

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1228-1238.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2023.01228 cstr: 32111.14.2023.01228
收稿日期:2022-10-18
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-04-23
通讯作者:
陈静, E-mail: jing2520@gmail.com
CHEN Jing( ), ZHANG Manlu, LI Yuyang
), ZHANG Manlu, LI Yuyang
Received:2022-10-18
Online:2023-07-15
Published:2023-04-23
摘要:
身体活动当量标签(physical activity calorie equivalent, PACE)提供关于食物的两种信息, 即能量值以及消耗该能量所需要的身体活动量, 它被认为是一种应对日益严重的肥胖问题的有效策略。PACE标签可以有效降低消费者在实验室实验和现场实验中的不健康食物选择和能量摄入, 促进健康食物的选择, 同时提高运动意愿和运动行为, 即PACE标签可以促进健康行为。PACE标签起效应的认知机制包括两条路径, 即PACE标签−心理模拟−情绪−行为路径和PACE标签−心理模拟−健康目标−行为路径。未来研究可以进一步深入探讨两条路径的适用群体和适用条件, PACE标签可能产生的消极影响, 以及综合不同的饮食干预和调节方法帮助消费者形成可持续的健康饮食习惯和运动习惯。
中图分类号:
陈静, 章曼露, 李雨阳. (2023). 管住嘴迈开腿:身体活动当量标签促进健康行为及其认知机制. 心理科学进展 , 31(7), 1228-1238.
CHEN Jing, ZHANG Manlu, LI Yuyang. (2023). The promotive effect of Physical activity calorie equivalent (PACE) labels on healthy behaviors and its cognitive mechanisms. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(7), 1228-1238.
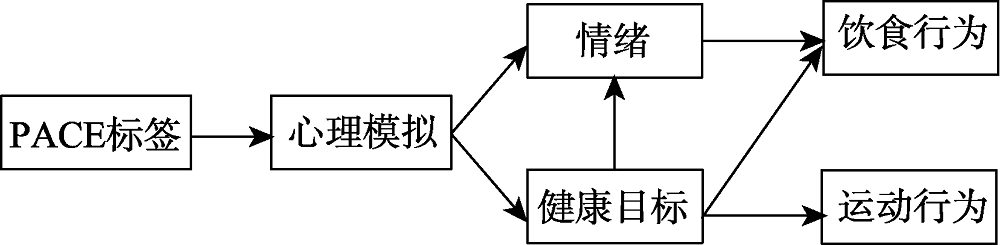
图1 PACE标签促进健康行为的认知模型。 注:该模型包含两条路径, 第一条路径为PACE标签−心理模拟−情绪−行为路径, 即PACE标签通过心理模拟, 影响个体对摄入食物的情绪反应, 从而影响饮食行为。第二条路径为PACE标签−心理模拟−健康目标−行为路径, 即PACE标签通过心理模拟, 激活个体的健康目标, 进一步影响后续的饮食行为和运动相关行为; 同时健康目标的激活也可能进一步影响个体对摄入食物的情绪反应, 进而影响被试的食物决策和行为。
| [1] |
耿晓伟, 张峰, 王艳净, 范琳琳, 姚艳. (2018). 健康目标启动降低高热量食物消费. 心理学报, 50(8), 840-847.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2018.00840 |
| [2] |
李佳洁, 于彤彤. (2020). 基于助推的健康饮食行为干预策略. 心理科学进展, 28(12), 2052-2063.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.02052 |
| [3] | 李开云, 许利慧, 禤宇明, 傅小兰. (2015). 暗示性运动加工的认知神经机制. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 42(6), 519-532. |
| [4] |
Abarca-Gómez, L., Abdeen, Z. A., Hamid, Z. A., Abu- Rmeileh, N. M., Acosta-Cazares, B., Acuin, C., … Ezzati, M. (2017). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet, 390(10113), 2627-2642.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 URL |
| [5] |
Andersson, E. K., & Moss, T. P. (2011). Imagery and implementation intention: A randomised controlled trial of interventions to increase exercise behaviour in the general population. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 12(2), 63-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2010.07.004 URL |
| [6] | Antonelli, R., & Viera, A. J. (2015). Potential effect of physical activity calorie equivalent (PACE) labeling on adult fast food ordering and exercise. PLoS ONE, 10(7), e0134289. |
| [7] |
Barsalou, L. W. (2003). Situated simulation in the human conceptual system. Language and Cognitive Processes, 18(5-6), 513-562.
