

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 221-235.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00221
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
ZHOU Zinuan, CHEN Yanzhang, FU Shimin( )
)
Received:2021-07-21
Published:2022-03-25
Online:2022-01-25
Contact:
FU Shimin
E-mail:fusm@gzhu.edu.cn
Supported by:ZHOU Zinuan, CHEN Yanzhang, FU Shimin. (2022). The effects of expectation on attention are dependent on whether expectation is on the target or on the distractor. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 54(3), 221-235.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00221
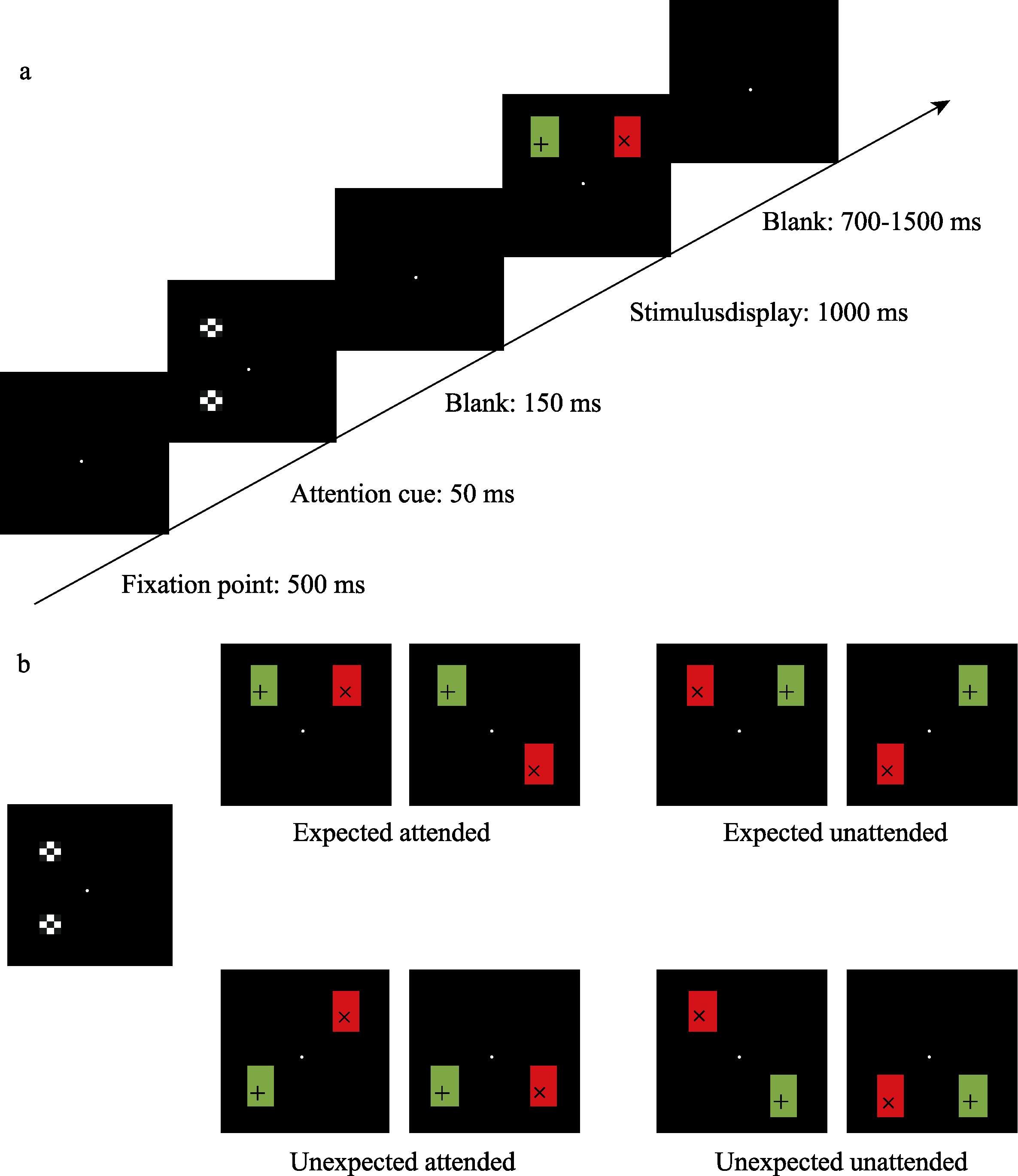
Figure 1. Illustration of the procedure and stimuli of Experiment 1. A shows the procedure of Experiment 1; During the experiment, the central fixation point was presented for 500 ms, and then two square cues were presented vertically on the left or right side; After the cues disappeared, a target rectangle and a distractor rectangle were presented on the stimulus display screen. The task of the participants was to make discrimination response to symbols in the target rectangle. B shows an example of the experimental conditions. In this example, the expected subject was the target, the target was a green rectangle, and the distractor was a red rectangle. The attention cues appeared on the left side vertically, and the instruction guided the participants to expect the upper locations (the target had an 80% probability appearing in one of the two upper locations).
