

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 590-602.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2026.0590
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Yi1( ), ZHAO Yajun2, ZENG Qingzhang3, ZHANG Zhijun3, WU Shengnan1
), ZHAO Yajun2, ZENG Qingzhang3, ZHANG Zhijun3, WU Shengnan1
Published:2026-04-25
Online:2026-01-16
Contact:
TANG Yi, E-mail: TANG Yi, ZHAO Yajun, ZENG Qingzhang, ZHANG Zhijun, WU Shengnan. (2026). Cross-modal transfer of statistical learning under unimodal and multimodal learning conditions. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 58(4), 590-602.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2026.0590
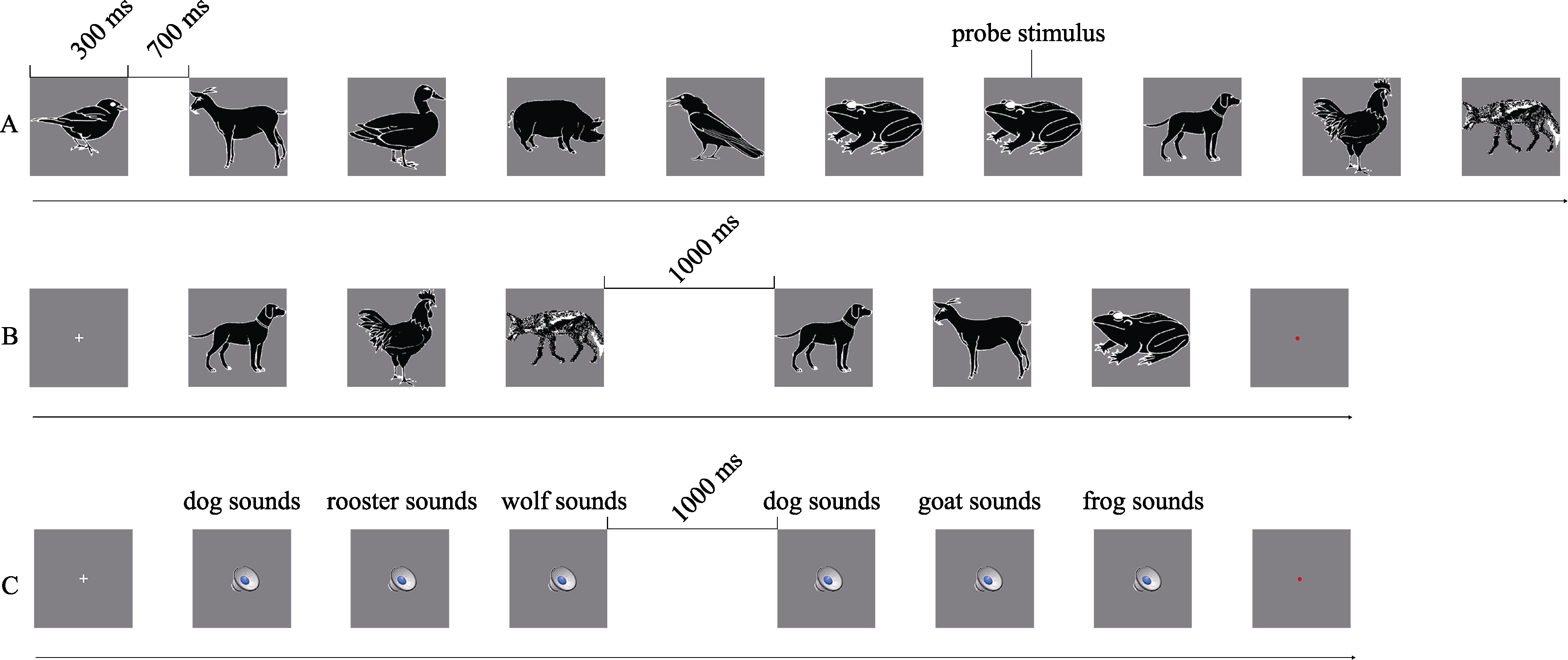
Figure 3. Examples of stimulus presentation during the familiarization phase (A) and the animal picture triplets (B) and animal sound triplets (C) during the test phase in Experiment 2.
