

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 182-198.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00182 cstr: 32110.14.2021.00182
江光荣1, 李丹阳1, 任志洪1( ), 闫玉朋1, 伍新春2, 朱旭1, 于丽霞3, 夏勉1, 李凤兰4, 韦辉1,5, 张衍1,6, 赵春晓1, 张琳1
), 闫玉朋1, 伍新春2, 朱旭1, 于丽霞3, 夏勉1, 李凤兰4, 韦辉1,5, 张衍1,6, 赵春晓1, 张琳1
收稿日期:2020-05-21
发布日期:2020-12-29
出版日期:2021-02-25
基金资助:
JIANG Guangrong1, LI Danyang1, REN Zhihong1( ), YAN Yupeng1, WU Xinchun2, ZHU Xu1, YU Lixia3, XIA Mian1, LI Fenglan4, WEI Hui1,5, ZHANG Yan1,6, ZHAO Chunxiao1, ZHANG Lin1
), YAN Yupeng1, WU Xinchun2, ZHU Xu1, YU Lixia3, XIA Mian1, LI Fenglan4, WEI Hui1,5, ZHANG Yan1,6, ZHAO Chunxiao1, ZHANG Lin1
Received:2020-05-21
Online:2020-12-29
Published:2021-02-25
摘要:
本研究以系统的全国抽样调查方式, 了解我国国民心理健康素养现状。结果显示, 我国成年公众的心理健康素养总体处于中偏低水平; 其发展水平在地域、人口学分布上比较均衡; 在结构上, 公众心理健康素养的发展表现出心理健康维护和促进的素养高于心理疾病应对的素养, 自助的素养高于助人的素养两个特点。调查还发现, 个体心理健康素养中, 知识观念部分个体差异较大, 态度和习惯部分个体差异较小; 在心理健康素养的社会性影响因素方面, 社会经济地位是所考察变量中效应最大的因素, 且其对素养的知识观念方面影响较大, 对素养的态度习惯方面影响较小。调查结果提示, 要充分认识心理健康素养提升任务的艰巨性; 在实践策略上, 宜以提升心理疾病应对的素养作为当前的工作重点和突破口。
中图分类号:
江光荣, 李丹阳, 任志洪, 闫玉朋, 伍新春, 朱旭, 于丽霞, 夏勉, 李凤兰, 韦辉, 张衍, 赵春晓, 张琳. (2021). 中国国民心理健康素养的现状与特点. 心理学报, 53(2), 182-198.
JIANG Guangrong, LI Danyang, REN Zhihong, YAN Yupeng, WU Xinchun, ZHU Xu, YU Lixia, XIA Mian, LI Fenglan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin. (2021). The status quo and characteristics of Chinese mental health literacy. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(2), 182-198.
| 变量 | 人数 | 百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| 城乡来源 | ||
| 农村 | 2563 | 28.9% |
| 城镇 | 6287 | 70.9% |
| 性别 | ||
| 男 | 4010 | 45.2% |
| 女 | 4827 | 54.4% |
| 年龄 | ||
| 18~35岁 | 2668 | 30.1% |
| 36~59岁 | 4816 | 54.3% |
| 60岁以上 | 1358 | 15.3% |
| 受教育程度 | ||
| 初中及以下 | 2939 | 33.1% |
| 中专或高中 | 2490 | 28.1% |
| 大学专科或本科 | 2744 | 30.9% |
| 硕士研究生及以上 | 604 | 6.8% |
| 家庭人均可支配年收入 | ||
| 5500元以下 | 2847 | 32.1% |
| 5501~13000元 | 1776 | 20.0% |
| 13001~21000元 | 869 | 9.8% |
| 21001~32000元 | 892 | 10.1% |
| 32001~60000元 | 1179 | 13.3% |
| 60000元以上 | 1256 | 14.2% |
表1 样本的性别、年龄、受教育程度和家庭人均可支配年收入分布情况
| 变量 | 人数 | 百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| 城乡来源 | ||
| 农村 | 2563 | 28.9% |
| 城镇 | 6287 | 70.9% |
| 性别 | ||
| 男 | 4010 | 45.2% |
| 女 | 4827 | 54.4% |
| 年龄 | ||
| 18~35岁 | 2668 | 30.1% |
| 36~59岁 | 4816 | 54.3% |
| 60岁以上 | 1358 | 15.3% |
| 受教育程度 | ||
| 初中及以下 | 2939 | 33.1% |
| 中专或高中 | 2490 | 28.1% |
| 大学专科或本科 | 2744 | 30.9% |
| 硕士研究生及以上 | 604 | 6.8% |
| 家庭人均可支配年收入 | ||
| 5500元以下 | 2847 | 32.1% |
| 5501~13000元 | 1776 | 20.0% |
| 13001~21000元 | 869 | 9.8% |
| 21001~32000元 | 892 | 10.1% |
| 32001~60000元 | 1179 | 13.3% |
| 60000元以上 | 1256 | 14.2% |
| 变量 | 类别 | 有效样本量 | 取值范围 | 分数说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城市GDP水平 | 分类 | 8866 | 1~3 | 低 = 1, 中 = 2, 高 = 3 |
| 城市地域分布 | 分类 | 8866 | 1~3 | 西部 = 1, 中部 = 2, 东部 = 3 |
| 城乡来源 | 分类 | 8850 | 1、2 | 城镇 = 1, 农村 = 2 |
| 性别 | 分类 | 8837 | 1、2 | 男性 = 1, 女性 = 2 |
| 年龄 | 分类 | 8842 | 1~3 | 青年 = 1, 中年 = 2, 老年 = 3 |
| 受教育程度 | 等级 | 8777 | 1~4 | 分数越高, 受教育程度越高 |
| 家庭人均可支配年收入 | 等级 | 8819 | 1~6 | 分数越高, 收入水平越高 |
| 职业阶层 | 等级 | 8605 | 1~10 | 分数越高, 职业阶层越高 |
| 社会经济地位 | 等距 | 8489 | -1.49~2.36 | 分数越高, 社会经济地位越高 |
| 专业身份 | 分类 | 8762 | 0、1 | 专业人员 = 1, 非专业人员 = 0 |
| 接触频率 | 等级 | 8828 | 1~7 | 分数越高, 与精神病人接触频率越高 |
| 熟悉程度 | 等级 | 8837 | 1~7 | 分数越高, 对专业服务熟悉程度越高 |
表2 主要变量说明
| 变量 | 类别 | 有效样本量 | 取值范围 | 分数说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城市GDP水平 | 分类 | 8866 | 1~3 | 低 = 1, 中 = 2, 高 = 3 |
| 城市地域分布 | 分类 | 8866 | 1~3 | 西部 = 1, 中部 = 2, 东部 = 3 |
| 城乡来源 | 分类 | 8850 | 1、2 | 城镇 = 1, 农村 = 2 |
| 性别 | 分类 | 8837 | 1、2 | 男性 = 1, 女性 = 2 |
| 年龄 | 分类 | 8842 | 1~3 | 青年 = 1, 中年 = 2, 老年 = 3 |
| 受教育程度 | 等级 | 8777 | 1~4 | 分数越高, 受教育程度越高 |
| 家庭人均可支配年收入 | 等级 | 8819 | 1~6 | 分数越高, 收入水平越高 |
| 职业阶层 | 等级 | 8605 | 1~10 | 分数越高, 职业阶层越高 |
| 社会经济地位 | 等距 | 8489 | -1.49~2.36 | 分数越高, 社会经济地位越高 |
| 专业身份 | 分类 | 8762 | 0、1 | 专业人员 = 1, 非专业人员 = 0 |
| 接触频率 | 等级 | 8828 | 1~7 | 分数越高, 与精神病人接触频率越高 |
| 熟悉程度 | 等级 | 8837 | 1~7 | 分数越高, 对专业服务熟悉程度越高 |
| 维度 | 计分方式 | 取值范围 | M | SD | 变差系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 心理健康素养总分 | —— | 0~60 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 22.50% |
| 心理健康相关知识和观念 | 0、1 | 0~9 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 35.43% |
| 心理疾病相关知识和观念 | 0、1 | 0~21 | 11.88 | 3.40 | 28.62% |
| 维护和促进自己心理健康的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 5~25 | 19.80 | 2.81 | 14.19% |
| 应对自己心理疾病的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 8~40 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 13.40% |
| 维护和促进他人心理健康的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 6~30 | 21.35 | 3.23 | 15.13% |
| 应对他人心理疾病的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 11~55 | 36.86 | 4.73 | 12.83% |
表3 心理健康素养及其各维度的描述性统计结果(N = 8866)
| 维度 | 计分方式 | 取值范围 | M | SD | 变差系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 心理健康素养总分 | —— | 0~60 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 22.50% |
