

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (11): 1173-1188.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.01173
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
TANG Xiaoyu1( ), TONG Jiageng1, YU Hong1, WANG Aijun2(
), TONG Jiageng1, YU Hong1, WANG Aijun2( )
)
Received:2021-01-08
Published:2021-11-25
Online:2021-09-23
Contact:
TANG Xiaoyu,WANG Aijun
E-mail:tangyu-2006@163.com;ajwang@suda.edu.cn
Supported by:TANG Xiaoyu, TONG Jiageng, YU Hong, WANG Aijun. (2021). Effects of endogenous spatial attention and exogenous spatial attention on multisensory integration. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(11), 1173-1188.
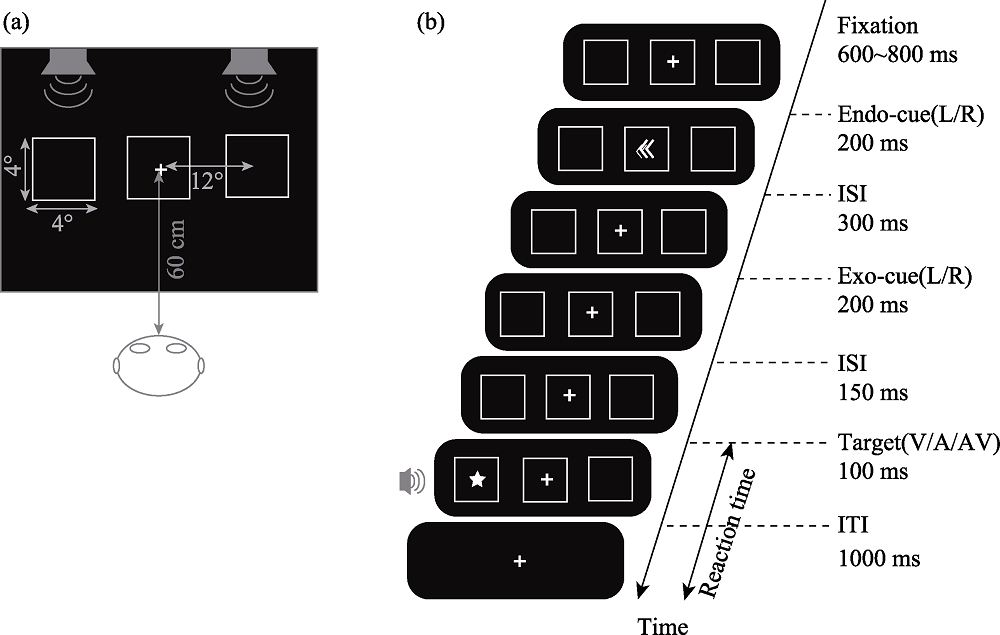
Figure 1. Flow diagram of Experiment 1. Note. Figure 1(a) is a schematic diagram of the target stimulus presentation, and Figure 1(b) is a flowchart of a single trial. The endogenous spatial cues in the right picture were 80% predictive of the spatial location of the following target stimulus, while exogenous spatial cues were not predictive of the spatial location of the target stimulus. Endo-cue (L/R) represents endogenous cues appearing on the left or right; exo-cue (L/R) represents exogenous cues appearing on the left or right. Target stimuli (V/A/AV) represent visual stimuli, auditory stimuli, and audiovisual stimuli, respectively.
