

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 807-820.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00807
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
ZHANG Rui, WANG Zhenhua, WANG Xiaojuan( ), YANG Jianfeng(
), YANG Jianfeng( )
)
Received:2020-08-07
Published:2021-08-25
Online:2021-06-25
Contact:
WANG Xiaojuan,YANG Jianfeng
E-mail:wangxj@snnu.edu.cn;yangjf@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:ZHANG Rui, WANG Zhenhua, WANG Xiaojuan, YANG Jianfeng. (2021). N170 adaptation effect of the sub-lexical phonological and semantic processing in Chinese character reading. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(8), 807-820.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00807
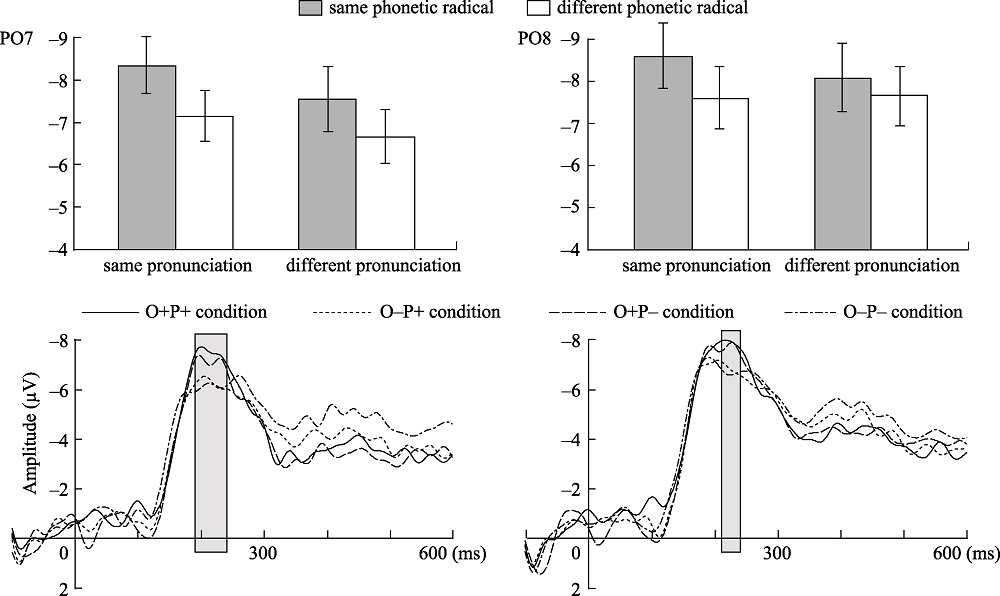
Figure 3. In Experiment 1, the neural adaptation between the conditions was different in the left fusiform gyrus (PO7), and no differences in the right fusiform gyrus (PO8).
| O+P+ | O+P- | O-P+ | O-P- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -10.041 | 0.000 | 1.58 | -8.654 | 0.000 | 1.51 | -9.251 | 0.000 | 1.54 | -8.293 | 0.000 | 1.46 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -9.441 | 0.000 | 1.58 | -7.71 | 0.000 | 1.43 | -8.415 | 0.000 | 1.26 | -8.493 | 0.000 | 1.29 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -7.302 | 0.000 | 1.14 | -6.441 | 0.000 | 1.01 | -6.453 | 0.000 | 0.94 | -6.168 | 0.000 | 0.92 |
| S2 vs. S3 | -0.087 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 0.367 | 1.000 | 0.03 | 2.854 | 0.049 | 0.26 | 1.052 | 1.000 | 0.09 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 3.905 | 0.003 | 0.33 | 5.647 | 0.000 | 0.48 | 5.517 | 0.000 | 0.50 | 4.602 | 0.001 | 0.48 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 4.805 | 0.000 | 0.34 | 4.84 | 0.000 | 0.43 | 2.845 | 0.050 | 0.25 | 4.769 | 0.000 | 0.38 |
Appendix Table 1 Paired comparison of N170 amplitudes of four Chinese characters on PO7 electrode in Experiment 1
| O+P+ | O+P- | O-P+ | O-P- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -10.041 | 0.000 | 1.58 | -8.654 | 0.000 | 1.51 | -9.251 | 0.000 | 1.54 | -8.293 | 0.000 | 1.46 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -9.441 | 0.000 | 1.58 | -7.71 | 0.000 | 1.43 | -8.415 | 0.000 | 1.26 | -8.493 | 0.000 | 1.29 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -7.302 | 0.000 | 1.14 | -6.441 | 0.000 | 1.01 | -6.453 | 0.000 | 0.94 | -6.168 | 0.000 | 0.92 |
| S2 vs. S3 | -0.087 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 0.367 | 1.000 | 0.03 | 2.854 | 0.049 | 0.26 | 1.052 | 1.000 | 0.09 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 3.905 | 0.003 | 0.33 | 5.647 | 0.000 | 0.48 | 5.517 | 0.000 | 0.50 | 4.602 | 0.001 | 0.48 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 4.805 | 0.000 | 0.34 | 4.84 | 0.000 | 0.43 | 2.845 | 0.050 | 0.25 | 4.769 | 0.000 | 0.38 |