doi: 10.1080/01690960344000026 URL |
| [8] |
Barsalou, L. W. (2008). Grounded cognition. Annual Review of Psychology, 59, 617-645.
pmid: 17705682 |
| [9] |
Bleich, S. N., Herring, B. J., Flagg, D. D., & Gary-Webb, T. L. (2012). Reduction in purchases of sugar-sweetened beverages among low-income black adolescents after exposure to caloric information. American Journal of Public Health, 102(2), 329-335.
doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300350 pmid: 22390447 |
| [10] |
Breathnach, S., Koutoukidis, D. A., Lally, P., Boniface, D., Sutherland, A., & Llewellyn, C. H. (2021). The effect of messaging on the acceptance of swaps to reduce the energy content of snacks and non-alcoholic drinks ordered in an experimental online workplace canteen: A randomised controlled trial. Appetite, 162, 105171.
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2021.105171 URL |
| [11] | Breathnach, S., Llewellyn, C. H., Koutoukidis, D. A., van Rugge, C. R., Sutherland, A., & Lally, P. (2020). Experience of using an online pre-ordering system for a workplace canteen that offers lower-energy swaps: A think-aloud study. Nutrients, 12(12), 3878. |
| [12] |
Brown, H. M., Rollo, M. E., de Vlieger, N. M., Collins, C. E., & Bucher, T. (2018). Influence of the nutrition and health information presented on food labels on portion size consumed: A systematic review. Nutrition Reviews, 76(9), 655-677.
doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy019 pmid: 29767760 |
| [13] | Buckland, N. J., Er, V., Redpath, I., & Beaulieu, K. (2018). Priming food intake with weight control cues: Systematic review with a meta-analysis. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 15(1), 66. |
| [14] |
Cameron, L. D., & Chan, C. K. Y. (2008). Designing health communications: Harnessing the power of affect, imagery, and self-regulation. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2(1), 262-282.
doi: 10.1111/spco.2008.2.issue-1 URL |
| [15] |
Campos, S., Doxey, J., & Hammond, D. (2011). Nutrition labels on pre-packaged foods: A systematic review. Public Health Nutrition, 14(8), 1496-1506.
doi: 10.1017/S1368980010003290 pmid: 21241532 |
| [16] |
Cecchini, M., & Warin, L. (2016). Impact of food labelling systems on food choices and eating behaviours: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized studies. Obesity Reviews, 17(3), 201-210.
doi: 10.1111/obr.12364 pmid: 26693944 |
| [17] |
Chen, J., Papies, E. K., & Barsalou, L. W. (2016). A core eating network and its modulations underlie diverse eating phenomena. Brain and Cognition, 110, 20-42.
doi: S0278-2626(16)30033-1 pmid: 27156016 |
| [18] |
Conroy, D., & Hagger, M. S. (2018). Imagery interventions in health behavior: A meta-analysis. Health Psychology, 37(7), 668-679.
doi: 10.1037/hea0000625 pmid: 29809020 |
| [19] | Cumming, J., & Williams, S. E. (2012). The role of imagery in performance. In S. M. Murphy (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of sport and performance psychology (pp. 213-232). Oxford University Press. |
| [20] |
Daley, A. J., McGee, E., Bayliss, S., Coombe, A., & Parretti, H. M. (2020). Effects of physical activity calorie equivalent food labelling to reduce food selection and consumption: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled studies. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 74(3), 269-275.
doi: 10.1136/jech-2019-213216 pmid: 31822568 |
| [21] | Deery, C. B., Hales, D., Viera, L., Lin, F.-C., Liu, Z., Olsson, E.,... Viera, A. J. (2019). Physical activity calorie expenditure (PACE) labels in worksite cafeterias: Effects on physical activity. BMC Public Health, 19(1), 1596. |
| [22] |
Dowray, S., Swartz, J. J., Braxton, D., & Viera, A. J. (2013). Potential effect of physical activity based menu labels on the calorie content of selected fast food meals. Appetite, 62, 173-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2012.11.013 pmid: 23220355 |
| [23] |
Duncan, L. R., Hall, C. R., Wilson, P. M., & Rodgers, W. M. (2012). The use of a mental imagery intervention to enhance integrated regulation for exercise among women commencing an exercise program. Motivation and Emotion, 36(4), 452-464.