| Target stimulus type | Endogenous valid | Endogenous invalid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exogenous valid | Exogenous invalid | Exogenous valid | Exogenous invalid | |
| Visual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 390.92 ± 57.34 | 408.06 ± 65.76 | 404.22 ± 54.76 | 413.42 ± 64.94 |
| ACC (%) | 98.75 ± 1.38 | 97.19 ± 2.33 | 98.02 ± 2.50 | 96.16 ± 3.86 |
| Audiovisual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 330.15 ± 36.51 | 357.75 ± 45.41 | 339.71 ± 37.18 | 368.74 ± 42.60 |
| ACC (%) | 99.36 ± 0.72 | 98.27 ± 1.54 | 99.41 ± 1.44 | 97.33 ± 3.07 |
| Auditory stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 361.03 ± 42.10 | 432.79 ± 78.71 | 373.75 ± 41.18 | 448.32 ± 82.17 |
| ACC (%) | 98.97 ± 1.20 | 94.33 ± 4.22 | 98.52 ± 1.94 | 91.27 ± 5.35 |
Table 1 Reaction time (RT/ms) and accuracy (ACC/%) (M ± SD) under different conditions in Experiment 1
| Target stimulus type | Endogenous valid | Endogenous invalid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exogenous valid | Exogenous invalid | Exogenous valid | Exogenous invalid | |
| Visual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 390.92 ± 57.34 | 408.06 ± 65.76 | 404.22 ± 54.76 | 413.42 ± 64.94 |
| ACC (%) | 98.75 ± 1.38 | 97.19 ± 2.33 | 98.02 ± 2.50 | 96.16 ± 3.86 |
| Audiovisual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 330.15 ± 36.51 | 357.75 ± 45.41 | 339.71 ± 37.18 | 368.74 ± 42.60 |
| ACC (%) | 99.36 ± 0.72 | 98.27 ± 1.54 | 99.41 ± 1.44 | 97.33 ± 3.07 |
| Auditory stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 361.03 ± 42.10 | 432.79 ± 78.71 | 373.75 ± 41.18 | 448.32 ± 82.17 |
| ACC (%) | 98.97 ± 1.20 | 94.33 ± 4.22 | 98.52 ± 1.94 | 91.27 ± 5.35 |
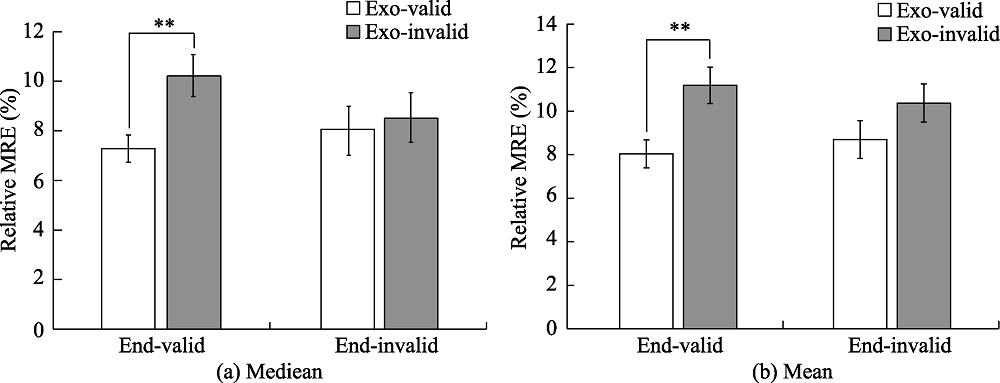
Figure 2. (a) rMRE results under different cue conditions when the reaction time is the median; (b) rMRE results under different cue conditions when the reaction time is the average. Note. rMRE (relative amount of multisensory response enhancement); * p < 0.01.
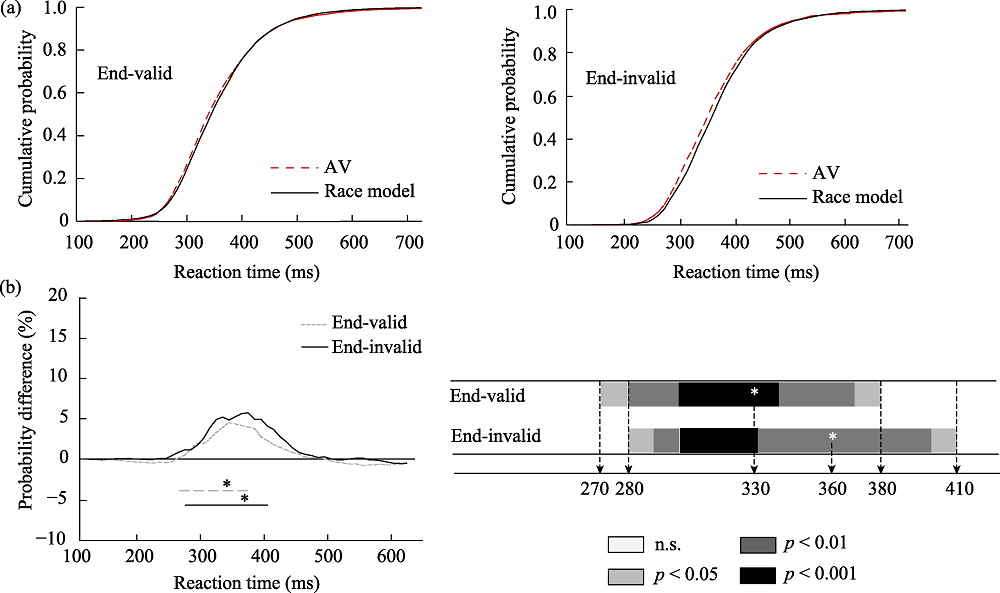
Figure 3. (a) was the cumulative probability distribution of endogenous cue in Experiment 1, and (b) was the result of race model of endogenous cue in Experiment 1. Note. The thick lines represent a window of time in which significant integration of audiovisual stimuli takes place. A dotted line is a valid clue, and a solid line is an invalid clue. * represents the time at which the peak (maximum probability) occurs.
