

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 1656-1666.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2019.01656 cstr: 32111.14.2019.01656
• 研究前沿 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2019-01-14
出版日期:2019-09-15
发布日期:2019-07-24
基金资助:
PENG Suhao, TAO Dan, LENG Yue( ), DENG Huihua
), DENG Huihua
Received:2019-01-14
Online:2019-09-15
Published:2019-07-24
摘要:
社会排斥损害个体基本的归属需要, 对个体的心理和生理会造成严重影响。根据需要威胁时间模型, 社会排斥后的心理和行为特征可以分为三个阶段。社交媒体的发展使社会排斥出现了新的心理和行为特征。近年来功能性磁共振成像研究发现, 突显网络和默认网络等网络中的一些核心脑区都参与了社会排斥各阶段的情绪和认知加工过程。未来研究应以需要威胁时间模型为基础, 以脑网络方法为手段, 探索社会排斥神经机制, 预测排斥后的心理和行为反应模式。
中图分类号:
彭苏浩, 陶丹, 冷玥, 邓慧华. (2019). 社会排斥的心理行为特征及其脑机制. 心理科学进展 , 27(9), 1656-1666.
PENG Suhao, TAO Dan, LENG Yue, DENG Huihua. (2019). The psychological and behavior characteristics of social exclusion and its brain mechanisms. Advances in Psychological Science, 27(9), 1656-1666.
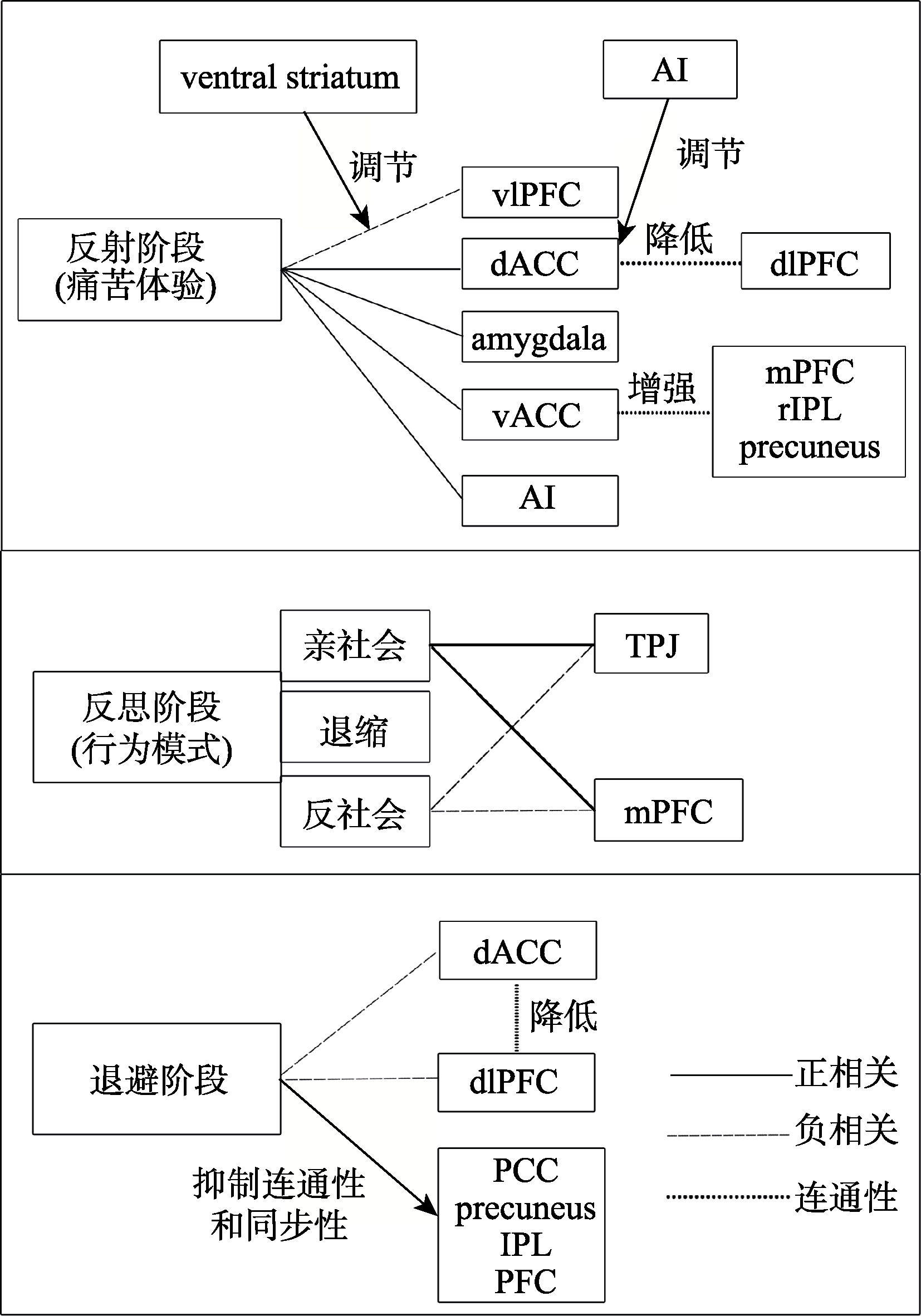
图2 社会排斥各阶段脑网络中相关脑区的神经活动模式 注:突显网络主要涉及腹侧纹状体(ventral striatum), 背侧前扣带皮层(dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, dACC), 杏仁核(amygdala); 前脑岛(anterior insula, AI); 默认模式网络主要涉及后扣带回皮层(posterior cingulate cortex, PCC), 楔前叶(precuneus), 内侧前额叶皮层(media prefrontal cortex, mPFC), 顶下小叶(inferior parietal lobe, IPL), 颞顶联合区(temporoparietal junction, TPJ); 执行控制网络主要涉及背外侧前额皮层(dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, dlPFC); 其他脑区包括腹外侧前额叶皮层(ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, vlPFC)和腹前扣带回皮层(ventral anterior cingulate cortex, vACC)。
| 1 | 蔡强, 吴寅, 刘金婷 . (2011). 社会排斥及其神经机制. 心理研究, 4(5), 3-9. |
| 2 | 陈晨, 杨付, 李永强 . (2017). 职场排斥的作用机制与本土化发展. 心理科学进展, 25(8), 1387-1400. |
| 3 | 程苏, 刘璐, 郑涌 . (2011). 社会排斥的研究范式与理论模型. 心理科学进展, 19(6), 905-915. |
| 4 | 杜建政, 夏冰丽 . (2008). 心理学视野中的社会排斥. 心理科学进展, 16(6), 981-986. |
| 5 | 王紫薇, 涂平 . (2014). 社会排斥情境下自我关注变化的性别差异. 心理学报, 46(11), 1782-1792. |
| 6 | = Andrews-Hanna, J. R . (2012). The brain's default network and its adaptive role in internal mentation. Neuroscientist, 18(3), 251-270. |
| 7 | Bassett, D. S., & Sporns, O. (2017). Network neuroscience. Nature Neuroscience, 20(3), 353-364. |
| 8 | Bassett D. S., Zurn P., & Gold J. I . (2018). On the nature and use of models in network neuroscience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 19(9), 566-578. |
| 9 | Berger, M. & Sarnyai, Z. (2015). "More than skin deep": Stress neurobiology and mental health consequences of racial discrimination. Stress-the International Journal on the Biology of Stress, 18(1), 1-10. |
| 10 | Bolling D. Z., Pitskel N. B., Deen B., Crowley M. J., McPartland J. C., Mayes L. C., & Pelphrey K. A . (2011). Dissociable brain mechanisms for processing social exclusion and rule violation. NeuroImage, 54(3), 2462-2471. |
| 11 | Cacioppo S., Frum C., Asp E., Weiss R. M., Lewis J. W., & Cacioppo J. T . (2013). A quantitative meta-analysis of functional imaging studies of social rejection. Scientific Reports, 3, 2027. |
| 12 | Che X. W., Zhang Q. L., Zhao J. Z., Wei D. T., Li B. B., Guo Y. A., .. Liu Y. j . (2014). Synchronous activation within the default mode network correlates with perceived social support. Neuropsychologia, 63(1), 26-33. |
