

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 946-957.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00946
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qi1, DENG Nali1, JIANG Xiumin2, LI Weijun1( )
)
Received:2019-07-31
Published:2020-08-25
Online:2020-06-28
Contact:
LI Weijun
E-mail:li_wj@126.com
Supported by:ZHANG Qi, DENG Nali, JIANG Xiumin, LI Weijun. (2020). The time course of self-relevance affecting emotional word processing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(8), 946-957.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00946
| Variable | Negative | Neutral | Positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 3.31 ± 0.77 | 5.11 ± 0.37 | 6.33 ± 0.84 |
| Arousal | 5.12 ± 1.31 | 3.44 ± 1.20 | 4.71 ± 1.20 |
| Concreteness | 4.77 ± 1.32 | 4.73 ± 1.37 | 4.95 ± 1.34 |
| Word frequency | 34.43 ± 100.63 | 53.53 ± 110.01 | 42.29 ± 69 |
Table 1 Descriptive statistics and rating values (Means and Standard Deviations) of critical words
| Variable | Negative | Neutral | Positive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | 3.31 ± 0.77 | 5.11 ± 0.37 | 6.33 ± 0.84 |
| Arousal | 5.12 ± 1.31 | 3.44 ± 1.20 | 4.71 ± 1.20 |
| Concreteness | 4.77 ± 1.32 | 4.73 ± 1.37 | 4.95 ± 1.34 |
| Word frequency | 34.43 ± 100.63 | 53.53 ± 110.01 | 42.29 ± 69 |
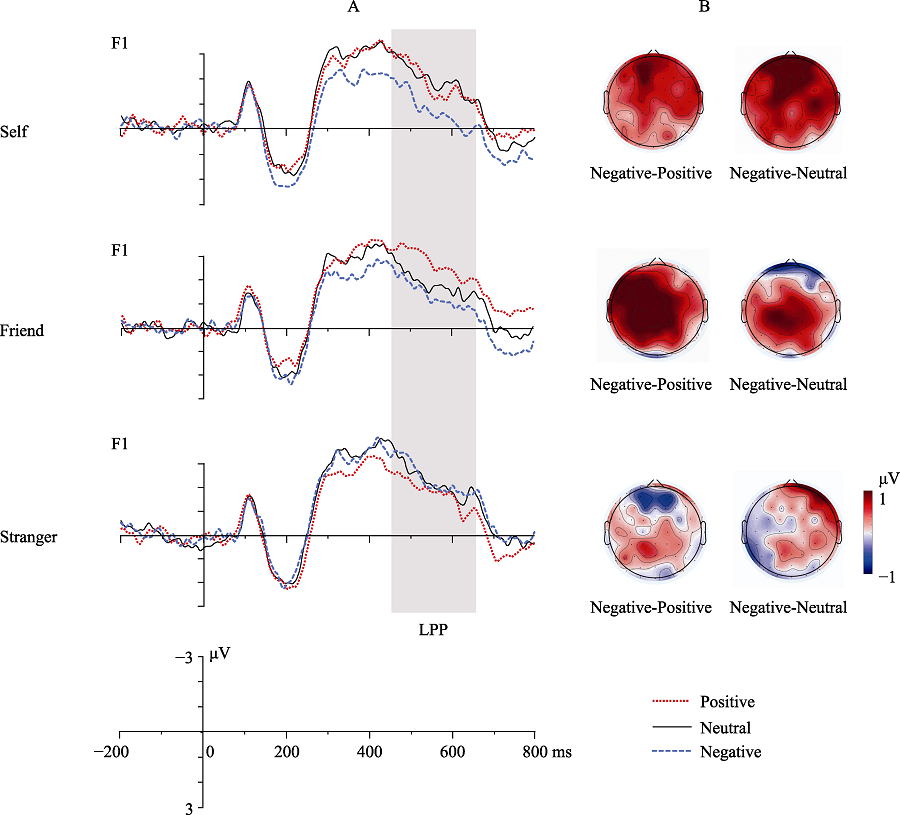
Figure 4. The interaction between Emotion Valence and Name Type on the LPP component (A) and the topographies of negative-positive and negative-neutral difference waves in 450~650 ms time window (B).
