

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 727-738.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2018.00727 cstr: 32110.14.2018.00727
收稿日期:2017-07-03
发布日期:2018-05-29
出版日期:2018-07-15
基金资助:Received:2017-07-03
Online:2018-05-29
Published:2018-07-15
摘要:
以往的影像学研究表明右侧背外侧前额叶皮层(DLPFC)在视觉工作记忆中发挥重要作用, 然而缺乏因果性的证据。本研究旨在考察右侧DLPFC的激活与视觉工作记忆容量的因果关系, 并探讨这一关系受到记忆负荷的调节及其神经机制。被试接受经颅直流电刺激之后完成视觉工作记忆变化检测任务, 根据被试在虚假刺激情况下从负荷4到负荷6任务记忆容量的增量将被试分为低记忆增长潜力组(简称低潜力组)和高记忆增长潜力组(简称高潜力组), 结果发现正性电刺激右侧DLPFC相对于虚假电刺激显著提升了高潜力组被试在低记忆负荷(负荷4)下的记忆容量及其对应的提取阶段的脑电指标SPCN成分。表明右侧DLPFC在视觉工作记忆的提取阶段发挥重要的因果性作用; 正性经颅直流电刺激右侧DLPFC可使工作记忆容量高潜力被试获得更多的脑活动增益, 并导致更好的行为提升效果。
中图分类号:
王思思, 库逸轩. (2018). 右侧背外侧前额叶在视觉工作记忆中的因果性作用. 心理学报, 50(7), 727-738.
WANG Sisi, KU Yixuan. (2018). The causal role of right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in visual working memory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50(7), 727-738.

图4 所有被试以及高低潜力组被试在示例序列出现后的ERP成分 注:灰色虚线和实线框包住的分别是N2pc和SPCN成分。黑色实线表示虚假刺激负荷4情况, 黑色虚线表示电刺激右侧DLPFC负荷4情况, 灰色实线表示虚假刺激负荷6情况, 灰色虚线表示电刺激右侧DLPFC负荷6情况。所有ERP均为CP5/6, P7/8, O1/2三对电极对侧电极减同侧电极波幅差值的均值。
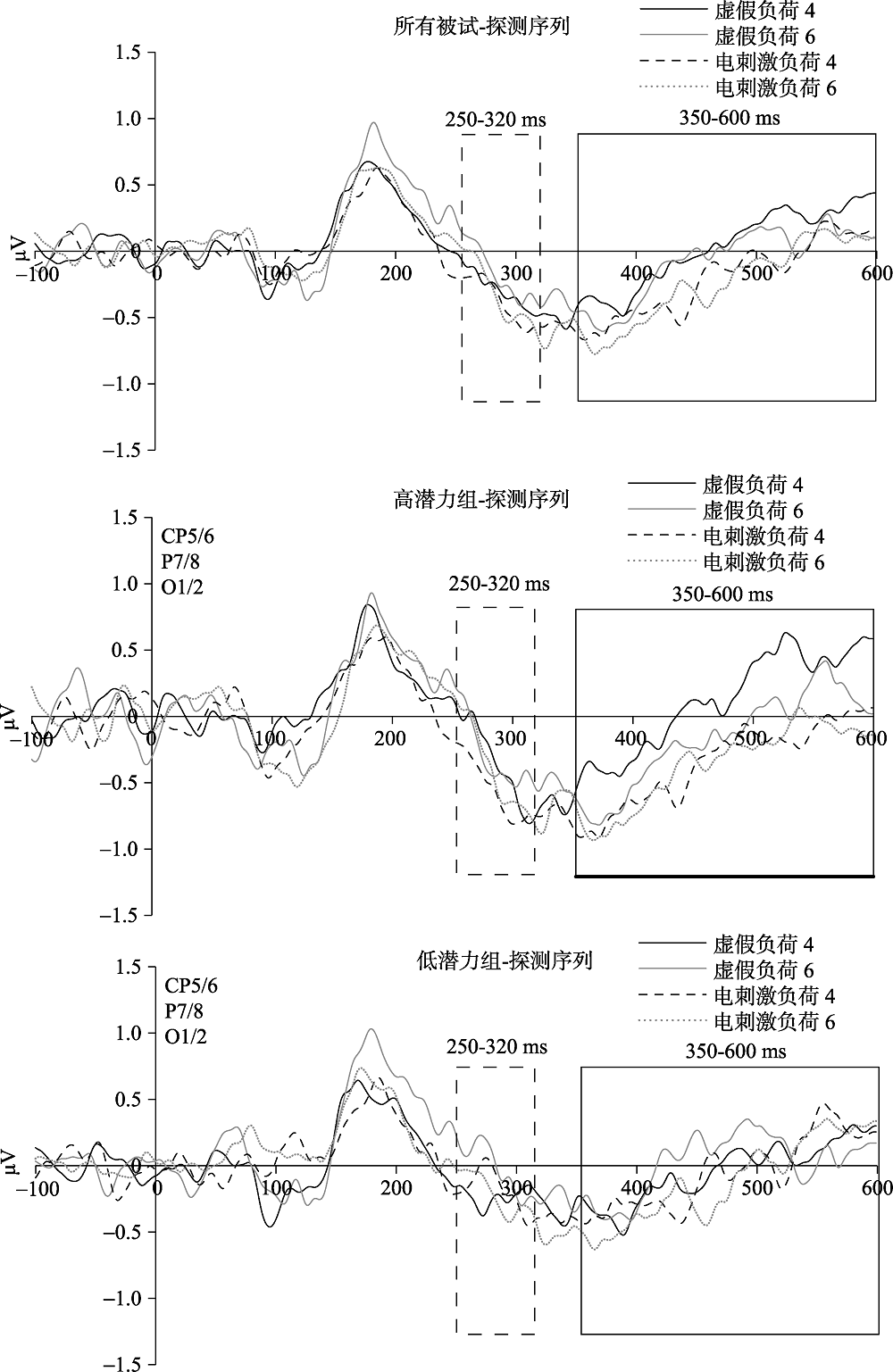
图5 所有被试以及高低潜力组被试在探测序列出现后的ERP成分 注:灰色虚线和实线框包住的分别是N2pc和SPCN成分, 高潜力组SPCN下方加粗黑线部分表示电刺激负荷4和虚假刺激负荷4差异显著区域。黑色实线表示虚假刺激负荷4情况, 黑色虚线表示电刺激右侧DLPFC负荷4情况, 灰色实线表示虚假刺激负荷6情况, 灰色虚线表示电刺激右侧DLPFC负荷6情况。所有ERP均为CP5/6, P7/8, O1/2三对电极对侧电极减同侧电极波幅差值的均值。
| [1] |
Alloway, T.P., &Alloway R.G . ( 2010). Investigating the predictive roles of working memory and IQ in academic attainment. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 106( 1), 20-29.
doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2009.11.003 URL pmid: 20018296 |
| [2] |
Anderson M. C., Ochsner K. N., Kuhl B., Cooper J., Robertson E., Gabrieli S. W., .. Gabrieli ,J. D. E. ( 2004). Neural systems underlying the suppression of unwanted memories. Science, 303( 5655), 232-235.
doi: 10.1126/science.1089504 URL pmid: 14716015 |
| [3] |
Andrews S. C., Hoy K. E., Enticott P. G., Daskalakis Z. J., & Fitzgerald P. B . ( 2011). Improving working memory: The effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Stimulation, 4( 2), 84-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2010.06.004 URL pmid: 21511208 |