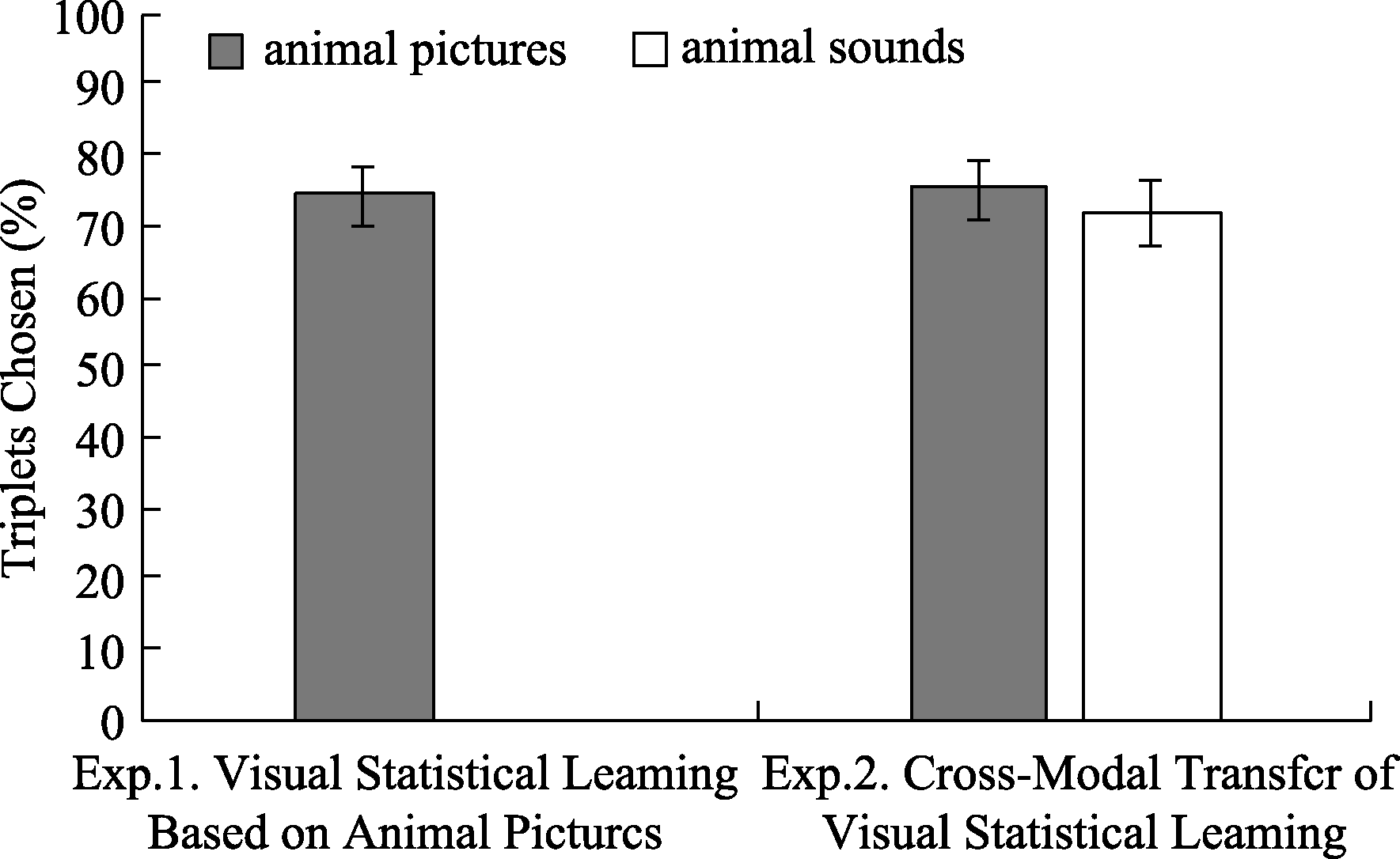
Figure 4. Percentage of triplets chosen as familiar in experiment 1 and experiment 2. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. Chance level, indicated by the dashed line, is 50%.

