1 问题提出
在当今社会, 领导者不可避免地需要面对、处理诸多“互异”诉求, 如关注任务还是关心下属, 以自我为中心还是以下属为中心。新近研究指出(Owens, Wallace, & Waldman, 2015), 单一的领导行为已无法满足组织及其成员的多样化需求, 取而代之的是需要一种运用“既/又”整合思维的领导方式, 即双元领导(Ambidextrous Leadership) (Rosing, Frese, & Bausch, 2011)。双元领导是由两种差异互补的领导行为构成的新型领导风格(Rosing et al., 2011), 并被视为影响工作产出的重要驱动力。纵观现状, 双元领导研究主要聚焦在西方情境, 关注探索与利用 (Keller & Weibler, 2015)、变革和交易(Schreuders & Legesse, 2012)等领导行为的整合, 而根植于中国情境的双元领导探索还比较匮乏。鉴于此, 本文拟立足于中国本土情境, 开展具有中国文化特色的双元领导研究。在中国, 由于受泛家族主义的影响(杨国枢, 2004), 组织中上下级之间会呈现类似父子般的关系。此时, 领导者(Leader)像父亲一样, 既会树立威严来监管下属, 又会表现出关怀下属的仁慈一面, 由此展现出“恩威并施”的领导行为。目前, 不少研究表明恩威并施与下属工作表现呈正相关(Tsai, Spain, & Wang, 2013; Wang, Wang, Tang, Tang, & Al, 2016)。然而, 也有一些研究发现, 仁慈和权威领导并不能交互影响下属工作产出(李珲, 丁刚, 李新建, 2014), 甚至负向影响公平感(周浩, 龙立荣, 2007)。出现上述问题的原因可能在于:其一, 恩威并施与工作产出之间很可能存在复杂的影响路径, 而不同路径则会给恩威并施带来不同的影响效果。其二, 在恩威并施过程中, “仁慈领导者的施恩”和“权威领导者的立威”存在着不同组合情况, 而不同组合中下属受到的对待也不尽相同, 这可能给其工作产出造成差异化的影响效果。
为了解决上述议题, 本文拟基于追随力理论(Followership Theory) (Uhl-Bien, Riggio, Lowe, & Carsten, 2014), 以期打开恩威并施影响下属工作绩效的黑箱。追随力作为一种拥护并支持领导者工作的行为表现, 其中重要且具有高度共识的维度是积极执行, 即下属在执行领导者指令过程中体现出来的克服困难、精益求精等行为(周文杰, 宋继文, 李浩澜, 2015)。本研究认为, 领导者恩威并施会直接决定下属在任务执行过程中的积极性, 最终影响到任务执行的质量和效率。具体来讲, 仁慈的领导者, 会激发下属产生感恩与回报之情, 从而引发下属效忠; 而威权的领导者, 则会展现出高绩效指标、形象整饰及教诲行为(Farh & Cheng, 2000), 这会促使下属公开附和、服从指派。倘若领导者采取恩威并施, 下属在这种“宽严并济”的工作氛围中, 可能会善意地理解威权领导行为(石冠峰, 李琨, 2014), 认为威权仅仅是对工作方面的严格要求, 对事不对人。这种理解会影响下属在任务执行过程中的态度——积极执行的程度, 最终影响到任务执行的质量和效率(魏蕾, 时勘, 2010)。
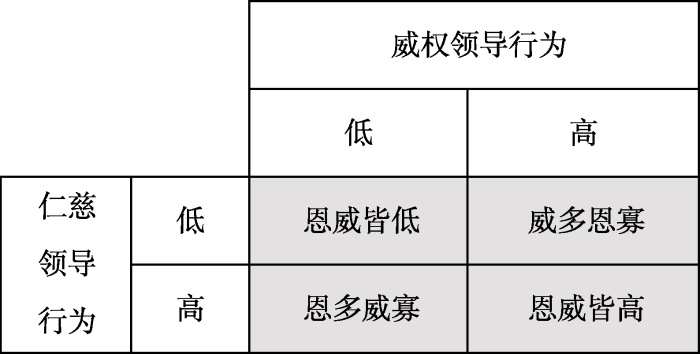
恩威并施是两种领导行为的组合, 它们之间作用效果会受到彼此的影响。当领导者同时实施仁慈与威权两种领导行为时, 由于程度差异可能会形成图1所示的四种不同组合情形:高-高、低-低、高-低、低-高, 我们分别将其命名为:恩威皆高、恩威皆低、恩多威寡、威多恩寡。基于上述分类, 本文拟探讨:第一, 程度相同时, 下属积极执行是否会随着仁慈领行为与威权领导行为程度的升高而升高?第二, 程度不同时, 与威多恩寡相比, 恩多威寡下的积极执行是否更优?第三, 积极执行是否能够将恩威并施的影响效应传递至工作绩效?
图1
1.1 恩威并施与积极执行
恩威并施是一种具有颇具中国本土特色的双元领导行为。在工作中, 仁慈的领导者体恤下属, 关心下属工作需求; 而威权领导者则严密控制下属绩效表现, 要求下属服从。由此, 我们基于双元领导视角将恩威并施定义为:领导者具备仁慈与威权两种差异互补的领导行为, 并能够依据所处情境协调运用这两种领导行为。其中, 仁慈领导是指领导者对下属工作和个人福祉表现出长久关怀(郑伯埙, 周丽芳, 樊景立, 2000), 包括工作上的宽容体谅和生活上的个别照顾。这种较为周全的照顾虽有利于提升下属效忠与工作努力(Shin, Taylor, & Seo, 2012), 但领导者一味地实施仁慈领导行为还可能引起下属的亲社会性规则违背(李锐, 田晓明, 柳士顺, 2015), 或导致下属的过度依赖。针对仁慈领导行为的阴暗面, 领导者的任务监控与规范维护等威权行为就显得尤为重要。威权领导是一种主张权威不容挑战, 严密控制下属, 要求下属完全服从的领导方式(郑伯埙等, 2000)。这种领导行为既会展现出专断独权的作风, 又会监控下属、严格要求下属绩效表现。在这种情况下, 下属不得不表现出顺从、公开附和(Farh & Cheng, 2000)。因此, 我们认为仁慈领导行为与威权领导行为搭配互动, 可能会扬长避短、相互增益, 产生1 + 1 > 2 的作用功效。
依据追随力理论(Uhl-Bien et al., 2014), 下属在追随领导者的过程中会产生相应的行为反应。在中国情境下, 仁慈领导者和威权领导者在塑造下属追随行为方面具有重要作用。下属在追随仁慈领导者的过程中会更加努力工作(Shin et al., 2012), 而当面对威权领导者时, 下属的追随则常常表现为对领导者的服从、依附(De Cremer & Van Dijk, 2005)。基于整合视角我们认为, 仁慈领导行为与威权领导行为的协调运用同样会引发下属追随, 这种追随既包括仁慈领导者所引发的积极态度, 又包括威权领导者所催生的服从执行, 最终表现为下属的积极执行。
领导者在展现仁慈和威权两种不同行为时, 可能存在程度上的差异, 而这种程度差异可能导致下属在追随过程中所表现出的积极执行发生变化。具体而言, 在施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度相当时, 领导者可能展现出“恩威皆高”, 亦可能表现出“恩威皆低”。当恩威皆高时, 领导者一方面会表现出专权, 从而使下属老实地执行工作指令(Cheng, Chou, Wu, Huang, & Farh, 2004), 一方面又会对下属提携照顾、关怀生活, 从而使下属感恩戴德, 善意地理解领导者的专权作风。在这种情况下, 下属在执行任务过程中会展现出更加积极的态度, 以此来报答领导者的恩惠(周婉茹, 周丽芳, 郑伯埙, 任金刚, 2010)。恩威皆低时, 低威权领导者会让下属放松警惕, 在工作中出现怠慢的情况(任金刚, 樊景立, 郑伯埙, 周丽芳, 2003); 倘若领导者同时较少施展关怀与辅导, 这会任由下属惰性的滋长, 以至于无法真正激发出下属的积极主动性。在这种既缺乏监管又没有温暖的组织中, 下属很可能会产生“当一天和尚撞一天钟”的心理, 出现消极怠工的状态, 终将不利于工作任务的积极执行。
H1:当施恩(仁慈领导行为)与立威(威权领导行为)水平一致时, 恩威皆高情况下的积极执行要高于恩威皆低。
在水平不一致时, 领导者可能会形成“恩多威寡”和“威多恩寡”两种不同领导行为。当恩多威寡时, 在高仁慈领导者的关怀下, 下属会产生回报领导者的动机。此时, 倘若领导者威权行为较低, 则能够增加下属在工作中享有的自主性与掌控感(Deci & Ryan, 1985), 这为下属将互惠动机转换为实际行动提供了有利的激活环境。概言之, 恩多威寡能促使下属在轻松、愉悦的状态下, 表现出积极执行来报答领导者的关怀照顾。然而, 当领导者表现出威多恩寡时, 下属的积极执行相对较弱。具体来说, 高威权的领导者为了维系其权力距离的优势, 有时会干涉下属工作、漠视下属建议(周婉茹等, 2010)。倘若此时领导者仅施以较少的关怀照顾, 会使下属认为领导者不关心个人需求与发展(Farh & Cheng, 2000), 从而萌生“未善待自己”的认知。这种认知无法有效激发下属的积极主动性。
H2:当施恩(仁慈领导行为)与立威(威权领导行为)水平不一致时, 恩多威寡的情形下的积极执行要高于威多恩寡。
1.2 积极执行的中介作用
追随力理论提出了一个包括领导者特征、下属特征和追随产出的理论框架(Uhl-Bien et al., 2014)。该理论不仅概括了领导者因素如何影响下属的追随力, 还包括下属的追随力所产生的能动结果。积极执行作为一种积极主动的追随行为, 它意味着下属将大量精力和资源投入到工作角色、任务的执行中, 这可以保证下属完成工作的时效性与精确性, 有利于提升工作绩效(彭坚, 王霄, 冉雅璇, 韩雪亮, 2016)。将上述论点与假设1、2结合, 本文认为, 恩威并施的组合情形会影响积极执行, 继而影响下属工作绩效。首先, 在施恩和立威程度一致时, 领导者的恩威皆高会促使下属以积极的状态完成工作, 最终获得最优的绩效表现。然而, 领导者的恩威皆低不但会抑制下属的积极性还会降低其执行任务的时效性, 必然会影响到最终的绩效表现。其次, 在施恩和立威程度不一致时, 面对恩多威寡的领导者, 下属会以积极执行工作任务的方式回报领导者的关怀照顾, 从而有利于完成基本的绩效目标。而在威多恩寡情形下, 下属只是机械地服从命令, 缺乏工作积极性。这不仅会影响到任务执行, 还会降低绩效表现。
H3:恩威并施能通过下属积极执行来影响工作绩效。其中, 恩威皆高通过积极执行影响工作绩效的间接效应最强。
2 程序与方法
2.1 研究对象与程序
本研究采用问卷调查法, 联系重庆、上海及新疆3地的3家企业收集数据, 涉及的行业包括电力与建筑设计行业。首先, 研究者面向企业内部招募“联络人”, “联络人”负责在其组织内寻找愿意参加本研究的员工, 并帮忙发放与回收问卷。在施测前, “联络人”先确定好参与人的名单并进行编号, 使其与问卷匹配。本研究进行两时点施测, 其中:时间点一邀请204名下属填写基本信息, 并评价直属领导者的仁慈与权威情况。问卷回收后, 剔除乱答、漏答的问卷。共回收有效问卷183份, 回收率为89.71%。1个月后, 本研究邀请183名完成了时间点一调查的下属继续参与调研。鉴于以往研究(许晟, 李元清, 曹元坤, 2017)采用了自评的方式测量追随力, 本研究同样让下属自评积极执行情况, 并邀请直属领导者对下属工作绩效进行评价。此轮调查共获得有效配对问卷130份( 本研究进行了Power analysis (Cohen, 1992), 用来分析本研究的统计检验力。通过Power analysis 分析后, 得到本研究中的统计检验力为0.83, 超过标准值0.8 (Cohen, 1992), 这说明本研究具有较高的统计检验力。故本研究130样本量能够满足本研究需要。), 回收率为71.04%。在下属样本中, 男性占52.31%, 平均年龄为 21岁, 本科及以上学历占94.62%, 入职时间为17个月, 与领导者共事时间平均为17个月。在领导者样本中, 男性占59.09%, 平均年龄为25岁, 本科及以上学历占98.46%, 任领导职务时间为40个月。
2.2 测量工具
本研究采用“翻译-回译”程序将英文量表翻译成中文。量表均采用李克特5点计分, 从“1”到“5”表示符合程度由低到高。
恩威并施:恩威并施主要由仁慈领导和权威领导构成。仁慈领导采用郑伯埙等(2000)开发的家长式领导中的仁慈领导分量表, 权威领导则采用周婉茹等(2010)开发的威权领导量表。其中, 仁慈领导包括“个别照顾” (6题)和“宽容体谅” (5题)两个维度, 例题如:“他/她会根据我个人的需要, 来满足我的要求”, “当我碰到难题时, 他/她会及时给我鼓励”。α系数分别为0.91和0.93; 权威领导包括“专权领导” (8题)和“尚严领导” (10题)两个维度, 例题如:“他/她要求下属完全服从他/她的领导”, “他/她会督促我的工作进度, 要求我全力达成”。α系数分别为0.96和0.93。
积极执行:采用周文杰等(2015)在中国情境开发的追随力量表中的积极执行维度(2题), 题目分别为:“我对他/她布置的工作精益求精, 力求最好的表现”, “他/她布置的任务我会想尽办法克服困难完成” (α = 0.91)。
工作绩效:采用Chen, Tsui和Farh (2002)开发的工作绩效量表(4题), 如:“我能按时完成分派给我的工作任务”, “我的表现总能达到领导的期望” (α = 0.70)。
控制变量:依据以往研究(彭坚, 王霄, 2016), 本研究将领导者-下属的人口特征差值作为控制变量。除此之外, 还将具有西方特色的“开放-闭合”双元领导作为控制变量, 采用Rosing等(2011)开发的开放型领导量表(7题)与闭合型领导量表(7题)。本研究中α系数分别为0.85与0.90。需要说明的是, 本研究借鉴Zacher和Rosing (2015)的研究, 取开放领导与闭合领导两个变量平均值的乘积项测量“开放-闭合”这一双元领导, 加入这一控制变量是为了控制西方双元领导的影响。
2.3 统计分析
本研究采用SPSS 20.0进行描述性统计与相关分析, 并采用AMOS 18.0进行验证性因素分析以检验变量的结构效度和区分效度。对于假设1、2与3的检验, 本文运用多项式回归和响应面分析(Edwards & Parry, 1993), 相比传统的调节回归分析和差异值分析, 此种分析方法能提供更精确的结果。该方法模型公式如下:
$\begin{align} & {{Z}_{ij}}=+{{b}_{0}}+{{b}_{1}}(X)+{{b}_{2}}(Y)+ \\ & \ \ \ \ {{b}_{3}}({{X}^{2}})+{{b}_{4}}(X\times Y)+{{b}_{5}}({{Y}^{2}}) \\ \end{align}$
在上述公式中, Zij代表下属积极执行, X代表仁慈领导行为, Y代表威权领导行为。在检验恩威并施对下属积极执行影响时, 在一致性线(X = Y)对应的截面上, 斜率(b1 + b2)用于检验假设1。在不一致线(X = -Y)对应的截面上, 斜率(b1 - b2)用于检验假设2。
检验假设3时, 由于恩威并施由5个多项式组成, 中介效应中前半段路径系数实则为5个多项式对积极执行共同作用的结果。为了更准确地分析这一关系, 我们参考了Edwards和Cable (2009)的建议, 先将仁慈和威权领导行为生成一个组块变量(Block Variable), 并将其用于后续中介效应分析。具体做法是将5个多项式的原始值分别乘以对应的回归系数, 进行加总。之后, 采用Bootstrapping法, 估计效应值的偏差矫正95%置信区间以检验中介效应。
3 研究结果
3.1 共同方法偏差检验
为了控制同源方差, 本研究在施测程序上采用了多来源、多时间点的数据搜集方式。同时根据Podsakoff, MacKenzie, Lee和Podsakoff (2003)以及Dulac, Coyle Shapiro, Henderson和Wayne (2008)的建议, 我们采用了“Harman单因子法”和“未测单一方法潜因子法(Single-Common-Method-Factor Approach)”来检验本研究的同源方差。Harman单因子检验法结果显示, 未经旋转的探索性因素分析析出的第一个因子为27.84%, 不到总解释量的一半。基于未测单一方法潜因子法结果显示, 模型中同源方差平均变异抽取量为0.37, 低于同源方差可判定为潜因子的标准0.50 (Dulac et al., 2008)。综上, 同源方差并未严重影响本研究的结果。
3.2 验证性因素分析与区分效度
为了检验主要研究变量的结构效度和区分效度, 本文对仁慈领导行为、威权领导行为、积极执行和工作绩效进行验证性因素分析。结果如表1所示, 与其他3个竞争模型相比, 四因素模型拟合指数都达到要求(RMSEA < 0.08, NFI/CFI/TLI > 0.90)且呈现最优结果, 这说明本研究中4个变量具有良好的区分效度。
表1 验证性因素分析结果
| 模型 | χ2 | df | χ2/df | RMSEA | NFI | CFI | TLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 四因素:AL; BL; JJZX; JP | 63.05 | 29 | 2.17 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| 三因素:AL + BL; JJZX; JP | 223.87 | 32 | 7.00 | 0.22 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.64 |
| 二因素:AL + BL + JJZX; JP | 149.41 | 34 | 4.39 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.79 |
| 单因素:AL + BL + JJZX + JP | 432.43 | 35 | 12.36 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.30 |
注:n = 130。AL = 威权领导行为, BL = 仁慈领导行为, JJXZ = 积极执行, JP = 工作绩效。符号“+”表示将变量合并。
3.3 描述性统计与相关分析
由表2可知, 仁慈领导行为与积极执行(r = 0.66, p < 0.01)和下属工作绩效(r = 0.33, p < 0.05)呈显著正相关。下属积极执行与下属工作绩效(r = 0.33, p < 0.01)呈显著正相关。
表2 主要研究变量的平均数、标准差和相关系数
| 变量 | 平均数 | 标准差 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 开放-闭合双元领导 | 0.24 | 0.27 | ||||
| 2 仁慈领导行为 | 4.07 | 0.73 | -0.12 | |||
| 3 威权领导行为 | 2.89 | 0.88 | 0.36** | -0.12 | ||
| 4 积极执行 | 4.34 | 0.62 | -0.24** | 0.66** | -0.07 | |
| 5 工作绩效 | 4.12 | 0.65 | -0.09 | 0.33** | 0.07 | 0.33** |
注:n = 130。** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05。
3.4 假设检验结果
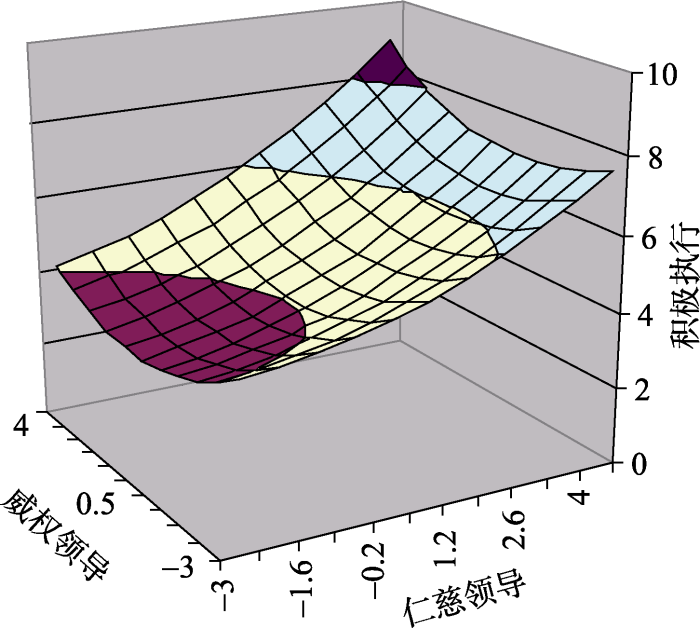