| [4] |
Baddeley, A.D., &Hitch G.J . ( 1974). Working memory. Psychology of Learning and Motivation,8, 47-89.
doi: 10.1016/S0079-7421(08)60452-1 URL |
| [5] |
Berryhill, M.E., &Jones K.T . ( 2012). tDCS selectively improves working memory in older adults with more education. Neuroscience Letters, 521( 2), 148-151.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.05.074 URL pmid: 22684095 |
| [6] |
Coffman B. A., Clark V. P., & Parasuraman R . ( 2014). Battery powered thought: Enhancement of attention, learning, and memory in healthy adults using transcranial direct current stimulation. NeuroImage, 85, 895-908.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.083 URL pmid: 23933040 |
| [7] |
Courtney S. M., Petit L., Maisog J. M., Ungerleider L. G., & Haxby J. V . ( 1998). An area specialized for spatial working memory in human frontal cortex. Science, 279( 5355), 1347-1351.
doi: 10.1126/science.279.5355.1347 URL pmid: 9478894 |
| [8] |
Cowan ,N. ( 2001). Metatheory of storage capacity limits. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 24( 1), 154-176.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X0161392X URL |
| [9] |
Curtis,C.E . ( 2006). Prefrontal and parietal contributions to spatial working memory. Neuroscience, 139( 1), 173-180.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.04.070 URL |
| [10] |
Dedoncker J., Brunoni A. R., Baeken C., & Vanderhasselt M. A . ( 2016). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in healthy and neuropsychiatric samples: Influence of stimulation parameters. Brain Stimulation, 9( 4), 501-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2016.04.006 URL |
| [11] | D'Esposito M., Postle B. R., Ballard D., & Lease J . ( 1999). Maintenance versus manipulation of information held in working memory: An event-related fMRI study. Brain and Cognition, 1( 1), 66-86. |
| [12] |
Druzgal, T.J., &D'Esposito M. , ( 2003). Dissecting contributions of prefrontal cortex and fusiform face area to face working memory. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15( 6), 771-784.