Figure 5. Examples of stimulus presentation during the familiarization phase(A) and the animal picture triplets(B), animal sound triplets(C) and nonsense syllable triplets(D) during the test phase in Experiment 3.
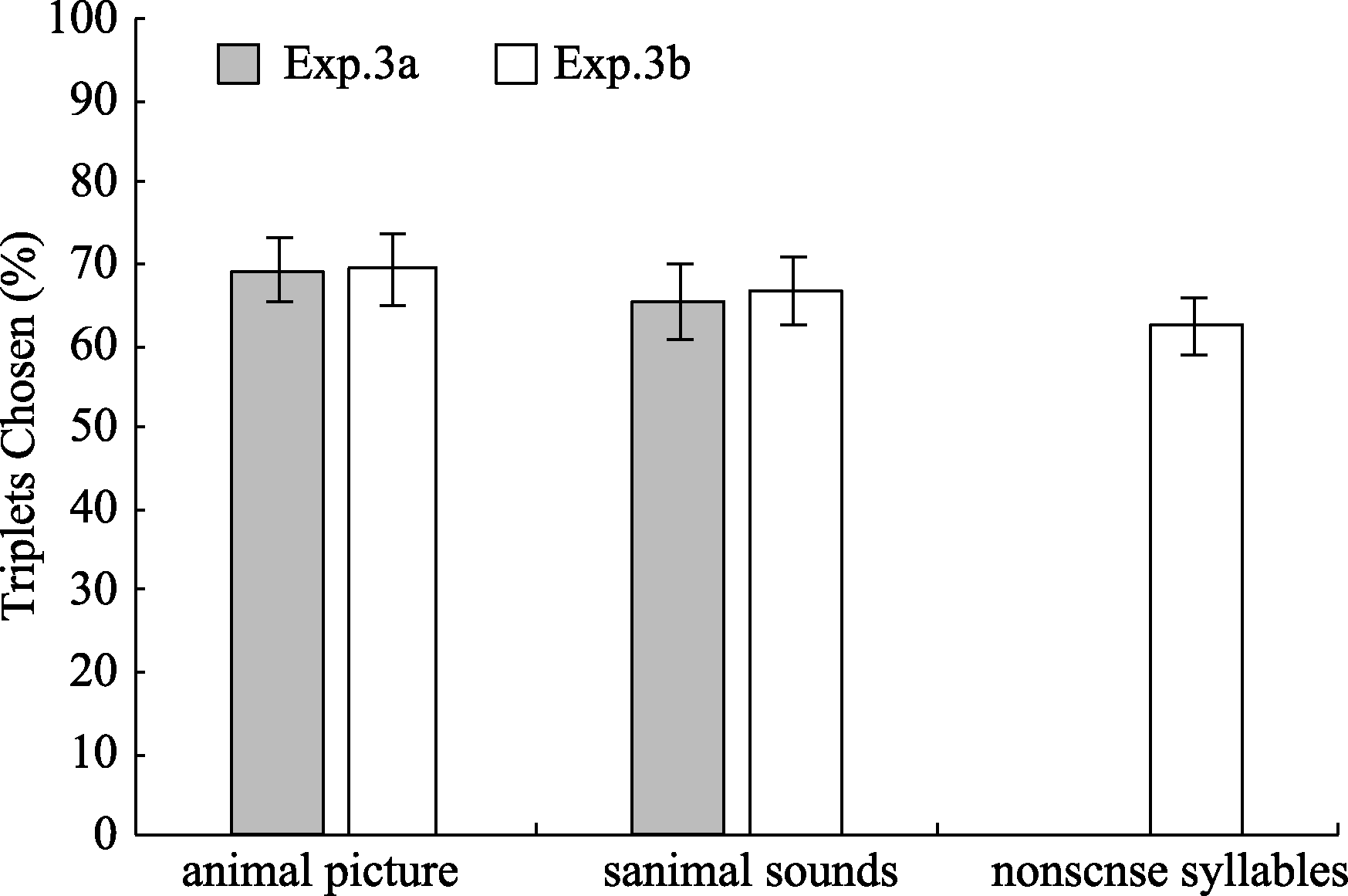
Figure 6. Percentage of triplets chosen as familiar in experiment 3. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. Chance level, indicated by the dashed line, is 50%.