| 13 | Clemens B., Wagels L., Bauchmuller M., Bergs R., Habel U., & Kohn N . (2017). Alerted default mode: Functional connectivity changes in the aftermath of social stress. Scientific Reports, 7, 40180. |
| 14 | Chiou W.-B., Lee C.-C., & Liao D.-C . (2015). Facebook effects on social distress: Priming with online social networking thoughts can alter the perceived distress due to social exclusion. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 230-236. |
| 15 | Eisenberger, N. I . (2012). The pain of social disconnection: examining the shared neural underpinnings of physical and social pain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 13(6), 421-434. |
| 16 | Eisenberger, N. I . (2015a). Meta-analytic evidence for the role of the anterior cingulate cortex in social pain. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(1), 1-2. |
| 17 | Eisenberger, N. I . (2015b). Social pain and the brain: Controversies, questions, and where to go from here. Annual Review of Psychology, 66(1), 601-629. |
| 18 | Eisenberger N. I., Lieberman M. D., & Williams K. D . (2003). Does rejection hurt? An FMRI study of social exclusion. Science, 302(5643), 290-292. |
| 19 | Falk, E. B., & Bassett, D. S . (2017). Brain and social networks: fundamental building blocks of human experience. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(9), 674-690. |
| 20 | Fitzgibbon B. M., Kirkovski M., Bailey N. W., Thomson R. H., Eisenberger N., Enticott P. G., & Fitzgerald P. B . (2017). Low-frequency brain stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex increases the negative impact of social exclusion among those high in personal distress. Social Neuroscience, 12(3), 237-241. |
| 21 | Fossati P.. (2019). Circuit based anti-correlation, attention orienting, and major depression. CNS Spectrums, 1-8. |
| 22 | Goulden N., Khusnulina A., Davis N. J., Bracewell R. M., Bokde A. L., McNulty J. P., & Mullins P. G . (2014). The salience network is responsible for switching between the default mode network and the central executive network: replication from DCM. NeuroImage, 99, 180-190. |
| 23 | Greicius M. D., Flores B. H., Menon V., Glover G. H., Solvason H. B., Kenna H., .. Schatzberg A. F . (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62(5), 429-437. |
| 24 | Hales A. H., Wesselmann E. D., & Williams K. D . (2016). Prayer, self-affirmation, and distraction improve recovery from short-term ostracism. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 64, 8-20. |
| 25 | Iannetti, G. D., & Mouraux, A. (2011). Can the functional MRI responses to physical pain really tell us why social rejection "hurts"? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(30), E343. |
| 26 | Iannetti G. D., Salomons T. V., Moayedi M., Mouraux A., & Davis K. D . (2013). Beyond metaphor: contrasting mechanisms of social and physical pain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17(8), 371-378. |
