1 问题提出
互联网改变了人们的生活方式, 网络社交、购物、娱乐、游戏等方式让人们获益的同时, 也给人们造成损害(Gosling & Mason, 2015)。研究表明, 适度玩网络游戏对个体大有益处(Hofferth & Moon, 2012; Przybylski, 2014), 但网络游戏成瘾则导致失眠、情绪不适应等诸多问题(Carras et al., 2017; Dreier et al., 2017; Lam, 2014)。以往有关网络游戏成瘾发生机制的研究主要关注了情绪、人格、动机等个体因素; 沉浸感、控制感、社交体验等网络游戏因素; 同伴、家庭、学校等环境因素(李董平, 周月月, 赵力燕, 王艳辉, 孙文强, 2016; 魏华, 周宗奎, 田媛, 鲍娜, 2012; 张国华, 雷雳, 2015; Kuss & Lopez-Fernandez, 2016; Kuss, Louws, & Wiers, 2012; Mehroof & Griffiths, 2010)。虽然已有研究注意到环境因素对网络游戏成瘾的重要性, 但是大部分考察的是同伴、家庭或学校等微系统和中系统的作用(李董平等, 2016), 很少有研究关注宏观系统即个体感知到的社会环境的作用。然而, 宏观社会环境对个体的暴力、赌博、犯罪等多种不良行为具有显著影响(Bernburg, Thorlindsson, & Sigfusdottir, 2009; Callan, Ellard, Shead, & Hodgins, 2008)。
随着我国经济快速增长, 人们收入大幅提高的同时, 贫富差距却日益扩大, 这种宏观社会环境很容易导致部分群体在心理上产生主观的“相对剥夺感” (熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016)。作为一种反映宏观系统的社会心理因素, 相对剥夺感能够解释个体因身心失调而导致的多种不良适应(马皑, 2012; Greitemeyer & Sagioglou, 2017; Pettigrew, 2016; Walker & Smith, 2002), 例如吸烟、酗酒、赌博和物质成瘾等(Callan, Shead, & Olson, 2011; Eibner & Evans, 2005; Smith, Pettigrew, Pippin, & Bialosiewicz, 2012)。在校大学生是一个折射社会现象、情绪发展不稳定、有分层且聚集生活的群体(王伟, 2011)。对那些处于相对经济劣势的大学生而言, 相对剥夺感或许已成为影响其网络游戏成瘾等不良适应的风险因素之一。因此, 本研究拟考察相对剥夺感与大学生网络游戏成瘾的关系及其作用机制, 以期丰富网络游戏成瘾发生机制的研究, 为科学预防和干预提供理论依据。
1.1 相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾
经典的相对剥夺感理论认为, 个体主要通过与他人比较来评价自身的处境和地位, 弱势群体成员经常感觉基本权利被剥夺, 这种被剥夺感会对其心理发展造成严重损害(熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016; Mummendey, Kessler, Klink, & Mielke, 1999; Walker & Smith, 2002)。例如, 相对剥夺感对个体的抑郁、焦虑等心理健康障碍具有显著正向预测作用(Eibner, Sturm, & Gresenz, 2004); 大学生的相对剥夺感越强, 其抑郁和自杀意念越高(Zhang & Tao, 2013)。
相对剥夺感也可能引起网络游戏成瘾。其一, 相对剥夺感会导致个体的偏差行为。研究发现, 感知到相对剥夺会引发个体的不满和愤怒等消极自我体验, 导致赌博成瘾等偏差行为(Callan, Shead, & Olson, 2015; Mishra, Lalumière, Daly, & Williams, 2012)。而网络游戏成瘾是与赌博成瘾具有一定相似性的典型的线上偏差行为(严万森, 张冉冉, 刘苏姣, 2016)。赌博为高相对剥夺感的个体提供了短时间改变经济水平和地位的可能性, 网络游戏则为其提供了短暂摆脱现实身份、建立新身份和地位的可能性(Callan et al., 2015; Ng & Wiemer-Hastings, 2005)。如同沉迷赌博, 沉迷网络游戏也可能是个体扭转相对剥夺感劣势的一种偏差行为。因此, 相对剥夺感可能导致网络游戏成瘾。其二, 相对剥夺感会导致个体的逃避行为。研究表明, 处于相对弱势地位的个体可能会体验到较强的压力和抑郁, 增强个体参与吸烟、酗酒、药物滥用等危险逃避行为的风险(Eibner & Evans, 2005; 熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016)。而网络游戏成瘾是大学生应对现实的典型逃避行为。研究发现, 逃避现实是个体使用网络游戏和成瘾的重要内在动机(Kwon, Chung, & Lee, 2011; 张红霞, 谢毅, 2008)。网络游戏因其刺激性、易用性、可接近性等特征, 更容易成为大学生逃避现实的首选途径。实证研究也发现, 逃避动机增强大学生网络游戏成瘾(Billieux et al., 2013; 魏华, 周宗奎, 李雄, 罗青, 高洁, 2014)。综合上述分析, 大学生网络游戏成瘾作为线上偏差行为和逃避行为可能被相对剥夺感所激发。由此, 我们提出假设H1:相对剥夺感正向预测大学生网络游戏成瘾。
1.2 非适应性认知的中介作用
在网络成瘾的理论中, Davis (2001)的病态网络使用的认知-行为模型(Pathological Internet Use, PIU)得到了最广泛的认可。非适应性认知指个体对网络世界具有过度正性的观念和不恰当的期望, 因而更偏好网络世界而非现实世界。该理论认为, 非适应性认知是影响网络成瘾形成和维持的最关键和最稳定的近端因素, 而个体脆弱(如抑郁、孤独)和环境压力(如负性生活事件)等素质-压力(diathesis-stress)是远端因素, 远端因素通过近端因素的中介作用影响网络成瘾(Davis, 2001; Mai et al., 2012)。网络游戏成瘾作为网络成瘾的重要子类同样受非适应性认知的影响(Davis, 2001; Peng & Liu, 2010)。实证研究表明, 非适应性认知在线下同伴玩家比例与大学生网络游戏成瘾之间起中介作用(汪涛等, 2015)、在基本心理需要与青少年网络游戏成瘾之间起中介作用(甄霜菊, 喻承甫, 胡谏萍, 鲍振宙, 张卫, 2016)。
作为一种反映环境压力的因素, 相对剥夺感也可能影响非适应性认知。两者的关系可以从相对剥夺感个体对世界公正的认知和需要的满足两方面来解释:(1)对世界公正的认知。相对剥夺感高的个体可能会感觉现实世界不公正, 而网络游戏世界更公正。研究发现, 相对剥夺感显著负向预测个体的公正世界信念(Birt & Dion, 1987)。也就是说, 相对剥夺感高的个体在现实世界中常常感到不公正。然而, 在网络游戏这个虚拟世界中, 由于匿名性的存在, 现实世界中的地位和财富不再起作用, 人们处于一个相对公正的环境; 并且, 网络游戏的程序和规则也是相对公正的(Jang, 2007; Song & Lee, 2007)。因此, 对于相对剥夺感高的个体, 他们一方面觉得现实世界不公正, 另一方面容易认为网络游戏世界更公正, 从而产生偏好虚拟世界而贬低现实世界的非适应性认知。(2)需要的满足。研究表明, 相对剥夺感高的个体在现实生活中改善社会地位和经济状况的需要难以被满足, 他们更容易将能满足其需要的风险行为(例如赌博)视作有效途径, 产生非适应性认知(Callan et al., 2008, 2015)。相比于现实世界的不满, 网络游戏世界为个体提供了更多的满足。例如, 网络游戏的匿名性让个体可以在游戏世界建立新的身份, 暂时摆脱现实身份的约束; 网络游戏中的角色扮演让个体可以寻求高等级的游戏角色体验, 获得地位满足(Hsu, Wen, & Wu, 2009; Ng & Wiemer-Hastings, 2005; 张国华, 雷雳, 2015)。因此, 当个体在现实生活中体验相对剥夺、感觉不公正和需要不被满足, 更容易将网络游戏世界视为获得公正和满足的有效方式, 两者“一推一拉”导致个体对网络游戏产生非适应性认知。
