

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 248-258.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00248
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIA Shiwei, QI Congcong, CHEN Lele, REN Yanju( )
)
Received:2021-04-19
Published:2022-03-25
Online:2022-01-25
Contact:
REN Yanju
E-mail:renyanju@gmail.com
Supported by:JIA Shiwei, QI Congcong, CHEN Lele, REN Yanju. (2022). The effect of working memory load on feedback processing: Evidence from an event-related potentials (ERP) study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 54(3), 248-258.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00248

Figure 1. Examples of memory materials for high WM load and low WM load conditions (1a), and the illustration of one trial (1b). As shown in 1b, the experiment is a dual-task paradigm, and the simple gambling task is embedded in the working memory task.
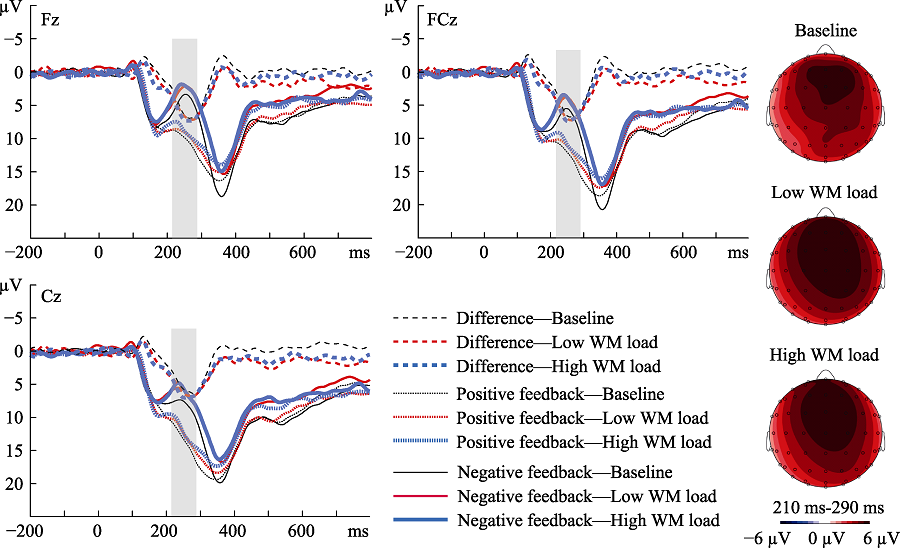
Figure 2. The grand average RewP waveforms and the difference waveforms between positive and negative feedback (Fz, FCz and Cz points), and RewP difference wave topographies under different WM load conditions.
| [1] |
Alexander, W. H., & Brown, J. W. (2010). Computational models of performance monitoring and cognitive control. Topics in Cognitive Science, 2(4), 658-677.
pmid: 21359126 |
| [2] |
Alexander, W. H., & Brown, J. W. (2011). Medial prefrontal cortex as an action-outcome predictor. Nature Neuroscience, 14(10), 1338-1344.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2921 pmid: 21926982 |
| [3] |
Baker, T. E., & Holroyd, C. B. (2011). Dissociated roles of the anterior cingulate cortex in reward and conflict processing as revealed by the feedback error-related negativity and N200. Biological Psychology, 87, 25-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.01.010 URL |
| [4] |
Bernat, E. M., Nelson, L. D., Steele, V. R., Gehring, W. J., & Patrick, C. J. (2011). Externalizing psychopathology and gain-loss feedback in a simulated gambling task: Dissociable components of brain response revealed by time-frequency analysis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 120, 352-364.
