

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 199-214.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00199
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
NI Dan, LIU Chenlin, ZHENG Xiaoming( )
)
Received:2020-05-02
Published:2021-02-25
Online:2020-12-29
Contact:
ZHENG Xiaoming
E-mail:zhengxm@sem.tsinghua.edu.cn
Supported by:NI Dan, LIU Chenlin, ZHENG Xiaoming. (2021). The effects of employee mindfulness on spouse family satisfaction and work engagement. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(2), 199-214.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00199
| Variables | Within-person variance (e2) | Between-person variance (r2) | Percentage of within-person variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee mindfulness | 0.54 | 0.85 | 38.79% |
| Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 0.63 | 0.59 | 51.44% |
| Spouse family satisfaction | 0.42 | 0.54 | 43.71% |
| Spouse work engagement in the next morning | 0.41 | 0.86 | 32.31% |
Table 1 Percentage of within-person variance of the variables
| Variables | Within-person variance (e2) | Between-person variance (r2) | Percentage of within-person variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee mindfulness | 0.54 | 0.85 | 38.79% |
| Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 0.63 | 0.59 | 51.44% |
| Spouse family satisfaction | 0.42 | 0.54 | 43.71% |
| Spouse work engagement in the next morning | 0.41 | 0.86 | 32.31% |
| Variables | M | SDwithin-person level | SDbetween-person level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Employee mindfulness | 5.20 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.10 | -0.32*** | |
| 2. Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 5.18 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.15*** | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.07 | -0.06 | |
| 3. Spouse family satisfaction | 5.98 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.02 | 0.09** | 0.38*** | -0.10 | -0.33*** | |
| 4. Spouse work engagement in the next morning | 4.66 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.08* | 0.08* | 0.05 | -0.34*** | |
| 5. Employee gender | 0.76 | — | 0.43 | — | — | — | — | -0.23* | |
| 6. Spouse family negative emotional expression | 3.61 | — | 1.02 | — | — | — | — | — |
Table 2 Descriptive statistics
| Variables | M | SDwithin-person level | SDbetween-person level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Employee mindfulness | 5.20 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.10 | -0.32*** | |
| 2. Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 5.18 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.15*** | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.07 | -0.06 | |
| 3. Spouse family satisfaction | 5.98 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.02 | 0.09** | 0.38*** | -0.10 | -0.33*** | |
| 4. Spouse work engagement in the next morning | 4.66 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.08* | 0.08* | 0.05 | -0.34*** | |
| 5. Employee gender | 0.76 | — | 0.43 | — | — | — | — | -0.23* | |
| 6. Spouse family negative emotional expression | 3.61 | — | 1.02 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Model | χ2 | df | Δχ2 | TLI | CFI | RMSEA | SRMRwithin-person | SRMRbetween-person |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Five-factor model | 336.37 | 180 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |
| Four-factor model | ||||||||
| Employee mindfulness and employee strategic emotional connecting display were combined into a single factor | 1285.17 | 187 | 948.80*** | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Spouse family satisfaction and spouse work engagement in the next morning were combined into one factor | 1503.10 | 187 | 1166.73*** | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Three-factor Model | ||||||||
| Employee mindfulness and employee strategic emotional connecting display were combined into one factor, and spouse family satisfaction and spouse work engagement in the next morning were combined into one factor | 2352.16 | 192 | 2015.79*** | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Two-factor model | ||||||||