综合上述分析及假设H1的推导, 相对剥夺感既影响网络游戏成瘾, 又影响非适应性认知。根据病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 远端因素相对剥夺感影响近端因素非适应性认知, 进而影响大学生网络游戏成瘾。由此, 我们提出假设H2:相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知的中介作用正向预测网络游戏成瘾。
1.3 内隐人格观的调节作用
作为一种认知因素, 非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的影响很可能受到个体因素的调节。例如, 行为激动/抑制系统这一动机因素调节非适应性认知与网络游戏成瘾的关系(甄霜菊等, 2016)。作为一种重要的个体差异, 内隐人格观(mindsets or implicit theories)也可能是两者间的调节因素。内隐人格观是普通人对人的基本特性持有的认知图式或朴素理论, 即人的特性是可塑变化的还是固定不变的(王墨耘, 傅小兰, 2003; Dweck & Leggett, 1988; Dweck, 2012; Murphy & Dweck, 2016)。依据所持有的内隐人格观, 个体被分为两大类:渐变观者(incremental theorist)和实体观者(entity theorist)。渐变观者认为人的特性是动态可塑和发展变化的, 偏好“学习目标” (learning goals), 认为可以通过努力得到发展和提高; 与之对立的, 实体观者认为人的特性是固定不变的, 偏好“表现目标” (performance goals), 认为能力需要被展现出来(李爱梅, 刘楠, 孙海龙, 熊冠星, 2016; Mathur, Chun, & Maheswaran, 2016)。所以, 渐变观者更注重“提高”自己, 更愿意付出努力; 实体观者更注重“显示”自己, 更不愿意付出努力(李爱梅等, 2016; Murphy & Dweck, 2016)。实证研究也发现, 相比于渐变观者, 实体观者更愿意通过品牌展现自己, 他们使用某品牌是因为该品牌“能显示我是谁, 能向别人展示我是怎样的人, 会让自己感觉更好” (Park & John, 2010)。同理, 正因为实体观者不相信个体可以改变, 更在意表现目标, 当他们的非适应性认知水平较高时, 网络游戏能更快地帮助其实现表现目标, 显示“我在网络游戏世界中是个人物”, 从而更容易成瘾。与实体观者不同, 渐变观者会认为“网络游戏中自己更好, 线下现实中自己更差”的状况是可以改变的, 他们会投入更多的线下努力去改变现实的自己, 而不太在意网络游戏提供的较为容易的表现目标。因此, 同等非适应性认知水平下, 相对于实体观者, 渐变观者的网络成瘾程度更低。于是, 我们提出假设H3:内隐人格观调节相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知影响网络游戏成瘾的后半路径, 相对于持渐变观的大学生, 持实体观(即低渐变观)的大学生的非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的预测作用更大。
综上所述, 本研究基于病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 建构了一个有调节的中介模型, 考察相对剥夺感与大学生网络游戏成瘾的关系及其作用机制。
2 方法
2.1 对象
采取整群抽样, 从武汉市某所综合型大学选取大一至大三的学生1678名, 以班级为单位, 由经过统一培训的心理学专业硕士研究生操作完成标准化团体测验。其中, 符合本研究需要的对象即具有网络游戏使用经验的大学生1115名, 占总人数的66.45%。剔除漏答和反应一致的废卷后, 得到有效问卷1008份, 有效率为90.40%。男生795人(78.9%), 女生213人(21.1%)。被试年龄为16~23岁, 平均年龄19.03岁(标准差0.97岁)。被试平均玩网络游戏经验为5.99年(标准差3.62年), 近半年平均每天玩网络游戏时间为1.74小时(标准差2.21小时)。
2.2 测量工具
2.2.1 经济相对剥夺感问卷
参考前人研究, 将经济相对剥夺感作为大学生相对剥夺感的测量指标(熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016; Zagefka, Binder, Brown, & Hancock, 2013)。具体将Zagefk等(2013)根据认知-情感RD双维结构模型编制的经济相对剥夺感问卷, 应用于大学生与周围人比较的日常情境, 共2个项目, 分别测量相对剥夺感的认知和情感成分, 要求个体评估自己的总体经济状况, 如“与周围的大学生相比, 你认为自己的经济状况如何?” (认知成分)、“与周围的大学生相比, 你对自己经济状况的满意度如何?” (情感成分)。采用Likert-7点评分, 将两个项目反向计分, 然后相加得到总分, 总分越高表示相对剥夺感越强烈(熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016)。本研究中, 该问卷的α系数为0.72。
2.2.2 非适应性认知量表
采用Peng和Liu (2010)根据Davis (2001)的病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 编译的网络游戏非适应性认知量表, 共4个项目, 如“网络游戏是我唯一能够得到尊重的地方”、“离开网络游戏我没有价值, 只有在网络游戏中我才算个人物”。采用Likert-5点评分, 总分越高表示个体对网络游戏的非适应性认知越严重。量表验证性因素分析的拟合指标显示, χ2 /df = 5.19, RMSEA = 0.09, NFI = 0.99, IFI = 0.99, TLI = 0.98, CFI = 0.98, 表明问卷结构效度可以接受。本研究中, 该量表的α系数为0.96。
2.2.3 内隐人格观量表
采用Plaks, Stroessner, Dweck和Sherman (2001)编制的内隐人格观量表, 共8个项目, 如“人们做事的方式各有不同, 但体现他们本质的重要部分是难以改变的(实体观特征)”、“任何人, 不管他是谁, 都能改变自己的基本特质(渐变观特征)”。采用Likert-6点评分, 其中实体观特征的项目反向计分, 总分越高表示个体渐变观倾向越明显, 总分越低表示个体实体观倾向越明显。该量表已被诸多研究证明具有较好的信度和效度(银成钺, 王影, 2014)。本研究中, 该量表的α系数为0.87。
2.2.4 网络游戏成瘾量表
采用Petry等人(2014)编制的网络游戏成瘾量表, 共9个项目, 如“我在没有玩网络游戏的时候也会花大量时间想着游戏, 或计划着下一次什么时候能玩”、“因为网络游戏, 我失去了兴趣或减少了其他娱乐活动(爱好、会见朋友等)”。采用Likert-5点评分, 总分越高表示个体的网络游戏成瘾程度越严重。研究表明, 该量表中文版具有较好的信度和效度(Petry et al., 2014)。本研究中, 该量表的α系数为0.91。
2.3 程序及数据处理
以年级为单位, 由两名研究生使用统一的指导语和网络问卷进行现场团体施测, 指导语强调作答真实性以及调查匿名性, 被试当场填写网络问卷。采用SPSS 21.0软件对数据进行管理、储存和分析。根据以往研究, 性别和年龄对网络游戏成瘾可能存在一定影响, 例如男生的网络游戏成瘾高于女生, 青少年组的网络游戏成瘾高于成年组(甄霜菊等, 2016; 张国华, 雷雳, 2015; Carras et al., 2017; Mentzoni et al., 2011)。因此, 本研究将性别和年龄作为控制变量纳入分析。
2.4 共同方法偏差检验
采用自我报告收集数据可能导致共同方法偏差。本研究在程序上通过匿名调查、部分题目反向计分的方式进行了一定控制。同时, 采取Harman单因子检验进行了共同方法偏差的检验。结果显示, 特征根大于1的因素共5个, 其中第一个因素解释的累计变异量仅29.86%, 小于40%的临界值, 表明本研究不存在严重共同方法偏差问题(周浩, 龙立荣, 2004)。
3 结果
3.1 相对剥夺感、非适应性认知、内隐人格观和网络游戏成瘾的相关分析
