

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 847-860.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00847
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Rui, LU Kelong, HAO Ning( )
)
Received:2020-09-08
Published:2021-08-25
Online:2021-06-25
Contact:
HAO Ning
E-mail:nhao@psy.ecnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CHENG Rui, LU Kelong, HAO Ning. (2021). The effect of anger on malevolent creativity and strategies for its emotion regulation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(8), 847-860.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00847
| Experimental conditions | Pre-test | Post-test | t (33) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger group | ||||
| Valence | 6.18 ± 1.22 | 3.74 ± 1.58 | 8.80 | 0.000*** |
| Arousal | 4.97 ± 1.57 | 5.91 ± 2.15 | -2.26 | 0.030* |
| Anger | 1.56 ± 0.93 | 5.18 ± 1.83 | -10.80 | 0.000*** |
| Sadness | 2.74 ± 1.85 | 3.15 ± 1.86 | -1.19 | 0.242 |
| Sadness Group | ||||
| Valence | 5.65 ± 1.18 | 3.27 ± 1.40 | 8.41 | 0.000*** |
| Arousal | 4.82 ± 1.31 | 3.56 ± 1.71 | 4.07 | 0.000*** |
| Anger | 1.97 ± 1.64 | 2.62 ± 1.74 | -1.55 | 0.131 |
| Sadness | 2.03 ± 1.19 | 5.00 ± 1.81 | -7.70 | 0.000*** |
| Control group | ||||
| Valence | 5.62 ± 1.30 | 5.38 ± 1.21 | 1.19 | 0.224 |
| Arousal | 4.71 ± 1.36 | 4.59 ± 1.64 | 0.37 | 0.711 |
| Anger | 1.88 ± 1.30 | 1.79 ± 1.18 | 0.46 | 0.646 |
| Sadness | 2.53 ± 1.85 | 2.62 ± 2.03 | -0.26 | 0.795 |
Table 1 Experiment 1: descriptive statistics of emotions (M ± SD) and paired-sample t-tests
