

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 1099-1114.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01099
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Bo( ), WANG Xiaoping, YIN Jun, LI Weiqiang(
), WANG Xiaoping, YIN Jun, LI Weiqiang( )
)
Received:2021-12-30
Published:2023-07-25
Online:2023-04-21
Contact:
YUAN Bo, E-mail: yuanbopsy@gmail.com;LI Weiqiang, E-mail: liweiqiang@nbu.edu.cn
YUAN Bo, WANG Xiaoping, YIN Jun, LI Weiqiang. (2023). The role of cross-situational stimulus generalization in the formation of trust towards face: A perspective based on direct and observational learning. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(7), 1099-1114.

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the construction process of face stimulation. (A) The original faces and 6 pre-rated faces were morphed in 11% increments. To avoid too similar with each other, only the faces with two increments along the same continuum were selected. (B) The original face that was eventually used in the experiment and the corresponding morphed face.

Figure 4. (A) Regression analysis of face similarity and ratio of selected morphed faces under different face association types; (B) Posterior probability distribution of fair/unfair face association × face similarity regression coefficient and corresponding confidence interval CIs.

Figure 5. Probability density distribution of four parameters of DDM under different face connection types. (A) represents the table drift rate v; (B) represents the boundary height α; (C) represents the boundary starting point deviation z; (D) represents non-decision time τ.
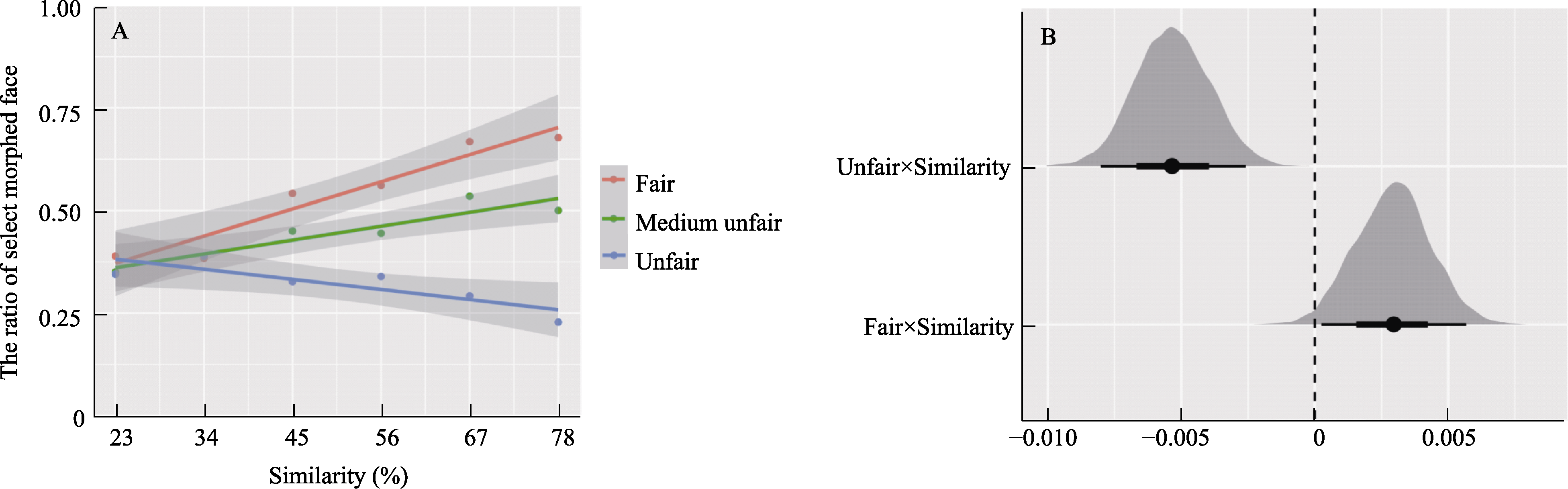
Figure 6. (A) Regression analysis of face similarity and ratio of selected deformable faces under the same face association type; (B) Posterior probability distribution of fair/unfair face association × face similarity regression coefficient and correspo nding confidence interval CIs.

Figure 7. Probability density distribution of four parameters of DDM under different face association types. (A) represents the table drift rate v; (B) represents the boundary height α; (C) represents the boundary starting point deviation z; (D) represents non-decision time τ.

Figure 8. (A) Regression analysis of face similarity and ratio of selected morphed faces under different face association types; (B) Posterior probability distribution of fair/unfair face association × face similarity regression coefficient and corresponding confidence interval CIs.