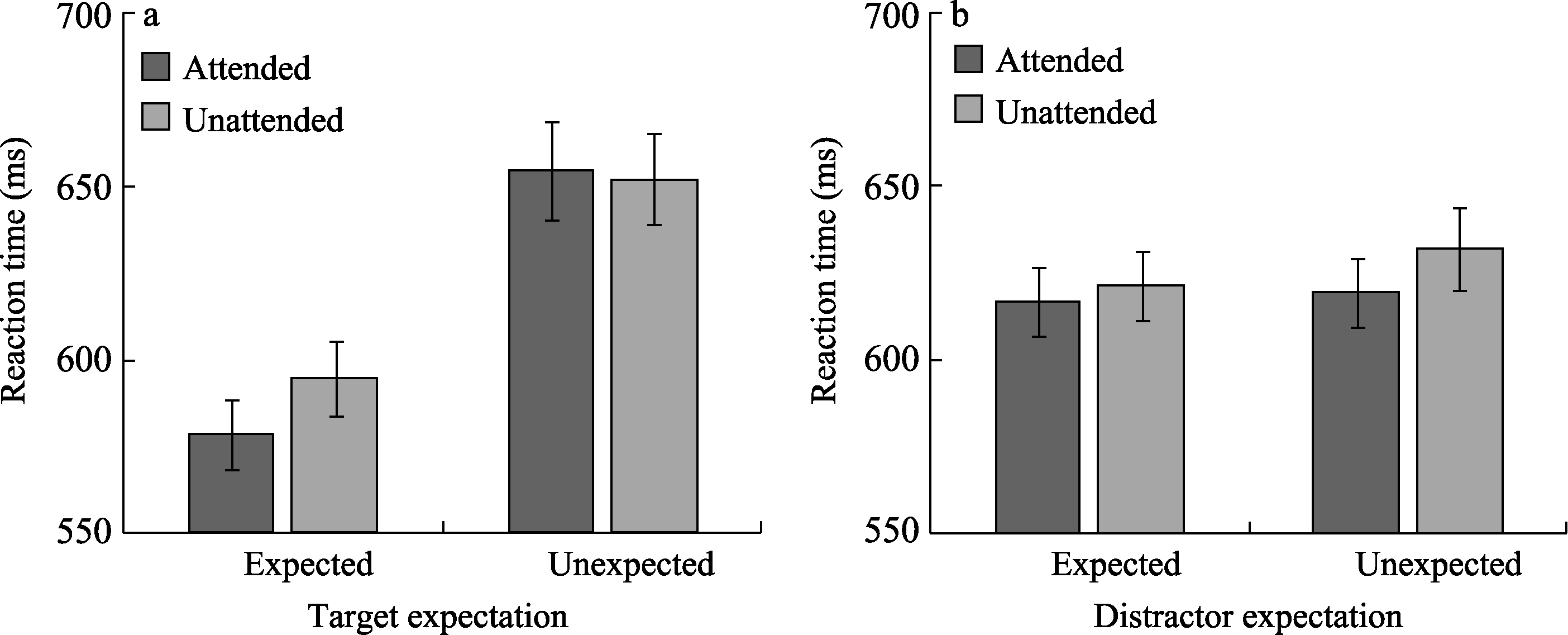
Figure 2. a. Interaction between expectation and attention on reaction time when the expected subject was the target; b. The independent effects of expectation and attention on reaction time when the expected subject was distractor.
