

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 255-267.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.00255 cstr: 32110.14.2024.00255
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-03-28
发布日期:2023-12-11
出版日期:2024-03-25
通讯作者:
周可, E-mail: kzhou@bnu.edu.cn;基金资助:
LIU Yujie1,2, LIU Chenmiao3, ZHOU Liqin3( ), ZHOU Ke3(
), ZHOU Ke3( )
)
Received:2023-03-28
Online:2023-12-11
Published:2024-03-25
摘要:
序列依赖效应反映了当前的知觉体验不仅取决于当下的刺激输入, 还受到近期历史的影响。这一效应对于我们在动态变化的环境中形成相对稳定的知觉至关重要。本研究使用点阵作为刺激材料, 在数量/面积(实验1)或数量/大小(实验2)两个维度上进行正交设计, 旨在通过估计任务探索任务相关性如何影响线性分布特征的序列依赖效应。结果显示无论特征是否与任务相关, 前一试次与当前试次同一特征总会对当前试次的知觉产生相反的影响。对于任务相关特征, 前一试次产生的序列依赖始终为排斥效应。而对于任务无关特征, 如果在当前试次中无关特征对被试的知觉反应有正向预测作用, 则前一试次无关特征产生排斥的序列依赖效应; 反之, 如果在当前试次中无关特征对被试的知觉反应有负向预测, 则前一试次无关特征产生吸引的序列依赖效应。任务相关性对序列依赖效应的影响主要体现在效应幅值的降低。这些发现揭示了线性分布特征的序列依赖效应受任务相关性以及特征本身特性的共同影响, 而无关特征的序列依赖效应则暗示在客体水平也可以产生序列依赖效应。
中图分类号:
刘雨杰, 刘晨淼, 周丽琴, 周可. (2024). 任务相关性对数量感序列依赖效应的影响. 心理学报, 56(3), 255-267.
LIU Yujie, LIU Chenmiao, ZHOU Liqin, ZHOU Ke. (2024). The effect of task relevance on serial dependence in numerosity. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(3), 255-267.
| 实验 | 任务 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1 | 数量估计任务 | 8533 | 8158 | 8589 | 8052 |
| 面积估计任务 | 11713 | 10882 | 11838 | 10713 | |
| 实验2 | 数量估计任务 | 9638 | 9621 | 9721 | 9493 |
| 大小估计任务 | 19002 | 18183 | 19200 | 17936 |
表1 各模型BIC值
| 实验 | 任务 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1 | 数量估计任务 | 8533 | 8158 | 8589 | 8052 |
| 面积估计任务 | 11713 | 10882 | 11838 | 10713 | |
| 实验2 | 数量估计任务 | 9638 | 9621 | 9721 | 9493 |
| 大小估计任务 | 19002 | 18183 | 19200 | 17936 |
| 实验 | 任务 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1 | 数量估计任务 | 7661 | 7166 | 7783 | 6943 |
| 面积估计任务 | 9823 | 8651 | 10066 | 8239 | |
| 实验2 | 数量估计任务 | 8896 | 8806 | 9041 | 8572 |
| 大小估计任务 | 17604 | 16523 | 17902 | 16070 |
表2 各模型MSE值
| 实验 | 任务 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验1 | 数量估计任务 | 7661 | 7166 | 7783 | 6943 |