表3呈现了多项式回归的结果。如表3所示, 加入了平方项和交互项后, 模型3的解释量得到显著提升(ΔR2 = 0.04, p < 0.05)。接下来, 基于模型3的数据, 本研究进行了响应面分析, 结果如表4所示。首先, 为了检验假设1(恩威皆高优于恩威皆低)对称效应, 本研究拟检验一致性线(X = Y)的斜率(b1 + b2)是否显著。倘若斜率显著为正, 则说明下属的积极执行随着施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度的升高而递增; 反之, 这说明下属的积极执行随着施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度的升高而递减。如表4中显示, 响应面沿着一致性线(X = Y)的斜率显著且为正值(斜率 = 0.47, p < 0.01), 这说明与恩威皆低相比, 恩威皆高时, 下属积极执行更高。因此, 假设H1得到支持。其次, 为了检验假设2(恩多威寡优于威多恩寡)非对称效应, 本研究拟检验不一致性线(X = -Y)的斜率(b1 - b2)是否显著。倘若斜率显著为正, 这说明恩多威寡(右边)时下属积极执行高于威多恩寡(左边)。如表4所示, 响应面沿着不一致线(X = -Y)的斜率显著为正值(斜率 = 0.51, p < 0.01), 且侧向位移量(Lateral Shift Quantity)为-1.96 (95%CI = [-2.34, -0.67])。即当领导者的施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度不一致时, 与威多恩寡相比, 下属积极执行在恩多威寡的情形下更高。因此假设H2得到支持。
表3 多项式回归结果
| 变量 | 积极执行 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |
| 常数项 | 4.33** | 4.39** | 4.27** |
| 性别差异 | -0.06 | -0.031 | -0.01 |
| 年龄差异 | -0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 |
| 学历差异 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| 任职时间差异 | -0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 |
| 共事时长 | 0.02** | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 开放×闭合 | -0.43* | -0.40* | -0.52** |
| 自变量 | |||
| 仁慈领导行为(X)b1 | 0.52** | 0.49** | |
| 威权领导行为(Y)b2 | 0.59 | -0.02 | |
| 仁慈平方(X2)b3 | 0.12* | ||
| 仁慈×威权(X×Y)b4 | 0.08 | ||
| 威权平方(X2)b5 | 0.09* | ||
| R2 | 0.14 | 0.47 | |
| ΔR2 | 0.33** | 0.04* | |
注:n = 130。** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05。
表4 响应面系数检验
| 估计参数 | 积极执行 |
|---|---|
| 一致性线X = Y | |
| 斜率(b1 + b2) | 0.47** |
| 曲率(b3 + b4 + b5) | 0.29 |
| 不一致性线X = -Y | |
| 斜率(b1 - b2) | 0.51** |
| 曲率(b3 - b4 + b5) | 0.13 |
注:n = 130。** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05
图2
3.5 下属积极执行的中介效应的检验结果
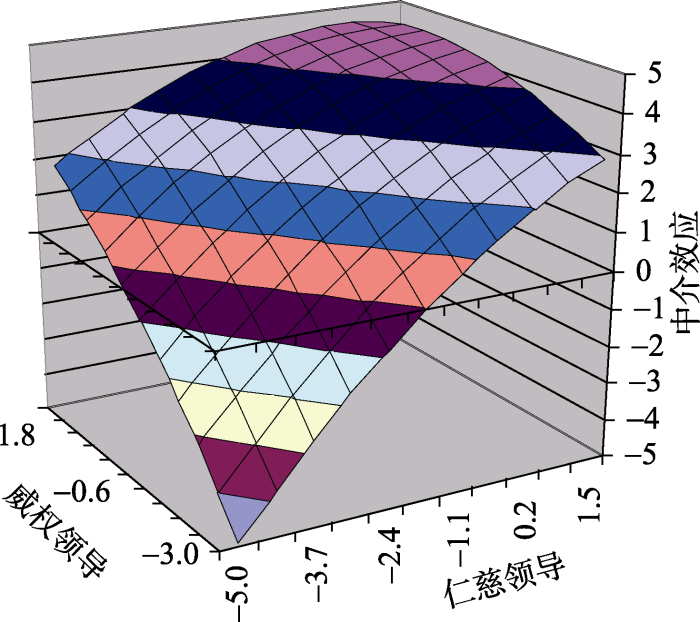
为了检验中介效应, 我们参考了Edwards和Cable (2009)的建议, 先将仁慈领导行为和威权领导行为生成一个组块变量(Block Variable)。组块变量可以更好地评估施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度一致与不一致的直接与间接效应(Edward & Cable, 2009)。更重要的是, 运用组块变量不会改变方程中其他变量的评估系数与总解释率(Zhang, Tsui, & Wang, 2011)。具体做法是将5个多项式的原始值分别乘以对应的回归系数, 进行加总。之后, 进行中介效应的检验。我们运用目前学术界普遍认可并广泛使用的Bootstrap法来检验中介效应值(Zhao, Lynch, & Chen, 2010)( 2 Bootstrap方法进行中介检验(Zhao, Lynch, & Chen, 2010)无需正态分布假设和大样本数据, 操作简便, 已被心理学、组织行为学等领域的顶级学术期刊广泛使用。Bootstrap方法对于中介效应的检验不需要对主效应进行检验, 只需直接检验a (自变量到中介变量的路径系数)×b (中介变量到因变量的路径系数)是否显著(Zhao et al., 2010)。若中介效应的95%置信区间不包括0, 则说明中介效应显著(温忠麟, 叶宝娟, 2012)。), 结果见表5。恩威并施合成变量通过积极执行影响工作绩效的中介效应为0.16, 95%CI = [0.04, 0.37], 不包括0。这说明中介效应显著, 即假设3得到验证。同时, 我们绘制了积极执行中介作用效果图, 如图3所示。与前部相比, 后部深蓝色处的工作绩效更高, 这说明与恩威皆低相比, 恩威皆高通过积极执行对工作绩效的正向影响更强; 同时, 左角位置的工作绩效要低于右角位置, 这表明与威多恩寡相比, 恩多威寡通过积极执行对工作绩效的正向影响更强。图3所描述的情况与本研究对中介效应统计分析的结果相一致, 即恩威并施通过下属积极执行来影响工作绩效。
表5 中介效应检验结果
| 模型 | 前半段路径系数 | 后半段路径系数 | 中介效应 | 95%置信区间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 恩威并施组块变量→积极执行→工作绩效 | 0.66** | 0.24* | 0.16 | [0.03, 0.35] |
| 恩威皆高→积极执行→工作绩效 | 9.60* | 0.28* | 2.69 | [0.30, 5.56] |
| 恩威皆低→积极执行→工作绩效 | 0.76*** | 0.28* | 0.21 | [0.05, 0.42] |
| 恩多威寡→积极执行→工作绩效 | 5.92* | 0.28* | 1.66 | [0.17, 3.40] |
| 威多恩寡→积极执行→工作绩效 | 3.16* | 0.28* | 0.88 | [0.09, 2.02] |
注:n = 130。**p < 0.001, *p < 0.05, +p < 0.10
图3
此外, 为了进一步解释积极执行的中介作用, 借鉴Matta, Scott, Koopman和Conlon (2015)的研究, 还分析了仁慈领导行为与威权领导行为的组合情况通过积极执行对下属工作绩效的影响, 具体操作如下:针对所讨论组合情况的不同, 将多项式中X (仁慈领导行为)的值分别取1(低)或5(高), Y (威权领导行为)的值分别取1(低)或5(高)。结果如表5所示:在恩威皆高领导行为下, 积极执行的中介效应最大(中介效应 = 2.69, 95%CI = [0.30, 5.56])。其次是恩多威寡情形(中介效应 = 1.66, 95%CI = [0.17, 3.40])、威多恩寡(中介效应 = 0.88, 95%CI = [0.09, 2.02])、恩威皆低(中介效应 = 0.21, 95%CI = [0.05, 0.42])。综上, 假设H3得到支持。
4 讨论
4.1 结果分析
虽然已有研究认为, 在华人组织中, 恩威并施会对下属行为与产出产生积极影响, 但是, 仁慈领导行为和威权领导行为的不同组合对下属工作产出是否会产生差异化的影响效果?其内在机制又是什么?这些问题均尚未得到深入探究。本研究基于上述疑问, 采用问卷调查法揭示了:在施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)水平相当情况下, 恩威皆高时下属积极执行程度要高于恩威皆低; 在施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)水平不一致情况下, 恩多威寡时下属积极执行程度要高于威多恩寡; 施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)组合情况对下属积极执行的影响能够波及至下属工作绩效, 其中, 恩威皆高通过积极执行对工作绩效间接效应是最强。
第一, 恩威并施这一典型的本土双元领导行为, 同样会引发下属积极执行这一追随行为的产生。这一结论呼应了中国历代兵法思想, 即带兵作战的将领, 除了必须展现严明的纪律之外, 亦需搭配仁慈之心方能发挥最大作战力。具体而言, 一方面, 当施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)程度相当时, 领导者恩威皆高更有利于促进下属积极执行。这是因为, 领导者的恩威皆高不但会引发下属效忠、感恩, 还会使下属老实地服从与执行工作指令(Cheng et al., 2004)。这会促使下属积极、有效地执行工作任务; 与之相对, 领导者的恩威皆低不但会导致低质量的交换关系, 还会使下属放松警惕, 怠慢领导者安排(任金刚等, 2003), 影响下属的工作状态, 以至于无法真正激发下属的积极主动性。另一方面, 当施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)水平不一致时, 恩多威寡的领导者更有利于促进下属积极执行的产生。究其原因, 领导者恩多威寡会使下属产生报恩的动机与信念, 在一定程度上促使下属较为配合任务执行。相反, 威多恩寡的领导者通常会对下属实施严密的监管, 并缺乏对下属的关照。在这种情形下, 下属只会被动地服从指令, 缺乏工作积极性, 从而影响到任务执行。
第二, 恩威并施领导行为能通过下属积极执行来影响工作绩效。其中, 恩威皆高通过积极执行对工作绩效的影响作用是最强的。四种组合情形中, 领导者恩威并施通过积极执行对下属工作绩效影响的效果由强到弱排列顺序为, 恩威皆高>恩多威寡>威多恩寡>恩威皆低。这说明, 在相同机制作用下, 恩威并施并不一定都会带来好的绩效。只有恩威并施处于高水平时, 才是最有效的领导行为(周婉茹等, 2010), 能最大限度激发下属的积极执行并带来高绩效(Özçelik & Cenkci, 2014); 而恩威皆低, 积极执行及其催生的绩效表现是最差的。具体来说, 恩威皆高由于领导者体现了较高程度的仁慈, 会让下属认为领导者高威权不是要贬低他们的贡献、看轻他们的能力, 而是旨在促进组织的发展(Aycan, 2006)。在这种情况下, 下属更能善意的理解领导行为, 有利于培养下属积极的心理认知与情绪(Cheng et al., 2004;), 促使下属采取积极执行的方式来回应领导者, 而这种积极回应方式最终提升了下属工作绩效(Luthans, 2002)。而恩威皆低营造的疏于监管并缺乏关怀的环境, 使下属不愿积极执行工作任务, 进而有碍于工作绩效提升。
需要澄清的是, 从理论上讲, 恩威并施是通过积极执行才能影响工作绩效, 倘若缺乏积极执行的传导作用, 恩威并施与工作绩效的关系比较难以论证, 正因如此, 本研究并未直接提出主效应假设。这说明恩威并施与工作绩效的关系依赖于积极执行的中介作用。
4.2 理论意义
第一, 本研究通过探究领导者施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)不同组合对下属产生的差异化影响, 揭示了以往恩威并施相关研究存在分歧的原因。现有研究虽已探究恩威并施对下属的影响(Cheng et al., 2004; Chan, Huang, Snape, & Lan, 2013), 但研究结论并未达成一致。例如, 一些研究表明恩威并施能提高下属工作表现(Tsai et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2016); 而另一些研究则没有支持这一观点(李珲等, 2014)。其实, 这些研究只探究了仁慈领导行为与威权领导行为之间的简单交互作用, 忽略施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)不同组合对下属的影响。为了突破以往研究的窠臼, 本研究首次探究施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)不同组合对下属的影响, 并发现:施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)分别在“高-高一致”和“低-低一致”、“高-低”和“低-高”情况下会对下属积极执行产生差异化影响, 继而带来不同的绩效产出。这不仅有助于学界更深入地理解恩威并施之作用效果分歧的原因, 并在一定程度上挑战了“恩威并施即为最优”的传统思维定势, 也为后续研究的开展提供了一定启发。
第二, 本研究对恩威并施领导行为与下属工作绩效间的机理进行了深入挖掘, 打开了恩威并施与下属产出间的内部黑箱。Chan等(2013)虽然探索了领导者恩威并施对下属的影响效果, 但尚未阐清其中的内部过程, 并号召未来研究要丰富领导者恩威并施与下属绩效之间内在机理, 以更全面地阐释其假设模型。鉴于此, 本研究基于追随力理论(Uhl-Bien et al., 2014), 发现了追随力中重要且具有高度共识维度——积极执行(Uhl-Bien et al., 2014, 周文杰等, 2015), 在恩威并施与下属工作绩效间所起的重要作用, 且施恩(仁慈领导行为)和立威(威权领导行为)不同组合情况正是借由积极执行才得以对下属工作绩效产生差异化影响。上述结果从新的理论视角, 解释了领导者恩威并施为何能够提升下属工作绩效。
第三, 本研究回应了罗瑾琏、赵莉、韩杨、钟竞和管建世(2016)以及赵红丹和郭利敏(2017)的呼吁, 将双元领导研究置于中国情境, 帮助国内学者认识本土双元领导在华人组织中的作用功效。由于双元领导诞生于西方情境, 以往相关研究大多聚焦于变革-交易(Schreuders & Legesse, 2012)、开发-闭合(Rosing et al., 2011)等互异领导行为的整合。然而, 由于东、西方文化的差异, 学界和商界皆认识到, 将西方研究结论直接套用在其他文化地区容易产生削足适履的现象(Smith & Wang, 1996)。因此, 扎根于中国情境, 开展本土双元领导研究显得尤为迫切。鉴于此, 本研究从中国传统的“家文化”出发, 探索了像父亲一样仁慈又权威的领导者在华人组织中究竟会如何影响下属产出。上述探索既响应罗瑾琏等(2016)的号召, 又呼应了“华人领导者具有一种恩威并施典型行为”的观点(郑伯埙, 1995)。需要强调的是, 本研究还发现, 控制了“开放-闭合”这一西方双元领导行为后, 恩威并施对下属行为及其工作产出的解释力具有增益效度。这更加凸显了中国情境下本土双元领导具有更强而应景的预测力, 并启发后续双元领导研究可以尝试扎根于中国情境下的现实管理问题。
第四, 本研究将追随力理论引入到双元领导研究领域中, 拓展了追随力理论在领导力研究领域的解释力。近年来, 学者们逐渐意识到领导行为与下属追随行为存在密不可分的联系。同时, 现有研究也相继表明领导行为会引发下属追随(Bjugstad, Thach, Thompson, & Morris, 2006; 李浩澜, 宋继文, 周文杰, 2015), 但这些研究大多集中在对单一领导行为的研究, 而忽略了领导行为的复杂性及其对下属追随力的影响。为了填补上述不足, 本研究基于追随力理论, 遵循“领导者特征-下属的追随特征-下属产出”这一理论框架(Uhl-Bien et al., 2014), 探究了恩威并施这种复杂领导模式对下属追随的影响。通过这项努力, 本研究将追随力理论及其理论框架的适用范围从单一领导行为领域拓展到双元领导领域, 能够检验、拓展追随力理论的解释或应用范围。
4.3 实践意义
提升下属工作绩效一直是组织管理中的重要实践议题。本文通过揭示恩威并施、下属积极执行与工作绩效的关系, 为提升下属工作绩效提供了新思考。第一, 面对当今复杂多变的外部环境, 领导者应该培养整合思维, 比如在培训领导者时拿出组织中的差异实例, 让领导者分析、讨论, 能够辩证地看待组织中的问题。这样有利于领导者在不同的情境下采取有效的双元领导行为来整合问题、平衡组织中的张力。第二, 领导者不应单纯的实施仁慈领导行为或威权领导行为, 而是应高度重视威权与仁慈领导行为的配合实施, 培养领导者恩威并施。具体而言, 领导者应根据下属的实际情况适度的集权并对下属任务执行情况进行监管, 提出一定的绩效要求, 同时要更加关心下属的工作与生活情况, 及时给予下属鼓励与支持, 借由恩威并施这种双元领导行为, 提升下属的工作表现与组织的有效运营。第三, 应注重提高下属积极执行。下属积极执行对其工作绩效表现出更为直接与有效的促进作用。因此, 在实践中应积极协调威权与仁慈领导行为, 保证下属在宽严并济的氛围中, 积极主动地执行工作任务, 最终提升其工作绩效。
4.4 不足与展望
本研究也存在一些不足, 首先, 本研究采用自评法测量下属积极执行, 但自评与他评的工作行为可能存在差异。例如, 自评工作行为可能会受到更多主观因素的影响。因此, 后续研究可以通过自评与他评相结合的方法来弥补由下属自我评价所产生的不足。此外, 本研究还存在着样本量较少以及样本过于年轻化的问题。在日后研究中, 会扩充样本量, 并从多年龄段、多行业等方面进行数据收集, 使数据来源更多样化, 结论更具说服力。其次, 本文没有考虑影响领导者效能发挥的情境因素, 如外部环境动态性。当今组织、领导者面临着充满不确定性、极端模糊的环境, 领导者的工作也相应的充满了变化与挑战, 他们需要时刻应对瞬息万变的工作需求。因此, 在这种情境下, 领导者恩威并施是否能有效协调组织内外环境, 是未来研究的方向。再者, 本研究中, 恩威并施与下属工作绩效间直接效应不显著。MacKinnon, Krull和Lockwood (2000)指出, 总效应不显著原因之一, 是由于存在两条符号相反的中介路径, 从而使得主效应不显著。因此, 除了本研究探索的恩威并施之积极作用, 后续研究可以基于认知失调理论, 探究恩威并施的阴暗面。例如, 恩威并施是否会影响下属心理安全(印田彬, 邹艳春, 2017)或自我损耗, 进而对绩效产生负面影响; 或者虽然能提升绩效, 但是否以牺牲幸福感为代价(彭坚, 王震, 2018)。最后, 不同于西方双元领导研究, 本研究关注具有中国本土特色的恩威并施对下属行为与绩效的影响。那么, 恩威并施与西方双元领导行为对下属行为与产出方面的影响是否存在差异, 哪种领导行为的效用更强, 均是未来的研究应考虑的问题。
致谢:感谢江西省南丰县重点办何超对本研究的支持。
参考文献
Paternalism: Towards conceptual refinement and operationalization
In K. S. Yang, K. K. Hwang, & U. Kim (Eds.),
A fresh look at followership: A model for matching followership and leadership styles
The janus face of paternalistic leaders: Authoritarianism, benevolence, subordinates' organization-based self-esteem, and performance
DOI:10.1002/job.1797
URL
[本文引用: 2]