| Experimental conditions | Pre-test | Post-test | t (33) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger group | ||||
| Valence | 6.18 ± 1.22 | 3.74 ± 1.58 | 8.80 | 0.000*** |
| Arousal | 4.97 ± 1.57 | 5.91 ± 2.15 | -2.26 | 0.030* |
| Anger | 1.56 ± 0.93 | 5.18 ± 1.83 | -10.80 | 0.000*** |
| Sadness | 2.74 ± 1.85 | 3.15 ± 1.86 | -1.19 | 0.242 |
| Sadness Group | ||||
| Valence | 5.65 ± 1.18 | 3.27 ± 1.40 | 8.41 | 0.000*** |
| Arousal | 4.82 ± 1.31 | 3.56 ± 1.71 | 4.07 | 0.000*** |
| Anger | 1.97 ± 1.64 | 2.62 ± 1.74 | -1.55 | 0.131 |
| Sadness | 2.03 ± 1.19 | 5.00 ± 1.81 | -7.70 | 0.000*** |
| Control group | ||||
| Valence | 5.62 ± 1.30 | 5.38 ± 1.21 | 1.19 | 0.224 |
| Arousal | 4.71 ± 1.36 | 4.59 ± 1.64 | 0.37 | 0.711 |
| Anger | 1.88 ± 1.30 | 1.79 ± 1.18 | 0.46 | 0.646 |
| Sadness | 2.53 ± 1.85 | 2.62 ± 2.03 | -0.26 | 0.795 |
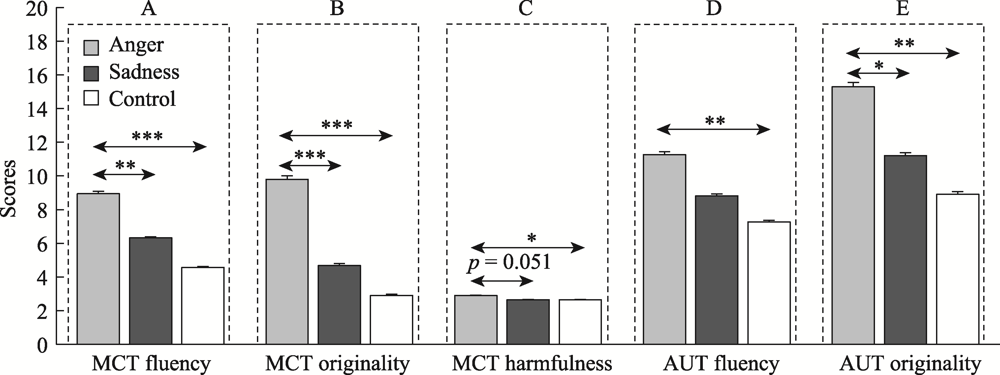
Figure 2. Malevolent and general creative performance in different emotion groups in Experiment 1. Note. (A) MCT fluency; (B) MCT originality; (C) MCT harmfulness; (D) AUT fluency; (E) AUT originality. The error bars represent standard errors. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
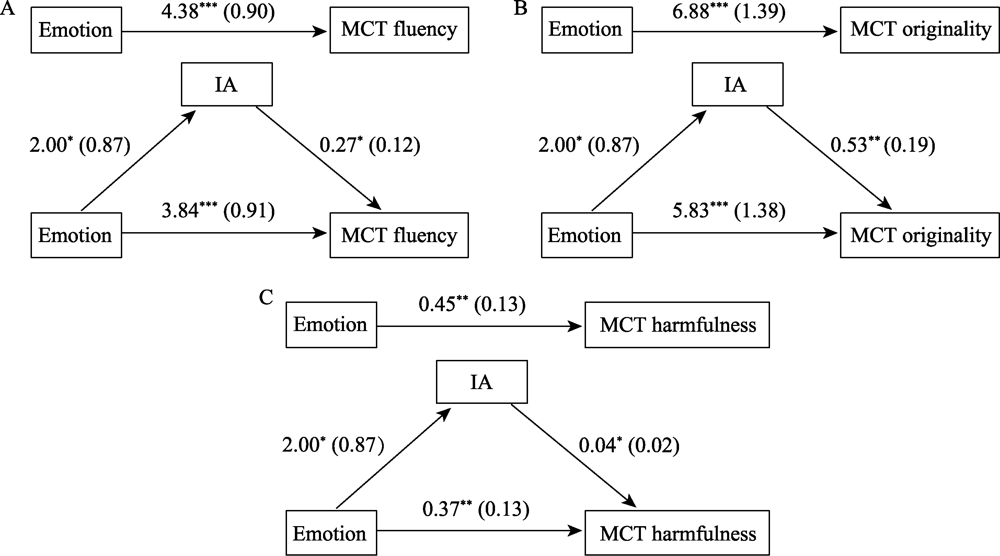
Figure 3. Mediation analysis using IA as the mediator in Experiment 1. Note. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The coefficient is non-standard coefficient, and the standard error is presented in ().

Figure 4. Mediation analysis using emotional arousal as the mediator in Experiment 1. Note. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The coefficient is non-standard coefficient, and the standard error is in ().