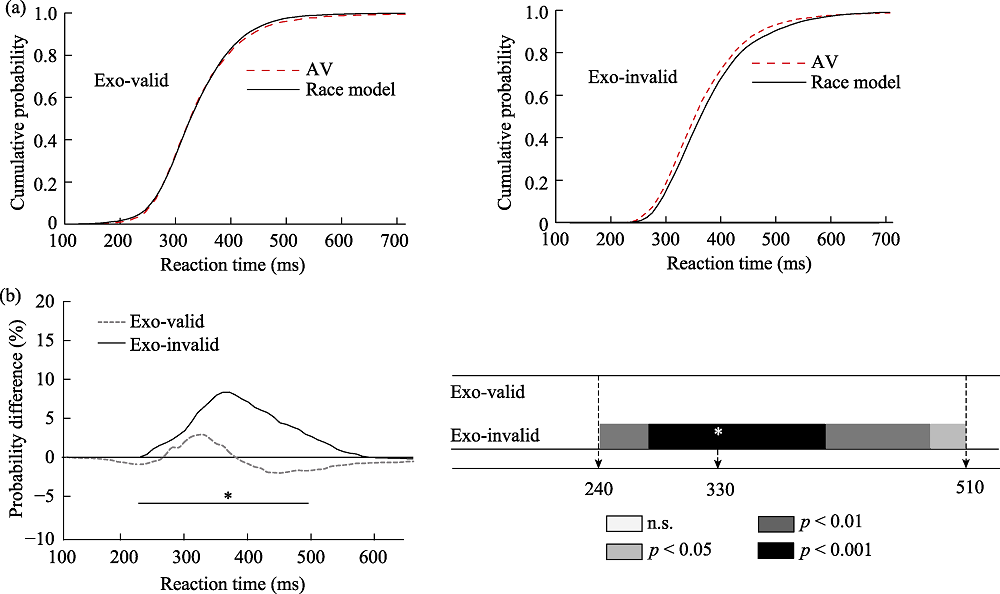
Figure 4. (a) was the cumulative probability distribution of exogenous cue in Experiment 1, and (b) was the result of race model of exogenous cue in Experiment 1. Note. The thick lines represent a window of time in which significant integration of audiovisual stimuli takes place. A dotted line is a valid clue, and a solid line is an invalid clue. * represents the time at which the peak (maximum probability) occurs.