| O+P+ | O+P- | O-P+ | O-P- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -8.937 | 0.000 | 1.87 | -8.531 | 0.000 | 1.74 | -8.123 | 0.000 | 1.74 | -8.673 | 0.000 | 1.86 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -8.333 | 0.000 | 1.65 | -7.126 | 0.000 | 1.59 | -8.183 | 0.000 | 1.47 | -8.099 | 0.000 | 1.71 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -5.808 | 0.000 | 1.12 | -5.332 | 0.000 | 1.00 | -6.453 | 0.000 | 1.10 | -5.766 | 0.000 | 1.15 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 1.419 | 1.000 | 0.13 | 0.932 | 1.000 | 0.08 | 1.741 | 0.558 | 0.20 | 2.379 | 0.148 | 0.18 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 4.808 | 0.000 | 0.65 | 6.67 | 0.001 | 0.75 | 4.528 | 0.001 | 0.56 | 6.783 | 0.000 | 0.63 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 5.084 | 0.000 | 0.50 | 6.619 | 0.000 | 0.64 | 3.815 | 0.004 | 0.35 | 5.617 | 0.000 | 0.47 |
Appendix Table 2 Paired comparison of N170 amplitudes of four Chinese characters on PO8 electrode in Experiment 1
| O+P+ | O+P- | O-P+ | O-P- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -8.937 | 0.000 | 1.87 | -8.531 | 0.000 | 1.74 | -8.123 | 0.000 | 1.74 | -8.673 | 0.000 | 1.86 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -8.333 | 0.000 | 1.65 | -7.126 | 0.000 | 1.59 | -8.183 | 0.000 | 1.47 | -8.099 | 0.000 | 1.71 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -5.808 | 0.000 | 1.12 | -5.332 | 0.000 | 1.00 | -6.453 | 0.000 | 1.10 | -5.766 | 0.000 | 1.15 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 1.419 | 1.000 | 0.13 | 0.932 | 1.000 | 0.08 | 1.741 | 0.558 | 0.20 | 2.379 | 0.148 | 0.18 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 4.808 | 0.000 | 0.65 | 6.67 | 0.001 | 0.75 | 4.528 | 0.001 | 0.56 | 6.783 | 0.000 | 0.63 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 5.084 | 0.000 | 0.50 | 6.619 | 0.000 | 0.64 | 3.815 | 0.004 | 0.35 | 5.617 | 0.000 | 0.47 |
| O+S+ | O+S- | O-S+ | O-S- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -11.519 | 0.000 | 1.90 | -10.18 | 0.000 | 1.64 | -11.41 | 0.000 | 1.81 | -8.293 | 0.000 | 1.46 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -9.439 | 0.000 | 1.56 | -9.145 | 0.000 | 1.47 | -10.84 | 0.000 | 1.61 | -8.493 | 0.000 | 1.29 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -5.977 | 0.000 | 0.96 | -4.975 | 0.000 | 0.87 | -7.637 | 0.000 | 1.01 | -6.168 | 0.000 | 0.92 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 1.182 | 1.000 | 0.09 | 0.055 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 1.284 | 1.000 | 0.11 | 1.052 | 1.000 | 0.09 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 6.401 | 0.000 | 0.66 | 4.484 | 0.001 | 0.53 | 6.513 | 0.000 | 0.62 | 4.602 | 0.001 | 0.48 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 6.482 | 0.000 | 0.52 | 5.261 | 0.000 | 0.48 | 6.122 | 0.050 | 0.50 | 4.769 | 0.000 | 0.38 |
Appendix Table 3 Paired comparison of N170 amplitudes of four Chinese characters on PO7 electrode in Experiment 2
