

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 677-696.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.00677 cstr: 32111.14.2021.00677
黎穗卿, 陈新玲, 翟瑜竹, 张怡洁, 章植鑫, 封春亮( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-10
出版日期:2021-04-15
发布日期:2021-02-22
基金资助:
LI Suiqing, CHEN Xinling, ZHAI Yuzhu, ZHANG Yijie, ZHANG Zhixing, FENG Chunliang( )
)
Received:2020-08-10
Online:2021-04-15
Published:2021-02-22
摘要:
人类在社会互动中通过他人的行为对他人特质、意图及特定情境下的社会规范进行学习, 是优化决策、维护积极社会互动的重要条件。近年来, 越来越多的研究通过结合计算模型与神经影像技术对社会学习的认知计算机制及其神经基础进行了深入考察。已有研究发现, 人类的社会学习过程能够较好地被强化学习模型与贝叶斯模型刻画, 主要涉及的认知计算过程包括主观期望、预期误差和不确定性的表征以及信息整合的过程。大脑对这些计算过程的执行主要涉及奖惩加工相关脑区(如腹侧纹状体与腹内侧前额叶)、社会认知加工相关脑区(如背内侧前额叶和颞顶联合区)及认知控制相关脑区(如背外侧前额叶)。需要指出的是, 计算过程与大脑区域之间并不是一一映射的关系, 提示未来研究可借助多变量分析与脑网络分析等技术从系统神经科学的角度来考察大尺度脑网络如何执行不同计算过程。此外, 将来研究应注重生态效度, 利用超扫描技术考察真实互动下的社会学习过程, 并更多地关注内隐社会学习的计算与神经机制。
中图分类号:
黎穗卿, 陈新玲, 翟瑜竹, 张怡洁, 章植鑫, 封春亮. (2021). 人际互动中社会学习的计算神经机制. 心理科学进展 , 29(4), 677-696.
LI Suiqing, CHEN Xinling, ZHAI Yuzhu, ZHANG Yijie, ZHANG Zhixing, FENG Chunliang. (2021). The computational and neural substrates underlying social learning. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(4), 677-696.
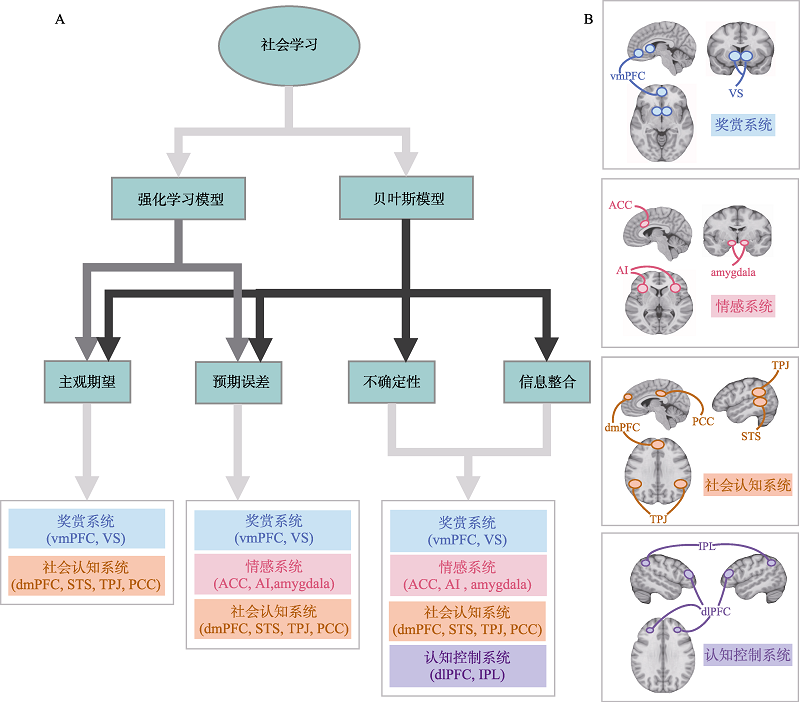
图1 社会学习的计算神经机制 A:社会学习的计算模型及神经基础。强化学习模型下社会学习的认知过程主要包括主观期望和预期误差的计算, 贝叶斯模型下社会学习的认知过程包括主观期望、预期误差的计算、不确定性的表征以及信息整合。主观期望的计算涉及奖赏系统与社会认知系统; 预期误差的计算涉及奖赏系统、情感系统与社会认知系统; 不确定性的表征及信息整合涉及奖赏系统、情感系统、社会认知系统与认知控制系统。B:社会学习涉及的大脑系统:奖赏系统主要包括VS、vmPFC; 情感系统主要包括ACC、AI、amygdala ; 社会认知系统主要包括dmPFC、TPJ、STS、PCC; 认知控制系统主要包括dlPFC、IPL。 VS:ventral striatum, 腹侧纹状体; vmPFC:ventromedial prefrontal cortex, 腹内侧前额叶皮层; ACC:anterior cingulate cortex, 前扣带皮层; AI:anterior insula, 前侧脑岛; amygdala:杏仁核; dmPFC:dorsalmedial prefrontal cortex, 背内侧前额叶皮层; TPJ:temporo-parietal junction, 颞顶联合区; STS, superior temporal sulcus, 颞上沟; PCC:posterior cingulate cortex, 后扣带皮层; dlPFC:dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, 背外侧前额叶皮层; IPL:inferior parietal lobule, 顶下小叶。
| [1] | 高青林, 周媛. (2021). 计算模型视角下信任形成的心理和神经机制——基于信任博弈中投资者的角度. 心理科学进展, 29(1),178-189. |
| [2] | 张银花, 李红, 吴寅. (2020). 计算模型在道德认知研究中的应用. 心理科学进展, 28(7),1042-1055. |
| [3] |
Ahn, W.-Y., Haines, N., & Zhang, L. (2017). Revealing neurocomputational mechanisms of reinforcement learning and decision-making with the hBayesDM package. Computational Psychiatry, 1,24-57.