| 面积估计任务 | 9823 | 8651 | 10066 | 8239 | |
| 实验2 | 数量估计任务 | 8896 | 8806 | 9041 | 8572 |
| 大小估计任务 | 17604 | 16523 | 17902 | 16070 |
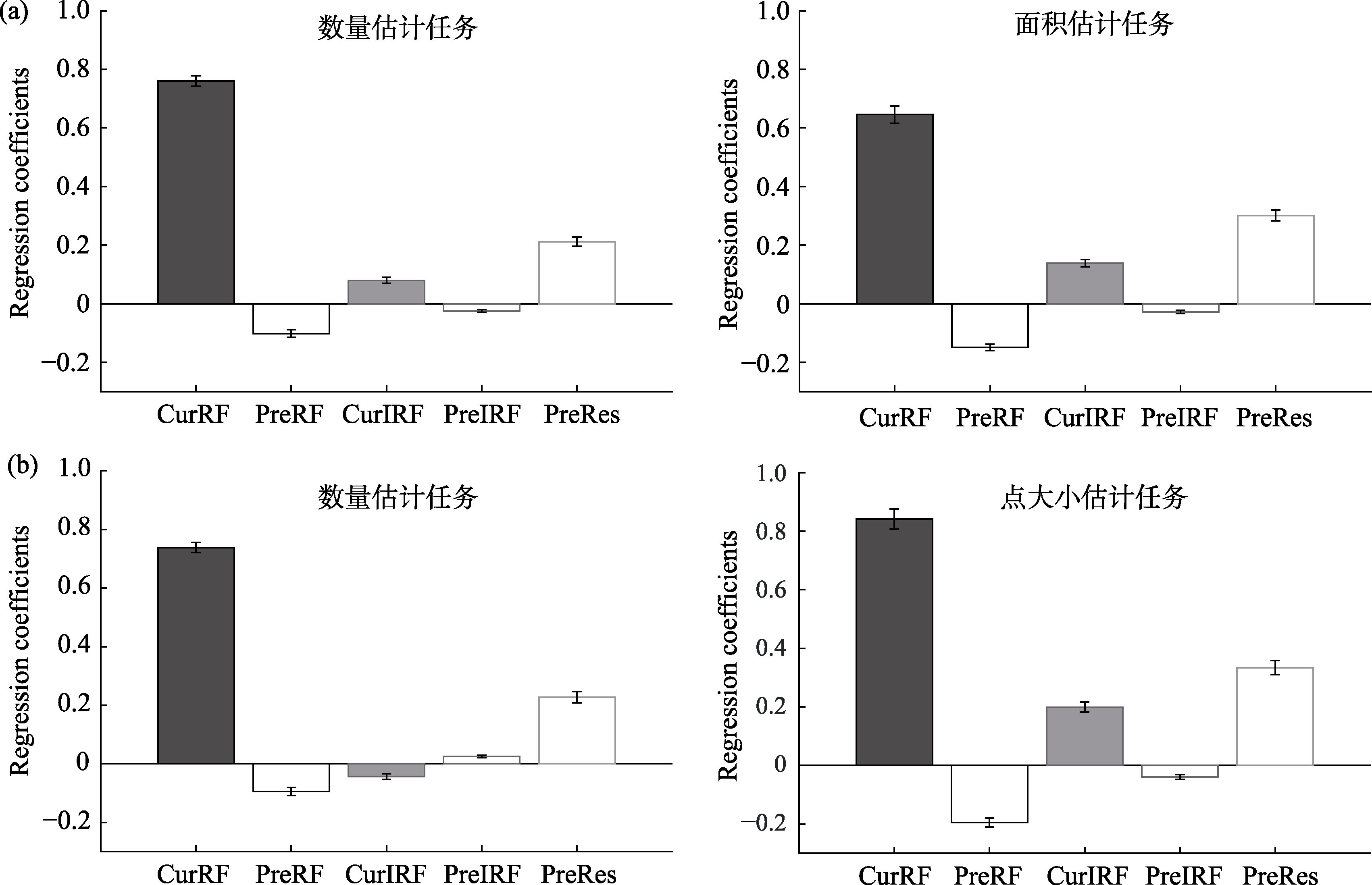
图2 (a)实验1两个任务全模型的各自变量的回归系数(β)值。CurRF (Current Relevant Feature)为当前任务相关特征, 例如在数量估计任务中是指当前刺激点阵中点的个数; PreRF (Previous Relevant Feature)为前一试次任务相关特征, 例如在数量估计任务中是指上一试次的刺激点阵中点的个数; CurIRF (Current Irrelevant Feature)为当前任务无关特征, 例如在数量估计任务中是指当前刺激点阵的面积; PreIRF (Previous Irrelevant Feature)为前一试次任务无关特征, 例如在数量估计任务中是指上一试次的刺激点阵的面积; PreRes (Previous Response)为前一试次被试估计值, 例如在数量估计任务中是指被试对上一试次中刺激点阵的点的个数的估计值。图中误差线代表β值的一倍标准误(Standard Error, SE); (b)实验2两个任务全模型的各自变量的回归系数(β)值。
| [1] | Adelson, E. H., & Bergen, J. R. (1991). The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision. In M. S.Landy & J. A.Movshon (Eds.), Computational models of visual processing (pp. 3-20). The MIT Press. |
| [2] | Agrillo, C., Petrazzini, M. E. M., & Bisazza, A. (2016). Number versus continuous quantities in lower vertebrates. In A.Henik (Ed.), Continuous issues in numerical cognition (pp. 149-174). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801637-4.00007-X |
| [3] |
Anobile, G., Cicchini, G. M., & Burr, D. C. (2012). Linear mapping of numbers onto space requires attention. Cognition, 122(3), 454-459. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2011.11.006
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2011.11.006 URL pmid: 22154543 |
| [4] |
Barbosa, J., & Compte, A. (2020). Build-up of serial dependence in color working memory. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 10959. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67861-2
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67861-2 URL pmid: 32616792 |
| [5] |
Bolker, B. M., Brooks, M. E., Clark, C. J., Geange, S. W., Poulsen, J. R., Stevens, M. H. H., & White, J. S. S. (2009). Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 24(3), 127-135.