| [1] |
Angelaki D. E., Gu Y., & DeAngelis G. C. (2009). Multisensory integration: Psychophysics, neurophysiology, and computation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 19(4), 452-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2009.06.008
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2009.06.008 URL |
| [2] |
Batterink L. J., Reber P. J., Neville H. J., & Paller K. A. (2015). Implicit and explicit contributions to statistical learning. Journal of Memory and Language, 83, 62-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2015.04.004
URL pmid: 26034344 |
| [3] |
Brady T. F., & Oliva A. (2008). Statistical learning using real-world scenes: Extracting categorical regularities without conscious intent. Psychological Science, 19(7), 678-685. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02142.x
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02142.x URL pmid: 18727783 |
| [4] |
Casale M. B., Roeder J. L., & Ashby F. G. (2012). Analogical transfer in perceptual categorization. Memory & Cognition, 40(3), 434-449. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-011-0154-4
doi: 10.3758/s13421-011-0154-4 URL |
| [5] | Conway C. M., & Christiansen M. H. (2005). Modality- constrained statistical learning of tactile, visual, and auditory sequences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cogniton, 31( 1), 24-39. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.31.1.24 |
| [6] |
Conway C. M., & Christiansen M. H. (2006). Statistical learning within and between modalities: Pitting abstract against stimulus-specific representations. Psychological Science, 17(10), 905-912. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01801.x
URL pmid: 17100792 |
| [7] | Eberhardt S. P., Auer E. T., & Bernstein L. E. (2014). Multisensory training can promote or impede visual perceptual learning of speech stimuli: Visual-tactile vs. visual-auditory training. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 829. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00829 |
| [8] | Edmunds C. E. R., Inkster A. B., Jones P. M., Milton F., & Wills A. J. (2020). Absence of cross-modality analogical transfer in perceptual categorization. Open Journal of Experimental Psychology and Neuroscience, 1, 3-13. https://doi.org/10.46221/ojepn.2020.8639 |
| [9] |
Emberson L. L., & Rubinstein D. Y. (2016). Statistical learning is constrained to less abstract patterns in complex sensory input (but not the least). Cognition, 153, 63-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2016.04.010
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2016.04.010 URL pmid: 27139779 |
| [10] |
Faul F., Erdfelder E., Lang A. G., & Buchner A. (2007). G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193146
doi: 10.3758/bf03193146 URL pmid: 17695343 |
| [11] |
Fiser J., & Aslin R. N. (2001). Unsupervised statistical learning of higher-order spatial structures from visual scenes. Psychological Science, 12(6), 499-504. https://doi. org/10.1111/1467-9280.00392
pmid: 11760138 |
| [12] | Fiser J., & Aslin R. N. (2002). Statistical learning of higher- order temporal structure from visual shape sequences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 28( 3), 458-467. https://doi.org/10.1037//0278-7393.28.3.458 |
| [13] |
Fiser J., & Aslin R. N. (2005). Encoding multielement scenes: Statistical learning of visual feature hierarchies. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 134(4), 521-537. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.134.4.521
doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.134.4.521 URL |
| [14] |
Frost R., Armstrong B. C., Siegelman N., & Christiansen M. H. (2015). Domain generality versus modality specificity: The paradox of statistical learning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(3), 117-125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2014.12.010
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2014.12.010 URL pmid: 25631249 |
| [15] |
Han Y. C., & Reber P. J. (2022). Implicit sequence learning using auditory cues leads to modality-specific representations. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 29(2), 541-551. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-021-02001-z
doi: 10.3758/s13423-021-02001-z URL |
| [16] |
Hocking J., Dzafic I., Kazovsky M., & Copland D. A. (2013). Nessti: Norms for environmental sound stimuli. PloS One, 8(9), e73382-e73382. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073382
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073382 URL |
| [17] |
Jun J., & Chong S. C. (2018). Visual statistical learning at basic and subordinate category levels in real-world images. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 80(8), 1946-1961. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-018-1566-z
doi: 10.3758/s13414-018-1566-z URL |