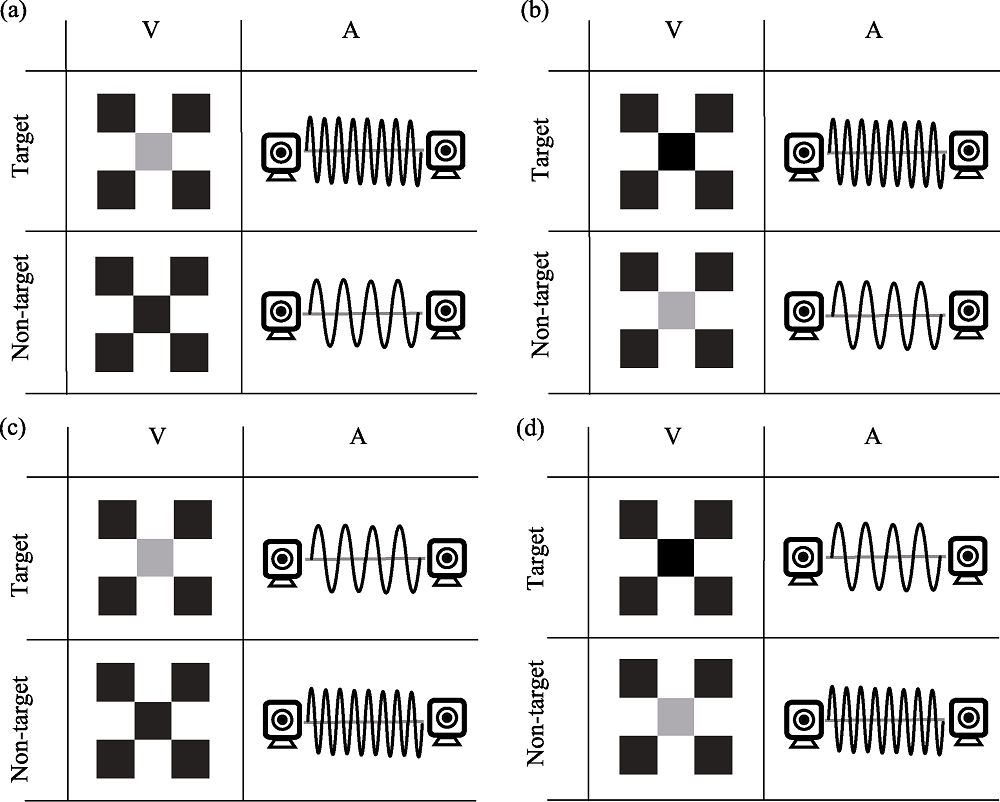
Figure 5. Target stimulus types in Experiment 2. Note. Figure 5 shows Experiment 2 with four types of target stimuli. The task of Experiment 2 was to determine the spatial location of target stimuli and not to respond to non-target stimuli.
| Target stimulus type | Endogenous valid | Endogenous invalid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exogenous valid | External invalid | Exogenous valid | External invalid | |
| Visual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 462.68 ± 41.87 | 499.19 ± 52.29 | 526.97 ± 54.44 | 577.86 ± 72.07 |
| ACC (%) | 97.17 ± 2.35 | 93.61 ± 4.29 | 88.55 ± 5.96 | 82.14 ± 7.24 |
| Audiovisual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 437.68 ± 48.56 | 466.07 ± 55.96 | 482.93 ± 71.26 | 513.86 ± 67.59 |
| ACC (%) | 98.82 ± 0.86 | 97.67 ± 1.68 | 96.50 ± 2.00 | 94.70 ± 3.89 |
| Auditory stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 494.43 ± 55.11 | 554.21 ± 75.59 | 499.29 ± 55.99 | 576.97 ± 72.94 |
| ACC (%) | 97.52 ± 1.70 | 95.38 ± 3.28 | 96.00 ± 2.82 | 92.14 ± 5.45 |
Table 2 Reaction time (RT/MS) and accuracy (ACC/%) (M ± SD) under different conditions in Experiment 2
| Target stimulus type | Endogenous valid | Endogenous invalid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exogenous valid | External invalid | Exogenous valid | External invalid | |
| Visual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 462.68 ± 41.87 | 499.19 ± 52.29 | 526.97 ± 54.44 | 577.86 ± 72.07 |
| ACC (%) | 97.17 ± 2.35 | 93.61 ± 4.29 | 88.55 ± 5.96 | 82.14 ± 7.24 |