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2008.10.008 URL |
| [6] |
Brainard, D. H. (1997). The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision, 10(4), 433-436.
pmid: 9176952 |
| [7] | Burnham, K. P., & Anderson, D. R. (2004). Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociological Methods & Research, 33(2), 261-304. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124104268644 |
| [8] |
Cantlon, J. F., Platt, M. L. & Brannon, E. M. (2009). Beyond the number domain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13(2), 83-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.11.007 pmid: 19131268 |
| [9] | Castaldi, E., Mirassou, A., Dehaene, S., Piazza, M., & Eger, E. (2018). Asymmetrical interference between number and item size perception provides evidence for a domain specific impairment in dyscalculia. Plos One, 13(12), e209256. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209256 |
| [10] |
Cicchini, G. M., Anobile, G., & Burr, D. C. (2014). Compressive mapping of number to space reflects dynamic encoding mechanisms, not static logarithmic transform. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(21), 7867-7872. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1402785111
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402785111 URL |
| [11] |
Cicchini, G. M., Benedetto, A., & Burr, D. C. (2021). Perceptual history propagates down to early levels of sensory analysis. Current Biology, 31(6), 1245-1250.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.12.004 URL |
| [12] |
Cicchini, G. M., Mikellidou, K., & Burr, D. (2017). Serial dependencies act directly on perception. Journal of Vision, 17(14), 6. http://doi.org/10.1167/17.14.6
doi: 10.1167/17.14.6 URL pmid: 29209696 |
| [13] | Cicchini, G. M., Mikellidou, K., & Burr, D. C. (2018). The functional role of serial dependence. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 285(1890). http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.1722 |
| [14] |
Collins, T. (2022a). Serial dependence occurs at the level of both features and integrated object representations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 151(8), 1821-1832. http://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001159
doi: 10.1037/xge0001159 URL |
| [15] | Collins, T. (2022b). Serial dependence tracks objects and scenes in parallel and independently. Journal of Vision, 22(7), 4. http://doi.org/10.1167/jov.22.7.4 |
| [16] | Cremers, J. (2021). bpnreg: Bayesian projected normal regression models for circular data (2.0.2) [Computer software]. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/bpnreg/index.html |
| [17] | Cremers, J., & Klugkist, I. (2018). One direction? A tutorial for circular data analysis using R with examples in cognitive psychology. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 2040. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02040 |
| [18] |
Dehaene, S. (2002). Précis of the number sense. Mind & Language, 16(1), 16-36.
