

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 571-589.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2026.0571
• Original article • Next Articles
WANG Aijun1,2( ), HUANG Jie1,2(
), HUANG Jie1,2( ), ZHAO Danna3, LI Xin3, ZHANG Ming4,5
), ZHAO Danna3, LI Xin3, ZHANG Ming4,5
Published:2026-04-25
Online:2026-01-16
Contact:
Wang Ai-Jun, E-mail: WANG Aijun, HUANG Jie, ZHAO Danna, LI Xin, ZHANG Ming. (2026). Stimulus similarity modulated sensory dominance effects in cross-modal conflicts. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 58(4), 571-589.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2026.0571
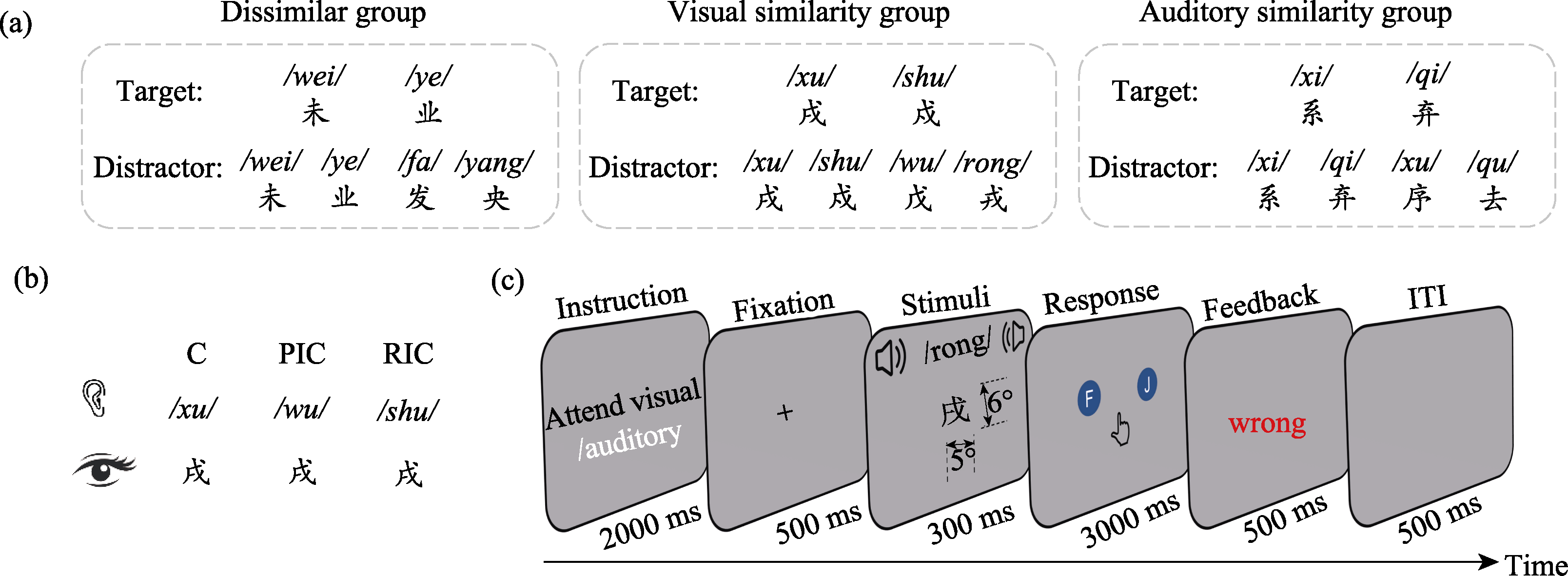
Figure 1. (a) stimuli under different similarity conditions; (b) schematic of audiovisual congruency conditions, using visual similarity as an example; (c) 2-1 mapping experimental flowchart.
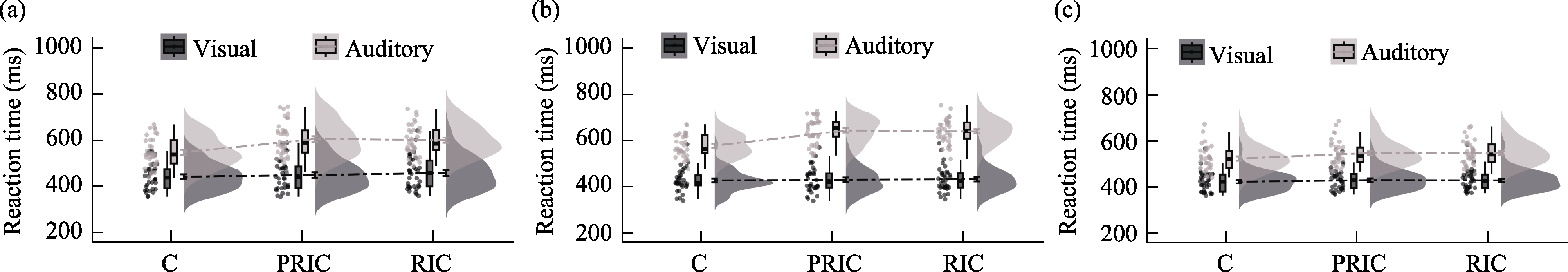
Figure 2. RT results across three similarity conditions. (a) dissimilarity group; (b) visual similarity group; (c) auditory similarity group. Note. Cloud plots represent the distribution of reaction time data. Each point denotes a participant's reaction time, the box represents the interquartile range of reaction times, and the line inside the box indicates the median RT.