| [18] | Kirkham N. Z., Slemmer J. A., & Johnson S. P. (2002). Visual statistical learning in infancy: Evidence for a domain general learning mechanism. Cognition, 83(2), B35-B42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-0277(02)00004-5 |
| [19] |
Kligler N., & Gabay Y. (2023). A cross-modal investigation of statistical learning in developmental dyslexia. Scientific Studies of Reading, 27(4), 334-354. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2023.2166413
doi: 10.1080/10888438.2023.2166413 URL |
| [20] | Lengyel G., & Fiser J. (2019). The relationship between initial threshold, learning, and generalization in perceptual learning. Journal of Vision, 19(4), 28. https://doi.org/10.1167/19.4.28 |
| [21] |
Li X. J., Zhao X. D., Shi W. D., Lu Y., & Conway C. M. (2018). Lack of cross-modal effects in dual-modality implicit statistical learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00146
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00146 URL |
| [22] |
Liu Z. Y., Liao S. Y., & Seger C. A. (2023). Rule and exemplar-based transfer in category learning. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 35(4), 628-644. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01963
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01963 URL |
| [23] | Mitchel A. D., & Weiss D. J. (2011). Learning across senses: Cross-modal effects in multisensory statistical learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 37( 5), 1081-1091. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0023700 |
| [24] |
Otsuka S., Nishiyama M., & Kawaguchi J. (2014). Constraint on the semantic flexibility in visual statistical learning. Visual Cognition, 22(7), 865-880. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506285.2014.923548
doi: 10.1080/13506285.2014.923548 URL |
| [25] | Otsuka S., Nishiyama M., Nakahara F., & Kawaguchi J. (2013). Visual statistical learning based on the perceptual and semantic information of objects. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 39( 1), 196-207. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028645 |
| [26] | Pascual-Leone A., & Hamilton R. (2001). Chapter 27 the metamodal organization of the brain. In Progress in brain research (Vol. 134, pp. 427-445). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(01)34028-1 |
| [27] | Pavlovskaya M., & Hochstein S. (2011). Perceptual learning transfer between hemispheres and tasks for easy and hard feature search conditions. Journal of Vision, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.1167/11.1.8 |
| [28] |
Ricciardi E., & Pietrini P. (2011). New light from the dark: What blindness can teach us about brain function. Current Opinion in Neurology, 24(4), 357-363. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e 328348bdbf
doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e328348bdbf URL pmid: 21677583 |
| [29] |
Saffran J. R., Aslin R. N., & Newport E. L. (1996). Statistical learning by 8-month-old infants. Science, 274(5294), 1926-1928. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5294.1926
doi: 10.1126/science.274.5294.1926 URL pmid: 8943209 |
| [30] |
Saffran J. R., Newport E. L., Aslin R. N., Tunick R. A., & Barrueco S. (1997). Incidental language learning: Listening (and learning) out of the corner of your ear. Psychological Science, 8(2), 101-105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00690.x
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00690.x URL |
| [31] |
Seitz A. R., Kim R., van Wassenhove V., & Shams L. (2007). Simultaneous and independent acquisition of multisensory and unisensory associations. Perception, 36(10), 1445-1453. https://doi.org/10.1068/p5843
URL pmid: 18265827 |
| [32] |
Shanks D. R., Johnstone T., & Staggs L. (1997). Abstraction processes in artificial grammar learning. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 50(1), 216-252. https://doi.org/10.1080/713755680
doi: 10.1080/713755680 URL |
| [33] |
Shi W. D., Li X. J., Wang W., & Yan W. H. (2013). Comparison of implicit learning effect between multisensory and unisensory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45(12), 1313-1323. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2013.01313
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2013.01313 URL |
| [34] |
Siegelman N., & Frost R. (2015). Statistical learning as an individual ability: Theoretical perspectives and empirical evidence. Journal of Memory and Language, 81, 105-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2015.02.001
URL pmid: 25821343 |
| [35] |
Sun X. W., Yao L. S., Fu Q. F., & Fu X. L. (2023). Multisensory transfer effects in implicit and explicit category learning. Psychological Research-Psychologische Forschung, 87(5), 1353-1369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-022-01754-z
doi: 10.1007/s00426-022-01754-z URL |
| [36] |
