

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2142-2154.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2023.02142 cstr: 32111.14.2023.02142
收稿日期:2023-04-24
出版日期:2023-11-15
发布日期:2023-08-28
通讯作者:
高军, E-mail: gaojunscience@126.com基金资助:
ZHAO Rong, HUANG Yujie, KE Libinuer·aierken, LI Jingjing, GAO Jun( )
)
Received:2023-04-24
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-08-28
摘要:
应激传染是指个体在观察或接触到另一个处于急性应激状态下的个体时, 不自觉地受到对方负面情绪的影响, 在生理与心理上将自己的状态与对方匹配。应激传染的实验范式分为替代应激与交叉应激两种类型。在替代应激范式中, 观察者通过隔板观察, 接受来自示范者单一或多个感觉通道传递的应激信息。在交叉应激中, 观察者在示范者受到应激之后直接与示范者接触, 通过多种感觉通道接受示范者传递的应激信息。不同感觉信息引发应激传染的行为反应具有相似性, 都伴随自主活动减少、焦虑行为增加以及皮质醇水平升高, 其背后的神经环路与关键脑区并不完全一致。相比单一感觉通道(视觉、听觉与嗅觉), 多感觉通道引发的应激传染效应更强。杏仁核是应激传染的热点脑区, 在不同的应激传染实验范式中均观察到显著激活。未来的研究需要在重视应激传染实验范式的基础上, 根据不同感觉通道影响应激传染的神经机制确定研究需要关注的脑区。
中图分类号:
赵荣, 黄钰杰, 克丽比努尔·艾尔肯, 李晶晶, 高军. (2023). 不同感觉通道在应激传染中的作用及其神经机制. 心理科学进展 , 31(11), 2142-2154.
ZHAO Rong, HUANG Yujie, KE Libinuer·aierken, LI Jingjing, GAO Jun. (2023). The role of different sensory channels in stress contagion and its neural mechanisms. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(11), 2142-2154.