将相对剥夺感、非适应性认知、内隐人格观和网络游戏成瘾四者的总均分做相关分析, 结果表明, 相对剥夺感与非适应性认知、网络游戏成瘾呈显著正相关, 与内隐人格观相关不显著; 非适应性认知与内隐人格观、网络游戏成瘾显著正相关; 内隐人格观与网络游戏成瘾相关不显著(详见表1)。
表1 各变量的描述统计与相关系数矩阵
| 变量 | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 性别 | 0.79 | 0.41 | 1 | |||||
| 2. 年龄 | 19.03 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 1 | ||||
| 3. 相对剥夺感 | 3.56 | 1.27 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 1 | |||
| 4. 非适应性认知 | 1.44 | 0.80 | 0.09** | 0.10** | 0.27*** | 1 | ||
| 5. 内隐人格观 | 3.28 | 0.65 | 0.05 | -0.03 | 0.02 | 0.10** | 1 | |
| 6. 网络游戏成瘾 | 2.21 | 0.87 | 0.19*** | 0.08** | 0.15*** | 0.47*** | -0.00 | 1 |
注:M为平均数, SD为标准差。性别为虚拟变量, 女生 = 0, 男生 = 1; N = 1008; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
3.2 相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾的关系:有调节的中介模型检验
根据Hayes (2013)、温忠麟和叶宝娟(2014)的观点, 首先采用SPSS宏程序PROCESS的模型4检验非适应性认知在相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾之间的中介作用, 结果显示, 控制性别和年龄后(甄霜菊等, 2016), 相对剥夺感能显著预测非适应性认知, a = 0.27, SE = 0.03, p < 0.001; 相对剥夺感、非适应性认知同时进入回归方程, 相对剥夺感不能显著预测网络游戏成瘾, c° = 0.01, SE = 0.03, p > 0.05, 非适应性认知能显著预测网络游戏成瘾, b = 0.46, SE = 0.03, p < 0.001。偏差校正的百分位Bootstrap方法检验表明, 非适应性认知在相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾之间的中介作用显著, ab = 0.12, Boot SE = 0.02, 95%的置信区间为[0.08, 0.17]。中介效应占总效应的比例ab/(ab+c°) = 92.55%。
第二步, 采用SPSS宏程序PROCESS的模型14检验内隐人格观的调节作用。有调节的中介模型检验需要对3个回归方程的参数进行估计。方程1估计相对剥夺感对网络游戏成瘾的总体效应; 方程2估计相对剥夺感对非适应性认知的预测效应; 方程3估计内隐人格观在非适应性认知与网络游戏成瘾之间的调节效应。在每个方程中, 对所有预测变量做标准化处理, 对性别和年龄进行控制。如果模型估计满足以下3个条件, 则有调节的中介效应存在:(a)方程1中, 相对剥夺感对网络游戏成瘾的总效应显著; (b)方程2中, 相对剥夺感对非适应性认知的预测效应显著; (c)方程3中, 非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的主效应显著, 且内隐人格观与非适应性认知交互项的效应显著(Hayes, 2013; 温忠麟, 叶宝娟, 2014)。
此外, 本研究所有预测变量方差膨胀因子均不高于1.2, 说明不存在多重共线性问题。
如表2所示, 方程1显著, 相对剥夺感正向预测网络游戏成瘾, 满足条件(a); 方程2显著, 相对剥夺感正向预测非适应性认知, 满足条件(b); 方程3显著, 非适应性认知正向预测网络游戏成瘾, 且内隐人格观与非适应性认知的交互项显著, 满足条件(c)。
表2 相对剥夺感对网络游戏成瘾的有调节的中介效应检验
| 变量 | 方程1 | 方程2 | 方程3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (效标: 网络游戏成瘾) | (效标: 非适应性认知) | (效标: 网络游戏成瘾) | |||||||
| SE | β | t | SE | β | t | SE | β | t | |
| 性别 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.07 | -0.00 | -0.04 |
| 年龄 | 0.03 | 0.07* | 2.33 | 0.03 | 0.09** | 2.91 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.96 |
| 相对剥夺感 | 0.03 | 0.13*** | 4.29 | 0.03 | 0.27*** | 8.82 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.37 |
| 内隐人格观 | 0.03 | -0.09** | -2.75 | ||||||
| 非适应性认知 | 0.03 | 0.49*** | 15.62 | ||||||
| 非适应性认知×内隐人格观 | 0.04 | -0.09* | -2.10 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.22 | ||||||
| F | 8.23*** | 29.53*** | 47.83*** | ||||||
注:* p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001
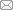
为了更清楚地解释非适应性认知与内隐人格观交互效应的实质, 我们将内隐人格观按平均数加减一个标准差分出高、低分组, 进行简单斜率检验并绘制了简单效应分析图(图1)。结果表明, 对于低分组即实体观的大学生, 非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的正向预测显著(Bsimple = 0.58, t = 9.80, p < 0.001); 对于高分组即渐变观的大学生, 非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的正向预测作用减弱(Bsimple = 0.40, t = 9.46, p < 0.001; Bsimple = 0.58减弱为Bsimple = 0.40)。
图1
综合来看, 相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾产生影响的过程受到内隐人格观的调节。对于渐变观大学生, 相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的间接效应index = 0.10, Boot SE = 0.02, 95%的置信区间为[0.07, 0.14]; 对于实体观大学生, 该间接效应相对更大, index = 0.15, Boot SE = 0.03, 95%的置信区间为[0.10, 0.23]。
4 讨论
本研究在病态网络使用的认知-行为模型的理论视角下, 揭示了相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾的关系及其作用机制。一方面阐明了相对剥夺感“怎样起作用”, 即通过非适应性认知的中介作用影响网络游戏成瘾; 另一方面剖析了“何时作用更大”即这一中介过程的后半路径受到内隐人格观的调节, 相对于渐变观大学生, 实体观大学生的非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的预测作用更大。研究结果对网络游戏成瘾的科学预防和干预具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。
4.1 相对剥夺感与网络游戏成瘾