| 27 | Kaiser R. H., Andrews-Hanna J. R., Wager T. D., & Pizzagalli D. A . (2015). Large-Scale Network Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder: A meta-analysis of resting- state functional connectivity. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(6), 603-611. |
| 28 | Knausenberger, J., & Echterhoff, G. (2018). Recovering from social exclusion: The interplay of subtle Facebook reminders and collectivistic orientation. Computers in Human Behavior, 78, 298-305. |
| 29 | Knowles, M. L . (2014). Social rejection increases perspective taking. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 55, 126-132. |
| 30 | Kross E., Berman M. G., Mischel W., Smith E. E., & Wager T. D . (2011). Social rejection shares somatosensory representations with physical pain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(15), 6270-6275. |
| 31 | Lieberman, M. D., & Eisenberger, N. I . (2015). The dorsal anterior cingulate cortex is selective for pain: Results from large-scale reverse inference. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(49), 15250-15255. |
| 32 | Lin X. Q., Li S. Y., & Qu C . (2017). Social network sites influence recovery from social exclusion: Individual differences in social anxiety. Computers in Human Behavior, 75, 538-546. |
| 33 | Martelli A. M., Chester D. S., Brown W. K., Eisenberger N. I., & DeWall C. N . (2018). When less is more: mindfulness predicts adaptive affective responding to rejection via reduced prefrontal recruitment. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(6), 648-655. |
| 34 | Martin J. L., Richman L. S., & Leary M. R . (2017). A lasting sting: Examining the short-term and long-term effects of real-life group rejection. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 21(8), 1109-1124. |
| 35 | Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q . (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: A network model of insula function. Brain Structure and Function, 214(5-6), 655-667. |
| 36 | Moor B. G., Guroglu B., Op de Macks, Z. A., Rombouts S. A., van der Molen, M. W., & Crone E. A . (2012). Social exclusion and punishment of excluders: neural correlates and developmental trajectories. NeuroImage, 59(1), 708-717. |
| 37 | Nezlek J. B., Wesselmann E. D., Wheeler L., & Williams K. D . (2012). Ostracism in everyday life. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice, 16(2), 91-104. |
| 38 | Nowland R., Necka E. A., & Cacioppo J. T . (2018). Loneliness and social internet use: Pathways to reconnection in a digital world? Perspectives on Psychological Science, 13(1), 70-87. |
| 39 | Olie, E., & Courtet, P. (2018). Interest of neuroimaging of social exclusion in suicide. Journal of Neuroscience Research. |
| 40 | Onoda K., Okamoto Y., Nakashima K., Nittono H., Yoshimura S., Yamawaki S., .. Ura M . (2010). Does low self-esteem enhance social pain? The relationship between trait self-esteem and anterior cingulate cortex activation induced by ostracism. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 5(4), 385-391. |
