

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (9): 1622-1637.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1622
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Bo( ), ZHAO Jingshi, QI Dan, ZHAO Tong, HU Jiaqi
), ZHAO Jingshi, QI Dan, ZHAO Tong, HU Jiaqi
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-06-26
Contact:
YUAN Bo
E-mail:yuanbopsy@gmail.com
YUAN Bo, ZHAO Jingshi, QI Dan, ZHAO Tong, HU Jiaqi. (2025). The influence of social reward and punishment on deception. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(9), 1622-1637.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1622
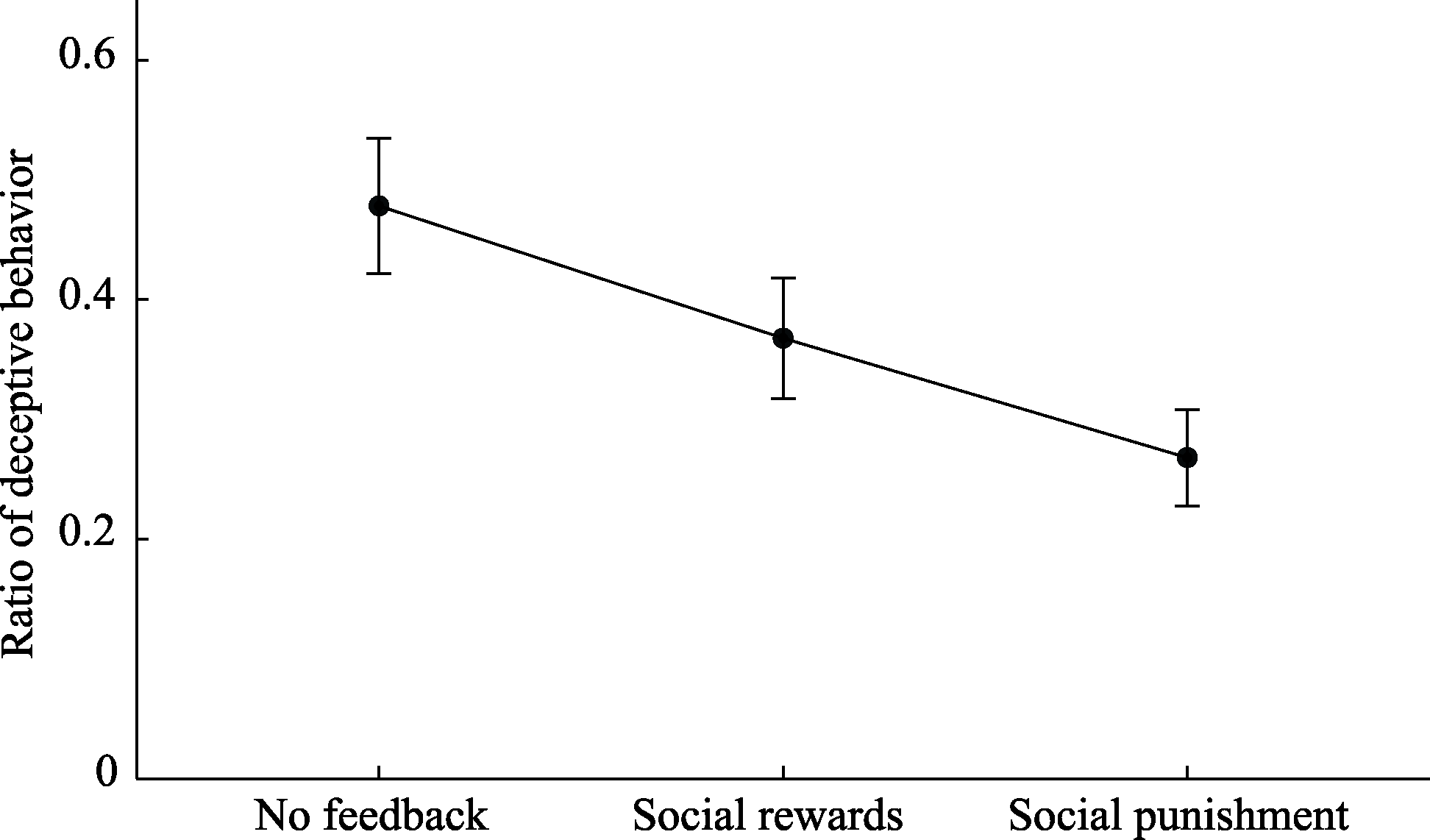
Figure 4. Deception rates in the next trial after participants received social reward and punishment feedback compared to the deception rates under the no feedback condition.

