

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 173-183.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00173 cstr: 32110.14.2020.00173
白学军1,2, 邵梦灵1,2, 刘婷1,2, 尹建忠3, 金花1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2018-11-08
发布日期:2019-12-24
出版日期:2020-02-25
基金资助:
BAI Xuejun1,2, SHAO Mengling1,2, LIU Ting1,2, YIN Jianzhong3, JIN Hua1,2( )
)
Received:2018-11-08
Online:2019-12-24
Published:2020-02-25
摘要:
以往研究发现, 球类运动员视知觉脑区的结构不同于非运动员, 但这些脑区结构的差异是训练经历引起还是天生结构不同所导致的, 尚未可知。本研究拟采用纵向设计, 以处于成年早期的成人非运动员为被试(23~27岁), 随机分成实验组和对照组, 实验组参加12周的羽毛球运动训练, 对照组在此期间不进行任何有规律的运动训练, 采集干预实验前后所有被试的结构像和弥散张量成像数据。结果发现, 实验组训练后左下枕叶、颞中回、颞下回灰质体积增加, 双侧内囊后肢、上放射冠各向异性分数(FA)增加, 进一步分析发现, FA增加的原因是径向扩散系数(RD)下降。提示羽毛球运动可增加成人与视运动知觉有关脑区的灰质容量, 增加纤维束的髓鞘厚度。
中图分类号:
白学军, 邵梦灵, 刘婷, 尹建忠, 金花. (2020). 羽毛球运动重塑成年早期的大脑灰质和白质结构. 心理学报, 52(2), 173-183.
BAI Xuejun, SHAO Mengling, LIU Ting, YIN Jianzhong, JIN Hua. (2020). Altered structural plasticity in early adulthood after badminton training. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(2), 173-183.
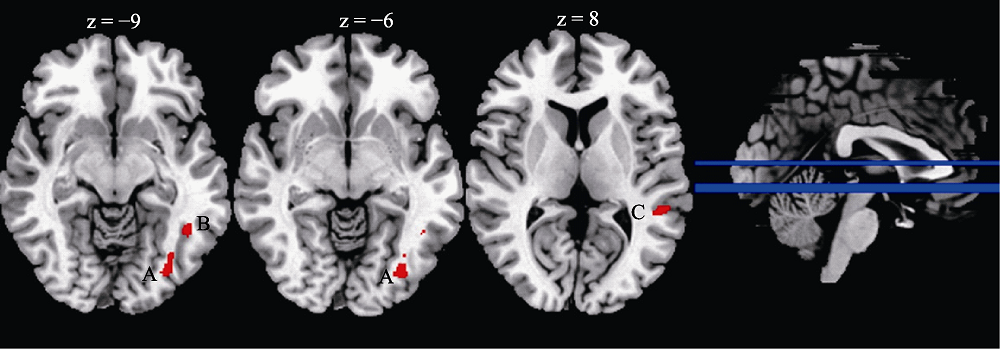
图1 交互作用显著的灰质体积脑区 注:该图为MNI空间下的轴状图, 图中左为右半球, 右为左半球。A:左下枕叶(x = -33, y = -78, z = -6, k = 111, F = 60.50, pFWE < 0.001), B:左颞下回(x = -44, y = -50, z = -9, k = 127, F = 56.18, pFWE = 0.001), C:左颞中回(x = -51, y = -39, z = 8, k = 79, F = 51.08, pFWE = 0.002)。
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 左下枕叶 | 0.243 ± 0.042 | 0.243 ± 0.043 | 0.227 ± 0.034 | 0.252 ± 0.039 |
| 左颞下回 | 0.323 ± 0.073 | 0.321 ± 0.074 | 0.286 ± 0.048 | 0.310 ± 0.045 |
| 左颞中回 | 0.390 ± 0.089 | 0.379 ± 0.091 | 0.368 ± 0.067 | 0.382 ± 0.068 |
表1 两组被试交互作用显著脑区的灰质体积值(M ± SD)
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 左下枕叶 | 0.243 ± 0.042 | 0.243 ± 0.043 | 0.227 ± 0.034 | 0.252 ± 0.039 |
| 左颞下回 | 0.323 ± 0.073 | 0.321 ± 0.074 | 0.286 ± 0.048 | 0.310 ± 0.045 |
| 左颞中回 | 0.390 ± 0.089 | 0.379 ± 0.091 | 0.368 ± 0.067 | 0.382 ± 0.068 |

图3 FA交互作用显著的脑区 注:该图为MNI空间下的轴状图, 图中的左为右半球, 右为左半球。A:左内囊后肢(x = -24, y = -11, z = 15, k = 32, pTFCE = 0.045), B:右内囊后肢(x = 25, y = -13, z = 15, k = 253, pTFCE = 0.019), C:左上放射冠(x = -27, y = -18, z = 21, k = 79, pTFCE = 0.040), D:右上放射冠(x = 29, y = -17, z = 21, k = 22, pTFCE = 0.049; x = 27, y = -20, z = 25, k = 6, pTFCE = 0.050; x = 21, y = -17, z = 39, k = 126, pTFCE = 0.044)。绿色:平均FA骨架。底图:标准空间MNI152图。
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 左内囊后肢 | 0.664 ± 3.64×10-2 | 0.645 ± 3.25×10-2 | 0.638 ± 3.24×10-2 | 0.656 ± 3.41×10-2 |
| 右内囊后肢 | 0.686 ± 3.16×10-2 | 0.673 ± 2.85×10-2 | 0.659 ± 3.20×10-2 | 0.676 ± 2.48×10-2 |
| 左上放射冠 | 0.642 ± 2.80×10-2 | 0.627 ± 2.89×10-2 | 0.617 ± 2.54×10-2 | 0.629 ± 2.69×10-2 |
| 右上放射冠 | 0.601 ± 3.42×10-2 | 0.59 ± 3.63×10-2 | 0.561 ± 2.80×10-2 | 0.576 ± 2.66×10-2 |
表2 两组被试的FA值(M ± SD)
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | 前测 | 后测 | |
| 左内囊后肢 | 0.664 ± 3.64×10-2 | 0.645 ± 3.25×10-2 | 0.638 ± 3.24×10-2 | 0.656 ± 3.41×10-2 |
| 右内囊后肢 | 0.686 ± 3.16×10-2 | 0.673 ± 2.85×10-2 | 0.659 ± 3.20×10-2 | 0.676 ± 2.48×10-2 |
| 左上放射冠 | 0.642 ± 2.80×10-2 | 0.627 ± 2.89×10-2 | 0.617 ± 2.54×10-2 | 0.629 ± 2.69×10-2 |