| 41 | Ophir Y., Asterhan C. S. C., & Schwarz B. B . (2019). The digital footprints of adolescent depression, social rejection and victimization of bullying on Facebook. Computers in Human Behavior, 91, 62-71. |
| 42 | Oxman-Martinez J., Rummens A. J., Moreau J., Choi Y. R., Beiser M., Ogilvie L., & Armstrong R . (2012). Perceived ethnic discrimination and social exclusion: newcomer immigrant children in Canada. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 82(3), 376-388. |
| 43 | Park C.-h., Lee J.-E., Kim Y.-H., Kim K.-T., Kim Y.-J., & Lee K.-U . (2016). Modulation of prefrontal-cingulate connectivity in affective processing of children with experiences of ostracism. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 21(1), 37-43. |
| 44 | Premkumar, P. (2012). Are you being rejected or excluded? Insights from neuroimaging studies using different rejection paradigms. Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, 10(3), 144-154. |
| 45 | Puetz V. B., Kohn N., Dahmen B., Zvyagintsev M., Schuppen A., Schultz R. T., .. Konrad K . (2014). Neural response to social rejection in children with early separation experiences. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 53(12), 1328-1337.e8. |
| 46 | Raichle M. E., MacLeod A. M., Snyder A. Z., Powers W. J., Gusnard D. A., & Shulman G. L . (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 98(2), 676-682. |
| 47 | Ren D., Wesselmann E., & Williams K. D . (2016). Evidence for another response to ostracism: Solitude seeking. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 7(3), 204-212. |
| 48 | Ren D., Wesselmann E., & Williams K. D . (2018). Hurt people hurt people: Ostracism and aggression. Current Opinion in Psychology, 19, 34-38. |
| 49 | Rigney A. E., Koski J. E., & Beer J. S . (2018). The functional role of ventral anterior cingulate cortex in social evaluation: Disentangling valence from subjectively rewarding opportunities. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(1), 14-21. |
| 50 | Rotge J. Y., Lemogne C., Hinfray S., Huguet P., Grynszpan O., Tartour E., .. Fossati P . (2015). A meta-analysis of the anterior cingulate contribution to social pain. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(1), 19-27. |
| 51 | Schmalzle R., Brook O'Donnell M., Garcia J. O., Cascio C. N., Bayer J., Bassett D. S., .. Falk E. B . (2017). Brain connectivity dynamics during social interaction reflect social network structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(20), 5153-5158. |
| 52 | Schwartz J., Ordaz S. J., Kircanski K., Ho T. C., Davis E. G., Camacho M. C., & Gotlib I. H . (2019). Resting-state functional connectivity and inflexibility of daily emotions in major depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 249, 26-34. |
| 53 | Seeley W. W., Menon V., Schatzberg A. F., Keller J., Glover G. H., Kenna H., .. Greicius M. D . (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349-2356. |