Figure 9. Probability density distribution of four parameters of DDM under different face connection types. (A) represents the table drift rate v; (B) represents the boundary height α; (C) represents the boundary starting point deviation z; (D) represents non-decision time τ.
| [1] |
Allidina, S., & Cunningham, W. A. (2021). Avoidance begets avoidance: A computational account of negative stereotype persistence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 150(10), 2078-2099.
doi: 10.1037/xge0001037 URL |
| [2] |
Baayen, R. H., Davidson, D. J., & Bates, D. M. (2008). Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for participants and items. Journal of Memory and Language, 59(4), 390-412.
doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005 URL |
| [3] |
Bateson, M., Brilot, B., & Nettle, D. (2011). Anxiety: An evolutionary approach. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 56(12), 707-715.
doi: 10.1177/070674371105601202 URL |
| [4] |
Baumeister, R. F., Bratslavsky, E., Finkenauer, C., & Vohs, K. D. (2001). Bad is stronger than good. Review of General Psychology, 5(4), 323-370.
doi: 10.1037/1089-2680.5.4.323 URL |
| [5] |
Buckholtz, J. W., Asplund, C. L., Dux, P. E., Zald, D. H., Gore, J. C., Jones, O. D., & Marois, R. (2008). The neural correlates of third-party punishment. Neuron, 60(5), 930-940.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.016 pmid: 19081385 |
| [6] | Bürkner, P. C. (2017). Brms: An R package for Bayesian multilevel models using Stan. Journal of Statistical Software, 80(1), 1-28. |
| [7] |
Chang, L. J., & Sanfey, A. G. (2013). Great expectations: Neural computations underlying the use of social norms in decision-making. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8(3), 277-284.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsr094 pmid: 22198968 |
| [8] | Cushman, F., Dreber, A., Wang, Y., & Costa, J. (2009). Accidental outcomes guide punishment in a “trembling hand” game. PloS one, 4(8), e6699. |
| [9] |
Cushman, F., Sheketoff, R., Wharton, S., & Carey, S. (2013). The development of intent-based moral judgment. Cognition, 127(1), 6-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.11.008 pmid: 23318350 |
| [10] | Dayan, P., & Berridge, K. C. (2014). Model-based and model-free Pavlovian reward learning: Revaluation, revision, and revelation. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), 473-492. |
| [11] | de Boeck, P., Bakker, M., Zwitser, R., Nivard, M., Hofman, A., Tuerlinckx, F., & Partchev, I. (2011). The estimation of item response models with the lmer function from the lme4 package in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 39(12), 1-28. |
| [12] |
Dufwenberg, M., & Kirchsteiger, G. (2004). A theory of sequential reciprocity. Games and Economic Behavior, 47(2), 268-298.
doi: 10.1016/j.geb.2003.06.003 URL |
| [13] |
Earley, R. L. (2010). Social eavesdropping and the evolution of conditional cooperation and cheating strategies. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1553), 2675-2686.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0147 URL |
| [14] | Erev, I., & Roth, A. E. (1998). Predicting how people play games: Reinforcement learning in experimental games with unique, mixed strategy equilibria. American Economic Review, 88(4), 848-881. |
| [15] |
Fareri, D. S., Chang, L. J., & Delgado, M. R. (2012). Effects of direct social experience on trust decisions and neural reward circuitry. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 148.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00148 pmid: 23087604 |
| [16] |
FeldmanHall, O., Dunsmoor, J. E., Tompary, A., Hunter, L. E., Todorov, A., & Phelps, E. A. (2018). Stimulus generalization as a mechanism for learning to trust. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(7), 1690-1697.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1800256115 URL |
| [17] |
Forstmann, B. U., Ratcliff, R., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2016). Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: Advantages, applications, and extensions. Annual Review of Psychology, 67(1), 641-666.
doi: 10.1146/psych.2015.67.issue-1 URL |
| [18] |
Frith, C. D., & Frith, U. (2012). Mechanisms of social cognition. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 287-313.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100449 pmid: 21838544 |
| [19] |
Gao, Q. L., & Zhou, Y. (2021). Psychological and neural mechanisms of trust formation: A perspective from computational modeling based on the decision of investor in the trust game. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(1), 178-189.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.00178 URL |
| [20] |
Gao, W., Cao, B., Shan, S., Chen, X., Zhou, D., Zhang, X., & Zhao, D. (2007). The CAS-PEAL large-scale Chinese face database and baseline evaluations. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 38(1), 149-161.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2007.909557 URL |
| [21] |
Gawronski, B., & Quinn, K. A. (2013). Guilty by mere similarity: Assimilative effects of facial resemblance on automatic evaluation. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49(1), 120-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2012.07.016 URL |
| [22] |