本研究发现, 相对剥夺感对大学生网络游戏成瘾具有显著预测作用, 该结果支持相对剥夺感作为一种反映宏观系统的社会心理因素对个体适应具有消极作用的结论(Callan et al., 2011; Greitemeyer & Sagioglou, 2017; Zhang & Tao, 2013; 马皑, 2012)。以往研究发现, 当个体体验相对剥夺感, 会认为自己生活在不公平的环境, 更渴望获得即时满足, 由此增强对小而即时的奖励的兴趣, 提高问题行为如赌博成瘾的发生率(Callan et al., 2011, 2015)。而网络游戏成瘾与赌博成瘾具有一定的相似性(严万森等, 2016)。赌博为人们提供了短时间改变经济水平和地位的可能性, 网络游戏则为个体提供了建立新身份地位、逃避现实不利处境的空间(魏华等, 2014; Ng & Wiemer-Hastings, 2005)。在网络游戏这个相对匿名的空间里, 个体更具控制感, 可以通过努力获得地位提升和心理安慰(张国华, 雷雳, 2015)。除赌博、网络游戏成瘾以外, 相对剥夺感还导致个体的攻击、吸烟、酗酒、偷窃等偏差行为(熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016)。说明, 相对剥夺感对个体偏差/风险行为的作用可能具有跨领域的一致性。
更重要的是, 本研究发现大学生的相对剥夺感可以显著正向预测其网络游戏成瘾, 这一结果表明相对剥夺感理论可以在一定程度上解释大学生网络游戏成瘾, 因此, 本研究扩展了大学生网络游戏成瘾的研究视角。以往研究表明, 支持性资源匮乏的客观生态风险环境是诱发青少年沉迷网络的重要原因(李董平等, 2016), 而本研究的结果显示, 主观的经济剥夺环境就可能导致网络游戏成瘾。本研究中的相对剥夺是个体通过与参照群体比较而感知到自身处于不利地位, 从而体验到愤怒和不满等负性情绪, 是一种主观状态; 而绝对剥夺是个体由于缺少食物、水、住所等基本生活所需从而体验到
不满足, 是一种客观状态(熊猛, 叶一舵, 2016)。通常我们很容易注意到身处绝对剥夺环境的个体所面临的风险(例如贫困阶层和各类社会弱势群体), 而处于相对剥夺的个体, 尤其是其中可能包含的部分社会优势群体所面临的风险适应却容易被忽视。这提示我们, 在考虑风险行为的影响因素时, 不仅要关注学校、家庭和同伴等客观环境因素, 还要重视大学生在宏观社会生活中的主观体验。正如本研究的发现, 相对剥夺感可能将大学生的现实生活制造成缺乏公正和满足的“不舒适场所”, 让其转而向网络游戏世界寻求安慰。相对剥夺感理论可能为大学生网络游戏成瘾提供了新的解释和干预视角, 相对于客观资源的难以改变, 主观体验可以通过认知训练等手段在较短时间内得到有效改善。
4.2 非适应性认知的中介作用
本研究发现, 非适应性认知在相对剥夺感与大学生网络游戏成瘾之间起中介作用, 即相对剥夺感通过提高网络游戏非适应性认知, 进而增加大学生网络游戏成瘾风险。该结果支持病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 说明非适应性认知也是相对剥夺感影响网络游戏成瘾的重要中介机制。以往研究明确指出, 网络非适应性认知对网络成瘾的形成和维持起重要作用(Davis, 2001; Peng & Liu, 2010); 而近期的研究则表明, 网络游戏非适应性认知在网络游戏成瘾形成过程中扮演核心的中介作用(汪涛等, 2015; 甄霜菊等, 2016)。网络游戏成瘾作为网络成瘾的一个重要子类, 同样遵循“现实不舒适→网络游戏非适应性认知→成瘾行为”的作用模型, 即大学生在现实生活中认为自己经济水平比不上周围同学, 对自己的经济状况不满意, 体验愤怒和不满, 由此对网络游戏寄予发泄情绪、逃避现实、提升地位等厚望, 产生非适应性认知偏差, 进而导致沉迷网络游戏。因此, 非适应认知的中介作用不仅支持病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 而且将相对剥夺感理论整合进网络游戏成瘾领域的研究, 提示相对剥夺感也是大学生对网络游戏产生偏差认知和行为的前置和远端影响因素。
4.3 内隐人格观的调节作用
本研究发现, 内隐人格观调节相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知影响大学生网络游戏成瘾的后半路径, 具体而言, 相对于渐变观的大学生, 间接效应对于实体观的大学生作用更大。实体观者相信特质是固定的、无法改变, 这种信念导致他们更容易寻求机会表现自我, 一旦形成“网络游戏是我唯一能够得到尊重的地方”、“离开网络游戏我没有价值, 只有在网络游戏中我才算个人物”等非适应性认知, 他们就会长时间地玩网络游戏, 更容易沉迷于此。
尽管以往研究从理论和实证两方面明确了病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 即非适应性认知与一般网络成瘾和网络游戏成瘾的关系, 但是很少有研究考察两者间的调节机制(Davis, 2001; Peng & Liu, 2010; 汪涛等, 2015)。甄霜菊等(2016)的研究已经证实, 非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的效应大小并非人人同等, 对于行为抑制/激活系统中驱力水平较高的个体, 其效应更大。本研究则首次从内隐人格观的角度, 考察了“非适应性认知→网络游戏成瘾行为”的调节机制, 将认知、人格观念和行为整合于网络游戏成瘾问题的研究。这在一定程度上拓展了病态网络使用的认知-行为模型, 提示网络游戏成瘾的干预工作者关注实体观者和渐变观者的个体差异, 对个体采取渐变观的干预可以有效缓解非适应性认知对其网络游戏成瘾的影响。近期研究发现, 渐变观可以通过干预训练获得, 它能有效阻止个体做出固定的特质归因, 转而将自己和他人看作是可塑的、可改善的(Yeager, Lee, & Jamieson, 2016)。此外, 以往有关内隐人格观的研究强调的是渐变观对学业、工作和人际等适应的保护作用(崔诣晨, 王沛, 谈晨皓, 2016; Heslin, Vandewalle, & Latham, 2006; King, 2012; Maxwell et al., 2017), 还没有研究探讨渐变观对网络成瘾这种数字化时代适应不良的保护作用。内隐人格观的调节作用为网络游戏成瘾的理论研究和干预工作打开了新的思路, 这也是本研究的重要贡献所在, 将渐变观和实体观整合进网络游戏成瘾的干预工作可能会有新的收获。
4.4 研究局限与展望
本研究也存在如下一些局限:其一, 本研究采用的横断设计虽然建立在一定的理论基础之上, 但依然不能完全推断变量间的因果关系和中介作用, 这是研究的不足。未来研究可以选择干预实验方法, 通过干预组和控制组的对照, 继续检验本研究建立的有调节的中介模型; 还可以采取纵向追踪方法, 理清变量间的因果作用。其二, 本研究只关注了个体的相对剥夺, 而未考虑绝对剥夺。未来研究可以同时考察相对剥夺和绝对剥夺对网络游戏成瘾的影响, 一方面通过主观和客观的对比更深刻地揭示相对剥夺感对网络游戏成瘾的作用, 另一方面通过主观体验和客观条件的交互还能反映个体与环境的互动作用。
5 结论
综上所述, 本研究发现:(1)相对剥夺感对大学生网络游戏成瘾具有显著正向预测作用; (2)非适应性认知在相对剥夺感与大学生网络游戏成瘾之间起中介作用; (3)相对剥夺感通过非适应性认知对网络游戏成瘾的间接效应受到内隐人格观的调节。具体来说, 相对于渐变观的大学生, 间接效应对于实体观的大学生作用更大。
参考文献
Relative deprivation and adolescent outcomes in Iceland: A multilevel test
DOI:10.1353/sof.0.0177