| 右上放射冠 | 0.601 ± 3.42×10-2 | 0.59 ± 3.63×10-2 | 0.561 ± 2.80×10-2 | 0.576 ± 2.66×10-2 |
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | η2 | 前测 | 后测 | η2 | |
| 左内囊后肢 | 3.83 × 10-4 ± 8.56 × 10-6 | 4.10 × 10-4 ± 8.23 × 10-6 | 0.34 | 4.17 × 10-4 ± 7.93 × 10-6 | 3.98 × 10-4 ± 7.62 × 10-6 | 0.24 |
| 右内囊后肢 | 3.68 × 10-4 ± 7.96 × 10-6 | 3.84 × 10-4 ± 6.37 × 10-6 | 0.23 | 4.04 × 10-4 ± 7.37 × 10-6 | 3.83 × 10-4 ± 5.89 × 10-6 | 0.34 |
| 左上放射冠 | 4.28 × 10-4 ± 8.83 × 10-6 | 4.55 × 10-4 ± 8.94 × 10-6 | 0.29 | 4.71 × 10-4 ± 8.18 × 10-6 | 4.60 × 10-4 ± 8.27 × 10-6 | - |
| 右上放射冠 | 4.36 × 10-4 ± 6.21 × 10-6 | 4.54 × 10-4 ± 6.79 × 10-6 | 0.35 | 4.84 × 10-4 ± 5.75 × 10-6 | 4.69 × 10-4 ± 6.29 × 10-6 | 0.30 |
表3 两组被试4个ROIs脑区的RD值(M ± SD)
| 脑区 | 对照组 | 实验组 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前测 | 后测 | η2 | 前测 | 后测 | η2 | |
| 左内囊后肢 | 3.83 × 10-4 ± 8.56 × 10-6 | 4.10 × 10-4 ± 8.23 × 10-6 | 0.34 | 4.17 × 10-4 ± 7.93 × 10-6 | 3.98 × 10-4 ± 7.62 × 10-6 | 0.24 |
| 右内囊后肢 | 3.68 × 10-4 ± 7.96 × 10-6 | 3.84 × 10-4 ± 6.37 × 10-6 | 0.23 | 4.04 × 10-4 ± 7.37 × 10-6 | 3.83 × 10-4 ± 5.89 × 10-6 | 0.34 |
| 左上放射冠 | 4.28 × 10-4 ± 8.83 × 10-6 | 4.55 × 10-4 ± 8.94 × 10-6 | 0.29 | 4.71 × 10-4 ± 8.18 × 10-6 | 4.60 × 10-4 ± 8.27 × 10-6 | - |
| 右上放射冠 | 4.36 × 10-4 ± 6.21 × 10-6 | 4.54 × 10-4 ± 6.79 × 10-6 | 0.35 | 4.84 × 10-4 ± 5.75 × 10-6 | 4.69 × 10-4 ± 6.29 × 10-6 | 0.30 |
| [1] | Abernethy B . (1996). Training the visual-perceptual skills of athletes: Insights from the study of motor expertise. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 24(6), S89-S92. |
| [2] | Abernethy B., & Zawi K . (2007). Pickup of essential kinematics underpins expert perception of movement patterns. Journal of Motor Behavior, 39(5), 353-367. |
| [3] | Abreu A. M., Macaluso E., Azevedo R. T., Cesari P., Urgesi C., & Aglioti S. M . (2012). Action anticipation beyond the action observation network: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study in expert basketball players. European Journal of Neuroscience, 35(10), 1646-1654. |
| [4] | Alder D., Ford P. R., Causer J., & Williams A. M . (2014). The coupling between gaze behavior and opponent kinematics during anticipation of badminton shots. Human Movement Science, 37, 167-179. |
| [5] | Baeck J., Kim Y., Seo J., Ryeom H., Lee J., Choi S., ... Chang Y . (2012). Brain activation patterns of motor imagery reflect plastic changes associated with intensive shooting training. Behavioural Brain Research, 234(1), 26-32. |
| [6] | Beaulieu C . (2002). The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - A technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(7-8), 435-455. |
| [7] | Bezzola L., Merillat S., Gaser C., & Jancke L . (2011). Training-induced neural plasticity in golf novices. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(35), 12444-12448. |
| [8] | Bilalic M., Langner R., Erb M., & Grodd W . (2010). Mechanisms and neural basis of object and pattern recognition: A study with chess experts. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 139(4), 728-742. |
