

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 300-312.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00300
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU WenXing1, ZHU YangHao1, BAI Yang2( ), WANG HaiJiang3, HAN Yi1
), WANG HaiJiang3, HAN Yi1
Received:2021-05-07
Published:2022-03-25
Online:2022-01-25
Contact:
BAI Yang
E-mail:ybai@gsm.pku.edu.cn
Supported by:LIU WenXing, ZHU YangHao, BAI Yang, WANG HaiJiang, HAN Yi. (2022). Indulge in self-admiration or offer help to others? The influence of employee narcissism on prosocial behavior. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 54(3), 300-312.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00300
| Factors | χ² | df | χ²/df | ∆χ²/∆df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six-factor model (AN; RN; TI; APM; AVM; PSB) | 374.99 | 120 | 3.13 | / | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Five-factor model (AN + RN; TI; APM; AVM; PSB) | 748.51 | 125 | 5.99 | 373.52(5)*** | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.15 | 0.10 |
| Four-factor model (AN + RN; TI; APM + AVM; PSB) | 1495.17 | 129 | 11.59 | 1120.19(9)*** | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| Three-factor model (AN + RN + TI; APM + AVM; PSB) | 2252.12 | 132 | 17.06 | 1877.14(12)*** | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Two-factor model (AN + RN + TI; APM + AVM + PSB) | 2799.65 | 134 | 20.89 | 2424.66(14)*** | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.20 |
| Single factor model (AN + RN + TI + APM + AVM + PSB) | 3573.91 | 135 | 26.47 | 3198.93(15)*** | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.26 |
Table 1 Confirmatory factor analysis results
| Factors | χ² | df | χ²/df | ∆χ²/∆df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six-factor model (AN; RN; TI; APM; AVM; PSB) | 374.99 | 120 | 3.13 | / | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Five-factor model (AN + RN; TI; APM; AVM; PSB) | 748.51 | 125 | 5.99 | 373.52(5)*** | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.15 | 0.10 |
| Four-factor model (AN + RN; TI; APM + AVM; PSB) | 1495.17 | 129 | 11.59 | 1120.19(9)*** | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| Three-factor model (AN + RN + TI; APM + AVM; PSB) | 2252.12 | 132 | 17.06 | 1877.14(12)*** | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Two-factor model (AN + RN + TI; APM + AVM + PSB) | 2799.65 | 134 | 20.89 | 2424.66(14)*** | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.20 |
| Single factor model (AN + RN + TI + APM + AVM + PSB) | 3573.91 | 135 | 26.47 | 3198.93(15)*** | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.26 |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gender | ||||||||||||
| 2. Age | 0.31** | |||||||||||
| 3.Education level | -0.06 | -0.29** | ||||||||||
| 4. Industry 1 | -0.08 | -0.01 | -0.12 | |||||||||
| 5. Industry 2 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | -0.31** | ||||||||
| 6. Industry 3 | 0.04 | -0.02 | 0.07 | -0.33** | -0.37** | |||||||
| 7. AN | -0.11 | -0.27** | -0.19** | 0.10 | -0.03 | -0.05 | ||||||
| 8. RN | 0.03 | -0.06 | -0.22** | 0.04 | -0.08 | 0.02 | 0.41** | |||||
| 9. TI | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.17** | 0.03 | 0.09 | -0.11 | -0.10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 10. APM | 0.06 | -0.19** | 0.11 | -0.09 | 0.07 | -0.05 | 0.18** | 0.03 | -0.01 | |||
| 11. AVM | 0.06 | -0.05 | -0.11 | 0.10 | -0.08 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.20** | 0.04 | -0.30** | ||
| 12. PSB | -0.07 | -0.24** | 0.21** | -0.12 | 0.11 | -0.01 | 0.18** | -0.20** | -0.03 | 0.44** | -0.19** | |