doi: 10.1162/CPSY_a_00002 URL pmid: 29601060 |
| [4] |
Alcalá-López, D., Smallwood, J., Jefferies, E., van Overwalle, F., Vogeley, K., Mars, R. B., ... Bzdok, D. (2018). Computing the social brain connectome across systems and states. Cerebral Cortex, 28(7),2207-2232.
URL pmid: 28521007 |
| [5] |
Anderson, C., Brion, S., Moore, D. A., & Kennedy, J. A. (2012). A status-enhancement account of overconfidence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 103(4),718-735.
doi: 10.1037/a0029395 URL pmid: 22800286 |
| [6] |
Apps, M. A., Rushworth, M. F., & Chang, S. W. (2016). The anterior cingulate gyrus and social cognition: Tracking the motivation of others. Neuron, 90(4),692-707.
URL pmid: 27196973 |
| [7] |
Barrett, L. F., & Satpute, A. B. (2013). Large-scale brain networks in affective and social neuroscience: Towards an integrative functional architecture of the brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 23(3),361-372.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.12.012 URL pmid: 23352202 |
| [8] |
Basile, B. M., Schafroth, J. L., Karaskiewicz, C. L., Chang, S. W., & Murray, E. A. (2020). The anterior cingulate cortex is necessary for forming prosocial preferences from vicarious reinforcement in monkeys. Plos Biology, 18(6),e3000677.
URL pmid: 32530910 |
| [9] |
Bassett, D. S., & Sporns, O. (2017). Network neuroscience. Nature Neuroscience, 20(3),353-364.
doi: 10.1038/nn.4502 URL pmid: 28230844 |
| [10] |
Behrens, T. E., Hunt, L. T., Woolrich, M. W., & Rushworth, M. F. (2008). Associative learning of social value. Nature, 456(7219),245-249.
URL pmid: 19005555 |
| [11] |
Bellucci, G., Molter, F., & Park, S. Q. (2019). Neural representations of honesty predict future trust behavior. Nature Communications, 10(1),1-12.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 URL pmid: 30602773 |
| [12] |
Bellucci, G., & Park, S. Q. (2020). Honesty biases trustworthiness impressions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 149(8),1567-1586.
doi: 10.1037/xge0000730 URL |
| [13] |
Blair, K., Marsh, A. A., Morton, J., Vythilingam, M., Jones, M., Mondillo, K., ... Blair, J. R. (2006). Choosing the lesser of two evils, the better of two goods: Specifying the roles of ventromedial prefrontal cortex and dorsal anterior cingulate in object choice. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(44),11379-11386.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1640-06.2006 URL pmid: 17079666 |
| [14] |
Boorman, E. D., O'Doherty, J. P., Adolphs, R., & Rangel, A. (2013). The behavioral and neural mechanisms underlying the tracking of expertise. Neuron, 80(6),1558-1571.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.024 URL |
| [15] |
Burke, C. J., Tobler, P. N., Schultz, W., & Baddeley, M. (2010). Striatal BOLD response reflects the impact of herd information on financial decisions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 4,48.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2010.00048 URL pmid: 20589242 |
| [16] |
Campbell-Meiklejohn, D. K., Simonsen, A., Frith, C. D., & Daw, N. D. (2017). Independent neural computation of value from other people's confidence. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(3),673-684.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4490-15.2016 URL pmid: 28100748 |
| [17] |
Chang, L. J., Doll, B. B., van't Wout, M., Frank, M. J., & Sanfey, A. G. (2010). Seeing is believing: Trustworthiness as a dynamic belief. Cognitive Psychology, 61(2),87-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2010.03.001 URL |
| [18] |
Charpentier, C. J., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2018). The application of computational models to social neuroscience: Promises and pitfalls. Social Neuroscience, 13(6),637-647.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2018.1518834 URL pmid: 30173633 |
| [19] |
Chien, S., Wiehler, A., Spezio, M., & Gläscher, J. (2016). Congruence of inherent and acquired values facilitates reward-based decision-making. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(18),5003-5012.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3084-15.2016 URL pmid: 27147653 |
| [20] |
Cohen, J. D., Daw, N., Engelhardt, B., Hasson, U., Li, K. Niv, Y., ... Willke, T.L (2017). Computational approaches to fMRI analysis. Nature Neuroscience, 20(3),304-313.