| All the variables at the within-level were combined into one factor | 4078.60 | 195 | 3742.23*** | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
Table 3 Results of confirmatory factor analysis
| Model | χ2 | df | Δχ2 | TLI | CFI | RMSEA | SRMRwithin-person | SRMRbetween-person |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Five-factor model | 336.37 | 180 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |
| Four-factor model | ||||||||
| Employee mindfulness and employee strategic emotional connecting display were combined into a single factor | 1285.17 | 187 | 948.80*** | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Spouse family satisfaction and spouse work engagement in the next morning were combined into one factor | 1503.10 | 187 | 1166.73*** | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Three-factor Model | ||||||||
| Employee mindfulness and employee strategic emotional connecting display were combined into one factor, and spouse family satisfaction and spouse work engagement in the next morning were combined into one factor | 2352.16 | 192 | 2015.79*** | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Two-factor model | ||||||||
| All the variables at the within-level were combined into one factor | 4078.60 | 195 | 3742.23*** | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| Variables | Employee strategic emotional connecting display | Spouse family satisfaction | Spouse work engagement in the next morning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Within-person level variables | |||
| Employee mindfulness | 0.15** (0.05) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.04 (0.03) |
| Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 0.07* (0.03) | 0.06* (0.02) | |
| Between-person level variables | |||
| Employee gender | 0.10 (0.18) | -0.20 (0.16) | 0.09 (0.20) |
| Spouse family negative emotional expression | -0.04 (0.07) | ||
| Multi-level interaction term | |||
| Employee mindfulness × spouse family negative emotional expression | -0.10* (0.04) |
Table 4 Multi-level path analysis results
| Variables | Employee strategic emotional connecting display | Spouse family satisfaction | Spouse work engagement in the next morning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Within-person level variables | |||
| Employee mindfulness | 0.15** (0.05) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.04 (0.03) |
| Employee strategic emotional connecting display | 0.07* (0.03) | 0.06* (0.02) | |
| Between-person level variables | |||
| Employee gender | 0.10 (0.18) | -0.20 (0.16) | 0.09 (0.20) |
| Spouse family negative emotional expression | -0.04 (0.07) | ||
| Multi-level interaction term | |||
| Employee mindfulness × spouse family negative emotional expression | -0.10* (0.04) |
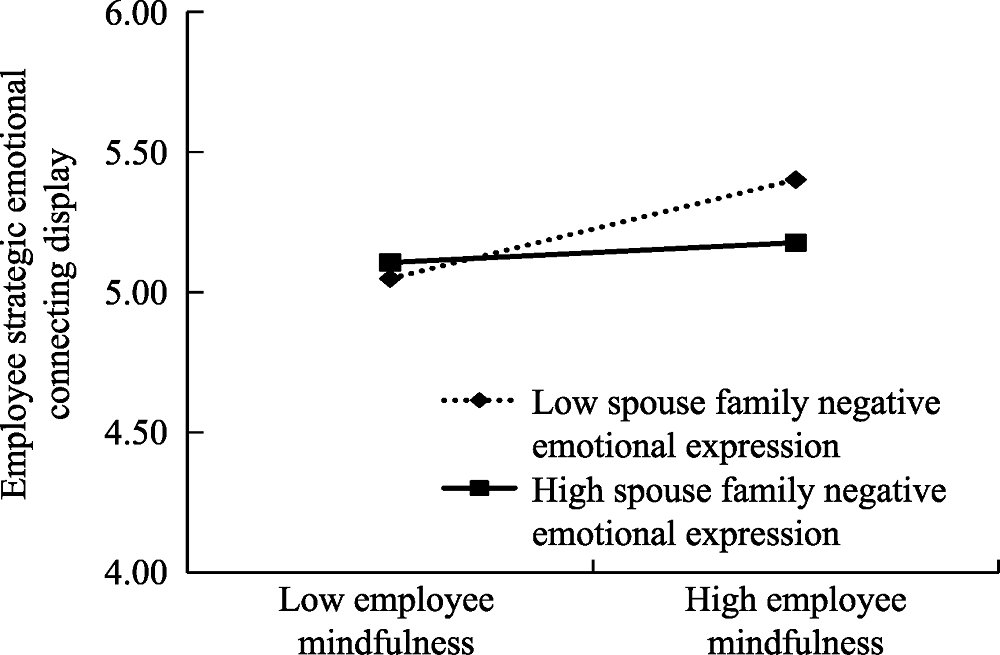
Figure 2. The moderating effect of spouse family negative emotional expression on the relationship between employee mindfulness and employee strategic emotional connecting display.
| [1] |
Arch, J. J., & Craske, M. G. (2010). Laboratory stressors in clinically anxious and non-anxious individuals: The moderating role of mindfulness. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48(6), 495-505.
doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2010.02.005 URL |
| [2] |
Aryee, S., & Luk, V. (1996). Balancing lwo major parts of adult life experience: Work and family identity among dual-earner couples. Human Relations, 49(4), 465-487.
doi: 10.1177/001872679604900404 URL |
| [3] |
Baer, R. A. (2003). Mindfulness training as a clinical intervention: A conceptual and empirical review. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 10(2), 125-143.
doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bpg015 URL |
| [4] |
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., & Allen, K. B. (2004). Assessment of mindfulness by self-report: The Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Skills. Assessment, 11(3), 191-206.
doi: 10.1177/1073191104268029 URL pmid: 15358875 |
| [5] |
Bakker, A. B., Demerouti, E., & Burke, R. (2009). Workaholism and relationship quality: A spillover-crossover perspective. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 14(1), 23-33.