| [9] | Bishop D. T., Wright M. J., Jackson R. C., & Abernethy B . (2013). Neural bases for anticipation skill in soccer: An fMRI Study. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 35, 98-109. |
| [10] | Blumenfeld-Katzir T., Pasternak O., Dagan M., & Assaf Y . (2011). Diffusion MRI of structural brain plasticity induced by a learning and memory task. PLoS One, 6(6), e20678. |
| [11] | Chekroud S. R., Gueorguieva R., Zheutlin A. B., Paulus M., Krumholz H. M., Krystal J. H., & Chekroud A. M . (2018). Association between physical exercise and mental health in 1·2 million individuals in the USA between 2011 and 2015: A cross-sectional study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 5(9), 739-746. |
| [12] | Di X., Zhu S., Jin H., Wang P., Ye Z., Zhou K., ... Rao H . (2012). Altered resting brain function and structure in professional badminton players. Brain Connectivity, 2(4), 225-233. |
| [13] | Draganski B., Gaser C., Busch V., Schuierer G., Bogdahn U., & May A . (2004). Neuroplasticity: Changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature, 427, 311-312. |
| [14] | Everts R., Lidzba K., Wilke M., Kiefer C., Mordasini M., Schroth G., ... Steinlin M . (2009). Strengthening of laterality of verbal and visuospatial functions during childhood and adolescence. Human Brain Mapping, 30(2), 473-483. |
| [15] | Gaser C., & Schlaug G . (2003). Brain structures differ between musicians and non-musicians. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(27), 9240-9245. |
| [16] | Ge Y., Grossman R. I., Babb J. S., Rabin M. L., Mannon L. J., & Kolson D. L . (2002). Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: Volumetric MR imaging analysis. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23, 1327-1333. |
| [17] | Gong D., He H., Ma W., Liu D., Huang M., Dong L., ... Yao D . (2016). Functional integration between salience and central executive networks: A role for action video game experience. Neural Plasticity, 2016, 1-9. |
| [18] | Gong D., Ma W., Gong J., He H., Dong L., Zhang D., ... Yao D . (2017). Action video game experience related to altered large-scale white matter networks. Neural Plasticity, 2017, 1-7. |
| [19] | Grezes J., Fonlupt P., Bertenthal B., Delon-Martin C., Segebarth C., & Decety J . (2001). Does perception of biological motion rely on specific brain regions? Neuroimage, 13(5), 775-785. |
| [20] | Hamzei F., Glauche V., Schwarzwald R., & May A . (2012). Dynamic gray matter changes within cortex and striatum after short motor skill training are associated with their increased functional interaction. Neuroimage, 59(4), 3364-3372. |
| [21] | Hohmann T., Troje N. F., Olmos A., & Munzert J . (2011). The influence of motor expertise and motor experience on action and actor recognition. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 23, 403-415. |
| [22] | Hu J., Ma H., Zhu S., Li P., Xu H., Fang Y., ... Lu H. D . (2018). Visual motion processing in macaque V2. Cell Report, 25(1), 157-167. |
| [23] | Hulsdunker T., Struder H. K., & Mierau A . (2017). Visual motion processing subserves faster visuomotor reaction in badminton players. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 49(6), 1097-1110. |