| 心理健康相关知识和观念 | 0、1 | 0~9 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 35.43% |
| 心理疾病相关知识和观念 | 0、1 | 0~21 | 11.88 | 3.40 | 28.62% |
| 维护和促进自己心理健康的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 5~25 | 19.80 | 2.81 | 14.19% |
| 应对自己心理疾病的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 8~40 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 13.40% |
| 维护和促进他人心理健康的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 6~30 | 21.35 | 3.23 | 15.13% |
| 应对他人心理疾病的态度和习惯 | Likert 5 | 11~55 | 36.86 | 4.73 | 12.83% |
| 维度 | 城市 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京 (n = 1033) | 武汉 (n = 1090) | 成都 (n = 994) | 丽水 (n = 900) | 开封 (n = 898) | 桂林 (n = 1183) | 张掖 (n = 962) | 保定 (n = 931) | 临汾 (n = 875) | |||||
| 总分 | 38.39(8.54) | 36.36(7.87) | 35.48(7.97) | 36.76(8.02) | 36.26(7.60) | 35.47(7.82) | 34.44(7.80) | 35.21(8.12) | 33.62(7.83) | 29.25 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | |
| 维度1 | 6.88(1.99) | 6.09(1.98) | 5.61(2.08) | 5.78(2.08) | 5.94(1.88) | 5.71(2.10) | 5.32(2.10) | 5.98(2.03) | 5.45(2.06) | 50.08 | < 0.001 | 4.3% | |
| 维度2 | 13.54(3.60) | 12.38(3.20) | 11.58(3.21) | 12.02(3.26) | 11.97(3.17) | 11.74(3.31) | 10.98(3.28) | 11.71(3.44) | 10.78(3.29) | 58.54 | < 0.001 | 5.0% | |
| 维度3 | 19.87(2.70) | 19.75(2.72) | 20.00(2.76) | 20.21(2.94) | 20.03(2.80) | 19.77(2.85) | 19.44(2.88) | 19.53(2.76) | 19.56(2.82) | 7.78 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | |
| 维度4 | 29.13(3.98) | 29.52(4.00) | 30.01(3.87) | 30.56(4.07) | 29.82(3.99) | 29.69(3.95) | 29.83(3.94) | 29.25(3.74) | 29.58(4.13) | 10.86 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | |
| 维度5 | 21.78(3.23) | 21.48(3.21) | 21.12(3.12) | 21.78(3.37) | 21.72(3.19) | 21.27(3.36) | 20.99(3.13) | 21.23(3.09) | 20.78(3.17) | 11.80 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | |
| 维度6 | 37.40(4.73) | 36.63(4.59) | 36.85(4.72) | 37.75(4.96) | 36.94(4.76) | 36.89(4.70) | 36.91(4.58) | 36.13(4.35) | 36.18(4.98) | 11.17 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | |
| 维度 | GDP水平 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 低 (n = 2768) | 中 (n = 2981) | 高 (n = 3117) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 34.44 (7.94) | 36.10 (7.83) | 36.75 (8.22) | 64.17 | < 0.001 | 1.4% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 5.58 (2.08) | 5.80 (2.03) | 6.20 (2.08) | 67.36 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.16 (3.36) | 11.89 (3.26) | 12.51 (3.43) | 118.50 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 19.51 (2.82) | 19.98 (2.86) | 19.87 (2.73) | 22.18 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.56 (3.94) | 29.99 (4.01) | 29.55 (3.97) | 12.17 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.01 (3.13) | 21.56 (3.32) | 21.46 (3.20) | 23.86 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.41 (4.65) | 37.16 (4.81) | 36.96 (4.69) | 19.17 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | |||||||
| 维度 | 地域 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 西部(n = 3139) | 中部(n = 2863) | 东部(n = 2864) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.16 (7.87) | 35.49 (7.87) | 36.85 (8.35) | 36.59 | < 0.001 | 0.8% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 5.56 (2.10) | 5.84 (1.99) | 6.24 (2.09) | 81.60 | < 0.001 | 1.8% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.45 (3.28) | 11.76 (3.29) | 12.47 (3.54) | 70.54 | < 0.001 | 1.6% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 19.74 (2.84) | 19.78 (2.78) | 19.86 (2.81) | 1.44 | 0.238 | —— | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.83 (3.92) | 29.63 (4.04) | 29.62 (3.98) | 2.83 | 0.059 | —— | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.14 (3.22) | 21.34 (3.22) | 21.60 (3.24) | 15.54 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.88 (4.67) | 36.59 (4.77) | 37.09 (4.73) | 8.17 | < 0.001 | 0.2% | |||||||
| 维度 | 城乡来源 | t | p | d | |||||||||
| 城镇 (n = 6287) | 农村(n = 2563) | ||||||||||||
| 总分 | 36.53 (7.95) | 34.07 (8.05) | 13.19 | < 0.001 | 0.31 | ||||||||
| 维度1 | 6.06 (2.05) | 5.41 (2.07) | 13.59 | < 0.001 | 0.32 | ||||||||
| 维度2 | 12.30 (3.36) | 10.88 (3.25) | 18.44 | < 0.001 | 0.43 | ||||||||
| 维度3 | 19.98 (2.73) | 19.34 (2.95) | 9.44 | < 0.001 | 0.23 | ||||||||
| 维度4 | 29.68 (3.94) | 29.75 (4.08) | -0.78 | 0.434 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度5 | 21.49 (3.18) | 21.01 (3.32) | 6.40 | < 0.001 | 0.15 | ||||||||
| 维度6 | 36.93 (4.66) | 36.70 (4.88) | 2.03 | 0.043* | 0.05 | ||||||||
| 维度 | 性别 | t | p | d | |||||||||
| 男(n = 4010) | 女(n = 4827) | ||||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.58 (8.20) | 36.01 (7.94) | -2.46 | 0.014* | -0.05 | ||||||||