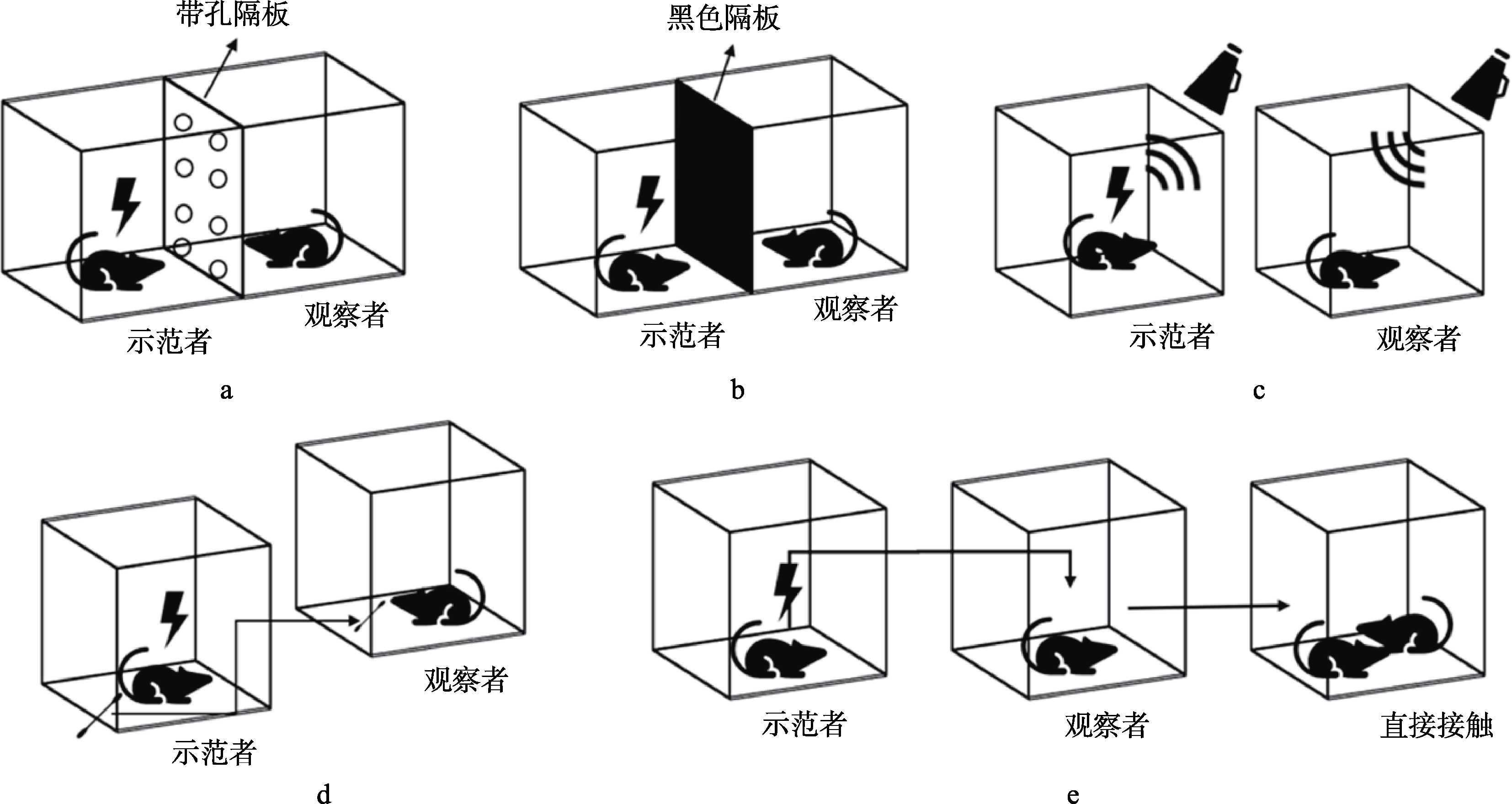
图1 abcd图为旁观者应激范式, e图为交叉应激范式:(a)观察者通过带孔的隔板, 可以接受示范者多感觉通道传递的信息; (b)物理阻断观察者的视觉信息, 阻止示范者向观察者传递视觉信息; (c)记录示范者受到应激时发出的声音, 向观察者播放录音; (d)在示范者受到应激后收集示范者肛门处分泌物, 将收集物呈现给观察者; (e)示范者与观察者在应激期间分开饲养, 在示范者应激结束后将两个被试合笼直接接触。
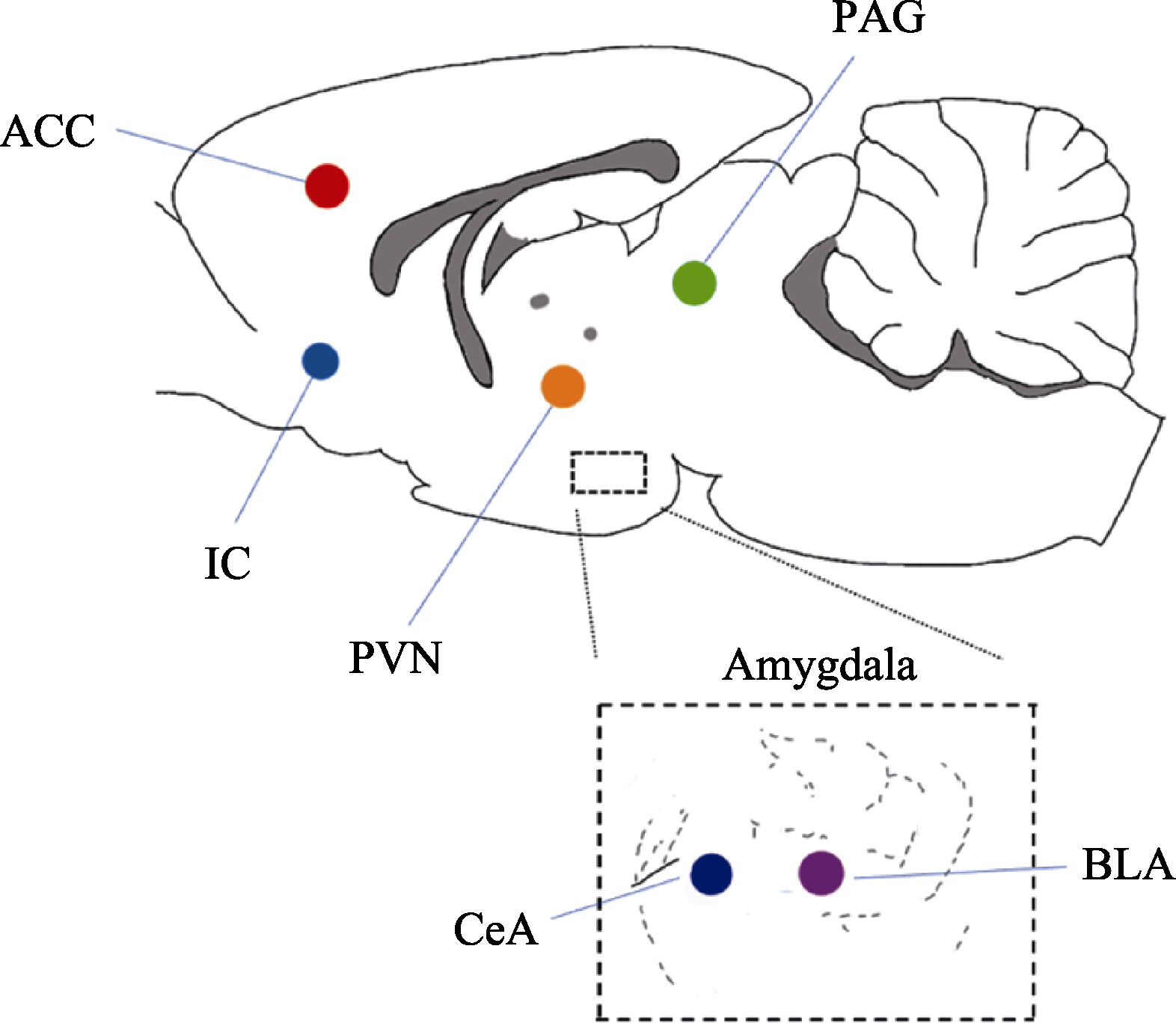
图2 应激传染过程中的关键脑区:BLA (basolateral amygdala, 基底外侧杏仁核); CeA (central amygdala, 中央杏仁核); PVN (paraventricular nucleus, 室旁核); ACC (anterior cingulate cortex, 前扣带皮层); IC (insular cortex, 岛叶); PAG (periaqueductal gray matter, 导水管周围灰质)。
| [1] |
Akitsuki, Y., & Decety, J. (2009). Social context and perceived agency affects empathy for pain: An event- related fMRI investigation. Neuroimage, 47(2), 722-734.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.04.091 pmid: 19439183 |
| [2] |
Allsop, S. A., Wichmann, R., Mills, F., Burgos-Robles, A., Chang, C.-J., Felix-Ortiz, A. C., ... Tye, K. M. (2018). Corticoamygdala transfer of socially derived information gates observational learning. Cell, 173(6), 1329-1342 e1318.