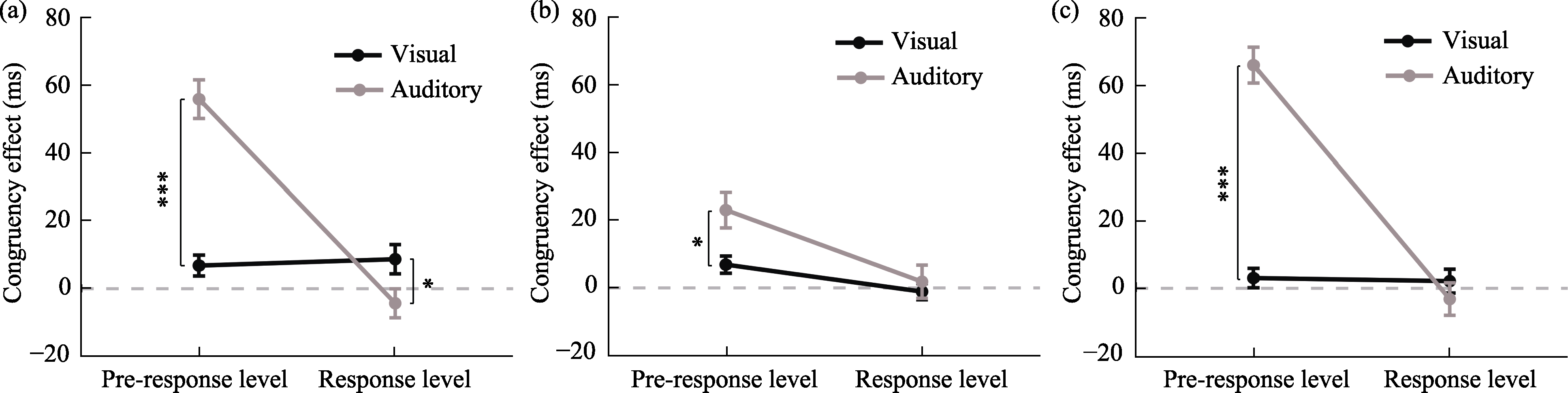
Figure 3. Congruency effect results under different similarity conditions. (a) dissimilarity group; (b) visual similarity group; (c) auditory similarity group. Note. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05, same below.
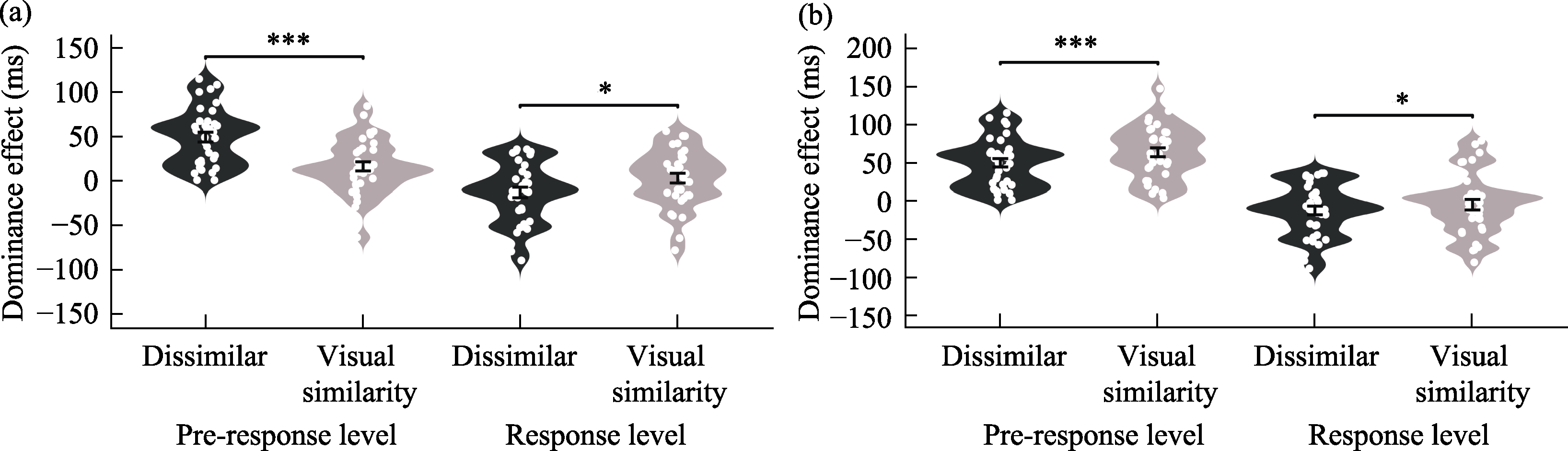
Figure 4. Differences in visual dominance effects at pre-response and response levels under different similarity conditions; (a) visual similarity vs. dissimilarity groups; (b) auditory similarity vs. dissimilarity groups.