doi: 10.1037/a0013290 URL pmid: 19210044 |
| [6] |
Barbier, M., Hansez, I., Chmiel, N., & Demerouti, E. (2013). Performance expectations, personal resources, and job resources: How do they predict work engagement?. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 22(6), 750-762.
doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2012.704675 URL |
| [7] |
Barnes, C. M., Lucianetti, L., Bhave, D. P., & Christian, M. S. (2015). “You wouldn’t like me when I’m sleepy”: Leaders’ sleep, daily abusive supervision, and work unit engagement. Academy of Management Journal, 58(5), 1419-1437.
doi: 10.5465/amj.2013.1063 URL |
| [8] |
Bauer, D. J., Preacher, K. J., & Gil, K. M. (2006). Conceptualizing and testing random indirect effects and moderated mediation in multilevel models: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 11(2), 142-163.
URL pmid: 16784335 |
| [9] |
Beitel, M., Ferrer, E., & Cecero, J. J. (2005). Psychological mindedness and awareness of self and others. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 61(6), 739-750.
URL pmid: 15546143 |
| [10] |
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., … Devins, G. (2004). Mindfulness: A proposed operational definition. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 11(3), 230-241.
doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bph077 URL |
| [11] | Brislin, R. W. (1986). The wording and translation of research instruments. In W. J. Lonner & J. W. Berry (Eds.), Cross-cultural research and methodology series: Vol. 8. Field methods in cross-cultural research (pp. 137-164). Sage Publications, Inc. |
| [12] |
Broderick, P. C. (2005). Mindfulness and coping with dysphoric mood: Contrasts with rumination and distraction. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 29(5), 501-510.
doi: 10.1007/s10608-005-3888-0 URL |
| [13] |
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 822-848.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822 URL pmid: 12703651 |
| [14] |
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2004). Perils and promise in defining and measuring mindfulness: Observations from experience. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 11(3), 242-248.
doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bph078 URL |
| [15] |
Chambers, R., Gullone, E., & Allen, N. B. (2009). Mindful emotion regulation: An integrative review. Clinical Psychology Review, 29(6), 560-572.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.06.005 URL pmid: 19632752 |
| [16] |
Chen, G. D., & Yang, T. P. (2020). The influence of mindfulness on intimate relationships. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(9), 1551-1563.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01551 URL |
| [17] |
Chen, Z., Allen, T. D., & Hou, L. (2020). Mindfulness, empathetic concern, and work-family outcomes: A dyadic analysis. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 119. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2020.103402
doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2020.103435 URL pmid: 32382161 |
| [18] |
Cohen, S., & Wills, T. A. (1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin, 98(2), 310-357.
URL pmid: 3901065 |
| [19] |
Cutrona, C. E., & Suhr, J. A. (1992). Controllability of stressful events and satisfaction with spouse support behaviors. Communication Research, 19(2), 154-174.
doi: 10.1177/009365092019002002 URL |
| [20] |
Davila, J., Wodarczyk, H., & Bhatia, V. (2017). Positive emotional expression among couples: The role of romantic competence. Couple and Family Psychology: Research and Practice, 6(2), 94-105.
doi: 10.1037/cfp0000077 URL |
| [21] |
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). The general causality orientations scale: Self-determination in personality. Journal of Research in Personality, 19(2), 109-134.
doi: 10.1016/0092-6566(85)90023-6 URL |
| [22] |
de Jonge, J., Dormann, C., Janssen, P. P. M., Dollard, M. F., Landeweerd, J. A., & Nijhuis, F. J. N. (2001). Testing reciprocal relationships between job characteristics and psychological well-being: A cross-lagged structural equation model. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 74(1), 29-46.
doi: 10.1348/096317901167217 URL |
| [23] |
Dimotakis, N., Scott, B. A., & Koopman, J. (2011). An experience sampling investigation of workplace interactions, affective states, and employee well-being. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32(4), 572-588.
doi: 10.1002/job.722 URL |
| [24] |
Duncan, L. G., Coatsworth, J. D., & Greenberg, M. T. (2009). A model of mindful parenting: Implications for parent-child relationships and prevention research. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 12(3), 255-270.
doi: 10.1007/s10567-009-0046-3 URL pmid: 19412664 |
| [25] |
Fisher, C. D., & To, M. L. (2012). Using experience sampling methodology in organizational behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(7), 865-877.