| 维度1 | 5.83 (2.11) | 5.91 (2.05) | -1.84 | 0.066 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度2 | 11.92 (3.43) | 11.85 (3.37) | 0.90 | 0.369 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度3 | 19.66 (2.77) | 19.92 (2.84) | -4.31 | < 0.001 | -0.09 | ||||||||
| 维度4 | 29.35 (3.93) | 29.99 (4.00) | -7.55 | < 0.001 | -0.16 | ||||||||
| 维度5 | 21.25 (3.24) | 21.44 (3.22) | -2.89 | 0.004** | -0.06 | ||||||||
| 维度6 | 36.79 (4.74) | 36.91 (4.71) | -1.12 | 0.265 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度 | 年龄 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 青年(n = 2668) | 中年(n = 4816) | 老年(n = 1358) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.87 (7.94) | 36.54 (7.98) | 33.16 (8.03) | 95.08 | < 0.001 | 2.1% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 6.00 (2.04) | 6.05 (2.02) | 4.99 (2.15) | 150.92 | < 0.001 | 3.3% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.85 (3.35) | 12.16 (3.40) | 10.96 (3.31) | 67.58 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 20.00 (2.84) | 20.01 (2.73) | 18.67 (2.75) | 133.51 | < 0.001 | 2.9% | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.78 (4.00) | 29.88 (3.98) | 28.94 (3.83) | 30.18 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.45 (3.24) | 21.53 (3.26) | 20.55 (2.97) | 50.63 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.83 (4.83) | 37.05 (4.78) | 36.23 (4.28) | 16.24 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | |||||||
表4 心理健康素养及各维度的方差分析和差异检验结果
| 维度 | 城市 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北京 (n = 1033) | 武汉 (n = 1090) | 成都 (n = 994) | 丽水 (n = 900) | 开封 (n = 898) | 桂林 (n = 1183) | 张掖 (n = 962) | 保定 (n = 931) | 临汾 (n = 875) | |||||
| 总分 | 38.39(8.54) | 36.36(7.87) | 35.48(7.97) | 36.76(8.02) | 36.26(7.60) | 35.47(7.82) | 34.44(7.80) | 35.21(8.12) | 33.62(7.83) | 29.25 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | |
| 维度1 | 6.88(1.99) | 6.09(1.98) | 5.61(2.08) | 5.78(2.08) | 5.94(1.88) | 5.71(2.10) | 5.32(2.10) | 5.98(2.03) | 5.45(2.06) | 50.08 | < 0.001 | 4.3% | |
| 维度2 | 13.54(3.60) | 12.38(3.20) | 11.58(3.21) | 12.02(3.26) | 11.97(3.17) | 11.74(3.31) | 10.98(3.28) | 11.71(3.44) | 10.78(3.29) | 58.54 | < 0.001 | 5.0% | |
| 维度3 | 19.87(2.70) | 19.75(2.72) | 20.00(2.76) | 20.21(2.94) | 20.03(2.80) | 19.77(2.85) | 19.44(2.88) | 19.53(2.76) | 19.56(2.82) | 7.78 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | |
| 维度4 | 29.13(3.98) | 29.52(4.00) | 30.01(3.87) | 30.56(4.07) | 29.82(3.99) | 29.69(3.95) | 29.83(3.94) | 29.25(3.74) | 29.58(4.13) | 10.86 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | |
| 维度5 | 21.78(3.23) | 21.48(3.21) | 21.12(3.12) | 21.78(3.37) | 21.72(3.19) | 21.27(3.36) | 20.99(3.13) | 21.23(3.09) | 20.78(3.17) | 11.80 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | |
| 维度6 | 37.40(4.73) | 36.63(4.59) | 36.85(4.72) | 37.75(4.96) | 36.94(4.76) | 36.89(4.70) | 36.91(4.58) | 36.13(4.35) | 36.18(4.98) | 11.17 | < 0.001 | 1.0% | |
| 维度 | GDP水平 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 低 (n = 2768) | 中 (n = 2981) | 高 (n = 3117) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 34.44 (7.94) | 36.10 (7.83) | 36.75 (8.22) | 64.17 | < 0.001 | 1.4% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 5.58 (2.08) | 5.80 (2.03) | 6.20 (2.08) | 67.36 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.16 (3.36) | 11.89 (3.26) | 12.51 (3.43) | 118.50 | < 0.001 | 2.6% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 19.51 (2.82) | 19.98 (2.86) | 19.87 (2.73) | 22.18 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.56 (3.94) | 29.99 (4.01) | 29.55 (3.97) | 12.17 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.01 (3.13) | 21.56 (3.32) | 21.46 (3.20) | 23.86 | < 0.001 | 0.5% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.41 (4.65) | 37.16 (4.81) | 36.96 (4.69) | 19.17 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | |||||||
| 维度 | 地域 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 西部(n = 3139) | 中部(n = 2863) | 东部(n = 2864) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.16 (7.87) | 35.49 (7.87) | 36.85 (8.35) | 36.59 | < 0.001 | 0.8% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 5.56 (2.10) | 5.84 (1.99) | 6.24 (2.09) | 81.60 | < 0.001 | 1.8% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.45 (3.28) | 11.76 (3.29) | 12.47 (3.54) | 70.54 | < 0.001 | 1.6% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 19.74 (2.84) | 19.78 (2.78) | 19.86 (2.81) | 1.44 | 0.238 | —— | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.83 (3.92) | 29.63 (4.04) | 29.62 (3.98) | 2.83 | 0.059 | —— | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.14 (3.22) | 21.34 (3.22) | 21.60 (3.24) | 15.54 | < 0.001 | 0.3% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.88 (4.67) | 36.59 (4.77) | 37.09 (4.73) | 8.17 | < 0.001 | 0.2% | |||||||
| 维度 | 城乡来源 | t | p | d | |||||||||
| 城镇 (n = 6287) | 农村(n = 2563) | ||||||||||||