Figure 5. The left column shows the posterior probability density distributions of the four DDM parameters under different reward and punishment conditions. From top to bottom, the parameters are drift rate (v), boundary height (α), starting point bias (z), and non-decision time (τ). The orange line represents the no reward or punishment condition, the green line represents the social reward and punishment condition, and the blue line represents the monetary reward and punishment condition. The right column shows the corresponding posterior trace plots for each model parameter. Color figures are available in the electronic version, and the same applies hereafter.

Figure 9. The left column shows the posterior probability density distributions of the four parameters of the DDM under different reward and punishment conditions. From top to bottom, these are the drift rate (v), boundary height (α), starting point bias (z), and non-decision time (τ). The orange line represents the no reward and punishment condition, the green line represents the social reward and punishment condition, and the blue line represents the monetary reward and punishment condition. The right column shows the corresponding posterior trace plots for each model parameter.

Figure 10. Deception rates of proself and prosocial individuals under different reward and punishment conditions. The red solid circles represent the mean for each condition, while each semi-transparent circle represents the deception rate of each participant. The symmetric shapes on both sides indicate the probability distribution of the deception rate.
| Outcome Variable | Predictor Variable | Overall Fit Indicators | Regression Coefficient Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | F | β | t | ||
| Reputation Concern | 0.10 | 13.64*** | |||
| Social Rewards and Punishments | 0.88 | 4.50*** | |||
| Social Value Orientation | 0.82 | 3.99*** | |||
| Social Rewards × Social Value Orientation | 0.90 | 2.18* | |||
| Deceptive Behavior | 0.27 | 35.82*** | |||
| Reputation Concern | −0.06 | −7.79*** | |||
| Social Rewards and Punishments | −0.05 | −1.83 | |||
| Social Value Orientation | −0.20 | −6.48*** | |||
| Social Rewards × Social Value Orientation | −0.03 | −0.45 | |||
Table 1 Results of the moderation analysis of social value orientation.
| Outcome Variable | Predictor Variable | Overall Fit Indicators | Regression Coefficient Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | F | β | t | ||
| Reputation Concern | 0.10 | 13.64*** | |||
| Social Rewards and Punishments | 0.88 | 4.50*** | |||
| Social Value Orientation | 0.82 | 3.99*** | |||
| Social Rewards × Social Value Orientation | 0.90 | 2.18* | |||
| Deceptive Behavior | 0.27 | 35.82*** | |||
| Reputation Concern | −0.06 | −7.79*** | |||
| Social Rewards and Punishments | −0.05 | −1.83 | |||
| Social Value Orientation | −0.20 | −6.48*** | |||
| Social Rewards × Social Value Orientation | −0.03 | −0.45 | |||

Figure 11. The left column shows the posterior probability density distributions of the four DDM parameters under different reward and punishment conditions. From top to bottom, they are the drift rate (v), boundary height (α), starting point bias (z), and non-decision time (τ). The orange line represents the no reward/punishment condition, the green line represents the social reward/punishment condition, and the blue line represents the monetary reward/punishment condition. The right column shows the posterior trace plots for the corresponding model parameters.
| [1] | Allingham, M. G., & Sandmo, A. (1972). Income tax evasion: A theoretical analysis. Journal of Public Economics, 1(3-4), 323-338. |
| [2] | Balliet, D., Parks, C., & Joireman, J. (2009). Social value orientation and cooperation in social dilemmas: A meta-analysis. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 12(4), 533-547. |
| [3] |
Balliet, D., & Van Lange, P. A. (2013). Trust, conflict, and cooperation: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 139(5), 1090-1112.