Figure 5. Electric field intensity and current flow patterns simulated by HD-explore software for 1.5 mA HD-tDCS stimulation of the left fusiform gyrus and left inferior parietal lobule.
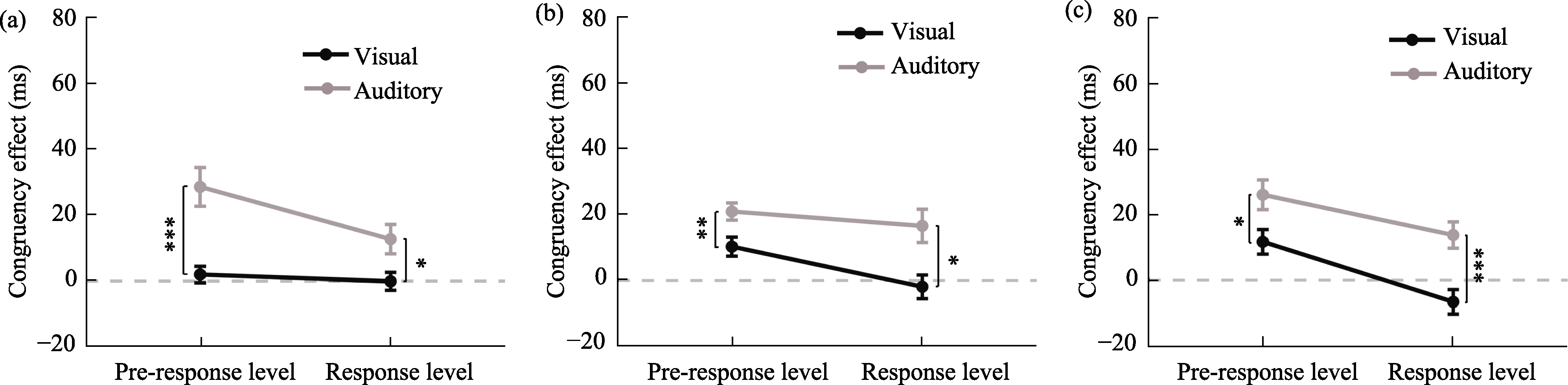
Figure 7. Congruency effect results under all experimental conditions for the three electrode types. (a) sham stimulation; (b) anodal stimulation; (c) cathodal stimulation.
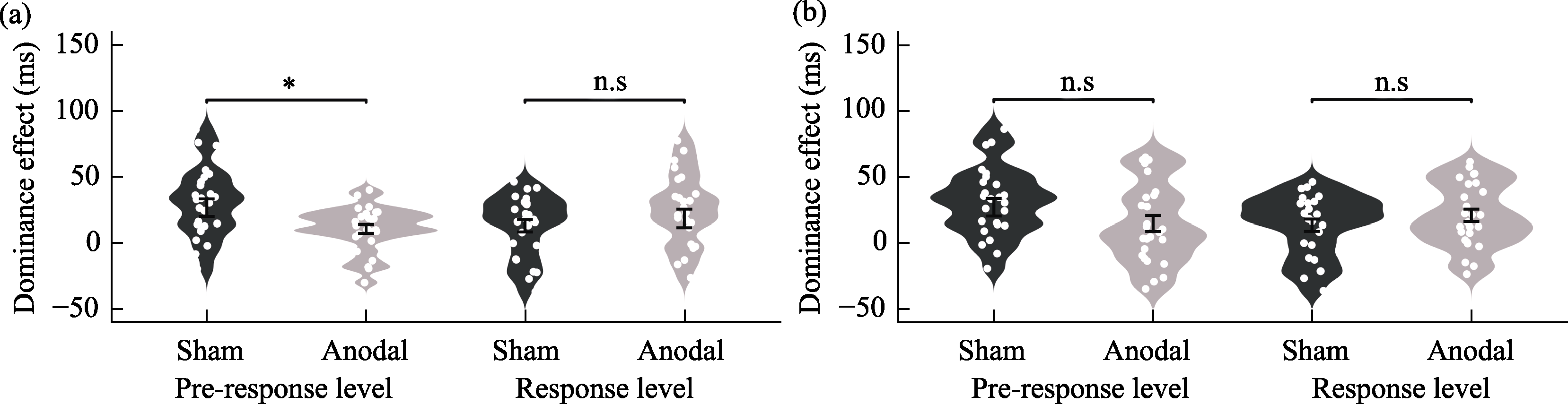
Figure 8. Differences in sensory dominance effects at pre-response and response levels under different electrode types. (a) anodal stimulation vs. sham stimulation; (b) cathodal stimulation vs. sham stimulation.