| 54 | Starr, L. R., & Davila, J. (2008). Excessive reassurance seeking, depression, and interpersonal rejection: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117(4), 762-775. |
| 55 | Wager T. D., Atlas L. Y., Botvinick M. M., Chang L. J., Coghill R. C., Davis K. D., .. Yarkoni T . (2016). Pain in the ACC? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(18), E2474-E2475. |
| 56 | Wang H. Y., Braun C., & Enck P . (2017). How the brain reacts to social stress (exclusion) - A scoping review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 80, 80-88. |
| 57 | White L. O., Klein A. M., von Klitzing K., Graneist A., Otto Y., Hill J., .. Crowley M. J . (2016). Putting ostracism into perspective: young children tell more mentalistic stories after exclusion, but not when anxious. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1926. |
| 58 | Will G. J., Crone E. A., & Guroglu B . (2015). Acting on social exclusion: Neural correlates of punishment and forgiveness of excluders. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(2), 209-218. |
| 59 | Williams, K. D . (2007). Ostracism. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 425-452. |
| 60 | Williams, K. D . (2009). Chapter 6 Ostracism: A temporal need-threat model. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 41, 275-314. |
| [1] | 王新刚, 李祖兰, 张婷. 社交媒体环境下被伤害品牌双面效价应对策略:群体极化理论视角[J]. 心理科学进展, 2023, 31(5): 709-720. |
| [2] | 陈婧, 王玉正, 王锦琰, 罗非. 正念在缓解社会排斥中的作用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(6): 1294-1302. |
| [3] | 林雯仪, 何昊, 关青. 反刍思维的脑功能网络机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(6): 1262-1269. |
| [4] | 张姝玥, 黄骏青, 赵峰, 徐科朋. 社会排斥影响跨期决策的心理机制探讨[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(3): 486-498. |
| [5] | 麻雅洁, 赵鑫, 贺相春, 任丽萍. 社交媒体使用对执行功能的影响:有益还是有害?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(2): 406-413. |
| [6] | 黄观澜, 周晓璐. 抑郁症患者的语言使用模式[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(5): 838-848. |
| [7] | 苏悦, 刘明明, 赵楠, 刘晓倩, 朱廷劭. 基于社交媒体数据的心理指标识别建模: 机器学习的方法[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(4): 571-585. |
| [8] | 柴唤友, 牛更枫, 褚晓伟, 魏 祺, 宋玉红, 孙晓军. 错失恐惧:我又错过了什么?[J]. 心理科学进展, 2018, 26(3): 527-537. |
| [9] | 王海璐, 刘兴华. 开放监控冥想的特定影响效果[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(8): 1337-1348. |
| [10] | 史燕伟;徐富明;王伟;李燕;刘程浩. 感同身受的社会痛苦:来自神经影像学的证据[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(9): 1608-1616. |
| [11] | 徐晓晓;喻婧;雷旭. 想象未来的认知加工成分及其脑网络[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(3): 394-404. |
| [12] | 吴金峰;汪宇;陈红;黄俊锋. 从自我到社会认知:默认网络和镜像神经元系统[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(10): 1808-1817. |
| [13] | 李雨;舒华. 默认网络的神经机制、功能假设及临床应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22(2): 234-249. |
| [14] | 程苏;刘璐;郑涌. 社会排斥的研究范式与理论模型[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(6): 905-915. |
| [15] | 宋晓兰;王晓;唐孝威. 心智游移:现象、机制及意义[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(4): 499-509. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||