doi: 10.1037/a0030939 pmid: 23231532 |
| [4] | Baumeister, R. F., Bratslavsky, E., Finkenauer, C., & Vohs, K. D. (2001). Bad is stronger than good. Review of General Psychology, 5(4), 323-370. |
| [5] | Becker, G. S. (1968). Crime and punishment: An economic approach. Journal of Political Economy, 76(2), 169-217. |
| [6] | Behnk, S., Barreda-Tarrazona, I., & Garcia-Gallego, A. (2018). Punishing liars-How monitoring affects honesty and trust. PLoS One, 13(10), e0205420. |
| [7] | Berman, J. Z., Levine, E. E., Barasch, A., & Small, D. A. (2015). The Braggart's dilemma: On the social rewards and penalties of advertising prosocial behavior. Journal of Marketing Research, 52(1), 90-104. |
| [8] | Beston, P. (2019). The effect of social rewards and punishments on learning and cooperative decision-making [Unpublished master’s thesis]. Bangor University, United Kingdom. |
| [9] | Boutet, I., LeBlanc, M., Chamberland, J. A., & Collin, C. A. (2021). Emojis influence emotional communication, social attributions, and information processing. Computers in Human Behavior, 119, 106722. |
| [10] | Brady, W. J., Wills, J. A., Jost, J. T., Tucker, J. A., & Van Bavel, J. J. (2017). Emotion shapes the diffusion of moralized content in social networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(28), 7313-7318. |
| [11] |
Cameron, C. D., & Payne, B. K. (2011). Escaping affect: How motivated emotion regulation creates insensitivity to mass suffering. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100(1), 1-15.
doi: 10.1037/a0021643 pmid: 21219076 |
| [12] | Carr, Z. M., Solbu, A., & Frank, M. G. (2019). Why methods matter:Approaches to the study of deception and considerations for the future. In T. Docan-Morgan (Ed.), The Palgrave Handbook of deceptive communication (pp. 267-286). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. |
| [13] | Cherbonnier, A., & Michinov, N. (2021). The recognition of emotions beyond facial expressions: Comparing emoticons specifically designed to convey basic emotions with other modes of expression. Computers in Human Behavior, 118, 106689. |
| [14] | Cinyabuguma, M., Page, T., & Putterman, L. (2005). Cooperation under the threat of expulsion in a public goods experiment. Journal of Public Economics, 89(8), 1421-1435. |
| [15] | De Cremer, D., & Tyler, T. R. (2005). Managing group behavior:The interplay between procedural justice, sense of self, and cooperation. In M. P. Zanna (Ed.), Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, (Vol. 37, pp. 151-218). Elsevier Academic Press. |
| [16] | De Cremer, D., & Van Lange, P. A. (2001). Why prosocials exhibit greater cooperation than proselfs: The roles of social responsibility and reciprocity. European Journal of Personality, 15(S1), S5-S18. |
| [17] |
Debey, E., Ridderinkhof, R. K., De Houwer, J., De Schryver, M., & Verschuere, B. (2015). Suppressing the truth as a mechanism of deception: Delta plots reveal the role of response inhibition in lying. Consciousness and Cognition, 37, 148-159.
doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2015.09.005 pmid: 26397036 |
| [18] | Deci, E. L. (1971). Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 18(1), 105-115. |
| [19] |
Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., & Ryan, R. M. (1999). A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 125(6), 627-668.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.125.6.627 pmid: 10589297 |
| [20] |
Depaulo, B. M., Lindsay, J. J., Malone, B. E., Muhlenbruck, L., Charlton, K., & Cooper, H. (2003). Cues to deception. Psychological Bulletin, 129(1), 74-118.
pmid: 12555795 |
| [21] |
Eisenberger, N. I., Lieberman, M. D., & Williams, K. D. (2003). Does rejection hurt? An fMRI study of social exclusion. Science, 302(5643), 290-292.
doi: 10.1126/science.1089134 pmid: 14551436 |
| [22] | Ellingsen, T., & Johannesson, M. (2008). Pride and Prejudice: The human side of incentive theory. American Economic Review, 98(3), 990-1008. |
| [23] |
Feinberg, M., Willer, R., & Schultz, M. (2014). Gossip and ostracism promote cooperation in groups. Psychological Science, 25(3), 656-664.