| 总分 | 36.53 (7.95) | 34.07 (8.05) | 13.19 | < 0.001 | 0.31 | ||||||||
| 维度1 | 6.06 (2.05) | 5.41 (2.07) | 13.59 | < 0.001 | 0.32 | ||||||||
| 维度2 | 12.30 (3.36) | 10.88 (3.25) | 18.44 | < 0.001 | 0.43 | ||||||||
| 维度3 | 19.98 (2.73) | 19.34 (2.95) | 9.44 | < 0.001 | 0.23 | ||||||||
| 维度4 | 29.68 (3.94) | 29.75 (4.08) | -0.78 | 0.434 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度5 | 21.49 (3.18) | 21.01 (3.32) | 6.40 | < 0.001 | 0.15 | ||||||||
| 维度6 | 36.93 (4.66) | 36.70 (4.88) | 2.03 | 0.043* | 0.05 | ||||||||
| 维度 | 性别 | t | p | d | |||||||||
| 男(n = 4010) | 女(n = 4827) | ||||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.58 (8.20) | 36.01 (7.94) | -2.46 | 0.014* | -0.05 | ||||||||
| 维度1 | 5.83 (2.11) | 5.91 (2.05) | -1.84 | 0.066 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度2 | 11.92 (3.43) | 11.85 (3.37) | 0.90 | 0.369 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度3 | 19.66 (2.77) | 19.92 (2.84) | -4.31 | < 0.001 | -0.09 | ||||||||
| 维度4 | 29.35 (3.93) | 29.99 (4.00) | -7.55 | < 0.001 | -0.16 | ||||||||
| 维度5 | 21.25 (3.24) | 21.44 (3.22) | -2.89 | 0.004** | -0.06 | ||||||||
| 维度6 | 36.79 (4.74) | 36.91 (4.71) | -1.12 | 0.265 | —— | ||||||||
| 维度 | 年龄 | F | p | η2 | |||||||||
| 青年(n = 2668) | 中年(n = 4816) | 老年(n = 1358) | |||||||||||
| 总分 | 35.87 (7.94) | 36.54 (7.98) | 33.16 (8.03) | 95.08 | < 0.001 | 2.1% | |||||||
| 维度1 | 6.00 (2.04) | 6.05 (2.02) | 4.99 (2.15) | 150.92 | < 0.001 | 3.3% | |||||||
| 维度2 | 11.85 (3.35) | 12.16 (3.40) | 10.96 (3.31) | 67.58 | < 0.001 | 1.5% | |||||||
| 维度3 | 20.00 (2.84) | 20.01 (2.73) | 18.67 (2.75) | 133.51 | < 0.001 | 2.9% | |||||||
| 维度4 | 29.78 (4.00) | 29.88 (3.98) | 28.94 (3.83) | 30.18 | < 0.001 | 0.7% | |||||||
| 维度5 | 21.45 (3.24) | 21.53 (3.26) | 20.55 (2.97) | 50.63 | < 0.001 | 1.1% | |||||||
| 维度6 | 36.83 (4.83) | 37.05 (4.78) | 36.23 (4.28) | 16.24 | < 0.001 | 0.4% | |||||||
| 变量 | M | SD | SES | 熟悉程度 | 接触频率 | 总分 | 维度1 | 维度2 | 维度3 | 维度4 | 维度5 | 维度6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SES | 0.004 | 1.00 | 1 | |||||||||
| 熟悉程度 | 2.22 | 1.56 | 0.145*** | 1 | ||||||||
| 接触频率 | 1.59 | 1.16 | 0.065*** | 0.380*** | 1 | |||||||
| 总分 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 0.308*** | 0.207*** | 0.059*** | 1 | ||||||
| 维度1 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 0.331*** | 0.113*** | 0.036** | 0.644*** | 1 | |||||
| 维度2 | 11.88 | 3.39 | 0.377*** | 0.163*** | 0.080*** | 0.779*** | 0.584*** | 1 | ||||
| 维度3 | 19.79 | 2.80 | 0.152*** | 0.160*** | -0.003 | 0.493*** | 0.145*** | 0.214*** | 1 | |||
| 维度4 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 0.033** | 0.144*** | 0.002 | 0.536*** | 0.143*** | 0.186*** | 0.430*** | 1 | ||
| 维度5 | 21.35 | 3.22 | 0.140*** | 0.137*** | 0.016 | 0.539*** | 0.193*** | 0.241*** | 0.407*** | 0.404*** | 1 | |
| 维度6 | 36.86 | 4.72 | 0.086*** | 0.142 *** | 0.057*** | 0.573*** | 0.180*** | 0.236*** | 0.350*** | 0.472*** | 0.486*** | 1 |
表5 心理健康素养总分及各维度与社会经济地位、接触频率和熟悉程度的相关系数
| 变量 | M | SD | SES | 熟悉程度 | 接触频率 | 总分 | 维度1 | 维度2 | 维度3 | 维度4 | 维度5 | 维度6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SES | 0.004 | 1.00 | 1 | |||||||||
| 熟悉程度 | 2.22 | 1.56 | 0.145*** | 1 | ||||||||
| 接触频率 | 1.59 | 1.16 | 0.065*** | 0.380*** | 1 | |||||||
| 总分 | 35.81 | 8.06 | 0.308*** | 0.207*** | 0.059*** | 1 | ||||||
| 维度1 | 5.87 | 2.08 | 0.331*** | 0.113*** | 0.036** | 0.644*** | 1 | |||||
| 维度2 | 11.88 | 3.39 | 0.377*** | 0.163*** | 0.080*** | 0.779*** | 0.584*** | 1 | ||||
| 维度3 | 19.79 | 2.80 | 0.152*** | 0.160*** | -0.003 | 0.493*** | 0.145*** | 0.214*** | 1 | |||
| 维度4 | 29.70 | 3.98 | 0.033** | 0.144*** | 0.002 | 0.536*** | 0.143*** | 0.186*** | 0.430*** | 1 | ||
| 维度5 | 21.35 | 3.22 | 0.140*** | 0.137*** | 0.016 | 0.539*** | 0.193*** | 0.241*** | 0.407*** | 0.404*** | 1 | |
| 维度6 | 36.86 | 4.72 | 0.086*** | 0.142 *** | 0.057*** | 0.573*** | 0.180*** | 0.236*** | 0.350*** | 0.472*** | 0.486*** | 1 |
| 维度 | 接触频率 | t | p | d | 熟悉程度 | t | p | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低接触 (n = 7348) | 高接触 (n = 184) | 低熟悉 (n = 5877) | 高熟悉 (n = 406) | |||||||
| 总分 | 35.55 (7.89) | 35.12 (9.05) | 0.634 | 0.527 | —— | 34.73 (7.92) | 37.68 (7.96) | -7.263 | < 0.001 | -0.37 |
| 维度1 | 5.84 (2.06) | 5.66 (2.28) | 1.044 | 0.298 | —— | 5.72 (2.10) | 5.79 (2.08) | -0.662 | 0.508 | —— |
| 维度2 | 11.74 (3.35) | 11.64 (3.71) | 0.389 | 0.697 | —— | 11.51 (3.39) | 12.07 (3.38) | -3.217 | 0.001** | -0.17 |
| 维度3 | 19.80 (2.77) | 19.83 (3.20) | -0.126 | 0.900 | —— | 19.53 (2.80) | 20.99 (2.89) | -10.114 | < 0.001 | -0.51 |
| 维度4 | 29.67 (3.94) | 29.46 (4.54) | 0.630 | 0.529 | —— | 29.36 (3.92) | 31.17 (4.38) | -8.073 | < 0.001 | -0.44 |
| 维度5 | 21.33 (3.19) | 21.31 (3.65) | 0.063 | 0.950 | —— | 21.09 (3.14) | 22.17 (3.70) | -5.689 | < 0.001 | -0.31 |
| 维度6 | 36.71 (4.68) | 36.97 (5.30) | -0.660 | 0.510 | —— | 36.41 (4.63) | 38.05 (5.30) | -6.066 | < 0.001 | -0.33 |