| Experimental conditions | Pre-test | PI | PR | F (2, 78) | p | Post hoc tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive reappraisal group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.25 ± 1.35 | 4.15 ± 1.33 | 5.93 ± 1.10 | 40.77 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** PI < PR*** |
| Arousal | 4.65 ± 1.75 | 5.33 ± 2.07 | 4.40 ± 1.39 | 3.50 | 0.035* | PI > PR* |
| Anger | 1.63 ± 1.01 | 4.15 ± 1.72 | 1.98 ± 1.03 | 60.64 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** PI > PR*** |
| Expression inhibition group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.38 ± 1.31 | 4.25 ± 1.37 | 5.03 ± 1.39 | 42.54 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** Pre-test > PR** IR < PR*** |
| Arousal | 4.85 ± 1.31 | 5.93 ± 1.64 | 4.25 ± 1.50 | 12.23 | 0.000*** | Pre-test < PI* PI > PR*** |
| Anger | 1.70 ± 0.94 | 4.47 ± 1.75 | 2.88 ± 1.47 | 54.97 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** Pretest < PR** PI > PR*** |
| Control group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.25 ± 1.71 | 4.33 ± 1.54 | 4.28 ± 1.78 | 25.17 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** Pre-test > PR |
| Arousal | 4.72 ± 1.31 | 5.50 ± 1.95 | 5.15 ± 1.96 | 2.02 | 0.14 | |
| Anger | 1.79 ± 1.18 | 4.35 ± 2.34 | 4.00 ± 2.92 | 24.11 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** Pretest < PR*** |
Table 2 Experiment 2: descriptive statistics of emotion induction and regulation (M ± SD) and ANOVAs
| Experimental conditions | Pre-test | PI | PR | F (2, 78) | p | Post hoc tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive reappraisal group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.25 ± 1.35 | 4.15 ± 1.33 | 5.93 ± 1.10 | 40.77 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** PI < PR*** |
| Arousal | 4.65 ± 1.75 | 5.33 ± 2.07 | 4.40 ± 1.39 | 3.50 | 0.035* | PI > PR* |
| Anger | 1.63 ± 1.01 | 4.15 ± 1.72 | 1.98 ± 1.03 | 60.64 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** PI > PR*** |
| Expression inhibition group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.38 ± 1.31 | 4.25 ± 1.37 | 5.03 ± 1.39 | 42.54 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** Pre-test > PR** IR < PR*** |
| Arousal | 4.85 ± 1.31 | 5.93 ± 1.64 | 4.25 ± 1.50 | 12.23 | 0.000*** | Pre-test < PI* PI > PR*** |
| Anger | 1.70 ± 0.94 | 4.47 ± 1.75 | 2.88 ± 1.47 | 54.97 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** Pretest < PR** PI > PR*** |
| Control group | ||||||
| Valence | 6.25 ± 1.71 | 4.33 ± 1.54 | 4.28 ± 1.78 | 25.17 | 0.000*** | Pre-test > PI*** Pre-test > PR |
| Arousal | 4.72 ± 1.31 | 5.50 ± 1.95 | 5.15 ± 1.96 | 2.02 | 0.14 | |
| Anger | 1.79 ± 1.18 | 4.35 ± 2.34 | 4.00 ± 2.92 | 24.11 | 0.000*** | Pretest < PI*** Pretest < PR*** |
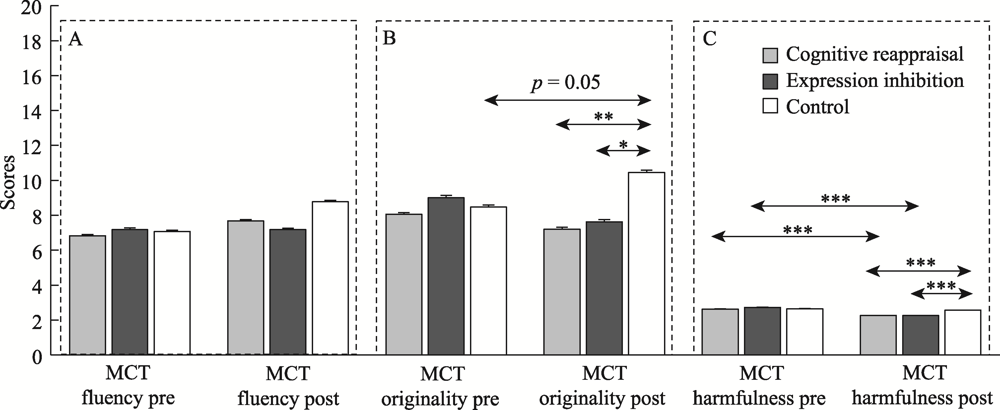
Figure 6. The pre-test and post-test malevolent creative performance in different groups in Experiment 2. Note. (a) MCT fluency; (b) MCT originality; (C) MCT harmfulness. The error bars represent standard errors. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ‘Pre’ indicated the pre-test and ‘post’ indicated the post-test.