doi: 10.1038/nn.4499 URL pmid: 28230848 |
| [21] |
Collins, A. G., & Cockburn, J. (2020). Beyond dichotomies in reinforcement learning. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 21,576-586.
doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0355-6 URL pmid: 32873936 |
| [22] | Cone, J., Mann, T. C., & Ferguson, M. J. (2017). Changing our implicit minds: How, when, and why implicit evaluations can be rapidly revised. In Advances in experimental social psychology, (Vol. 56, pp.131-199). Elsevier. |
| [23] | Corrado, G. S., Sugrue, L. P., Brown, J. R., & Newsome, W. T. (2017). The trouble with choice:Studying decision variables in the brain. Neuroeconomics: Decision making and the brain: Chap. 30 (pp.463-480). Londen, UK: Elsevier Academic Press. |
| [24] |
Daunizeau, J., Adam, V., & Rigoux, L. (2014). VBA: A probabilistic treatment of nonlinear models for neurobiological and behavioural data. PLoS Computational biology, 10(1),e1003441.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003441 URL pmid: 24465198 |
| [25] |
Daw, N. D., Gershman, S. J., Seymour, B., Dayan, P., & Dolan, R. J. (2011). Model-based influences on humans' choices and striatal prediction errors. Neuron, 69(6),1204-1215.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.027 URL pmid: 21435563 |
| [26] |
Dayan, P., Kakade, S., & Montague, P. R. (2000). Learning and selective attention. Nature Neuroscience, 3(11),1218-1223.
doi: 10.1038/81504 URL |
| [27] |
de Martino, B., Bobadilla-Suarez, S., Nouguchi, T., Sharot, T., & Love, B. C. (2017). Social information is integrated into value and confidence judgments according to its reliability. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(25),6066-6074.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3880-16.2017 URL pmid: 28566360 |
| [28] |
DeMayo, M. M., Young, L. J., Hickie, I. B., Song, Y. J. C., & Guastella, A. J. (2019). Circuits for social learning: A unified model and application to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 107,388-398.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.09.034 URL pmid: 31560922 |
| [29] |
Devaine, M., Hollard, G., & Daunizeau, J. (2014). The social Bayesian brain: Does mentalizing make a difference when we learn? PLoS Computational Biology, 10(12),e1003992.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003992 URL pmid: 25474637 |
| [30] |
Diaconescu, A. O., Mathys, C., Weber, L. A., Daunizeau, J., Kasper, L., Lomakina, E. I., ... Stephan, K. E. (2014). Inferring on the intentions of others by hierarchical Bayesian learning. PLoS Computational Biology, 10(9),e1003952.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003952 URL |
| [31] |
Diaconescu, A. O., Mathys, C., Weber, L. A., Kasper, L., Mauer, J., & Stephan, K. E. (2017). Hierarchical prediction errors in midbrain and septum during social learning. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(4),618-634.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsw171 URL pmid: 28119508 |
| [32] |
Diaconescu, A. O., Stecy, M., Kasper, L., Burke, C. J., Nagy, Z., Mathys, C., & Tobler, P. (2020). Neural Arbitration between Social and Individual Learning Systems. eLife, 9,e54051.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.54051 URL pmid: 32779568 |
| [33] |
Dolan, R. J., & Dayan, P. (2013). Goals and habits in the brain. Neuron, 80(2),312-325.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.09.007 URL |
| [34] |
FeldmanHall, O., Otto, A. R., & Phelps, E. A. (2018). Learning moral values: Another's desire to punish enhances one's own punitive behavior. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 147(8),1211-1224.
doi: 10.1037/xge0000405 URL |
| [35] |
Feng, C., Azarian, B., Ma, Y., Feng, X., Wang, L., Luo, Y. J., & Krueger, F. (2017). Mortality salience reduces the discrimination between in‐group and out‐group interactions: A functional MRI investigation using multi‐voxel pattern analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 38(3),1281-1298.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.23454 URL pmid: 27859936 |
| [36] |
Ferguson, M. J., Mann, T. C., Cone, J., & Shen, X. (2019). When and how implicit first impressions can be updated. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 28(4),331-336.
doi: 10.1177/0963721419835206 URL |
| [37] |
Franklin, N. T., & Frank, M. J. (2015). A cholinergic feedback circuit to regulate striatal population uncertainty and optimize reinforcement learning. eLife, 4,e12029.