| Audiovisual stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 437.68 ± 48.56 | 466.07 ± 55.96 | 482.93 ± 71.26 | 513.86 ± 67.59 |
| ACC (%) | 98.82 ± 0.86 | 97.67 ± 1.68 | 96.50 ± 2.00 | 94.70 ± 3.89 |
| Auditory stimuli | ||||
| RT (ms) | 494.43 ± 55.11 | 554.21 ± 75.59 | 499.29 ± 55.99 | 576.97 ± 72.94 |
| ACC (%) | 97.52 ± 1.70 | 95.38 ± 3.28 | 96.00 ± 2.82 | 92.14 ± 5.45 |

Figure 6. (a) rMRE results under different cue conditions when the reaction time is median; (b) rMRE results under different cue conditions when the reaction time is average. Note. rMRE (relative amount of multisensory response enhancement); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
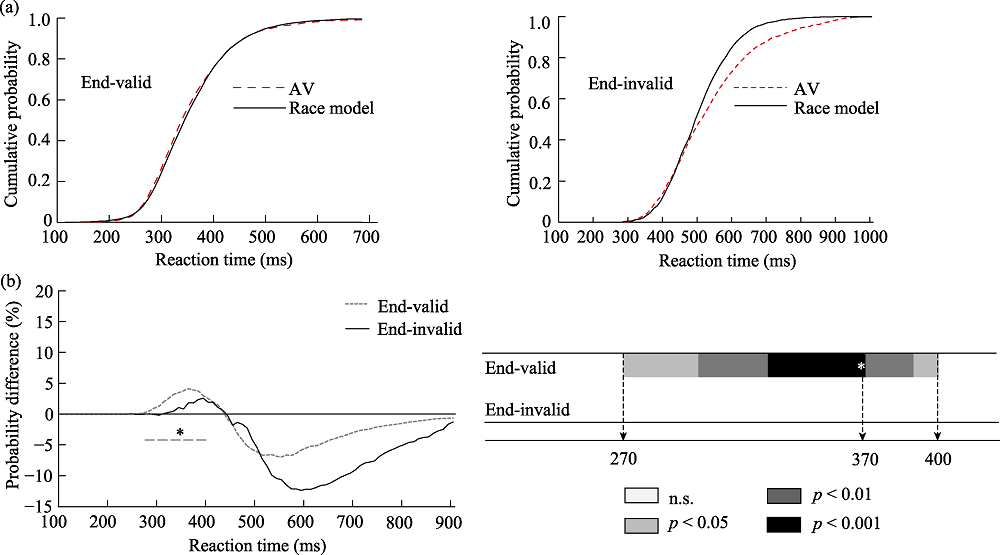
Figure 7. (a) is the cumulative probability distribution of the endogenous cue in Experiment 2, and (b) is the result of the race model of the endogenous cue in Experiment 2 Note. The thick lines represent a window of time in which significant integration of audiovisual stimuli takes place. A dotted line is a valid clue, and a solid line is an invalid clue. * represents the time at which the peak (maximum probability) occurs.
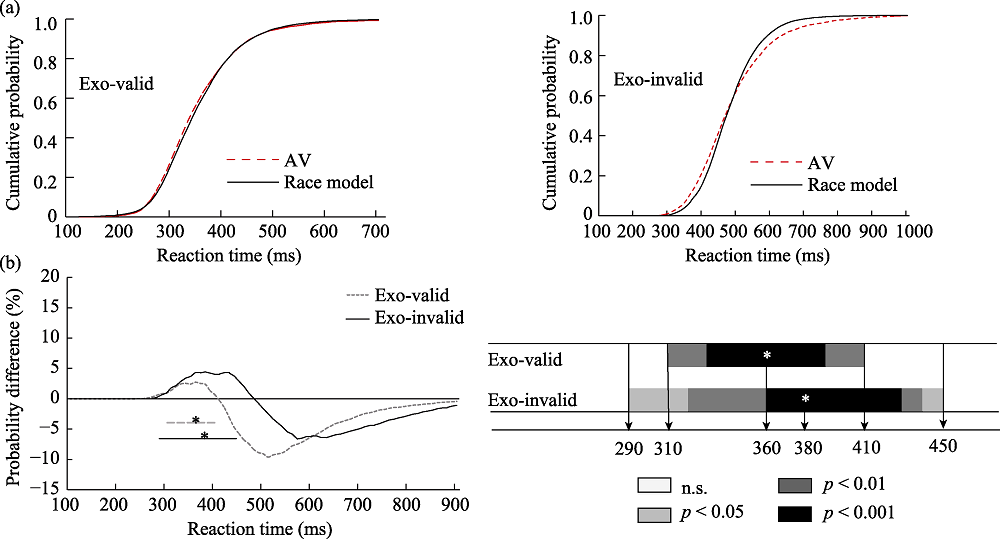
Figure 8. (a) is the cumulative probability distribution of exogenous cue in Experiment 2, and (b) is the result of race model of exogenous cue in Experiment 2. Note. The thick lines represent a window of time in which significant integration of audiovisual stimuli takes place. A dotted line is a valid clue, and a solid line is an invalid clue. * represents the time at which the peak (maximum probability) occurs.