| [24] | iReaerch. (2015. China internet + sports report. Retrieved February 11, 2019, from http://report.iresearch.cn/report_pdf.aspx?id=2423 |
| [ 艾瑞咨询. (2015. 中国互联网+体育报告. 2019-02-11取自 http://report.iresearch.cn/report_pdf.aspx?id=2423] | |
| [25] | Jancke L., Koeneke S., Hoppe A., Rominger C., & Hanggi J . (2009). The architecture of the golfer's brain. PLoS One, 4(3), e4785. |
| [26] | Jin H., Xu G., Zhang J. X., Gao H., Ye Z., Wang P., ... Lin C . (2011). Event-related potential effects of superior action anticipation in professional badminton players. Neuroscience Letters, 492(3), 139-144. |
| [27] | Jin H., Xu G., Zhang J. X., Ye Z., Wang S., Zhao L., ... Mo L . (2010). Athletic training in badminton players modulates the early C1 component of visual evoked potentials: A preliminary investigation. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 78(3), 308-314. |
| [28] | Jonasson L. S., Nyberg L., Kramer A. F., Lundquist A., Riklund K., & Boraxbekk C . (2017). Aerobic exercise intervention, cognitive performance, and brain structure: Results from the physical influences on brain in aging (PHIBRA) study. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 8, 1-15. |
| [29] | Kalpouzos G., Chetelat G., Baron J. C., Landeau B., Mevel K., Godeau C., ... Desgranges B . (2009). Voxel-based mapping of brain gray matter volume and glucose metabolism profiles in normal aging. Neurobiology of Aging, 30(1), 112-124. |
| [30] | Kim J., Loy D. N., Liang H., Trinkaus K., Schmidt R. E., & Song S . (2007). Noninvasive diffusion tensor imaging of evolving white matter pathology in a mouse model of acute spinal cord injury. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 58(2), 253-260. |
| [31] | Kong L., Wang S., Gao H., Wang P., Lin H., Bai L., ... Jin H . (2012). Better processing of dynamic information in badminton player with higher action anticipatory skill. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Physical Education (Social Science), 26(2), 105-109. |
| [ 孔丽娜, 王树芳, 高宏巍, 王品, 林慧妍, 白利华 , .. 金花. (2012). 高球路预期能力的羽毛球运动员能更好地加工动态信息. 南京体育学院学报(社会科学版), 26(2), 105-109.] | |
| [32] | Lakhani B., Borich M. R., Jackson J. N., Wadden K. P., Peters S., Villamayor A., ... Boyd L. A . (2016). Motor skill acquisition promotes human brain myelin plasticity. Neural Plasticity, 2016, 1-7. |
| [33] | Lestou V., Pollick F. E., & Kourtzi Z . (2008). Neural substrates for action understanding at different description levels in the human brain. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(2), 324-341. |
| [34] | Liang Z., Yin D., Liu T., Zhu Z., Lin H., & Jin H . (2019). High perceptual sensitivity to global motion in badminton players. International Journal of Sport Psychology, under review. |
| [35] | Liu L . (2018). Analysis on the development status of badminton and table tennis industries in 2018 Domestic competition strength is strong. Retrieved February 11, 2019, from https://www.sohu.com/a/221173517_99900941. |
| [ 刘凌云 . (2018). 2018年羽毛球、乒乓球行业发展现状分析国内竞争实力强. 2019-02-11取自https://www.sohu.com/a/221173517_99900941.] | |