We investigated how the two components of paternalistic leadership, namely authoritarianism and benevolence, jointly influenced work performance through their impacts on organization-based self-esteem (OBSE). Using a sample of 686 supervisor ubordinate dyads collected from a manufacturing firm in the People's Republic of China, we found that OBSE mediated the negative relationship between authoritarian leadership on one hand and subordinate task performance and organizational citizenship behavior toward the organization (OCBO) on the other. We also found that the negative effect of authoritarian leadership on subordinate OBSE, task performance, and OCBO was weaker when supervisors exhibited higher levels of leader benevolence. Also, OBSE mediated the joint effect of authoritarian leadership and benevolent leadership on subordinate task performance and OCBO. Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Loyalty to supervisor vs. organizational commitment: Relationships to employee performance in China
DOI:10.1348/096317902320369749
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this research, we investigated the relationship between loyalty to supervisor and employee's in-role and extra-role performance in comparison with that of organizational commitment in the People's Republic of China. Two studies were conducted. In the first study, a five-dimension loyalty to supervisor scale was developed and validated. In the second study, the relationships between loyalty to supervisor, organizational commitment and employee performance were examined. Results indicated that loyalty to supervisor was more strongly associated with both in-role and extra-role performance than organizational commitment. The findings are discussed in terms of their implications for future research and management practices in cross-cultural settings.
The relationship between parental authority and leadership behavior: A case study of a moderator in a private enterprise in Taiwan
家长权威与领导行为之关系:一个台湾民营企业主持人的个案研究
Paternalistic leadership and subordinate responses: Establishing a leadership model in Chinese organizations
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-839X.2004.00137.x
URL
[本文引用: 4]

