

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (9): 1529-1539.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1529 cstr: 32110.14.2025.1529
李毕琴1( ), 张美霞1, 杨少云2, 黄鹏飞3, 王爱君4, 党君华5
), 张美霞1, 杨少云2, 黄鹏飞3, 王爱君4, 党君华5
收稿日期:2024-04-19
发布日期:2025-06-26
出版日期:2025-09-25
通讯作者:
李毕琴, E-mail: psy_lbq@jxnu.edu.cn基金资助:
LI Biqin1( ), ZHANG Meixia1, YANG Shaoyun2, HUANG Pengfei3, WANG Aijun4, DANG Junhua5
), ZHANG Meixia1, YANG Shaoyun2, HUANG Pengfei3, WANG Aijun4, DANG Junhua5
Received:2024-04-19
Online:2025-06-26
Published:2025-09-25
摘要:
客观时距会影响自我相关刺激下的时距知觉, 但秒内不同时间间隔下自我加工优势是否存在分段性差异仍存在争议。本研究通过两个实验考察秒内不同时距下的自我加工优势效应。实验1采用自我时距比较任务, 探讨自我相关刺激对秒内时距知觉判断的影响。结果发现,在长时距条件下, 与陌生人相比自我的主观相等点更长, 表明秒内长时距下个体对自我相关刺激的时长存在低估现象。实验2采用知觉匹配范式, 探讨自我对秒内时距知觉过程的影响。结果发现,不同秒内时距下, 自我相关信息的累积速率漂移率(v)和非决策时间(t)均优于陌生人条件,且在长时距下自我的决策阈限(a)和决策偏好(z)显著高于陌生人条件。 综上, 自我相关刺激在秒内时距知觉上存在加工优势, 且该优势存在分段性差异。
中图分类号:
李毕琴, 张美霞, 杨少云, 黄鹏飞, 王爱君, 党君华. (2025). 秒内不同时距下自我加工优势效应. 心理学报, 57(9), 1529-1539.
LI Biqin, ZHANG Meixia, YANG Shaoyun, HUANG Pengfei, WANG Aijun, DANG Junhua. (2025). Self-prioritization effect across varying intervals in sub-second duration perception. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(9), 1529-1539.
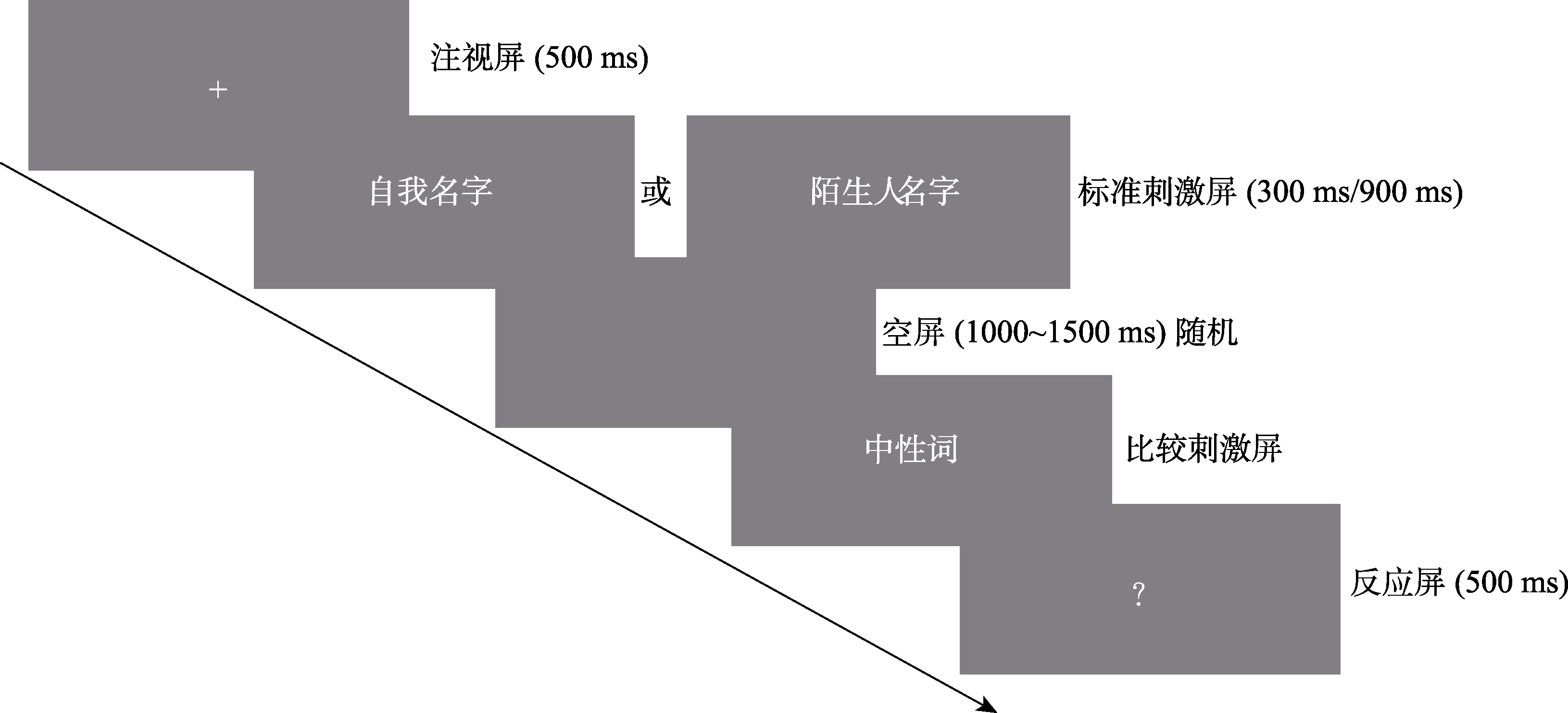
图1 实验1流程图。首先屏幕中央呈现白色注视点(500 ms)。接着呈现标准刺激(自我/陌生人姓名), 呈现时间为300 ms或900 ms。刺激消失后呈现空屏, 呈现时间在1000~1500 ms之间随机, 紧接着呈现中性词作为比较刺激, 要求被试判断两个刺激哪个时距更长, 通过按键(q/p)进行反应。