表7 心理健康素养及各维度在接触频率和熟悉程度上的差异
| 维度 | 接触频率 | t | p | d | 熟悉程度 | t | p | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低接触 (n = 7348) | 高接触 (n = 184) | 低熟悉 (n = 5877) | 高熟悉 (n = 406) | |||||||
| 总分 | 35.55 (7.89) | 35.12 (9.05) | 0.634 | 0.527 | —— | 34.73 (7.92) | 37.68 (7.96) | -7.263 | < 0.001 | -0.37 |
| 维度1 | 5.84 (2.06) | 5.66 (2.28) | 1.044 | 0.298 | —— | 5.72 (2.10) | 5.79 (2.08) | -0.662 | 0.508 | —— |
| 维度2 | 11.74 (3.35) | 11.64 (3.71) | 0.389 | 0.697 | —— | 11.51 (3.39) | 12.07 (3.38) | -3.217 | 0.001** | -0.17 |
| 维度3 | 19.80 (2.77) | 19.83 (3.20) | -0.126 | 0.900 | —— | 19.53 (2.80) | 20.99 (2.89) | -10.114 | < 0.001 | -0.51 |
| 维度4 | 29.67 (3.94) | 29.46 (4.54) | 0.630 | 0.529 | —— | 29.36 (3.92) | 31.17 (4.38) | -8.073 | < 0.001 | -0.44 |
| 维度5 | 21.33 (3.19) | 21.31 (3.65) | 0.063 | 0.950 | —— | 21.09 (3.14) | 22.17 (3.70) | -5.689 | < 0.001 | -0.31 |
| 维度6 | 36.71 (4.68) | 36.97 (5.30) | -0.660 | 0.510 | —— | 36.41 (4.63) | 38.05 (5.30) | -6.066 | < 0.001 | -0.33 |
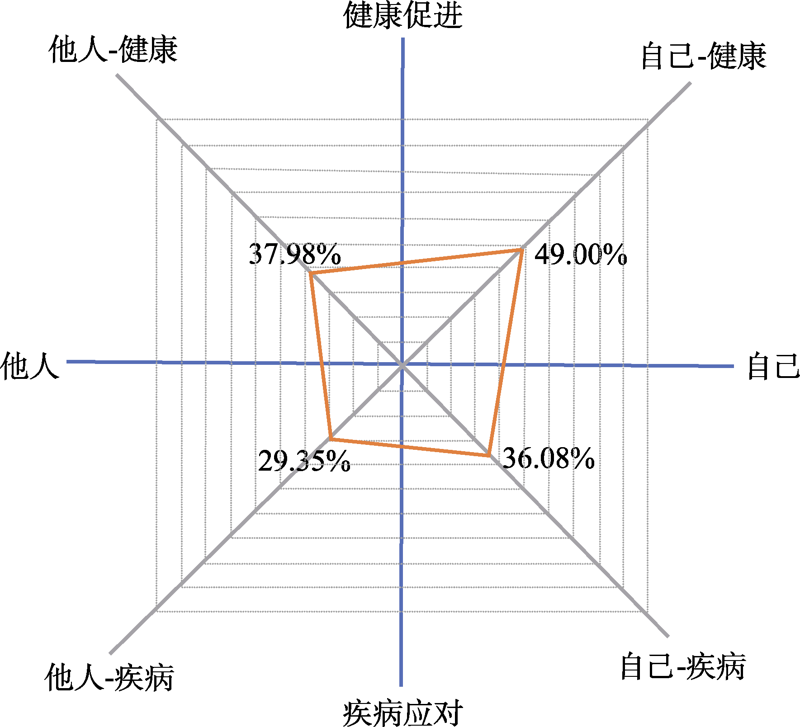
图1 心理健康素养二级维度得分情况1 1数据变换计算的方式为:他人-健康 = 心理健康相关知识和观念正确率×维护和促进他人心理健康的态度和习惯正确率; 自己-健康 = 心理健康相关知识和观念正确率×维护和促进自己心理健康的态度和习惯正确率; 自己-疾病 = 心理疾病相关知识和观念正确率×应对自己心理疾病的态度和习惯; 他人-疾病 = 心理疾病相关知识和观念×应对他人心理疾病的态度和习惯。
| [1] |
Aghukwa, C. N. (2010). Medical students' beliefs and attitudes toward mental illness: Effects of a psychiatric education. Academic Psychiatry, 34(1), 67-70.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ap.34.1.67 URL pmid: 20071734 |
| [2] | Andrews, G., Hall, W. D., Teesson, M., & Henderson, S. (1999). The mental health of Australians. In National Survey of Mental Health & Well-being Report No 2. Canberra: Mental Health Branch, Commonwealth Department of Aged Care. |
| [3] |
Angermeyer, M. C., & Dietrich, S. (2006). Public beliefs about and attitudes towards people with mental illness: A review of population studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 113(3), 163-179.
URL pmid: 16466402 |
| [4] |
Angermeyer, M. C., Holzinger, A., & Matschinger, H. (2009). Mental health literacy and attitude towards people with mental illness: A trend analysis based on population surveys in the eastern part of Germany. European Psychiatry, 24(4), 225-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.06.010 URL pmid: 19361961 |
| [5] |
Angermeyer, M. C., & Matschinger, H. (2004). The stereotype of schizophrenia and its impact on discrimination against people with schizophrenia: Results from a representative survey in Germany. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 30(4), 1049-1061.
URL pmid: 15954207 |
| [6] |
Bjørnsen, H. N., Eilertsen, M.-E. B., Ringdal, R., Espnes, G. A., & Moksnes, U. K. (2017). Positive mental health literacy: Development and validation of a measure among Norwegian adolescents. BMC Public Health, 17(1), 717-726.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4733-6 URL pmid: 28923031 |
| [7] | Cao, S., Cao, R. X., Sun, X. Y., Guo, H. J., Li, X. N., & Xu, Q. (2016). Item Response Theory in the application of ‘Residents Health Literacy Criterion-Referenced Test’. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 33(1), 31-34+38. |
| [ 曹尚, 曹荣祥, 孙昕霙, 郭海建, 李小宁, 徐勤. (2016). 项目反应理论在居民健康素养标准参照测验中的应用研究. 中国卫生统计, 33(1), 31-34+38.] | |
| [8] | Chen, X. S. (1986). The progress of Psychiatry. In Qian, X. Z. (Ed.). Chinese yearbook of medical science (1985) (p. 167). Tianjin, China: Tianjin Science and Technology Press. |
| [ 陈学诗. (1986). 精神医学的进展. 见钱信忠(编). 中国医学科学年鉴(1985) (p. 167). 天津: 天津科学技术出版社.] | |
| [9] | Chen, Z. Y., Wang, Y. X., Guo, F., Zhang, J., & Jiang, L. (2019). Survey on mental health literacy in China. In Fu X. L. & Zhang K. (Eds.), Report on national mental health development in China (2017-2018) (pp. 220-263). . Beijing,China: Social Sciences Academic Press. |
| [ 陈祉妍, 王雅芯, 郭菲, 章婕, 江兰. (2019). 国民心理健康素养调查. 见 傅小兰, 张侃(编). 心理健康蓝皮书:中国国民心理健康发展报告(2017~2018) (pp. 220-263). 北京: 社会科学文献出版社.] | |
| [10] | Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. |
| [11] | Cohen, J. (1992). Statistical power analysis. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 1(3), 98-101. |
| [12] | Coles, M. E., Ravid, A., Gibb, B., George-Denn, D., Bronstein, L. R., & McLeod, S. (2016). Adolescent mental health literacy: Young people’s knowledge of depression and social anxiety disorder. Journal of Adolescent Health, 58(1), 57-62. |
| [13] | Corrigan, P. W. (2002). Empowerment and serious mental illness: Treatment partnerships and community opportunities. Psychiatric Quarterly, 73(3), 217-228. |
| [14] |
Demyttenaere, K., Bruffaerts, R., Posada-Villa, J., Gasquet, I., Kovess, V., Lepine, J. P., … Brugha, T. S. (2004). Prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Journal of the American Medical Association, 291(21), 2581-2590.
