

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 798-806.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00798
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles
QI Yapeng1, WANG Yixuan1, ZHU Hua2, ZHOU Chenglin1, WANG Yingying1( )
)
Received:2020-07-16
Published:2021-07-25
Online:2021-05-24
Contact:
WANG Yingying
E-mail:wyycris@sina.com
Supported by:QI Yapeng, WANG Yixuan, ZHU Hua, ZHOU Chenglin, WANG Yingying. (2021). Effects associated with long-term training in sports requiring high levels of strategy on brain white matter structure in expert athletes: A DTI study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(7), 798-806.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00798
| Characteristic | Expert Group | Control Group |
|---|---|---|
| N (men/women) | 31(14/17) | 28(13/15) |
| Age (M ± SD) | 20.06 ± 1.69 years | 20.68 ± 1.66 years |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.21 ±2.59 | 20.84 ± 2.33 |
| Years of training | 11.97 ± 2.68 years | 0 |
| Training intensity | 5 times per week, 2 hours per time | 0 |
Table 1 Demographic and sports training characteristics of the participants
| Characteristic | Expert Group | Control Group |
|---|---|---|
| N (men/women) | 31(14/17) | 28(13/15) |
| Age (M ± SD) | 20.06 ± 1.69 years | 20.68 ± 1.66 years |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.21 ±2.59 | 20.84 ± 2.33 |
| Years of training | 11.97 ± 2.68 years | 0 |
| Training intensity | 5 times per week, 2 hours per time | 0 |
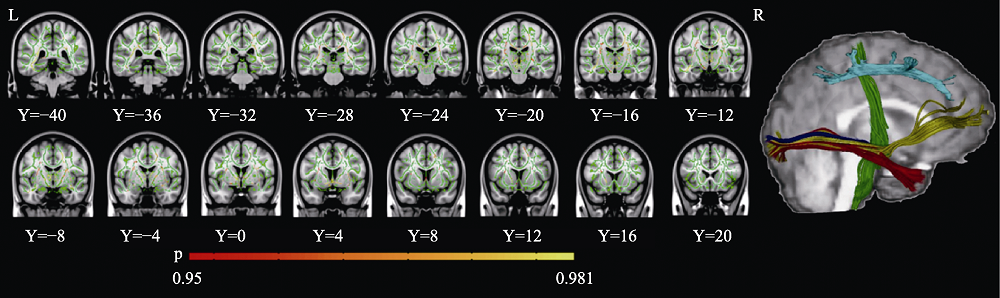
Figure 1. Structure diagram of white matter fibers. Left: green areas represent the fiber skeleton, and red areas represent fibers with higher fractional anisotropy values in the expert group than in the control group. Right: anatomic location of white matter fibers with intergroup differences in fractional anisotropy. Green represents corticospinal fibers; red, inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus; yellow, inferior longitudinal fasciculus; and blue, superior longitudinal fasciculus.
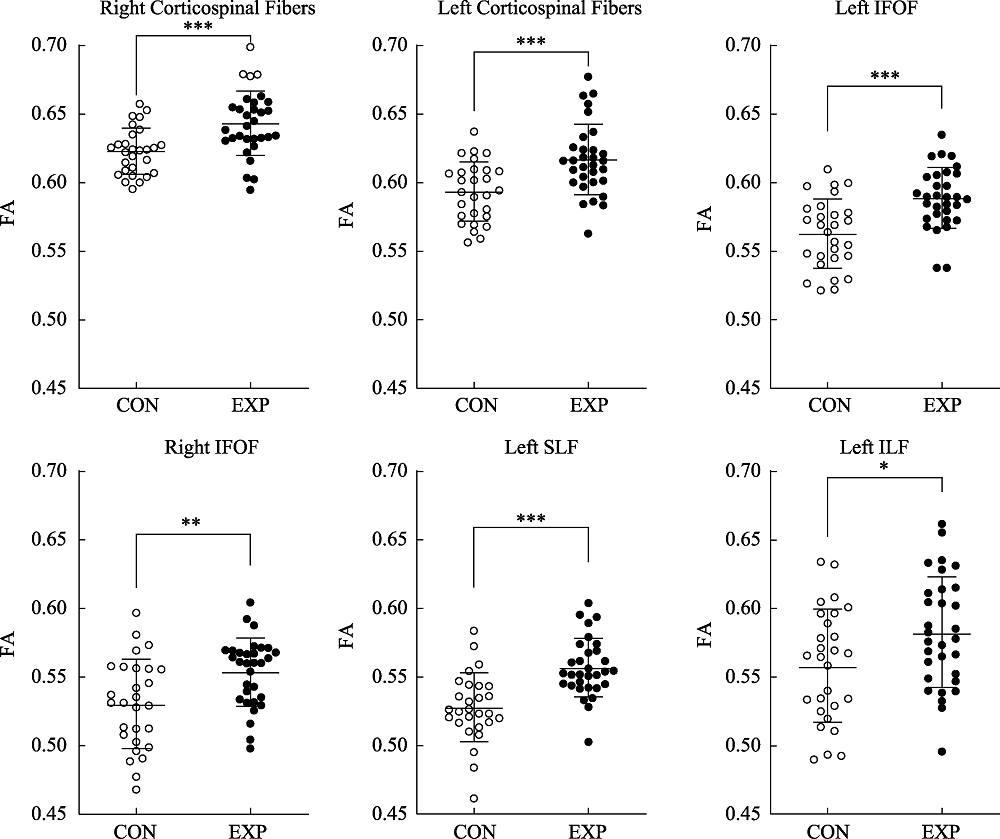
Figure 2. Bar graphs comparing fractional anisotropy (FA) values in the bilateral corticospinal fibers, bilateral inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF), left hemisphere inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF), and left hemisphere superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) between the expert group (EXP) and the control (CON) group. Filled circles represented the expert group; open circles, the control group; middle horizontal bars, means; and error bars, standard error. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
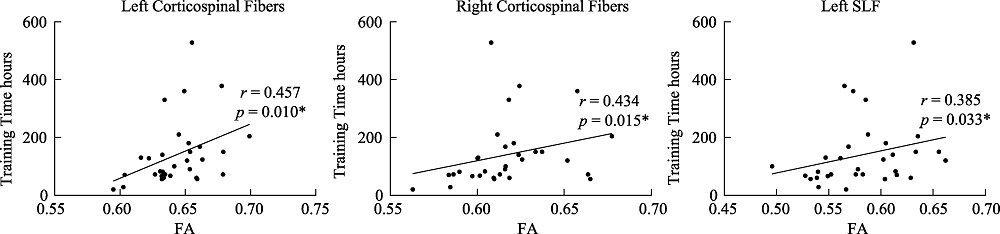
Figure 3. Scatter plots of fractional anisotropy (FA) and training time in the left and right hemisphere corticospinal fiber tracts and the left hemisphere superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) in the expert group. *p < 0.05.