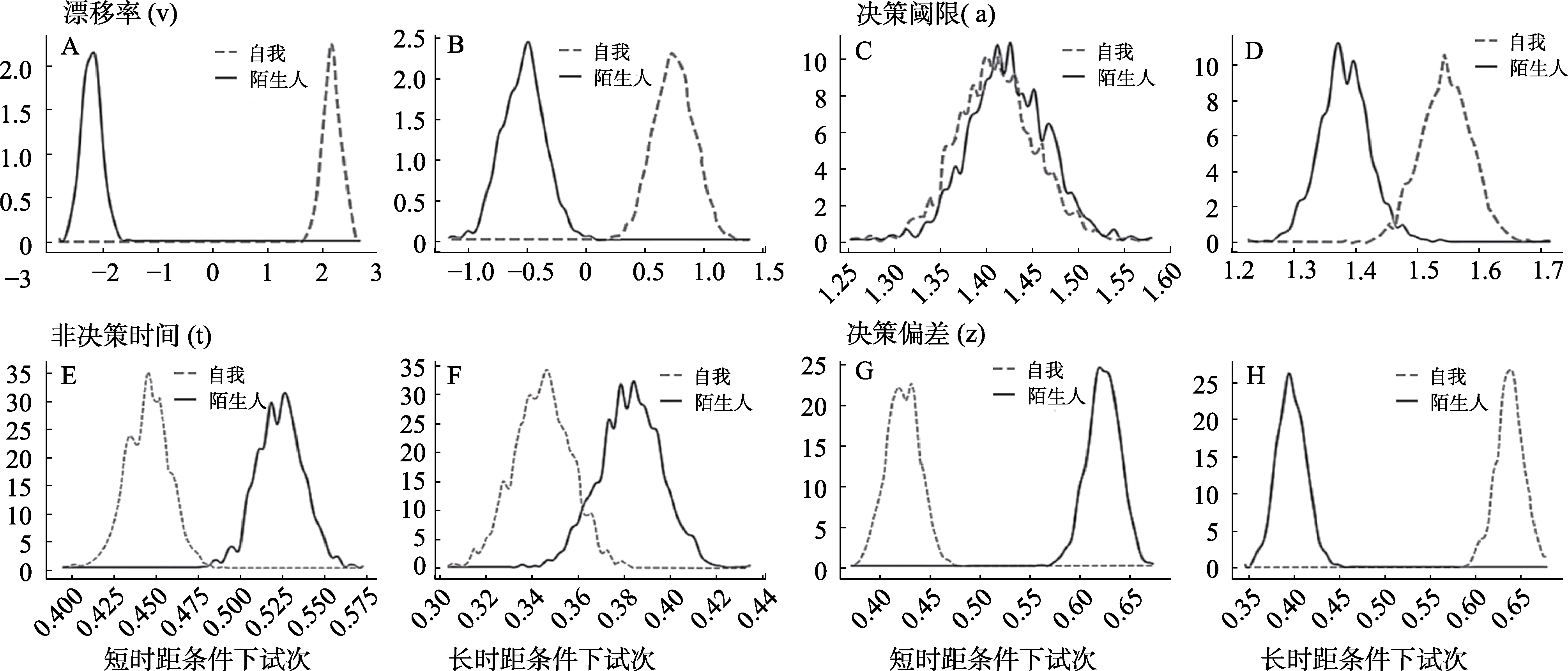
图6 漂移扩散模型参数在匹配试次下不同实验条件间的后验分布图。图A和B (左上)为漂移率(v)代表信息累积速率, 反映个体在某一选项上的偏好, 偏好越强烈, 信息累积速度越快; 图C和D (右下)是决策阈限(a)代表做出决策所需要的信息累积量, 数值越大, 个体决策越谨慎; 图E和F (左下)为非决策时间(t)表示个体对刺激编码和反应行为所需要花费的时长。t值越大, 意味着在非决策过程上花费的时长越长; 图G和H (右下)为决策偏差(z), 即个体在决策前的先验偏好在决策上的影响。z值越大, 意味着个体对该选项有更强烈的预先偏好。每个参数中, 左图为客观短时距条件, 右图为客观长时距条件。
| [25] | Li, Q., Song, S., Pan, L., Huang, X., & Chen, H. (2019). The influence of self-referential stimuli on duration perception. Acta Psychologica, 201, 102934. |
| [26] |
Liu, P., Yang, W., Yuan, X., Bi, C., Chen, A., & Huang, X. (2015). Individual alerting efficiency modulates time perception. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 386.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00386 pmid: 25904881 |
| [27] | Liu, R. G., & Huang, X. T. (2006). Scalar property in short duration estimation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 38(5), 724-733. |
| [刘瑞光, 黄希庭. (2006). 短时距估计中的标量特性. 心理学报, 38(5), 724-733 ] | |
| [28] |
Matthews, W. J., & Meck, W. H. (2016). Temporal cognition: Connecting subjective time to perception, attention, and memory. Psychological Bulletin, 142(8), 865-907.
doi: 10.1037/bul0000045 pmid: 27196725 |
| [29] | Mioni, G., Zangrossi, A., & Cipolletta, S. (2023). Me, myself and you: How self-consciousness influences time perception. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, 85( 8), 2626-2636. |