doi: 10.1007/s11031-011-9271-4 URL |
| [24] | Elbel, B., Kersh, R., Brescoll, V. L., & Dixon, L. B. (2009). Calorie labeling and food choices:A first look at the effects on low-income people in New York city. Health Affairs, 28(6), w1110-w1121. |
| [25] |
Evans, A. E., Weiss, S. R., Meath, K. J., Chow, S., Vandewater, E. A., & Ness, R. B. (2016). Adolescents’ awareness and use of menu labels in eating establishments: Results from a focus group study. Public Health Nutrition, 19(5), 830-840.
doi: 10.1017/S1368980015001044 URL |
| [26] |
Gordon-Larsen, P., Wang, H., & Popkin, B. M. (2014). Overweight dynamics in Chinese children and adults. Obesity Reviews, 15(S1), 37-48.
doi: 10.1111/obr.2014.15.issue-s1 URL |
| [27] |
Gortmaker, S. L., Swinburn, B. A., Levy, D., Carter, R., Mabry, P. L., Finegood, D. T.,... Moodie, M. L. (2011). Changing the future of obesity: Science, policy, and action. The Lancet, 378(9793), 838-847.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60815-5 URL |
| [28] |
Greitemeyer, T., & Würz, D. (2006). Mental simulation and the achievement of health goals: The role of goal difficulty. Imagination, Cognition and Personality, 25(3), 239-251.
doi: 10.2190/D4UA-RQFQ-0H5T-W9YY URL |
| [29] | Hartley, C., Keast, R. S., & Liem, D. G. (2019). The response of more health focused and less health focused people to a physical activity calorie equivalent label on discretionary snack foods. Nutrients, 11(3), 525. |
| [30] |
Hartley, I. E., Keast, R. S., & Liem, D. G. (2018). Physical activity-equivalent label reduces consumption of discretionary snack foods. Public Health Nutrition, 21(8), 1435-1443.
doi: 10.1017/S1368980018000228 pmid: 29493474 |
| [31] |
Hill, J. O., & Peters, J. C. (1998). Environmental contributions to the obesity epidemic. Science, 280(5368), 1371-1374.
doi: 10.1126/science.280.5368.1371 pmid: 9603719 |
| [32] |
Hill, J. O., Wyatt, H. R., Reed, G. W., & Peters, J. C. (2003). Obesity and the environment: Where do we go from here? Science, 299(5608), 853-855.
doi: 10.1126/science.1079857 pmid: 12574618 |
| [33] | Huang, Y., Yang, X., & Chen, Q. (2022). The negative effects of long time physical activity calorie equivalent labeling on purchase intention for unhealthy food. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(6), 3463. |
| [34] |
Inauen, J., Radtke, T., Rennie, L., Scholz, U., & Orbell, S. (2018). Transfer or compensation? An experiment testing the effects of actual and imagined exercise on eating behavior. Swiss Journal of Psychology, 77(2), 59-67.
doi: 10.1024/1421-0185/a000207 URL |
| [35] |
James, A., Adams-Huet, B., & Shah, M. (2015). Menu labels displaying the kilocalorie content or the exercise equivalent: Effects on energy ordered and consumed in young Adults. American Journal of Health Promotion, 29(5), 294-302.
doi: 10.4278/ajhp.130522-QUAN-267 pmid: 24575727 |
| [36] |
Jin, H., Li, Y.-N., Li, D., & Zheng, J. (2020). The effects of physical activity calorie equivalent labeling on dieters’ food consumption and post-consumption physical activity. Journal of Consumer Affairs, 54(2), 723-741.
doi: 10.1111/joca.v54.2 URL |
| [37] |
Kim, B. H., Newton, R. A., Sachs, M. L., Giacobbi, P. R., & Glutting, J. J. (2011). The Effect of guided relaxation and exercise imagery on self-reported leisure-time exercise behaviors in older adults. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, 19(2), 137-146.