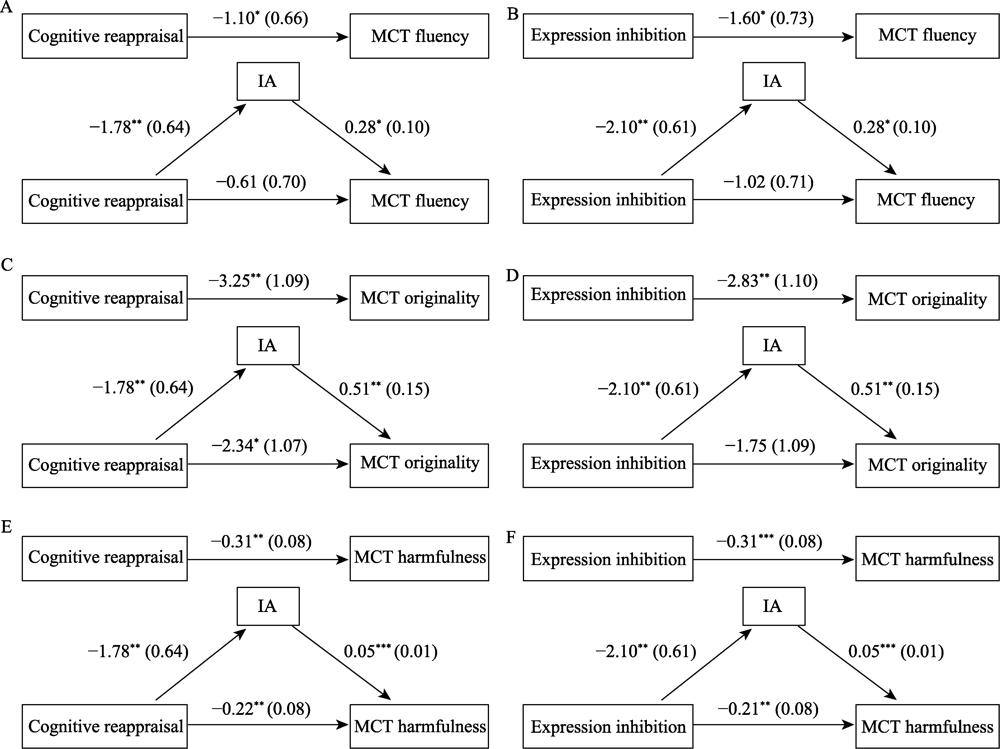
Figure 7. Mediation analysis using IA as the mediator in Experiment 2. Note. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The coefficient is non-standard coefficient, and the standard error is presented in ().