URL pmid: 15173149 |
| [15] | Du, W. J., Zhou, J., & Li, H. B. (2013). The item parameters’ estimation accuracy of two-parameter logistic model. Acta Psychological Sinica, 45(10), 1179-1186. |
| [ 杜文久, 周娟, 李洪波. (2013). 二参数逻辑斯蒂模型项目参数的估计精度. 心理学报, 45(10), 1179-1186.] | |
| [16] | Eckert, K. A., Kutek, S. M., Dunn, K. I., Air, T. M., & Goldney, R. D. (2010). Changes in depression-related mental health literacy in young men from rural and urban South Australia. Australian Journal of Rural Health, 18(4), 153-158. |
| [17] | Fan, M. Y. (2011). Research on quality control of the data in web survey (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China. |
| [ 樊茗玥. (2011). 网络调查数据质量控制研究(博士学位论文). 江苏大学, 镇江.] | |
| [18] | Farrer, L., Christensen, H., Leach, L., Griffiths, K. M., & Jorm, A. F. (2008). Age differences in mental health literacy. BMC Public Health, 8(1), 1-8. |
| [19] | Fu, W. Z. (2005). A Survey of the aware of knowledge about mental health rates among middle school students: 4007 Questionnaires Analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 12-13. |
| [ 傅伟忠. (2005). 4007名大中学生心理卫生知识知晓率的现状调查. 上海精神医学, 17(z1), 12-13.] | |
| [20] |
Furnham, A., Annis, J., & Cleridou, K. (2014). Gender differences in the mental health literacy of young people. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 26(2), 283-292.
doi: 10.1515/ijamh-2013-0301 URL pmid: 23843570 |
| [21] |
Furnham, A., & Lousley, C. (2013). Mental health literacy and the anxiety disorders. Health, 5(3A), 521-531.
doi: 10.4236/health.2013.53A071 URL |
| [22] | Gao, W. J., & Li, Q. (2008). Primary research on the impact of mental health illness stigma social representations. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 14(4), 358-364. |
| [ 高文珺, 李强. (2008). 心理疾病污名社会表征公众影响初探. 应用心理学, 14(4), 358-364.] | |
| [23] | Guimón, J., Fischer, W., & Sartorius, N. (1999). The image of madness: The public facing mental illness and psychiatric treatment (pp. 56-71). Basel: Karger Press. |
| [24] | Gulliver, A., Griffiths, K. M., Christensen, H., & Brewer, J. (2012). A systematic review of help-seeking interventions for depression, anxiety and general psychological distress. BMC Psychiatry, 12(1), 81-92. |
| [25] | Guo, F., Huang, Z., & Chen, Z. Y. (2019). Survey on mental health in China. In Fu X. L. & Zhang K. (Eds.), Report on national mental health development in China (2017-2018) (pp. 1-55). Beijing, China: Social Sciences Academic Press. |
| [ 郭菲, 黄峥, 陈祉妍. (2019). 国民心理健康状况调查. 见 傅小兰, 张侃(编). 心理健康蓝皮书:中国国民心理健康发展报告(2017~2018) (pp. 1-55). 北京, 社会科学文献出版社.] | |
| [26] |
Have, M. T., de Graaf, R., Ormel, J., Vilagut, G., Kovess, V., Alonso, J., & the ESEMeD/MHEDEA 2000 Investigators. (2010). Are attitudes towards mental health help-seeking associated with service use? Results from the European study of epidemiology of mental disorders. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 45(2), 153-163.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-009-0050-4 URL pmid: 19381427 |
| [27] |
Hengartner, M. P., Loch, A. A., Lawson, F. L., Guarniero, F. B., Wang, Y.-P., Rössler, W., & Gattaz, W. F. (2013). Public stigmatization of different mental disorders: A comprehensive attitude survey. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 22(3), 269-274.
doi: 10.1017/S2045796012000376 URL pmid: 22831815 |
| [28] | Hollingshead, A. B., & Redlich, F. C. (1958). Social class and mental illness: a community study. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 29(1), 192-201. |
| [29] |
Holman, D. (2014). Exploring the relationship between social class, mental illness stigma and mental health literacy using British national survey data. Health, 19(4), 413-429.
doi: 10.1177/1363459314554316 URL pmid: 25323051 |
| [30] | Holzinger, A., Floris, F., Schomerus, G., Carta, M. G., & Angermeyer, M. C. (2012). Gender differences in public beliefs and attitudes about mental disorder in western countries: A systematic review of population studies. Epidemiology Psychiatric Science, 21(1), 73-85. |
| [31] |
Huang, Y. Q., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Z. R., Yu, X., Yan, J., … Wu, Y. (2019). Prevalence of mental disorders in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(3), 211-224.
doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30511-X URL pmid: 30792114 |
| [32] | Jiang, G. R., & Xia, M. (2006). Psychological help-seeking: Current research and the phases-decision-making model. Advances in Psychological Science, 14(6), 888-894. |
| [ 江光荣, 夏勉. (2006). 心理求助行为: 研究现状及阶段-决策模型. 心理科学进展, 14(6), 888-894.] | |
| [33] | Jiang, G. R., Zhao, C. X., Wei, H., Yu, L. X., Li, D. Y., Lin, X. B., & Ren, Z. H. (2020). Mental health literacy: Connotation, measurement and new framework. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 232-238. |
| [ 江光荣, 赵春晓, 韦辉, 于丽霞, 李丹阳, 林秀彬, 任志洪. (2020). 心理健康素养: 内涵、测量与新概念框架. 心理科学, 43(1), 232-238.] | |
| [34] |
Jorm, A. F. (2012). Mental health literacy: Empowering the community to take action for better mental health. American Psychologist, 67(3), 231-243.
doi: 10.1037/a0025957 URL |
| [35] |
Jorm, A. F., Korten, A. E., Jacomb, P. A., Christensen, H., Rodgers, B., & Pollitt, P. (1997). Mental health literacy: A survey of the public’s ability to recognise mental disorders and their beliefs about the effectiveness of treatment. The Medical journal of Australia, 166(4), 182-186.
doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1997.tb140071.x URL pmid: 9066546 |
| [36] |
Koyama, T., Tachimori, H., Sawamura, K., Koyama, A., Naganuma, Y., Makino, H., & Takeshima, T. (2009). Mental health literacy of autism spectrum disorders in the Japanese general population. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 44(8), 651-657.