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The theory of relative deprivation emphasizes that social comparisons contextualize how people experience impoverishment. An important application of this theory argues that relative deprivation that stems from unfavorable social comparisons can result in anger, normlessness and an increased likelihood of deviant behavior. We test this theory in a new societal setting Iceland. Specifically, we test the proposition that the effects of economic deprivation on individual outcomes are contingent on the standard of living enjoyed by the person's reference groups. Using multilevel data on 5,491 Icelandic adolescents in 83 school-communities, we find consistent support for the theory. We show that the effects of economic deprivation on adolescent anger, normlessness, delinquency, violence and subjective relative family status are weak in school-communities where economic deprivation is common, while the effects are significantly stronger in school-communities where economic deprivation is rare.
Why do you play World of Warcraft? An in-depth exploration of self-reported motivations to play online and in-game behaviours in the virtual world of Azeroth
Relative deprivation theory and responses to discrimination in a gay male and lesbian sample
DOI:10.1111/j.2044-8309.1987.tb00774.x
URL
PMID:3607390
[本文引用: 1]

Relative deprivation (RD) theory states that the perception of the relative positions of one's group and an out-group in terms of status and privilege is psychologically important. RD theory predictions for members of oppressed groups include increased endorsement of militant acts, decreased feelings of control and life-satisfaction as a function of perceived relative deprivation and perceived discrimination. In the present study, these predictions were tested with 74 members of Toronto's gay male and lesbian community. RD measures encompassed the cognitive-affective (i.e. concerned with knowledge vs. feelings about the deprivation) and egoistical-fraternal (i.e. concerned with the status of the individual vs. the in-group) dimensions, with a measure of concrete fraternal discrimination (CFD) also included for comparison. The results indicated that CFD was the best predictor of increased militancy, decreased control and decreased satisfaction. Implications for RD theory are discussed.
Gambling as a search for justice: Examining the role of personal relative deprivation in gambling urges and gambling behavior
DOI:10.1177/0146167208322956 URL [本文引用: 2]
Personal relative deprivation, delay discounting, and gambling
DOI:10.1037/a0024778
URL
PMID:21875231
[本文引用: 3]

Several lines of research have provided evidence for a relation between personal relative deprivation and gambling. Despite this knowledge, little is known about possible psychological mechanisms through which personal relative deprivation exerts its influence on gambling. The authors of this research sought to examine one such mechanism: the desire for immediate rewards. Using complementary approaches to studying psychological mechanisms, they tested in four studies the general hypothesis that personal relative deprivation translates into gambling urges and behavior in part via increased desires for immediate, even if smaller, rewards. Study 1 showed that an experimental manipulation of personal relative deprivation increased participants' preferences for smaller-sooner over larger-later rewards during a delay-discounting task. Studies 2 and 3 showed that a decreased willingness to delay gratification led to increased gambling behavior. Study 4 showed that preferences for smaller-sooner over larger-later rewards statistically mediated the relation between self-reported personal relative deprivation and gambling urges among a community sample of gamblers. The implications and potential applications of these findings are discussed. 2011 American Psychological Association.