| [30] | Neisser, U. (1988). Five kinds of self-knowledge. Philosophical Psychology, 1(1), 35-59. |
| [31] | Pan, W., Geng, H., Zhang, L., Fengler, A., Frank, M., Zhang, R. Y., & Hu, C. P. (2022). A hitchhiker’s guide to bayesian hierarchical drift-diffusion modeling with dockerHDDM. PsyArXiv. |
| [32] |
Pannese, A., & Hirsch, J. (2010). Self-specific priming effect. Consciousness and Cognition, 19, 962-968
doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2010.06.010 pmid: 20598907 |
| [33] |
Qin, P., & Northoff, G. (2011). How is our self related to midline regions and the default-mode network? NeuroImage, 57(3), 1221-1233.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.05.028 pmid: 21609772 |
| [34] | Rammsayer, T. H., & Lima, S. D. (1991). Duration discrimination of filled and empty auditory intervals: Cognitive and perceptual factors. Perception & Psychophysics, 50, 565-574. |
| [35] | Ratcliff, R. (1978). A theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review, 85(2), 59-108. |
| [36] | Ratcliff, R., & Childers, R. (2015). Individual differences and fitting methods for the two-choice diffusion model of decision making. Decision, 2015(4), 237-279. |
| [37] |
Ratcliff, R., Smith, P. L., Brown, S. D., & McKoon, G. (2016). Diffusion decision model: Current issues and history. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(4), 260-281.
