

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 1059-1070.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.01059
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
XING Qiang( ), WU Xiao, WANG Jiawei, ZHANG Zhonglu
), WU Xiao, WANG Jiawei, ZHANG Zhonglu
Received:2020-06-25
Published:2021-10-25
Online:2021-08-23
Contact:
XING Qiang
E-mail:Qiang_xingpsy@126.com
Supported by:XING Qiang, WU Xiao, WANG Jiawei, ZHANG Zhonglu. (2021). The influence of the matching of modality presentation mode and perceptual learning style on the bidialectal switching cost of Cantonese-Mandarin. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(10), 1059-1070.
| Channel presentation | Familiarity | Consistency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | |
| Auditory Presentation | 6.58 | 0.35 | 6.17 | 0.68 |
| Visual presentation | 6.63 | 0.42 | 6.32 | 0.46 |
Table 1 Familiarity and consistency of stimuli under different channel presentation modes
| Channel presentation | Familiarity | Consistency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | |
| Auditory Presentation | 6.58 | 0.35 | 6.17 | 0.68 |
| Visual presentation | 6.63 | 0.42 | 6.32 | 0.46 |
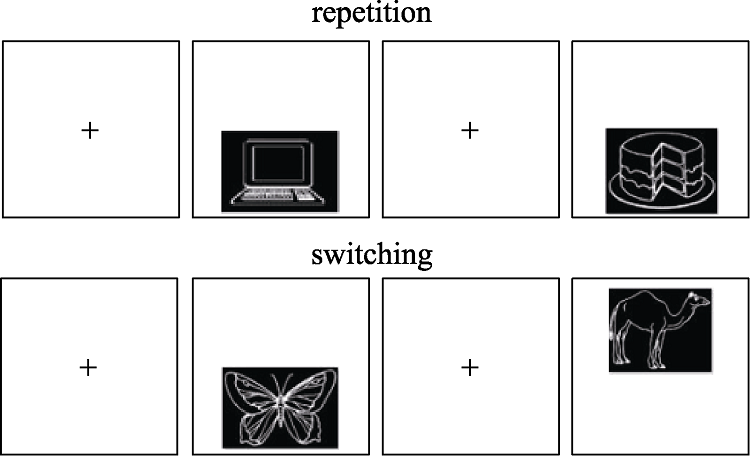
Figure 1. Visual naming task. In the case of repetition, participants named the two pictures in Mandarin; in the case of switching, participants named the former picture in Mandarin and the latter one in Cantonese.
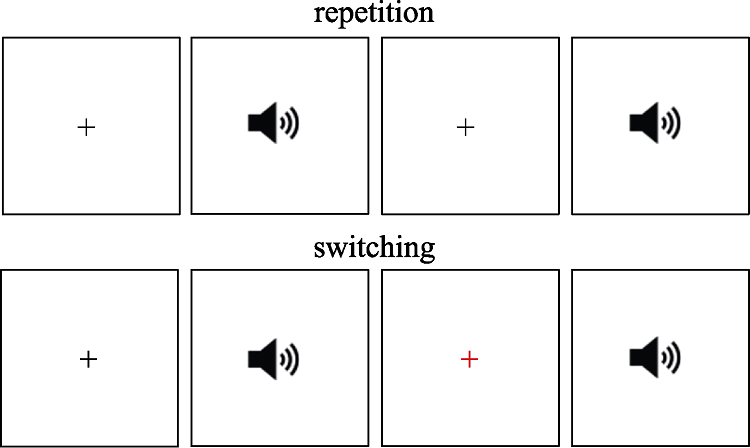
Figure 2. Auditory naming task. In the case of repetition, participants named the first and second audio in Mandarin; in the case of switching, participants named the first audio in Mandarin and the second audio in Cantonese.