doi: 10.1002/job.1803 URL |
| [26] |
Fisher, D. M., Kerr, A. J., & Cunningham, S. (2019). Examining the moderating effect of mindfulness on the relationship between job stressors and strain outcomes. International Journal of Stress Management, 26(1), 78-88.
doi: 10.1037/str0000090 URL |
| [27] |
Ford, M. T., Heinen, B. A., & Langkamer, K. L. (2007). Work and family satisfaction and conflict: A meta-analysis of cross-domain relations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(1), 57-80.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.1.57 URL |
| [28] |
Gable, S. L., Reis, H. T., Impett, E. A., & Asher, E. R. (2004). What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87(2), 228-245.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.87.2.228 URL pmid: 15301629 |
| [29] |
Garland, E., Gaylord, S., & Park, J. (2009). The role of mindfulness in positive reappraisal. Explore, 5(1), 37-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2008.10.001 URL pmid: 19114262 |
| [30] |
Glasø, L., & Einarsen, S. (2008). Emotion regulation in leader-follower relationships. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 17(4), 482-500.
doi: 10.1080/13594320801994960 URL |
| [31] | Glomb, T. M., Duffy, M. K., Bono, J. E., & Yang, T. (2011). Mindfulness at work. Research in Personnel and Human Resources Management, 30(1), 115-157. |
| [32] | Goffman, E. (Ed.) (1959). The presentation of self in everyday life. New York: Doubleday Anchor. |
| [33] |
Gong, Z. H., & Zhao, C. (2014). Why is it difficult to balance work and family? An analysis based on work-family boundary theory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(4), 552-568.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00552 URL |
| [34] |
Good, D. J., Lyddy, C. J., Glomb, T. M., Bono, J. E., Brown, K. W., Duffy, M. K., … Lazar, S. W. (2016). Contemplating mindfulness at work: An integrative review. Journal of Management, 42(1), 114-142.
doi: 10.1177/0149206315617003 URL |
| [35] | Gordon, S. L. (1990). Social structural effects on emotions. In Kemper, T. D. (Ed.), Research agendas in the sociology of emotions (pp. 145-179). New York: State University of New York Press, Albany. |
| [36] |
Grover, S. L., Teo, S. T. T., Pick, D., & Roche, M. (2017). Mindfulness as a personal resource to reduce work stress in the job demands‐resources model. Stress and Health, 33(4), 426-436.
doi: 10.1002/smi.2726 URL pmid: 27862960 |
| [37] | Guerrero, L. K., & Andersen, P. A. (1998). The dark side of jealously and envy: Desire, delusion, desperation, and destructive communication. In B. H. Spitzberg & W. R. Cupach (Eds.), The dark side of close relationships (pp. 33-70). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. |
| [38] |
Halberstadt, A. G., Cassidy, J., Stifter, C. A., Parke, R. D., & Fox, N. A. (1995). Self-expressiveness within the family context: Psychometric support for a new measure. Psychological Assessment, 7(1), 93-103.
doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.7.1.93 URL |
| [39] |
Halbesleben, J. R. B., Neveu, J.-P., Paustian-Underdahl, S. C., & Westman, M. (2014). Getting to the “COR”: Understanding the role of resources in conservation of resources theory. Journal of Management, 40(5), 1334-1364.
doi: 10.1177/0149206314527130 URL |
| [40] |
Halbesleben, J. R. B., Wheeler, A. R., & Rossi, A. M. (2012). The costs and benefits of working with one’s spouse: A two‐sample examination of spousal support, work-family conflict, and emotional exhaustion in work‐linked relationships. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33(5), 597-615.
doi: 10.1002/job.771 URL |
| [41] |
Haun, V. C., Nübold, A., & Bauer, A. G. (2018). Being mindful at work and at home: Buffering effects in the stressor-detachment model. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 91(2), 385-410.
doi: 10.1111/joop.12200 URL |
| [42] |
Hershenberg, R., Mavandadi, S., Baddeley, J., & Libet, J. (2016). Capitalization in distressed couples: A pilot study and outline for future research. Personal Relationships, 23(4), 684-697.
doi: 10.1111/pere.2016.23.issue-4 URL |
| [43] |
Hill, C. L., & Updegraff, J. A. (2012). Mindfulness and its relationship to emotional regulation. Emotion, 12(1), 81-90.
doi: 10.1037/a0026355 URL pmid: 22148996 |
| [44] |
Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44(3), 513-524.
doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.44.3.513 URL |
| [45] | Hobfoll, S. E. (2011). Conservation of resource caravans and engaged settings. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology, 84(1), 116-122. |
| [46] |
Hobfoll, S. E., Johnson, R. J., Ennis, N., & Jackson, A. P. (2003). Resource loss, resource gain, and emotional outcomes among inner city women. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(3), 632-643.