Germar, M., Schlemmer, A., Krug, K., Voss, A., & Mojzisch, A. (2014). Social influence and perceptual decision making: A diffusion model analysis. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40(2), 217-231.
doi: 10.1177/0146167213508985 pmid: 24154917 |
| [23] |
Grady, C. L., Hongwanishkul, D., Keightley, M., Lee, W., & Hasher, L. (2007). The effect of age on memory for emotional faces. Neuropsychology, 21(3), 371-380.
doi: 10.1037/0894-4105.21.3.371 pmid: 17484600 |
| [24] |
Johnson, D. J., Hopwood, C. J., Cesario, J., & Pleskac, T. J. (2017). Advancing research on cognitive processes in social and personality psychology: A hierarchical drift diffusion model primer. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(4), 413-423.
doi: 10.1177/1948550617703174 URL |
| [25] |
Kocsor, F., & Bereczkei, T. (2017). First impressions of strangers rely on generalization of behavioral traits associated with previously seen facial features. Current Psychology, 36(3), 385-391.
doi: 10.1007/s12144-016-9427-1 URL |
| [26] |
Kraus, M. W., Chen, S., Lee, V. A., & Straus, L. D. (2010). Transference occurs across group boundaries. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(6), 1067-1073.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2010.05.003 URL |
| [27] | Luo, Q., Huang, L., Hou, Q., Aimaitijiang, R., Zhou, M., Zhou, X., & Chen, S. (2020). Generalization effect of gossip on interpersonal trust. Journal of Psychological Science, 43(1), 165-171. |
| [28] |
Ma, Q., Meng, L., Zhang, Z., Xu, Q., Wang, Y., & Shen, Q. (2015). You did not mean it: Perceived good intentions alleviate sense of unfairness. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 96(3), 183-190.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2015.03.011 pmid: 25863263 |
| [29] |
Mcauliffe, K., Jordan, J. J., & Warneken, F. (2015). Costly third-party punishment in young children. Cognition, 134, 1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2014.08.013 pmid: 25460374 |
| [30] | Milinski, M. (2016). Reputation, a universal currency for human social interactions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1687), 20150100. |
| [31] |
Mineka, S., & Öhman, A. (2002). Phobias and preparedness: The selective, automatic, and encapsulated nature of fear. Biological Psychiatry, 52(10), 927-937.
pmid: 12437934 |
| [32] |
Moretti, L., & Di Pellegrino, G. (2010). Disgust selectively modulates reciprocal fairness in economic interactions. Emotion, 10(2), 169-180.
doi: 10.1037/a0017826 pmid: 20364893 |
| [33] |
Offerman, T. (2002). Hurting hurts more than helping helps. European Economic Review, 46(8), 1423-1437.
doi: 10.1016/S0014-2921(01)00176-3 URL |
| [34] |
Olsson, A., Knapska, E., & Lindström, B. (2020). The neural and computational systems of social learning. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 21(4), 197-212.
doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0276-4 pmid: 32221497 |
| [35] |
Olsson, A., Nearing, K. I., & Phelps, E. A. (2007). Learning fears by observing others: The neural systems of social fear transmission. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 2(1), 3-11.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsm005 pmid: 18985115 |
|
Peirce,, J. W. (2009). Generating stimuli for neuroscience using PsychoPy. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 2, 10.
pmid: 18985115 |
|
| [36] |
Radell, M. L., Sanchez, R., Weinflash, N., & Myers, C. E. (2016). The personality trait of behavioral inhibition modulates perceptions of moral character and performance during the trust game: Behavioral results and computational modeling. PeerJ, 4, e1631.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.1631 URL |
| [37] |
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The diffusion decision model: Theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873-922.
doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.12-06-420 pmid: 18085991 |
| [38] |
Rescorla, R. A. (1976). Stimulus generalization: Some predictions from a model of Pavlovian conditioning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 2(1), 88-96.
doi: 10.1037/0097-7403.2.1.88 URL |
| [39] |
Rescorla, R. A., & Solomon, R. L. (1967). Two-process learning theory: Relationships between Pavlovian conditioning and instrumental learning. Psychological Review, 74(3),151-182.
doi: 10.1037/h0024475 pmid: 5342881 |
|
Rousseau, D. M., Sitkin, S. B., Burt, R. S., & Camerer, C. (1998). Not so different after all: A cross-discipline view of trust. Academy of Management Review, 23(3), 393-404.
doi: 10.5465/amr.1998.926617 URL pmid: 5342881 |
|
| [40] |
Rozin, P., & Royzman, E. B. (2001). Negativity bias, negativity dominance, and contagion. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 5(4), 296-320.
doi: 10.1207/S15327957PSPR0504_2 URL |
| [41] |
Ruff, C. C., & Fehr, E. (2014). The neurobiology of rewards and values in social decision making. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(8), 549-562.
doi: 10.1038/nrn3776 pmid: 24986556 |
| [42] |
Schechtman, E., Laufer, O., & Paz, R. (2010). Negative valence widens generalization of learning. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(31), 10460-10464.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2377-10.2010 pmid: 20685988 |
| [43] |