| [1] | Aron, A., Lewandowski, G. W., Mashek, D., & Aron, E. N. (2013) The self-expansion model of motivation and cognition in close relationships. In J. Simpson & L. Campbell (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of close relationships (pp. 90-115). New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [2] |
Bayer, M., Ruthmann, K., & Schacht, A. (2017). The impact of personal relevance on emotion processing: evidence from event-related potentials and pupillary responses. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(9), 1470-1479.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsx075 URL pmid: 28541505 |
| [3] |
Bernat, E., Bunce, S., & Shevrin, H. (2001). Event-related brain potentials differentiate positive and negative mood adjectives during both supraliminal and subliminal visual processing. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 42(1), 11-34.
doi: 10.1016/s0167-8760(01)00133-7 URL pmid: 11451477 |
| [4] |
Brück, C., Kreifelts, B., & Wildgruber, D. (2012). From evolutionary roots to a broad spectrum of complex human emotions: Future research perspectives in the field of emotional vocal communication. Reply to comments on “Emotional voices in context: A neurobiological model of multimodal affective information processing”. Physics of Life Reviews, 9(1), 9-12.
URL pmid: 22177278 |
| [5] | Cao, Y., & Wang, L. (2018). Processing of emotional information in written language (in Chinese). Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(2), 148-163. |
| [6] |
Chen, Y., Zhong, Y. P., Zhou, H. B., Zhang, S. M., Tan, Q. B., & Fan, W (2014). Evidence for implicit self-positivity bias: An event-related brain potential study. Experimental Brain Research, 232(3), 985-994.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3810-z URL pmid: 24395142 |
| [7] |
Cheng, Y. W., Chen, C. Y., Lin, C.-P., Chou, K.-H., & Decety, J. (2010). Love hurts: An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 51(2), 923-929.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.047 URL pmid: 20188182 |
| [8] |
Conway, A. R. A., Cowan, N., & Bunting, M. F. (2001). The cocktail party phenomenon revisited: The importance of working memory capacity. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 8(2), 331-335.
doi: 10.3758/bf03196169 URL pmid: 11495122 |
| [9] |
Cunningham, W. A., Espinet, S. D., Deyoung, C. G., & Zelazo, P. D. (2005). Attitudes to the right- and left: Frontal ERP asymmetries associated with stimulus valence and processing goals. NeuroImage, 28 (4), 827-834.
URL pmid: 11554801 |
| [10] |
Czigler, I., Cox, T. J., Gyimesi, K., & Horváth, J. (2007). Event-related potential study to aversive auditory stimuli. Neuroscience Letters, 420(3), 251-256.
URL pmid: 17556101 |
| [11] |
Decety, J., & Sommerville, J. A. (2003). Shared representations between self and other: A social cognitive neuroscience view. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(12), 527-533.
URL pmid: 14643368 |
| [12] |
Fan, W., Chen, J., Wang, X.-Y., Cai, R. H., Tan, Q. B., Chen, Y., & Zhong, Y. P. (2013). Electrophysiological correlation of the degree of self-reference effect. PLoS ONE, 8(12):e80289.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080289 URL pmid: 24312467 |
| [13] |
Fields, E. C., &, Kuperberg, G., R. (2012). It’s all about you: An ERP study of emotion and self-relevance in discourse. Neuroimage, 62(1), 562-574.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.05.003 URL pmid: 22584232 |
| [14] |
Fields, E. C., &, Kuperberg, G., R. (2015). Loving yourself more than your neighbor: ERPs reveal online effects of a self-positivity bias. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(9), 1202-1209.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv004 URL pmid: 25605967 |
| [15] |
Fields, E. C., & Kuperberg, G. R. (2016). Dynamic effects of self-relevance and task on the neural processing of emotional words in context. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1-12.