doi: 10.1177/0956797613510184 pmid: 24463551 |
| [24] | Fischer, B., & Herbert, C. (2021). Emoji as affective symbols: Affective judgments of emoji, emoticons, and human faces varying in emotional content. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 645173. |
| [25] |
Flynn, F. J., Reagans, R. E., Amanatullah, E. T., & Ames, D. R. (2006). Helping one's way to the top: Self-monitors achieve status by helping others and knowing who helps whom. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91(6), 1123-1137.
pmid: 17144769 |
| [26] | Frey, B. S., & Jegen, R. (2001). Motivation crowding theory. Journal of Economic Surveys, 15(5), 589-611. |
| [27] | Gächter, S., & Herrmann, B. (2009). Reciprocity, culture and human cooperation: Previous insights and a new cross-cultural experiment. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1518), 791-806. |
| [28] |
Gino, F., & Pierce, L. (2009). Dishonesty in the name of equity. Psychological Science, 20(9), 1153-1160.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02421.x pmid: 19674386 |
| [29] |
Gintis, H. (2000). Strong reciprocity and human sociality. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 206(2), 169-179.
pmid: 10966755 |
| [30] | Gneezy, U. (2005). Deception: The role of consequences. American Economic Review, 95(1), 384-394. |
| [31] |
Greene, J. D., Morelli, S. A., Lowenberg, K., Nystrom, L. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2008). Cognitive load selectively interferes with utilitarian moral judgment. Cognition, 107(3), 1144-1154.
pmid: 18158145 |
| [32] | Grosch, K., & Rau, H. A. (2017). Gender differences in honesty: The role of social value orientation. Journal of Economic Psychology, 62, 258-267. |
| [33] |
Guala, F. (2012). Reciprocity: Weak or strong? What punishment experiments do (and do not) demonstrate. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 35(1), 1-15.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X11000069 pmid: 22289303 |
| [34] | Hand, C. J., Kennedy, A., Filik, R., Pitchford, M., & Robus, C. M. (2023). Emoji identification and emoji effects on sentence emotionality in ASD-diagnosed adults and neurotypical controls. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 53(6), 2514-2528. |
| [35] |
Hardy, C. L., & Van Vugt, M. (2006). Nice guys finish first: The competitive altruism hypothesis. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 32(10), 1402-1413.
pmid: 16963610 |
| [36] | Jin, Y. C., Deng, C. L., Wu, P., Lin, X., Zheng, P. X., & An, J. X. (2022). Emoji image symbol’s social function and application. Advances in Psychological Science, 30(5), 1062-1077. |
| [37] | Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. Psychological Perspectives on the Self, 1(1), 231-262. |
| [38] | Karlan, D., & Mcconnell, M. A. (2014). Hey look at me: The effect of giving circles on giving. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 106, 402-412. |
| [39] | Kaushik, M., Singh, V., & Chakravarty, S. (2022). Experimental evidence of the effect of financial incentives and detection on dishonesty. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 2680. |
| [40] |
Kaye, L. K., Malone, S. A., & Wall, H. J. (2017). Emojis: Insights, affordances, and possibilities for psychological science. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(2), 66-68.
doi: S1364-6613(16)30178-4 pmid: 28107838 |
| [41] | Kaye, L. K., Wall, H. J., & Malone, S. A. (2016). “Turn that frown upside-down”: A contextual account of emoticon usage on different virtual platforms. Computers in Human Behavior, 60, 463-467. |
| [42] |
Kim, J., & Jeong, B. (2020). Expecting social punishment facilitates control over a decision under uncertainty by recruiting medial prefrontal cortex. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 15(11), 1260-1270.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa145 pmid: 33104801 |
| [43] |
Kohls, G., Perino, M. T., Taylor, J. M., Madva, E. N., Cayless, S. J., Troiani, V., … Schultz, R. T. (2013). The nucleus accumbens is involved in both the pursuit of social reward and the avoidance of social punishment. Neuropsychologia, 51(11), 2062-2069.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.07.020 pmid: 23911778 |
| [44] |
Kringelbach, M. L., & Rolls, E. T. (2003). Neural correlates of rapid reversal learning in a simple model of human social interaction. NeuroImage, 20(2), 1371-1383.
