

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 465-474.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2019.00465 cstr: 32111.14.2019.00465
收稿日期:2018-07-17
出版日期:2019-03-15
发布日期:2019-01-22
基金资助:Received:2018-07-17
Online:2019-03-15
Published:2019-01-22
摘要:
社会心理学对图像的心理表征研究一直难以将心理活动的内容准确刻画出来。近10年来出现了一种新心理物理学方法——“反向相关图像分类技术”, 该技术假定观察者的反应与视觉噪音存在相关关系, 且反应是依照观察者的社会判断标准进行而非随机做出; 通过对其做出反应的相应噪音模式的足够次数的权重计算与视觉代码显现, 从而将观察者内在的评估特点可视化。该技术已在特质研究、种族和群际偏见等领域取得了一些成果, 但是未来仍需解决实验次数过多, 分离混杂的噪音以及被试的表现等问题, 才能获得更为真实的心理表征。
中图分类号:
侯春娜, 刘志军. (2019). 心理表征的可视化途径:基于噪音的反向相关图像分类技术. 心理科学进展 , 27(3), 465-474.
HOU Chun-Na, LIU Zhi-Jun. (2019). Visualization of mental representation: Noise-based reverse correlation image classification technology. Advances in Psychological Science, 27(3), 465-474.
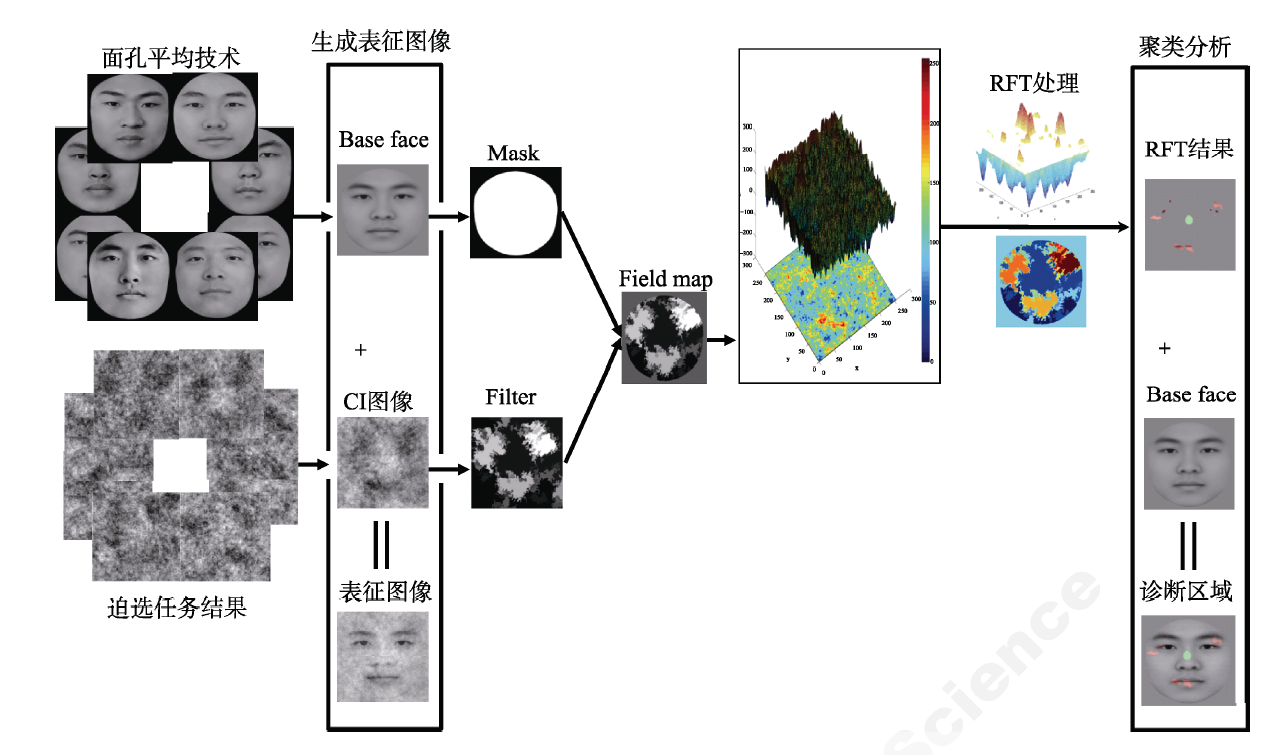
图1 RCIC生成表征图像与聚类分析示意图 注:(1)生成表征图像 将被试多次trials中所选择出的噪音模式通过权重计算并进行高斯平滑过滤得到CI图像, 将其覆盖在多张面孔平均合成的基本面孔(Base face)上, 从而获得表征图像; (2)聚类分析 将CI图像卷摺过滤(Filter)处理后与面孔有效区域(Mask)合成并进行标准化(Field map), 再依照RFT理论将超过固定阈值点进行簇聚, 将结果覆盖在Base face上得到诊断区域。 Base face来自侯春娜(2017); RFT处理结果来自刘志军(2017)。