The relation between personal relative deprivation and the urge to gamble among gamblers is moderated by problem gambling severity: A meta-analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.01.031 URL [本文引用: 4]
Video gaming in a hyperconnected world: A cross-sectional study of heavy gaming, problematic gaming symptoms, and online socializing in adolescents
DOI:10.1016/j.chb.2016.11.060 URL [本文引用: 2]
The influence of implicit theories of personality on processing strategy of person impressions
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01538
URL

The individuals can be divided into two categories in accordance with implicit theories of personality: the entity theorists, who believe that the personality and character are inherent, and the incremental theorists, who believe that the personality and character change gradually. As a significant individual difference, ITPs affect the mechanism of cognitive processing of social perception and impression formation of others. Although some studies on the individual difference about impression formation infer the existence of ITPs by the difference of behavioral outcome, there is no research to investigate the influence of impression formation to others by ITPs and it’s unclear whether exists the effect of impulsive-reflective system or not. In light of this, the aim of the research is to test whether different presentation forms can cause different processing strategies of impression formation to others and elucidate how ITPs affect the impression formation to others by observing entity theorists and incremental theorists. Three assumptions can be given in this research: (1) The ITPs of individuals can affect “top-down” and “down-top” on linkage effect as a kind of mental representation. So we can study the information judgment of person impression is instant or memory-based. (2) Entity theorists and incremental theorists perceive others in different ways that entity theorists adopt heuristic processing while incremental theorists analytic processing. (3) Through heuristic processing, entity theorists form impressions by real-time judgments while incremental theorists by memory-based judgments form through analytic processing. The experiment includes two stages. (1) Preliminary stage: 120 participants are selected as participants to be experimented with the adapted fairytale. As a result, 42 entity theory participants and 48 incremental theory participants are distinguished.(2) Experiment stage: 90 college students selected in the preliminary stage as participants who have different ITPs and directional situations to judge the information of behavior are designated to record the discrepant dates of free recall and frequency estimation through illusory correlation effect which includes mere exposure effect and co-occurrence memory judgment effect. The results of experiment lead to two conclusions. (1) Fairytale Test is capable to distinguish effectively the implicit theories of personality of participants which means the entity theory is opposite to incremental theory, and they are two extremes. Moreover, different personalities have the same implicit theory. (2) The ITPs can affect “top-down” and “down-top” on linkage effect as a kind of mental representation and then guide the social perception of people. Impression formation adopts real-time judgment under the influence of entity directional situations while memory-based judgments are adopted to form impressions through incremental directional situations. Comparing with entity theorists, the participants of incremental theorists use less initial information to built expression and there exist deviations of impression and consciousness when they are memorizing and judging. As a result, incremental theorists need more effort to form individual evaluative impression. In short, the individuals who have different implicit theories of personality adopt different information processing ways to perceive others. Entity theorists take heuristic processing and incremental theorists use analytic processing. When taking heuristic processing, entity theorists form impressions through real-time judgments while incremental theorists take memory-based judgments to form impressions through analytic processing, and finally person impression is formed by means of situational information. According to the research, the situational factors have effect in the intensity of the ITPs of individuals but don’t change inherent ITPs from research. And the information processing ways and ITPs have obvious interaction under the influence of different directional situations. So, the separation effect which is caused by processing methods of social cognition on the representation of ITPs, as a kind of important individual variables, has effect in individual emotion, attitude and behavior. As a result, combining the situations of real life, it has theoretical and applied values for us to discuss the basic issue that how the ITPs affect the processing strategy of impression formation. The ensuing research will enlarge the age range of samples and trace the physically and mentally changes of different types of object so that we can find the separation effect caused by processing methods of social cognition which includes automatic processing and controlling processing on the representation and brain mechanism of ITPs. Furthermore, whether Fairytale Test can test effectively the generality and difference of ITPs needs to be traced down by recording the real performance of participants in order to increase the repeatable verification and extrapolation efficacy.
内隐人格理论对他人印象加工策略的影响
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01538
URL
[本文引用: 1]

从表征状态与他人知觉信息加工方式两个角度探讨了内隐人格理论对他人印象加工策略的影响。首先采用自编的童话情境测验对120名被试的内隐人格理论进行维度分析,甄选出持不同内隐人格理论的被试(实体论42人、渐变论48人)。随后使用错觉关联效应的实验范式,要求两类被试(持不同内隐人格理论及其指向性情境)对他人行为信息进行判断,记录自由回忆和频率估计的差异值。结果发现:持不同内隐人格理论的个体在知觉他人时采用不同的信息加工方式。实体论者通常采用启发式加工,渐变论者通常采用分析式加工。实体论者在进行启发式加工时,通过对他人行为信息的即时性判断形成他人印象;渐变论者在进行分析式加工时,对他人行为信息进行记忆性判断,最终依赖情境信息形成他人印象。
A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use
DOI:10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00041-8
URL
[本文引用: 6]

Topology control for ad hoc networks aims to increase effective network capacity and conserve energy. Most proposed algorithms assume the use of isotropic antennas and thus only adjust the transmission power of each node. We propose a distributed topology control mechanism for ad hoc networks with directional antennas that adjusts antenna pattern (direction) in addition to transmission power. Simulation studies have been conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach, as well as to investigate its benefits and impacts on application layer performance.
Free-to-play: About addicted whales, at risk dolphins and healthy minnows. Monetarization design and internet gaming disorder
DOI:10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.03.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Implicit theories. In P. A. M. van Lange, A. W. Kruglanski, & E. T. Higgins (Eds.), Handbook of theories of social psychology
A social-cognitive approach to motivation and personality
DOI:10.1037/0033-295X.95.2.256
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A research-based model is presented that accounts for major patterns of adaptive and maladaptive behavior in terms of underlying psychological processes. It is postulated that as individuals' self-attributes are translated into allied goals, these goals generate corresponding behavior patterns. (SLD)
Relative deprivation, poor health habits, and mortality
Using individual-level data on males from the 1988-91 National Health Interview Survey Multiple Cause of Death Files, we examine the impact of relative deprivation within a reference group on health. We define reference groups using combinations of state, race, education, and age. High relative deprivation in the sense of Yitzhaki is associated with a higher probability of death, worse self-reported health, higher self-reported limitations, higher body mass index, and an increased probability of taking health risks.
Does relative deprivation predict the need for mental health services?
Internet research in psychology
DOI:10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015321 URL [本文引用: 1]
Increasing wealth inequality may increase interpersonal hostility: The relationship between personal relative deprivation and aggression
DOI:10.1080/00224545.2017.1288078 URL [本文引用: 2]
Keen to help? Managers' implicit person theories and their subsequent employee coaching
Electronic play, study, communication, and adolescent achievement, 2003-2008
DOI:10.1111/j.1532-7795.2011.00770.x
URL
PMID:3438518
[本文引用: 1]

Adolescents090005 time spent messaging, exploring websites, and studying on the computer increased between 2003 and 2008. Using data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics Child Development Supplement, this study examines how such changes have influenced individual achievement and behavior from childhood to adolescence. Greater communications and Internet web time proved detrimental to vocabulary and reading whereas the increased use of computer games was associated with increased reading and problem-solving scores, particularly for girls and minority children. Increased use of the computer for studying was associated with increased test scores for girls, but not boys. The consequences are more benign than many feared. Groups that have traditionally used the computer less (girls, minority children) appear to benefit from greater use.
Exploring user experiences as predictors of MMORPG addiction
DOI:10.1016/j.compedu.2009.05.016
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The overuse of Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Games (MMORPGs) is becoming a significant problem worldwide, especially among college students. Similar to Internet addiction, the pathological use of MMORPG is a kind of modern addiction that can affect students’ lives on both a physical and a psychological level. The purpose of this study is to understand MMORPG addiction from a user experience design approach. We first developed a complete model that includes eleven factors ( challenge, fantasy, curiosity, control, reward, cooperation, competition, recognition, belonging, obligation and role-playing) to represent users’ experience in MMORPGs. After that, we design a questionnaire to measure student’ gaming experience and level of addiction. Students’ demography information, including gender and game playing habits, was also collected. Four hundred and eighteen Taiwanese college students aged 18–25 years old took part in this online survey. Regression analysis was then conducted to evaluate the relative explanatory power of each variable, with addiction score as the dependent variable and the eleven user experience factors as the independent variables. The results of regression analysis reveal five critical factors (curiosity, role-playing, belonging, obligation and reward) that can be used to predict MMORPG addiction. In addition, this study also infers possible casual mechanisms for increasing college students’ level of addiction. The implications of our findings for both design and educational practitioners were also discussed.