URL pmid: 26705698 |
| [38] |
Garvert, M. M., Moutoussis, M., Kurth-Nelson, Z., Behrens, T. E., & Dolan, R. J. (2015). Learning-induced plasticity in medial prefrontal cortex predicts preference malleability. Neuron, 85(2),418-428.
URL pmid: 25611512 |
| [39] |
Gershman, S. J. (2015). A unifying probabilistic view of associative learning. PLoS Computational Biology, 11(11),e1004567.
URL pmid: 26535896 |
| [40] | Gläscher, J. P., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2010). Model‐based approaches to neuroimaging: Combining reinforcement learning theory with fMRI data. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 1(4),501-510. |
| [41] |
Gmytrasiewicz, P. J., & Doshi, P. (2005). A framework for sequential planning in multi-agent settings. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 24,49-79.
doi: 10.1613/jair.1579 URL |
| [42] | Greaves, C. J., & Farbus, L. (2006). Effects of creative and social activity on the health and well-being of socially isolated older people: Outcomes from a multi-method observational study. The Journal of the Royal Society for the Promotion of Health, 126(3),134-142. |
| [43] |
Gu, X., Wang, X., Hula, A., Wang, S., Xu, S., Lohrenz, T. M., ... Montague, P. R. (2015). Necessary, yet dissociable contributions of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal cortices to norm adaptation: Computational and lesion evidence in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(2),467-473.
URL pmid: 25589742 |
| [44] | Hackel, L. M., Doll, B. B., & Amodio, D. M. (2015). Instrumental learning of traits versus rewards: Dissociable neural correlates and effects on choice. Nature Neuroscience, 18(9),1233-1235. |
| [45] |
Hackel, L. M., & Zaki, J. (2018). Propagation of economic inequality through reciprocity and reputation. Psychological Science, 29(4),604-613.
URL pmid: 29474134 |
| [46] | Hampton, A. N., Bossaerts, P., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2008). Neural correlates of mentalizing-related computations during strategic interactions in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(18),6741-6746. |
| [47] | Hedge, C., Bompas, A., & Sumner, P. (2020). Task reliability considerations in computational psychiatry. Biological psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 5, (9),837-839. |
| [48] | Henco, L., Brandi, M.-L., Lahnakoski, J. M., Diaconescu, A. O., Mathys, C., & Schilbach, L. (2020). Bayesian modelling captures inter-individual differences in social belief computations in the putamen and insula. Cortex, 131,221-236. |
| [49] |
Hétu, S., Luo, Y., D'Ardenne, K., Lohrenz, T., & Montague, P. R. (2017). Human substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area involvement in computing social error signals during the ultimatum game. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12,1972-1982.
URL pmid: 28981876 |
| [50] | Hill, C. A., Suzuki, S., Polania, R., Moisa, M., O'Doherty, J. P., & Ruff, C. C. (2017). A causal account of the brain network computations underlying strategic social behavior. Nature Neuroscience, 20(8),1142-1149. |
| [51] | Hill, M. R., Boorman, E. D., & Fried, I. (2016). Observational learning computations in neurons of the human anterior cingulate cortex. Nature Communications, 7(1),1-12. |
| [52] |
Hula, A., Montague, P. R., & Dayan, P. (2015). Monte carlo planning method estimates planning horizons during interactive social exchange. PLoS Computational Biology, 11(6),e1004254.
URL pmid: 26053429 |
| [53] | Hula, A., Vilares, I., Lohrenz, T., Dayan, P., & Montague, P. R. (2018). A model of risk and mental state shifts during social interaction. PLoS Computational Biology, 14(2),e1005935. |
| [54] | Ivanchei, I. I., Moroshkina, N., Tikhonov, R., & Ovchinnikova, I. (2019). Implicit learning in attractiveness evaluation: The role of conformity and analytical processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 148(9),1505-1516. |
| [55] |
Jocham, G., Klein, T. A., & Ullsperger, M. (2011). Dopamine-mediated reinforcement learning signals in the striatum and ventromedial prefrontal cortex underlie value-based choices. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(5),1606-1613.
URL pmid: 21289169 |
| [56] | Joiner, J., Piva, M., Turrin, C., & Chang, S. W. (2017). Social learning through prediction error in the brain. NPJ Science of Learning, 2(1),1-9. |
| [57] |
Jones, R. M., Somerville, L. H., Li, J., Ruberry, E. J., Libby, V., Glover, G., ... Casey, B.. (2011). Behavioral and neural properties of social reinforcement learning. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(37),13039-13045.