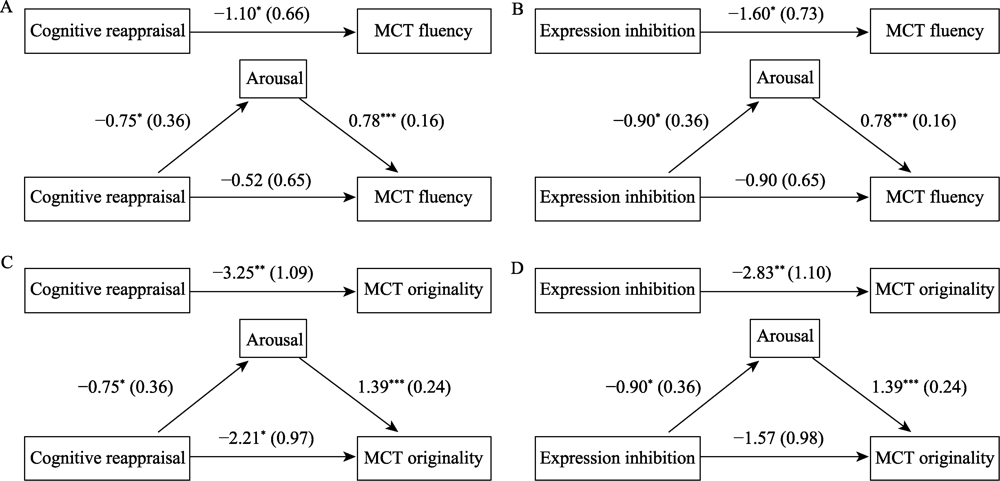
Figure 8. Mediation analysis using emotional arousal as the mediator in Experiment 2. Note. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The coefficient is non-standard coefficient, and the standard error is presented in ().
| [1] |
Anderson, C. A., Anderson, K. B., & Deuser, W. E. (1996). Examining an affective aggression framework: Weapon and temperature effects on aggressive thoughts, affect, and attitudes. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 22(4), 366-376.
doi: 10.1177/0146167296224004 URL |
| [2] |
Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2002). Human aggression. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 27-51.
pmid: 11752478 |
| [3] |
Baas, M., de Dreu, C. K. W., & Nijstad, B. A. (2008). A meta-analysis of 25 years of mood-creativity research: Hedonic tone, activation, or regulatory focus? Psychological Bulletin, 134(6), 779-806.
doi: 10.1037/a0012815 URL |
| [4] |
Baas, M., de Dreu, C. K. W., & Nijstad, B. A. (2011). Creative production by angry people peaks early on, decreases over time, and is relatively unstructured. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 47(6), 1107-1115.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2011.05.009 URL |
| [5] |
Berkowitz, L. (1990). On the formation and regulation of anger and aggression: A cognitive-neoassociationistic analysis. American Psychologist, 45(4), 494-503.
pmid: 2186678 |
| [6] |
Bless, H., Hamilton, D. L., & Mackie, D. M. (1992). Mood effects on the organization of person information. European Journal of Social Psychology, 22(5), 497-509.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0992 URL |
| [7] |
Bolte, A., Goschke, T., & Kuhl, J. (2003). Emotion and intuition: Effects of positive and negative mood on implicit judgments of semantic coherence. Psychological Science, 14(5), 416-421.
doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.01456 URL |
| [8] |
Bradley, M. M., & Lang, P. J. (1994). Measuring emotion: the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 25(1), 49-59.
doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(94)90063-9 URL |
| [9] |
Brewer, D., Doughtie, E. B., & Lubin, B. (1980). Induction of mood and mood shift. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 36(1), 215-226.
pmid: 7391236 |
| [10] |
Buss, A. H., &Perry, M.P. (1992). The aggression questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63(3), 452-459.
pmid: 1403624 |
| [11] |
Byron, K., Khazanchi, S., & Nazarian, D. (2010). The relationship between stressors and creativity: A meta-analysis examining competing theoretical models. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(1), 201-212.
doi: 10.1037/a0017868 URL |
| [12] | Carver, C. S. (2006). Approach, avoidance, and the self-regulation of affect and action. Motivation & Emotion, 30, 105-110. |
| [13] | Cropley, A. J. (2010). The dark side of creativity: What is it? In D. Cropley, A. Cropley, J. C. Kaufman & M. A. Runco (Eds.), The dark side of creativity (pp. 1-14). New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [14] |
Cropley, D. H., Kaufman, J. C., & Cropley, A. J. (2008). Malevolent creativity: A functional model of creativity in terrorism and crime. Creativity Research Journal, 20(2), 105-115.
doi: 10.1080/10400410802059424 URL |
| [15] |
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Guthrie, I. K., & Reiser, M. (2000). Dispositional emotionality and regulation: Their role in predicting quality of social functioning. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(1), 136-157.