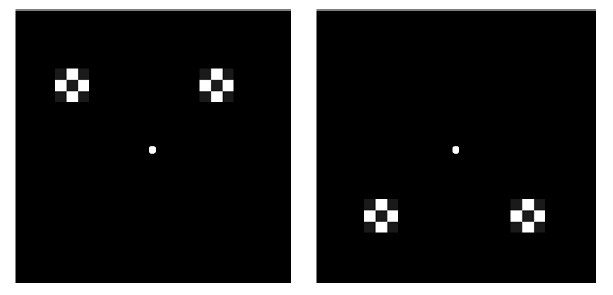
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of attention cues in Experiment 2. Note. In Experiment 2, attention cues were presented horizontally in random in the upper or lower locations, and the participants were instructed to expect the two locations on left or right through instructions.
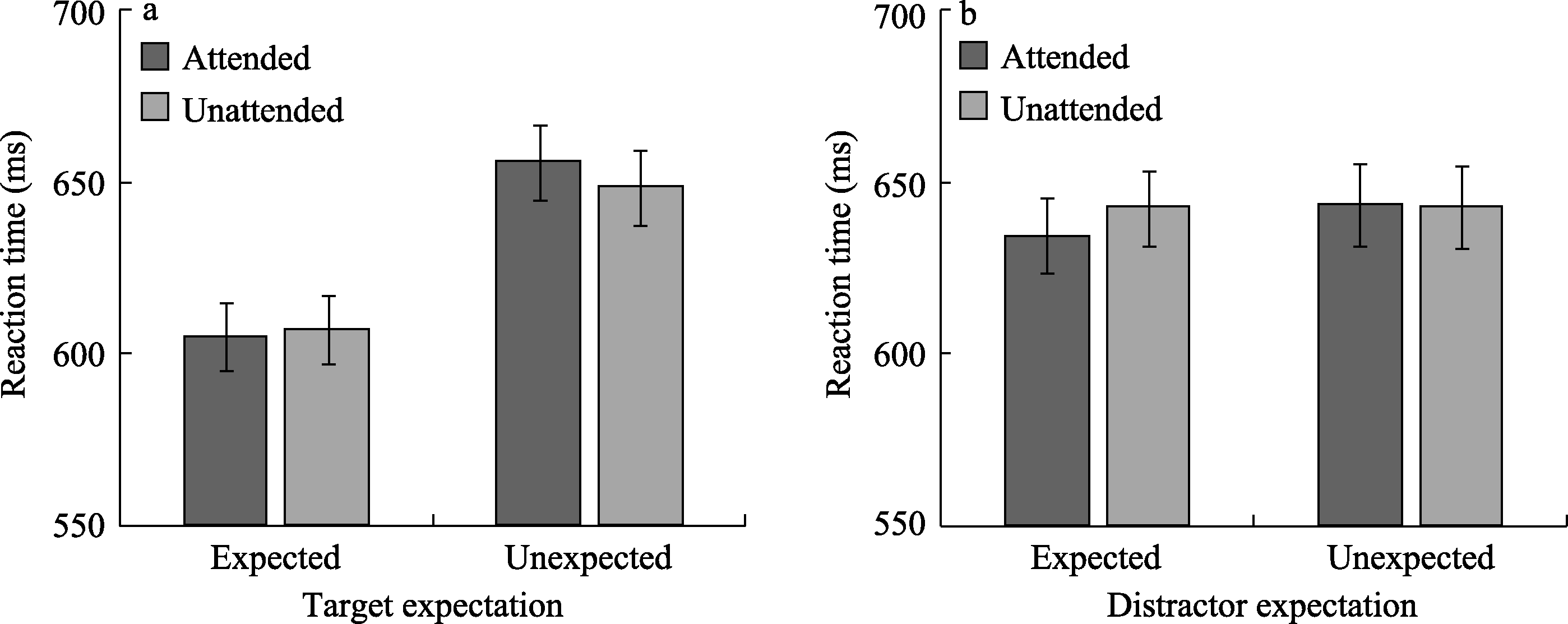
Figure 4. a. Experiment 2: Effect of expectation and attention on reaction times when expected subject was target. b. Experiment 2: The effect of expectation and attention on reaction time when expected subject was distractor.