| M | 0.57 | 29.05 | 3.36 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 3.84 | 2.25 | 3.50 | 5.55 | 1.40 | 5.78 |
| SD | 0.50 | 6.59 | 1.07 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 1.38 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.91 |
Table 2 Variable description statistics and correlation analysis results
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gender | ||||||||||||
| 2. Age | 0.31** | |||||||||||
| 3.Education level | -0.06 | -0.29** | ||||||||||
| 4. Industry 1 | -0.08 | -0.01 | -0.12 | |||||||||
| 5. Industry 2 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | -0.31** | ||||||||
| 6. Industry 3 | 0.04 | -0.02 | 0.07 | -0.33** | -0.37** | |||||||
| 7. AN | -0.11 | -0.27** | -0.19** | 0.10 | -0.03 | -0.05 | ||||||
| 8. RN | 0.03 | -0.06 | -0.22** | 0.04 | -0.08 | 0.02 | 0.41** | |||||
| 9. TI | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.17** | 0.03 | 0.09 | -0.11 | -0.10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 10. APM | 0.06 | -0.19** | 0.11 | -0.09 | 0.07 | -0.05 | 0.18** | 0.03 | -0.01 | |||
| 11. AVM | 0.06 | -0.05 | -0.11 | 0.10 | -0.08 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.20** | 0.04 | -0.30** | ||
| 12. PSB | -0.07 | -0.24** | 0.21** | -0.12 | 0.11 | -0.01 | 0.18** | -0.20** | -0.03 | 0.44** | -0.19** | |
| M | 0.57 | 29.05 | 3.36 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 3.84 | 2.25 | 3.50 | 5.55 | 1.40 | 5.78 |
| SD | 0.50 | 6.59 | 1.07 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 1.38 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.91 |
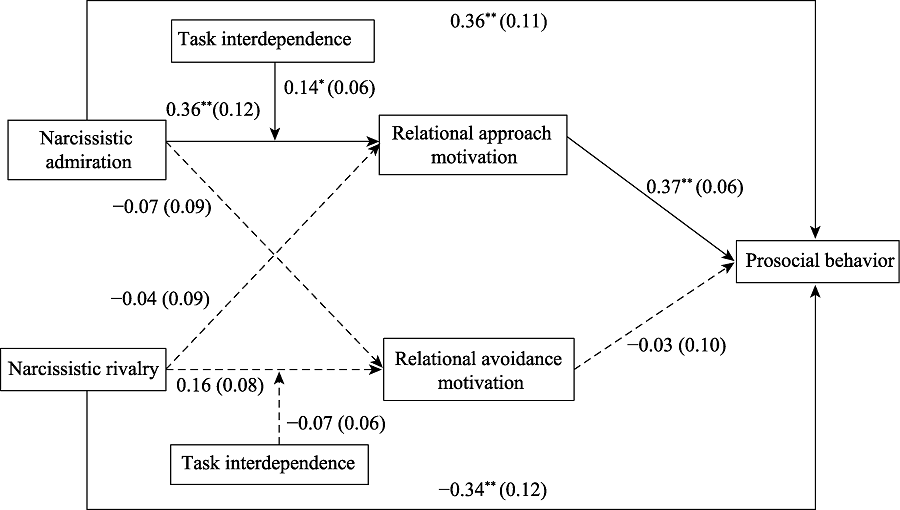
Figure 2. Path analysis results of the whole model. Note. The report is a non-standardized coefficient, and the standard error is in brackets; The solid line indicates that the path coefficient is significant, while the dashed line indicates that the path coefficient is not significant. For brevity, the control variable path coefficient has been omitted. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
| Task interdependence | Indirect effect | Standard error | 95% CI of indirect effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low task interdependence | 0.06 | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.16 |
| High task interdependence | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.36 |
| Difference of indirect effects under high and low conditions | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.30 |
Table 3 Results of mediating effect analysis
| Task interdependence | Indirect effect | Standard error | 95% CI of indirect effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low task interdependence | 0.06 | 0.05 | -0.02 | 0.16 |
| High task interdependence | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.36 |
| Difference of indirect effects under high and low conditions | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.30 |
| [1] | Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage Publications, Inc. |
| [2] | American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. |
| [3] | Back, M. D. (2018). The narcissistic admiration and rivalry concept. In A. D. Hermann, A. B. Brunell, & J. D. Foster (Eds.), The handbook of trait narcissism: Key advances, research methods, and controversies (pp.57-67). New York, NY: Springer. |
| [4] |
Back, M. D., Küfner, A. C., Dufner, M., Gerlach, T. M., Rauthmann, J. F., & Denissen, J. J. (2013). Narcissistic admiration and rivalry: Disentangling the bright and dark sides of narcissism. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 105(6), 1013-1037.