doi: S1364-6613(16)00025-5 pmid: 26952739 |
| [38] |
Ren, W., Guo, X., Liu, C., Yuan, T., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Effects of social information on duration perception by different mechanisms in sub- and supra-second range: Evidence from face features. PsyCh Journal, 10(3), 352-363.
doi: 10.1002/pchj.433 pmid: 33590688 |
| [39] | Scheller, M., Tünnermann, J., Fredriksson, K., Fang, H., & Sui, J. (2024). Self-association enhances early attentional selection through automatic prioritization of socially salient signals. eLife, 13, RP100932. |
| [40] |
Sui, J., He, X., & Humphreys, G. W. (2012). Perceptual effects of social salience: Evidence from self-prioritization effects on perceptual matching. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 38(5), 1105-1117.
pmid: 22963229 |
| [41] |
Sui, J., & Humphreys, G. W. (2015). The integrative self: How self-reference integrates perception and memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(12), 719-728.
doi: S1364-6613(15)00206-5 pmid: 26447060 |
| [42] | Sui, J., & Liu, C. H. (2009). Can beauty be ignored? Effects of facial attractiveness on covert attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(2), 276-281. |
| [43] |
Sui, J., & Rotshtein, P. (2019). Self-prioritization and the attentional systems. Current Opinion in Psychology, 29, 148-152.
doi: S2352-250X(18)30198-2 pmid: 30913475 |
| [44] | Svensson, S., Golubickis, M., Johnson, S., Falbén, J. K., & Macrae, C. N. (2023). Self-relevance and the activation of attentional networks. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 76(5), 1120-1130. |
| [45] |
Symons, C. S., & Johnson, B. T. (1997). The self-reference effect in memory: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 121(3), 371-394.
pmid: 9136641 |
| [46] | Ten, X. Q. (2009). Research on the neural mechanisms of self-reference effect on time perception [Unpublished master’s thesis]. Capital Normal University, China. |
| [滕西群. (2009). 自我对时距知觉影响的神经机制研究 (硕士学位论文). 首都师范大学.] | |
| [1] | Alexopoulos, T., Muller, D., Ric, F., & Marendaz, C. (2012). I, me, mine: Automatic attentional capture by self-related stimuli. European Journal of Social Psychology, 42(6), 770-779. |
| [2] | Allan, L. G. (1979). The perception of time. Perception & Psychophysics, 26(5), 340-354. |
| [3] | Axt, J. R., & Johnson, D. J. (2021). Understanding mechanisms behind discrimination using diffusion decision modeling. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 95(8), 104-134. |
| [4] | Azari, L., Mioni, G., Rousseau, R., & Grondin, S. (2020). An analysis of the processing of intramodal and intermodal time intervals. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 82(3), 1473-1487. |
| [5] | Baess, P., & Prinz, W. G. (2017). Face/Agent interference in individual and social context. Social Cognition, 35(2), 146-162. |
| [6] | Brée, D. S. (1992). Words for time. Springer Netherlands |
| [7] |
Brown, G. D. A., Lewandowsky, S., & Huang, Z. (2022). Social sampling and expressed attitudes: Authenticity preference and social extremeness aversion lead to social norm effects and polarization. Psychological Review, 129(1), 18-48.