doi: S0092-8674(18)30457-4 pmid: 29731170 |
| [3] |
Beckett, S. R., Duxon, M. S., Aspley, S., & Marsden, C. A. (1997). Central c-fos expression following 20kHz/ultrasound induced defence behaviour in the rat. Brain Research Bulletin, 42(6), 421-426.
pmid: 9128915 |
| [4] |
Benuzzi, F., Lui, F., Ardizzi, M., Ambrosecchia, M., Ballotta, D., Righi, S., Pagnoni, G., Gallese, V., & Porro, C. A. (2018). Pain mirrors: Neural correlates of observing self or others’ facial expressions of pain. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1825.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01825 URL |
| [5] | Bhatnagar, S., Vining, C., & Denski, K. A. I. (2004). Regulation of chronic stress-induced changes in hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal activity by the basolateral amygdala. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1032(1), 315-319. |
| [6] |
Botvinick, M., Jha, A. P., Bylsma, L. M., Fabian, S. A., Solomon, P. E., & Prkachin, K. M. (2005). Viewing facial expressions of pain engages cortical areas involved in the direct experience of pain. Neuroimage, 25(1), 312-319.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.11.043 pmid: 15734365 |
| [7] |
Brechbühl, J., Klaey, M., & Broillet, M. C. (2008). Grueneberg ganglion cells mediate alarm pheromone detection in mice. Science, 321(5892), 1092-1095.
doi: 10.1126/science.1160770 pmid: 18719286 |
| [8] |
Brechbühl, J., Moine, F., Klaey, M., Nenniger-Tosato, M., Hurni, N., Sporkert, F., ... Broillet, M.-C. (2013). Mouse alarm pheromone shares structural similarity with predator scents. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(12), 4762-4767
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214249110 pmid: 23487748 |
| [9] |
Cao, Y., Yusri, N. M., Powell, T., & Cunnington, R. (2019). Neural and behavioral markers of observed pain of older adults. Neuropsychologia, 131, 84-90.
doi: S0028-3932(19)30085-5 pmid: 31026475 |
| [10] |
Carnevali, L., Montano, N., Statello, R., Coude, G., Vacondio, F., Rivara, S., ... Sgoifo, A. (2017). Social stress contagion in rats: Behavioural, autonomic and neuroendocrine correlates. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 82, 155-163.
doi: S0306-4530(17)30103-8 pmid: 28550792 |
| [11] |
Carnevali, L., Montano, N., Tobaldini, E., Thayer, J. F., & Sgoifo, A. (2020). The contagion of social defeat stress: Insights from rodent studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 111, 12-18.
doi: S0149-7634(19)30876-0 pmid: 31931035 |
| [12] | Carrillo, M., Migliorati, F., Bruls, R., Han, Y., Heinemans, M., Pruis, I., ... Keysers, C. (2015). Repeated witnessing of conspecifics in pain: Effects on emotional contagion. PloS One, 10(9), e0136979. |
| [13] | Chen, Q., Panksepp, J. B., & Lahvis, G. P. (2009). Empathy is moderated by genetic background in mice. PloS One, 4(2), e4387. |
| [14] |
Choi, J.-S., & Brown, T. H. (2003). Central amygdala lesions block ultrasonic vocalization and freezing as conditional but not unconditional responses. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(25), 8713-8721.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-25-08713.2003 URL |
| [15] |
Christov-Moore, L., & Iacoboni, M. (2019). Sex differences in somatomotor representations of others’ pain: A permutation-based analysis. Brain Structure and Function, 224(2), 937-947.
doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1814-y |
| [16] |
Chun, E. K., Donovan, M., Liu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2022). Behavioral, neurochemical, and neuroimmune changes associated with social buffering and stress contagion. Neurobiology of Stress, 16, 100427.
doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100427 URL |
| [17] |
Concina, G., Renna, A., Grosso, A., & Sacchetti, B. (2019). The auditory cortex and the emotional valence of sounds. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 98, 256-264.
doi: S0149-7634(18)30761-9 pmid: 30664888 |
| [18] |
Corridi, P., Chiarotti, F., Bigi, S., & Alleva, E. (1993). Familiarity with conspecific odor and isolation-induced aggressive behavior in male mice (Mus domesticus). Journal of Comparative Psychology, 107(3), 328-335.