doi: 10.1037/a0034431 URL |
| [5] | Back, M. D., Küfner, A. C. P., & Leckelt, M. (2018). Early impressions of grandiose narcissists:A dual-pathway perspective. In A. D. Hermann, A. B. Brunell, & J. D. Foster (Eds.), The handbook of trait narcissism: Key advances, research methods, and controversies (pp.309-316). New York, NY: Springer. |
| [6] | Batson, C. D. (2011). Altruism in humans. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [7] | Batson, C. D., & Powell, A. A. (2003). Altruism and prosocial behavior. In T. Millon & M. J. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of psychology: Personality and social psychology, Vol. 5, (pp.463-484). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. |
| [8] |
Benson, A. J., Jeschke, J., Jordan, C. H., Bruner, M. W., & Arnocky, S. (2019). Will they stay or will they go? Narcissistic admiration and rivalry predict ingroup affiliation and devaluation. Journal of Personality, 87(4), 871-888.
doi: 10.1111/jopy.12441 pmid: 30317647 |
| [9] |
Bishop, J. W., & Scott, K. D. (2000). An examination of organizational and team commitment in a self-directed team environment. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85(3), 439-450.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.85.3.439 pmid: 10900817 |
| [10] |
Cain, N. M., Pincus, A. L., & Ansell, E. B. (2008). Narcissism at the crossroads: Phenotypic description of pathological narcissism across clinical theory, social/personality psychology, and psychiatric diagnosis. Clinical Psychology Review, 28(4), 638-656.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2007.09.006 URL |
| [11] | Campbell, W. K., & Campbell, S. M. (2009). On the self-regulatory dynamics created by the peculiar benefits and costs of narcissism: A contextual reinforcement model and examination of leadership. Self and Identity, 8(2-3), 214-232. |
| [12] | Campbell, W. K., & Miller, J. D. (2011). The handbook of narcissism and narcissistic personality disorder: Theoretical approaches, empirical findings, and treatments. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [13] | Chen, L., Qu, X., & Yang, B. Y. (2018). Are narcissistic subordinates more silent? Exploring the destructive effect of narcissistic leadership on subordinate job performance. Forecasting, 37(2), 9-14+21. |
| [14] |
Cheng, H., Zhang, Y. L., Yao, X., Zhang, X. K. (2021). The relationship between narcissism and BIS/BAS: A meta-analysis. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(10), 1796-1807.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.01796 URL |
| [15] |
Cheshure, A., Zeigler-Hill, V., Sauls, D., Vrabel, J. K., & Lehtman, M. J. (2020). Narcissism and emotion dysregulation: Narcissistic admiration and narcissistic rivalry have divergent associations with emotion regulation difficulties. Personality and Individual Differences, 154, 109679.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.109679 URL |
| [16] |
Ding, F. Q., & Lu, Z. H. (2016). Association between empathy and prosocial behavior: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Advances in Psychological Science, 24(8), 1159-1174.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.01159 URL |
| [17] |
Ding, R. Y., Zhou, H., Zhang, B., & Chen, X. (2016). Narcissism and adolescents’ prosocial behaviors: The role of public and private situations. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(8), 981-988.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00981 URL |
| [18] |
Eagly, A. H., & Crowley, M. (1986). Gender and helping behavior: A meta-analytic review of the social psychological literature. Psychological Bulletin, 100(3), 283-308.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.100.3.283 URL |
| [19] |
Edwards, J. R., & Lambert, L. S. (2007). Methods for integrating moderation and mediation: A general analytical framework using moderated path analysis. Psychological Methods, 12(1), 1-22.
doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.12.1.1 URL |
| [20] | Elliot, A. J. (2008). Approach and avoidance motivation. In A. J. Elliot (Ed.), Handbook of approach and avoidance motivation (pp.3-14). Psychology Press. |
| [21] |
Emmons, R. A. (1987). Narcissism: Theory and measurement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52(1), 11-17.
pmid: 3820065 |
| [22] |
Fatfouta, R. (2017). To be alone or not to be alone? Facets of narcissism and preference for solitude. Personality and Individual Differences, 114, 1-4.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.03.047 URL |
| [23] |
Fatfouta, R., Gerlach, T. M., Schröder-Abé, M., & Merkl, A. (2015). Narcissism and lack of interpersonal forgiveness: The mediating role of state anger, state rumination, and state empathy. Personality and Individual Differences, 75, 36-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2014.10.051 URL |
| [24] |
Fehn, T., & Schütz, A. (2021). What you get is what you see: Other-rated but not self-rated leaders’ narcissistic rivalry affects followers negatively. Journal of Business Ethics, 174(3), 549-566.
doi: 10.1007/s10551-020-04604-3 URL |
| [25] |
Ferris, D. L., Johnson, R. E., Rosen, C. C., Djurdjevic, E., Chang, C. H. D., & Tan, J. A. (2013). When is success not satisfying? Integrating regulatory focus and approach/avoidance motivation theories to explain the relation between core self-evaluation and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology, 98(2), 342-353.
doi: 10.1037/a0029776 pmid: 22963514 |
| [26] |
Foster, J. D., Campbell, W. K., & Twenge, J. M. (2003). Individual differences in narcissism: Inflated self-views across the lifespan and around the world. Journal of Research in Personality, 37(6), 469-486.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-6566(03)00026-6 URL |
| [27] |
Gable, P. A., & Harmon-Jones, E. (2008). Approach-motivated positive affect reduces breadth of attention. Psychological Science, 19(5), 476-482.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02112.x URL |
| [28] |
Geukes, K., Nestler, S., Hutteman, R., Dufner, M., Küfner, A. C. P., Egloff, B., … Back, M. D. (2017). Puffed-up but shaky selves: State self-esteem level and variability in narcissists. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 112(5), 769-786.
doi: 10.1037/pspp0000093 URL |
| [29] |
Grant, A. M., & Sumanth, J. J. (2009). Mission possible? The performance of prosocially motivated employees depends on manager trustworthiness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(4), 927-944.
doi: 10.1037/a0014391 pmid: 19594235 |
| [30] |
Grove, J. L., Smith, T. W., Girard, J. M., & Wright, A. G. (2019). Narcissistic admiration and rivalry: An interpersonal approach to construct validation. Journal of Personality Disorders, 33(6), 751-775.
doi: 10.1521/pedi_2019_33_374 URL |
| [31] |
He, N., & Zhu, Y. L. (2016). Self-love and other-love: Research on the relationships among narcissism, empathy and implicit altruism. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(2), 199-210.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00199 URL |
| [32] |
Helfrich, H., & Dietl, E. (2019). Is employee narcissism always toxic?-The role of narcissistic admiration, rivalry and leaders’ implicit followership theories for employee voice. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 28(2), 259-271.
doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2019.1575365 |
| [33] |
Hepper, E. G., Hart, C. M., & Sedikides, C. (2014). Moving Narcissus: Can narcissists be empathic? Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40(9), 1079-1091.