URL pmid: 12635922 |
| [47] |
Hofmann, D. A., & Gavin, M. B. (1998). Centering decisions in hierarchical linear models: Implications for research in organizations. Journal of Management, 24(5), 623-641.
doi: 10.1177/014920639802400504 URL |
| [48] |
Hülsheger, U. R., Alberts, H. J. E. M., Feinholdt, A., & Lang, J. W. B. (2013). Benefits of mindfulness at work: the role of mindfulness in emotion regulation, emotional exhaustion, and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98(2), 310-325.
doi: 10.1037/a0031313 URL |
| [49] |
Hülsheger, U. R., Lang, J. W. B., Depenbrock, F., Fehrmann, C., Zijlstra, F. R. H., & Alberts, H. J. E. M. (2014). The power of presence: The role of mindfulness at work for daily levels and change trajectories of psychological detachment and sleep quality. Journal of Applied Psychology, 99(6), 1113-1128.
doi: 10.1037/a0037702 URL |
| [50] |
Ilies, R., Liu, X. Y., Liu, Y. K., & Zheng, X. M. (2017). Why do employees have better family lives when they are highly engaged at work?. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(6), 956-970.
doi: 10.1037/apl0000211 URL |
| [51] |
Ilies, R., Schwind, K. M., Wagner, D. T., Johnson, M. D., DeRue, D. S., & Ilgen, D. R. (2007). When can employees have a family life? The effects of daily workload and affect on work-family conflict and social behaviors at home. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(5), 1368-1379.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.92.5.1368 URL |
| [52] |
Kanter, R. M. (1977). Some effects of proportions on group life: Skewed sex ratios and responses to token women. American Journal of Sociology, 82(5), 965-990.
doi: 10.1086/226425 URL |
| [53] |
Karremans, J. C., Schellekens, M. P. J., & Kappen, G. (2015). Bridging the sciences of mindfulness and romantic relationships: A theoretical model and research agenda. Personality & Social Psychology Review, 21(1), 29-49.
doi: 10.1177/1088868315615450 URL pmid: 26563236 |
| [54] |
Kemper, T. D. (1984). Power, status, and emotions: A sociological contribution to a psycho-physiological domain. In K. Scherer & P. Ekman (Eds.), Approaches to emotion (pp. 369-384). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
doi: 10.1037/a0029892 URL pmid: 22985342 |
| [55] |
Koopman, J., Lanaj, K., & Scott, B. A. (2016). Integrating the bright and dark sides of OCB: A daily investigation of the benefits and costs of helping others. Academy of Management Journal, 59(2), 414-435.
doi: 10.5465/amj.2014.0262 URL |
| [56] |
Kopelman, R. E., Greenhaus, J. H., & Connolly, T. F. (1983). A model of work, family, and interrole conflict: A construct validation study. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 32(2), 198-215.
doi: 10.1016/0030-5073(83)90147-2 URL |
| [57] |
Kopelman, S., Rosette, A. S., & Thompson, L. (2006). The three faces of Eve: Strategic displays of positive, negative, and neutral emotions in negotiations. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 99(1), 81-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2005.08.003 URL |
| [58] |
Kroon, B., Menting, C., & van Woerkom, M. (2015). Why mindfulness sustains performance: The role of personal and job resources. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 8(4), 638-642.
doi: 10.1017/iop.2015.92 URL |
| [59] |
Lau, M. A., Bishop, S. R., Segal, Z. V., Buis, T., Anderson, N. D., Carlson, L., … Devins, G. (2006). The Toronto mindfulness scale: Development and validation. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62(12), 1445-1467.
doi: 10.1002/jclp.20326 URL pmid: 17019673 |
| [60] |
Levesque, C., & Brown, K. W. (2007). Mindfulness as a moderator of the effect of implicit motivational self-concept on day-to-day behavioral motivation. Motivation and Emotion, 31(4), 284-299.
doi: 10.1007/s11031-007-9075-8 URL |
| [61] |
Li, W. D., Fay, D., Frese, M., Harms, P. D., & Gao, X. Y. (2014). Reciprocal relationship between proactive personality and work characteristics: A latent change score approach. Journal of Applied Psychology, 99(5), 948-965.