| O+S+ | O+S- | O-S+ | O-S- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -11.519 | 0.000 | 1.90 | -10.18 | 0.000 | 1.64 | -11.41 | 0.000 | 1.81 | -8.293 | 0.000 | 1.46 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -9.439 | 0.000 | 1.56 | -9.145 | 0.000 | 1.47 | -10.84 | 0.000 | 1.61 | -8.493 | 0.000 | 1.29 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -5.977 | 0.000 | 0.96 | -4.975 | 0.000 | 0.87 | -7.637 | 0.000 | 1.01 | -6.168 | 0.000 | 0.92 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 1.182 | 1.000 | 0.09 | 0.055 | 1.000 | 0.01 | 1.284 | 1.000 | 0.11 | 1.052 | 1.000 | 0.09 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 6.401 | 0.000 | 0.66 | 4.484 | 0.001 | 0.53 | 6.513 | 0.000 | 0.62 | 4.602 | 0.001 | 0.48 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 6.482 | 0.000 | 0.52 | 5.261 | 0.000 | 0.48 | 6.122 | 0.050 | 0.50 | 4.769 | 0.000 | 0.38 |
| O+S+ | O+S- | O-S+ | O-S- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -9.053 | 0.000 | 2.13 | -9.509 | 0.000 | 1.96 | -8.475 | 0.000 | 2.00 | -8.673 | 0.000 | 1.86 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -8.916 | 0.000 | 1.96 | -8.837 | 0.000 | 1.86 | -7.848 | 0.000 | 1.87 | -8.099 | 0.000 | 1.71 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -6.377 | 0.000 | 1.25 | -5.884 | 0.000 | 1.10 | -5.834 | 0.000 | 1.11 | -5.766 | 0.000 | 1.15 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 2.847 | 0.050 | 0.19 | 0.445 | 1.000 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 1.000 | 0.07 | 2.379 | 0.148 | 0.18 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 7.721 | 0.000 | 0.87 | 6.236 | 0.000 | 0.80 | 5.977 | 0.000 | 0.84 | 6.783 | 0.000 | 0.63 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 7.389 | 0.000 | 0.69 | 6.318 | 0.000 | 0.73 | 6.285 | 0.000 | 0.75 | 5.617 | 0.000 | 0.47 |
Appendix Table 4 Paired comparison of N170 amplitudes of four Chinese characters on PO8 electrode in Experiment 2
| O+S+ | O+S- | O-S+ | O-S- | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | t (27) | p | Cohen d | |
| S1 vs. S2 | -9.053 | 0.000 | 2.13 | -9.509 | 0.000 | 1.96 | -8.475 | 0.000 | 2.00 | -8.673 | 0.000 | 1.86 |
| S1 vs. S3 | -8.916 | 0.000 | 1.96 | -8.837 | 0.000 | 1.86 | -7.848 | 0.000 | 1.87 | -8.099 | 0.000 | 1.71 |
| S1 vs. S4 | -6.377 | 0.000 | 1.25 | -5.884 | 0.000 | 1.10 | -5.834 | 0.000 | 1.11 | -5.766 | 0.000 | 1.15 |
| S2 vs. S3 | 2.847 | 0.050 | 0.19 | 0.445 | 1.000 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 1.000 | 0.07 | 2.379 | 0.148 | 0.18 |
| S2 vs. S4 | 7.721 | 0.000 | 0.87 | 6.236 | 0.000 | 0.80 | 5.977 | 0.000 | 0.84 | 6.783 | 0.000 | 0.63 |
| S3 vs. S4 | 7.389 | 0.000 | 0.69 | 6.318 | 0.000 | 0.73 | 6.285 | 0.000 | 0.75 | 5.617 | 0.000 | 0.47 |
| [1] |
Binder, J. R., Medler, D. A., Westbury, C. F., Liebenthal, E., & Buchanan, L. (2006). Tuning of the human left fusiform gyrus to sublexical orthographic structure. Neuroimage, 33(2), 739-748.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.06.053 URL |
| [2] |
Bolger, D. J., Perfetti, C. A., & Schneider, W. (2005). Cross-cultural effect on the brain revisited: Universal structures plus writing system variation. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 92-104.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0193 URL |
| [3] | Booth, J. R., Lu, D., Burman, D. D., Chou, T. -L., Jin, Z., Peng, D. -L., … Liu, L. (2006). Specialization of phonological and semantic processing in Chinese word reading. Brain Research, 1071(1), 197-207. |
| [4] |