doi: 10.1111/mila.2001.16.issue-1 URL |
| [19] |
de Marco, D., & Cutini, S. (2020). Introducing CUSTOM: A customized, ultraprecise, standardization-oriented, multipurpose algorithm for generating nonsymbolic number stimuli. Behavior Research Methods, 52(4), 1528-1537. http://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-019-01332-z
doi: 10.3758/s13428-019-01332-z URL pmid: 31965476 |
| [20] |
DeWind, N. K., Adams, G. K., Platt, M. L., & Brannon, E. M. (2015). Modeling the approximate number system to quantify the contribution of visual stimulus features. Cognition, 142, 247-265. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2015.05.016
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2015.05.016 URL pmid: 26056747 |
| [21] |
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149-1160. http://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149
doi: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149 URL pmid: 19897823 |
| [22] |
Fischer, C., Czoschke, S., Peters, B., Rahm, B., Kaiser, J., & Bledowski, C. (2020). Context information supports serial dependence of multiple visual objects across memory episodes. Nature Communications, 11(1), 1932. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15874-w
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15874-w URL pmid: 32321924 |
| [23] |
Fischer, J., & Whitney, D. (2014). Serial dependence in visual perception. Nature Neuroscience, 17(5), 738-743. http://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3689
doi: 10.1038/nn.3689 URL pmid: 24686785 |
| [24] | Fisher, N. I. (1995). Statistical analysis of circular data. Cambridge University Press. |
| [25] |
Fisher, N. I., & Lee, A. J. (1992). Regression models for an angular response. Biometrics, 48(3), 665-677. https://doi.org/10.2307/2532334
doi: 10.2307/2532334 URL |
| [26] |
Flesch, T., Juechems, K., Dumbalska, T., Saxe, A., & Summerfield, C. (2022). Orthogonal representations for robust context-dependent task performance in brains and neural networks. Neuron, 110(7), 1258-1270. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.005
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.005 URL pmid: 35085492 |
| [27] |
Fornaciai, M., & Park, J. (2018a). Attractive serial dependence in the absence of an explicit task. Psychological Science, 29(3), 437-446. http://doi.org/10.1177/0956797617737385
doi: 10.1177/0956797617737385 URL |
| [28] | Fornaciai, M., & Park, J. (2018b). Serial dependence in numerosity perception. Journal of Vision, 18(9), 15. http://doi.org/10.1167/18.9.15 |
| [29] |
Fornaciai, M., & Park, J. (2019a). Serial dependence generalizes across different stimulus formats, but not different sensory modalities. Vision Research, 160, 108-115. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2019.04.011
doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2019.04.011 URL |
| [30] | Fornaciai, M., & Park, J. (2019b). Spontaneous repulsive adaptation in the absence of attractive serial dependence. Journal of Vision, 19(5), 21. http://doi.org/10.1167/19.5.21 |
| [31] |
Fornaciai, M., & Park, J. (2020). Attractive serial dependence between memorized stimuli. Cognition, 200, 104250. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2020.104250
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2020.104250 URL |
| [32] |
Fornaciai, M., Togoli, I., & Bueti, D. (2023). Perceptual history biases are predicted by early visual-evoked activity. Journal of Neuroscience, 43(21), 3860-3875.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1451-22.2023 pmid: 37085319 |
| [33] |
Franconeri, S. L., Bemis, D. K., & Alvarez, G. A. (2009). Number estimation relies on a set of segmented objects. Cognition, 113(1), 1-13. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2009.07.002
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2009.07.002 URL pmid: 19647817 |
| [34] |
Fritsche, M., & de Lange, F. P. (2019). The role of feature-based attention in visual serial dependence. Journal of Vision, 19(13), 21. http://doi.org/10.1167/19.13.21
doi: 10.1167/19.13.21 URL pmid: 31770772 |
| [35] |
Fritsche, M., Mostert, P., & de Lange, F. P. (2017). Opposite effects of recent history on perception and decision. Current Biology, 27(4), 590-595. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.006
doi: S0960-9822(17)30006-4 URL pmid: 28162897 |
| [36] |
Gekas, N., McDermott, K. C., & Mamassian, P. (2019). Disambiguating serial effects of multiple timescales. Journal of Vision, 19(6), 24. http://doi.org/10.1167/19.6.24
doi: 10.1167/19.6.24 URL pmid: 31251808 |
| [37] |
Gross, H. J., Pahl, M., Si, A., Zhu, H., Tautz, J., & Zhang, S. (2009). Number-based visual generalisation in the honeybee. PloS One, 4(1), e4263. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004263
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004263 URL |
| [38] |
Harvey, B. M., Fracasso, A., Petridou, N., & Dumoulin, S. O. (2015). Topographic representations of object size and relationships with numerosity reveal generalized quantity processing in human parietal cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(44), 13525-13530. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515414112
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515414112 URL |
| [39] |
Kahneman, D., Treisman, A., & Gibbs, B. J. (1992). The reviewing of object files: Object-specific integration of information. Cognitive Psychology, 24(2), 175-219. http://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0285(92)90007-o
doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(92)90007-o URL pmid: 1582172 |
| [40] |
Kramer, A. F., & Jacobson, A. (1991). Perceptual organization and focused attention: The role of objects and proximity in visual processing. Percept Psychophys, 50(3), 267-284. http://doi.org/10.3758/bf03206750
URL pmid: 1754368 |
| [41] |
Kutter, E. F., Bostroem, J., Elger, C. E., Mormann, F., & Nieder, A. (2018). Single neurons in the human brain encode numbers. Neuron, 100(3), 753-761.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.08.036
doi: S0896-6273(18)30741-4 URL pmid: 30244883 |
| [42] |
Kutter, E. F., Boström, J., Elger, C. E., Nieder, A., & Mormann, F. (2022). Neuronal codes for arithmetic rule processing in the human brain. Current Biology, 32(6), 1275-1284. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.01.054
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.01.054 URL |
| [43] |
Lagona, F. (2016). Regression analysis of correlated circular data based on the multivariate von Mises distribution. Environmental and Ecological Statistics, 23(1), 89-113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-015-0330-y
doi: 10.1007/s10651-015-0330-y URL |
| [44] |
Leibovich, T., Katzin, N., Harel, M., & Henik, A. (2017). From "sense of number" to "sense of magnitude": The role of continuous magnitudes in numerical cognition. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 40, e164. http://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X16000960
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X16000960 URL |
| [45] |
Liberman, A., Fischer, J., & Whitney, D. (2014). Serial dependence in the perception of faces. Current Biology, 24(21), 2569-2574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.025
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.025 URL pmid: 25283781 |
| [46] |
Liberman, A., Manassi, M., & Whitney, D. (2018). Serial dependence promotes the stability of perceived emotional expression depending on face similarity. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 80(6), 1461-1473. http://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-018-1533-8
doi: 10.3758/s13414-018-1533-8 URL |
| [47] |
Liberman, A., Zhang, K., & Whitney, D. (2016). Serial dependence promotes object stability during occlusion. Journal of Vision, 16(15), 16. http://doi.org/10.1167/16.15.16
doi: 10.1167/16.15.16 URL pmid: 28006066 |
| [48] |
Lourenco, S. F., & Aulet, L. S. (2023). A theory of perceptual number encoding. Psychological Review, 130(1), 155-182. http://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000380
doi: 10.1037/rev0000380 URL |
| [49] |
Manassi, M., Liberman, A., Kosovicheva, A., Zhang, K., & Whitney, D. (2018). Serial dependence in position occurs at the time of perception. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(6), 2245-2253. http://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-018-1454-5
doi: 10.3758/s13423-018-1454-5 URL |
| [50] |
Moon, J., & Kwon, O. (2022). Attractive and repulsive effects of sensory history concurrently shape visual perception. Bmc Biology, 20(1), 247. http://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-022-01444-7
doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01444-7 URL pmid: 36345010 |
| [51] |
Pascucci, D., Mancuso, G., Santandrea, E., Della Libera, C., Plomp, G., & Chelazzi, L. (2019). Laws of concatenated perception: Vision goes for novelty, decisions for perseverance. Plos Biology, 17(3), e3000144. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000144
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000144 URL |
| [52] |
Pascucci, D., & Plomp, G. (2021). Serial dependence and representational momentum in single-trial perceptual decisions. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 9910. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89432-9
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89432-9 URL pmid: 33972669 |
| [53] |
Pascucci, D., Tanrikulu, Ö. D., Ozkirli, A., Houborg, C., Ceylan, G., Zerr, P., Rafiei, M., & Kristjánsson, Á. (2023). Serial dependence in visual perception: A review. Journal of Vision, 23(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1167/jov.23.1.9
doi: 10.1167/jov.23.1.9 URL pmid: 36648418 |
| [54] |
Pisa, P. E., & Agrillo, C. (2009). Quantity discrimination in felines: A preliminary investigation of the domestic cat (Felis silvestris catus). Journal of Ethology, 27(2), 289-293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10164-008-0121-0
doi: 10.1007/s10164-008-0121-0 URL |
| [55] |
Printzlau, F. A. B., Myers, N. E., Manohar, S. G., & Stokes, M. G. (2022). Neural reinstatement tracks spread of attention between object features in working memory. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 34(9), 1681-1701. http://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01879
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01879 URL pmid: 35704549 |
| [56] |
Ravindran, P., & Ghosh, S. K. (2011). Bayesian analysis of circular data using wrapped distributions. Journal of Statistical Theory and Practice, 5(4), 547-561. https://doi.org/10.1080/15598608.2011.10483731
doi: 10.1080/15598608.2011.10483731 URL |
| [57] | Sadil, P., Cowell, R. A., & Huber, D. E. (2021). The push-pull of serial dependence effects: Attraction to the prior response and repulsion from the prior stimulus. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/f52yz |
| [58] |
Sadler, P. M., & Tai, R. H. (2007). The two high-school pillars supporting college science. Science, 317(5837), 457-458.