pmid: 24878930 |
| [34] |
Judge, T. A., LePine, J. A., & Rich, B. L. (2006). Loving yourself abundantly: Relationship of the narcissistic personality to self-and other perceptions of workplace deviance, leadership, and task and contextual performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(4), 762-775.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.91.4.762 URL |
| [35] |
Kauten, R., & Barry, C. T. (2014). Do you think I’m as kind as I do? The relation of adolescent narcissism with self-and peer-perceptions of prosocial and aggressive behavior. Personality and Individual Differences, 61-62, 69-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2014.01.014 URL |
| [36] |
Kauten, R. L., & Barry, C. T. (2016). Adolescent narcissism and its association with different indices of prosocial behavior. Journal of Research in Personality, 60, 36-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2015.11.004 URL |
| [37] |
Konrath, S., Ho, M. H., & Zarins, S. (2016). The strategic helper: Narcissism and prosocial motives and behaviors. Current Psychology, 35(2), 182-194.
doi: 10.1007/s12144-016-9417-3 URL |
| [38] | Konrath, S., & Tian, Y. (2018). Narcissism and prosocial behavior. In A. D. Hermann, A. B. Brunell, & J. D. Foster (Eds.), The handbook of trait narcissism: Key advances, research methods, and controversies (pp.371-378). New York, NY: Springer. |
| [39] |
Lange, J., Crusius, J., & Hagemeyer, B. (2016). The evil queen’s dilemma: Linking narcissistic admiration and rivalry to benign and malicious envy. European Journal of Personality, 30(2), 168-188.
doi: 10.1002/per.2047 URL |
| [40] |
Lannin, D. G., Guyll, M., Krizan, Z., Madon, S., & Cornish, M. (2014). When are grandiose and vulnerable narcissists least helpful? Personality and Individual Differences, 56, 127-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2013.08.035 URL |
| [41] |
Leckelt, M., Küfner, A. C. P., Nestler, S., & Back, M. D. (2015). Behavioral processes underlying the decline of narcissists’ popularity over time. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 109(5), 856-871.
doi: 10.1037/pspp0000057 pmid: 26191958 |
| [42] | Li, M. Z., Liu, W. X., & Zhou, K. (2017). Does narcissistic leadership evoke workplace deviance? --An explanation from moral disengagement and deontic justice theory. Human Resources Development of China, (4), 76-83. |
| [43] |
Li, M. Z., Ye, H. L., & Zhang, G. L. (2020). The influence mechanism of narcissistic leadership on the formation process of team creativity: A multi-perspective study. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(9), 1437-1453.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01437 URL |
| [44] | Liao, J. Q., Shaw, K. H., & Tian, T. (2016). Narcissistic leadership: The formation, function and management strategies. Management Review, 28(6), 131-139. |
| [45] | Liao, S. D., Liu, W. X., & Liao, J. Q. (2016). Research the impact of leader narcissism on employee silence behavior. Industrial Engineering and Management, 21(6), 130-137. |
| [46] |
Little, T. D., Cunningham, W. A., Shahar, G., & Widaman, K. F. (2002). To parcel or not to parcel: Exploring the question, weighing the merits. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 9(2), 151-173.