doi: 10.1162/089892903322370708 URL pmid: 14511531 |
| [13] |
Eimer, M. ( 1996). The N2pc component as an indicator of attentional selectivity. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 99( 3), 225-234.
doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(96)95711-9 URL |
| [14] |
Eimer, M. &Kiss M. , ( 2010). An electrophysiological measure of access to representations in visual working memory. Psychophysiology, 47( 1), 197-200.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00879.x URL pmid: 2860638 |
| [15] |
Fregni F., Boggio P. S., Nitsche M., Bermpohl F., Antal A., Feredoes E., .. Pascual-Leone A . ( 2005). Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex enhances working memory. Experimental Brain Research, 166( 1), 23-30.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-2334-6 URL pmid: 15999258 |
| [16] |
Fukuda K., Vogel E., Mayr U., & Awh E . ( 2010). Quantity, not quality: The relationship between fluid intelligence and working memory capacity. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 17( 5), 673-679.
doi: 10.3758/17.5.673 URL pmid: 21037165 |
| [17] |
Funahashi S., Bruce C. J., & Goldman-Rakic P. S . ( 1989). Mnemonic coding of visual space in the monkey's dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 61( 2), 331-349.
doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.2.331 URL |
| [18] |
Fuster,J.M., &AlexanderG.E . ( 1971). Neuron activity related to short-term memory. Science, 173( 3997), 652-654.
doi: 10.1126/science.173.3997.652 URL |
| [19] |
Giglia G., Brighina F., Rizzo S., Puma A., Indovino S., Maccora S., .. Fierro B . ( 2014). Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex enhances memory-guided responses in a visuospatial working memory task. Functional Neurology, 29( 3), 189-193.
doi: 10.11138/FNeur/2014.29.3.189 URL pmid: 25473739 |
| [20] |
Hopf J. M., Boelmans K., Schoenfeld M. A., Luck S. J., & Heinze H. J . ( 2004). Attention to features precedes attention to locations in visual search: Evidence from electromagnetic brain responses in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 24( 8), 1822-1832.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3564-03.2004 URL pmid: 14985422 |
| [21] |
Jacobson L., Koslowsky M., & Lavidor M . ( 2012). tDCS polarity effects in motor and cognitive domains: A meta- analytical review. Experimental Brain Research, 216( 1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-011-2891-9 URL pmid: 21989847 |
| [22] |
Jolicur P., Brisson B., & Robitaille N . ( 2008). Dissociation of the N2pc and sustained posterior contralateral negativity in a choice response task. Brain Research, 1215, 160-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.03.059 URL |
| [23] |
Jolicur P., Sessa P., Dell’Acqua R., & Robitaille N . ( 2006). On the control of visual spatial attention: Evidence from human electrophysiology. Psychological Research, 70( 6), 414-424.
doi: 10.1007/s00426-005-0008-4 URL pmid: 16184394 |
| [24] |
Jones, K.T., &Berryhill M.E . ( 2012). Parietal contributions to visual working memory depend on task difficulty. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 3, 81.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00081 URL pmid: 3437464 |
| [25] |
Klaver P., Talsma D., Wijers A. A., Heinze H. J., & Mulder G . ( 1999). An event-related brain potential correlate of visual short-term memory. NeuroReport, 10( 10), 2001-2005.
doi: 10.1097/00001756-199907130-00002 URL pmid: 10424664 |
| [26] |
Kubota, K., &Niki H. , ( 1971). Prefrontal cortical unit activity and delayed alternation performance in monkeys. Journal of Neurophysiology, 34( 3), 337-347.