doi: 10.1037/rev0000342 pmid: 35266789 |
| [8] | Bugg, J. M. (2012). Dissociating levels of cognitive control: The case of Stroop interference. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21(5), 302-309. |
| [9] |
Buhusi, C. V., & Meck, W. H. (2005). What makes us tick? Functional and neural mechanisms of interval timing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6(10), 755-765.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1764 pmid: 16163383 |
| [10] | Caughey, S., Falbén, J. K., Tsamadi, D., Persson, L. M., Golubickis, M., & Macrae, C. N. (2021). Self-prioritization during stimulus processing is not obligatory. Psychological Research, 85(2), 503-508. |
| [11] |
Clay, S. N., Clithero, J. A., Harris, A. M., & Reed, C. L. (2017). Loss aversion reflects information accumulation, not bias: A drift-diffusion model study. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1708.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01708 pmid: 29066987 |
| [12] | Conway, M. A. (2005). Memory and the self. Journal of Memory and Language, 53(4), 594-628. |
| [13] | Droit-Volet, S., Brunot, S., & Niedenthal, P. (2004). Brief report perception of the duration of emotional events. Cognition and Emotion, 18(6), 849-858. |
| [14] |
Failing, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2016). Reward alters the perception of time. Cognition, 148, 19-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2015.12.005 pmid: 26709497 |
| [15] | Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191. |
| [16] |
Forstmann, B. U., Ratcliff, R., & Wagenmakers, E. J. (2016). Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: Advantages, applications, and extensions. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 641-666.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033645 pmid: 26393872 |
| [17] |
Fraisse, P. (1984). Perception and estimation of time. Annual Review of Psychology, 35, 1-36.
pmid: 6367623 |
| [18] | Gable, P. A., & Poole, B. D. (2012). Time flies when you’re having approach-motivated fun: Effects of motivational intensity on time perception. Psychological Science, 23(8), 879-886. |
| [19] | Gebauer, J. E., Göritz, A. S., Hofmann, W., & Sedikides, C. (2012). Self-love or other-love? Explicit other-preference but implicit self-preference. PlOS One, 7(7), e41789. |
| [20] | Gibbon, J., Church, R. M., & Meck, W. H. (1984). Scalar timing in memory. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 423(1), 52-77. |
| [21] | Johnson, D. J., Hopwood, C. J., Cesario, J., & Pleskac, T. J. (2017). Advancing research on cognitive processes in social and personality psychology: A hierarchical drift diffusion model primer. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(4), 413-423. |
| [22] |
Kroger-Costa, A., Machado, A., & Santos, J. A. (2013). Effects of motion on time perception. Behavioural Processes, 95, 50-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2013.02.002 pmid: 23454436 |
| [23] |
Lewis, P. A., & Miall, R. C. (2003). Brain activation patterns during measurement of sub- and supra-second intervals. Neuropsychologia, 41(12), 1583-1592.
pmid: 12887983 |
| [24] | Li, B., Hu, W., Hunt, A., & Sui, J. (2022). Self-related objects increase alertness and orient attention through top-down saliency. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 84(2), 408-417. |
| [47] | Thomas, E. A., & Weaver, W. B. (1975). Cognitive processing and time perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 17(4), 363-367. |
| [48] |
Vandekerckhove, J., Tuerlinckx, F., & Lee, M. D. (2011). Hierarchical diffusion models for two-choice response times. Psychological Methods, 16(1), 44-62.
doi: 10.1037/a0021765 pmid: 21299302 |
| [49] |
Voss, A., Nagler, M., & Lerche, V. (2013). Diffusion models in experimental psychology: A practical introduction. Experimental Psychology, 60(6), 385-402.
doi: 10.1027/1618-3169/a000218 pmid: 23895923 |
| [50] | Weindel, G., Gajdos, T., Burle, B., & Alario, F. X. (2022). The decisive role of non-decision time for interpreting the parameters of decision making models. PsyArXiv. |
| [51] |
Wiecki, T. V., Sofer, I., & Frank, M. J. (2013). HDDM: Hierarchical Bayesian estimation of the drift-diffusion model in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 14.