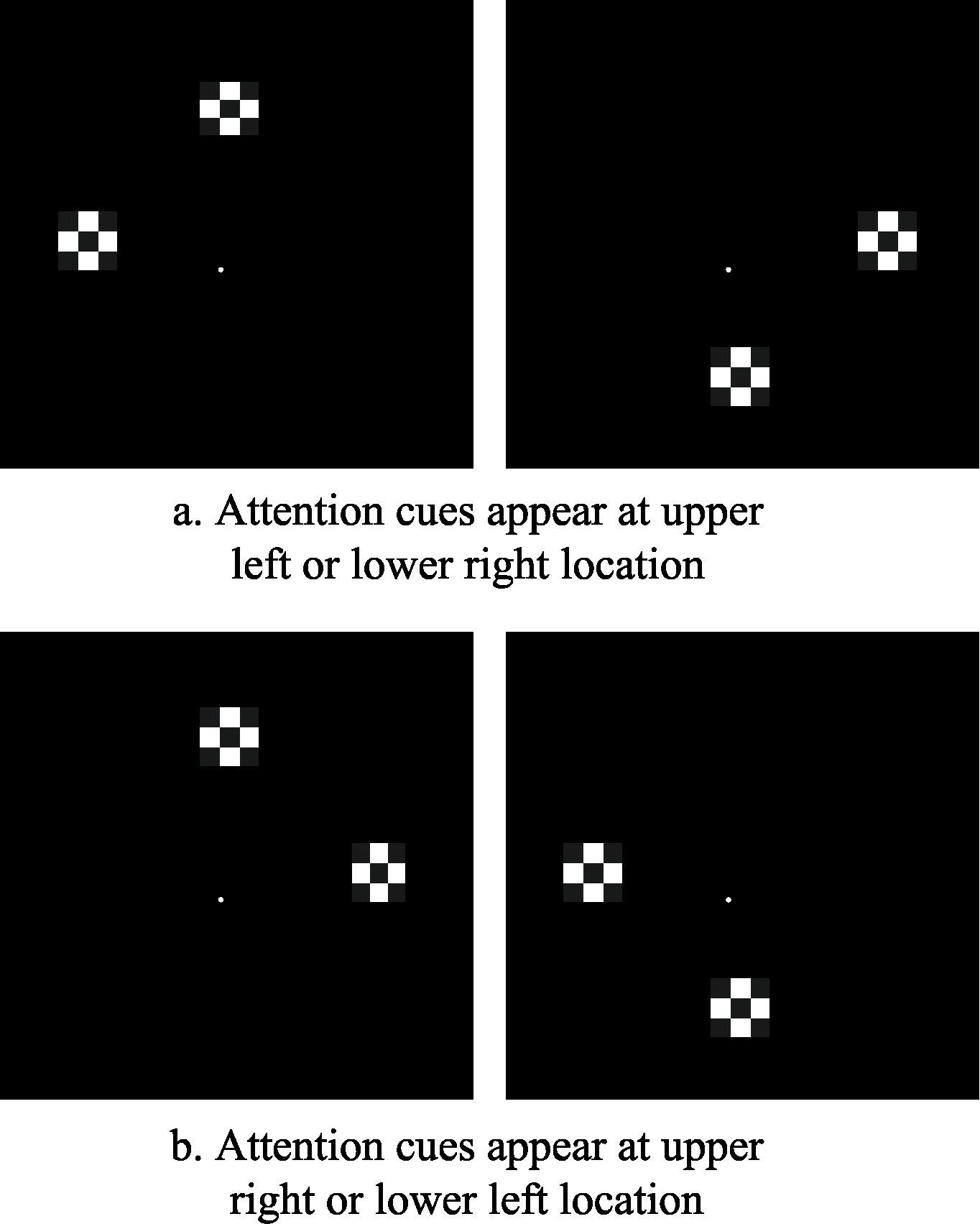

Figure 5. Attention cue diagram. A. When the attention cues are presented in the upper left or lower right, the instruction guides the participant to expect the upper right or lower left location. B. When the attention cues are presented in the upper right or lower left, the instruction guides the participant to expect the upper left or lower right location.