Brázdil, M., Mikl, M., Mareček, R., Krupa, P., & Rektor, I. (2007). Effective connectivity in target stimulus processing: A dynamic causal modeling study of visual oddball task. Neuroimage, 35(2), 827-835.
pmid: 17258910 |
| [5] |
Cao, X., Ma, X., & Qi, C. (2015). N170 adaptation effect for repeated faces and words. Neuroscience, 294, 21-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.009 pmid: 25772788 |
| [6] |
Cohen, L., Dehaene, S., Naccache, L., Lehéricy, S., Dehaene-Lambertz, G., Hénaff, M. -A., & Michel, F. (2000). The visual word form area. Brain, 123(2), 291-307.
doi: 10.1093/brain/123.2.291 URL |
| [7] |
Davis, C. P., Libben, G., & Segalowitz, S. J. (2019). Compounding matters: Event-related potential evidence for early semantic access to compound words. Cognition, 184, 44-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2018.12.006 URL |
| [8] |
Dehaene, S., & Cohen, L. (2011). The unique role of the visual word form area in reading. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(6), 254-262.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.04.003 URL |
| [9] |
Delorme, A., & Makeig, S. (2004) EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 134, 9-21
pmid: 15102499 |
| [10] |
Devlin, J. T., Jamison, H. L., Gonnerman, L. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2006). The role of the posterior fusiform gyrus in reading. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18(6), 911-922.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2006.18.6.911 URL |
| [11] |
Eulitz, C., Eulitz, H., Maess, B., Cohen, R., Pantev, C., & Elbert, T. (2000). Magnetic brain activity evoked and induced by visually presented words and nonverbal stimuli. Psychophysiology, 37(4), 447-455.
pmid: 10934903 |
| [12] |
Fraga González, G., Žarić, G., Tijms, J., Bonte, M., Blomert, L., Leppänen, P., & van der Molen, M. W. (2016). Responsivity to dyslexia training indexed by the N170 amplitude of the brain potential elicited by word reading. Brain and Cognition, 106, 42-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2016.05.001 pmid: 27200495 |
| [13] |
Glezer, L. S., Eden, G., Jiang, X., Luetje, M., Napoliello, E., Kim, J., & Riesenhuber, M. (2016). Uncovering phonological and orthographic selectivity across the reading network using fMRI-RA. Neuroimage, 138, 248-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.072 URL |
| [14] |
Glezer, L. S., Jiang, X., & Riesenhuber, M. (2009). Evidence for highly selective neuronal tuning to whole words in the “Visual Word Form Area”. Neuron, 62(2), 199-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.017 URL |
| [15] | Gold, B. T., Balota, D. A., Jones, S. J., Powell, D. K., Smith, C. D., & Andersen, A. H. (2006). Dissociation of automatic and strategic lexical-semantics: Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence for differing roles of multiple frontotemporal regions. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(24), 6523-6532. |
| [16] |
Hauk, O., Davis, M. H., Ford, M., Pulvermüller, F., & Marslen-Wilson, W. D. (2006). The time course of visual word recognition as revealed by linear regression analysis of ERP data. Neuroimage, 30(4), 1383-1400.