图2 随机噪音生成示意图 注:生成随机噪音:(1)以2个周期截断的正弦曲线图像片段在6个不同朝向(0°, 30°, 60°, 90°, 120°和150°)×2个相位(0, π/2)的12种图像变化融合成噪音单元; (2)将之依照5种空间尺度(2, 4, 8, 16和32个周期)进行排列, 形成包含4092个正弦函数参数的随机噪音图像。 文献来源:Mangini和Biederman (2004)

图3 双图片迫选任务研究范式示意图 注:双图片迫选任务范式(2IFC):(1)双图片刺激生成 将RCIC生成的原始噪音以及与之相应的负性噪音, 分别叠加至基本面孔(base face)生成两种噪音模式相反的刺激图像; (2)双图片迫选任务 每次试验中将两种相反噪音模式的刺激图像并排呈现, 要求被试选择出最接近目标类别的面孔。 文献来源:Brinkman, Todorov和Dotsch (2017)
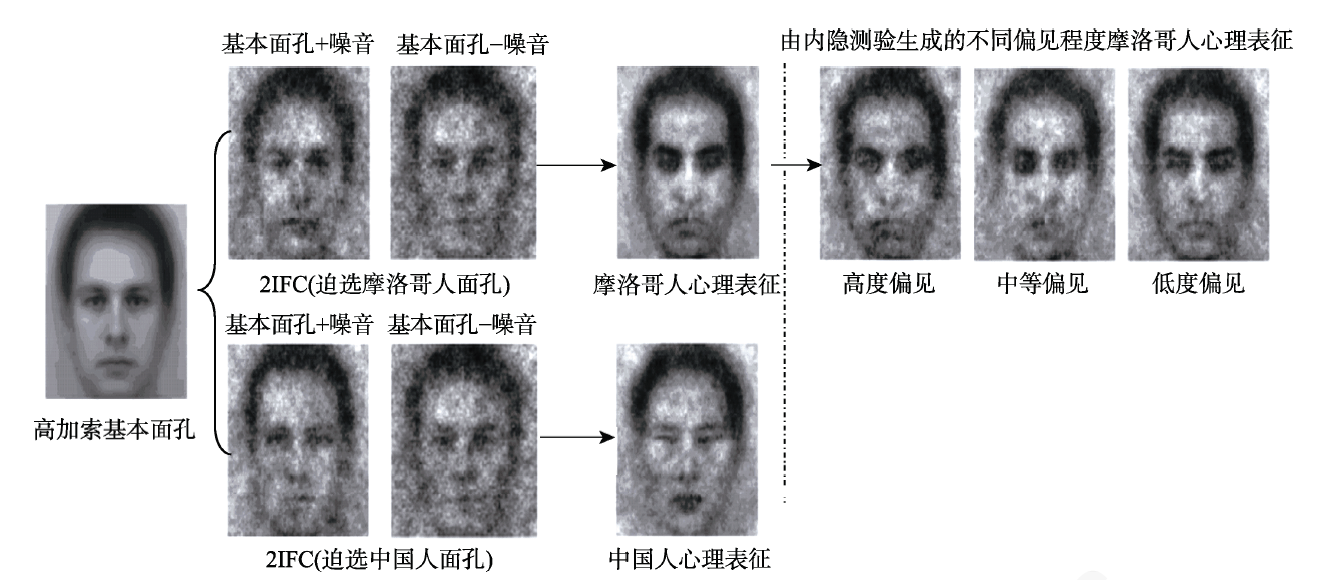
图4 基于相同基本面孔获得的摩洛哥人与中国人的面孔表征 注:Dotsch等人(2008)以高加索人(白种人)为基本面孔, 采用2IFC方式, 实验不仅生成摩洛哥人的心理表征图像, 也生成出中国人的心理表征图像。实验结果表明:基本面孔的选择不会影响最终的面孔分类表征图像。 文献来源:Dotsch, Wigboldus, Langner和van Knippenberg(2008)
| [1] | 侯春娜 . ( 2017). 面孔:群际信任的进化密码. 北京:科学出版社 |
| [2] | 刘志军 . ( 2017). 群际认知的面孔补偿效应——基于反向相关图像分类任务的研究(博士论文). 吉林大学. |
| [3] |
Adler R.J., & Hasofer A.M . ( 1976). Level crossings for random fields. The Annals of Probability, 4( 1), 1-12.
doi: 10.1214/aop/1176996176 URL |
| [4] |
Bijvank M. ( 2014). Periodic review inventory systems with a service level criterion. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 65( 12), 1853-1863.