| Language type | Task type | Auditory Presentation | Visual presentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Rate | Switching cost | Reaction Time | Switching cost | Accuracy Rate | Switching cost | Reaction Time | Switching cost | ||
| Cantonese | Repeat tasks | 0.72 ± 0.10 | -0.01 | 2503 ± 519 | 67 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | -0.04 | 1383 ± 244 | -3 |
| Switching tasks | 0.71 ± 0.12 | 2570 ± 381 | 0.91 ± 0.08 | 1380 ± 218 | |||||
| Mandarin | Repeat tasks | 0.73 ± 0.11 | -0.04 | 2358 ± 304 | 126 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | -0.05 | 1351 ± 258 | -20 |
| Switching tasks | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 2484 ± 351 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 1331 ± 249 | |||||
Table 2 The mean, standard deviation (M ± SD), and switching cost of the dependent variables under different experimental conditions
| Language type | Task type | Auditory Presentation | Visual presentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Rate | Switching cost | Reaction Time | Switching cost | Accuracy Rate | Switching cost | Reaction Time | Switching cost | ||
| Cantonese | Repeat tasks | 0.72 ± 0.10 | -0.01 | 2503 ± 519 | 67 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | -0.04 | 1383 ± 244 | -3 |
| Switching tasks | 0.71 ± 0.12 | 2570 ± 381 | 0.91 ± 0.08 | 1380 ± 218 | |||||
| Mandarin | Repeat tasks | 0.73 ± 0.11 | -0.04 | 2358 ± 304 | 126 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | -0.05 | 1351 ± 258 | -20 |
| Switching tasks | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 2484 ± 351 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 1331 ± 249 | |||||
| Perceptual learning style | Channel presentation | Cantonese | Mandarin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | ||
| Auditory type | Auditory Presentation | 2226 ± 205 | 2317 ± 292 | 91 | 2102 ± 228 | 2256 ± 301 | 154 |
| Visual presentation | 1287 ± 201 | 1336 ± 237 | 49 | 1271 ± 185 | 1293 ± 248 | 22 | |
| Visual type | Visual presentation | 2542 ± 319 | 2561 ± 384 | 19 | 2466 ± 281 | 2493 ± 245 | 27 |
| Auditory Presentation | 1158 ± 208 | 1157 ± 267 | -1 | 1084 ± 203 | 1105 ± 214 | 21 | |
Table 4 The mean, standard deviation (M ± SD), and switching cost of reaction time were measured under different experimental conditions
| Perceptual learning style | Channel presentation | Cantonese | Mandarin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | ||
| Auditory type | Auditory Presentation | 2226 ± 205 | 2317 ± 292 | 91 | 2102 ± 228 | 2256 ± 301 | 154 |
| Visual presentation | 1287 ± 201 | 1336 ± 237 | 49 | 1271 ± 185 | 1293 ± 248 | 22 | |
| Visual type | Visual presentation | 2542 ± 319 | 2561 ± 384 | 19 | 2466 ± 281 | 2493 ± 245 | 27 |
| Auditory Presentation | 1158 ± 208 | 1157 ± 267 | -1 | 1084 ± 203 | 1105 ± 214 | 21 | |
| Perceptual learning Style | Channel presentation | Cantonese | Mandarin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | ||
| Auditory type | Auditory Presentation | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.73 ± 0.18 | 0 | 0.81 ± 0.11 | 0.77 ± 0.20 | -0.04 |
| Visual presentation | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 0.96 ± 0.08 | -0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | -0.03 | |
| Visual type | Visual presentation | 0.74 ± 0.16 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | -0.03 | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 0.69 ± 0.16 | -0.07 |
| Auditory Presentation | 0.97 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.10 | -0.07 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | 0.90 ± 0.10 | -0.05 | |
Table 3 The mean accuracy, the standard deviation (M ± SD), and the switching cost under different experimental conditions
| Perceptual learning Style | Channel presentation | Cantonese | Mandarin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | Repetitive tasks | Switching tasks | Switching cost | ||
| Auditory type | Auditory Presentation | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.73 ± 0.18 | 0 | 0.81 ± 0.11 | 0.77 ± 0.20 | -0.04 |
| Visual presentation | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 0.96 ± 0.08 | -0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | -0.03 | |
| Visual type | Visual presentation | 0.74 ± 0.16 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | -0.03 | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 0.69 ± 0.16 | -0.07 |
| Auditory Presentation | 0.97 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.10 | -0.07 | 0.95 ± 0.06 | 0.90 ± 0.10 | -0.05 | |
| Experimental treatment | Accuracy | Reaction Time |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | 0.83 ± 0.14 | 1550 ± 557 |
| Random Group | 0.81 ± 0.13 | 2175 ± 551 |
Table 5 The mean and standard deviation (M ± SD) of the dependent variables under different experimental conditions
| Experimental treatment | Accuracy | Reaction Time |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | 0.83 ± 0.14 | 1550 ± 557 |
| Random Group | 0.81 ± 0.13 | 2175 ± 551 |
| [1] |
Bonfieni M., Branigan H. P., Pickering M. J., & Sorace A. (2019). Language experience modulates bilingual language control: The effect of proficiency, age of acquisition, and exposure on language switching. Acta Psychologica, 193, 160-170.