| [36] | Liu T., Shao M., Yin D., Li Y., Yang N., Yin R., ... Hong H . (2017). The effect of badminton training on the ability of same-domain action anticipation for adult novices: Evidence from behavior and ERPs. Neuroscience Letters, 660, 6-11. |
| [37] | Lovden M., Schaefer S., Noack H., Bodammer N. C., Kuhn S., Heinze H. J., ... Lindenberger U . (2012). Spatial navigation training protects the hippocampus against age-related changes during early and late adulthood. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(3), 620.e9-620.e22. |
| [38] | Luo C., Guo Z. W., Lai Y. X., Liao W., Liu Q., Kendrick K. M., ... Li H . (2012). Musical training induces functional plasticity in perceptual and motor networks: Insights from resting-state fMRI. PLoS One, 7(5), e36568. |
| [39] | Oldfield R. C . (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: The edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9(1), 97-113. |
| [40] | Park I. S., Lee Y. N., Kwon S., Lee N. J., & Rhyu I. J . (2015). White matter plasticity in the cerebellum of elite basketball athletes. Anatomy & Cell Biology, 48(4), 262-267. |
| [41] | Pelphrey K. A., Morris J. P., & McCarthy G . (2004). Grasping the intentions of others: The perceived intentionality of an action influences activity in the superior temporal sulcus during social perception. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 16(10), 1706-1716. |
| [42] | Peuskens H., Vanrie J., Verfaillie K., & Orban G. A . (2005). Specificity of regions processing biological motion. European Journal of Neuroscience, 21(10), 2864-2875. |
| [43] | Pfefferbaum A., Mathalon D. H., Sullivan E. V., Rawles J. M., Zipursky R. B., & Lim K. O . (1994). A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study of changes in brain morphology from infancy to late adulthood. Archives of Neurology, 51(9), 874-887. |
| [44] | Reid L. B., Sale M. V., Cunnington R., Mattingley J. B., & Rose S. E . (2017). Brain changes following four weeks of unimanual motor training: Evidence from fMRI-guided diffusion MRI tractography. Human Brain Mapping, 38(9), 4302-4312. |
| [45] | Rogge A. K., Roder B., Zech A., & Hotting K . (2018). Exercise-induced neuroplasticity: Balance training increases cortical thickness in visual and vestibular cortical regions. Neuroimage, 179, 471-479. |
| [46] | Schmithorst V. J., & Wilke M . (2002). Differences in white matter architecture between musicians and non-musicians: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroscience Letters, 321(1-2), 57-60. |
| [47] | Scholz J., Klein M. C., Behrens T. E., & Johansen-Berg H . (2009). Training induces changes in white-matter architecture. Nature Neuroscience, 12, 1370-1371. |
| [48] | Shen G., Zhang J., Wang H., Wu Y., Zeng Y., & Du X . (2014). Altered white matter architecture among college athletes: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2014(#4), 94-101. |
| [ 沈国华, 张剑, 王慧, 吴殷, 曾雨雯, 杜小霞 . (2014). 大学生运动员脑白质的变化: 基于磁共振扩散张量成像研究. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (#4), 94-101.] | |