URL pmid: 25688217 |
| [16] |
Fischler, I., & Bradley, M. (2006). Event-related potential studies of language and emotion: words, phrases, and task effects. Progress in Brain Research, 156, 185-203.
doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)56009-1 URL pmid: 17015080 |
| [17] |
Gronau, N., Cohen, A., & Ben-Shakhar, G. (2003). Dissociations of personally significant and task-relevant distractors inside and outside the focus of attention: A combined behavioral and psychophysiological study. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 132(4), 512-529.
doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.132.4.512 URL |
| [18] |
Hajcak, G., Macnamara, A., & Olvet, D. M. (2010). Event-related potentials, emotion, and emotion regulation: An integrative review. Developmental Neuropsychology, 35(2), 129-155.
doi: 10.1080/87565640903526504 URL pmid: 20390599 |
| [19] |
Harris, C. R., & Pashler, H. (2004). Attention and the processing of emotional words and names: Not so special after all. Psychological Science, 15(3), 171-178.
doi: 10.1111/j.0956-7976.2004.01503005.x URL pmid: 15016288 |
| [20] |
Herbert, C., Herbert, B. M., Ethofer, T., & Pauli, P. (2011a). His or mine? The time course of self-other discrimination in emotion processing. Social Neuroscience, 6(3), 277-288.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2010.523543 URL pmid: 21104542 |
| [21] |
Herbert, C., Herbert, B. M., & Pauli, P. (2011c). Emotional self-reference: brain structures involved in the processing of words describing one’s own emotions. Neuropsychologia, 49(10), 2947-2956.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.06.026 URL pmid: 21756925 |
| [22] |
Herbert, C., Junghöfer, M., & Kissler, J. (2008). Event related potentials to emotional adjectives during reading. Psychophysiology, 45(3), 487-498.
URL pmid: 18221445 |
| [23] |
Herbert, C., Kissler, J., Junghöfer, M., Peyk, P., & Rockstroh, B. (2006). Processing of emotional adjectives: Evidence from startle EMG and ERPs. Psychophysiology, 43(2), 197-206.
URL pmid: 16712590 |
| [24] |
Herbert, C., Pauli, P., & Herbert, B. M. (2011b). Self-reference modulates the processing of emotional stimuli in the absence of explicit self-referential appraisal instructions. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 6(5), 653-661.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsq082 URL pmid: 20855295 |
| [25] |
Holeckova, I., Fischer, C., Giard, M.-H., Delpuech, C., & Morlet, D. (2006). Brain responses to a subject's own name uttered by a familiar voice. Brain Research, 1082(1), 142-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.089 URL pmid: 16703673 |
| [26] | Ito, T. A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2000). Electrophysiological evidence of implicit and explicit categorization processes. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 36(6), 660-676. |
| [27] |
Kang, T. S. (1972). Name and group identification. Journal of Social Psychology, 86(1), 159-160.
doi: 10.1080/00224545.1972.9918610 URL pmid: 5008858 |
| [28] | Kanske, P., &Kotz, S. A. (2007). Concreteness in emotional words: ERP evidence from a hemifield study. Brain Research, 1148(1), 138-148. |
| [29] |
Kanske, P., Plitschka, J., & Kotz, S. A. (2011). Attentional orienting towards emotion: P2 and N400 ERP effects. Neuropsychologia, 49(11), 3121-3129.
URL pmid: 21816167 |
| [30] |
Kissler, J., Herbert, C., Peyk, P., & Junghofer, M. (2007). Buzzwords: Early cortical responses to emotional words during reading. Psychological Science, 18(6), 475-480.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01924.x URL pmid: 17576257 |
| [31] |
Kissler, J., Herbert, C., Winkler, I., & Junghofer, M. (2009). Emotion and attention in visual word processing: An ERP study. Biological Psychology, 80(1), 75-83.