How you think about your intelligence influences how adjusted you are: Implicit theories and adjustment outcomes
DOI:10.1016/j.paid.2012.05.031 URL [本文引用: 1]
Internet addiction and problematic Internet use: A systematic review of clinical research
DOI:10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.143
URL
PMID:27014605
[本文引用: 1]

AIM: To provide a comprehensive overview of clinical studies on the clinical picture of Internet-use related addictions from a holistic perspective. A literature search was conducted using the database Web of Science.METHODS: Over the last 15 years, the number of Internet users has increased by 1000%, and at the same time, research on addictive Internet use has proliferated. Internet addiction has not yet been understood very well, and research on its etiology and natural history is still in its infancy. In 2013, the American Psychiatric Association included Internet Gaming Disorder in the appendix of the updated version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders(DSM-5) as condition that requires further research prior to official inclusion in the main manual, with important repercussions for research and treatment. To date, reviews have focused on clinical and treatment studies of Internet addiction and Internet Gaming Disorder. This arguably limits the analysis to a specific diagnosis of a potential disorder that has not yet been officially recognised in the Western world, rather than a comprehensive and inclusive investigation of Internet-use related addictions(including problematic Internet use) more generally. RESULTS: The systematic literature review identified a total of 46 relevant studies. The included studies used clinical samples, and focused on characteristics of treatment seekers and online addiction treatment. Four main types of clinical research studies were identified, namely research involving(1) treatment seeker characteristics;(2) psychopharmacotherapy;(3) psychological therapy; and(4) combined treatment. CONCLUSION: A consensus regarding diagnostic criteria and measures is needed to improve reliability across studies and to develop effective and efficient treatment approaches for treatment seekers.
Online gaming addiction? Motives predict addictive play behavior in massively multiplayer online role-playing games
The effects of escape from self and interpersonal relationship on the pathological use of Internet games
DOI:10.1007/s10597-009-9236-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Internet gaming addiction, problematic use of the Internet, and sleep problems: A systematic review
DOI:10.1007/s11920-014-0444-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
A literature review of implicit theories and consumer decision-making
Implicit theories refer to the views on the variability of basic characteristics of human beings(such as intelligence,moral characters and personalities) and surrounding things,and can be divided into entity and incremental theories. This paper aims at the discussion of the application of implicit theories to the field of consumer behavior research. The views on the variability of basic characteristics of human beings and surrounding things can affect the motivations for consumption andthereby consumption decision-making. Entity theorists are likely to seek products in line with their performance goals and effortless success,and focus more on outcomes. But consumers who subscribe to incremental theory are likely to seek products in line with their development learning goals and which should be used by efforts,and focus more on process. In addition,brands and firms also can cast the propensity for entity theory or incremental theory and consumption accordingly evaluate firms.It also discusses the possibility of the measurement and start-up of implicit theories and their application to consumption field.
“内隐人格理论”与消费者决策研究述评
DOI:10.16538/j.cnki.fem.2016.09.003
URL
[本文引用: 2]

“内隐人格理论”是人们所持有的对人的基本特征(如智力、品德和人格特质)及周围事物可变性的看法,可分为实体论和渐变论。本文旨在探讨“内隐人格理论”在消费者行为领域的应用。对人的基本特质及周围事物可变性的看法会影响人们的消费动机,从而影响人们的消费决策。实体论者更希望选择能凸显自我且简单易用的商品,同时更加注重消费结果;而渐变论者则更倾向于选择能够使自己得到发展和学习的、需要花费努力才能使用的商品,同时更加注重消费过程。此外,品牌和企业同样可以投射出实体论或渐变论倾向,消费者会据此对企业做出评价。在本文中,我们也探讨了测量和启动内隐人格理论的可能性及其在消费领域的应用。
Cumulative ecological risk and adolescent Internet addiction: The mediating role of basic psychological need satisfaction and positive outcome expectancy
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01519 URL
累积生态风险与青少年网络成瘾: 心理需要满足和积极结果预期的中介作用
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.01519
URL
[本文引用: 3]

青少年网络成瘾与个体所处的生态背景密切相关。目前已有不少研究探讨家庭、学校、同伴背景中单个或少数风险因素对青少年网络成瘾的影响,但少有研究关注多个背景中生态风险因素的累积对青少年网络成瘾的影响及其心理机制。本研究基于累积风险模型和动机心理学理论,考察累积生态风险对青少年网络成瘾的影响及基本心理需要满足(个体在现实生活中需要被满足的情况)和积极结果预期(个体对网络使用诱因大小的判断)在其中的并行和/或链式中介作用。被试为5所中学的998名青少年。结构方程模型分析表明:(1)在控制了人口学变量后,累积生态风险对青少年网络成瘾具有显著的正向预测作用(呈"负加速模式")。(2)累积生态风险通过显著降低基本心理需要满足(表现出"梯度效应"),进而促进青少年网络成瘾。(3)累积生态风险通过显著提升积极结果预期(呈"负加速模式"),进而促进青少年网络成瘾。(4)累积生态风险对青少年网络成瘾的影响被基本心理需要满足和积极结果预期两条并行路径完全中介。上述结果表明,累积生态风险对青少年网络成瘾具有重要影响,且这种影响是通过需要和诱因两种动机力量一"推"一"拉"的合力来实现。
Relative deprivation and social adaption: The role of mediator and moderator
Deriving from R. Merton Anomie Theory, innovation and rebellion as two kinds of the social adaption are viewed as the strongest predictors of collective behavior, mass crime and mass disturbance. However, few empirical studies have been done to explore the relation between them and psychological variables. The aim of this study is to investigate the associations between relative deprivation and innovation and rebellion. Furthermore, through examining the mediating role and moderating role of attribution style in the associations between relative deprivation and innovation and rebellion. The present study also examine the moderating role of rebellion in the associations between relative deprivation and innovation. To test these hypotheses, the Relative Deprivation Questionnaire, Social Adaption Questionnaire, Attribution Questionnaire were administered to 6175 valid subjects. The results indicate: (1) The positive predicting effect of relative deprivation on innovation was significant. (2) The positive predicting effect of relative deprivation on rebellion was significant. (3) Attribution style served to partially mediate the association between relative deprivation and innovation, and also partially mediate the association between relative deprivation and rebellion. (4) As a moderator, attribution style strengthened the positive relation between relative deprivation and rebellion. (5) As a moderator, rebellion weakened the positive relation between relative deprivation and innovation in the lower social stratum. In sum, it could be concluded that relative deprivation played a positive predicting effect on social adaption. Attribution style partially mediated the relationship between relative deprivation and social adaption. Rebellion weakened the immediate impact of relative deprivation on innovation in the vulnerable group. These findings highlight the important role of relative deprivation and attribution style to the anomie social adaption, which may provide the policy makers with some implication in preventing collective behavior, mass crime and mass disturbance.