| [1] |
Amoruso, L., Gelormini, C., Aboitiz, F., Gonzalez, M. A., Manes, F., Cardona, J. F., & Ibanez, A. (2013). N400 ERPs for actions: Building meaning in context. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 57.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00057 pmid: 23459873 |
| [2] |
Bai, X., Shao, M., Liu, T., Yin, J., & Jin, H. (2020). Altered structural plasticity in early adulthood after badminton training. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(2), 173-183.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00173 URL |
| [3] |
Beilock, S. L., Lyons, I. M., Mattarella-Micke, A., Nusbaum, H. C., & Small, S. L. (2008). Sports experience changes the neural processing of action language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(36), 13269-13273.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803424105 pmid: 18765806 |
| [4] |
Bengtsson, S. L., Nagy, Z., Skare, S., Forsman, L., Forssberg, H., & Ullén, F. (2005). Extensive piano practicing has regionally specific effects on white matter development. Nature Neuroscience, 8(9), 1148-1150.
doi: 10.1038/nn1516 URL |
| [5] |
Bezzola, L., Merillat, S., Gaser, C., & Jancke, L. (2011). Training- induced neural plasticity in golf novices. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(35), 12444-12448.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1996-11.2011 URL |
| [6] |
Binder, J. R., Desai, R. H., Graves, W. W., & Conant, L. L. (2009). Where is the semantic system? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cerebral Cortex, 19(12), 2767-2796.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp055 URL |
| [7] |
Blakemore, S. J., & Decety, J. (2001). From the perception of action to the understanding of intention. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(8), 561-567.
pmid: 11483999 |
| [8] |
Buxbaum, L. J., & Kalenine, S. (2010). Action knowledge, visuomotor activation, and embodiment in the two action systems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1191(1), 201-218.
doi: 10.1111/nyas.2010.1191.issue-1 URL |
| [9] |
Calmels, C. (2019). Neural correlates of motor expertise: Extensive motor training and cortical changes. Brain Research, 1739, 146323.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146323 URL |
| [10] |
Catani, M., Dell'acqua, F., Bizzi, A., Forkel, S. J., Williams, S. C., Simmons, A., ... de Schotten, M. T., (2012). Beyond cortical localization in clinico-anatomical correlation. Cortex, 48(10), 1262-1287.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2012.07.001 pmid: 22995574 |
| [11] |
Critchley, H. D., Wiens, S., Rotshtein, P., Ohman, A., & Dolan, R. J. (2004). Neural systems supporting interoceptive awareness. Nature Neuroscience, 7(2), 189-195.