| [1] | Alink A., Schwiedrzik C. M., Kohler A., Singer W., & Muckli L. ( 2010). Stimulus predictability reduces responses in primary visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(8), 2960-2966. |
| [2] | Becker S. I., Lewis A. J., & Axtens J. E. ( 2017). Top-down knowledge modulates onset capture in a feedforward manner. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 24( 2), 436-446. |
| [3] | Beer, A. L., & Röder, B.( 2004). Unimodal and crossmodal effects of endogenous attention to visual and auditory motion. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 4( 2), 230-240. |
| [4] | Beer, A. L., & Röder, B.( 2005). Attending to visual or auditory motion affects perception within and across modalities: An event-related potential study. European Journal of Neuroscience 21( 4), 1116-1130. |
| [5] | Carrasco, M.( 2011). Visual attention: The past 25 years. Vision Research, 51( 13), 1484-1525. |
| [6] | Chang, S., & Egeth H.E. ( 2019). Enhancement and suppression flexibly guide attention. Psychological Science, 30( 12), 1724-1732. |
| [7] | Cheadle S., Egner T., Wyart V., Wu C., & Summerfield C. (2015). Feature expectation heightens visual sensitivity during fine orientation discrimination. Journal of Vision, 15(14), 14. |
| [8] | Chen A., Wang A., Wang T., Tang X., & Zhang M. ( 2017). Behavioral oscillations in visual attention modulated by task difficulty. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1630. |
| [9] | Clark, A. (2013). Whatever next? Predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 36( 3), 181-204. |
| [10] | de Lange F. P., Heilbron M., & Kok P. ( 2018). How do expectations shape perception?. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 22( 9), 764-779. |
| [11] | Egly R., Driver J., & Rafal R. D. ( 1994). Shifting visual attention between objects and locations: Evidence from normal and parietal lesion subjects. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 123( 2), 161-177. |
| [12] | Feldman, H.,& Friston, K. (2010). Attention, uncertainty, and free-energy. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 4, 215. |
| [13] | Gaspelin, N., & Luck S.J. ( 2018). The role of inhibition in avoiding distraction by salient stimuli. Trends in Cognitive Science, 22( 1), 79-92. |
| [14] | Gilbert, C.D., & Li, W.(2013). Top-down influences on visual processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14( 5), 350-363. |
| [15] | Heilbron, M., & Chait, M.(2018). Great expectations: Is there evidence for predictive coding in auditory cortex? Neuroscience, 389, 54-73. |
| [16] | Huang, L., & Pashler , H.( 2005). Attention capacity and task difficulty in visual search. Cognition, 94(3), B101-111. |
| [17] | Jiang J., Summerfield C., & Egner T. ( 2013). Attention sharpens the distinction between expected and unexpected percepts in the visual brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(47), 18438-18447. |
| [18] | Jiang J., Summerfield C., & Egner T . (2016). Visual prediction error spreads across object features in human visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 36(50), 12746-12763. |
| [19] | John-Saaltink E. S., Utzerath C., Kok P., Lau H. C., & de Lange, F. P.(2015). Expectation suppression in early visual cortex depends on task set. PLoS ONE, 10( 6), e0131172. |
| [20] | Kok P., Brouwer G. J., van Gerven, M. A. J., & de Lange, F.P.( 2013). Prior expectations bias sensory representations in visual cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(41), 16275-16284. |
| [21] | Kok P., Mostert P.,& de Lange, F. D. ( 2017). Prior expectations induce prestimulus sensory templates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(39), 10473-10478. |
| [22] | Kok P., Rahnev D., Jehee J. F., Lau H. C., & de Lange, F. P. (2012). Attention reverses the effect of prediction in silencing sensory signals. Cerebral Cortex, 22(9), 2197-2206. |
| [23] | Li Z., Goschl F., & Yang G. ( 2020). Dissociated neural mechanisms of target and distractor processing facilitated by expectations. The Journal of Neuroscience, 40(10), 1997-1999. |