pmid: 8375149 |
| [19] |
Damon, F., Mezrai, N., Magnier, L., Leleu, A., Durand, K., & Schaal, B. (2021). Olfaction in the multisensory processing of faces: A narrative review of the influence of human body odors. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 750944.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.750944 URL |
| [20] | Davis, M. H. (1980). A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy. JASA Catalog of Selected Documents in Psychology, 10, 85. |
| [21] |
Debiec, J., & Sullivan, R. M. (2014). Intergenerational transmission of emotional trauma through amygdala- dependent mother-to-infant transfer of specific fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(33), 12222-12227.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316740111 pmid: 25071168 |
| [22] | Dimitroff, S. J., Kardan, O., Necka, E. A., Decety, J., Berman, M. G., & Norman, G. J. (2017). Physiological dynamics of stress contagion. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 6168. |
| [23] |
Dou, H., Lei, Y., Pan, Y., Li, H., & Astikainen, P. (2023). Impact of observational and direct learning on fear conditioning generalization in humans. Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacol and Biological Psychiatry, 121, 110650.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2022.110650 URL |
| [24] |
Durand, K., Schaal, B., Goubet, N., Lewkowicz, D. J., & Baudouin, J.-Y. (2020). Does any mother's body odor stimulate interest in mother's face in 4-month-old infants. Infancy, 25(2), 151-164.
doi: 10.1111/infa.v25.2 URL |
| [25] |
Eisenberg, N. (2000). Emotion, regulation, and moral development. Annual Review of Psychology, 51(1), 665-697.
doi: 10.1146/psych.2000.51.issue-1 URL |
| [26] |
Engert, V., Linz, R., & Grant, J. A. (2019). Embodied stress: The physiological resonance of psychosocial stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 105, 138-146.
doi: S0306-4530(18)30596-1 pmid: 30594324 |
| [27] |
Engert, V., Plessow, F., Miller, R., Kirschbaum, C., & Singer, T. (2014). Cortisol increase in empathic stress is modulated by emotional closeness and observation modality. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 45, 192-201.
doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.04.005 URL |
| [28] |
Erkens, V. A., Nater, U. M., Hennig, J., & Hausser, J. A. (2019). Social identification and contagious stress reactions. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 102, 58-62.
doi: S0306-4530(18)30602-4 pmid: 30513501 |
| [29] |
Fallon, N., Roberts, C., & Stancak, A. (2020). Shared and distinct functional networks for empathy and pain processing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 15(7), 709-723.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa090 pmid: 32608498 |
| [30] |
Feldman, R. (2007). Parent-infant synchrony and the construction of shared timing: Physiological precursors, developmental outcomes, and risk conditions. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(3-4), 329-354.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01701.x pmid: 17355401 |
| [31] |
Finnell, J. E., Muniz, B. L., Padi, A. R., Lombard, C. M., Moffitt, C. M., Wood, C. S., Wilson, L. B., Reagan, L. P., Wilson, M. A., & Wood, S. K. (2018). Essential role of ovarian hormones in susceptibility to the consequences of witnessing social defeat in female rats. Biology Psychiatry, 84(5), 372-382.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.01.013 URL |
| [32] |
Gallese, V., & Goldman, A. (1998). Mirror neurons and the simulation theory of mind-reading. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2(12), 493-501.
doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(98)01262-5 pmid: 21227300 |
| [33] |
Gilpin, N. W., Herman, M. A., & Roberto, M. (2015). The central amygdala as an integrative hub for anxiety and alcohol use disorders. Biology Psychiatry, 77(10), 859-869.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.09.008 URL |
| [34] |
Gottfried, J. A., Deichmann, R., Winston, J. S., & Dolan, R. J. (2002). Functional heterogeneity in human olfactory cortex: An event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(24), 10819-10828.
pmid: 12486175 |
| [35] |
Gottfried, J. A., & Dolan, R. J. (2003). The nose smells what the eye sees: Crossmodal visual facilitation of human olfactory perception. Neuron, 39(2), 375-386.
doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00392-1 pmid: 12873392 |
| [36] |
Greer, P. L., Bear, D. M., Lassance, J.-M., Bloom, M. L., Tsukahara, T., Pashkovski, S. L., ... Datta, S. R. (2016). A family of non-GPCR chemosensors defines an alternative logic for mammalian olfaction. Cell, 165(7), 1734-1748.
doi: S0092-8674(16)30549-9 pmid: 27238024 |
| [37] |
Guzman, Y. F., Tronson, N. C., Guedea, A., Huh, K. H., Gao, C., & Radulovic, J. (2009). Social modeling of conditioned fear in mice by non-fearful conspecifics. Behavioural Brain Research, 201(1), 173-178.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.02.024 pmid: 19428631 |
| [38] |
Habib, K. E., Gold, P. W., & Chrousos, G. P. (2001). Neuroendocrinology of stress. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 30(3), 695-728.
doi: 10.1016/s0889-8529(05)70208-5 pmid: 11571937 |
| [39] |
Hernandez-Lallement, J., Gomez-Sotres, P., & Carrillo, M. (2022). Towards a unified theory of emotional contagion in rodents: A meta-analysis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 132, 1229-1248.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.010 URL |
| [40] |
Hess, U., & Blairy, S. (2001). Facial mimicry and emotional contagion to dynamic emotional facial expressions and their influence on decoding accuracy. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 40(2), 129-141.
