

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (10): 1653-1661.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01653
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
MENG Haijiang1( ), CHEN Lei1, WANG Gang1, ZHANG Jian2
), CHEN Lei1, WANG Gang1, ZHANG Jian2
Received:2021-09-24
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-08-03
Contact:
MENG Haijiang
E-mail:mhaijiang@163.com
Supported by:MENG Haijiang, CHEN Lei, WANG Gang, ZHANG Jian. (2023). Differences in motor cortex synaptic plasticity associated with two forms of exercise in older adults: Evidence from TMS studies. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(10), 1653-1661.
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. Aged 60~70 years | 1. Have Alzheimer's or other neurodegenerative disorder |
| 2. Volunteered to take part in the entire study | 2. Have Mini-Mental State Examination test score ≤ 26 |
| 3. Able to provide written informed consent | 3. Unable to exercise due to neuromuscular or musculoskeletal limitations |
| 4. Participated often in table tennis or tai chi exercise or were often sedentary | 4. Have schizophrenia, emotional disorder or depression, or other psychological disorder |
| 5. Have a history of sleep disorder | |
| 6. Have a history of alcohol use disorder within 2 years | |
| 7. Have a history of cancer or other serious systemic disease in the last 5 years | |
| 8. Have hypertension, coronary heart disease, or other organic heart disease | |
| 9. Have endocrine metabolism disorder or history of diabetes | |
| 10. Participate often in other sports in addition to table tennis or tai chi |
Table 1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria for participating in the study
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. Aged 60~70 years | 1. Have Alzheimer's or other neurodegenerative disorder |
| 2. Volunteered to take part in the entire study | 2. Have Mini-Mental State Examination test score ≤ 26 |
| 3. Able to provide written informed consent | 3. Unable to exercise due to neuromuscular or musculoskeletal limitations |
| 4. Participated often in table tennis or tai chi exercise or were often sedentary | 4. Have schizophrenia, emotional disorder or depression, or other psychological disorder |
| 5. Have a history of sleep disorder | |
| 6. Have a history of alcohol use disorder within 2 years | |
| 7. Have a history of cancer or other serious systemic disease in the last 5 years | |
| 8. Have hypertension, coronary heart disease, or other organic heart disease | |