pmid: 16460964 |
| [17] |
Hoversten, L. J., Brothers, T., Swaab, T. Y., & Traxler, M. J. (2017). Early processing of orthographic language membership information in bilingual visual word recognition: Evidence from ERPs. Neuropsychologia, 103, 183-190.
doi: S0028-3932(17)30279-8 pmid: 28743547 |
| [18] |
Hsiao, J. H. -W., Shillcock, R., & Lee, C. -Y. (2007). Neural correlates of foveal splitting in reading: Evidence from an ERP study of Chinese character recognition. Neuropsychologia, 45(6), 1280-1292.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.10.001 URL |
| [19] |
Hsu, C. -H., Tsai, J. -L., Lee, C. -Y., & Tzeng, O. -L. (2009). Orthographic combinability and phonological consistency effects in reading Chinese phonograms: An event-related potential study. Brain and Language, 108(1), 56-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2008.09.002 URL |
| [20] |
Kim, K. H., Yoon, H. W., & Park, H. W. (2004). Spatiotemporal brain activation pattern during word/picture perception by native Koreans. Neuroreport, 15(7), 1099-1103.
doi: 10.1097/00001756-200405190-00003 URL |
| [21] |
Krafnick, A. J., Tan, L. -H., Flowers, D. L., Luetje, M. M., Napoliello, E. M., Siok, W. -T., … Eden, G. F. (2016). Chinese character and English word processing in children’s ventral occipitotemporal cortex: fMRI evidence for script invariance. Neuroimage, 133, 302-312.
doi: S1053-8119(16)00219-6 pmid: 27012502 |
| [22] |
Krekelberg, B., Boynton, G. M., & van Wezel, R. J. A. (2006). Adaptation: From single cells to BOLD signals. Trends in Neurosciences, 29(5), 250-256.
pmid: 16529826 |
| [23] |
Kuo, W. -J., Yeh, T. -C., Lee, J. -R., Chen, L. -F., Lee, P. -L., Chen, S. -S., … Hsieh, J. -C. (2004). Orthographic and phonological processing of Chinese characters: An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 21(4), 1721-1731.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.12.007 URL |
| [24] |
Lee, C. -Y., Tsai, J. -L., Chan, W. -H., Hsu, C. -H., Hung, D. L., & Tzeng, O. J. L. (2007). Temporal dynamics of the consistency effect in reading Chinese: An event-related potentials study. NeuroReport, 18(2), 147-151.
doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e328010d4e4 URL |
| [25] |
Lindell, A. K., & Lum, J. A. G. (2008). Priming vs. rhyming: Orthographic and phonological representations in the left and right hemispheres. Brain and Cognition, 68(2), 193-203.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2008.04.005 URL |
| [26] |
Lin, S. E., Chen, H. C., Zhao, J., Li, S., He, S., & Weng, X. C. (2011). Left-lateralized N170 response to unpronounceable pseudo but not false Chinese characters—the key role of orthography. Neuroscience, 190, 200-206.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.05.071 pmid: 21704128 |
| [27] |
Liu, C., Zhang, W. -T., Tang, Y. -Y., Mai, X. -Q., Chen, H. -C., Tardif, T., & Luo, Y. -J. (2008). The visual word form area: Evidence from an fMRI study of implicit processing of Chinese characters. Neuroimage, 40(3), 1350-1361.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.014 URL |
| [28] |
Lu, Q., Tang, Y. -Y., Zhou, L., & Yu, Q. (2011). The different time courses of reading different levels of Chinese characters: An ERP study. Neuroscience Letters, 498(3), 194-198.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.03.061 URL |
| [29] |
Madden, D. J. (2004). Age-related changes in neural activity during visual target detection measured by fMRI. Cerebral Cortex, 14(2), 143-155.