URL pmid: 18439739 |
| [32] | Koole, S. L., &Pelham, B. W. (2003). On the nature of implicit self-esteem: The case of the name letter effect. In S. J. Spencer et al. (Eds.), Motivated social perception: The Ontario Symposium (Vol. 9, pp. 93-116). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. |
| [33] | Kutas, M., & Federmeier, K. D. (2000). Electrophysiology reveals semantic memory use in language comprehension. Trends in Cognitive Neuroscience, 4(12), 463-470. |
| [34] | Lang, P. J., & Bradley, M. M. (2010). Emotion and the motivational brain. Biological Psychology, 84(3), 437-450. |
| [35] |
Lau, E. F., Phillips, C., & Poeppel, D. (2008). A cortical network for semantics: (de)constructing the N400. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(12), 920-933.
URL pmid: 19020511 |
| [36] |
Li, W., &Han, S. H. (2010). Perspective taking modulates event-related potentials to perceived pain. Neuroscience Letters, 469(3), 328-332.
URL pmid: 20026179 |
| [37] | Öhman, A., Flykt, A., & Esteves, F. (2001). Emotion drives attention: Detecting the snake in the grass. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 130(3), 466-478. |
| [38] | Peeters, G., & Czapinski, J. (1990). Positive-negative asymmetry in evaluations: The distinction between affective and informational negativity effects. European Review of Social Psychology, 1(1), 33-60. |
| [39] |
Pinheiro, A. P., Rezaii, N., Rauber, A., & Niznikiewicz, M. (2016). Is this my voice or yours? The role of emotion and acoustic quality in self-other voice discrimination in schizophrenia. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 21(4), 335-353.
URL pmid: 27454152 |
| [40] |
Sass, S. M., Heller, W., Stewart, J. L., Silton, R. L., Edgar, J. C., Fisher, J. E., & Miller, G. A. (2010). Time course of attentional bias in anxiety: Emotion and gender specificity. Psychophysiology, 47(2), 247-259.
URL pmid: 19863758 |
| [41] |
Schacht, A., & Sommer, W. (2009). Time course and task dependence of emotion effects in word processing. Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 9(1), 28-43.
doi: 10.3758/CABN.9.1.28 URL pmid: 19246325 |
| [42] | Scherer, K. R., Schorr, A., & Johnstone, T. (2001) Appraisal Processes in Emotion: Theory, Methods, Research. New York: Oxford University Press Theory, Methods, Research. New York: Oxford University Press. |
| [43] |
Schupp, H. T., Öhman, A., Junghöfer, M., Weike, A. I., Stockburger, J., & Hamm, A. O. (2004). The facilitated processing of threatening faces: An erp analysis. Emotion, 4(2), 189-200.
doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.4.2.173 URL pmid: 15222854 |
| [44] |
Schupp, H. T., Stockburger, J., Codispoti, M., Junghöfer, M., Weike, A. I., & Hamm, A. O. (2007). Selective visual attention to emotion. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(5), 1082-1089.
URL pmid: 17267562 |
| [45] |
Scott, G. G., O'Donnell, P. J., Leuthold, H., & Sereno, S. C. (2009). Early emotion word processing: Evidence from event-related potentials. Biological Psychology, 80(1), 95-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.03.010 URL pmid: 18440691 |
| [46] |
Shestyuk, A. Y., & Deldin, P. J. (2010). Automatic and strategic representation of the self in major depression: Trait and state abnormalities. American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(5), 536-544.
URL pmid: 20360316 |
| [47] |
Suls, J., Lemos, K., & Stewart, H. L. (2002). Self-esteem, construal, and comparisons with the self, friends, and peers. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 82(2), 252-261.
URL pmid: 11831414 |
| [48] |
Tacikowski, P., Brechmann, A., Marchewka, A., Jednoróg, K., Dobrowolny, M., & Nowicka, A. (2011). Is it about the self or the significance? An fmri study of self-name recognition. Social Neuroscience, 6(1), 98-107.