doi: 10.1038/nn1176 URL |
| [12] |
Dayan, E., & Cohen, L. G. (2011). Neuroplasticity Subserving Motor Skill Learning. Neuron, 72(3), 443-454.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.008 pmid: 22078504 |
| [13] |
Dick, A. S., & Tremblay, P. (2012). Beyond the arcuate fasciculus: Consensus and controversy in the connectional anatomy of language. Brain, 135(12), 3529-3550.
doi: 10.1093/brain/aws222 URL |
| [14] |
Duffau, H., Gatignol, P., Mandonnet, E., Peruzzi, P., Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., & Capelle, L. (2005). New insights into the anatomo-functional connectivity of the semantic system: A study using cortico-subcortical electrostimulations. Brain, 128(4), 797-810.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awh423 URL |
| [15] |
Giacosa, C., Karpati, F. J., Foster, N. E. V., Penhune, V. B., & Hyde, K. L. (2016). Dance and music training have different effects on white matter diffusivity in sensorimotor pathways. Neuroimage, 135, 273-286.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.04.048 pmid: 27114054 |
| [16] | Guyton, A. C., & Hall, J. E. (2006). Textbook of medical physiology 11th ed. Elsevier Saunders, 788-817. |
| [17] |
Han, Z. Z., Ma, Y. J., Gong, G. L., He, Y., Caramazza, A., & Bi, Y. C. (2013). White matter structural connectivity underlying semantic processing: Evidence from brain damaged patients. Brain, 136(10), 2952-2965.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awt205 URL |
| [18] |
Hanggi, J., Langer, N., Lutz, K., Birrer, K., Merillat, S., & Jancke, L. (2015). Structural Brain Correlates Associated with Professional Handball Playing. Plos One, 10(4), e0124222.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124222 URL |
| [19] |
Herbet, G., Zemmoura, I., & Duffau, H. (2018). Functional Anatomy of the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus: From Historical Reports to Current Hypotheses. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 12, 77.
doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00077 URL |
| [20] | Kamali, A., Flanders, A. E., Brody, J., Hunter, J. V., & Hasan, K. M. (2014). Tracing superior longitudinal fasciculus connectivity in the human brain using high resolution diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Structure & Function, 219(1), 269-281. |
| [21] |
Keller, T. A., & Just, M. A. (2009). Altering cortical connectivity: Remediation-induced changes in the white matter of poor readers. Neuron, 64(5), 624-631.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.018 URL |
| [22] |
Kilner, J. M. (2011). More than one pathway to action understanding. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(8), 352-357.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.06.005 pmid: 21775191 |
| [23] |
Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., McInerney, S., Sorensen, A. G., Wang, R., Caviness, V. S., Jr., & Pandya, D. N. (2005). Segmentation of subcomponents within the superior longitudinal fascicle in humans: A quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cereb Cortex, 15(6), 854-869.
pmid: 15590909 |
| [24] |
Makris, N., Meyer, J. W., Bates, J. F., Yeterian, E. H., Kennedy, D. N., & Caviness, V. S. (1999). MRI-Based topographic parcellation of human cerebral white matter and nuclei II. Rationale and applications with systematics of cerebral connectivity. Neuroimage, 9(1), 18-45.
pmid: 9918726 |
| [25] |
Martino, J., Brogna, C., Robles, S. G., Vergani, F., & Duffau, H. (2010). Anatomic dissection of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus revisited in the lights of brain stimulation data. Cortex, 46(5), 691-699.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.07.015 pmid: 19775684 |
| [26] |
Monsell, S. (2003). Task switching. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(3), 134-140.
doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(03)00028-7 URL |
| [27] |
Pulvermuller, F. (2005). Brain mechanisms linking language and action. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6(7), 576-582.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1706 URL |
| [28] |
Reid, V. M., Hoehl, S., Grigutsch, M., Groendahl, A., Parise, E., & Striano, T. (2009). The neural correlates of infant and adult goal prediction: Evidence for semantic processing systems. Developmental Psychology, 45(3), 620-629.
doi: 10.1037/a0015209 URL |
| [29] |
Reid, V. M., & Striano, T. (2008). N400 involvement in the processing of action sequences. Neuroscience Letters, 433(2), 93-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.12.066 URL |
| [30] | Ren, Z., Hu, L., Zhang, Y., Xu, M., Li, L., Xia, F., & Huang, R. (2019). A review of brain plasticity of motor skill experts: Evidence from magnetic resonance imaging. China Sport Science and Technology, 55(2), 3-18. |
| [31] |
Rizzolatti, G., & Luppino, G. (2001). The cortical motor system. Neuron, 31(6), 889-901.
pmid: 11580891 |
| [32] |
Romanski, L. M., Tian, B., Fritz, J., Mishkin, M., Goldman-Rakic, P. S., & Rauschecker, J. P. (1999). Dual streams of auditory afferents target multiple domains in the primate prefrontal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 2(12), 1131-1136.