doi: 10.1037/a0022124 URL |
| [5] |
Broyd, S. J., Richards, H. J., Helps, S. K., Chronaki, G., Bamford, S., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2012). An electrophysiological monetary incentive delay (e-MID) task: A way to decompose the different components of neural response to positive and negative monetary reinforcement. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 209(1), 40-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.05.015 URL |
| [6] |
Cheng, J. P., Luo, Y. J., & Cui, F. (2017). Empathy for pain influenced by cognitive load: Evidence from an ERP study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(5), 622-630.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00622 URL |
| [7] |
Cohen, M. X., Elger, C. E., & Ranganath, C. (2007). Reward expectation modulates feedback-related negativity and EEG spectra. NeuroImage, 35(2), 968-978.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.056 URL |
| [8] |
Donaldson, K. R., Ait Oumeziane, B., Hélie, S., & Foti, D. (2016). The temporal dynamics of reversal learning: P3 amplitude predicts valence-specific behavioral adjustment. Physiology & Behavior, 161, 24-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.03.034 URL |
| [9] | Donchin, E., & Coles, M. G. H. (1988). Is the P300 component a manifestation of context updating? Behavioral & Brain Sciences, 11(03), 357-374. |
| [10] |
Ferdinand, N. K. (2019). The influence of task complexity and information value on feedback processing in younger and older adults: No evidence for a positivity bias during feedback-induced learning in older adults. Brain Research, 1717, 74-85.
doi: S0006-8993(19)30204-5 pmid: 30991040 |
| [11] |
Foti, D., Weinberg, A., Bernat, E. M., & Proudfit, G. H. (2015). Anterior cingulate activity to monetary loss and basal ganglia activity to monetary gain uniquely contribute to the feedback negativity. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126(7), 1338-1347.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.08.025 pmid: 25454338 |
| [12] |
Foti, D., Weinberg, A., Dien, J., & Hajcak, G. (2011). Event-related potential activity in the basal ganglia differentiates rewards from nonrewards: Temporospatial principal components analysis and source localization of the feedback negativity. Human Brain Mapping, 32, 2207-2216.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.21182 pmid: 21305664 |
| [13] |
Gehring, W. J., & Willoughby, A. R. (2002). The medial frontal cortex and the rapid processing of monetary gains and losses. Science, 295(5563), 2279-2282.
doi: 10.1126/science.1066893 URL |
| [14] |
Glazer, J. E., Kelley, N. J., Pornpattananangkul, N., Mittal, V. A., & Nusslock, R. (2018). Beyond the FRN: Broadening the time-course of EEG and ERP components implicated in reward processing. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 132, 184-202.
doi: S0167-8760(17)30473-7 pmid: 29454641 |
| [15] |
Hajcak, G., Dunning, J. P., & Foti, D. (2009). Motivated and controlled attention to emotion: Time-course of the late positive potential. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(3), 505-510.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2008.11.028 pmid: 19157974 |
| [16] |
Hajcak, G., Moser, J. S., Holroyd, C. B., & Simons, R. F. (2006). The feedback-related negativity reflects the binary evaluation of good versus bad outcomes. Biological psychology, 71(2), 148-154.
pmid: 16005561 |
| [17] |
Han, M., Shi, L., & Jia, S. (2017). Attentional resources modulate error processing-related brain electrical activity: Evidence from a dual-task design. Brain Research, 1670, 68-75.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.05.029 URL |
| [18] |
Hernandez Lallement, J., Kuss, K., Trautner, P., Weber, B., Falk, A., & Fliessbach, K. (2014). Effort increases sensitivity to reward and loss magnitude in the human brain. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(3), 342-349.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nss147 pmid: 23202663 |
| [19] |
Holroyd, C. B., & Coles, M. G. H. (2002). The neural basis of human error processing: Reinforcement learning, dopamine, and the error-related negativity. Psychological Review, 109(4), 679-709.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.109.4.679 pmid: 12374324 |
| [20] |
Holroyd, C. B., & Umemoto, A. (2016). The research domain criteria framework: The case for anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 418-443.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.09.021 URL |