Abstract Paternalistic leadership (PL) is the prevalent leadership style in Chinese business organizations. With an approach similar to patriarchy, PL entails an evident and powerful authority that shows consideration for subordinates with moral leadership. Although PL is widespread in Chinese business organizations, very few studies have focused on this leadership style and those that have were simply conceptual analyses and not empirical studies. We sampled 543 subordinates from local businesses in Taiwan to investigate PL, Western transformational leadership, and subordinate responses to these two leadership styles. Our hypotheses were as follows: (1) PL has a significant and unique effect on subordinate responses compared to Western transformational leadership; (2) there exists an interaction between the three elements of PL (benevolence, morality, and authoritarianism) and subordinate responses; and (3) the authority orientation of a subordinate's traditionality has a moderating effect upon the relation between PL and subordinate responses. Statistical analyses generally supported these hypotheses. Directions for follow-up studies are offered and implications for leadership theory and practice are discussed.
Paternalistic leadership: Construction and measurement of ternary mode
家长式领导: 三元模式的建构与测量
A power primer
DOI:10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155 URL [本文引用: 2]
Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior
When and why leaders put themselves first: Leader behaviour in resource allocations as a function of feeling entitled
DOI:10.1002/ejsp.260
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this article, we examine how being assigned the role of leader affects behaviour in resource sharing tasks. Previous research has shown that group members anchor their decision on the equal division rule prescribing that resources should be distributed equally. Following notions of equity theory and the literature on role schemas, we expected that adherence to the equal division rule would be moderated by role assignment. In particular, we expected leaders to take more than followers from a common resource and that this effect would be explained in terms of feelings of entitlement. The results of two experimental studies corroborate this reasoning. Study 1 demonstrated that leaders took more than followers and that leaders deviated more strongly from the equal division rule. In Study 2, it was found that legitimate leaders took more from the resource and deviated more strongly from the equal division rule than non-legitimate leaders. Additional analyses suggest that the leaders' tendency to make higher allocations to the self can be explained by feelings of entitlement. Copyright 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Not all responses to breach are the same: The interconnection of social exchange and psychological contract processes in organizations
DOI:10.5465/AMJ.2008.35732596
URL
[本文引用: 2]