doi: 10.1126/science.1144214 URL |
| [59] |
Schwiedrzik, C. M., Ruff, C. C., Lazar, A., Leitner, F. C., Singer, W., & Melloni, L. (2014). Untangling perceptual memory: Hysteresis and adaptation map into separate cortical networks. Cerebral Cortex, 24(5), 1152-1164. http://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhs396
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs396 URL |
| [60] |
Shan, J., & Postle, B. R. (2022). The influence of active removal from working memory on serial dependence. Journal of Cognition, 5(1), 31. http://doi.org/10.5334/joc.222
doi: 10.5334/joc.222 URL pmid: 36072093 |
| [61] | Starr, A., Libertus, M. E., & Brannon, E. M. (2013). Number sense in infancy predicts mathematical abilities in childhood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 110(45), 18116-18120. |
| [62] |
Stern, Y., Ben-Yehuda, I., Koren, D., Zaidel, A., & Salomon, R. (2022). The dynamic boundaries of the Self: Serial dependence in the Sense of Agency. Cortex, 152, 109-121. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2022.03.015
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2022.03.015 URL pmid: 35550935 |
| [63] |
Suárez-Pinilla, M., Seth, A. K., & Roseboom, W. (2018). Serial dependence in the perception of visual variance. Journal of Vision, 18(7), 4. http://doi.org/10.1167/18.7.4
doi: 10.1167/18.7.4 URL pmid: 29971350 |
| [64] |
Sun, Q., Zhang, H., Alais, D., & Li, L. (2020). Serial dependence and center bias in heading perception from optic flow. Journal of Vision, 20(10), 1. https://doi.org/10.1167/jov.20.10.1
doi: 10.1167/jov.20.10.1 URL pmid: 33001176 |
| [65] |
Togoli, I., Fedele, M., Fornaciai, M., & Bueti, D. (2021). Serial dependence in time and numerosity perception is dimension-specific. Journal of Vision, 21(5), 6. http://doi.org/10.1167/jov.21.5.6
doi: 10.1167/jov.21.5.6 URL pmid: 33956059 |
| [66] |
Tokita, M., & Ishiguchi, A. (2010). How might the discrepancy in the effects of perceptual variables on numerosity judgment be reconciled? Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, 72(7), 1839-1853. http://doi.org/10.3758/APP.72.7.1839
doi: 10.3758/APP.72.7.1839 URL |
| [67] |
van der Burg, E., Rhodes, G., & Alais, D. (2019). Positive sequential dependency for face attractiveness perception. Journal of Vision, 19(12), 6. http://doi.org/10.1167/19.12.6
doi: 10.1167/19.12.6 URL pmid: 31621804 |
| [68] |
Xia, Y., Leib, A. Y., & Whitney, D. (2016). Serial dependence in the perception of attractiveness. Journal of Vision, 16(15), 28. http://doi.org/10.1167/16.15.28
doi: 10.1167/16.15.28 URL pmid: 28006077 |
| [69] | Xu, L. H., Sun, Q., Zhang, B., & Li, X. (2022). Attractive serial dependence in heading perception from optic flow occurs at the perceptual and postperceptual stages. Journal of Vision, 22(12), 11. https://doi.org/10.1167/jov.22.12.11 |
| [70] |
Yang, W. X., Zhang, M. L., Li, H. X., Yang, Y. L., & Si, J. W. (2017). Evolutionary evidences of primitive mathematics ability in human beings. Advances in Psychological Science, 25(5), 810-824.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2017.00810 |
|
[ 杨伟星, 张明亮, 李红霞, 杨雅琳, 司继伟. (2017). 人类基本数学能力的进化证据. 心理科学进展, 25(5), 810-824.]
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2017.00810 |
|
| [71] |
Zhang, H., & Luo, H. (2023). Feature-specific reactivations of past information shift current neural encoding thereby mediating serial bias behaviors. Plos Biology, 21(3), e3002056. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002056
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002056 URL |
| [72] |
Zhou, J., Zhang, H., Ding, X., Shui, R., & Shen, M. (2016). Object formation in visual working memory: Evidence from object-based attention. Cognition, 154, 95-101. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2016.04.009
doi: S0010-0277(16)30097-X URL pmid: 27253863 |
| [1] | 王碧瑶, 陈晨, 胡晓斐, 王迪, 李宝林. 视觉时距知觉序列依赖效应的空间迁移性[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(4): 394-411. |
| [2] | 刘炜;张智君;赵亚军. 基于数量感知的数量适应[J]. 心理学报, 2012, 44(10): 1297-1308. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||