doi: 10.1123/japa.19.2.137 pmid: 21558568 |
| [38] |
Kleinert, S., & Horton, R. (2019). Obesity needs to be put into a much wider context. The Lancet, 393(10173), 724-726.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)33192-1 URL |
| [39] |
Kooij, D. T. A. M., Kanfer, R., Betts, M., & Rudolph, C. W. (2018). Future time perspective: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103(8), 867-893.
doi: 10.1037/apl0000306 pmid: 29683685 |
| [40] | Kossert, A. L., & Munroe-Chandler, K. (2007). Exercise imagery: A systematic review of the empirical literature. Journal of Imagery Research in Sport and Physical Activity, 2(1). |
| [41] |
Kumanyika, S. K., Obarzanek, E., Stettler, N., Bell, R., Field, A. E., Fortmann, S. P.,... Hong, Y. (2008). Population- based prevention of obesity. Circulation, 118(4), 428-464.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.189702 pmid: 18591433 |
| [42] |
Lee, M. S., & Thompson, J. K. (2016). Exploring enhanced menu labels’ influence on fast food selections and exercise- related attitudes, perceptions, and intentions. Appetite, 105, 416-422.
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2016.06.007 URL |
| [43] |
Masic, U., Christiansen, P., & Boyland, E. J. (2017). The influence of calorie and physical activity labelling on snack and beverage choices. Appetite, 112, 52-58.
doi: S0195-6663(17)30028-4 pmid: 28082195 |
| [44] | Mason, F., Farley, A., Pallan, M., Sitch, A., Easter, C., & Daley, A. J. (2018). Effectiveness of a brief behavioural intervention to prevent weight gain over the Christmas holiday period: Randomised controlled trial. The BMJ, 363, k4867. |
| [45] |
Mata, J., Silva, M. N., Vieira, P. N., Carraça, E. V., Andrade, A. M., Coutinho, S. R., Sardinha, L. B., & Teixeira, P. J. (2009). Motivational “spill-over” during weight control: Increased self-determination and exercise intrinsic motivation predict eating self-regulation. Health Psychology, 28(6), 709-716.
doi: 10.1037/a0016764 URL |
| [46] | Mehlhose, C., Schmitt, D., & Risius, A. (2021). PACE labels on healthy and unhealthy snack products in a laboratory shopping setting: Perception, visual Attention, and product choice. Foods, 10(4), 904. |
| [47] |
Montford, W. J., Peloza, J., & Goldsmith, R. E. (2017). No pain, no gain: How PACE information attenuates consumption. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 34(7), 525-540.
doi: 10.1108/JCM-10-2016-1974 URL |
| [48] |
Nikolova, H. D., & Inman, J. J. (2015). Healthy choice: The effect of simplified point-of-sale nutritional information on consumer food choice behavior. Journal of Marketing Research, 52(6), 817-835.
doi: 10.1509/jmr.13.0270 URL |
| [49] |
Okada, E. M. (2019). Differential construal of exercise versus diet and implications for weight Control. Journal of Consumer Research, 46(3), 528-544.
doi: 10.1093/jcr/ucy080 URL |
| [50] |
Oliveira, D., de Steur, H., Lagast, S., Gellynck, X., & Schouteten, J. J. (2020). The impact of calorie and physical activity labelling on consumer’s emo-sensory perceptions and food choices. Food Research International, 133, 109166.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109166 URL |
| [51] | Pan, X. F., Wang, L., & Pan, A. (2021). Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 9(6), 373-392. |
| [52] |
Pang, J., & Hammond, D. (2013). Efficacy and consumer preferences for different approaches to calorie labeling on menus. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 45(6), 669-675.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneb.2013.06.005 pmid: 23928179 |
| [53] |
Papies, E. K. (2016). Health goal priming as a situated intervention tool: How to benefit from nonconscious motivational routes to health behaviour. Health Psychology Review, 10(4), 408-424.