| 9. Have endocrine metabolism disorder or history of diabetes | |
| 10. Participate often in other sports in addition to table tennis or tai chi |
| Characteristic | Table tennis group (18) | Tai chi group (18) | Sedentary group (18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 66.11 ± 3.36 | 65.61 ± 3.40 | 64.89 ± 3.03 |
| Female sex (n) | 7 | 10 | 9 |
| Educational level (years) | 11.83 ± 2.36 | 11.33 ± 3.34 | 12.39 ± 2.35 |
| MMSE score | 27.83 ± 0.86 | 27.78 ± 1.06 | 27.61 ± 0.70 |
Table 2 Demographic characteristics of study participants, by group (M ± SD)
| Characteristic | Table tennis group (18) | Tai chi group (18) | Sedentary group (18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 66.11 ± 3.36 | 65.61 ± 3.40 | 64.89 ± 3.03 |
| Female sex (n) | 7 | 10 | 9 |
| Educational level (years) | 11.83 ± 2.36 | 11.33 ± 3.34 | 12.39 ± 2.35 |
| MMSE score | 27.83 ± 0.86 | 27.78 ± 1.06 | 27.61 ± 0.70 |
| Variable | Table tennis group (n = 18) | Tai chi group (n = 18) | Sedentary group (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Time (min/session) | 128.33 ± 9.01 | 116.67 ± 7.23 | N/A |
| Exercise intensity | Medium and greater | Medium and greater | N/A |
| Exercise frequency (sessions/wk) | 5.78 ± 0.29 | 6.28 ± 0.24 | N/A |
| Sedentary time (min/day) | 281.67 ± 30.40 | 271.67 ± 22.29 | 596.67 ± 29.29** |
| RMT (%) | 38.17 ± 1.28 | 39.67 ± 1.65 | 40.67 ± 1.38 |
| 1 mV stimulation intensity (%) | 52.17 ± 1.55 | 54.44 ± 2.19 | 54.56 ± 1.47 |
| Sensory threshold (mA) | 2.18 ± 0.06 | 2.18 ± 0.09 | 2.29 ± 0.07 |
Table 3 Sedentary and exercise times, exercise frequencies and intensities, and baseline TMS characteristics before application of the PAS25 protocol, by group
| Variable | Table tennis group (n = 18) | Tai chi group (n = 18) | Sedentary group (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Time (min/session) | 128.33 ± 9.01 | 116.67 ± 7.23 | N/A |
| Exercise intensity | Medium and greater | Medium and greater | N/A |
| Exercise frequency (sessions/wk) | 5.78 ± 0.29 | 6.28 ± 0.24 | N/A |
| Sedentary time (min/day) | 281.67 ± 30.40 | 271.67 ± 22.29 | 596.67 ± 29.29** |
| RMT (%) | 38.17 ± 1.28 | 39.67 ± 1.65 | 40.67 ± 1.38 |
| 1 mV stimulation intensity (%) | 52.17 ± 1.55 | 54.44 ± 2.19 | 54.56 ± 1.47 |
| Sensory threshold (mA) | 2.18 ± 0.06 | 2.18 ± 0.09 | 2.29 ± 0.07 |
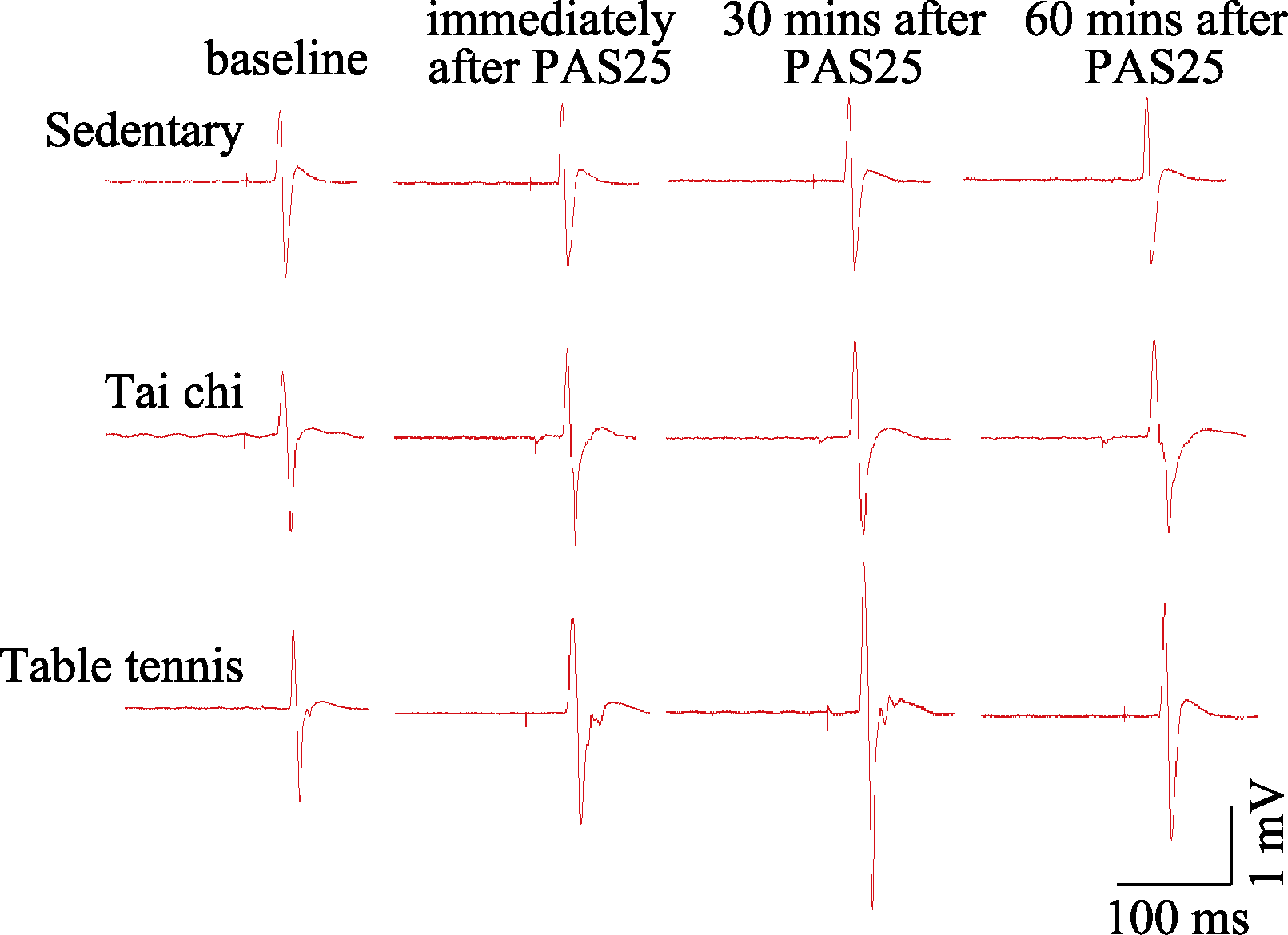
Figure 2. Average MEP amplitudes from the APB of one sedentary, one table tennis and one tai chi participant before and at the indicated time after PAS25.