We examined psychological contract breach and violation as they occur within social exchange relationships to account for employee outcomes. Results of a longitudinal study suggested that contract breach partially mediated the effects of perceived organizational support (POS) and leader-member exchange (LMX) (time 1 measures) on intentions to quit (time 2 measure). POS and LMX moderated the relationship between breach and violation (time 2 measure). Violation fully mediated the effects of breach on commitment and trust and partially mediated the effect of breach on turnover intentions. These findings highlight the interconnection of social exchange and psychological contract processes.
The value of value congruence
DOI:10.1037/a0014891 URL [本文引用: 3]
On the use of polynomial regression equations as an alternative to difference scores in organizational research
DOI:10.2307/256822
URL
[本文引用: 1]

For decades, difference scores have been widely used in studies of congruence in organizational research. Although methodological problems with difference scores are well known, few viable alternatives have been proposed. One alternative involves the use of polynomial regression equations, which permit direct tests of the relationships difference scores are intended to represent. Unfortunately, coefficients from polynomial regression equations are often difficult to interpret. We used response surface methodology to develop an interpretive framework and illustrate it using data from a well-known person-environment study. Several important findings not reported in the original study emerged.
A cultural analysis of paternalistic leadership in Chinese organizations
In J. T. Li, A. S. Tsui, & W. Weldon (Eds.),
DOI:10.1057/9780230511590_5
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Paternalistic leadership, which combines strong discipline and authority with fatherly benevolence and moral integrity couched in a ‘personalistic’ atmosphere, has been found to be prevalent in overseas Chinese family businesses (CFBs). After critically reviewing the extant literature, we identify three constituent elements of paternalistic leadership (PL): authoritarianism, benevolence and moral leadership. We trace the deep cultural roots of each element and explore their relevance to organizations in contemporary Chinese societies. We then identify key research issues and propose a preliminary PL model for future studies on leadership in Chinese organizations.
What it takes and costs to be an ambidextrous manager
The impact of leadership on employee innovation behavior in the context of China—The perspective paternalistic leadership ternary theory
基于家长式领导三元理论的领导方式对员工创新行为的影响
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2014.07.009
URL
[本文引用: 2]