pmid: 10653511 |
| [16] |
Friedman, R. S., & Förster, J. (2010). Implicit affective cues and attentional tuning: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 136(5), 875-893.
doi: 10.1037/a0020495 pmid: 20804240 |
| [17] |
Gilet, A.-L., & Jallais, C. (2011). Valence, arousal and word associations. Cognition and Emotion, 25(4), 740-746.
doi: 10.1080/02699931.2010.500480 URL |
| [18] |
Gill, P., Horgan, J., Hunter, S. T., & Cushenbery, L. D. (2013). Malevolent creativity in terrorist organizations. Journal of Creative Behavior, 47(2), 125-151.
doi: 10.1002/jocb.28 URL |
| [19] |
Goldin, P. R., Mcrae, K., Ramel, W., & Gross, J. J. (2008). The neural bases of emotion regulation: Reappraisal and suppression of negative emotion. Biological Psychiatry, 63(6), 577-586.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.05.031 URL |
| [20] |
Gross, J. J. (1998). Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: Divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74(1), 224-237.
pmid: 9457784 |
| [21] | Gross, J. J., & Thompson, R. A. (2007) Emotion regulation: Conceptual foundations.In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp.3-24). New York, NY: Guilford Press. |
| [22] |
Gutworth, M. B., Cushenbery, L., & Hunter, S. T. (2016). Creativity for deliberate harm: malevolent creativity and social information processing theory. Journal of Creative Behavior, 52(4), 305-322.
doi: 10.1002/jocb.2018.52.issue-4 URL |
| [23] |
Hao, N., Qiao, X., Cheng, R., Lu, K., Tang, M. Y., & Runco, M. A. (2020). Approach motivational orientation enhances malevolent creativity. Acta Psychologica, 203, 102985.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2019.102985 URL |
| [24] | Hao, N., Tang, M. Y., Yang, J., Wang, Q. F., & Runco, M. A. (2016). A new tool to measure malevolent creativity: The malevolent creativity behavior scale. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 682. |
| [25] |
Hao, N., Xue, H., Yuan, H., Wang, Q., & Runco, M. A. (2017). Enhancing creativity: Proper body posture meets proper emotion. Acta Psychologica, 173, 32-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2016.12.005 URL |
| [26] |
Harris, D. J., & Reiter-Palmon, R. (2015). Fast and furious: the influence of implicit aggression, premeditation, and provoking situations on malevolent creativity. Psychology of Aesthetics Creativity and the Arts, 9,(1), 54-64.
doi: 10.1037/a0038499 URL |
| [27] | Harris, D. J., Reiter-Palmon, R., & Kaufman, J. C. (2013). The effect of emotional intelligence and task type on malevolent creativity. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 7(3), 237-244. |
| [28] | Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-Based approach, New York: Guilford Press. |
| [29] |
Hayes, A. F., & Preacher, K. J. (2014). Statistical mediation analysis with a multicategorical independent variable. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 67(3), 451-470.
doi: 10.1111/bmsp.2014.67.issue-3 URL |
| [30] |
Higgins, E. T. (1997). Beyond pleasure and pain. American Psychologist, 52(12), 1280-1300.
pmid: 9414606 |
| [31] | Higgins, E. T. (2001). Promotion and prevention experiences: Relating emotions to nonemotional motivational states..In J. P. Forgas (Ed.), Handbook of affect and social cognition, (pp. 186-211). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [32] |
Higgins, E. T. (2006). Value from hedonic experience and engagement. Psychological Review, 113(3), 439-460.
pmid: 16802877 |
| [33] |
Jiang, J., Dai, B. H., Peng, D. L., Zhu, C. Z., Liu, L., & Lu, C. M. (2012). Neural synchronization during face-to-face communication. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(45), 16064-16069.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2926-12.2012 URL |
| [34] |
Lang, P. J. (1995). The emotion probe: Studies of motivation and attention. American Psychologist, 50(5), 372-385.