Figure 3. Changes in mean MEP amplitudes from baseline to the indicated times after PAS25 in the table tennis, tai chi, and sedentary groups. Note. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 for table tennis group vs. tai chi group; #p < 0.05 for tai chi group vs. sedentary group.
| [1] |
Adkins, D. L., Boychuk, J., Remple, M. S., & Kleim, J. A. (2006). Motor training induces experience-specific patterns of plasticity across motor cortex and spinal cord. Journal of Applied Physiology, 101(6), 1776-1782.
pmid: 16959909 |
| [2] |
Bai, X. J., Shao, M. L., Liu, T., Yin, J. Z., & Jin, H. (2020). Altered structural plasticity in early adulthood after badminton training. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(2), 173-183.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00173 |
| [3] |
Chekroud, S. R., Gueorguieva, R., Zheutlin, A. B., Paulus, M., Krumholz, H. M., Krystal, J. H., & Chekroud, A. M. (2018). Association between physical exercise and mental health in 1.2 million individuals in the USA between 2011 and 2015: A cross-sectional study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 5(9), 739-746.
doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30227-X URL |
| [4] |
Cirillo, J., Lavender, A. P., Ridding, M. C., & Semmler, J. G. (2009). Motor cortex plasticity induced by paired associative stimulation is enhanced in physically active individuals. The Journal of Physiology, 587(24), 5831-5842.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181834 URL |
| [5] | Dai, W., Zhang, J., & Tan, X. Y. (2017). Comparison of brain plasticity between table tennis and badminton athletes. China Sport Science and Technology, 53(6), 127-132. |
| [6] | Daoudal, G., & Debanne, D. (2003). Long-term plasticity of intrinsic excitability:Learning rules and mechanisms. Learning & Memory, 10(6), 456-465. |
| [7] |
Di Lazzaro, V., Oliviero, A., Saturno, E., Dileone., M., Pilato, F., Nardone, R., ... Tonali, P. (2005). Effects of lorazepam on short latency afferent inhibition and short latency intracortical inhibition in humans. The Journal of Physiology, 564(2), 661-668.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.061747 URL |
| [8] |
Elahi, B., Gunraj, C., & Chen, R. (2012). Short-interval intracortical inhibition blocks long-term potentiation induced by paired associative stimulation. Journal of Neurophysiology, 107(7), 1935-1941.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00202.2011 pmid: 22236712 |
| [9] |
Erickson, K. I., & Kramer, A. F. (2009). Aerobic exercise effects on cognitive and neural plasticity in older adults. British journal of sports medicine, 43(1), 22-24.
doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2008.052498 pmid: 18927158 |
| [10] |
Hallett, M. (2007). Transcranial magnetic stimulation: A primer. Neuron, 55(2), 187-199.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.026 pmid: 17640522 |
| [11] |
Heidegger, T., Krakow, K., & Ziemann, U. (2010). Effects of antiepileptic drugs on associative LTP-like plasticity in human motor cortex. European Journal of Neuroscience, 32(7), 1215-1222.
doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07375.x pmid: 20726885 |
| [12] |
Iino, Y., & Kojima, T. (2011). Kinetics of the upper limb during table tennis topspin forehands in advanced and intermediate players. Sports Biomechanics, 10(4), 361-377.
pmid: 22303787 |
| [13] |
Jones, E. G. (2000). Cortical and subcortical contributions to activity-dependent plasticity in primate somatosensory cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 23, 1-37.