doi: S0001-6918(17)30590-5 pmid: 30640064 |
| [2] |
Chang X., Bai H., & Wang P. (2017). The influenced factors of bilinguals’ language switching costs. Advances in Psychological Science, 25(9), 1469-1478.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2017.01469 URL |
| [3] | Chen B. G., & Peng D. L. (2001). The time course of graphic, phonological and semantic information processing in Chinese character recognition. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 33(1), 1-6. |
| [4] |
Costa A., & Santesteban M. (2004). Lexical access in bilingual speech production: Evidence from language switching in highly proficient bilinguals and l2 learners. Journal of Memory and Language, 50(4), 491-511.
doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2004.02.002 URL |
| [5] |
Costa A., Santesteban M., & Ivanova I. (2006). How do highly proficient bilinguals control their lexicalization process? Inhibitory and language-specific selection mechanisms are both functional. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32(5), 1057-1074.
doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.32.5.1057 URL |
| [6] |
Declerck M., Stephan D. N., Koch I., & Philipp A. M. (2015). The other modality: Auditory stimuli in language switching. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 27(6), 685-691.
doi: 10.1080/20445911.2015.1026265 URL |
| [7] | Derakhshan A., & Shakki F. (2018). An investigation into the relationship between Iranian EFL high- and low-proficient learners and their learning styles. SAGE Open, 8, 2158244018809408. |
| [8] | Ding D. Q., & Luo Y. M. (2009). The effect of cognitive style and information' s presentation format on cognitive load. Psychological Exploration, 29(3), 37-40+68. |
| [9] |
Faul F., Erdfelder E., Buchner A., & Lang A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41, 1149-1160.
doi: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149 URL |
| [10] |
Filippi R., Karaminis T., & Thomas M. S. C. (2014). Language switching in bilingual production: Empirical data and computational modelling. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 17(2), 294-315.
doi: 10.1017/S1366728913000485 URL |
| [11] | Guo A. P. (2004). The effect of audio processing on English vocabulary retention. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology (Social Science Edition), 22(3), 80-82. |
| [12] |
Hernandez A. E., & Kohnert K. J. (2015). Investigations into the locus of language-switching costs in older adult bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 18(1), 51-64.
doi: 10.1017/S136672891300045X URL |
| [13] | Kinsella K. (1995). Perceptual learning preferences survey. In J. M. Reid (Ed.), Learning styles in the ESL/EFL classroom (pp. 221e238). Boston: Heinle and Heinle. |
| [14] |
Leahy W., & Sweller J. (2011). Cognitive load theory, modality of presentation and the transient information effect. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 25(6), 943-951.
doi: 10.1002/acp.v25.6 URL |
| [15] |
Liu X. Y., He C. D., Chen J., & Deng Q. L. (2015). The bilingual cognitive control mechanism of highly proficient Cantonese-Mandarin speakers: Evidence from a dual-task switching paradigm. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(4), 439-454.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00439 URL |
| [16] | Liu Y. (2008). Error types and sequencing of Putonghua characters by Cantonese area: a quantitative analysis. Applied Linguistics, 66(2), 67-71. |
| [17] | Liu Y. (2014). An effect of perceptual learning style on the modality effect (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Hebei University, China. |
| [18] | Mayer R. E. (2009). Multimedia learning (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [19] | O'Brien L. (1989). Learning styles: Make the student aware. NASSP Bulletin, 73(519), 85-89. |
| [20] |
Wang F. X., Xie H. P., & Li H. (2016). Visual text or narration? Meta-analysis of the modality effect in multimedia learning. Advances in Psychological Science, 24(3), 335-350.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00335 URL |
| [21] | Zhang Q. F, Yang Y, F. (2003). The determiners of picture-naming latency. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 35(4), 447-454. |
| [22] |
Zhang J. J., & Wang Y. (2012). The proficient Chinese-English bilinguals’ mechanism of language switching in phrase level. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(2), 166-178.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.00166 URL |
| [23] |
Zhang J. J., & Zhang F. L. (2010). The asymmetric effect of bilingualism and diglossia on picture naming and picture classification. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 42(4), 452-466.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2010.00452 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||