pmid: 27144729 |
| [54] | Piqueras-Fiszman, B. (2020). The psychology of food choice:Anticipation and mental simulation. In H. L. Meiselman (Ed.), Handbook of eating and drinking: Interdisciplinary perspectives (pp. 185-198)Springer International Publishing. |
| [55] | Platkin, C., Yeh, M.-C., Hirsch, K., Wiewel, E. W., Lin, C.-Y., Tung, H.-J., & Castellanos, V. H. (2014). The effect of menu labeling with calories and exercise equivalents on food selection and consumption. BMC Obesity, 1(1), 21. |
| [56] | Proverbio, A. M., Riva, F., & Zani, A. (2009). Observation of static pictures of dynamic actions enhances the activity of movement-related brain areas. PLoS ONE, 4(5), e5389. |
| [57] | Razon, S. (2012). The effects of imagery on perceived exertion, attention, and exercise adherence (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Florida State University. |
| [58] | Reale, S., & Flint, S. W. (2016). Menu labelling and food choice in obese adults: A feasibility study. BMC Obesity, 3(1), 17. |
| [59] |
Renner, F., Murphy, F. C., Ji, J. L., Manly, T., & Holmes, E. A. (2019). Mental imagery as a “motivational amplifier” to promote activities. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 114, 51-59.
doi: S0005-7967(19)30019-1 pmid: 30797989 |
| [60] | Reynolds, J. P., Ventsel, M., Hobson, A., Pilling, M. A., Pechey, R., Jebb, S. A., Hollands, G. J., & Marteau, T. M. (2022). Effect of physical activity calorie equivalent (PACE) labels on energy purchased in cafeterias: A stepped- wedge randomised controlled trial. medRxiv, 2022-02. |
| [61] |
Robinson, E., Smith, J., & Jones, A. (2022). The effect of calorie and physical activity equivalent labelling of alcoholic drinks on drinking intentions in participants of higher and lower socioeconomic position: An experimental study. British Journal of Health Psychology, 27(1), 30-49.
doi: 10.1111/bjhp.v27.1 URL |
| [62] | Rodearmel, S. J., Wyatt, H. R., Stroebele, N., Smith, S. M., Ogden, L. G., & Hill, J. O. (2007). Small changes in dietary sugar and physical activity as an approach to preventing excessive weight gain: The America on the Move family study. Pediatrics, 120(4), e869-e879. |
| [63] |
Rozin, P., & Royzman, E. B. (2001). Negativity bias, negativity dominance, and contagion. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 5(4), 296-320.
doi: 10.1207/S15327957PSPR0504_2 URL |
| [64] |
Scourboutakos, M. J., Mah, C. L., Murphy, S. A., Mazza, F. N., Barrett, N., McFadden, B., & L’Abbé, M. R. (2017). Testing a beverage and fruit/vegetable education intervention in a university dining hall. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 49(6), 457-465.
doi: S1499-4046(17)30069-6 pmid: 28363803 |
| [65] | Seyedhamzeh, S., Bagheri, M., Keshtkar, A. A., Qorbani, M., & Viera, A. J. (2018). Physical activity equivalent labeling vs. calorie labeling: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 15(1), 88. |
| [66] |
Shah, M., Bouza, B., Adams-Huet, B., Jaffery, M., Esposito, P., & Dart, L. (2016). Effect of calorie or exercise labels on menus on calories and macronutrients ordered and calories from specific foods in Hispanic participants: A randomized study. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 64(8), 1261-1268.
pmid: 27402619 |
| [67] | Swartz, J. J., Dowray, S., Braxton, D., Mihas, P., & Viera, A. J. (2013). Simplifying healthful choices: A qualitative study of a physical activity based nutrition label format. Nutrition Journal, 12(1), 72. |
| [68] |
Temple, N. J. (2020). Front-of-package food labels: A narrative review. Appetite, 144, 104485.
doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2019.104485 URL |
| [69] |
Urgesi, C., Moro, V., Candidi, M., & Aglioti, S. M. (2006). Mapping implied body actions in the human motor system. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(30), 7942-7949.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1289-06.2006 pmid: 16870739 |
| [70] | Viera, A. J., & Antonelli, R. (2015). Potential effect of physical activity calorie equivalent labeling on parent fast food decisions. Pediatrics, 135(2), e376-e382. |
| [71] | Viera, A. J., Gizlice, Z., Tuttle, L., Olsson, E., Gras-Najjar, J., Hales, D.,... Ammerman, A. (2019). Effect of calories- only vs physical activity calorie expenditure labeling on lunch calories purchased in worksite cafeterias. BMC Public Health, 19(1), 107. |
| [72] |
Wadden, T. A., Brownell, K. D., & Foster, G. D. (2002). Obesity: Responding to the global epidemic. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70(3), 510-525.
doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.70.3.510 pmid: 12090366 |
| [73] |
Wang, L., Zhou, B., Zhao, Z., Yang, L., Zhang, M., Jiang, Y.,... Li, X. (2021). Body-mass index and obesity in urban and rural China: Findings from consecutive nationally representative surveys during 2004-18. The Lancet, 398(10294), 53-63.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00798-4 URL |
| [74] | Wang, Y., Wang, L., Xue, H., & Qu, W. (2016). A review of the growth of the fast food industry in China and its potential impact on obesity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(11), 1112. |
| [75] |
Wolfson, J. A., Graham, D. J., & Bleich, S. N. (2017). Attention to physical activity-equivalent calorie information on nutrition facts labels: An eye-tracking investigation. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 49(1), 35-42.
doi: S1499-4046(16)30835-1 pmid: 27865642 |
| [76] | Yang, X., Huang, Y., Han, M., Wen, X., Zheng, Q., Chen, Q., & Chen, Q. (2021). The differential effects of physical activity calorie equivalent labeling on consumer preferences for healthy and unhealthy food products: Evidence from a choice experiment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1860. |
| [77] |
Zeelenberg, M., Nelissen, R. M. A., Breugelmans, S. M., & Pieters, R. (2008). On emotion specificity in decision making: Why feeling is for doing. Judgment and Decision Making, 3(1), 18-27.
doi: 10.1017/S1930297500000139 URL |
| [78] |
Zhang, X., Zhang, M., Zhao, Z., Huang, Z., Deng, Q., Li, Y., … Wang, L. (2020). Geographic variation in prevalence of adult obesity in China: Results from the 2013- 2014 national chronic disease and risk factor surveillance. Annals of Internal Medicine, 172(4), 291-293.
doi: 10.7326/M19-0477 pmid: 31658469 |
| [1] | 郭艺, 张连成, 陶莹莹, 朱良昊, 王婷. BDNF是运动促进认知的生物学机制吗?证据、挑战与展望[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(3): 465-476. |
| [2] | 梁淑静, 杨光勇. 穷则思变, 富则思安? 金钱稀缺与富足感知对个体风险决策的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(8): 1233-1249. |
| [3] | 苏瑞, 王成志, 李昊, 马海林, 苏彦捷. 高原运动对认知功能的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(5): 800-812. |
| [4] | 褚昕宇, 王泽军. 竞技运动专家的认知优势及其形成机制——基于自动性特点和抽象化表征[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(4): 689-699. |
| [5] | 胡砚冰, 蒋晓鸣. 嗓音模仿认知神经加工的多阶段模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(3): 499-513. |
| [6] | 赵一帆, 李君君, 毕鸿燕. 视觉运动整合能力与阅读关系的发展[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(12): 2091-2099. |
| [7] | 杨颖华, 山周魁东, 李黎. 不同视觉线索对外界物体与自身运动判断的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 21-21. |
| [8] | 高芷晗, 王蕊, 蒋毅. 基于局部生物运动方向的适应后效[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 24-24. |
| [9] | 谢明阳, 李黎. 光流解析并不优先于深度运动感知[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 29-29. |
| [10] | 盛槿滺, 高在峰. 时间间隔对感知人人社会交互的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 37-37. |
| [11] | 周钧毅, 许文鑫. 不同运动水平青少年足球运动员的眼动特征差异:来自朝向眼跳任务的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 55-55. |
| [12] | 连玉净, 汪海玲. 面孔运动影响面孔整体加工[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 57-57. |
| [13] | 卞瑞晨, 郑晨豪, 周梁. 利用包含事件偏移的拍子同步范式比较视觉运动刺激与听觉刺激对动作的诱导作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 58-58. |
| [14] | 李丹, 姜霏霏, 邓栩瀛, 潘静. 视觉关联在双人协同运动中的作用:周期和速度变异性的变化趋势[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 60-60. |
| [15] | 姜一馨, 耿晓丽, 王悦, 周梁. 探究听力障碍者视觉运动拍子同步能力的表现和发展[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 62-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||