| [24] | Marzecova A., Schettino A., Widmann A., SanMiguel I., Kotz S. A., & Schroger E. ( 2018). Attentional gain is modulated by probabilistic feature expectations in a spatial cueing task: ERP evidence. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 54. |
| [25] | Marzecova A., Widmann A., SanMiguel I., Kotz S. A., & Schroger E. ( 2017). Interrelation of attention and prediction in visual processing: Effects of task-relevance and stimulus probability. Biological Psychology, 125, 76-90. |
| [26] | Petilli M. A., Marini F., & Daini R. (2020). Distractor context manipulation in visual search: How expectations modulate proactive control. Cognition, 196, 104129. |
| [27] | Posner, M. I . (1980). Orienting of attention. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 32(1), 3-25. |
| [28] | Rafal R. D., Posner M. I., Friedman J. H., Inhoff A. W., & Bernstein E. ( 1988). Orienting of visual attention in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain, 111(2), 267-280. |
| [29] | Rauss K., Schwartz S., & Pourtois G. (2011). Top-down effects on early visual processing in humans: A predictive coding framework. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35( 5), 1237-1253. |
| [30] | Reimer, C. B., & Schubert, T. ( 2019). More insight into the interplay of response selection and visual attention in dual-tasks: Masked visual search and response selection are performed in parallel. Psychological Research, 83(3), 459-475. |
| [31] | Rungratsameetaweemana N., Itthipuripat S., Salazar A., & Serences J. T. ( 2018). Expectations do not alter early sensory processing during perceptual decision-making. The Journal of Neuroscience, 38( 24), 5632-5648. |
| [32] | Rungratsameetaweemana, N., & Serences, J. T. ( 2019). Dissociating the impact of attention and expectation on early sensory processing. Current Opinion in Psychology, 29, 181-186. |
| [33] | Smout C. A., Garrido M. I., & Mattingley J. B. (2019). Global effects of feature-based attention depend on surprise. NeuroImage, 215, 116785. |
| [34] | Su Y., Huang W., Yang N., Yan K., Ding Y., & Qu Z. ( 2020). Attentional capture by a color singleton is stronger at spatially relevant than irrelevant locations: Evidence from an ERP study. Psychophysiology, 57( 10), e13640. |
| [35] | Summerfield, C., & de Lange, F. P. ( 2014). Expectation in perceptual decision making: Neural and computational mechanisms. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15( 11), 745-756. |
| [36] | Summerfield, C., & Egner, T. ( 2016). Feature-based attention and feature-based expectation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20( 6), 401-404. |
| [37] | van Moorselaar D., Daneshtalab N., & Slagter H. A. ( 2021). Neural mechanisms underlying distractor inhibition on the basis of feature and/or spatial expectations. Cortex, 137, 232-250. |
| [38] | van Moorselaar, D.,& Slagter, H.A. ( 2019). Learning what is irrelevant or relevant: Expectations facilitate distractor inhibition and target facilitation through distinct neural mechanisms. The Journal of Neuroscience, 39( 35), 6953-6967. |
| [39] | Wang, B.,& Theeuwes, J. (2018). How to inhibit a distractor location? Statistical learning versus active, top-down suppression. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 80( 4), 860-870. |
| [40] | Wang B., van Driel J., Ort E., & Theeuwes J . ( 2019). Anticipatory distractor suppression elicited by statistical regularities in visual search. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 31( 10), 1535-1548. |
| [41] | Wyart V., Nobre A. C., & Summerfield C . ( 2012). Dissociable prior influences of signal probability and relevance on visual contrast sensitivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109( 9), 3593-3598. |
| [42] | Yantis, S., & Jonides, J.( 1984). Abrupt visual onsets and selective attention: Evidence from visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 10(5), 601-621. |