URL pmid: 21917787 |
| [58] | Khalvati, K., Mirbagheri, S., Park, S. A., Dreher, J. -C., & Rao, R. P. (2019). A Bayesian theory of conformity in collective decision making. Paper presented at the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, |
| [59] |
Khalvati, K., Park, S. A., Mirbagheri, S., Philippe, R., Sestito, M., Dreher, J. -C., & Rao, R. P. (2019). Modeling other minds: Bayesian inference explains human choices in group decision-making. Science Advances, 5(11),eaax8783.
URL pmid: 31807706 |
| [60] | Kumar, S., Rusch, T., Doshi, P., Spezio, M., & Gläscher, J. (2019). Modeling cooperative and competitive decision-making in the Tiger Task. Paper presented at the The Multidisciplinary Conference on Reinforcement Learning and Decision Making, |
| [61] |
Kumaran, D., Banino, A., Blundell, C., Hassabis, D., & Dayan, P. (2016). Computations underlying social hierarchy learning: Distinct neural mechanisms for updating and representing self-relevant information. Neuron, 92(5),1135-1147.
URL pmid: 27930904 |
| [62] |
Kuss, K., Falk, A., Trautner, P., Elger, C. E., Weber, B., & Fliessbach, K. (2013). A reward prediction error for charitable donations reveals outcome orientation of donators. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8(2),216-223.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsr088 URL pmid: 22198972 |
| [63] |
Lamba, A., Frank, M. J., & FeldmanHall, O. (2020). Anxiety impedes adaptive social learning under uncertainty. Psychological Science, 31(5),592-603.
URL pmid: 32343637 |
| [64] |
Lawson, R. P., Mathys, C., & Rees, G. (2017). Adults with autism overestimate the volatility of the sensory environment. Nature Neuroscience, 20(9),1293-1299.
URL pmid: 28758996 |
| [65] | Lee, M. D., Criss, A. H., Devezer, B., Donkin, C., Etz, A., Leite, F. P., ... Vandekerckhove, J. (2019). Robust modeling in cognitive science. Computational Brain & Behavior, 2(3-4),141-153. |
| [66] | Leong, Y. C., & Zaki, J. (2018). Unrealistic optimism in advice taking: A computational account. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 147(2),170-189. |
| [67] |
Li, L., Li, K. K., & Li, J. (2019). Private but not social information validity modulates social conformity bias. Human Brain Mapping, 40(8),2464-2474.
URL pmid: 30697880 |
| [68] |
Ligneul, R., Obeso, I., Ruff, C. C., & Dreher, J.-C. (2016). Dynamical representation of dominance relationships in the human rostromedial prefrontal cortex. Current Biology, 26(23),3107-3115.
URL pmid: 28094034 |
| [69] | Lockwood, P. L., Apps, M. A., Valton, V., Viding, E., & Roiser, J. P. (2016). Neurocomputational mechanisms of prosocial learning and links to empathy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(35),9763-9768. |
| [70] |
Lockwood, P. L., Apps, M.A. J., & Chang, S.W. C. (2020). Is There a ‘Social' Brain? Implementations and Algorithms. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 24(10),802-813.
URL pmid: 32736965 |
| [71] |
Lockwood, P. L., Klein-Flügge, M. C., Abdurahman, A., & Crockett, M. J. (2020). Model-free decision making is prioritized when learning to avoid harming others. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(44),27719-27730.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010890117 URL |
| [72] |
Lockwood, P. L., O'Nell, K. C., & Apps, M. A. (2020). Anterior cingulate cortex: A brain system necessary for learning to reward others? Plos Biology, 18(6),e3000735.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000735 URL pmid: 32530924 |
| [73] |
Lockwood, P. L., Wittmann, M. K., Apps, M. A., Klein-Flügge, M. C., Crockett, M. J., Humphreys, G. W., & Rushworth, M. F. (2018). Neural mechanisms for learning self and other ownership. Nature Communications, 9(1),1-11.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02088-w URL |
| [74] |
Loughrey, D. G., Feeney, J., Kee, F., Lawlor, B. A., Woodside, J. V., Setti, A., & Power, J. M. (2020). Social factors may mediate the relationship between subjective age-related hearing loss and episodic memory. Aging & Mental Health,1-8.
URL pmid: 33719753 |
| [75] | Madva, A., & Brownstein, M. (2018). Stereotypes, prejudice, and the taxonomy of the implicit social mind1. Noûs, 52(3),611-644. |
| [76] |
Maia, T. V., Huys, Q. J., & Frank, M. J. (2017). Theory-based computational psychiatry. Biological Psychiatry, 82(6),382-384.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.07.016 URL pmid: 28838466 |
| [77] |
Mathys, C., Daunizeau, J., Friston, K. J., & Stephan, K. E. (2011). A Bayesian foundation for individual learning under uncertainty. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5,39.