| [49] | Smeeton N. J., Ward P., & Williams A. M . (2004). Do pattern recognition skills transfer across sports? A preliminary analysis. Journal of Sports Sciences, 22(2), 205-213. |
| [50] | Song S. K., Sun S. W., Ramsbottom M. J., Chang C., Russell J., & Cross A. H . (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage, 17(3), 1429-1436. |
| [51] | Sowell E. R., Peterson B. S., Thompson P. M., Welcome S. E., Henkenius A. L., & Toga A. W . (2003). Mapping cortical change across the human life span. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 309-315. |
| [52] | Sumiyoshi A., Taki Y., Nonaka H., Takeuchi H., & Kawashima R . (2014). Regional gray matter volume increases following 7 days of voluntary wheel running exercise: A longitudinal VBM study in rats. Neuroimage, 98, 82-90. |
| [53] | Sun S. W., Liang H. F., Cross A. H., & Song S. K . (2008). Evolving wallerian degeneration after transient retinal ischemia in mice characterized by diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage, 40(1), 1-10. |
| [54] | Tamnes C. K., Walhovd K. B., Dale A. M., Ostby Y., Grydeland H., Richardson G., ... Fjell A. M . (2013). Brain development and aging: Overlapping and unique patterns of change. Neuroimage, 68, 63-74. |
| [55] | Taubert M., Draganski B., Anwander A., Muller K., Horstmann A., Villringer A., & Ragert P . (2010). Dynamic properties of human brain structure: Learning- related changes in cortical areas and associated fiber connections. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(35), 11670-11677. |
| [56] | Tavor I., Botvinik-Nezer R., Bernstein-Eliav M., Tsarfaty G., & Assaf Y . (2019). Short-term plasticity following motor sequence learning revealed by diffusion MRI. bioRxiv, 553628. |
| [57] | Thomas A. G., Marrett S., Saad Z. S., Ruff D. A., Martin A., & Bandettini P. A . (2009). Functional but not structural changes associated with learning: An exploration of longitudinal voxel-based morphometry (VBM). NeuroImage, 48(1), 117-125. |
| [58] | Wang B., Fan Y., Lu M., Li S., Song Z., Peng X., ... Huang R . (2013). Brain anatomical networks in world class gymnasts: A DTI tractography study. Neuroimage, 65, 476-487. |
| [59] | Wang X., Casadio M., Weber K. N., Mussa-Ivaldi F. A., & Parrish T. B . (2014). White matter microstructure changes induced by motor skill learning utilizing a body machine interface. Neuroimage, 88, 32-40. |
| [60] | Wei G., & Luo J . (2010). Sport expert's motor imagery: Functional imaging of professional motor skills and simple motor skills. Brain Research, 1341, 52-62. |
| [61] | Wei G., Luo J., & Li Y . (2009). Brain structure in diving players on MR imaging studied with voxel-based morphometry. Progress in Natural Science, 19(10), 1397-1402. |
| [62] | Wei G., Zhang Y., Jiang T., & Luo J . (2011). Increased cortical thickness in sports experts: A comparison of diving players with the controls. PLoS One, 6(2), e17112. |
| [63] | Westlye L. T., Walhovd K. B., Dale A. M., Bjornerud A., Due-Tonnessen P., Engvig A., ... Fjell A. M . (2010). Life-span changes of the human brain white matter: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and volumetry. Cerebral Cortex, 20(9), 2055-2068. |