Shang, J., & Li, Y. (2020). The effects of participants’ sex and the facial trustworthiness of proposers on third-party decision-making in a dictator game. PsyCh Journal, 9(6), 877-884.
doi: 10.1002/pchj.v9.6 URL |
| [44] |
Singer, T., Seymour, B., O'Doherty, J. P., Stephan, K. E., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2006). Empathic neural responses are modulated by the perceived fairness of others. Nature, 439(7075), 466-469.
doi: 10.1038/nature04271 |
| [45] | Son, J.-Y., Bhandari, A., & FeldmanHall, O. (2019). Crowdsourcing punishment: Individuals reference group preferences to inform their own punitive decisions. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 11625. |
| [46] |
Sullivan, J. L., & Transue, J. E. (1999). The psychological underpinnings of democracy: A selective review of research on political tolerance, interpersonal trust, and social capital. Annual Review of Psychology, 50(1), 625-650.
doi: 10.1146/psych.1999.50.issue-1 URL |
| [47] |
Sun, Z., Ye, C., He, Z., & Yu, W. (2020). Behavioral intention promotes generalized reciprocity: Evidence from the dictator game. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 772.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00772 pmid: 32425857 |
| [48] |
Sutter, M. (2007). Outcomes versus intentions: On the nature of fair behavior and its development with age. Journal of Economic Psychology, 28(1), 69-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.joep.2006.09.001 URL |
| [49] |
Todorov, A., Baron, S. G., & Oosterhof, N. N. (2008). Evaluating face trustworthiness: A model based approach. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 3(2), 119-127.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsn009 pmid: 19015102 |
| [50] |
Vaish, A., Hepach, R., & Tomasello, M. (2018). The specificity of reciprocity: Young children reciprocate more generously to those who intentionally benefit them. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 167, 336-353.
doi: S0022-0965(17)30432-0 pmid: 29227851 |
| [51] |
van’t Wout, M., Kahn, R. S., Sanfey, A. G., & Aleman, A. (2006). Affective state and decision-making in the ultimatum game. Experimental Brain Research, 169(4), 564-568.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-006-0346-5 pmid: 16489438 |
| [52] |
Verosky, S. C., & Todorov, A. (2010). Generalization of affective learning about faces to perceptually similar faces. Psychological Science, 21(6), 779-785.
doi: 10.1177/0956797610371965 pmid: 20483821 |
| [53] |
Verosky, S. C., & Todorov, A. (2013). When physical similarity matters: Mechanisms underlying affective learning generalization to the evaluation of novel faces. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49(4), 661-669.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2013.02.004 URL |
| [54] |
Wang, T., Chen, Y., & Lu, J. (2020). The generalization effect in gap evaluation: How large is the gap between you and me? Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(11), 1327-1339.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.01327 URL |
| [55] |
Wiecki, T. V., Sofer, I., & Frank, M. J. (2013). HDDM: Hierarchical Bayesian estimation of the Drift-Diffusion Model in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 14. doi:10.3389/fninf.2013.00014
doi: 10.3389/fninf.2013.00014 pmid: 23935581 |
| [56] |
Willis, J., & Todorov, A. (2006). First impressions: Making up your mind after a 100-ms exposure to a face. Psychological Science, 17(7), 592-598.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01750.x pmid: 16866745 |
| [57] |
Wilson, R. K., & Eckel, C. C. (2006). Judging a book by its cover: Beauty and expectations in the trust game. Political Research Quarterly, 59(2), 189-202.
doi: 10.1177/106591290605900202 URL |
| [58] |
Xiang, T., Lohrenz, T., & Montague, P. R. (2013). Computational substrates of norms and their violations during social exchange. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(3), 1099-1108.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1642-12.2013 pmid: 23325247 |
| [59] |
Yu, H., Siegel, J. Z., Clithero, J. A., & Crockett, M. J. (2021). How peer influence shapes value computation in moral decision-making. Cognition, 211, 104641.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104641 URL |
| [60] |
Zak, P. J., & Knack, S. (2001). Trust and growth. The Economic Journal, 111(470), 295-321.
doi: 10.1111/1468-0297.00609 URL |
| [61] |
Zebrowitz, L. A., & Montepare, J. M. (2008). Social psychological face perception: Why appearance matters. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2(3), 1497-1517.
doi: 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2008.00109.x pmid: 20107613 |
| [62] |
Zhang, Y., Li, H., & Wu, Y. (2020). The application of computational modelling in the studies of moral cognition. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(7), 1042-1055.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01042 URL |
| [63] |
Zheng, X., Guo, W., Chen, M., Jin, J., & Yin, J. (2020). Influence of the valence of social actions on attentional capture: Focus on helping and hindering actions. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(5), 584-596.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00584 URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||