URL pmid: 20602286 |
| [49] | Tacikowski, P., Brechmann, A., & Nowicka, A. (2012). Cross-modal pattern of brain activations associated with the processing of self- and significant other’s name. Hum Brain Mapping, 34(9), 2069-2077. |
| [50] | Tacikowski, P., Cygan, H. B., & Nowicka, A. (2014). Neural correlates of own and close-other’s name recognition: ERP evidence. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 8, 194. |
| [51] |
Tateuchi, T., Itoh, K., & Nakada, T. (2012). Neural mechanisms underlying the orienting response to subject's own name: An event-relevant potential study. Psychophysiology, 49(6), 786-791.
URL pmid: 22416997 |
| [52] |
Thierry, G., & Roberts, M. V. (2007). Event-related potential study of attention capture by affective sounds. NeuroReport, 18(3), 245-248.
URL pmid: 17314665 |
| [53] | Vuilleumier, P. (2005). How brains beware: Neural mechanisms of emotional attention. Trends Cognitive Science, 9(12), 585-594. |
| [54] | Wang, Y. N., Zhou, L. M., & Luo, J. Y. (2008). The pilot establishment and evaluation of Chinese affective words system. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 22(8), 608-612. |
| [55] |
Watson, L. A., Dritschel, B., Obonsawin, M. C., & Jentzsch, I. (2007). Seeing yourself in a positive light: Brain correlates of the self-positivity bias. Brain Research, 1152, 106-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.049 URL pmid: 17462610 |
| [56] | Watson, R. S. (1986). The named and the nameless: Gender and person in Chinese society. American Ethnologist, 13(4), 619-631. |
| [57] |
Zhou, H. Y., Guo, J. L., Ma, X. M., Zhang, M. H., Liu, L. Q., Feng, L., … Zhong, N. (2017). Self-reference emerges earlier than emotion during an implicit self-referential emotion processing task: Event-related potential evidence. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 451.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00451 URL pmid: 28943845 |
| [1] | DENG Xiaohong, LI Ting, XUE Chao, J. Peter ROSENFELD, LU Yang, WANG Ying, ZHAN Xiaofei, YAN Gejun, OUYANG Dan. The Complex Trial Protocol based on self-referential encoding: Discriminating the guilty from the knowledgeable innocent [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(10): 1105-1119. |
| [2] | FU Yilei, LUO Yuejia, CUI Fang. Consistency of choice modulates outcome evaluation: Evidence from ERP studies [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1089-1099. |
| [3] | ZHONG Yiping, LI Jin, ZHAN Youlong, FAN Wei, YANG Zilu. Rotated self-face recognition: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(11): 1379-1389. |
| [4] | DOU Weiwei;ZHENG Xifu;YANG Huifang;WANG Junfang;LI Yue;E Xiaotian;Chen Qianqian. The Effect of Cognitive Distraction’s Intensity on the Process of Trauma-related Information: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(5): 656-665. |
| [5] | WU Yan,ZHOU Xiao-Lin. The Context-Dependency of Fairness Processing: Evidence from ERP Study [J]. , 2012, 44(6): 797-806. |
| [6] | GUO Jing-Jing,DU Yan-Peng,CHEN Yu-Xia,PENG Dan-Ling. The Modulation Mechanism of Emotional Words on Neutral Stimuli’s Preference [J]. , 2011, 43(04): 364-372. |
| [7] | LI Yue -Ting,LI Qi,GUO Chun-Yan. Differences of Emotional Words in Implicit and Explicit Memory Tests: An ERP Study [J]. , 2010, 42(07): 735-742. |
| [8] | GAO Pei-Xia,LIU Hui-Jun,DING Ni,GUO De-Jun. An Event-related-potential Study of Emotional Processing in Adolescence [J]. , 2010, 42(03): 342-351. |
| [9] | Ding Ni,Ding Jinhong,Guo Dejun. An Event-Related Potential Study of Neuroticism Influences on Emotional Processing [J]. , 2007, 39(04): 629-637. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||