URL pmid: 4997822 |
| [27] |
Li S. Y., Cai Y., Liu J., Li D. W., Feng Z. F., Chen C. S., & Xue G . ( 2017). Dissociated roles of the parietal and frontal cortices in the scope and control of attention during visual working memory. NeuroImage, 149, 210-219.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.01.061 URL pmid: 28131893 |
| [28] |
Luck, S.J., &Hillyard S.A . ( 1994 a). Spatial filtering during visual search: Evidence from human electrophysiology. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 20( 5), 1000-1014.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.20.5.1000 URL pmid: 7964526 |
| [29] |
Luck, S.J., &Hillyard S.A . ( 1994 b). Electrophysiological correlates of feature analysis during visual search. Psychophysiology, 31( 3), 291-308.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1994.tb02218.x URL pmid: 8008793 |
| [30] |
Luck, S.J., &Vogel E.K . ( 1997). The capacity of visual working memory for features and conjunctions. Nature, 390( 6657), 279-281.
doi: 10.1038/36846 URL |
| [31] |
Mazza, V., &Caramazza A. , ( 2012). Perceptual grouping and visual enumeration. PLoS One, 7( 11), e50862.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050862 URL pmid: 23226408 |
| [32] |
Meiron, O. , &Lavidor M. , ( 2013). Unilateral prefrontal direct current stimulation effects are modulated by working memory load and gender. Brain Stimulation, 6( 3), 440-447.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2012.05.014 URL pmid: 22743075 |
| [33] |
Nitsche, M.A., &Paulus W. , ( 2001). Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurology, 57( 10), 1899-1901.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00633.x URL pmid: 10990547 |
| [34] |
Nitsche M. A., Fricke K., Henschke U., Schlitterlau A., Liebetanz D., Lang N., .. Paulus W . ( 2003). Pharmacological modulation of cortical excitability shifts induced by transcranial direct current stimulation in humans. The Journal of Physiology, 553( 1), 293-301.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049916 URL pmid: 12949224 |
| [35] |
Nitsche M. A., Liebetanz D., Lang N., Antal A., Tergau F., & Paulus W . ( 2003). Safety criteria for transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in humans. Clinical Neurophysiology, 114( 11), 2220-2222.
doi: 10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00235-9 URL pmid: 14580622 |
| [36] |
Ohn S. H., Park C. I., Yoo W. K., Ko M. H., Choi K. P., Kim G. M., .. Kim Y. H . ( 2008). Time-dependent effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on the enhancement of working memory. NeuroReport, 19( 1), 43-47.
doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282f2adfd URL pmid: 18281890 |
| [37] |
Priori, A. ( 2003). Brain polarization in humans: A reappraisal of an old tool for prolonged non-invasive modulation of brain excitability. Clinical Neurophysiology, 114( 4), 589-595.
doi: 10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00437-6 URL pmid: 12686266 |
| [38] |
Robitaille N., Marois R., Todd J., Grimault S., Cheyne D., &Jolicur P . ( 2010). Distinguishing between lateralized and nonlateralized brain activity associated with visual short-term memory: fMRI, MEG, and EEG evidence from the same observers. NeuroImage, 53( 4), 1334-1345.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.027 URL pmid: 20643214 |
| [39] |
Rypma B., Berger J. S., & D'Esposito M . ( 2002). The influence of working-memory demand and subject performance on prefrontal cortical activity. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 14( 5), 721-731.
doi: 10.1162/08989290260138627 URL |
| [40] |
Smith E. E., Jonides J., & Koeppe R. A . ( 1996). Dissociating verbal and spatial working memory using PET. Cerebral Cortex, 6( 1), 11-20.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/6.1.11 URL pmid: 8670634 |
| [41] |
Todd, J.J., &Marois R. , ( 2004). Capacity limit of visual short-term memory in human posterior parietal cortex. Nature, 428( 6984), 751-754.
doi: 10.1038/nature02466 URL |
| [42] |
Toepper M., Gebhardt H., Beblo T., Thomas C., Driessen M., Bischoff M., .. & Sammer G . ( 2010). Functional correlates of distractor suppression during spatial working memory encoding. Neuroscience, 165( 4), 1244-1253.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.019 URL pmid: 19925856 |
| [43] |
Tseng P., Hsu T. Y., Chang C. F., Tzeng O. J. L., Hung D. L., Muggleton N. G ..&Juan , C. H. ., ( 2012). Unleashing potential: Transcranial direct current stimulation over the right posterior parietal cortex improves change detection in low-performing individuals. Journal of Neuroscience, 32( 31), 10554-10561.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0362-12.2012 URL pmid: 22855805 |
| [44] |
Vanderhasselt M. A., De Raedt R., & Baeken C . ( 2009). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and Stroop performance: Tackling the lateralization. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16( 3), 609-612.
doi: 10.3758/PBR.16.3.609 URL pmid: 19451392 |
| [45] |
Vogel, E.K., &Machizawa M.G . ( 2004). Neural activity predicts individual differences in visual working memory capacity. Nature, 428( 6984), 748-751.
doi: 10.1038/nature02447 URL |
| [46] |
Vogel E. K., McCollough A. W., & Machizawa M. G . ( 2005). Neural measures reveal individual differences in controlling access to working memory. Nature, 438( 7067), 500-503.