pmid: 14568506 |
| [45] |
Kujawa, A., Proudfit, G. H., Kessel, E. M., Dyson, M., Olino, T., & Klein, D. N. (2015). Neural reactivity to monetary rewards and losses in childhood: Longitudinal and concurrent associations with observed and self-reported positive emotionality. Biological Psychology, 104, 41-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.11.008 pmid: 25433097 |
| [46] | Leary, M. R., & Kowalski, R. M. (1990). Impression management: A literature review and two-component model. Psychological Bulletin, 107(1), 34-47. |
| [47] | Leimar, O., & Hammerstein, P. (2001). Evolution of cooperation through indirect reciprocity. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 268(1468), 745-753. |
| [48] | Li, J., Sun, Y., Yang, Z. L., & Zhong, Y. P. (2020). Social value orientation modulates the processing of social rewards for self: Evidence from ERPs study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(6), 786-800. |
| [49] | Li, S. J., Tang, Y. Y., & Zhang, D. D. (2024). Neural mechanism of monetary and social reward processing in healthy and depressed populations. Journal of Psychological Science, 47(6), 1317-1327. |
| [50] | Liu, C. J., & Hao, F. (2011). Social value orientation and cooperation in asymmetric social dilemmas. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 43(4), 432-441. |
| [51] | Lv, F. Y., Tan, J. B., Xu, P. F., Xiong, X. L., Jin, Z. H., & Gao, D. G. (2021). The social reward and the neurocognitive mechanism of social reward processing. Chinese Journal of Applied Psychology, 27(3), 189-203. |
| [52] |
Matyjek, M., Meliss, S., Dziobek, I., & Murayama, K. (2020). A multidimensional view on social and non-social rewards. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, 818.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00818 pmid: 32973574 |
| [53] | Mazar, N., Amir, O., & Ariely, D. (2008). The dishonesty of honest people: A theory of self-concept maintenance. Journal of Marketing Research, 45(6), 633-644. |
| [54] | Mazar, N., & Ariely, D. (2006). Dishonesty in everyday life and its policy implications. Journal of Public Policy & Marketing, 25(1), 117-126. |
| [55] | Milinski, M., Semmann, D., & Krambeck, H. J. (2002). Reputation helps solve the ‘tragedy of the commons’. Nature, 415(6870), 424-426. |
| [56] | Milinski, M., Semmann, D., Krambeck, H. J., & Marotzke, J. (2006). Stabilizing the Earth's climate is not a losing game: Supporting evidence from public goods experiments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(11), 3994-3998. |
| [57] | Mulder, L. B., van Dijk, E., de Cremer, D., & Wilke, H. A. M. (2006). Undermining trust and cooperation: The paradox of sanctioning systems in social dilemmas. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 42(2), 147-162. |
| [58] | Murphy, R. O., Ackermann, K. A., & Handgraaf, M. (2011). Measuring social value orientation. Judgment and Decision Making, 6(8), 771-781. |
| [59] | Nagin, D. S., & Pogarsky, G. (2003). An experimental investigation of deterrence: Cheating, self-serving bias, and impulsivity. Criminology, 41(1), 167-194. |
| [60] | Nowak, M. A., & Sigmund, K. (2005). Evolution of indirect reciprocity. Nature, 437(7063), 1291-1298. |
| [61] | Peirce, J. W. (2009). Generating stimuli for neuroscience using PsychoPy. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 2, 343. |
| [62] |
Pfeiffer, T., Tran, L., Krumme, C., & Rand, D. G. (2012). The value of reputation. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 9(76), 2791-2797.
pmid: 22718993 |
| [63] | Ramirez-Marin, J. Y., & Shafa, S. (2018). Social rewards: The basis for collaboration in honor cultures. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management, 25(1), 53-69. |
| [64] |
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The diffusion decision model: Theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873-922.
doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.12-06-420 pmid: 18085991 |
| [65] | Romano, A., Balliet, D., Yamagishi, T., & Liu, J. H. (2017). Parochial trust and cooperation across 17 societies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(48), 12702-12707. |
| [66] | Rosenbaum, S. M., Billinger, S., & Stieglitz, N. (2014). Let’s be honest: A review of experimental evidence of honesty and truth-telling. Journal of Economic Psychology, 45, 181-196. |
| [67] | Rozin, P., & Royzman, E. B. (2001). Negativity bias, negativity dominance, and contagion. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 5(4), 296-320. |
| [68] |
Russell, Y. I., Call, J., & Dunbar, R. I. M. (2008). Image scoring in great apes. Behavioural Processes, 78(1), 108-111.
pmid: 18068313 |
| [69] |
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68-78.
doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.55.1.68 pmid: 11392867 |
| [70] |
Shenhav, A., Botvinick, M. M., & Cohen, J. D. (2013). The expected value of control: An integrative theory of anterior cingulate cortex function. Neuron, 79(2), 217-240.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.007 pmid: 23889930 |
| [71] |
Shore, D. M., & Heerey, E. A. (2011). The value of genuine and polite smiles. Emotion, 11(1), 169-174.
doi: 10.1037/a0022601 pmid: 21401236 |
| [72] | Simpson, B., & Willer, R. (2008). Altruism and indirect reciprocity: The interaction of person and situation in prosocial behavior. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71(1), 37-52. |
| [73] |
Somerville, L. H., Jones, R. M., Ruberry, E. J., Dyke, J. P., Glover, G., & Casey, B. J. (2013). The medial prefrontal cortex and the emergence of self-conscious emotion in adolescence. Psychological Science, 24(8), 1554-1562.
doi: 10.1177/0956797613475633 pmid: 23804962 |
| [74] | Sommerfeld, R. D., Krambeck, H. J., Semmann, D., & Milinski, M. (2007). Gossip as an alternative for direct observation in games of indirect reciprocity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(44), 17435-17440. |
| [75] | Sperber, D., & Baumard, N. (2012). Moral reputation: An evolutionary and cognitive perspective. Mind & Language, 27(5), 495-518. |
| [76] |
Spreckelmeyer, K. N., Krach, S., Kohls, G., Rademacher, L., Irmak, A., Konrad, K., ... Gründer, G. (2009). Anticipation of monetary and social reward differently activates mesolimbic brain structures in men and women. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4(2), 158-165.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsn051 pmid: 19174537 |
| [77] | Steinel, W. (2015). Social value orientation and deception: Are proselfs liars? Current Opinion in Psychology, 6, 211-215. |
| [78] | Tamir, D. I., & Mitchell, J. P. (2012). Disclosing information about the self is intrinsically rewarding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(21), 8038-8043. |
| [79] | Tamir, D. I., Zaki, J., & Mitchell, J. P. (2015). Informing others is associated with behavioral and neural signatures of value. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 144(6), 1114-1123. |
| [80] | Trivers, R. L. (1971). The evolution of reciprocal altruism. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 46(1), 35-57. |
| [81] |
Vabba, A., Porciello, G., Panasiti, M. S., & Aglioti, S. M. (2022). Interoceptive influences on the production of self-serving lies in reputation risk conditions. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 177, 34-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2022.04.001 pmid: 35413427 |
| [82] | Van Kleef, G. A. (2009). How emotions regulate social life: The emotions as social information (EASI) model. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 18(3), 184-188. |
| [83] | Van Lange, P. A. (1999). The pursuit of joint outcomes and equality in outcomes: An integrative model of social value orientation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77(2), 337-349. |
| [84] | Walther, J. B. (1992). Interpersonal effects in computer-mediated interaction: A relational perspective. Human Communication Research, 19(1), 52-90. |
| [85] | Wang, D., Liu, T., & Shi, J. (2017). Development of monetary and social reward processes. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 11128. |
| [86] |
Wang, Z., Li, Q., Nie, L., & Zheng, Y. (2020). Neural dynamics of monetary and social reward processing in social anhedonia. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 15(9), 991-1003.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa128 pmid: 32945882 |
| [87] | Wu, J., Balliet, D., & van Lange, P. A. M. (2016). Reputation management: Why and how gossip enhances generosity. Evolution & Human Behavior, 37(3), 193-201. |
| [88] |
Yuan, B., Wang, X. P., Yin, J., & Li, W. Q. (2023). The role of cross-situational stimulus generalization in the formation of trust towards face: A perspective based on direct and observational learning. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(7), 1099-1114.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01099 |
| [89] |
Zhang, Y. H., Li, H., & Wu, Y. (2020). The application of computational modelling in the studies of moral cognition. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(7), 1042-1055.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01042 |
| [90] | Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., Yuan, S., Guo, F. B., & Wang, Y. W. (2015). Psychometric analysis of the SVO slider measure in Chinese cultural context. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 13(3), 404-409. |
| [91] |
Zhu, L., Jenkins, A. C., Set, E., Scabini, D., Knight, R. T., Chiu, P. H., King-Casas, B., & Hsu, M. (2014). Damage to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex affects tradeoffs between honesty and self-interest. Nature Neuroscience, 17(10), 1319-1321.