doi: 10.1037/a0036169 URL |
| [62] |
Little, T. D., Rhemtulla, M., Gibson, K., & Schoemann, A. M. (2013). Why the items versus parcels controversy needn’t be one. Psychological Methods, 18(3), 285-300.
doi: 10.1037/a0033266 URL pmid: 23834418 |
| [63] |
Litzinger, S., & Gordon, K. C. (2005). Exploring relationships among communication, sexual satisfaction, and marital satisfaction. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 31(5), 409-424.
doi: 10.1080/00926230591006719 URL pmid: 16169824 |
| [64] |
Liu, Y. M., Liu, J., & Wu, L. Z. (2012). Strategic emotional display: An examination of its interpersonal and career outcomes. Career Development International, 17(6), 518-536.
doi: 10.1108/13620431211280114 URL |
| [65] |
Lively, K. J., & Powell, B. (2006). Emotional expression at work and at home: Domain, status, or individual characteristics?. Social Psychology Quarterly, 69(1), 17-38.
doi: 10.1177/019027250606900103 URL |
| [66] |
Ma, H. Y., Sheng, C. G., Yang, J., Tang, H. Y., & Xie, J. L. (2014). Boundary flexibility and work-family conflict and enrichment: from person-environment fit perspective. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(4), 540-551.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00540 URL |
| [67] |
Miller, K. I. (2007). Compassionate communication in the workplace: Exploring processes of noticing, connecting, and responding. Journal of Applied Communication Research, 35(3), 223-245.
doi: 10.1080/00909880701434208 URL |
| [68] |
Montani, F., Dagenais-Desmarais, V., Giorgi, G., & Grégoire, S. (2018). A conservation of resources perspective on negative affect and innovative work behaviour: The role of affect activation and mindfulness. Journal of Business and Psychology, 33(1), 123-139
doi: 10.1007/s10869-016-9480-7 URL |
| [69] |
Montes-Maroto, G., Rodríguez-Muñoz, A., Antino, M., & Gil, F. (2018). Mindfulness beyond the individual: Spillover and crossover effects in working couples. Mindfulness, 9(4), 1258-1267.
doi: 10.1007/s12671-017-0868-x URL |
| [70] | Morgan, W. D., & Morgan, S. T.(2005). Cultivating attention and empathy. In C. K. Germer, R. D. Siegel, & P. R. Fulton (Eds.), Mindfulness and psychotherapy (pp. 73-90). New York: The Guilford Press. |
| [71] |
Moskowitz, D. S., & Young, S. N. (2006). Ecological momentary assessment: What it is and why it is a method of the future in clinical psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 31(1), 13-20.
URL pmid: 16496031 |
| [72] | Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (Eds.). (1998-2017). Mplus user’s guide (Eighth ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén. |
| [73] | Ni, D., & Zheng, X. M. (2019). Have you been mindfulness today? Mindfulness helps you improve your work and family experience. Tsinghua Business Review, (11), 42-49. |
| [74] |
Pakenham, K. I., & Samios, C. (2013). Couples coping with multiple sclerosis: A dyadic perspective on the roles of mindfulness and acceptance. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 36(4), 389-400.
doi: 10.1007/s10865-012-9434-0 URL pmid: 22689212 |
| [75] |
Parkinson, B. (1997). Untangling the appraisal-emotion connection. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 1(1), 62-79.
doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr0101_5 URL pmid: 15647129 |
| [76] | Pietrzak, T., Hauke, G., & Lohr, C. (2016). Connecting Couples Intervention: Improving couples’ empathy and emotional regulation using embodied empathy mechanisms. European Psychotherapy, 13, 66-98. |
| [77] |
Pratscher, S. D., Wood, P. K., King, L. A., & Bettencourt, B. A. (2019). Interpersonal mindfulness: Scale development and initial construct validation. Mindfulness, 10(6), 1044-1061.
doi: 10.1007/s12671-018-1057-2 URL |
| [78] |
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185-227.
doi: 10.1080/00273170701341316 URL pmid: 26821081 |
| [79] |
Preacher, K. J., Zhang, Z., & Zyphur, M. J. (2011). Alternative methods for assessing mediation in multilevel data: The advantages of multilevel SEM. Structural Equation Modeling, 18(2), 161-182.
doi: 10.1080/10705511.2011.557329 URL |
| [80] |
Preacher, K. J., Zyphur, M. J., & Zhang, Z. (2010). A general multilevel SEM framework for assessing multilevel mediation. Psychological Methods, 15(3), 209-233.