URL pmid: 19096742 |
| [37] |
Kutcher, S., Wei, Y. F., & Coniglio, C. (2016). Mental health literacy: Past, present, and future. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 61(3), 154-158.
doi: 10.1177/0706743715616609 URL |
| [38] |
Lee, S., Tsang, A., Huang, Y. Q., He, Y. L., Liu, Z. R., Zhang, M. Y., … Kessler, R. C. (2009). The epidemiology of depression in metropolitan China. Psychological Medicine, 39(5), 735-747.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291708004091 URL pmid: 18713484 |
| [39] |
Leiderman, E. A., Vazquez, G., Berizzo, C., Bonifacio, A., Bruscoli, N., Capria, J. I., … Milev, R. (2011). Public knowledge, beliefs and attitudes towards patients with schizophrenia: Buenos Aires. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 46(4), 281-290.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-010-0196-0 URL |
| [40] |
Levav, I., Shemesh, A., Grinshpoon, A., Aisenberg, E., Shershevsky, Y., & Kohn, R. (2004). Mental health-related knowledge, attitudes and practices in two kibbutzim. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 39(9), 758-764.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-004-0811-z URL |
| [41] | Li, F., Xiao, S. Y., Huang, Z. P., Shi, J. G., Cheng, Z. H., Luo, W. F., … Zhou, L. (2009). Mental health literacy in three cities of China: A survey study. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 23(12), 883-887. |
| [ 李飞, 肖水源, 黄志平, 师建国, 程灶火, 罗文凤, … 周亮. (2009). 中国三城市精神健康素养调查. 中国心理卫生杂志, 23(12), 883-887.] | |
| [42] | Li, F. L. (2015). The conception of mental illness in Chinese public: content, structure and measure (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China. |
| [ 李凤兰. (2015). 中国公众的心理疾病观: 内容、结构及测量 (博士学位论文). 华中师范大学, 武汉.] | |
| [43] | Li, L. H., Li, S. Y., Huang, L. H., & Mei, F. (2006). A survey of knowledge of mental health among the relatives of psychiatric patients. Journal of Nursing (China), 13(6), 19-21. |
| [ 李立华, 李穗云, 黄丽红, 梅芳. (2006). 精神病患者家属精神卫生知识水平及结构调查. 护理学报, 13(6), 19-21.] | |
| [44] | Liu, J. P., Zhang, Y. X., Yang, C., Huang, K. M., & Zhang, X. Q. (2017). The urban mental hygiene work and its suggestions: Base on the meta-analysis of urban citizen’s aware of knowledge about mental health rates from 2005 to 2015. China Journal of Health Psychology,(5), 666-670. |
| [ 刘建鹏, 张宇翔, 羊晨, 黄康妹, 张雪琴. (2017). 城镇精神卫生知识普及情况及推进建议——2005~2015年我国城镇居民精神卫生知识知晓率的Meta分析. 中国健康心理学杂志, (5), 666-670.] | |
| [45] | Liu, X., Yang, G., & Wang, F. Y. (2013). The structure of stigma of mental illness: IAT-based measurement. Journal of Gannan Normal University, (2), 92-94. |
| [ 刘欣, 杨钢, 汪凤炎. (2013). 心理疾病污名的结构: 基于IAT的测量. 赣南师范学院学报, (2), 92-94.] | |
| [46] |
Loureiro, L. M. J., Jorm, A. F., Oliveira, R. A., Mendes, A. M. O. C., dos Santos, J. C. P., Rodrigues, M. A., & Sousa, C. S. F. (2015). Mental health literacy about schizophrenia: A survey of Portuguese youth. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 9(3), 234-241.
doi: 10.1111/eip.12123 URL pmid: 24438429 |
| [47] | Lu, X. Y. (2002). An analysis of strata and classes of the contemporary China. Study and Practice, (3), 55-63. |
| [ 陆学艺. (2002). 当代中国社会十大阶层分析. 学习与实践, (3), 55-63.] | |
| [48] |
Madianos, M. G., Economou, M., Hatjiandreou, M., Papageorgiou, A., & Rogakou, E. (1999). Changes in public attitudes towards mental illness in the Athens area (1979/1980-1994). Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 99(1), 73-78.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1999.tb05387.x URL pmid: 10066010 |
| [49] |
Maunder, R. D., & White, F. A. (2019). Intergroup contact and mental health stigma: A comparative effectiveness meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 72, 101749.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101749 URL pmid: 31254936 |
| [50] | Mcleroy, K. R., Bibeau, D., Steckler, A., & Glanz, K. (1988). An ecological perspective on health promotion programs. Health Education and Behavior, 15(4), 351-377. |
| [51] | Meng, G. R., Yao, X. W., Zhu, Z. Q., & Zhang, M. Y. (2002). A survey of mental health awareness among Shanghai citizen: 2697 questionnaires analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 14(z1), 56-57. |
| [ 孟国荣, 姚新伟, 朱紫青, 张明园. (2002). 上海市市民精神卫生知识知晓率调查: 2697份问卷分析. 上海精神医学, 14(z1), 56-57.] | |
| [52] | Ming, Z. J., & Chen, Z.Y . (2020). Mental health literacy: Concept, measurement, intervention and factors. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(1), 1-12. |
| [ 明志君, 陈祉妍. (2020). 心理健康素养: 概念、评估、干预与作用. 心理科学进展, 28(1), 1-12.] | |
| [53] | Mojtabai, R. (2010). Mental illness stigma and willingness to seek mental health care in the European Union. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 45(7), 1741-1752. |
| [54] | Morgan, A. J., Reavley, N. J., Ross, A., Too, L. S., & Jorm, A. F. (2018). Interventions to reduce stigma towards people with severe mental illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 103(5), 120-133. |
| [55] | Morgan, A. J., Ross, A., & Reavley, N. J. (2018). Systematic review and meta-analysis of mental health first aid training: Effects on knowledge, stigma, and helping behaviour. Plos One, 13(5), e0197102. |
| [56] |
Olfson, M., Blanco, C., & Marcus, S. C. (2016). Treatment of adult depression in the United States. JAMA Internal Medicine, 176(10), 1482-1491.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.5057 URL pmid: 27571438 |
| [57] |
Phillips, M. R. (2004). Suicide in China: Current status and suggestions for future work. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 25(4), 277-279.