| [21] | Holroyd, C. B., & Yeung, N. (2011). An integrative theory of anterior cingulate cortex function:Option selection in hierarchical reinforcement learning. In: Mars, R.B., Sallet, J., Rushworth, M.F.S., Yeung, N. (Eds.), Neural Basis of Motivational and Cognitive Control (pp.333-349). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. |
| [22] |
Hsieh, L. T., & Ranganath, C. (2014). Frontal midline theta oscillations during working memory maintenance and episodic encoding and retrieval. Neuroimage. 85, 721-729.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.08.003 URL |
| [23] |
Huang, C., & Yu, R. (2018). Making mistakes in public: Being observed magnifies physiological responses to errors. Neuropsychologia, 119, 214-222.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.08.015 URL |
| [24] |
Krigolson, O. E., Hassall, C. D., Satel, J., & Klein, R. M. (2015). The impact of cognitive load on reward evaluation. Brain Research, 1627, 225-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.09.028 pmid: 26431993 |
| [25] |
Krigolson, O. E., Heinekey, H., Kent, C. M., & Handy, T. C. (2012). Cognitive load impacts error evaluation within medial-frontal cortex. Brain Research, 1430, 62-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.10.028 pmid: 22099261 |
| [26] |
Langeslag, S. J. E., & van Strien, J. W. (2013). Up-regulation of emotional responses to reward-predicting stimuli: An ERP study. Biological Psychology, 94(1), 228-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.05.021 pmid: 23770414 |
| [27] | Li, P., Peng, W., Li, H., & Holroyd, C. B. (2018). Electrophysiological measures reveal the role of anterior cingulate cortex in learning from unreliable feedback. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 18(5), 949-963. |
| [28] |
Luft, C. D. B. (2014). Learning from feedback: The neural mechanisms of feedback processing facilitating better performance. Behavioural Brain Research, 261, 356-368.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.12.043 URL |
| [29] |
Meadows, C. C., Gable, P. A., Lohse, K. R., & Miller, M. W. (2016). The effects of reward magnitude on reward processing: An averaged and single trial event-related potential study. Biological Psychology, 118, 154-160.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.06.002 URL |
| [30] |
Miltner, W. H. R., Braun, C. H., & Coles, M. G. H. (1997). Event-related brain potentials following incorrect feedback in a time-estimation task: Evidence for a "generic" neural system for error detection. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 9(6), 788-798.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.1997.9.6.788 pmid: 23964600 |
| [31] |
Mitchell, D. J., McNaughton, N., Flanagan, D., & Kirk, I. J. (2008). Frontal-midline theta from the perspective of hippocampal theta. Progress In Neurobiology, 86, 156-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.09.005 pmid: 18824212 |
| [32] |
Nieuwenhuis, S., Aston-Jones, G., & Cohen, J. D. (2005). Decision making, the P3, and the locus coeruleus--norepinephrine system. Psychological Bulletin, 131(4), 510-532.
pmid: 16060800 |
| [33] |
Oliveira, F. T., Mcdonald, J. J., & Goodman, D. (2007). Performance monitoring in the anterior cingulate is not all error related: Expectancy deviation and the representation of action-outcome associations. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(12), 1994-2004.
pmid: 17892382 |
| [34] |
Polich, J. (2007). Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(10), 2128-2148.
pmid: 17573239 |
| [35] |
Proudfit, G. H. (2015). The reward positivity: From basic research on reward to a biomarker for depression. Psychophysiology, 52(4), 449-459.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.12370 pmid: 25327938 |
| [36] |
Rodriguez Buritica, J. M., Heekeren, H. R., Li, S.-C., & Eppinger, B. (2018). Developmental differences in the neural dynamics of observational learning. Neuropsychologia, 119, 12-23.
doi: S0028-3932(18)30373-7 pmid: 30036542 |
| [37] |
Sambrook, T. D., & Goslin, J. (2015). A neural reward prediction error revealed by a meta-analysis of ERPs using great grand averages. Psychological bulletin, 141(1), 213-235.
doi: 10.1037/bul0000006 pmid: 25495239 |
| [38] |
Shahnazian, D., Shulver, K., & Holroyd, C. B. (2018). Electrophysiological responses of medial prefrontal cortex to feedback at different levels of hierarchy. NeuroImage, 183, 121-131.