URL pmid: 21629826 |
| [78] |
Mathys, C. D., Lomakina, E. I., Daunizeau, J., Iglesias, S., Brodersen, K. H., Friston, K. J., & Stephan, K. E. (2014). Uncertainty in perception and the Hierarchical Gaussian Filter. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8,825.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00825 URL pmid: 25477800 |
| [79] |
Meshi, D., Biele, G., Korn, C. W., & Heekeren, H. R. (2012). How expert advice influences decision making. PloS One, 7(11),e49748.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049748 URL pmid: 23185425 |
| [80] |
Miletić, S., Boag, R. J., & Forstmann, B. U. (2020). Mutual benefits: Combining reinforcement learning with sequential sampling models. Neuropsychologia, 136,107261.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107261 URL pmid: 31733237 |
| [81] |
Montague, P. R., Berns, G. S., Cohen, J. D., McClure, S. M., Pagnoni, G., Dhamala, M., ... Fisher, R. E. (2002). Hyperscanning: Simultaneous fMRI during linked social interactions. NeuroImage, 16(4),1159-1164.
URL pmid: 12202103 |
| [82] |
Morris, R. W., Dezfouli, A., Griffiths, K. R., Le Pelley, M. E., & Balleine, B. W. (2017). The algorithmic neuroanatomy of action-outcome learning. bioRxiv, 137851.
doi: 10.1101/2021.03.22.436465 URL pmid: 33791707 |
| [83] |
Nosek, B. A., Hawkins, C. B., & Frazier, R. S. (2011). Implicit social cognition: From measures to mechanisms. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(4),152-159.
URL pmid: 21376657 |
| [84] |
O'Doherty, J. P., Cockburn, J., & Pauli, W. M. (2017). Learning, reward, and decision making. Annual Review of Psychology, 68,73-100.
URL pmid: 27687119 |
| [85] |
O'Doherty, J. P., Dayan, P., Schultz, J., Deichmann, R., Friston, K., & Dolan, R. J. (2004). Dissociable roles of ventral and dorsal striatum in instrumental conditioning. Science, 304(5669),452-454.
URL pmid: 15087550 |
| [86] | O'Doherty, J. P., Hampton, A., & Kim, H. (2007). Model‐based fMRI and its application to reward learning and decision making. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1104(1),35-53. |
| [87] | Ottaway, S. A., Hayden, D. C., & Oakes, M. A. (2001). Implicit attitudes and racism: Effects of word familiarity and frequency on the implicit association test. Social Cognition, 19(2),97-144. |
| [88] | Palminteri, S., Khamassi, M., Joffily, M., & Coricelli, G. (2015). Contextual modulation of value signals in reward and punishment learning. Nature Communications, 6(1),1-14. |
| [89] | Palminteri, S., Wyart, V., & Koechlin, E. (2017). The importance of falsification in computational cognitive modeling. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(6),425-433. |
| [90] | Panagopoulos, C., & van der Linden, S. (2016). Conformity to implicit social pressure: The role of political identity. Social Influence, 11(3),177-184. |
| [91] |
Park, S. A., Goïame, S., O'Connor, D. A., & Dreher, J.-C. (2017). Integration of individual and social information for decision-making in groups of different sizes. PLoS Biology, 15(6),e2001958.
URL pmid: 28658252 |
| [92] | Park, S. A., Miller, D. S., Nili, H., Ranganath, C., & Boorman, E. D. (2020). Map making: Constructing, combining, and inferring on abstract cognitive maps. Neuron, 107(6),1-13. |
| [93] |
Park, S. A., Sestito, M., Boorman, E. D., & Dreher, J.-C. (2019). Neural computations underlying strategic social decision-making in groups. Nature Communications, 10(1),1-12.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 URL pmid: 30602773 |
| [94] | Paulus, M. P., Huys, Q. J., & Maia, T. V. (2016). A roadmap for the development of applied computational psychiatry. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 1(5),386-392. |
| [95] | Pedersen, M. L., & Frank, M. J. (2020). Simultaneous Hierarchical Bayesian Parameter Estimation for Reinforcement Learning and Drift Diffusion Models: A Tutorial and Links to Neural Data. Computational Brain & Behavior, 3,458-471. |
| [96] |
Piray, P., Dezfouli, A., Heskes, T., Frank, M. J., & Daw, N. D. (2019). Hierarchical Bayesian inference for concurrent model fitting and comparison for group studies. PLoS Computational Biology, 15(6),e1007043.