doi: 10.1038/nature04171 URL pmid: 16306992 |
| [47] |
Walter H., Bretschneider V., Grön G., Zurowski B., Wunderlich A. P., Tomczak R., & Spitzer M . ( 2003). Evidence for quantitative domain dominance for verbal and spatial working memory in frontal and parietal cortex. Cortex, 39( 4-5), 897-911.
doi: 10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70869-4 URL pmid: 14584558 |
| [48] |
Woodman, G.F . ( 2010). A brief introduction to the use of event-related potentials in studies of perception and attention. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 72( 8), 2031-2046.
doi: 10.3758/APP.72.8.2031 URL pmid: 3816929 |
| [49] |
Woodman G. F., Arita J. T., & Luck S. J . ( 2009). A cuing study of the N2pc component: An index of attentional deployment to objects rather than spatial locations. Brain Research,1297, 101-111.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.011 URL pmid: 2758329 |
| [50] |
Woodman, G.F., &Luck S.J . ( 2003). Serial deployment of attention during visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 29( 1), 121-138.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.29.1.121 URL pmid: 12669752 |
| [51] |
Wu Y. J., Tseng P., Chang C. F., Pai M. C., Hsu K. S., Lin C. C., & Juan C. H . ( 2014). Modulating the interference effect on spatial working memory by applying transcranial direct current stimulation over the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Brain and Cognition, 91, 87-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2014.09.002 URL pmid: 25265321 |
| [1] | 连浩敏, 张倩, 谷雪敏, 李寿欣. 持续性视觉注意对视觉工作记忆项目优先加工的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2025, 57(2): 191-206. |
| [2] | 李子媛, 雷鸣, 刘强. 视觉工作记忆离线态表征的生成机制[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(4): 412-420. |
| [3] | 邱义, 常香玉, 涂毅恒. 双靶点经颅直流电刺激调控短时和持续性疼痛:一项双盲、随机对照研究[J]. 心理学报, 2024, 56(10): 1313-1327. |
| [4] | 庞超, 陈颜璋, 王莉, 杨喜端, 贺雅, 李芷莹, 欧阳小钰, 傅世敏, 南威治. 客体信息在视觉工作记忆编码和维持阶段的不同注意选择模式[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(9): 1397-1410. |
| [5] | 高可翔, 张岳瑶, 李思瑾, 袁加锦, 李红, 张丹丹. 腹内侧前额叶在内隐认知重评中的因果作用[J]. 心理学报, 2023, 55(2): 210-223. |
| [6] | 孙彦良, 宋佳汝, 辛晓雯, 丁晓伟, 李寿欣. 视觉工作记忆的同类别存储优势[J]. 心理学报, 2021, 53(11): 1189-1202. |
| [7] | 华艳, 李明霞, 王巧婷, 冯彩霞, 张晶. 左侧眶额皮层在自动情绪调节下注意选择中的作用:来自经颅直流电刺激的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(9): 1048-1056. |
| [8] | 叶超雄, 胡中华, 梁腾飞, 张加峰, 许茜如, 刘强. 视觉工作记忆回溯线索效应的产生机制:认知阶段分离[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 399-413. |
| [9] | 罗禹, 念靖晴, 鲍未, 张静静, 赵守盈, 潘运, 许爽, 张禹. 急性应激损害对威胁刺激的注意解除[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(1): 26-37. |
| [10] | 张頔, 郝仁宁, 刘强. 注意范围分布对视觉工作记忆巩固过程的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(7): 772-780. |
| [11] | 李寿欣, 车晓玮, 李彦佼, 王丽, 陈恺盛. 视觉工作记忆负载类型对注意选择的影响[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(5): 527-542. |
| [12] | 殷西乐, 李建标, 陈思宇, 刘晓丽, 郝洁. 第三方惩罚的神经机制:来自经颅直流电刺激的证据[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(5): 571-583. |
| [13] | 张丹丹, 刘珍莉, 陈钰, 买晓琴. 右腹外侧前额叶对高抑郁水平成年人社会情绪调节的作用:一项tDCS研究[J]. 心理学报, 2019, 51(2): 207-2015. |
| [14] | 王慧慧, 罗玉丹, 石冰, 余凤琼, 汪凯. 经颅直流电刺激对健康大学生反应抑制的影响 *[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(6): 647-654. |
| [15] | 王静, 薛成波, 刘强. 客体同维度特征的视觉工作记忆存储机制[J]. 心理学报, 2018, 50(2): 176-185. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