pmid: 11165351 |
| [41] |
Inagaki, H., Kiyokawa, Y., Tamogami, S., Watanabe, H., Takeuchi, Y., & Mori, Y. (2014). Identification of a pheromone that increases anxiety in rats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(52), 18751-18756.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414710112 URL |
| [42] |
Iniguez, S. D., Flores-Ramirez, F. J., Riggs, L. M., Alipio, J. B., Garcia-Carachure, I., Hernandez, M. A., ... Castillo, S. A. (2018). Vicarious social defeat stress induces depression- related outcomes in female mice. Biological Psychiatry, 83(1), 9-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.07.014 URL |
| [43] |
Jackson, P. L., Meltzoff, A. N., & Decety, J. (2005). How do we perceive the pain of others? A window into the neural processes involved in empathy. Neuroimage, 24(3), 771-779.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.09.006 pmid: 15652312 |
| [44] |
Jeon, D., Kim, S., Chetana, M., Jo, D., Ruley, H. E., Lin, S.-Y., ... Shin, H.-S. (2010). Observational fear learning involves affective pain system and Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels in ACC. Nature Neuroscience, 13(4), 482-488.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2504 |
| [45] |
Jessen, S. (2020). Maternal odor reduces the neural response to fearful faces in human infants. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 45, 100858.
doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100858 URL |
| [46] | Jin, J., Zelano, C., Gottfried, J. A., & Mohanty, A. (2015). Human amygdala represents the complete spectrum of subjective valence. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(45), 15145-15156. |
| [47] |
Jones, C. E., & Monfils, M.-H. (2016). Dominance status predicts social fear transmission in laboratory rats. Animal Cognition, 19(6), 1051-1069.
pmid: 27411940 |
| [48] |
Kamiloglu, R. G., Smeets, M. A. M., de Groot, J. H. B., & Semin, G. R. (2018). Fear odor facilitates the detection of fear expressions over other negative expressions. Chemical Senses, 43(6), 419-426.
doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjy029 pmid: 29796589 |
| [49] |
Keum, S., & Shin, H.-S. (2019). Neural basis of observational fear learning: A potential model of affective empathy. Neuron, 104(1), 78-86.
doi: S0896-6273(19)30786-X pmid: 31600517 |
| [50] | Kim, E. J., Kim, E. S., Covey, E., & Kim, J. J. (2010). Social transmission of fear in rats: The role of 22-kHz ultrasonic distress vocalization. PloS One, 5(12), e15077. |
| [51] |
Kiyokawa, Y., Kawai, K., & Takeuchi, Y. (2018). The benefits of social buffering are maintained regardless of the stress level of the subject rat and enhanced by more conspecifics. Physiology and Behavior, 194, 177-183.
doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.05.027 URL |
| [52] |
Kiyokawa, Y., Kikusui, T., Takeuchi, Y., & Mori, Y. (2004). Alarm pheromones with different functions are released from different regions of the body surface of male rats. Chemical Senses, 29(1), 35-40.
pmid: 14752038 |
| [53] |
Kiyokawa, Y., Kikusui, T., Takeuchi, Y., & Mori, Y. (2005). Mapping the neural circuit activated by alarm pheromone perception by c-Fos immunohistochemistry. Brain Research, 1043(1-2), 145-154.
pmid: 15862528 |
| [54] |
Kiyokawa, Y., Kodama, Y., Kubota, T., Takeuchi, Y., & Mori, Y. (2013). Alarm pheromone is detected by the vomeronasal organ in male rats. Chemical Senses, 38(8), 661-668.
doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt030 pmid: 23821727 |
| [55] |
Kiyokawa, Y., Takeuchi, Y., Nishihara, M., & Mori, Y. (2009). Main olfactory system mediates social buffering of conditioned fear responses in male rats. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29(4), 777-785.
doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06618.x pmid: 19250440 |
| [56] |
Knapska, E., Nikolaev, E., Boguszewski, P., Walasek, G., Blaszczyk, J., Kaczmarek, L., & Werka, T. (2006). Between-subject transfer of emotional information evokes specific pattern of amygdala activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(10), 3858-3862.
pmid: 16497832 |
| [57] |
Knapska, E., Radwanska, K., Werka, T., & Kaczmarek, L. (2007). Functional internal complexity of amygdala: Focus on gene activity mapping after behavioral training and drugs of abuse. Physiological Review, 87(4), 1113-1173.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00037.2006 URL |
| [58] |
Kong, M. S., & Zweifel, L. S. (2021). Central amygdala circuits in valence and salience processing. Behaviour Brain Research, 410, 113355.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113355 URL |
| [59] |
Lamm, C., Batson, C. D., & Decety, J. (2007). The neural substrate of human empathy: Effects of perspective-taking and cognitive appraisal. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(1), 42-58.
pmid: 17214562 |
| [60] |
Lamm, C., Decety, J., & Singer, T. (2011). Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain. Neuroimage, 54(3), 2492-2502.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.014 pmid: 20946964 |
| [61] |
Lamm, C., Meltzoff, A. N., & Decety, J. (2010). How do we empathize with someone who is not like us? A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(2), 362-376.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21186 pmid: 19199417 |
| [62] |
Langford, D. J., Crager, S. E., Shehzad, Z., Smith, S. B., Sotocinal, S. G., Levenstadt, J. S., ... Mogil, J. S. (2006). Social modulation of pain as evidence for empathy in mice. Science, 312(5782), 1967-1970.