doi: 10.1037/a0020141 URL pmid: 20822249 |
| [81] |
Purser, R. E., & Milillo, J. (2015). Mindfulness revisited: A Buddhist-based conceptualization. Journal of Management Inquiry, 24(1), 3-24.
doi: 10.1177/1056492614532315 URL |
| [82] |
Reb, J., Narayanan, J., & Chaturvedi, S. (2014). Leading mindfully: Two studies on the influence of supervisor trait mindfulness on employee well-being and performance. Mindfulness, 5(1), 36-45.
doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0144-z URL |
| [83] |
Sanz-Vergel, A. I., Rodríguez-Muñoz, A., Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2012). The daily spillover and crossover of emotional labor: Faking emotions at work and at home. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 81(2), 209-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2012.07.003 URL |
| [84] |
Schaufeli, W. B., Bakker, A. B., & Salanova, M. (2006). The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: A cross-national study. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66(4), 701-716.
doi: 10.1177/0013164405282471 URL |
| [85] |
Schuh, S. C., Zheng, M. X., Xin, K. R., & Fernandez, J. A. (2019). The interpersonal benefits of leader mindfulness: A serial mediation model linking leader mindfulness, leader procedural justice enactment, and employee exhaustion and performance. Journal of Business Ethics, 156(4), 1007-1025.
doi: 10.1007/s10551-017-3610-7 URL |
| [86] |
Schutte, N. S., & Malouff, J. M. (2011). Emotional intelligence mediates the relationship between mindfulness and subjective well-being. Personality and Individual Differences, 50(7), 1116-1119.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2011.01.037 URL |
| [87] | Selig, J. P., & Preacher, K. J. (2008). Monte Carlo method for assessing mediation: An interactive tool for creating confidence intervals for indirect effects. [Computer software]. Retrieved from http://quantpsy.org. |
| [88] |
Shapiro, S. L., Carlson, L. E., Astin, J. A., & Freedman, B. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62(3), 373-386.
doi: 10.1002/jclp.20237 URL pmid: 16385481 |
| [89] | Snijders, T. A., & Bosker, R. J. (Eds.). (1999). Multilevel analysis: An introduction to basic and advanced multilevel modeling. Sage, London. |
| [90] |
Song, Z., Foo, M. D., & Uy, M. A. (2008). Mood spillover and crossover among dual-earner couples: A cell phone event sampling study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(2), 443-452.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.93.2.443 URL |
| [91] |
Song, Z., Foo, M. D., Uy, M. A., & Sun, S. (2011). Unraveling the daily stress crossover between unemployed individuals and their employed spouses. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(1), 151-168.
doi: 10.1037/a0021035 URL |
| [92] |
Sonnentag, S., & Bayer, U. V. (2005). Switching off mentally: Predictors and consequences of psychological detachment from work during off-job time. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 10(4), 393-414.
doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.10.4.393 URL pmid: 16248688 |
| [93] |
Staw, B. M., Sutton, R. I., & Pelled, L. H. (1994). Employee positive emotion and favorable outcomes at the workplace. Organization Science, 5(1), 51-71.
doi: 10.1287/orsc.5.1.51 URL |
| [94] |
Sun., X., Yan, M., & Chu, X. P. (2014). Passive mood and work behavior: The cross-level mediating effect of zhong-yong thinking style. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(11), 1704-1718.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01704 URL |
| [95] |
Sutcliffe, K. M., Vogus, T. J., & Dane, E. (2016). Mindfulness in organizations: A cross-level review. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 3, 55-81.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-041015-062531 URL |
| [96] |
Takeuchi, R., Yun, S., & Tesluk, P. E. (2002). An examination of crossover and spillover effects of spousal and expatriate cross-cultural adjustment on expatriate outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(4), 655-666.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.87.4.655 URL |
| [97] |
Taylor, N. Z., & Millear, P. M. R. (2016). The contribution of mindfulness to predicting burnout in the workplace. Personality and Individual Differences, 89, 123-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.10.005 URL |
| [98] |
Thoits, P. A. (1986). Multiple identities: Examining gender and marital status differences in distress. American Sociological Review, 51(2), 259-272.
doi: 10.2307/2095520 URL |
| [99] |
Thompson, B. M., & Cavallaro, L. (2007). Gender, work‐based support and family outcomes. Stress and Health, 23(2), 73-85.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1532-2998 URL |
| [100] |
Turpyn, C. C., & Chaplin, T. M. (2016). Mindful parenting and parents’ emotion expression: Effects on adolescent risk behaviors. Mindfulness, 7(1), 246-254.