doi: 10.1207/S15328007SEM0902_1 URL |
| [47] | Liu, M. W., Wang, H. Y., & Li, M. Z. (2020). Does self-righteous promote taking the initiative to change? Research on the relationship between employee narcissism and taking charge behavior. Human Resources Development of China, 37(2), 21-33. |
| [48] |
Liu, Y. P., Li, S. S., He, Y., Wang, D. D., & Yang, B. (2021). Eliminating threat or venting rage? The relationship between narcissism and aggression in violent offenders. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(3), 244-258.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00244 URL |
| [49] |
Liu, Y. X., Chen, C., Zhu, N., Zhang, J. W., & Wang, S. (2020). How does “one takes on the attributes of one's associates”? The past, present, and future of Trait Activation Theory. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(1), 161-177.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.00161 URL |
| [50] |
Manley, H., Jarukasemthawee, S., & Pisitsungkagarn, K. (2019). The effect of narcissistic admiration and rivalry on mental toughness. Personality and Individual Differences, 148, 1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.05.009 |
| [51] |
Manley, H., Paisarnsrisomsuk, N., & Roberts, R. (2020). The effect of narcissistic admiration and rivalry on speaking performance. Personality and Individual Differences, 154, 109624.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.109624 URL |
| [52] |
Miao, C., Humphrey, R. H., & Qian, S. (2017). Are the emotionally intelligent good citizens or counterproductive? A meta-analysis of emotional intelligence and its relationships with organizational citizenship behavior and counterproductive work behavior. Personality and Individual Differences, 116, 144-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.04.015 URL |
| [53] |
Miller, J. D., & Campbell, W. K. (2008). Comparing clinical and social‐personality conceptualizations of narcissism. Journal of Personality, 76(3), 449-476.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2008.00492.x URL |
| [54] |
Miller, J. D., Lynam, D. R., McCain, J. L., Few, L. R., Crego, C., Widiger, T. A., & Campbell, W. K. (2016). Thinking structurally about narcissism: An examination of the Five-Factor Narcissism Inventory and its components. Journal of Personality Disorders, 30(1), 1-18.
doi: 10.1521/pedi_2015_29_177 URL |
| [55] |
Morf, C. C., & Rhodewalt, F. (2001). Unraveling the paradoxes of narcissism: A dynamic self-regulatory processing model. Psychological Inquiry, 12(4), 177-196.
doi: 10.1207/S15327965PLI1204_1 URL |
| [56] |
Owens, B. P., Wallace, A. S., & Waldman, D. A. (2015). Leader narcissism and follower outcomes: The counterbalancing effect of leader humility. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100(4), 1203-1213.
doi: 10.1037/a0038698 |
| [57] |
Piff, P. K., Kraus, M. W., Côté, S., Cheng, B. H., & Keltner, D. (2010). Having less, giving more: The influence of social class on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 99(5), 771-784.
doi: 10.1037/a0020092 URL |
| [58] |
Pincus, A. L., & Lukowitsky, M. R. (2010). Pathological narcissism and narcissistic personality disorder. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 6, 421-446.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131215 pmid: 20001728 |
| [59] |
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879-903.
pmid: 14516251 |
| [60] |
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 539-569.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452 pmid: 21838546 |
| [61] | Qureshi, S. U., Ashfaq, J., ul Hassan, M., & Imdadullah, M. (2015). Impact of extroversion and narcissism on in role and extra role performance: Moderating role of impression management motives. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences(PJCSS), 9(1), 96-119. |
| [62] |
Rogoza, R., Wyszyńska, P., Maćkiewicz, M., & Cieciuch, J. (2016). Differentiation of the two narcissistic faces in their relations to personality traits and basic values. Personality and Individual Differences, 95, 85-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2016.02.038 URL |
| [63] |
Sargent, L. D., & Sue-Chan, C. (2001). Does diversity affect group efficacy? The intervening role of cohesion and task interdependence. Small Group Research, 32(4), 426-450.
doi: 10.1177/104649640103200403 URL |
| [64] |
Sauls, D., & Zeigler-Hill, V. (2020). Basic emotional systems and narcissistic personality features: What is the emotional core of narcissism? Personality and Individual Differences, 162, 110032.