URL pmid: 31211783 |
| [97] |
Piray, P., & Daw, N. D. (2020). A simple model for learning in volatile environments. PLoS Computational Biology. 16(7),e1007963.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007963 URL pmid: 32609755 |
| [98] |
Powers, A. R., Mathys, C., & Corlett, P. (2017). Pavlovian conditioning-induced hallucinations result from overweighting of perceptual priors. Science, 357(6351),596-600.
doi: 10.1126/science.aan3458 URL pmid: 28798131 |
| [99] |
Pulcu, E., & Browning, M. (2019). The misestimation of uncertainty in affective disorders. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(10),865-875.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2019.07.007 URL pmid: 31431340 |
| [100] |
Ratcliff, R., Smith, P. L., Brown, S. D., & McKoon, G. (2016). Diffusion decision model: Current issues and history. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(4),260-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2016.01.007 URL pmid: 26952739 |
| [101] | Reiter, A. M., Suzuki, S., O'Doherty, J. P., Li, S.-C., & Eppinger, B., (2019). Risk contagion by peers affects learning and decision-making in adolescents. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 148(9),1494-1504. |
| [102] | Rescorla, R. A., & Wagner, A. R. (1972). A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: Variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory, 2,64-99. |
| [103] |
Ruff, C. C., & Fehr, E. (2014). The neurobiology of rewards and values in social decision making. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(8),549-562.
URL pmid: 24986556 |
| [104] |
Rusch, T., Steixner-Kumar, S., Doshi, P., Spezio, M., & Gläscher, J. (2020). Theory of mind and decision science: Towards a typology of tasks and computational models. Neuropsychologia, 146,107488.
URL pmid: 32407906 |
| [105] | Seppala, E., Rossomando, T., & Doty, J. R. (2013). Social connection and compassion: Important predictors of health and well-being. Social Research: An International Quarterly, 80(2),411-430. |
| [106] |
Siegel, J. Z., Mathys, C., Rutledge, R. B., & Crockett, M. J. (2018). Beliefs about bad people are volatile. Nature Human Behaviour, 2(10),750-756.
URL pmid: 31406285 |
| [107] |
Soltani, A., & Izquierdo, A. (2019). Adaptive learning under expected and unexpected uncertainty. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 20(10),635-644.
doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0180-y URL pmid: 31147631 |
| [108] | Soon, V. (2020). Implicit bias and social schema: A transactive memory approach. Philosophical Studies, 177(7),1857-1877. |
| [109] | Stanley, D. A. (2016). Getting to know you: General and specific neural computations for learning about people. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(4),525-536. |
| [110] | Steingroever, H., Wetzels, R., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2014). Absolute performance of reinforcement-learning models for the Iowa Gambling Task. Decision, 1(3),161-183. |
| [111] | Sutton, R. S., & Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement learning: An introduction. Cambridge, MA: MIT press, |
| [112] |
Suzuki, S., Adachi, R., Dunne, S., Bossaerts, P., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2015). Neural mechanisms underlying human consensus decision-making. Neuron, 86(2),591-602.
URL pmid: 25864634 |
| [113] |
Suzuki, S., Harasawa, N., Ueno, K., Gardner, J. L., Ichinohe, N., Haruno, M., ... Nakahara, H. (2012). Learning to simulate others' decisions. Neuron, 74(6),1125-1137.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.030 URL pmid: 22726841 |
| [114] |
Suzuki, S., Jensen, E. L., Bossaerts, P., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2016). Behavioral contagion during learning about another agent's risk-preferences acts on the neural representation of decision-risk. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(14),3755-3760.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600092113 URL |
| [115] |
Suzuki, S., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2020). Breaking human social decision making into multiple components and then putting them together again. Cortex, 127,221-230.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2020.02.014 URL pmid: 32224320 |
| [116] | Thornton, M. A., & Tamir, D. I. (2017). Mental models accurately predict emotion transitions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(23),5982-5987. |
| [117] |
Toelch, U., Bach, D. R., & Dolan, R. J. (2014). The neural underpinnings of an optimal exploitation of social information under uncertainty. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(11),1746-1753.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nst173 URL pmid: 24194580 |
| [118] |
Toyokawa, W., Whalen, A., & Laland, K. N. (2019). Social learning strategies regulate the wisdom and madness of interactive crowds. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(2),183-193.
doi: 10.1038/s41562-018-0518-x URL pmid: 30944445 |
| [119] |
Tump, A. N., Pleskac, T. J., & Kurvers, R. H. (2020). Wise or mad crowds? The cognitive mechanisms underlying information cascades. Science Advances, 6(29),eabb0266.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb0266 URL pmid: 32832634 |
| [120] |
van, Baar, J.M., Chang, L. J., & Sanfey, A. G. (2019). The computational and neural substrates of moral strategies in social decision-making. Nature Communications, 10(1),1-14.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 URL pmid: 30602773 |
| [121] |
Wang, Y., & Olson, I. R. (2018). The original social network: White matter and social cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 22(6),504-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2018.03.005 URL pmid: 29628441 |
| [122] |
Wilson, R. C., & Collins, A. G. (2019). Ten simple rules for the computational modeling of behavioral data. Elife, 8,e49547.