This study explores the impact of three patterns of paternalistic leadership (benevolence leadership, moral leadership and authoritarianism leadership) on employee innovation behavior in Chinese context, and direct, interact and mediating impact are analyzed based on the data collected from 312 employees. The research results demonstrate: benevolence leadership and moral leadership have positive impact on employee innovation behavior; authoritarianism leadership has negative impact on employee innovation behavior; and the interaction between moral and benevolence leadership also positively influence employee innovation behavior .In addition, psychological empowerment plays a partial mediating role in the impact of benevolence leadership and moral leadership on employee innovation behavior, and plays a full mediating role in the impact of authoritarianism leadership on employee innovation behavior.
The impact of transformational leadership on employee followership in the Chinese context
中国文化背景下变革型领导风格对员工追随力的作用机制
培养高追随力的下属是领导研究与管理实践中的新兴重要话题。文章基于本土文化情境,探究了变革型领导风格对员工追随力的影响作用以及潜在的影响机制。基于706名员工的实证研究表明,变革型领导对于员工追随力有显著的正向影响;员工心理授权在变革型领导与追随力之间起部分中介作用,而权力距离在变革型领导与员工心理授权之间、变革型领导与员工追随力之间的负向调节作用得到部分支持。本研究揭示了中国文化背景下变革型领导对下属追随力的影响关系,并给出了相应的实践启示,旨在推动本土研究的深化与企业管理实践的发展。
Does benevolent leadership increase employee pro-social rule breaking?
仁慈领导会增加员工的亲社会性规则违背吗?
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00637
URL
[本文引用: 1]

采用情境实验(以126名在职MBA学员为被试)与问卷调查(以187名企业员工为研究对象)相结合的方法,考察了中国文化情境下注重"施恩"的仁慈领导方式对员工亲社会性规则违背(PSRB)的影响效果及其边界条件。结果发现:(1)仁慈领导对员工PSRB具有正向影响;(2)组织不确定性对员工PSRB亦具有正向影响,并对仁慈领导与员工PSRB的关系存在负向调节效应。当组织不确定性较高时,这一关系较弱;(3)权力距离取向对员工PSRB具有负向影响,并同样对仁慈领导与员工PSRB的关系存在负向调节效应。当员工权力距离取向较高时,仁慈领导对PSRB的影响较小。不过就调节仁慈领导对员工PSRB影响效果的具体方式而言,组织不确定性发挥着一种替代物的作用,而员工权力距离取向则起着一种抵消物的作用。
Overview and prospect on research of ambidextrous leadership
双元领导研究进展述评
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2016.12.018
URL
[本文引用: 2]

双元领导是利用矛盾思维和整合思维解决张力的动态过程。作为一个组织双元性和领导学交叉的前沿主题,双元领导理论的研究呼应了当前不确定性环境下为满足矛盾和竞争需求对当代领导理论提出的新要求。通过相关研究的系统分析,首先,阐述了双元及双元领导的内涵,对双元领导行为策略组合进行了总结;然后,评介了双元领导的测量方式,以及系统归纳了触发双元领导的因素、双元领导影响作用效果及机制;最后,对双元领导的未来研究方向进行了展望。
The need for and meaning of positive organizational behavior
DOI:10.1002/job.165
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This essay draws from the emerging positive psychology movement and the author's recent articles on the need for and meaning of a positive approach to organizational behavior. Specifically, the argument is made that at this time, the OB field needs a proactive, positive approach emphasizing strengths, rather than continuing in the downward spiral of negativity trying to fix weaknesses. However, to avoid the surface positivity represented by the non-sustainable best-sellers, the case is made for positive organizational behavior (POB) to take advantage of the OB field's strength of being theory and research driven. Additional criteria for this version of POB are to identify unique, state-like psychological capacities that can not only be validly measured, but also be open to development and performance management. Confidence, hope, and resiliency are offered as meeting such POB inclusion criteria. The overall intent of the essay is to generate some positive thinking and excitement for the OB field and 'hopefully' stimulate some new theory building, research, and effective application.
Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect
DOI:10.1023/A:1026595011371
URL
PMID:11523746
[本文引用: 1]