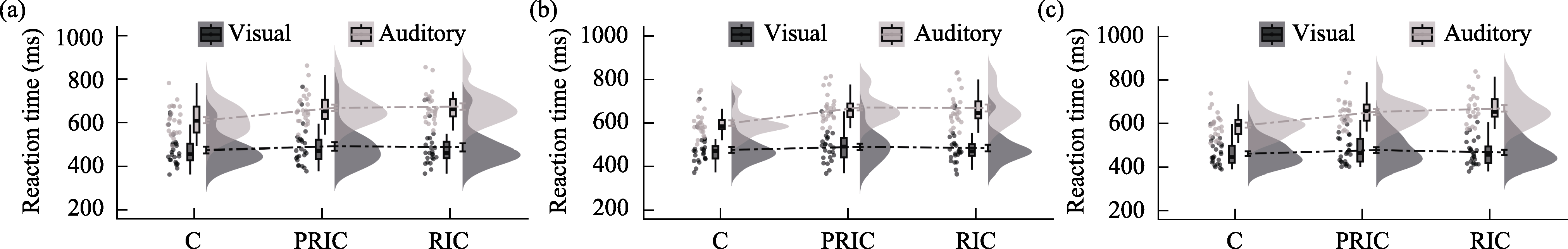
Figure 9. RT results for all experimental conditions across three types of electrical stimulation. (a) sham stimulation; (b) anodal stimulation; (c) cathodal stimulation.
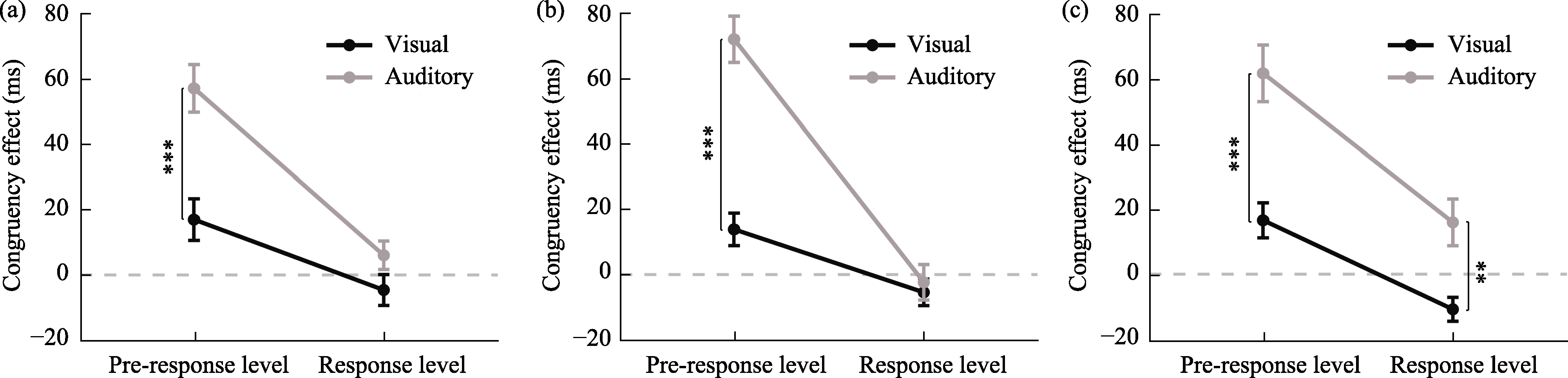
Figure 10. Congruency effect results for all experimental conditions across three electrode types. (a) shame stimulation; (b) anodal stimulation; (c) cathodal stimulation.
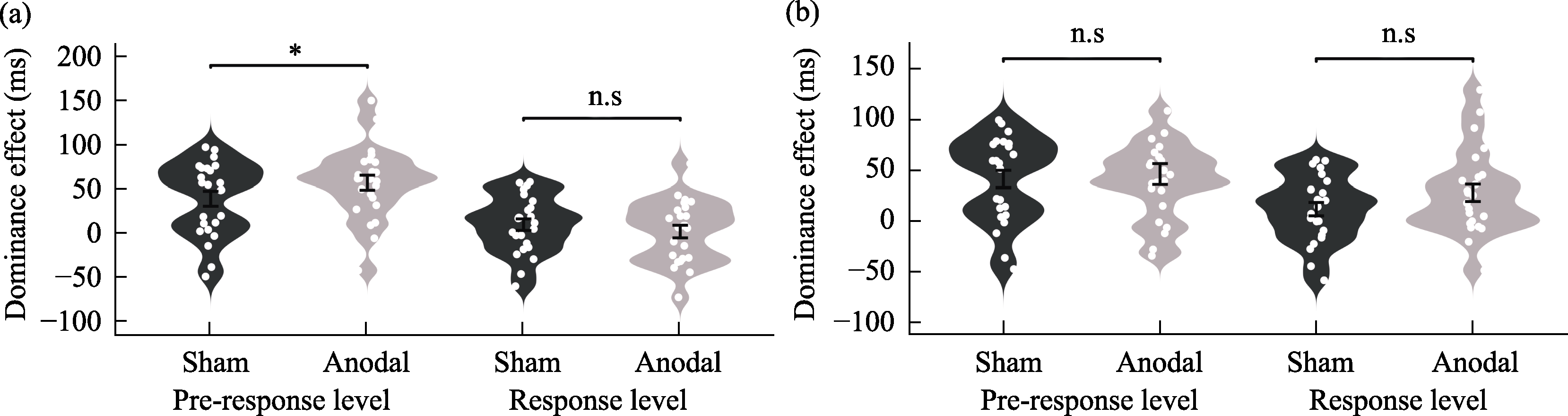
Figure 11. Differences in sensory dominance effects at pre-response and response levels across electrode types. (a) anodal stimulation vs. sham stimulation; (b) cathodal stimulation vs. sham stimulation.