URL pmid: 15231190 |
|
[ 费立鹏. (2004). 中国的自杀现状及未来的工作方向. 中华流行病学杂志, 25(4), 277-279.]
pmid: 15231190 |
|
| [58] |
Piper, S. E., Bailey, P. E., Lam, L. T., & Kneebone, I. I. (2018). Predictors of mental health literacy in older people. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 79, 52-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.07.010 URL pmid: 30107312 |
| [59] | Rabkin, J. (1974). Public attitudes toward mental illness: A review of the literature. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1(10), 9-33. |
| [60] | Ren, C. R. (2010). Measurement methodology on social economic status index of students. Journal of Educational Studies, 6(5), 77-82. |
| [ 任春荣. (2010). 学生家庭社会经济地位(SES)的测量技术. 教育学报, 6(5), 77-82.] | |
| [61] | Ren, Z. H., Zhao, C. X., Tian, F., Yan, Y. P., Li, D. Y., Zhao, Z. Y., … Jiang, G. R. (2020). Meta-analysis of the effect of mental health literacy intervention in Chinese people. Acta Psychological Sincia, 52(4), 497-512. |
| [ 任志洪, 赵春晓, 田凡, 闫玉朋, 李丹阳, 赵子仪, … 江光荣. (2020). 中国人心理健康素养干预效果的元分析. 心理学报, 52(4), 497-512.] | |
| [62] | Schnyder, N., Panczak, R., Groth, N., & Schultze-Lutter, F. (2017). Association between mental health-related stigma and active help-seeking: systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Psychiatry: the Journal of Mental Science, 210(4), 261-268. |
| [63] |
Stanton, R., Rosenbaum, S., & Rebar, A. (2019). Associations between ability to recognise a mental health disorder and lived experience of mental illness in an Australian sample. Psychiatry Research, 272, 206-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.098 URL |
| [64] |
Shi, Y., Shao, Y. P., Li, H. H., Wang, S. Q., Ying, J., Zhang, M. L., … Sun, J. (2019). Correlates of affiliate stigma among family caregivers of people with mental illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, 26(1-2), 49-61.
doi: 10.1111/jpm.12505 URL pmid: 30472763 |
| [65] | Sun, X., Li, X. Y., & Phillips, M. R. (2009). A cross-sectional survey of the awareness of common mental disorders among urban and rural residents in northern China. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 23(10), 729-733+741. |
| [ 孙霞, 李献云, 费立鹏. (2009). 中国北方两地城乡居民常见精神卫生知识知晓情况现况调查. 中国心理卫生杂志, 23(10), 729-733+741..] | |
| [66] | Tang, D. D., & Wen, Z. L. (2020). Statistical approaches for testing common method bias: Problems and suggestions. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 215-223. |
| [ 汤丹丹, 温忠麟. (2020). 共同方法偏差检验:问题与建议. 心理科学, 43(1), 215-223.] | |
| [67] |
Tay, J. L., Tay, Y. F., & Klainin-Yobas, P. (2018). Mental health literacy levels. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 32(5), 757-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2018.04.007 URL pmid: 30201205 |
| [68] |
Vidourek, R. A., & Burbage, M. (2019). Positive mental health and mental health stigma: A qualitative study assessing student attitudes. Mental Health and Prevention, 13, 1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.mhp.2018.11.006 URL |
| [69] | Wampold, B. E., & Imel, Z. E. (2015). The great psychotherapy debate: The evidence for what makes psychotherapy work (second edition). New York: Routledge. |
| [70] | Wang, J. C., Wang, X. Q., & Jiang, B. F. (2011). Structural equation models: Methods and applications. Beijing, China: Higher Education Press. |
| [ 王济川, 王小倩, 姜宝法. (2011). 结构方程模型:方法与应用. 北京: 高等教育出版社.] | |
| [71] | Wu, J., Zhu, X., Li, Y. Q., Liu, G. D., Zhang, L. K., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Development and validation of the Mental Health Literacy Questionnaire for Chinese Adults. [ChinaXiv:202012.00020] |
| [ 吴珏, 朱旭, 李艳青, 刘光大, 张灵楷, 张衍. (2020). 心理健康素养问卷编制. [ChinaXiv:202012.00020] | |
| [72] |
Xu, Z. Y., Huang, F. F., Kösters, M., Staiger, T., Becker, T., Thornicroft, G., & Rüsch, N. (2018). Effectiveness of interventions to promote help-seeking for mental health problems: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Medicine, 48(16), 2658-2667.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291718001265 URL pmid: 29852885 |
| [73] | Yan, B. P., Li, J. F., Li, K. Q., Zhang, Y., Fu, X. G., Wei, Z. G., … Sun, X. L. (2014). Investigation of the awareness rate for mental health knowledge and attitude about mental health illness in urban and rural general population. Modern Preventive Medicine, 41(9), 1636-1639. |
| [ 严保平, 李建峰, 栗克清, 张勇, 付希光, 魏志刚, … 孙秀丽. (2014). 城市与农村普通人群精神卫生知识知晓率及对精神疾病的态度. 现代预防医学, 41(9), 1636-1639.] | |
| [74] | Yu, X. M., & Jiang, G. R. (2004). The psychological help-seeking behavior and its influencing factors. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 18(6), 426-428. |
| [ 余晓敏, 江光荣. (2004). 心理求助行为及其影响因素. 中国心理卫生杂志, 18(6), 426-428.] | |
| [75] | Zhang, G. F., Zhao, J., Rao, S. C., & Shen, W. L. (2005). Investigation of the awareness rate for mental health knowledge among medical personnel in general hospital: 2345 questionnaires analysis. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 17-18. |
| [ 张国芳, 赵军, 饶顺曾, 沈文龙. (2005). 2345名综合医院医务人员精神卫生知识知晓率的调查. 上海精神医学, 17(z1), 17-18.] | |
| [76] | Zhang, H. C., & Xu, J. P. (Eds). (2003). Modern psychology and education statistics. Beijing, China: Beijing Normal University Press. |
| [ 张厚粲, 徐建平. (编).(2003). 现代心理与教育统计学. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社.] | |
| [77] | Zhou, C. Y., & Guo, Y. Y. (2013). Impact of family social status on mental health: Mediating role of belief in a just world. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 21(4), 636-640. |
| [ 周春燕, 郭永玉. (2013). 家庭社会阶层对大学生心理健康的影响: 公正世界信念的中介作用. 中国临床心理学杂志, 21(4), 636-640.] | |
| [78] | Zhou, H., & Long, L. R. (2004). Statistical remedies for common method biases. Advances in Psychological Science, 12(6), 942-950. |
| [ 周浩, 龙立荣. (2004). 共同方法偏差的统计检验与控制方法. 心理科学进展, 12(6), 942-950.] | |
| [79] | Zhu, Z. Q., & Zhang, M. Y. (2005). Questionnaire design of the baseline survey on the awareness rate for mental health knowledge among the key population. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 17(z1), 5-11. |
| [ 朱紫青, 张明园. (2005). 重点人群心理卫生知识知晓率基线调查的问卷设计. 上海精神医学, 17(z1), 5-11.] |
| [1] | 任志洪, 赵春晓, 田凡, 闫玉朋, 李丹阳, 赵子仪, 谭梦鸰, 江光荣. 中国人心理健康素养干预效果的元分析[J]. 心理学报, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||