doi: 10.1057/jors.2013.160 URL |
| [5] |
Brinkman L., Todorov A., & Dotsch R . ( 2017). Visualising mental representations: A primer on noise-based reverse correlation in social psychology. European Review of Social Psychology, 28( 1), 333-361.
doi: 10.1080/10463283.2017.1381469 URL |
| [6] |
Brown-Iannuzzi J. L., Dotsch R., Cooley E., & Payne B. K . ( 2017). The relationship between mental representations of welfare recipients and attitudes toward welfare. Psychological Science, 28( 1), 92-103.
doi: 10.1177/0956797616674999 URL |
| [7] |
Chen C., Garrod O., Schyns P., & Jack R . ( 2017). Mapping dynamic conversational facial expressions across cultures. Journal of Vision, 17( 10), 834-834.
doi: 10.1167/17.10.834 URL |
| [8] |
Clark C. M., Gosselin F., & Goghari V. M . ( 2013). Aberrant patterns of visual facial information usage in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 122( 2), 513-519.
doi: 10.1037/a0031944 URL pmid: 23713505 |
| [9] |
Dotsch R. & Todorov A., ( 2012). Reverse correlating social face perception. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 3( 5), 562-571.
doi: 10.1177/1948550611430272 URL |
| [10] |
Dotsch R., Wigboldus D. H. J., Langner O., & van Knippenberg A . ( 2008). Ethnic out-group faces are biased in the prejudiced mind. Psychological Science, 19( 10), 978-980.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02186.x URL pmid: 19000205 |
| [11] |
Dunham Y., Srinivasan M., Dotsch R., & Barner D . ( 2014). Religion insulates ingroup evaluations: The development of intergroup attitudes in India. Developmental Science, 17( 2), 311-319.
doi: 10.1111/desc.12105 URL pmid: 24205988 |
| [12] |
Dotsch R.., Wigboldus D.H, & Van K.A . ( 2011). Biased allocation of faces to social categories. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100(6), 999-1014.
doi: 10.1037/a0023026 URL pmid: 21443368 |
| [13] |
Fiske S.T . ( 2015). Intergroup biases: A focus on stereotype content. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 3, 45-50.
doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2015.01.010 URL pmid: 4955357 |
| [14] |
Gosselin F., Bacon B. A., & Mamassian P . ( 2004). Internal surface representations approximated by reverse correlation. Vision research, 44( 21), 2515-2520.
doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2004.05.016 URL pmid: 15358086 |
| [15] |
Gunaydin G., & Delong J.E . ( 2015). Reverse correlating love: Highly passionate women idealize their partner's facial appearance. Plos One, 10( 3), e0121094.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121094 URL pmid: 4373891 |
| [16] |
Imhoff R., Woelki J., Hanke S., & Dotsch R . ( 2013). Warmth and competence in your face! Visual encoding of stereotype content. Frontiers in Psychology, 4( 386), 1-8.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00386 URL pmid: 23825468 |
| [17] |
Jack R. E., Caldara R., & Schyns P. G . ( 2012). Internal representations reveal cultural diversity in expectations of facial expressions of emotion. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 141( 1), 19-25.
doi: 10.1037/a0023463 URL pmid: 21517206 |
| [18] |
Johnson K. L., Iida M., & Tassinary L. G . ( 2012). Person (mis)perception: functionally biased sex categorization of bodies. Proceedings of the Royal Society B Biological Sciences, 279( 1749), 4982-4989.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.2060 URL pmid: 3497247 |
| [19] |
Karremans J.C., Dotsch R., & Corneille O . ( 2011). Romantic relationship status biases memory of faces of attractive opposite-sex others: Evidence from a reverse-correlation paradigm. Cognition, 121( 3), 422-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2011.07.008 URL pmid: 21903209 |
| [20] |
Krosch A.R., & Amodio D.M . ( 2014). Economic scarcity alters the perception of race. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111( 25), 9079-9084.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404448111 URL pmid: 24927595 |
| [21] |
Lick D. J., Carpinella C. M., Preciado M. A., Spunt R. P., & Johnson K. L . ( 2013). Reverse-correlating mental representations of sex-typed bodies: The effect of number of trials on image quality. Frontiers in Psychology, 4( 2), 476-484.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00476 URL pmid: 3727110 |
| [22] |
Mangini M.C., & Biederman I. , ( 2004). Making the ineffable explicit: Estimating the information employed for face classifications. Cognitive Science, 28( 2), 209-226.