pmid: 14704211 |
| [30] |
Maurer, U., Brem, S., Bucher, K., & Brandeis, D. (2005). Emerging neurophysiological specialization for letter strings. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(10), 1532-1552.
pmid: 16269095 |
| [31] | Maurer, U., & McCandliss, B. D. (2007). The development of visual expertise for words: The contribution of electrophysiology. In E. L. Grigorenko & A. J. Naples (Eds.), Single-word reading: Behavioral and biological perspectives. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. |
| [32] |
Maurer, U., Zevin, J. D., & McCandliss, B. D. (2008). Left-lateralized N170 effects of visual expertise in reading: Evidence from Japanese syllabic and logographic scripts. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(10), 1878-1891.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2008.20125 pmid: 18370600 |
| [33] |
Mechelli, A., Sartori, G., Orlandi, P., & Price, C. J. (2006). Semantic relevance explains category effects in medial fusiform gyri. Neuroimage, 30(3), 992-1002.
pmid: 16343950 |
| [34] |
Mei, L., Xue, G., Lu, Z.-L., He, Q., Zhang, M., Xue, F., … Dong, Q. (2013). Orthographic transparency modulates the functional asymmetry in the fusiform cortex: An artificial language training study. Brain and Language, 125(2), 165-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2012.01.006 URL |
| [35] |
Mo, C., Yu, M., Seger, C., & Mo, L. (2015). Holistic neural coding of Chinese character forms in bilateral ventral visual system. Brain and Language, 141, 28-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2014.11.008 URL |
| [36] |
Pattamadilok, C., Chanoine, V., Pallier, C., Anton, J. -L., Nazarian, B., Belin, P., & Ziegler, J. C. (2017). Automaticity of phonological and semantic processing during visual word recognition. Neuroimage, 149, 244-255.
doi: S1053-8119(17)30107-6 pmid: 28163139 |
| [37] |
Price, C. J., & Devlin, J. T. (2011). The interactive account of ventral occipitotemporal contributions to reading. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(6), 246-253.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.04.001 URL |
| [38] |
Proverbio, A. M., & Zani, A. (2003). Time course of brain activation during graphemic/phonologic processing in reading: An ERP study. Brain and Language, 87(3), 412-420.
pmid: 14642543 |
| [39] |
Raposo, A., Moss, H. E., Stamatakis, E. A., & Tyler, L. K. (2006). Repetition suppression and semantic enhancement: An investigation of the neural correlates of priming. Neuropsychologia, 44(12), 2284-2295.
pmid: 16806317 |
| [40] |
Rossion, B., Joyce, C. A., Cottrell, G. W., & Tarr, M. J. (2003). Early lateralization and orientation tuning for face, word, and object processing in the visual cortex. Neuroimage, 20(3), 1609-1624.
pmid: 14642472 |
| [41] |
Sacchi, E., & Laszlo, S. (2016). An event-related potential study of the relationship between N170 lateralization and phonological awareness in developing readers. Neuropsychologia, 91, 415-425.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.09.001 URL |
| [42] |
Saygin, Z. M., Osher, D. E., Norton, E. S., Youssoufian, D. A., Beach, S. D., Feather, J., … Kanwisher, N. (2016). Connectivity precedes function in the development of the visual word form area. Nature Neuroscience, 19(9), 1250-1255.
doi: 10.1038/nn.4354 URL |
| [43] |
Scott, G. G., O’Donnell, P. J., Leuthold, H., & Sereno, S. C. (2009). Early emotion word processing: Evidence from event-related potentials. Biological Psychology, 80(1), 95-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.03.010 URL |
| [44] |
Segalowitz, S. J., & Zheng, X. (2009). An ERP study of category priming: Evidence of early lexical semantic access. Biological Psychology, 80(1), 122-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.04.009 pmid: 18524454 |
| [45] | Shaywitz, B. A., Shaywitz, S. E., Pugh, K. R., Mencl, W. E., Fulbright, R. K., Skudlarski, P., … Gore, J. C. (2002). Disruption of posterior brain systems for reading in children with developmental dyslexia. Biological Psychiatry, 52(2), 101-110. |
| [46] |
Siok, W. T., Perfetti, C. A., Jin, Z., & Tan, L. H. (2004). Biological abnormality of impaired reading is constrained by culture. Nature, 431(7004), 71-76.