doi: 10.3389/fninf.2013.00014 pmid: 23935581 |
| [52] |
Yin, H. Z., Cui, X. B., Bai, Y. L., Cao, G. G., Deng, J. X., & Li, D. (2020). The important time parameters and related evidences from dual perspectives of temporal information processing and temporal processing of information. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(11), 1853-1864.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01853 |
|
[尹华站, 崔晓冰, 白幼玲, 曹格格, 邓靖歆, 李丹. (2020). 时间信息加工与信息加工时间特性双视角下的重要时间参数及其证据. 心理科学进展, 28(11), 1853-1864 ]
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01853 |
|
| [53] | Yin, H. Z., Li, D., Chen, Y. Y., & Huang, X. T. (2017). The study of the characteristic of duration cognition segmentation in 1 second. Psychological Science, 40(2), 321-328. |
| [尹华站, 李丹, 陈盈羽, 黄希庭. (2017). 1 s范围视听时距认知的分段性研究. 心理科学, 40(2), 321-328 ] | |
| [54] | Yin, T. Z., & Huang, X. T. (2009). Research methods of temporal order perception and influencing factors. Psychological Exploration, 29(5), 22-26. |
| [尹天子, 黄希庭. (2009). 时序知觉研究方法及其影响因素. 心理学探新, 29(5), 22-26 ] | |
| [55] | Yuasa, K., & Yotsumoto, Y. (2015). Opposite distortions in interval timing perception for visual and auditory stimuli with temporal modulations. PLOS ONE, 10(8), e0135646. |
| [56] | Zauberman, G., Kim, B. K., Malkoc, S. A., & Bettman, J. R. (2009). Discounting time and time discounting: Subjective time perception and intertemporal preferences. Journal of Marketing Research, 46(4), 543-556. |
| [57] | Zhang, J., Chen, X., Qian, B., Han, D., Wang, L., & Zhang, Z. J. (2021). The influence of event segmentation on duration perception: A research of memento effect. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 19(2), 145-151. |
| [58] |
Zhu, S., Yang, J., Li, H., & Yuan, J. (2022). Shared surname enhances our preference to famous people: Multimodal eeg evidence. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 16(6), 1351-1359.
doi: 10.1007/s11571-022-09784-4 pmid: 36408066 |
| [59] | Zhu, Z. (2011). The effect of self on temporal bisection: Evidence from behavioral experiments and ERP [Unpublished master’s thesis]. Hunan Normal University, China. |
| [朱占占. (2011). 自我对时距知觉的影响:来自行为与ERP的证据 (硕士学位论文). 湖南师范大学.] |
| [1] | 袁博, 赵靖实, 漆丹, 赵彤, 胡佳琪. 社会奖惩对欺骗行为的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(9): 1622-1637. |
| [2] | 吴洁, 车子轩. 多通道类别学习的认知特征与神经机制:EEG与DDM证据[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(10): 1715-1728. |
| [3] | 王碧瑶, 陈晨, 胡晓斐, 王迪, 李宝林. 视觉时距知觉序列依赖效应的空间迁移性[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(4): 394-411. |
| [4] | 尹华站, 肖春花, 夏安妮, 袁中静, 崔晓冰, 李丹. 基本情绪对时距知觉的影响: 来自三水平元分析和网络元分析的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(12): 1676-1690. |
| [5] | 袁博, 王晓萍, 尹军, 李伟强. 跨情境的刺激泛化在面孔信任形成中的作用:基于直接互动与观察学习的视角[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(7): 1099-1114. |
| [6] | 尹华站, 张丽, 刘鹏玉, 李丹. 负性情绪的动机维度对时距知觉的影响:注意控制和注意偏向的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(12): 1917-1931. |
| [7] | 王盼盼, 何嘉梅. 情景预见对跨期决策的影响机制[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(1): 38-54. |
| [8] | 刘静远, 李虹. 状态焦虑对时距知觉的影响:认知评价和注意偏向有调节的中介作用[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(7): 747-758. |
| [9] | 李宝林;陈有国;袁祥勇;Todd Jackson;黄希庭. 拓扑性质对视觉新异刺激时距知觉的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2013, 45(12): 1324-1333. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||