doi: 10.1007/s12671-015-0440-5 URL pmid: 27087861 |
| [101] |
Wachs, K., & Cordova, J. V. (2007). Mindful relating: Exploring mindfulness and emotion repertoires in intimate relationships. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 33(4), 464-481.
doi: 10.1111/j.1752-0606.2007.00032.x URL pmid: 17935530 |
| [102] |
Wang, Y. L., Zhang, Z. Y., He, Y. (2012). The research on the effects of work-family support on employees’ creativity. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(12), 1651-1662.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.01651 URL |
| [103] |
Wang, Z. J., Jex, S. M., Peng, Y. S., Liu, L., & Wang, S. (2019). Emotion regulation in supervisory interactions and marital well-being: A spillover-crossover perspective. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 24(4), 467-481.
doi: 10.1037/ocp0000150 URL pmid: 30945923 |
| [104] |
Westman, M., Etzion, D., & Chen, S. (2009). Crossover of positive experiences from business travelers to their spouses. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 24(3), 269-284.
doi: 10.1108/02683940910939340 URL |
| [105] |
Williams, A. M., & Cano, A. (2014). Spousal mindfulness and social support in couples with chronic pain. The Clinical Journal of Pain, 30(6), 528-535.
doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000009 URL pmid: 24281274 |
| [106] |
Williams, J. M. G. (2008). Mindfulness, depression and modes of mind. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 32(6), 721-733.
doi: 10.1007/s10608-008-9204-z URL |
| [107] |
Williams, L. J., Vandenberg, R. J., & Edwards, J. R. (2009). 12 structural equation modeling in management research: A guide for improved analysis. Academy of Management Annals, 3(1), 543-604.
doi: 10.5465/19416520903065683 URL |
| [108] |
Wright, D. L., Aquilino, W. S., & Supple, A. J. (1998). A comparison of computer-assisted and paper-and-pencil self-administered questionnaires in a survey on smoking, alcohol, and drug use. Public Opinion Quarterly, 62(3), 331-353.
doi: 10.1086/297849 URL |
| [109] |
Xanthopoulou, D., Bakker, A. B., Demerouti, E., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2007). The role of personal resources in the job demands-resources model. International Journal of Stress Management, 14(2), 121-141.
doi: 10.1037/1072-5245.14.2.121 URL |
| [110] |
Xanthopoulou, D., Bakker, A. B., Dollard, M. F., Demerouti, E., Schaufeli, W. B., Taris, T. W., & Schreurs, P. J. (2007). When do job demands particularly predict burnout? The moderating role of job resources. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 22(8), 766-786.
doi: 10.1108/02683940710837714 URL |
| [111] |
Xie, J., Zhou, Z. E., & Gong, Y. (2018). Relationship between proactive personality and marital satisfaction: A spillover-crossover perspective. Personality and Individual Differences, 128, 75-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2018.02.011 URL |
| [112] |
Xie, J. L., Ma, H. Y., Tang, H. Y., & Jiang, H. (2017). Family supportive supervisor behavior and marital satisfaction among Chinese dual-earner couples: Testing a positive spillover-crossover model. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(3), 359-369.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00359 URL |
| [113] |
Yoo, H., Bartle-Haring, S., Day, R. D., & Gangamma, R. (2014). Couple communication, emotional and sexual intimacy, and relationship satisfaction. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 40(4), 275-293.
doi: 10.1080/0092623X.2012.751072 URL pmid: 24111536 |
| [114] | Zhang, J., Song, J. W., & Wang, Y. (2017). Mindfulness in the workplace: A literature review and prospects. Foreign Economics & Management, 39(8), 56-70. |
| [115] |
Zhao, K., Zhang, M., Kraimer, M. L., & Yang, B. (2019). Source attribution matters: Mediation and moderation effects in the relationship between work-to-family conflict and job satisfaction. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 40(4), 492-505.
doi: 10.1002/job.v40.4 URL |
| [116] | Zheng, X. M., & Ni, D. (2018). Review of mindfulness research in organizational management. Management Review, 30(10), 155-170. |
| [117] | Zheng, X. M., Ni, D., & Liu, X. (2019). The effect of mindfulness on work-to-family enrichment: Evidence from experience sampling methods. Chinese Journal of Management, 16(3), 360-368. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||