| [64] | Wright M. J., Bishop D. T., Jackson R. C., & Abernethy B . (2011). Cortical fMRI activation to opponents' body kinematics in sport-related anticipation: Expert-novice differences with normal and point-light video. Neuroscience Letters, 500(3), 216-221. |
| [65] | Wu Y., Zhang J., Zeng Y., & Shen C . (2015). Structural brain plasticity change in athletes associated with different sports. China Sport Science, 35(4), 52-57. |
| [ 吴殷, 张剑, 曾雨雯, 沈城 . (2015). 不同类型运动项目对运动员大脑结构可塑性变化研究. 体育科学, 35(4), 52-57.] | |
| [66] | Zhang J., Jones M., DeBoy C. A., Reich D. S., Farrell J. A., Hoffman P. N., ... Calabresi P. A . (2009). Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of wallerian degeneration in rat spinal cord after dorsal root axotomy. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(10), 3160-3171. |
| [67] | Zhang Y., Wei G., Zhuo J., Li Y., Ye W., & Jiang T . (2013). Regional inflation of the thalamus and globus pallidus in diving players. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 45(6), 1077-1082. |
| [1] | 郝磊, 许天委, 周文龙, 杨杰, 彭思雅, 刘明兰, 徐家华, 王延培, 谭淑平, 高家红, 贺永, 陶沙, 董奇, 秦绍正. 多种情感与认知任务驱动下大脑可泛化神经表征的发育模式[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(2): 218-231. |
| [2] | 杨子健, 赵小淋, 郭凯格, 罗家豪, 杜腾飞, 张雅洁, 胡月琴, 杨娟. 睡眠效率相关的皮质醇觉醒反应的变异性及其与特质焦虑和心理弹性的关系[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(1): 84-99. |
| [3] | 王婷, 赵梁佛, 杨金朋, 张丹丹, 雷震. 分配意图与上行间接互惠:来自行为与ERP的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(12): 1788-1799. |
| [4] | 陈伟, 姚霖, 倪晓冰, 李俊娇, 吴子悠, 郑希付. 提取暴露时长对恐惧记忆再巩固与消退的调控[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(8): 1076-1090. |
| [5] | 崔一岑, 张易晓, 陈曦梅, 肖明岳, 刘永, 宋诗情, 高笑, 郭成, 陈红. 工具性喂养对9~12岁儿童挑食行为的影响:来自静息态功能磁共振的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(6): 731-744. |
| [6] | 朱怡, 胡谊. 师生互动中组块化反馈促进长时学习迁移:行为和近红外超扫描研究[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(5): 555-576. |
| [7] | 董琳, 叶扬华, 黄慧雅, 李丽娜, 李何慧, 罗跃嘉. 外语阅读焦虑对大脑和小脑阅读网络影响的差异[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(1): 93-106. |
| [8] | 杨周, 朱嘉雯, 苏琳, 熊明洁. 对疼痛线索的晚期注视偏向预测慢性疼痛的维持:来自眼动的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(1): 44-60. |
| [9] | 钟毅平, 牛娜娜, 范伟, 任梦梦, 李梅. 动作自主性与社会距离对主动控制感的影响:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1932-1948. |
| [10] | 徐楚言, 朱麟, 王芸萍, 王瑞冰, 刘聪慧. 外语口语焦虑对言语互动质量的影响:fNIRS超扫描研究[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1949-1965. |
| [11] | 郝子雨, 李欢欢, 林亦轩. 抑郁症自杀未遂者的痛苦逃避与背外侧前额叶−脑岛有效连接特征[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1966-1978. |
| [12] | 尤婷婷, 张利平, 祁国梅, 龙长权. 机会公平在早期加工阶段影响个体实际结果的评价[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1997-2012. |
| [13] | 李梅, 李琎, 张冠斐, 钟毅平, 李红. 承诺水平与社会距离对信任投资的影响:来自行为与ERPs的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(11): 1859-1871. |
| [14] | 覃慧怡, 丁丽洪, 段威, 雷旭. 脑电的重测信度:在多项静息态和任务态实验中的对比[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(10): 1587-1596. |
| [15] | 曹衍淼, 方惠慈, 朱欣悦, 纪林芹, 张文新. BDNF基因、同伴关系与青少年早期抑郁:基于动态发展视角[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(10): 1620-1636. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||