| [1] |
Abdel Rahman R., & Melinger A. (2009). Semantic context effects in language production: A swinging lexical network proposal and a review. Language and Cognitive Processes, 24(5), 713-734.
doi: 10.1080/01690960802597250 URL |
| [2] |
Ashby F. G., & Ell S. W. (2001). The neurobiology of human category learning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(5), 204-210.
pmid: 11323265 |
| [3] |
Boggio P. S., Zaghi S., & Fregni F. (2009). Modulation of emotions associated with images of human pain using anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Neuropsychologia, 47(1), 212-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.07.022 pmid: 18725237 |
| [4] |
Booth J. R., Burman D. D., Meyer J. R., Gitelman D. R., Parrish T. B., & Mesulam M. M. (2002). Functional anatomy of intra- and cross-modal lexical tasks. NeuroImage, 16(1), 7-22.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1081 pmid: 11969313 |
| [5] |
Bosworth R. G., Binder E. M., Tyler S. C., & Morford J. P. (2021). Automaticity of lexical access in deaf and hearing bilinguals: Cross-linguistic evidence from the color Stroop task across five languages. Cognition, 212, 104659.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104659 URL |
| [6] |
Breining B., Nozari N., & Rapp B. (2016). Does segmental overlap help or hurt? Evidence from blocked cyclic naming in spoken and written production. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(2), 500-506.
doi: 10.3758/s13423-015-0900-x URL |
| [7] |
Cao F., Lee R., Shu H., Yang Y., Xu G., Li K., & Booth J. R. (2010). Cultural constraints on brain development: Evidence from a developmental study of visual word processing in mandarin Chinese. Cerebral Cortex, 20(5), 1223-1233.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp186 URL |
| [8] |
Chen Q., & Zhou X. L. (2013). Vision dominates at the pre-response level and audition dominates at the response level in cross-modal interaction: Behavioral and neural evidence. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(17), 7109-7121.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1985-12.2013 URL |
| [9] |
Chikazoe J., Jimura K., Asari T., Yamashita K., Morimoto H., Hirose S., Miyashita Y., & Konishi S. (2009). Functional dissociation in right inferior frontal cortex during performance of go/no-go task. Cerebral Cortex, 19(1), 146-152.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn065 URL |
| [10] | Ciaramidaro A., Toppi J., Casper C., Freitag C. M., Siniatchkin M., & Astolfi L. (2018). Multiple-brain connectivity during third party punishment: An EEG hyperscanning study. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 6822. |
| [11] |
Dalrymple-Alford E. C. (1972). Sound similarity and color- word interference in the Stroop task. Psychonomic Science, 28(4), 209-210.
doi: 10.3758/BF03328712 URL |
| [12] |
Dehaene S., & Cohen L. (2011). The unique role of the visual word form area in reading. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(6), 254-262.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.04.003 pmid: 21592844 |
| [13] |
De Houwer J. (2003). On the role of stimulus-response and stimulus-stimulus compatibility in the Stroop effect. Memory and Cognition, 31(3), 353-359.
doi: 10.3758/BF03194393 URL |
| [14] | DeWitt I., & Rauschecker J. P. (2012). Phoneme and word recognition in the auditory ventral stream. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(8), E505- E514. |
| [15] |
Diaconescu A. O., Alain C., & McIntosh A. R. (2011). The co-occurrence of multisensory facilitation and cross-modal conflict in the human brain. Journal of Neurophysiology, 106(6), 2896-2909.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00303.2011 pmid: 21880944 |
| [16] | Donohue S. E., Appelbaum L. G., Park C. J., Roberts K. C., & Woldorff M. G. (2013). Cross-modal stimulus conflict: The behavioral effects of stimulus input timing in a visual-auditory Stroop task. PloS ONE, 8(4), e62802. |
| [17] | Fitzhugh M. C., Whitehead P. S., Johnson L., Cai J. M., Baxter L. C., & Rogalsky C. (2019). A functional MRI investigation of cross-modal interference in an audiovisual Stroop task. PLoS ONE, 14(1), e0210736. |
| [18] |
Floyer-Lea A., Wylezinska M., Kincses T., & Matthews P. M. (2006). Rapid modulation of GABA concentration in human sensorimotor cortex during motor learning. Journal of Neurophysiology, 95(3), 1639-1644.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00346.2005 pmid: 16221751 |
| [19] |
Folstein J. R., Fuller K., Howard D., & DePatie T. (2017). The effect of category learning on attentional modulation of visual cortex. Neuropsychologia, 104, 18-30.