doi: 10.1038/nature02865 URL |
| [47] |
Szwed, M., Qiao, E., Jobert, A., Dehaene, S., & Cohen, L. (2014). Effects of literacy in early visual and occipitotemporal areas of Chinese and French readers. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(3), 459-475.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00499 URL |
| [48] |
Tan, L. H., Liu, H. -L., Perfetti, C. A., Spinks, J. A., Fox, P. T., & Gao, J. -H. (2001). The neural system underlying Chinese logograph reading. Neuroimage, 13(5), 836-846.
pmid: 11304080 |
| [49] |
Vinckier, F., Dehaene, S., Jobert, A., Dubus, J. P., Sigman, M., & Cohen, L. (2007). Hierarchical coding of letter strings in the ventral stream: Dissecting the inner organization of the visual word-form system. Neuron, 55(1), 143-156.
pmid: 17610823 |
| [50] | Wang, X., Shu, H., & Yang, J. (2010). Visual word form area and its functional role in the neural network of reading. Advances in Psychological Science, 18(8), 1199-1207. |
| [51] |
Wang, X., Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhang, J., Ling, Z., & Bi, Y. (2018). Representational similarity analysis reveals task-dependent semantic influence of the visual word form area. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 3047.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21062-0 URL |
| [52] |
Wang, X., Yang, J., Shu, H., & Zevin, J. D. (2011). Left fusiform BOLD responses are inversely related to word-likeness in a one-back task. Neuroimage, 55(3), 1346-1356.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.062 URL |
| [53] | Wang, X., Zhao, R., Zevin, J. D., & Yang, J. (2016). The neural correlates of the interaction between semantic and phonological processing for Chinese character reading. Frontiers in Psychology, 7(518). |
| [54] |
Wheatley, T., Weisberg, J., Beauchamp, M. S., & Martin, A. (2005). Automatic priming of semantically related words reduces activity in the fusiform gyrus. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(12), 1871-1885.
pmid: 16356325 |
| [55] |
Xue, G., Chen, C., Jin, Z., & Dong, Q. (2006). Language experience shapes fusiform activation when processing a logographic artificial language: An fMRI training study. Neuroimage, 31(3), 1315-1326.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.055 URL |
| [56] |
Yang, J., Mccandliss, B. D., Shu, H., & Zevin, J. D. (2009). Simulating language-specific and language-general effects in a statistical learning model of Chinese reading. Journal of Memory and Language, 61(2), 238-257.
doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2009.05.001 URL |
| [57] |
Yang, J., Wang, X., Shu, H., & Zevin, J. D. (2011). Brain networks associated with sublexical properties of Chinese characters. Brain and Language, 119(2), 68-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2011.03.004 URL |
| [58] |
Yang, J., Wang, X., Shu, H., & Zevin, J. D. (2012). Task by stimulus interactions in brain responses during Chinese character processing. Neuroimage, 60(2), 979-990.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.036 URL |
| [59] | Yum, Y. N., Law, S. -P., Su, I. -F., Lau, K. -Y. D., & Mo, K. N. (2014). An ERP study of effects of regularity and consistency in delayed naming and lexicality judgment in a logographic writing system. Frontiers in Psychology, 5(5), 315. |
| [60] | Zhao, L., Chen, C., Shao, L., Wang, Y., Xiao, X., Chen, C., .. Xue, G. (2017). Orthographic and phonological representations in the fusiform cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 27(11), 5197-5210. |
| [61] |
Zhao, J., Li, S., Lin, S. -E., Cao, X. -H., He, S., & Weng, X. -C. (2012). Selectivity of N170 in the left hemisphere as an electrophysiological marker for expertise in reading Chinese. Neuroscience Bulletin, 28(5), 577-584.
doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1274-y URL |
| [62] | Zhou, L., Peng, G., Zheng, H. -Y., Su, I. -F., & Wang, W. S. -Y. (2012). Sub-lexical phonological and semantic processing of semantic radicals: A primed naming study. Reading and Writing, 26(6), 967-989. |
| [63] | Zhou, X. L., Lu, X. M., & Shu, H. (2000). The nature of sublexical processing in reading Chinese: Phonological activation of semantic radials. Acta Psychologica Sinica. 32(1), 20-24. |
| [64] | Zhou, X., & Marslen-Wilson, W. (1999). Phonology, orthography, and semantic activation in reading Chinese. Journal of Memory and Language, 41(4), 579-606. |
| [1] | CHENG Yahua, WANG Jian, WU Xinchun. The role of morphological awareness in Chinese children’s reading comprehension: The mediating effect of word reading fluency [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(4): 413-425. |
| [2] | LUO Yu, FENG Lihong, REN Min, GU Qiuyu, ZHAO Shouying, ZHANG Yu. The effect of perceptual load on processing and memorizing negative facial distractor [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(10): 1256-1266. |
| [3] | ZHONG Yiping, LI Jin, ZHAN Youlong, FAN Wei, YANG Zilu. Rotated self-face recognition: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(11): 1379-1389. |
| [4] | CHEN Jingjun; XU Lei; CHENG Xiaorong; LIU Huashan. Chinese character practice: Comparison between children using handwriting and Pinyin keyboarding [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(10): 1258-1269. |
| [5] | YANG Yaping, XU Qiang, ZHANG Lin, DENG Peizhuang, LIANG Ningjian. Scenes Differing in Spatial Frequencies Affect Facial Expression Processing: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(12): 1433-1444. |
| [6] | WU Shiyu; MA Zheng. Cross-linguistic Phonological Interference in L2 Visual Word Reading: #br# Evidence from the Semantic Relatedness Decision Task [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(11): 1318-1327. |
| [7] | SUN Tianyi;XU yuanli;GUO Chunyan. The Brain Potential Features of Human Face Recognition during Working Memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(10): 1072-1084. |
| [8] | LI Ya-Dan,MA Wen-Juan,LUO Jun-Long,ZHANG Qing-Lin. Competition and Emotion Impact on Effect of Prototype Elicitation during Insight Problem Solving [J]. , 2012, 44(1): 1-13. |
| [9] | ZHAI Hong-Chang,REN Jing,XIAO Sheng-Yong,DENG Bo-Ping,XU Xiao-Xia. Brain Activations of the Processing of the “Reading-only Without Writing” Character [J]. , 2011, 43(02): 132-142. |
| [10] | HAN Lei,MA Juan,JIAO Ting,GAO Feng-Qiang,GUO Yong-Yu,WANG Peng. Differences in Early Face Processing between Shy and Nonshy Undergraduates: Electrophysiological Evidence from an ERP Study [J]. , 2010, 42(02): 271-278. |
| [11] | ZHU Zhao-Xia,LIU Li,DING Guo-Sheng,PENG Dan-Ling. The Influence of Pinyin Typewriting Experience on Orthographic and Phonological Processing of Chinese Characters [J]. , 2009, 41(09): 785-792. |
| [12] | YANG Jian-Feng,SHU Hua. A Connectionist Model of Chinese Characters Reading [J]. , 2008, 40(05): 516-522. |
| [13] | Chen Li,Zhang Qinglin,Yan Xia,Zhang Ying,Liao Xianghui,Chen Yi. The Emotion Promoting Effect in the Logogriph Activation of Chinese Characters [J]. , 2008, 40(02): 127-135. |
| [14] | Wang Yiwen, Lin Chongde, Wei Jinghan, Luo Yuejia, Wei Xing. ERP Effects of Dynamic Maintenance of Chinese Characters and Spatial Information in Working Memory [J]. , 2004, 36(03): 253-259. |
| [15] | Zhou-Xinlin,Zeng-Jieying. VISUAL PERCEPTION OF CHINESE CHARACTERS [J]. , 2003, 35(04): 514-519. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||