| [1] |
Atchley, P., Jones, S. E., & Hoffman, L. (2003). Visual marking: A convergence of goal- and stimulus-driven processes during visual search. Percept Psychophys, 65(5), 667.
pmid: 12956576 |
| [2] |
Berger, A., & Henik, A. (2000). The endogenous modulation of IOR is nasal-temporal asymmetric. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(3), 421-428.
pmid: 10931769 |
| [3] |
Berger, A., Henik, A., & Rafal, R. (2005). Competition between endogenous and exogenous orienting of visual attention. Journal Experimental Psychology General, 134(2), 207-221.
doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.134.2.207 URL |
| [4] | Botta, F., Lupiáñez, J., & Chica, A. B. (2014). When endogenous spatial attention improves conscious perception: Effects of alerting and bottom-up activation. Consciousness & Cognition, 23, 63-73. |
| [5] | Burg, E. V. D., Olivers, C. N. L., Bronkhorst, A. W., & Theeuwes, J. (2008). Pip and pop: Non-spatial auditory signals improve spatial visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 34(5), 1053-1065. |
| [6] |
Busse, L., Katzner, S., & Treue, S. (2008). Temporal dynamics of neuronal modulation during exogenous and endogenous shifts of visual attention in macaque area MT. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(42), 16380-16385.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707369105 URL |
| [7] |
Chica, A. B., Paolo, Bartolomeo, Juan, & Lupiáñez. (2013). Two cognitive and neural systems for endogenous and exogenous spatial attention. Behavioural Brain Research, 237, 107-123.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.09.027 pmid: 23000534 |
| [8] |
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(3), 201.
doi: 10.1038/nrn755 URL |
| [9] |
Fairhall, S. L., & Macaluso, E. (2009). Spatial attention can modulate audiovisual integration at multiple cortical and subcortical sites. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29(6), 1247-1257.
doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06688.x pmid: 19302160 |
| [10] | Folk, C. L., & Remington, R. (1998). Selectivity in distraction by irrelevant featural singletons: Evidence for two forms of attentional capture. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performan, 24(3), 847. |
| [11] |
Gowen, E., Abadi, R. V., Poliakoff, E., Hansen, P. C., & Miall, R. C. (2007). Modulation of saccadic intrusion by exogenous and endogenous attention. Brain Research, 1141(1), 154-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.047 URL |
| [12] |
Granholm, E., Asarnow, R. F., Sarkin, A. J., & Dykes, K. L. (1996). Pupillary responses index cognitive resource limitations. Psychophysiology, 33(4), 457-461.
pmid: 8753946 |
| [13] |
Grubb, M. A., White, A. L., Heeger, D. J., & Carrasco, M. (2015). Interactions between voluntary and involuntary attention modulate the quality and temporal dynamics of visual processing. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(2), 437-444.
doi: 10.3758/s13423-014-0698-y URL |
| [14] |
Grundy, J. G., Barker, R. M., Anderson, J. A. E., & Shedden, J. M. (2019). The relation between brain signal complexity and task difficulty on an executive function task. NeuroImage, 198, 104-113.
doi: S1053-8119(19)30437-9 pmid: 31112787 |
| [15] |
Gustavo, R., Coull, J. T., Nobre, A. C., & Sam, G. (2011). Behavioural dissociation between exogenous and endogenous temporal orienting of attention. Plos One, 6(1), e14620.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014620 URL |
| [16] |
Hopfinger, J. B., & West, V. M. (2006). Interactions between endogenous and exogenous attention on cortical visual processing. NeuroImage, 31(2), 774-789.
pmid: 16490366 |
| [17] | Johnston, W. A., & Heinz, S. P. (1979). Depth of nontarget processing in an attention task. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 5(1), 168. |
| [18] | Julia, F. C., Daniel, C., Beer, A. L., & Daphne, B. (2018). Neural bases of enhanced attentional control: Lessons from action video game players. Brain & Behavior, 8(7), e01019. |
| [19] |
Kosslyn, S. M., Thompson, W. L., Wraga, M., & Alpert, N. M. (2001). Imagining rotation by endogenous versus exogenous forces: Distinct neural mechanisms. Neuroreport, 12(11), 2519-2525.