doi: S0028-3932(17)30278-6 pmid: 28754490 |
| [20] |
Fong M. C. M., Hui N. Y., Fung E. S. W., Chu P. C. K., & Wang W. S. Y. (2018). Conflict monitoring in multi-sensory flanker tasks: Effects of cross-modal distractors on the N2 component. Neuroscience Letters, 670, 31-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.01.037 URL |
| [21] |
Gale T. M., Laws K. R., & Foley K. (2006). Crowded and sparse domains in object recognition: Consequences for categorization and naming. Brain and Cognition, 60(2), 139-145.
pmid: 16377049 |
| [22] |
Gao Y., Wei N., Wang Z. K., Jian J., Ding G. S., Meng X. Z., & Liu L. (2015). Interaction between native and second language processing: Evidence from a functional magnetic resonance imaging study of Chinese-English bilingual children. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(12), 1419-1432.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.01419 |
| [23] |
Gerlach C., Zhu X., & Joseph J. E. (2015). Structural similarity exerts opposing effects on perceptual differentiation and categorization: An FMRI study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(5), 974-987.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00748 pmid: 25390196 |
| [24] |
Grill-Spector K., & Weiner K. S. (2014). The functional architecture of the ventral temporal cortex and its role in categorization. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(8), 536-548.
doi: 10.1038/nrn3747 pmid: 24962370 |
| [25] | Guo W., Geng S., Cao M., & Feng J. (2022). Functional gradient of the fusiform cortex for Chinese character recognition. eNeuro, 9(3), 0495. |
| [26] |
Hecht D., & Reiner M. (2009). Sensory dominance in combinations of audio, visual and haptic stimuli. Experimental Brain Research, 193(2), 307-314.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-008-1626-z pmid: 18985327 |
| [27] |
Hickok G. (2009). Eight problems for the mirror neuron theory of action understanding in monkeys and humans. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(7), 1229-1243.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21189 pmid: 19199415 |
| [28] |
Hickok G., & Poeppel D. (2007). The cortical organization of speech processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(5), 393-402.
doi: 10.1038/nrn2113 pmid: 17431404 |
| [29] |
Hirst R. J., Kicks E. C., Allen H. A., & Cragg L. (2019). Cross- modal interference-control is reduced in childhood but maintained in aging: A cohort study of stimulus- and response-interference in cross-modal and unimodal Stroop tasks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 45(5), 553-572.
doi: 10.1037/xhp0000608 URL |
| [30] |
Huang S., Li Y., Zhang W., Zhang B., Liu X., Mo L., & Chen Q. (2015). Multisensory competition is modulated by sensory pathway interactions with fronto-sensorimotor and default-mode network regions. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(24), 9064-9077.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3760-14.2015 pmid: 26085631 |
| [31] | Joseph J. E., & Gathers A. D. (2003). Effects of structural similarity on neural substrates for object recognition. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 3( 1), 1-16. |
| [32] |
Kho S. K., Keeble D. R. T., Wong H. K., & Estudillo A. J. (2023). Investigating the role of the fusiform face area and occipital face area using multifocal transcranial direct current stimulation. Neuropsychologia, 189, 108663.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2023.108663 URL |
| [33] |
Kornblum S., Hasbroucq T., & Osman A. (1990). Dimensional overlap: Cognitive basis for stimulus-response compatibility-A model and taxonomy. Psychological Review, 97(2), 253-270.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.97.2.253 pmid: 2186425 |
| [34] |
Krause B., & Cohen Kadosh R. (2014). Not all brains are created equal: The relevance of individual differences in responsiveness to transcranial electrical stimulation. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 8, 25.
doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00025 pmid: 24605090 |
| [35] |
Krause B., Márquez-Ruiz J., & Cohen Kadosh R. (2013). The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation: A role for cortical excitation/inhibition balance? Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 602.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00602 pmid: 24068995 |
| [36] |
Li Z., Gu R., Qi M., Cen J., Zhang S., Gu J., Zeng X., & Chen Q. (2019). Loss of vision dominance at the preresponse level in tinnitus patients: Preliminary behavioral evidence. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13, 482.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00482 pmid: 31139048 |
| [37] | Liu C. L., Lai M. H., Tien K. W., Chuang Y. H., Wu S. H., & Lee C. Y. (2011). Visually and phonologically similar characters in incorrect Chinese words: Analysis, identification, and applications. ACM Transactions on Asian Language Information Processing, 10, 1-39. |
| [38] | Little D. R., Nosofsky R., & Denton S. E. (2011). Response-time tests of logical-rule models of categorization. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 37( 1), 1-27. |
| [39] |
Little J. L., & McDaniel M A., (2015). Individual differences in category learning: Memorization versus rule abstraction. Memory and Cognition, 43, 283-297.
doi: 10.3758/s13421-014-0475-1 URL |
| [40] |
Marmurek H. H., Proctor C., & Javor A. (2006). Stroop-like serial position effects in color naming of words and nonwords. Experimental Psychology, 53(2), 105-110.