pmid: 10845057 |
| [14] |
Kujirai, T., Caramia, M. D., Rothwell, J. C., Day, B. L., Thompson, P. D., Ferbert, A., ... Marsden, C. D. (1993). Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. The Journal of Physiology, 471, 501-519.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019912 URL |
| [15] |
Malenka, R. C., & Bear, M. F. (2004). LTP and LTD: An embarrassment of riches. Neuron, 44(1), 5-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.09.012 pmid: 15450156 |
| [16] | Maruyama, A., Takahashi, K., Eto, S., Kawahira, K., & Rothwell, J. C. (2008). Sensory-motor intracortical excitability and imagery of grip touch in racket players. Brain Stimulation, 1(3), 245. |
| [17] |
Milkman, K. L., Gromet, D., Ho, H., Kay, J. S., Lee, T. W., Pandiloski, P., ... Duckworth, A. L. (2021). Megastudies improve the impact of applied behavioural science. Nature, 600(7889), 478-483.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04128-4 |
| [18] |
Morgante, F., Espay, A. J., Gunraj, C., Lang, A. E., & Chen, R. (2006). Motor cortex plasticity in Parkinson's disease and levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Brain, 129(4), 1059-1069.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awl031 URL |
| [19] |
Morishita, T., Ninomiya, M., Uehara, K., & Funase, K. (2011). Increased excitability and reduced intracortical inhibition in the ipsilateral primary motor cortex during a fine-motor manipulation task. Brain Research, 1371, 65-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.049 pmid: 21093420 |
| [20] |
Muellbacher, W., Facchini, S., Boroojerdi, B., & Hallett, M. (2000). Changes in motor cortex excitability during ipsilateral hand muscle activation in humans. Clinical Neurophysiology, 111(2), 344-349.
pmid: 10680571 |
| [21] |
Ni, Z., Gunraj, C., Kailey, P., Cash, R. F. H., & Chen, R. (2014). Heterosynaptic modulation of motor cortical plasticity in human. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(21), 7314-7321.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4714-13.2014 pmid: 24849363 |
| [22] |
Ni, Z., Isayama, R., Castillo, G., Gunraj, C., Saha, U., & Chen, R. (2015). Reduced dorsal premotor cortex and primary motor cortex connectivity in older adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 36(1), 301-303.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.08.017 pmid: 25216584 |
| [23] |
Ni, Z., Müller-Dahlhaus, F., Chen, R., & Ziemann, U. (2011). Triple-pulse TMS to study interactions between neural circuits in human cortex. Brain Stimulation, 4(4), 281-293.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2011.01.002 pmid: 22032744 |
| [24] |
Okano, A. H., Fontes, E. B., Montenegro, R. A., Farinatti, P. T. V., Cyrino, E. S., Li, L. M., Bikson, M., & Noakes, T. D. (2015). Brain stimulation modulates the autonomic nervous system, rating of perceived exertion and performance during maximal exercise. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 49(18), 1213-1218.
doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091658 pmid: 23446641 |
| [25] |
Pascual-Leone, A., Amedi, A., Fregni, F., & Merabet, L. B. (2005). The plastic human brain cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 28, 377-401.
pmid: 16022601 |
| [26] |
Patterson, R., McNamara, E., Tainio, M., Hérick de Sá, T., Smith, A. D., Sharp, S. J., Edwards, P., Woodcock, J., Brage, S., & Wijndaele, K. (2018). Sedentary behaviour and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer mortality, and incident type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and dose response meta-analysis. European Journal of Epidemiology, 33(9), 811-829.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-018-0380-1 pmid: 29589226 |
| [27] |
Pearce, A. J., Thickbroom, G. W., Byrnes, M. L., & Mastaglia, F. L. (2000). Functional reorganisation of the corticomotor projection to the hand in skilled racquet players. Experimental Brain Research, 130(2), 238-243.
doi: 10.1007/s002219900236 pmid: 10672477 |
| [28] |
Rogge, A. K., Röder, B., Zech, A., & Hötting, K. (2018). Exercise-induced neuroplasticity: Balance training increases cortical thickness in visual and vestibular cortical regions. Neuroimage, 179, 471-479.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.06.065 URL |
| [29] |
Rosenkranz, K., Williamon, A., & Rothwell, J. C. (2007). Motorcortical excitability and synaptic plasticity is enhanced in professional musicians. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(19), 5200-5206.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0836-07.2007 pmid: 17494706 |
| [30] |
Stefan, K., Kunesch, E., Cohen, L. G., Benecke, R., & Classen, J. (2000). Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain, 123(3), 572-584.