pmid: 11496141 |
| [20] | Lavie, N. (1995). Perceptual load as a necessary condition for selective attention. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 21(3), 451-468. |
| [21] |
Lavie , & N. (2010). Attention, distraction, and cognitive control under load. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19(3), 143-148.
doi: 10.1177/0963721410370295 URL |
| [22] |
Lunn, J., Sjoblom, A., Ward, J., Soto-Faraco, S., & Forster, S. (2019). Multisensory enhancement of attention depends on whether you are already paying attention. Cognition, 187, 38-49.
doi: S0010-0277(19)30035-6 pmid: 30825813 |
| [23] |
Lupiáñez, J., Botta, F., Martín-Arévalo, E., Chica, A. B. (2014). The spatial orienting paradigm: How to design and interpret spatial attention experiments. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 40, 35-51.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.01.002 pmid: 24462751 |
| [24] |
Mayer, A. R., Dorflinger, J. M., Rao, S. M., & Seidenberg, M. (2004). Neural networks underlying endogenous and exogenous visual-spatial orienting. Neuroimage, 23(2), 534-541.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.027 URL |
| [25] |
Meyer, K. N., Du, F., Parks, E., & Hopfinger, J. B. (2018). Exogenous vs. endogenous attention: Shifting the balance of fronto-parietal activity. Neuropsychologia, 111, 307-316.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.02.006 URL |
| [26] |
Miller, J. (1982). Divided attention: Evidence for coactivation with redundant signals. Cognitive Psychology, 14(2), 247-279.
pmid: 7083803 |
| [27] |
Odegaard, B., Wozny, D. R., & Shams, L. (2016). The effects of selective and divided attention on sensory precision and integration. Neuroscience Letters, 614(9), 24-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.12.039 URL |
| [28] |
Otten, M., Schreij, D., & Los, S. A. (2016). The interplay of goal-driven and stimulus-driven influences on spatial orienting. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 78(6), 1642-1654.
doi: 10.3758/s13414-016-1121-8 URL |
| [29] |
Pauszek, J. R., & Gibson, B. S. (2016). High spatial validity is not sufficient to elicit voluntary shifts of attention. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 78(7), 2110-2123.
doi: 10.3758/s13414-016-1097-4 URL |
| [30] |
Peelen, M. V., Heslenfeld, D. J., & Theeuwes, J. (2004). Endogenous and exogenous attention shifts are mediated by the same large-scale neural network. NeuroImage, 22(2), 822-830.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.01.044 URL |
| [31] |
Peng, X., Chang, R, S., Li, Q., Wang, A, J., & Tang, X, Y. (2019). Visually induced inhibition of return affects the audiovisual integration under different SOA conditions. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 51(7), 759-771.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2019.00759 URL |
| [32] | Peng, X., Chang, R, S., Ren, G, Q., Wang, A, J., & Tang, X, Y. (2018). The interaction between exogenous attention and multisensory integration. Advances in Psychological Science, 26(12), 43-54. |
| [33] |
Posner, M. I. (1980). "Orienting of attention." Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 32(1), 3-25.
doi: 10.1080/00335558008248231 URL |
| [34] |
Senkowski, D., Saint-Amour, D., Hofle, M., & Foxe, J. J. (2011). Multisensory interactions in early evoked brain activity follow the principle of inverse effectiveness. NeuroImage, 56(4), 2200-2208.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.075 pmid: 21497200 |
| [35] |
Senkowski, D., Talsma, D., Herrmann, C. S., & Woldorff, M. G. (2005). Multisensory processing and oscillatory gamma responses: Effects of spatial selective attention. Experimental Brain Research, 166(3-4), 411-426.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-2381-z URL |
| [36] |
Sugihara, T., Diltz, M. D., Averbeck, B. B., & Romanski, L. M. (2006). Integration of auditory and visual communication information in the primate ventrolateral prefrontal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(43), 11138-11147.
pmid: 17065454 |
| [37] |
Talsma, D., Doty, T. J., & Woldorff, M. G. (2007). Selective attention and audiovisual integration: Is attending to both modalities a prerequisite for early integration? Cerebral Cortex, 17(3), 679-690.