URL pmid: 31769410 |
| [123] |
Wittmann, M. K., Kolling, N., Faber, N. S., Scholl, J., Nelissen, N., & Rushworth, M. F. (2016). Self-other mergence in the frontal cortex during cooperation and competition. Neuron, 91(2),482-493.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.06.022 URL pmid: 27477020 |
| [124] |
Xiang, T., Lohrenz, T., & Montague, P. R. (2013). Computational substrates of norms and their violations during social exchange. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(3),1099-1108.
URL pmid: 23325247 |
| [125] |
Xiang, T., Ray, D., Lohrenz, T., Dayan, P., & Montague, P. R. (2012). Computational phenotyping of two-person interactions reveals differential neural response to depth-of-thought. PLoS Computational Biology, 8(12),e1002841.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002841 URL pmid: 23300423 |
| [126] |
Yang, J., Zhang, H., Ni, J., de Dreu, C. K., & Ma, Y. (2020). Within-group synchronization in the prefrontal cortex associates with intergroup conflict. Nature Neuroscience, 23(6),754-760.
URL pmid: 32341541 |
| [127] |
Yoshida, W., Seymour, B., Friston, K. J., & Dolan, R. J. (2010). Neural mechanisms of belief inference during cooperative games. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(32),10744-10751.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5895-09.2010 URL pmid: 20702705 |
| [128] | Yu, A., & Dayan, P. (2003). Expected and unexpected uncertainty: ACh and NE in the neocortex. Paper presented at the Advances in neural information processing systems. |
| [129] |
Zhang, L., & Gläscher, J. (2020). A brain network supporting social influences in human decision-making. Science Advances, 6(34),eabb4159.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb4159 URL pmid: 32875112 |
| [130] |
Zhang, L., Lengersdorff, L., Mikus, N., Gläscher, J., & Lamm, C. (2020). Using reinforcement learning models in social neuroscience: Frameworks, pitfalls and suggestions of best practices. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 15(6),695-707.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa089 URL pmid: 32608484 |
| [131] | Zhu, L., Mathewson, K. E., & Hsu, M. (2012). Dissociable neural representations of reinforcement and belief prediction errors underlie strategic learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(5),1419-1424. |
| [1] | 温秀娟, 马毓璟, 谭斯祺, 李芸, 刘文华. 身体还是认知努力的损害?抑郁症努力奖赏动机评估及计算模型应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2025, 33(1): 107-122. |
| [2] | 李兴珊, 张淇玮, 黄林洁琼. 中文词汇语义加工过程的计算模拟与实验验证[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(9): 1379-1392. |
| [3] | 涂画, 张春妹. 亲密伴侣暴力的成因:社会学习和女性主义理论下基于态度的解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(11): 1898-1911. |
| [4] | 郭鸣谦, 潘晚坷, 胡传鹏. 认知建模中模型比较的方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2024, 32(10): 1736-1756. |
| [5] | 韩宜瑾, 朱金丽, 侯方. 弱视视觉系统的对比度增益研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(suppl.): 4-4. |
| [6] | 余婕, 陈有国. 时空干扰效应:基于贝叶斯模型的解释[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(4): 597-607. |
| [7] | 王海珍, 耿紫珍, 丁琳, 单春霞. 辱虐管理的成因[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(4): 906-921. |
| [8] | 高青林, 周媛. 计算模型视角下信任形成的心理和神经机制——基于信任博弈中投资者的角度[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 178-189. |
| [9] | 张银花, 李红, 吴寅. 计算模型在道德认知研究中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7): 1042-1055. |
| [10] | 李精精, 张剑, 田慧荣, Jeffrey B.Vancouver. 动态计算模型在组织行为学研究中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(2): 368-380. |
| [11] | 陈维扬, 谢天. 文化演化的认知视角——从个体社会学习出发探究文化动态性[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(12): 2137-2149. |
| [12] | 区健新, 吴寅, 刘金婷, 李红. 计算精神病学:抑郁症研究和临床应用的新视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(1): 111-127. |
| [13] | 高绍兵, 李永杰. 结合视觉自底向上和自顶向下机制的多光源颜色恒常性算法研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(suppl.): 96-96. |
| [14] | 徐胜, 田蜜, 罗天瑞, 赛李阳. 基于选择反应的学习迁移效应:从个人情境到社会情境[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(7): 1215-1223. |
| [15] | 严瑜, 李彤. 工作场所不文明行为受害者向实施者反转的机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(7): 1307-1318. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||