pmid: 16909934 |
| [41] |
Martin A. (2007). The representation of object concepts in the brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 25-45.
pmid: 16968210 |
| [42] |
Mate J., & Baqués J. (2009). Visual similarity at encoding and retrieval in an item recognition task. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62(7), 1277-1284.
doi: 10.1080/17470210802680769 URL |
| [43] | Mayer A. R., Ryman S. G., Hanlon F. M., Dodd A. B., & Ling J. M. (2016). Look hear! The prefrontal cortex is stratified by modality of sensory input during multisensory cognitive control. Cerebral Cortex, 27(5), 2831-2840. |
| [44] | Misselhorn J., Friese U., & Engel A. K. (2019). Frontal and parietal alpha oscillations reflect attentional modulation of cross-modal matching. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 5030. |
| [45] |
Molholm S., Ritter W., Javitt D. C., & Foxe J. J. (2004). Multisensory visual-auditory object recognition in humans: A high-density electrical mapping study. Cerebral Cortex, 14(4), 452-465.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhh007 pmid: 15028649 |
| [46] |
Montgomery J. W. (1995). Examination of phonological working memory in specifically language-impaired children. Applied Psycholinguistics, 16(4), 355-378.
doi: 10.1017/S0142716400065991 URL |
| [47] |
Mummery C. J., Patterson K., Hodges J. R., & Price C. J. (1998). Functional neuroanatomy of the semantic system: Divisible by what? Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 10(6), 766-777.
pmid: 9831743 |
| [48] |
Napolitano A. C., & Sloutsky V. M. (2004). Is a picture worth a thousand words? The flexible nature of modality dominance in young children. Child Development, 75(6), 1850-1870.
pmid: 15566384 |
| [49] |
Nitsche M. A., & Paulus W. (2001). Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurology, 57(10), 1899-1901.
doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.10.1899 pmid: 11723286 |
| [50] |
Nikolin S., Martin D., Loo C. K., & Boonstra T. W. (2018). Effects of TDCS dosage on working memory in healthy participants. Brain Stimulation, 11(3), 518-527.
doi: S1935-861X(18)30031-7 pmid: 29361442 |
| [51] |
Nosofsky R. M., Palmeri T. J., & McKinley S. C. (1994). Rule-plus- exception model of classification learning. Psychological Review, 101(1), 53-79.
pmid: 8121960 |
| [52] |
Parkin B. L., Ekhtiari H., & Walsh V. F. (2015). Non- invasive human brain stimulation in cognitive neuroscience: A primer. Neuron, 87(5), 932-945.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.032 pmid: 26335641 |
| [53] |
Phillipou A., Kirkovski M., Castle D. J., Gurvich C., Abel L. A., Miles S., & Rossell S. L. (2019). High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation in anorexia nervosa: A pilot study. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 52(11), 1274-1280.
doi: 10.1002/eat.v52.11 URL |
| [54] |
Poreisz C., Boros K., Antal A., & Paulus W. (2007). Safety aspects of transcranial direct current stimulation concerning healthy subjects and patients. Brain Research Bulletin, 72(4), 208-214.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.01.004 URL |
| [55] |
Qu Q., Feng C., & Damian M. F. (2021). Interference effects of phonological similarity in word production arise from competitive incremental learning. Cognition, 212, 104738.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104738 URL |
| [56] | Quinlan P. T., & Cohen D. J. (2012). Grouping and binding in visual short-term memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 38( 5), 1432-1438. |
| [57] |
Ragert P., Vandermeeren Y., Camus M., & Cohen L. G. (2008). Improvement of spatial tactile acuity by transcranial direct current stimulation. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119(4), 805-811.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.12.001 pmid: 18203660 |
| [58] | Storkel H. L., Bontempo D. E., & Pak N. S. (2014). Online learning from input versus offline memory evolution in adult word learning: Effects of neighborhood density and phonologically related practice. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 57( 5), 1708-1721. |
| [59] |
Swick D., Ashley V., & Turken A. U. (2008). Left inferior frontal gyrus is critical for response inhibition. BMC Neuroscience, 9, 1-11.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-1 |
| [60] |
Van Veen V., & Carter C. S. (2006). Conflict and cognitive control in the brain. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15(5), 237-240.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2006.00443.x URL |
| [61] |
Vinckier F., Dehaene S., Jobert A., Dubus J. P., Sigman M., & Cohen L. (2007). Hierarchical coding of letter strings in the ventral stream: Dissecting the inner organization of the visual word-form system. Neuron, 55(1), 143-156.