pmid: 7762889 |
| [35] |
Lu, K. L., Xue, H., Nozawa, T., & Hao, N. (2019). Cooperation makes a group be more creative. Cerebral Cortex, 29(8), 3457-3470.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy215 URL |
| [36] |
Molho, C., Tybur, J. M., Balliet, D., Güler, E., & Hofmann, W. (2017). Disgust and anger relate to different aggressive responses to moral violations. Psychological Science, 28(5), 609-619.
doi: 10.1177/0956797617692000 URL |
| [37] |
Perchtold‐Stefan, C. M., Fink, A., Rominger, C., & Papousek, I. (2020). Creative, antagonistic, and angry? Exploring the roots of malevolent creativity with a real‐world idea generation task. The Journal of Creative Behavior. doi: 10.1002/jocb.484.
doi: 10.1002/jocb.484 |
| [38] |
Plucker, J. A., Beghetto, R. A., & Dow, G. T. (2004). Why isn’t creativity more important to educational psychologists? Potentials, pitfalls, and future directions in creativity research. Educational Psychologist, 39(2), 83-96.
doi: 10.1207/s15326985ep3902_1 URL |
| [39] |
Ray, R. D., Wilhelm, F. H., & Gross, J. J. (2008). All in the mind’s eye? Anger rumination and reappraisal. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 94(1), 133-145.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.94.1.133 URL |
| [40] |
Richetin, J., & Richardson, D. S. (2008). Automatic processes and individual differences in aggressive behavior. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 13(6), 423-430.
doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2008.06.005 URL |
| [41] |
Roseman, I. J., Wiest, C., & Swartz, T. S. (1994). Phenomenology, behaviors, and goals differentiate discrete emotions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(2), 206-221.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.67.2.206 URL |
| [42] |
Runco, M. A., Abdulla, A. M., Paek, S. H., Al-Jasim, F. A., & Alsuwaidi, H. N. (2016). Which test of divergent thinking is best? Creativity. Theories - Research - Applications, 3(1), 4-18.
doi: 10.1515/ctra-2016-0001 URL |
| [43] |
Runco, M. A., & Acar, S. (2012). Divergent thinking as an indicator of creative potential. Creativity Research Journal, 24(1), 66-75.
doi: 10.1080/10400419.2012.652929 URL |
| [44] |
Runco, M. A., & Jaeger, G. J. (2012). The standard definition of creativity. Creativity Research Journal, 24(1), 92-96.
doi: 10.1080/10400419.2012.650092 URL |
| [45] | Runco, M. A., Plucker, J. A., & Lim, W. (2001). Development and psychometric integrity of a measure of ideational behavior. Creativity Research Journal, 13(3-4), 393-400. |
| [46] |
Russ, S. W., & Kaugars, A. S. (2001). Emotion in children’s play and creative problem solving. Creativity Research Journal, 13(2), 211-219.
doi: 10.1207/S15326934CRJ1302_8 URL |
| [47] |
Russell, J. A. (2003). Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychological Review, 110(1), 145-172.
pmid: 12529060 |
| [48] |
van Kleef, G. A., Anastasopoulou, C., & Nijstad, B. A. (2010). Can expressions of anger enhance creativity? A test of the emotions as social information (EASI) model. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(6), 1042-1048.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2010.05.015 URL |
| [49] | Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063-1070. |
| [50] |
Webb, T. L., Miles, E., & Sheeran, P. (2012). Dealing with feeling: A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of strategies derived from the process model of emotion regulation. Psychological Bulletin, 138(4), 775-808.
doi: 10.1037/a0027600 URL |
| [51] | Zhu, C. M., Gong, H. L., & Zheng, X. F. (2006). An experimental research on character of implicit aggression among juveniles. Psychological Exploration, 26(2), 48-50. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||