Tang Y., Zhang Z. J., Zeng M. M., Huang K., Liu W., & Zhao Y. J. (2015). Visual statistical learning based on the visual feature and semantic information of famous faces. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(7), 837-850. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00837
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00837 URL |
| [37] |
Thiessen E. D. (2010). Effects of visual information on adults' and infants' auditory statistical learning. Cognitive Science, 34(6), 1093-1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01118.x
doi: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01118.x URL pmid: 21564244 |
| [38] |
Tunney R. J., & Altmann G. T. M. (2001). Two modes of transfer in artificial grammar learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 27(3), 614-639. https://doi.org/10.1037//0278-7393.27.3.614
doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.27.3.614 URL |
| [39] | Turk-Browne N. B., Isola P. J., Scholl B. J., & Treat T. A. (2008). Multidimensional visual statistical learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 34(2), 399-407. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.34.2.399 |
| [40] |
Turk-Browne N. B., Junge J. A., & Scholl B. J. (2005). The automaticity of visual statistical learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 134(4), 552-564. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.134.4.552
doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.134.4.552 URL |
| [41] |
Turk-Browne N. B., & Scholl B. J. (2009). Flexible visual statistical learning: transfer across space and time. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(1), 195-202. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.35.1.195
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.35.1.195 URL |
| [42] |
Uno K., Asano M., Kadowaki H., & Yokosawa K. (2020). Grapheme-color associations can transfer to novel graphemes when synesthetic colors function as grapheme "discriminating markers". Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 27(4), 700-706. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-020-01732-9
doi: 10.3758/s13423-020-01732-9 URL |
| [43] |
von der Emde, G., & de Perera, T. B. 2020). Cross-modal sensory transfer: Bumble bees do it Stored sensory input permits two sensory channels to exchange and compare information. Science, 367(6480), 850-851. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba8519
doi: 10.1126/science.aba8519 URL pmid: 32079758 |
| [44] |
Xiong Y. Z., Guan S. C., & Yu C. (2022). A supramodal and conceptual representation of subsecond time revealed with perceptual learning of temporal interval discrimination. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 10668. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14698-6
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14698-6 URL |
| [45] |
Xu G. P., Fan R. L., & Jin H. (2020). The cognitive and neural mechanisms of statistical learning and its relationship with language. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(9), 1525-1538. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J. 1042.2020.01525
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01525 URL |
| [46] | Zaltz Y., Kishon-Rabin L., Karni A., & Ari-Even Roth D. (2020). Practice makes transfer imperfect: Evidence from auditory learning. Ear and Hearing, 41(6), 1470-1482. https://doi.org/10.1097/aud.0000000000000860 |
| [47] | Zhang Q. F., & Yang Y. F. (2003). The determiners of picture- naming latency. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 35(4), 447-454. https://journal.psych.ac.cn/xlxb/CN/ |
| [48] |
Zhao J., Al-Aidroos N., & Turk-Browne N. B. (2013). Attention is spontaneously biased toward regularities. Psychological Science, 24(5), 667-677. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612460407
doi: 10.1177/0956797612460407 URL pmid: 23558552 |
| [1] | ZHOU Zisen, HUANG Qi, TAN Zehong, LIU Rui, CAO Ziheng, MU Fangman, FAN Yachun, QIN Shaozheng. Emotional capabilities evaluation of multimodal large language model in dynamic social interaction scenarios [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(11): 1988-2000. |
| [2] | ZHAN Peida. Joint-cross-loading multimodal cognitive diagnostic modeling incorporating visual fixation counts [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(11): 1416-1432. |
| [3] | YU Wenbo, WANG Lu, QU Xingfang, WANG Tianlin, ZHANG Jingjing, LIANG Dandan. Transitional probabilities and expectation for word length impact verbal statistical learning [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(6): 565-574. |
| [4] | TANG Yi, ZHANG Zhijun, ZENG Meimei, HUANG Ke, LIU Wei, ZHAO Yajun. Visual Statistical Learning Based on the Visual Feature and Semantic Information of Famous Faces [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(7): 837-850. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||