doi: 10.1038/nn.3798 pmid: 25174003 |
| [1] | CHEN Peiqi, ZHANG Yinling, HU Xinmu, WANG Jing, MAI Xiaoqin. The effect of social value orientation on third-party altruistic behaviors in children aged 10-12 years: The role of emotion [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(8): 1255-1269. |
| [2] | ZHAN Youlong, XIAO Xiao, TAN Qianbao, LI Jin, ZHONG Yiping. Influence of reputational concern and social distance on moral decision-making under the harmful dilemma: Evidence from behavioral and ERPs study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(6): 613-627. |
| [3] | FAN Wei, REN Mengmeng, ZHANG Wenjie, ZHONG Yiping. The impact of feedback on self-deception: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 481-496. |
| [4] | LI Jin, SUN Yu, YANG Zilu, ZHONG Yiping. Social value orientation modulates the processing of social rewards for self: Evidence from ERPs study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(6): 786-800. |
| [5] | FAN Wei, REN Mengmeng, XIAO Junze, JIAN Zengdan, DU Xiaoming, FU Xiaolan. The influence of shame on deceptive behavior: The role of self-control [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(9): 992-1006. |
| [6] | ZHONG Luojin, RU Taotao, FAN Meng, MO Lei. The effect of cognitive vagueness and motivation on conscious and unconscious self-deception [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(12): 1330-1340. |
| [7] | CUI Liying, HE Xing, LUO Junlong, HUANG Xiaojiao, CAO Weijia, CHEN Xiaomei. The effects of moral punishment and relationship punishment on junior middle school students’ cooperation behaviors in public goods dilemma [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(10): 1322-1333. |
| [8] | FAN Wei, ZHONG Yiping, LI Huiyun, MENG Chuyi, YOU Chang, FU Xiaolan. The influence of self-control in the perceived of deception and deception [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(7): 845-856. |
| [9] | FU Xinyuan; LU Zhiyuan; KOU Yu. Effects of a Stranger’s Presence and Behavior on Moral Hypocrisy [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(8): 1058-1066. |
| [10] | LU Hui-Jing. Self-Deception: Deceiving Yourself to Better Deceive Others [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2012, 44(9): 1265-1278. |
| [11] | LIU Chang-Jiang,HAO Fang. Social Value Orientation and Cooperation in Asymmetric Social Dilemmas [J]. , 2011, 43(04): 432-441. |
| [12] | WANG Pei,CHEN Li. The Effects of Sanction and Social Value Orientation on Trust and Cooperation in Public Goods Dilemmas [J]. , 2011, 43(01): 52-64. |
| [13] | ZHANG Li-Jin,WU Nan,ZHENG Yan. The Training Effects of Different Linguistic Interference on Young Chinese Children’s Performance on A Theory of Mind Task [J]. , 2008, 40(07): 819-827. |
| [14] | Shi-Bing,Su-Yanjie. Children’s Deceptive Behaviors And Related Social Characters [J]. , 2007, 39(01): 111-117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||