pmid: 16707740 |
| [38] |
Talsma, D., Senkowski, D., Soto-Faraco, S., & Woldorff, M. G. (2010). The multifaceted interplay between attention and multisensory integration. Trends in Cognitive Science, 14(9), 400-410.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.06.008 URL |
| [39] |
Talsma, D., & Woldorff, M. G. (2005). Selective attention and multisensory integration: Multiple phases of effects on the evoked brain activity. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(7), 1098-1114.
pmid: 16102239 |
| [40] |
Tang, X., Wu, J., & Shen, Y. (2016). The interactions of multisensory integration with endogenous and exogenous attention. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 61, 208-224.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.11.002 URL |
| [41] |
Tang, X, Y., Sun, J, Y., & Peng, X. (2020). The effect of bimodal divided attention on inhibition of return with audiovisual targets. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(3), 257-268.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00257 URL |
| [42] |
Tang, X, Y., Wu, Y, N., Peng, X., Wang, A, J., & Li, Q. (2020). The influence of endogenous spatial cue validity on audiovisual integration. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(7), 835-846.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00835 URL |
| [43] |
van der Stoep, N., van der Stigchel, S., & Nijboer, T. C. W. (2015). Exogenous spatial attention decreases audiovisual integration. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 77(2), 464-482.
doi: 10.3758/s13414-014-0785-1 URL |
| [44] |
van der Stoep, N., van der Stigchel, S., Nijboer, T. C. W., & Spence, C. (2016). Visually induced inhibition of return affects the integration of auditory and visual information. Perception, 46(1), 6-17.
doi: 10.1177/0301006616661934 URL |
| [45] | Washburn, D. A., & Putney, R. T. (2001). Attention and task difficulty: When is performance facilitated?. Learning & Motivation, 32(1), 36-47. |
| [46] | Yantis, S., & Jonides, J. (1990). Abrupt visual onsets and selective attention: Voluntary versus automatic allocation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 16(1), 121-134. |
| [47] | Yu, H. (2019). The effects of attention on multisensory integration (Unpublished master’s thesis). Liaoning Normal University, Dalian, China. |
| [1] | TANG Xiaoyu, WU Yingnan, PENG Xing, WANG Aijun, LI Qi. The influence of endogenous spatial cue validity on audiovisual integration [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(7): 835-846. |
| [2] | PENG Xing, CHANG Ruosong, LI Qi, WANG Aijun, TANG Xiaoyu. Visually induced inhibition of return affects the audiovisual integration under different SOA conditions [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(7): 759-771. |
| [3] | YU Wei, WANG Aijun, ZHANG Ming. Effect of selective and divided attentions on auditory dominance in multisensory integration [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(2): 164-173. |
| [4] | MA Wen-Juan,SUO Tao,LI Ya-Dan,LUO Li-Zhu,FENG Ting-Yong,LI Hong. Dissecting the Win-Loss Framing Effect of Intertemporal Choice: Researches from Intertemporal Choice of Money-Gain & Loss [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2012, 44(8): 1038-1046. |
| [5] | SUN Yuan-Lu,HU Zhong-Hua,ZHANG Rui-Ling,XUN Mang-Mang,LIU Qiang,ZHANG Qing-Lin. An Investigation on the Effect Factors in the Paradigm of Multisensory Integration [J]. , 2011, 43(11): 1239-1246. |
| [6] | LIU Qiang,HU Zhong-Hua,ZHAO Guang,TAO Wei-Dong,ZHANG Qing-Lin,SUN Hong-Jin. The Prior Knowledge of the Reliability of Sensory Cues Affects the Multisensory Integration in the Early Perceptual Processing Stage [J]. , 2010, 42(02): 227-234. |
| [7] | YANG Ji-Ping,ZHENG Jian-Jun. The Effect of Emotion on the Quality of Crisis Decision-making [J]. , 2009, 41(06): 481-491. |
| [8] | Cai Houde. TASK DIFFICULTY IN PERCEPTUAL IDENTIFICATION OF STIMULUS AND DISTRIBUTING PROCESSING ACROSS TWO HEMISPHERES [J]. , 2005, 37(01): 14-18. |
| [9] | Ge Liezhong,Zhu Zuxiang(Dept.of Psychology,Hangzhou University,310028). RESEARCH ON THE EFFECTS OF THE OUTCOME CONFLICT AND TASK DIFFICULTY ON DUAL-TASK PERFORMANCE [J]. , 1995, 27(03): 247-253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||