doi: 10.1093/brain/123.3.572 URL |
| [31] |
Stefan, K., Wycislo, M., Gentner, R., Schramm, A., Naumann, M., Reiners, K., & Classen, J. (2006). Temporary occlusion of associative motor cortical plasticity by prior dynamic motor training. Cerebral Cortex, 16(3), 376-385.
pmid: 15930370 |
| [32] |
Stinear, C. M., Walker, K. S., & Byblow, W. D. (2001). Symmetric facilitation between motor cortices during contraction of ipsilateral hand muscles. Experimental Brain Research, 139(1), 101-105.
doi: 10.1007/s002210100758 pmid: 11482835 |
| [33] | Vaynman, S., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2005). License to run: Exercise impacts functional plasticity in the intact and injured central nervous system by using neurotrophins. Neurorehabilitation & Neural Repair, 19(4), 283-295. |
| [34] |
Ward, N. S. (2006). Compensatory mechanisms in the aging motor system. Ageing Research Reviews, 5(3), 239-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2006.04.003 pmid: 16905372 |
| [35] |
Wu, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Wang, D., Tan, X., Zhu, X., Zhang, J., & Zhang, J. (2013). The role of visual perception in action anticipation in basketball athletes. Neuroscience, 237, 29-41.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.01.048 pmid: 23384606 |
| [36] | Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Zeng, Y., & Shen, C. (2015). Structural brain plasticity change in athletes associated with different sports. China Sport Science, 35(4), 52-57. |
| [37] |
Ziemann, U., Iliać, T. V., Pauli, C., Meintzschel, F., & Ruge, D. (2004). Learning modifies subsequent induction of long-term potentiation-like and long-term depression-like plasticity in human motor cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(7), 1666-1672.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5016-03.2004 pmid: 14973238 |
| [1] | WANG Mei, CHENG Si, LI Yiwei, LI Hong, ZHANG Dandan. The role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on placebo effect of regulating social pain: A TMS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(7): 1063-1073. |
| [2] | ZHANG Baoshan, JIN Dou, MA Mengjia, XU Ran. The effect of aging stereotypes on the quality of medical decision-making and the mediating role of attribution bias [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(8): 951-963. |
| [3] | MO Licheng, GUO Tianyou, ZHANG Yueyao, XU Feng, ZHANG Dandan. The role of ventrolateral prefrontal cortex on emotional regulation of social pain in depressed patients: A TMS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(5): 494-504. |
| [4] | CHEN Yuming, LI Sijin, GUO Tianyou, XIE Hui, XU Feng, ZHANG Dandan. The role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on voluntary forgetting of negative social feedback in depressed patients: A TMS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(10): 1094-1104. |
| [5] | CAO Na, MENG Haijiang, WANG Yanqiu, QIU Fanghui, TAN Xiaoying, WU Yin, ZHANG Jian. Functional role of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in procedural motor learning [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(5): 597-608. |
| [6] | WANG Tangsheng, YANG Chunliang, ZHONG Nian. Forward testing effect on new learning in older adults [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(11): 1266-1277. |
| [7] | BAI Xuejun, ZHANG Qihan, ZHANG Peng, ZHOU Song, LIU Ying, SONG Xing, PENG Guohui. Comparison of motor execution and motor imagery brain activation patterns: A fNIRS Study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(5): 495-508. |
| [8] | ZHOU AiBao;LIU PeiRu;ZHANG YanChi;YIN YuLong. Friend-reference Effect in Older Adults [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(9): 1143-1151. |
| [9] | WANG Dahua; YANG Xiaoyang; WANG Yan; Richard B. Miller. The Assessment of Marital Attachment and Its Relationship with General Attachment among Older Adults [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(9): 1133-1142. |
| [10] | XIAO Hongrui;GONG Xianmin;WANG Dahua. Effect of Emotional Valence and Time Interval on the False Memory of Pictures among Older Adults [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(7): 922-930. |
| [11] | LIU Yingjie;WEI Ping;DING Jinhong;GUO Chunyan. Age Differences in the Repetition Effect for Studied or New Objects [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(3): 321-330. |
| [12] | Chen-Zuosong,Ji Liu. The Effects of Physical Exercise on Subjective Well Being of Senior High School Students and Their Psychological Mechanism [J]. , 2006, 38(04): 562-575. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||