doi: S1053-8119(18)30680-3 pmid: 30081194 |
| [39] |
Stewart, J. G., Singleton, P., Benau, E. M., Foti, D., Allchurch, H., Kaplan, C. S.,... Auerbach, R. P. (2019). Neurophysiological activity following rewards and losses among female adolescents and young adults with borderline personality disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 128(6), 610-621.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000439 pmid: 31318241 |
| [40] |
Webb, C. A., Auerbach, R. P., Bondy, E., Stanton, C. H., Foti, D., & Pizzagalli, D. A. (2017). Abnormal neural responses to feedback in depressed adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 126(1), 19-31.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000228 URL |
| [41] |
White, E. J., & Grant, D. M. (2017). Electrocortical consequences of image processing: The influence of working memory load and worry. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 261, 1-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.01.003 URL |
| [42] |
Yang, Q., Zhao, D., Wu, Y., Tang, P., Gu, R., & Luo, Y.-j. (2018). Differentiating the influence of incidental anger and fear on risk decision-making. Physiology & Behavior, 184, 179-188.
doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.11.028 URL |
| [43] |
Yeung, N., & Sanfey, A. G. (2004). Independent coding of reward magnitude and valence in the human brain. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(28), 6258-6264.
pmid: 15254080 |
| [44] |
Zhou, Z., Yu, R., & Zhou, X. (2010). To do or not to do? Action enlarges the FRN and P300 effects in outcome evaluation. Neuropsychologia, 48(12), 3606-3613.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.08.010 URL |
| [1] | FAN Wei, REN Mengmeng, ZHANG Wenjie, ZHONG Yiping. The impact of feedback on self-deception: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 481-496. |
| [2] | SUN Qiwu, WU Caizhi, YU Lixia, WANG Weixin, SHEN Guocheng. Progress feedback and its effects on working alliance and treatment outcomes [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(4): 349-361. |
| [3] | CHEN Yuming, LI Sijin, GUO Tianyou, XIE Hui, XU Feng, ZHANG Dandan. The role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on voluntary forgetting of negative social feedback in depressed patients: A TMS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(10): 1094-1104. |
| [4] | WANG Yuan, LI Ke, GAI Xiaosong, CAO Yifei. Training and transfer effects of response inhibition training with online feedback on adolescents and adults’ executive function [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(10): 1212-1223. |
| [5] | ZHU Shuqing, ZHAI Yu, JIA Shiwei. Local context dependence in feedback evaluation: An ERP study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(11): 1198-1207. |
| [6] | WANG Haibo,YAN Ming,WU Haibo,LI Jinrong,WANG Xiaohui. Hostile retaliation or identity motivation? The mechanisms of how newcomers’ role organizational socialization affects their workplace ostracism [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(1): 128-140. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiuling, HOU Yanan, ZHANG Fuxu, MEI Songli, KANG Jingmei. The adaptation to Kanizsa-type illusory contours [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(2): 168-175. |
| [8] | Shengming LIU,Lifan CHEN,Simai WANG. Modesty brings gains: The effect of humble leader behavior on team creativity from a team communication perspective [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(10): 1159-1168. |
| [9] | WANG Yiwen, FU Chao, REN Xiangfeng, LIN Yuzhong, GUO Fengbo. Narcissistic personality modulates outcome evaluation in the trust game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1080-1088. |
| [10] | LI Tingyu, LIU Li, ZHU Liqi. 4~6 year-old children’s trust in economic game and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(1): 17-27. |
| [11] | LI WenFu, TONG DanDan, QIU Jiang, ZHANG QingLin. The neural basis of scientific innovation problems solving [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(4): 331-342. |
| [12] | ZHANG Qiyong, CHEN Chenghui, LU Jiamei, ZHANG Pengcheng. The mechanism of emotional contagion [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(11): 1423-1433. |
| [13] | WANG Yiwen, ZHANG Zhen, YUAN Sheng, GUO Fengbo, HE Shaoying, JING Yiming. The Decision-making and Outcome Evaluation during a Repeated Trust Game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(8): 1028-1038. |
| [14] | ZHU Xiangru, ZHANG Yan, YANG Suyong, WU Haiyan, WANG Lili, GU Ruolei. The Motivational Hierarchy between Self and Mother: Evidence from the Feedback-related Negativity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(6): 807-813. |
| [15] | CHEN Xuqian;ZHANG Jijia;LI Yunheng. Feedback Consistent Effect: Evidence from Chinese Homophones with High-frequency [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(1): 47-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||