pmid: 16809545 |
| [63] |
Lassalle, A., Zürcher, N. R., Porro, C. A., Benuzzi, F., Hippolyte, L., Lemonnier, E., ... Hadjikhani, N. (2019). Influence of anxiety and alexithymia on brain activations associated with the perception of others’ pain in autism. Social Neuroscience, 14(3), 359-377.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2018.1468358 URL |
| [64] |
Laukka, P., Linnman, C., Åhs, F., Pissiota, A., Frans, Ö., Faria, V., ... Furmark, T. (2008). In a nervous voice: Acoustic analysis and perception of anxiety in social phobics’ speech. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 32(4), 195-214.
doi: 10.1007/s10919-008-0055-9 URL |
| [65] |
Lee, I. C., Yu, T.-H., Liu, W.-H., & Hsu, K.-S. (2021). Social transmission and buffering of hippocampal metaplasticity after stress in mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 41(6), 1317-1330.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1751-20.2020 pmid: 33310752 |
| [66] |
Lidhar, N. K., Insel, N., Dong, J. Y., & Takehara-Nishiuchi, K. (2017). Observational fear learning in degus is correlated with temporal vocalization patterns. Behavioural Brain Research, 332, 362-371.
doi: S0166-4328(17)30435-7 pmid: 28627387 |
| [67] |
Mackay-Sim, A., & Laing, D. G. (1981). The sources of odors from stressed rats. Physiology Behavior, 27(3), 511-513.
doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(81)90340-1 URL |
| [68] |
Markovic, J., Anderson, A. K., & Todd, R. M. (2014). Tuning to the significant: Neural and genetic processes underlying affective enhancement of visual perception and memory. Behavioural Brain Research, 259, 229-241.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.11.018 pmid: 24269973 |
| [69] | Nakashima, S. F., Ukezono, M., Nishida, H., Sudo, R., & Takano, Y. (2015). Receiving of emotional signal of pain from conspecifics in laboratory rats. Royal Society Open Science, 2(4), 140381. |
| [70] |
Olsson, A., Nearing, K. I., & Phelps, E. A. (2007). Learning fears by observing others: The neural systems of social fear transmission. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 2(1), 3-11.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsm005 pmid: 18985115 |
| [71] |
Olsson, A., & Phelps, E. A. (2007). Social learning of fear. Nature Neuroscience, 10(9), 1095-1102.
pmid: 17726475 |
| [72] |
Ouda, L., Jilek, M., & Syka, J. (2016). Expression of c-Fos in rat auditory and limbic systems following 22-kHz calls. Behavioural Brain Research, 308, 196-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.030 pmid: 27102341 |
| [73] |
Panksepp, J. B., & Lahvis, G. P. (2011). Rodent empathy and affective neuroscience. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review, 35(9), 1864-1875.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.05.013 URL |
| [74] |
Park, J., Carrillo, B., & Mendes, W. B. (2021). Is vicarious stress functionally adaptive? Perspective-taking modulates the effects of vicarious stress on future firsthand stress. Emotion, 21(6), 1131-1143.
doi: 10.1037/emo0000963 pmid: 34060861 |
| [75] | Pärnamets, P., Espinosa, L., & Olsson, A. (2020). Physiological synchrony predicts observational threat learning in humans. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 287(1927), 20192779. |
| [76] |
Parsana, A. J., Li, N., & Brown, T. H. (2012). Positive and negative ultrasonic social signals elicit opposing firing patterns in rat amygdala. Behavioral Brain Research, 226(1), 77-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.08.040 URL |
| [77] |
Pause, B. M. (2012). Processing of Body Odor Signals by the Human Brain. Chemosens Percept, 5(1), 55-63.
pmid: 22448299 |
| [78] |
Peen, N. F., Duque-Wilckens, N., & Trainor, B. C. (2021). Convergent neuroendocrine mechanisms of social buffering and stress contagion. Hormones and Behavior, 129, 104933.
doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2021.104933 URL |
| [79] | Pereira, A. G., Cruz, A., Lima, S. Q., & Moita, M. A. (2012). Silence resulting from the cessation of movement signals danger. Current Biology, 22(16), R627-628. |
| [80] | Perez-Manrique, A., & Gomila, A. (2022). Emotional contagion in nonhuman animals: A review. Wiley Interdiscip Reviews-Cognitive-Science, 13(1), e1560. |
| [81] |
Pfeifer, L. S., Heyers, K., Ocklenburg, S., & Wolf, O. T. (2021). Stress research during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 131, 581-596.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.045 pmid: 34599918 |
| [82] |
Pisansky, M. T., Hanson, L. R., Gottesman, II, & Gewirtz, J. C. (2017). Oxytocin enhances observational fear in mice. Nature Communication, 8(1), 2102.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02279-5 |
| [83] |
Rabinak, C. A., Angstadt, M., Welsh, R. C., Kenndy, A. E., Lyubkin, M., Martis, B., & Phan, K. L. (2011). Altered amygdala resting-state functional connectivity in post-traumatic stress disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2, 62.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00062 pmid: 22102841 |
| [84] |
Rudrauf, D., David, O., Lachaux, J.-P., Kovach, C. K., Martinerie, J., Renault, B., & Damasio, A. (2008). Rapid interactions between the ventral visual stream and emotion-related structures rely on a two-pathway architecture. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(11), 2793-2803.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3476-07.2008 pmid: 18337409 |
| [85] |
Saarela, M. V., Hlushchuk, Y., Williams, A. C. d. C., Schurmann, M., Kalso, E., & Hari, R. (2006). The compassionate brain: Humans detect intensity of pain from another's face. Cerebral Cortex, 17(1), 230-237.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhj141 URL |
| [86] |
Sadananda, M., Wohr, M., & Schwarting, R. K. (2008). Playback of 22-kHz and 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations induces differential c-fos expression in rat brain. Neuroscience Letters, 435(1), 17-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.02.002 pmid: 18328625 |
| [87] |
Seo, D., Olman, C. A., Haut, K. M., Sinha, R., MacDonald, A. W.,3rd, & Patrick, C. J. (2014). Neural correlates of preparatory and regulatory control over positive and negative emotion. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(4), 494-504.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nst115 pmid: 23887812 |
| [88] |
Singer, T., Seymour, B., O'Doherty, J., Kaube, H., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2004). Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science, 303(5661), 1157-1162.
doi: 10.1126/science.1093535 pmid: 14976305 |
| [89] |
Sliwa, J., Mallet, M., Christiaens, M., & Takahashi, D. Y. (2022). Neural basis of multi-sensory communication in primates. Ethology Ecology and Evolution, 34(3), 322-343.
doi: 10.1080/03949370.2021.2024266 URL |
| [90] |
Smith, C. G., Jones, E. J. H., Charman, T., Clackson, K., Mirza, F. U., & Wass, S. V. (2021). Vocalization and physiological hyperarousal in infant-caregiver dyads where the caregiver has elevated anxiety. Development and Psychopathology, 35(2), 459-470.
doi: 10.1017/S095457942100153X URL |
| [91] | Smith, M. L., Walcott, A. T., Heinricher, M. M., & Ryabinin, A. E. (2017). Anterior cingulate cortex contributes to alcohol withdrawal-induced and socially transferred hyperalgesia. Eneuro, 4(4), doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0087-17.2017 |
| [92] |
Spampanato, J., Polepalli, J., & Sah, P. (2011). Interneurons in the basolateral amygdala. Neuropharmacology, 60(5), 765-773.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.11.006 pmid: 21093462 |
| [93] |
Sterley, T. L., Baimoukhametova, D., Füzesi, T., Zurek, A. A., Daviu, N., Rasiah, N. P., ... Bains, J. S. (2018). Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress. Nature Neuroscience, 21(3), 393-403.
doi: 10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 URL |
| [94] |
Stevenson, R. J. (2010). An initial evaluation of the functions of human olfaction. Chemical Senses, 35(1), 3-20.
doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjp083 pmid: 19942579 |
| [95] |
Swain, M., Routray, A., & Kabisatpathy, P. (2018). Databases, features and classifiers for speech emotion recognition: A review. International Journal of Speech Technology, 21(1), 93-120.
doi: 10.1007/s10772-018-9491-z |
| [96] |
Tirindelli, R., Dibattista, M., Pifferi, S., & Menini, A. (2009). From pheromones to behavior. Physiological Reviews, 89(3), 921-956.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00037.2008 pmid: 19584317 |
| [97] | Tsigos, C., & Chrousos, G. P. (2002). Hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. Journal of Psychosmatic Research, 53(4), 865-871. |
| [98] |
Ueda, H., & Neyama, H. (2017). LPA1 receptor involvement in fibromyalgia-like pain induced by intermittent psychological stress, empathy. Neurobiology of Pain, 1, 16-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2017.04.002 pmid: 31194005 |
| [99] |
Ueno, H., Suemitsu, S., Murakami, S., Kitamura, N., Wani, K., Takahashi, Y., ... Ishihara, T. (2020). Conformity-like behaviour in mice observing the freezing of other mice: A model of empathy. BMC Neuroscience, 21(1), 1-16.
doi: 10.1186/s12868-020-0551-3 |
| [100] |
Vermeulen, N., & Mermillod, M. (2010). Fast emotional embodiment can modulate sensory exposure in perceivers. Communicative and Integrative Biology, 3(2), 184-187.
doi: 10.4161/cib.3.2.10922 pmid: 20585518 |
| [101] |
Vesker, M., Bahn, D., Kauschke, C., Tschense, M., Dege, F., & Schwarzer, G. (2018). Auditory emotion word primes influence emotional face categorization in children and adults, but not vice versa. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 618.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00618 pmid: 29765346 |
| [102] |
von Dawans, B., Strojny, J., & Domes, G. (2021). The effects of acute stress and stress hormones on social cognition and behavior: Current state of research and future directions. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review, 121, 75-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.11.026 URL |
| [103] |
Walcott, A. T., Smith, M. L., Loftis, J. M., & Ryabinin, A. E. (2018). Social transfer of alcohol withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia in female prairie voles. Social Neuroscience, 13(6), 710-717.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2018.1456957 pmid: 29564972 |
| [104] | Wang, H., Chen, J., Xu, X., Sun, W.-J., Chen, X., Zhao, F., ... Zhang, Z. (2019). Direct auditory cortical input to the lateral periaqueductal gray controls sound-driven defensive behavior. PLoS Biology, 17(8), e3000417. |
| [105] |
Warren, B. L., Mazei-Robison, M. S., Robison, A. J., & Iniguez, S. D. (2020). Can I get a witness? Using vicarious defeat stress to study mood-related illnesses in traditionally understudied populations. Biological Psychiatry, 88(5), 381-391.