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2020.110032 URL |
| [65] | Schermelleh-Engel, K., Moosbrugger, H., & Müller, H. (2003). Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods of Psychological Research Online, 8(2), 23-74. |
| [66] | Tang, D. D., & Wen, Z. L. (2020). Statistical approaches for testing common method bias: Problems and suggestions. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 215-223. |
| [67] |
Tett, R. P., & Burnett, D. D. (2003). A personality trait-based interactionist model of job performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(3), 500-517.
doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.3.500 URL |
| [68] |
Tett, R. P., & Guterman, H. A. (2000). Situation trait relevance, trait expression, and cross-situational consistency: Testing a principle of trait activation. Journal of Research in Personality, 34(4), 397-423.
doi: 10.1006/jrpe.2000.2292 URL |
| [69] | Tett, R. P., Simonet, D. V., Walser, B., & Brown, C. (2013). Trait activation theory:Applications, developments, and implications for person-workplace fit. In N. D. Christiansen & R. P. Tett (Eds.), Handbook of personality at work (pp.71-100). New York, NY: Routledge. |
| [70] | Tracy, J. L., Cheng, J. T., Martens, J. P., & Robins, R. W. (2011). The emotional dynamics of narcissism: Inflated by pride, deflated by shame. In W. K. Campbell & J. D. Miller (Eds.), The handbook of narcissism and narcissistic personality disorder: Theoretical approaches, empirical findings, and treatments (pp.330-343). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. |
| [71] |
Treadway, D. C., Yang, J., Bentley, J. R., Williams, L. V., & Reeves, M. (2019). The impact of follower narcissism and LMX perceptions on feeling envied and job performance. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30(7), 1181-1202.
doi: 10.1080/09585192.2017.1288151 URL |
| [72] | Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2009). The narcissism epidemic: Living in the age of entitlement. Free Press. |
| [73] |
Twenge, J. M., & Foster, J. D. (2010). Birth cohort increases in narcissistic personality traits among American college students, 1982-2009. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 1(1), 99-106.
doi: 10.1177/1948550609355719 URL |
| [74] |
van der Vegt, G. S., & Janssen, O. (2003). Joint impact of interdependence and group diversity on innovation. Journal of Management, 29(5), 729-751.
doi: 10.1016/S0149-2063(03)00033-3 URL |
| [75] | van der Vegt, G. S., van de Vliert, E., & Oosterhof, A. (2003). Informational dissimilarity and organizational citizenship behavior: The role of intrateam interdependence and team identification. Academy of Management Journal, 46(6), 715-727. |
| [76] |
Wang, D. X., Zeng, K. & Zheng, X. W. (2017). How employee’s unethical behavior leads to coworker-initiated aggression: The perspective of deontic justice. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(6), 829- 840.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00829 URL |
| [77] | Wang, M. Y., Wang, Z. H., Zhang, W. J., & Yin, Z. Z. (2018). Narcissism and pro-social behavior of college students: The mediate effect of the cognitive empathy. China Journal of Health Psychology, 26(3), 430-433. |
| [78] |
Watson, P. J., Grisham, S. O., Trotter, M. V., & Biderman, M. D. (1984). Narcissism and empathy: Validity evidence for the narcissistic personality inventory. Journal of Personality Assessment, 48(3), 301- 305.
pmid: 16367529 |
| [79] | Weiss, B., & Miller, J. D. (2018). Distinguishing between grandiose narcissism, vulnerable narcissism, and narcissistic personality disorder. In A. D. Hermann, A. B. Brunell, & J. D. Foster (Eds.), The handbook of trait narcissism: Key advances, research methods, and controversies (pp.3-13). New York, NY: Springer. |
| [80] | Wu, Y., & Wen, Z. L. (2011). Item parceling strategies in structural equation modeling. Advances in Psychological Science, 19(12), 1859-1867. |
| [81] | Yang, C., & Zhang, L. (2021). The double-edged sword effect of employee narcissism on knowledge hiding. Management Review, 33(3), 192-201. |
| [82] | Zhou, H., Zhou, H., & Zhang, B. (2010). Relationships among narcissism, empathy, and prosocial behaviours. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(2), 228-231. |
| [83] |
Zhou, K., Liu, W., Li, M., Cheng, Z., & Hu, X. (2020). The relationship between narcissism and taking charge: The role of energy at work and hierarchical level. Psychological Reports, 123(2), 472-487.
doi: 10.1177/0033294118811615 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||