This paper describes the statistical similarities among mediation, confounding, and suppression. Each is quantified by measuring the change in the relationship between an independent and a dependent variable after adding a third variable to the analysis. Mediation and confounding are identical statistically and can be distinguished only on conceptual grounds. Methods to determine the confidence intervals for confounding and suppression effects are proposed based on methods developed for mediated effects. Although the statistical estimation of effects and standard errors is the same, there are important conceptual differences among the three types of effects.
Does seeing "eye to eye" affect work engagement and organizational citizenship behavior? A role theory perspective on LMX agreement
DOI:10.5465/amj.2014.0106 URL [本文引用: 1]
Moderating effects of job embeddedness on the relationship between paternalistic leadership and in-role job performance
DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.09.096
URL
[本文引用: 1]

http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877042814051453
Leader narcissism and follower outcomes: The counterbalancing effect of leader humility
DOI:10.1037/a0038698
URL
PMID:25621592
[本文引用: 1]

In response to recent calls to theorize and examine how multiple leader characteristics may work together in their effects, the current research examines how leader narcissism and humility interact to predict perceived leader effectiveness and follower (i.e., direct-report) job engagement and performance. Although an examination of leaders who are narcissistic yet humble may seem oxymoronic and even paradoxical, researchers have suggested that seemingly contradictory personal attributes may exist simultaneously and may actually work together to produce positive outcomes. Results from survey data from followers and leaders working for a large health insurance organization showed that the interaction of leader narcissism and leader humility is associated with perceptions of leader effectiveness, follower job engagement, and subjective and objective follower job performance. Together, these results suggest that narcissistic leaders can have positive effects on followers when their narcissism is tempered by humility.
I will perform effectively if you are with me: Leader-follower congruence in followership prototype, job engagement and job performance
与上司“心有灵犀”会让你的工作更出色吗?——追随原型一致性、工作投入与工作绩效
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01151
URL

内隐追随作为一种关于追随角色的认知结构,包括追随原型和反原型两种。其中,追随原型表征了个体对追随角色的积极预期。本研究基于角色理论,考察了领导者-追随者的追随原型一致性对工作绩效的影响及工作投入的中介作用。采用跨层次多项式回归和响应面分析技术,对64个工作团队的数据进行分析,发现追随原型能否提升工作绩效主要取决于领导-追随双方的匹配情况。具体而言,(1)领导-追随双方的追随原型越一致,关系绩效越高。但上述结论并不适用于任务绩效。(2)在一致情况下,与"低-低"一致相比,任务绩效和关系绩效在双方追随原型的"高-高"一致时更高。(3)在不一致情况下,与"领导者的追随原型高-追随者的追随原型低"相比,任务绩效和关系绩效在"领导者的追随原型低-追随者的追随原型高"时相对更高。(4)追随原型一致性通过工作投入影响任务绩效和关系绩效。
Being a prototypic follower: Burdening or enabling? The paradoxical effect of followership prototype-trait match
做上司的“意中人”:负担还是赋能?追随原型-特质匹配的双刃剑效应
传统观点认为,倘若下属能够达到领导心目中的理想标准(即追随原型),成为领导的“意中人”,便容易在工作中获得资源,感到幸福。然而,在现实情境中,身为“意中人”的下属还可能面临着工作超载、身心受累的潜在威胁。基于工作要求-资源模型,本研究认为“做上司的意中人”既要付出代价又能受益,并提出一个追随原型-特质匹配的双刃剑模型。该模型包括远离幸福的负担之路和迈向幸福的赋能之路。基于132份两时间点的上下级配对数据,采用路径分析对理论模型进行检验,结果表明:当下属的追随特质契合领导的追随原型(成为领导的“意中人”)后,下属既可能因为工作负担的增多而付出心理代价,出现高情绪枯竭、低情感承诺和低工作满意度;又可能因为自我效能的增强而收获工作幸福,表现为高工作满意度。以上结果能为管理员工幸福感提供一定的实践指导。
Can positive followership characteristic always promote work outcomes? The activation effect of benevolent leadership
积极追随特质一定能提升工作产出吗——仁慈领导的激活作用
以往学界和商界将焦点投向领导力,相对不注重考察追随力在组织中的功效。本文基于追随力的特质观.整合社会交换理论和特质激活理论,探讨了积极追随特质对工作产出(任务绩效和情感承诺)的影响效果、内部机理和边界条件。采用多层线性模型(HLM)对119个工作团队的上下级配对数据进行分析,结果表明:(1)积极追随特质正向影响任务绩效和情感承诺。(2)领导一成员交换(LMX)中介积极追随特质与任务绩效和情感承诺的关系。(3)仁慈领导正向调节上述中介模型的直接路径和第一阶段:在低仁慈领导下,积极追随特质对任务绩效和情感承诺的影响(直接路径)不显著,对LMX的正向影响(第一阶段)较弱;在高仁慈领导下,积极追随特质对任务绩效、情感承诺和LMX的正向影响被激活得更强。(4)仁慈领导正向调节积极追随特质与情感承诺之间经由LMX的间接效应,积极追随特质与任务绩效之间经由LMX的间接效应并未受仁慈领导的调节。
Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies
DOI:10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
URL
PMID:1451625114516251
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract Interest in the problem of method biases has a long history in the behavioral sciences. Despite this, a comprehensive summary of the potential sources of method biases and how to control for them does not exist. Therefore, the purpose of this article is to examine the extent to which method biases influence behavioral research results, identify potential sources of method biases, discuss the cognitive processes through which method biases influence responses to measures, evaluate the many different procedural and statistical techniques that can be used to control method biases, and provide recommendations for how to select appropriate procedural and statistical remedies for different types of research settings.
Paternalistic leadership and organizational effectiveness of senior executives: An analysis of individual and organizational levels. Chinese indigenous psychology research in ministry of education. Taibei: Ministry of
高阶主管之家长式领导与组织效能: 一项个人与组织层次的分析
Explaining the heterogeneity of the leadership-innovation relationship: Ambidextrous leadership
DOI:10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.07.014
URL
[本文引用: 4]

The authors review and meta-analytically integrate the existing literature on leadership and innovation to show a complex and inconsistent picture of this relationship. Current research has mostly neglected the complex nature of innovation processes that leads to changing requirements within these processes. The main requirements of innovation are exploration and exploitation as well as a flexibility to switch between those two activities. The authors propose an ambidexterity theory of leadership for innovation that specifies two complementary sets of leadership behavior that foster exploration and exploitation in individuals and teams opening and closing leader behaviors, respectively. We call this ambidextrous leadership because it utilizes opening and closing leader behaviors and switches between them to deal with the ever-changing requirements of the innovation process. Routes to ambidextrous leadership and opportunities for future research on leadership and innovation are discussed.
Organizational ambidexterity: How small technology firms balance innovation and support
The impact of authoritarian leadership and benevolent leadership on team creativity–Test of a mediated interaction model
威权领导、仁慈领导对团队创造力—一个有中介的交互效应模型检验
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6636.2014.05.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

团队创造力是组织创新的基石。领导方式对团队创造力的激发作用成为研究热点,但威权领导和仁慈领导对团队创造力的作用机制尚未得到充分诠释。基于文献研究,将威权领导、仁慈领导、团队自省性及团队创造力纳入同一框架,构建有中介的交互作用模型。基于128个团队的调研数据,运用结构方程模型和层次回归方法,研究表明:威权领导对团队创造力有消极影响,而仁慈领导对团队创造力有积极影响,两者对团队创造力有正向交互影响。此外,团队自省性能有效促进团队创造力的提升,并完成中介威权领导和仁慈领导对团队创造力的单独效应及交互效应。
Resources for change: The relationships of organizational inducements and psychological resilience to employees' attitudes and behaviors toward organizational change
DOI:10.5465/amj.2010.0325
URL
[本文引用: 2]