doi: S0006-3223(20)30093-7 pmid: 32228871 |
| [106] |
Warren, B. L., Vialou, V. F., Iñiguez, S. D., Alcantara, L. F., Wright, K. N., Feng, J., ... Bolanos-Guzman, C. A. (2013). Neurobiological sequelae of witnessing stressful events in adult mice. Biological Psychiatry, 73(1), 7-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.06.006 pmid: 22795644 |
| [107] |
Waters, S. F., West, T. V., Karnilowicz, H. R., & Mendes, W. B. (2017). Affect contagion between mothers and infants: Examining valence and touch. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146(7), 1043-1051.
doi: 10.1037/xge0000322 URL |
| [108] |
White, C. N., & Buchanan, T. W. (2016). Empathy for the stressed. Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology, 2(4), 311-324.
doi: 10.1007/s40750-016-0049-5 URL |
| [109] | Wöhr, M. (2018). Ultrasonic communication in rats: Appetitive 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations as social contact calls. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 72(1), 14. |
| [110] | Wöhr, M., & Schwarting, R. K. (2007). Ultrasonic communication in rats: can playback of 50-kHz calls induce approach behavior?. PloS One, 2(12), e1365. |
| [111] |
Wöhr, M., & Schwarting, R. K. W. (2008). Ultrasonic calling during fear conditioning in the rat: No evidence for an audience effect. Animal Behaviour, 76(3), 749-760.
doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.04.017 URL |
| [112] |
Xiao, Z., Martinez, E., Kulkarni, P. M., Zhang, Q., Hou, Q., Rosenberg, D., ... Chen, Z. S. (2019). Cortical pain processing in the rat anterior cingulate cortex and primary somatosensory cortex. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 13, 165.
doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00165 pmid: 31105532 |
| [113] |
Zaki, J., Wager, T. D., Singer, T., Keysers, C., & Gazzola, V. (2016). The anatomy of suffering: Understanding the relationship between nociceptive and empathic pain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(4), 249-259.
doi: S1364-6613(16)00044-9 pmid: 26944221 |
| [114] |
Zhang, M.-M., Geng, A.-Q., Chen, K., Wang, J., Wang, P., Qiu, X.-T., ... Chen, T. (2022). Glutamatergic synapses from the insular cortex to the basolateral amygdala encode observational pain. Neuron, 110(12), 1993-2008.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.03.030 URL |
| [1] | 冯攀, 赵恒越, 姜雨矇, 张悦彤, 冯廷勇. 催产素影响条件化恐惧情绪加工的认知机制及神经基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(4): 557-567. |
| [2] | 赵辉, 张亚冉, 肖玉琴, 张卓, 杨波. “忽冷忽热”的杏仁核:与攻击相关的重要核团[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(7): 1206-1277. |
| [3] | 戴晓妍, 胡谊, 张亚. 人际同步性现象:探索心理咨询过程中同盟关系的新视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(9): 2078-2087. |
| [4] | 万必成, 杨振, 李宏汀, 马舒. “有声有色”的触觉体验:来自多感觉通道整合的线索[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(3): 580-590. |
| [5] | 冯攀, 杨可, 冯廷勇. 催产素影响恐惧习得和消退的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(2): 365-374. |
| [6] | 崔琳, 郭冰冰, 李佳欣, 骆钰, 赵丹, 孟明. 加工情绪性电影刺激一致性体验与特异性体验分离的神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(suppl.): 137-137. |
| [7] | 张慧会, 张亮. 早期应激对情绪调节的影响及其神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1193-1203. |
| [8] | 荆伟, 刘仔琴. 孤独症者面孔加工中眼部注视不足, 是回避还是忽视?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(3): 476-487. |
| [9] | 李雪娟, 张灵聪, 李红. 情绪唤醒影响记忆巩固过程的神经生理机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(10): 1749-1757. |
| [10] | 王丽丽; 贾丽娜; 罗跃嘉. 情绪自动化加工的证据与争议[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1185-1197. |
| [11] | 苏琳;杨周;Todd Jackson ;陈红;黄承志. 疼痛恐惧的形成及其对疼痛知觉的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(8): 1228-1236. |
| [12] | 冯攀;郑涌. 睡眠剥夺影响恐惧情绪加工的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(9): 1579-1587. |
| [13] | 吕遥迪;吴恺君;张雨青. 中国创伤后应激反应量表在大学生群体中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(8): 1324-1330. |
| [14] | 黄雅梅;周仁来;吴梦莹. 神经质人格的神经生理基础[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(4): 602-613. |
| [15] | 陈珊珊;蔡厚德. 丘脑枕核参与情绪信息加工的多条通路[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(2): 234-240. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||