| [43] | Zareian B., Maboudi K., Daliri M. R., Abrishami Moghaddam H., Treue S., & Esghaei M. ( 2020). Attention strengthens across-trial pre-stimulus phase coherence in visual cortex, enhancing stimulus processing. Scientific Reports, 10( 1), 4837. |
| [44] | Zhang F., Chen A., Dong B., Wang A., & Zhang M. ( 2021). Rapid disengagement hypothesis and signal suppression hypothesis of visual attentional capture. Advances in Psychological Science, 29( 1), 45-55. |
| [45] | Zuanazzi, A., & Noppeney, U. (2018). Additive and interactive effects of spatial attention and expectation on perceptual decisions. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 6732. |
| [46] | Zuanazzi, A., & Noppeney, U.( 2019). Distinct neural mechanisms of spatial attention and expectation guide perceptual inference in a multisensory World. The Journal of Neuroscience, 39(12), 2301-2312. |
| [1] | LI Jie, YANG Yue, ZHAO Jing. The development of visual simultaneous processing skill subcomponents of Chinese children with developmental dyslexia and its relationship with reading [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(8): 821-836. |
| [2] | TANG Xiaoyu, TONG Jiageng, YU Hong, WANG Aijun. Effects of endogenous spatial attention and exogenous spatial attention on multisensory integration [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(11): 1173-1188. |
| [3] | SUN Juncai, XUN Fengjiao, LIU Ping, ZHANG Wenhai. The implicit advantage of a high kindness trait in the action control of emotion regulation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(7): 781-794. |
| [4] | Lu LIU, Guoli YAN. Effect of parafoveal visual attention enhancement in deaf reading: Evidence from disappearing text [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(7): 715-726. |
| [5] | Xiaojun YUAN, Xiaoxia CUI, Zhengcao CAO, Hong KAN, Xiao WANG, Yamin WANG. Attentional bias towards threatening visual stimuli in a virtual reality-based visual search task [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(6): 622-636. |
| [6] | LI Biqin, LI Ling, WANG Aijun, ZHANG Ming. Visual and auditory verbal working memory affects visual attention in the semantic matching [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(5): 483-493. |
| [7] | Qun TAN, Yueyang YIN, Shen LIU, Shangfeng HAN, Qiang XU, Lin ZHANG. The processing advantage of self-positive expression: Evidence from an ERPs study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(10): 1120-1130. |
| [8] | LI Yangzhuo, QIAN Haoyue, ZHU Min, GAO Xiangping. Self association facilitates attentional inhibition in human visual search [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(1): 28-35. |
| [9] | ZHANG Bao, HU Cenlou, Huang Sai. What do eye movements reveal about the role of cognitive control in attention guidance from working memory representation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(9): 1105-1118. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wei, ZHOU Bingping, ZANG Ling, MO Shuliang. The Attentional Capture of Internet Addicts under the Guidance of Visual Working Memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(10): 1223-1234. |
| [11] | WEI Liuqing;ZHANG Xuemin;LI Yongna;MA Yu. The Effects of Visual and Auditory Dual-task on Multiple Object Tracking Performance: Interference or Promotion? [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(6): 727-739. |
| [12] | REN Yanju; SUN Qi. Effects of Visuo-spatial Working Memory Loads on the Real-World Scene Search Performance [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(11): 1613-1627. |
| [13] | MU Bingbing; WAN Xiaoang. The Emotional Distractor Previewing Effect in Visual Search [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(11): 1603-1612. |
| [14] | LIN Ou;WANG Zhengke;MENG Xiangzhi. Visual Perceptual Learning in Chinese Developmental Dyslexia [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(7): 762-772. |
| [15] | ZHANG Bao;HUANG Sai;QI Lu. Working Memory Representation Does Guide Visual Attention: Evidence from Eye Movements [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(2): 139-148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||