We tested the importance of two hypothesized resources-organizational inducements and employee psychological resilience-in determining employees' commitment to, and supportive behaviors for, organizational change. Conducting a two-wave survey in a sample of 234 employees and 45 managers, we found that organizational inducements and resilience were positively related to two types of employees' commitment to change (normative and affective) and that these effects were mediated through state positive affect and social exchange. We also found that the two types of commitment to change were positively but differentially related to behavioral and creative support for change, and negatively related to turnover.
Paternalistic leadership: Impact of authoritarianism and benevolence on subordinate performance.
Followership theory: A review and research agenda
DOI:10.1016/j.leaqua.2013.11.007
URL
[本文引用: 6]

While theory and research on leaders and leadership abound, followers and followership theory have been given short shrift. It is accepted wisdom that there is no leadership without followers, yet followers are very often left out of the leadership research equation. Fortunately this problem is being addressed in recent research, with more attention being paid to the role of followership in the leadership process. The purpose of this article is to provide a systematic review of the followership literature, and from this review, introduce a broad theory of followership into leadership research. Based on our review, we identify two theoretical frameworks for the study of followership, one from a role-based approach (“reversing the lens”) and one from a constructionist approach (“the leadership process”). These frameworks are used to outline directions for future research. We conclude with a discussion of conceptual and methodological issues in the study of followership theory.
Land collectivization and the structural transformation of traditional rural families
DOI:10.1080/02529203.2016.1194632
URL
[本文引用: 2]

We use oral history materials from elderly rural people aged over seventy to analyze the circumstances of rural family production and daily life prior to collectivization in the mid-1950s; during collectivization in the 1950 s to the 1970s; and under the household contract responsibility system of the late 1970 s. We fi nd that the transition from the traditional to the nuclear family did not involve industrialization in the traditional Western sense. As an early state industrialization strategy after 1949, rural collectivization fundamentally changed the organizational pattern of traditional family production and daily life and of inter-generational relations and structures under the patriarchal system, launching the historical process of structural transition in the family. This explanation differs from the classic "theory of modernization" of family change.
Paternalistic leadership and job involvement: The mediating role of psychological empowerment
家长式领导与员工工作投入: 心理授权的中介作用
This research was conducted to explore the relationship between paternalistic leadership, which is prevalent in Chinese organizations, and job involvement in the background of the economic crisis in a Chinese context. We also examined the contribution of psychological empowerment in mediating the relation between paternalistic leadership and job involvement. Through statistical analysis of survey data collected from 402 employees in China, the results indicated: authoritarianism leadership and benevolence leadership had significant predictive effect on job involvement; Psychological empowerment was a mediator in the relationship between benevolence leadership and job involvement.
The influence of individual personlity traits on followership behavior: A construction of modulating meditation model
Ambidextrous leadership and team innovation
DOI:10.1108/LODJ-11-2012-0141
URL
[本文引用: 1]

PurposeThe purpose of this paper is to report the first empirical test of the recently proposed ambidexterity theory of leadership for innovation (Rosing et al., 2011). This theory proposes that the interaction between two complementary leadership behaviors – opening and closing – predicts team innovation, such that team innovation is highest when both opening and closing leadership behaviors are high. Design/methodology/approachMulti-source survey data came from 33 team leaders of architectural and interior design firms and 90 of their employees. FindingsResults supported the interaction hypothesis, even after controlling for leaders’ transformational leadership behavior and general team success. Research limitations/implicationsThe relatively small sample size and the cross-sectional design are potential limitations of the study. The findings provide initial support for the central hypothesis of the ambidexterity theory of leadership for innovation. Practical implicationsThe results suggest that organizations could train team leaders’ ambidextrous leadership behaviors to increase team innovation. Social implicationsIdentifying ways to facilitate organizational innovation is important, as it contributes to employment and company growth as well as individual and societal well-being. Originality/valueThis multi-source study contributes to the literatures on leadership and innovation in organizations by showing that ambidextrous leadership behaviors predict team innovation above and beyond transformational leadership behavior.
Leadership behaviors and group creativity in Chinese organizations: The role of group processes
DOI:10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.07.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In seeking to understand the factors contributing to work group creativity in Chinese organizations, we explored the roles of two different leadership styles (transformational and authoritarian) that Chinese leaders play in group creativity through influencing internal group processes, i.e., collective efficacy and knowledge sharing among group members. We tested our hypotheses with a sample of 163 work groups involving 973 employees in twelve Chinese companies. We found transformational leadership to relate positively but authoritarian leadership to relate negatively to group creativity, mediated by both collective efficacy and knowledge sharing among members within the group. We discuss the implications of these findings for research on group leadership, group creativity and cross-cultural management.
The best of both worlds: The conceptual structure and influencing mechanisms of ambidextrous leadership
组织中的双面娇娃: 双元领导的概念结构与作用机制
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4124.2017.04.008
URL
[本文引用: 1]

双元领导是指由两种差异互补的领导行为所组成的一种新型领导风格,体现了双元理论在领导力领域的延伸与应用.相较于单一领导风格,双元领导满足了复杂、动态环境下组织竞争及可持续发展的需求,日益引起理论界与实务界的关注.从现有研究来看:(1)研究者主要从能力和行为两种视角界定双元领导;(2)双元领导会通过内在动机、自我调节、社会认知、社会交换、社会影响、行为整合等机制发挥作用;(3)双元领导的作用效果会受到领导力、认知、社会环境和组织特征等因素的影响.未来研究议题应当关注:清晰界定双元领导的内涵;从社会认同和辩证思维视角丰富双元领导相关机制的研究;关注双元领导的本土化研究.
Reconsidering baron and kenny: Myths and truths about mediation analysis
DOI:10.1086/651257
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Baron and Kenny’s procedure for determining if an independent variable affects a dependent variable through some mediator is so well known that it is used by authors and requested by reviewers almost reflexively. Many research projects have been terminated early in a research program or later in the review process because the data did not conform to Baron and Kenny’s criteria, impeding theoretical development. While the technical literature has disputed some of Baron and Kenny’s tests, this literature has not diffused to practicing researchers. We present a nontechnical summary of the flaws in the Baron and Kenny logic, some of which have not been previously noted. We provide a decision tree and a step‐by‐step procedure for testing mediation, classifying its type, and interpreting the implications of findings for theory building and future research.
Relationship between paternalistic leadership and organizational justice
家长式领导与组织公正感的关系
DOI:10.1360/aas-007-0297
URL
[本文引用: 1]

以428名企事业单位员工为调查对象,采用问卷法,探讨了家长式领导与组织公正感的关系,结果表明:(1)仁慈领导对组织公正感各维度有显著的积极影响;德行领导对组织公正感各维度有显著的积极影响;权威领导对领导公正有显著的消极影响;(2)在分配公正、程序公正上,德行与权威领导有显著负交互效应;在领导公正、领导解释上,仁慈与权威领导有显著负交互效应.最后,对研究的理论和实践意义作了探讨,并提出了未来的研究方向.
Juan-chiuan and shang-yan: The components of authoritarian leadership
专权与尚严之辨: 再探威权领导的内涵与恩威并济的效果
The definition, structure and measurement of followship in Chinese context
中国情境下追随力的内涵、结构与测量
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2015.03.006
URL
[本文引用: 3]

After reviewing the extant literature, this study first adopts the qualitative research method to develop a preliminary followership scale in the Chinese context. We then use EFA and CFA approaches to validate the scale, resulting in a measure of Chinese Followership Behavior Questionnaires (CFBQ). CFBQ includes 21 items in 6 dimensions. Rooted in the Chinese context, this study revises and develops the definition of followership, explores its structure and dimensions, and contributes an empirically validated measurement scale. It paves the way of in-depth understanding on followership and leadership,and also contributes to the cultivation of followership in firms.
A multi-level perspective on the review of psychological safety
多层次视角下的心理安全研究评述
当今社会,为了适应快速变化的外部环境,企业需要不断进行变革与创新,以谋得生存与发展。然而,变革与创新往往会给组织成员带来不确定性,容易遭遇挫折。在这种现实背景下,心理安全作为一种能够有效推动企业变革与创新的员工心理素质,得到了大量研究的探讨。为了推进学界人士更好地了解和掌握这个重要概念,本文拟对心理安全进行研究述评。具体而言,本文从多层次视角出发,梳理了个体、团队、组织三个层面上心理安全的定义与测量,然后回顾了心理安全的研究现状,尤其是系统梳理了影响因素、影响效果与作用机制。在此基础上,文章对未来研究做了几点展望。