao, Z. Y., .. Jiang, G. R. (2020). Meta-analysis of the effect of mental health literacy intervention in Chinese people. Acta Psychological Sincia, 52(4), 497-512. |
| [62] |
Schnyder, N., Panczak, R., Groth, N., & Schultze-Lutter, F. (2017). Association between mental health-related stigma and active help-seeking: systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Psychiatry: the Journal of Mental Science, 210(4), 261-268.
doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.116.189464 URL |
| [63] |
Stanton, R., Rosenbaum, S., & Rebar, A. (2019). Associations between ability to recognise a mental health disorder and lived experience of mental illness in an Australian sample. Psychiatry Research, 272, 206-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.098 URL pmid: 30590273 |
| [64] |
Shi, Y., Shao, Y. P., Li, H. H., Wang, S. Q., Ying, J., Zhang, M. L., … Sun, J. (2019). Correlates of affiliate stigma among family caregivers of people with mental illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, 26(1-2), 49-61.
doi: 10.1111/jpm.12505 URL pmid: 30472763 |
| [65] | Sun, X., Li, X. Y., & Phillips, M. R. (2009). A cross-sectional survey of the awareness of common mental disorders among place of residence residents in northern China. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 23(10), 729-733+741. |
| [66] | Tang, D. D., & Wen, Z. L. (2020). Statistical Approaches for Testing Common Method Bias: Problems and Suggestions. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 215-223. |
| [67] |
Tay, J. L., Tay, Y. F., & Klainin-Yobas, P. (2018). Mental health literacy levels. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 32(5), 757-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2018.04.007 URL pmid: 30201205 |
| [68] |
Vidourek, R. A., & Burbage, M . (2019). Positive mental health and mental health stigma: A qualitative study assessing student attitudes. Mental Health and Prevention, 13, 1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.mhp.2018.11.006 URL |
| [69] | Wampold, B. E., & Imel, Z. E. (2015). The Great Psychotherapy Debate: The Evidence for What Makes Psychotherapy Work (second edition). New York: Routledge. |
| [70] | Wang, J. C., Wang, X. Q., & Jiang, B. F. (2011). Structural Equation Models: Methods and Applications. Beijing, China: Higher Education Press. |
| [71] | Wu, J., Zhu, X., Li, Y. Q., Liu, G. D., Zhang, L. K., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Development and Validation of the Mental Health Literacy Questionnaire for Chinese Adults. [ChinaXiv:202012.00020] |
| [72] |
Xu, Z. Y., Huang, F. F., Kösters, M., Staiger, T., Becker, T., Thornicroft, G., & Rüsch, N. (2018). Effectiveness of interventions to promote help-seeking for mental health problems: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Medicine, 48(16), 2658-2667.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291718001265 URL pmid: 29852885 |
| [73] | Yan, B. P., Li, J. F., Li, K. Q., Zhang, Y., Fu, X. G., Wei, Z. G., .. Sun, X. L. (2014). Investigation of the awareness rate for mental health knowledge and attitude about mental health illness in place of residence general population. Modern Preventive Medicine, 41(9), 1636-1639. |
| [74] | Yu, X. M., & Jiang, G. R. (2004). The psychological help-seeking behavior and its influencing factors. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 18(6), 426-428. |
| [75] | Zhang, G. F., Zhao, J., Rao, S. C, & Shen, W. L. (2005). Investigation of the awareness rate for mental health knowledge among medical personnel in general hospital: 2345 Questionnaires Analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 17-18. |
| [76] | Zhang, H. C., & Xu, J. P (Eds). (2003) . Modern psychology and education statistics. Beijing, China: Beijing Normal University Press. |
| [77] | Zhou, C. Y., & Guo, Y. Y. (2013). Impact of family social status on mental health: Mediating role of belief in a just world. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 21(4), 636-640. |
| [78] | Zhou, H., & Long, L. R. (2004). Statistical Remedies for Common Method Biases. Advances in Psychological Science. 12(6), 942-950. |
| [79] | Zhu, Z. Q., & Zhang, M. Y. (2005). Questionnaire design of the baseline survey on the awareness rate for mental health knowledge among the key population. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 5-11. |
| [1] | REN Zhihong, ZHAO Chunxiao, TIAN Fan, YAN Yupeng, LI Danyang, ZHAO Ziyi, TAN Mengling, JIANG Guangrong. Meta-analysis of the effect of mental health literacy intervention in Chinese people [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| [2] | Fanny M Cheung, Shu-fai Cheung, Zhang Jianxin. What is “Chinese” Personality? Subgroup Differences in the Chinese Personality Assessment Inventory (CPAI-2) [J]. , 2004, 36(04): 491-499. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||