pmid: 17610823 |
| [62] |
Weiss M., & Lavidor M. (2012). When less is more: Evidence for a facilitative cathodal tDCS effect in attentional abilities. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 24(9), 1826-1833.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00248 pmid: 22624605 |
| [63] |
Wu D., Zhang P., Liu N., Sun K., & Xiao W. (2021). Effects of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation over the left fusiform face area on face view discrimination depend on the individual baseline performance. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 704880.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.704880 URL |
| [64] | Yeh S. L., & Li J. L. (2002). Role of structure and component in judgments of visual similarity of Chinese characters. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Human Perception and Performance, 28( 4), 933-947. |
| [65] |
Younger J. W., Randazzo Wagner M., & Booth J. R. (2016). Weighing the cost and benefit of transcranial direct current stimulation on different reading subskills. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 10, 262.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00262 pmid: 27375421 |
| [66] |
Yuval-Greenberg S., & Deouell L. Y. (2009). The dog’s meow: Asymmetrical interaction in cross-modal object recognition. Experimental Brain Research, 193(4), 603-614.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-008-1664-6 pmid: 19066869 |
| [67] |
Zatorre R. J., Chen J. L., & Penhune V. B. (2007). When the brain plays music: Auditory-motor interactions in music perception and production. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(7), 547-558.
doi: 10.1038/nrn2152 pmid: 17585307 |
| [68] |
Zeithamova D., Maddox W. T., & Schnyer. D. M.. (2008). Dissociable prototype learning systems: Evidence from brain imaging and behavior. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(49), 13194-13201.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2915-08.2008 URL |
| [69] |
Zhang H., & Kornblum S. (1998). The effects of stimulus- response mapping and irrelevant stimulus-response and stimulus-stimulus overlap in four-choice Stroop tasks with single-carrier stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 24(1), 3-19.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.24.1.3 URL |
| [70] | Zhang J. L. (2005). The distinctive features for standard Chinese. Acta Acustica, 30(6), 506-514. |
| [71] |
Zhou H., Wang A. J., Yuan X. Y., & Jiang Y. (2025a). Object category differences regulate the sensory dominance of the response level in an audiovisual cross-modal conflict. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(6), 1001-1012.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1001 URL |
| [72] |
Zhou H., Yuan X., Xie P., Wang A., & Jiang Y. (2025b). Distinct processing stages of cross-modal conflict in schizophrenia: The role of auditory cortex underactivation. Schizophrenia Research, 281, 191-200.
doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2025.05.014 URL |
| [1] | PAN Yuean, JIANG Yunpeng, GUO Maojie, WU Xia. The influence of uncertainty and validity of expectation on the perceptual decision of motion direction [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(6): 595-603. |
| [2] | CHEN Li, SHI Xiao-ke, LI Wei-na, HU Yan. Influence of cognitive control based on different conflict levels on the expression of gender stereotypes [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(6): 628-645. |
| [3] | LI Jianhua, XIE Jiajia, ZHUANG Jin-Ying. An effect of menstrual cycle phase on episodic memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 466-480. |
| [4] | WU Jianxiao, CAO Bihua, CHEN Yun, LI Zixia, LI Fuhong. Hierarchical control in task switching: Electrophysiological evidence [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(10): 1167-1180. |
| [5] | ZHANG Mengke, LI Qing, YIN Shouhang, CHEN Antao. Changes in the level of conflict trigger conflict adaptation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(2): 128-138. |
| [6] | HUANG Yuesheng, ZHANG Bao, FAN Xinhua, HUANG Jie. Can negative emotion of task-irrelevant working memory representation affect its attentional capture? A study of eye movements [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(1): 26-37. |
| [7] | SUN Yan, LV Jiaojiao, LAN Fan, ZHANG Lina. Emotion regulation strategy of self-focused and situation-focused reappraisal and their impact on subsequent cognitive control [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(12): 1393-1406. |
| [8] | CUI Yichen, WANG Pei, CUI Yajuan. Cognitive control strategies from the perspective of perceptual conflict: An example of stereotyped information and counterstereotyped information [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(10): 1157-1170. |
| [9] | WANG Yanqing, CHEN Antao, HU Xueping, YIN Shouhang. Reward improves cognitive control by enhancing signal monitoring [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(1): 48-57. |
| [10] | HU Cenlou, ZHANG Bao, HUANG Sai. Does irrelevant long-term memory representation guide the deployment of visual attention? [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(5): 590-601. |
| [11] | ZHANG Bao, HU Cenlou, Huang Sai. What do eye movements reveal about the role of cognitive control in attention guidance from working memory representation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(9): 1105-1118. |
| [12] | LIU Cong, JIAO Lu, SUN Xun, WANG Ruiming. Immediate effect of language switch on non-proficient bilinguals’ cognitive control components [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(5): 472-481. |
| [13] | WANG Jiaying, JIAO Runkai, ZHANG Ming. The mechanism of the effect of task setting on negative compatibility effect: The effect of top-down cognition control on subliminal prime processing [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(11): 1370-1378. |
| [14] | LIU Xiaoyu; HE Chaodan; CHEN Jun; DENG Qinli. The Bilingual Cognitive Control Mechanism of Highly Proficient Cantonese-Mandarin Speakers: Evidence from A Dual-task Switching Paradigm [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(4): 439-454. |
| [15] | DOU Weiwei;ZHENG Xifu;YANG Huifang;WANG Junfang;LI Yue;E Xiaotian;Chen Qianqian. The Effect of Cognitive Distraction’s Intensity on the Process of Trauma-related Information: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(5): 656-665. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||