doi: 10.1038/16056 URL |
| [33] | Sarubbo, S., de Benedictis, A., Maldonado, I. L., Basso, G., & Duffau, H. (2013). Frontal terminations for the inferior fronto-occipital fascicle: Anatomical dissection, DTI study and functional considerations on a multi-component bundle. Brain Structure & Function, 218(1), 21-37. |
| [34] |
Schlaffke, L., Lissek, S., Lenz, M., Brune, M., Juckel, G., Hinrichs, T., ... Schmidt-Wilcke, T. (2014). Sports and brain morphology - A voxel-based morphometry study with endurance athletes and martial artists. Neuroscience, 259, 35-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.046 pmid: 24291669 |
| [35] |
Shinoura, N., Midorikawa, A., Onodera, T., Tsukada, M., Yamada, R., Tabei, Y., . . . Yagi, K. (2013). Damage to the left ventral, arcuate fasciculus and superior longitudinal fasciculus-related pathways induces deficits in object naming, phonological language function and writing, respectively. Int J Neurosci, 123(7), 494-502. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.765420.
doi: 10.3109/00207454.2013.765420 URL |
| [36] |
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., ... Behrens, T. E. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage, 31(4), 1487-1505.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024 URL |
| [37] |
Song, S. K., Sun, S. W., Ramsbottom, M. J., Chang, C., Russell, J., & Cross, A. H. (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage, 17(3), 1429-1436.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1267 URL |
| [38] |
Taubert, M., Draganski, B., Anwander, A., Muller, K., Horstmann, A., Villringer, A., & Ragert, P. (2010). Dynamic properties of human brain structure: Learning-related changes in cortical areas and associated fiber connections. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(35), 11670-11677.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2567-10.2010 URL |
| [39] |
Urger, S. E., de Bellis, M. D., Hooper, S. R., Woolley, D. P., Chen, S. D., & Provenzale, J. (2015). The superior longitudinal fasciculus in typically developing children and adolescents: Diffusion tensor imaging and neuropsychological correlates. Journal of Child Neurology, 30(1), 9-20.
doi: 10.1177/0883073813520503 URL |
| [40] |
Vandermosten, M., Boets, B., Poelmans, H., Sunaert, S., Wouters, J., & Ghesquiere, P. (2012). A tractography study in dyslexia: Neuroanatomic correlates of orthographic, phonological and speech processing. Brain, 135(3), 935-948.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awr363 URL |
| [41] |
Vigneau, M., Beaucousin, V., Herve, P. Y., Duffau, H., Crivello, F., Houde, O., ... Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2006). Meta-analyzing left hemisphere language areas: Phonology, semantics, and sentence processing. Neuroimage, 30(4), 1414-1432.
pmid: 16413796 |
| [42] |
Wang, B., Fan, Y., Lu, M., Li, S., Song, Z., Peng, X., ... Huang, R. (2013). Brain anatomical networks in world class gymnasts: A DTI tractography study. Neuroimage, 65, 476-487.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.007 pmid: 23073234 |
| [43] |
Wang, Y., Lu, Y., Deng, Y., Gu, N., Parviainen, T., & Zhou, C. (2019). Predicting domain-specific actions in expert table tennis athletes activates the semantic brain network. Neuroimage, 200, 482-489.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.06.035 URL |
| [44] |
Wilson, S. M., Galantucci, S., Tartaglia, M. C., Rising, K., Patterson, D. K., Henry, M. L., . . . Gorno-Tempini, M. L., (2011). Syntactic processing depends on dorsal language tracts. Neuron, 72(2), 397-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.014 URL |
| [45] |
Winkler, A. M., Ridgway, G. R., Webster, M. A., Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2014). Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage, 92, 381-397.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.060 URL |
| [46] | Wright, M. J., Bishop, D. T., Jackson, R. C., & Abernethy, B. (2013). Brain regions concerned with the identification of deceptive soccer moves by higher-skilled and lower-skilled players. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 851. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00851. |
| [47] | Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Zeng, Y., & Shen, C. (2015). Structural brain plasticity change in athletes associated with different sports. China Sport Science, 35(4), 52-57. |
| [48] | Yeatman, J. D., Rauschecker, A. M., & Wandell, B. A. (2013). Anatomy of the visual word form area: Adjacent cortical circuits and long- range white matter connections. Brain & Language, 125(2), 146-155. |
| [49] |
Zhang, J., Jones, M., DeBoy, C. A., Reich, D. S., Farrell, J. A., Hoffman, P. N., ... Calabresi, P. A. (2009). Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of wallerian degeneration in rat spinal cord after dorsal root axotomy. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(10), 3160-3171.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3941-08.2009 URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||