doi: 10.1207/s15516709cog2802_4 URL |
| [23] |
Martin-Malivel J., Mangini M. C., Fagot J., & Biederman I . ( 2010). Do humans and baboons use the same information when categorizing human and baboon faces?. Psychological Science, 17( 7), 599-607.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01751.x URL pmid: 16866746 |
| [24] | Nunnari F. & Heloir A., ( 2017). Generating virtual characters from personality traits via reverse correlation and linear programming. Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, 1661-1663. |
| [25] |
Oosterhof N.N., & Todorov A. , ( 2008). The functional basis of face evaluation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105( 32), 11087-11092.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805664105 URL pmid: 18685089 |
| [26] |
Paulus A., Rohr M., Dotsch R., & Wentura D . ( 2016). Positive feeling, negative meaning: Visualizing the mental representations of in-group and out-group smiles. PloS one, 11( 3), e0151230.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151230 URL pmid: 4786158 |
| [27] |
Ponsot E., Arias P., & Aucouturier J. J . ( 2018). Uncovering mental representations of smiled speech using reverse correlation. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 143( 1), 19-24.
doi: 10.1121/1.5020989 URL pmid: 29390775 |
| [28] |
Ratner K. G., Dotsch R., Wigboldus D. H., van Knippenberg A., & Amodio D. M . ( 2014). Visualizing minimal ingroup and outgroup faces: implications for impressions, attitudes, and behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106( 6), 897-911.
doi: 10.1037/a0036498 URL pmid: 24841095 |
| [29] | Saegusa C., Yamaoka M., & Watanabe K . ( 2015). Seeing faces in noise: Exploring machine and human face detection processes by the reverse correlation method. Paper presented at the Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Siem Reap, Cambodia. |
| [30] |
Todorov A., Dotsch R., Wigboldus D. H. J., & Said C. P . ( 2011). Data-driven methods for modeling social perception. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 5( 10), 775-791.
doi: 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2011.00389.x URL |
| [31] |
Todorov A., Olivola C. Y., Dotsch R., & Mende-Siedlecki P . ( 2015). Social attributions from faces: determinants, consequences, accuracy, and functional significance. Annual Review of Psychology, 66( 1), 519-545.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143831 URL pmid: 25196277 |
| [32] | van Driel, S. D . ( 2017). Prediction of Self Perception based on Dominance and Trustworthiness by using Reverse Correlation. ( Unpublished master’s thesis). Utrecht University, Netherlands. |
| [33] |
Van Rijsbergen N., Jaworska K., Rousselet G. A., & Schyns P. G . ( 2014). With age comes representational wisdom in social signals. Current Biology, 24( 23), 2792-2796.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.075 URL pmid: 4251953 |
| [34] | Young A.I . ( 2014). Seeing scary: Predicting variation in the scariness of the mental representations of spiders. ( Unpublished doctoral dissertation). The Ohio State University, Ohio State. |
| [1] | 贾云丞, 程刚, 丁芳媛, 陈加, 龙女, 陈玉荣, 林楠. 对中性婴儿面孔注意偏向与表情不确定性的关系[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(9): 1393-1407. |
| [2] | 常茜芮, 何蔚祺. 网络游戏成瘾者的情绪加工异常[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(7): 1152-1163. |
| [3] | 王羽凌, 陆晓伟, 武宗杰, 李国根, 张林. 面孔吸引力判断中的跨通道整合过程[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(5): 790-799. |
| [4] | 郑远霞, 刘国雄, 辛聪, 程黎. 以貌取人:儿童基于面孔的信任判断[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(2): 300-317. |
| [5] | 莫李澄, 李奇, 张丹丹. 婴儿对情绪信息的加工:认知发展特征及脑机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(12): 2100-2108. |
| [6] | 郭桐阳, 莫李澄, 张丹丹. 婴儿面孔和注视方向加工的认知神经机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(10): 1670-1679. |
| [7] | 陈子龙, 季琭妍. 多面孔情绪变异性的自动化加工:来自视觉失匹配负波的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 34-34. |
| [8] | Yongyi Chen, Yu Zou, Xiaoyan Li, Ying Zhang, Guomei Zhou. “反差美”是否存在[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 39-39. |
| [9] | 连玉净, 汪海玲. 面孔运动影响面孔整体加工[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 57-57. |
| [10] | 方海情, 汪海玲. 面孔运动影响情绪面孔的整体加工[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 65-65. |
| [11] | 卢和和, 林子涵, 朱莎莎, 蒋柯. 情绪面孔识别的注意瞬脱效应[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 83-83. |
| [12] | 应浩江, 俞珺洺. 面孔序列加工中的统计性质[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 173-173. |
| [13] | 陆晓伟, 郭治斌, 程雨, 沈洁, 贵文君, 张林. 老年人面孔信任评价的积极效应及其发生机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(8): 1496-1503. |
| [14] | 蒲小萍, 胡浩, 朱继娜, 汤一鹏. 面孔吸引力对注意资源分配的影响:进化动机的调节作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(7): 1109-1120. |
| [15] | 陈子炜, 付迪, 刘勋. 错认总比错过好——面孔视错觉的发生机制及其应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(2): 240-255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