相对剥夺感与社会适应方式: 中介效应和调节效应
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.00377
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Deriving from R. Merton Anomie Theory, innovation and rebellion as two kinds of the social adaption are viewed as the strongest predictors of collective behavior, mass crime and mass disturbance. However, few empirical studies have been done to explore the relation between them and psychological variables. The aim of this study is to investigate the associations between relative deprivation and innovation and rebellion. Furthermore, through examining the mediating role and moderating role of attribution style in the associations between relative deprivation and innovation and rebellion. The present study also examine the moderating role of rebellion in the associations between relative deprivation and innovation. To test these hypotheses, the Relative Deprivation Questionnaire, Social Adaption Questionnaire, Attribution Questionnaire were administered to 6175 valid subjects. The results indicate: (1) The positive predicting effect of relative deprivation on innovation was significant. (2) The positive predicting effect of relative deprivation on rebellion was significant. (3) Attribution style served to partially mediate the association between relative deprivation and innovation, and also partially mediate the association between relative deprivation and rebellion. (4) As a moderator, attribution style strengthened the positive relation between relative deprivation and rebellion. (5) As a moderator, rebellion weakened the positive relation between relative deprivation and innovation in the lower social stratum. In sum, it could be concluded that relative deprivation played a positive predicting effect on social adaption. Attribution style partially mediated the relationship between relative deprivation and social adaption. Rebellion weakened the immediate impact of relative deprivation on innovation in the vulnerable group. These findings highlight the important role of relative deprivation and attribution style to the anomie social adaption, which may provide the policy makers with some implication in preventing collective behavior, mass crime and mass disturbance.
Structure and function of maladaptive cognitions in pathological Internet use among Chinese adolescents
DOI:10.1016/j.chb.2012.07.009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Consumer mindsets and self-enhancement: Signaling versus learning
DOI:10.1016/j.jcps.2015.06.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The mindset framework and its downstream effects provide exciting new opportunities to explore one of the powerful drivers of consumer and organizational behavior. To advance discussions on the concept and applications of mindsets in consumer research and in the marketplace, we (1) provide conceptual and contextual clarity into the signaling mechanism and the process/outcome focus by identifying relevant and meaningful consumer contexts, (2) consider the unique theoretical contributions implicit theory may make to the field of consumer psychology, and (3) suggest potential solutions for important methodological challenges researchers and practitioners may face when implementing the mindsets framework. Finally, we (4) highlight the managerial and organizational relevance of mindsets.
How implicit theories of sexuality shape sexual and relationship well-being
DOI:10.1037/pspi0000078
URL
PMID:27808534
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract How do people believe they can best maintain sexual satisfaction in their romantic relationships? In the current research, we draw upon the literature on implicit theories of relationships to develop and validate a scale examining 2 types of lay beliefs about how sexual satisfaction can be maintained over time. Individuals high in sexual growth beliefs think that sexual satisfaction is attained from hard work and effort, whereas individuals high in sexual destiny beliefs think that sexual satisfaction is attained through finding a compatible sexual partner. Across 6 studies (2 cross-sectional online studies, a 21-day daily experience study, 2 dyadic studies, and an experimental manipulation; N = 1,896), we find evidence that those higher in sexual growth beliefs experience higher relationship and sexual satisfaction, and have partners who are more satisfied. Conversely, the effects of sexual destiny beliefs on satisfaction are contingent upon signs of partner compatibility: When individuals high in sexual destiny beliefs experience greater sexual disagreements in their relationship, they experience lower relationship quality. These results are independent of general relationship implicit beliefs, providing evidence for the uniqueness of these 2 constructs and the importance of examining implicit beliefs in the domain of sexuality. Overall, these results provide novel evidence that individuals' lay beliefs about maintaining sexual satisfaction are important for understanding the quality of their sex lives and relationships. (PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2017 APA, all rights reserved).
Online gaming addiction: The role of sensation seeking, self-control, neuroticism, aggression, state anxiety, and trait anxiety
DOI:10.1089/cyber.2009.0229 URL [本文引用: 1]
Problematic video game use: Estimated prevalence and associations with mental and physical health
DOI:10.1089/cyber.2010.0260 URL [本文引用: 1]
Determinants of risky decision-making and gambling: The effects of need and relative deprivation
Strategies to cope with negative social identity: Predictions by social identity theory and relative deprivation theory
DOI:10.1037/0022-3514.76.2.229 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mindsets shape consumer behavior
DOI:10.1016/j.jcps.2015.06.005 URL [本文引用: 2]
Addiction to the Internet and online gaming
DOI:10.1089/cpb.2005.8.110
URL
PMID:15938649
[本文引用: 3]

As computer and Internet use become a staple of everyday life, the potential for overuse is introduced, which may lead to addiction. Research on Internet addiction has shown that users can become addicted to it. Addiction to the Internet shares some of the negative aspects of substance addiction and has been shown to lead to consequences such as failing school, family, and relationship problems.
Got to get you into my life: Do brand personalities rub off on consumers?
DOI:10.1086/655807 URL [本文引用: 1]
Online gaming dependency: A preliminary study in China
DOI:10.1089/cyber.2009.0082
URL
PMID:20557254
[本文引用: 4]

Based on theories and previous studies on problematic Internet use, we propose a model to better understand the contributors to and consequences of online gaming dependency. A preliminary study was conducted through a survey of online gamers in China. The results of path analysis found that maladaptive , shyness, and are positively related to online gaming dependency. Online gaming dependency was also positively related to different types of negative life outcomes. The findings of this study have implications for the prevention and treatment of addictive online gaming.
An international consensus for assessing Internet gaming disorder using the new DSM‐5 approach
DOI:10.1111/add.12457
URL
PMID:24456155
[本文引用: 1]

AbstractAimsFor the first time, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) introduces non-substance addictions as psychiatric diagnoses. The aims of this paper are to (i) present the main controversies surrounding the decision to include internet gaming disorder, but not internet addiction more globally, as a non-substance addiction in the research appendix of the DSM-5, and (ii) discuss the meaning behind the DSM-5 criteria for internet gaming disorder. The paper also proposes a common method for assessing internet gaming disorder. Although the need for common diagnostic criteria is not debated, the existence of multiple instruments reflect the divergence of opinions in the field regarding how best to diagnose this condition.MethodsWe convened international experts from European, North and South American, Asian and Australasian countries to discuss and achieve consensus about assessing internet gaming disorder as defined within DSM-5.ResultsWe describe the intended meaning behind each of the nine DSM-5 criteria for internet gaming disorder and present a single item that best reflects each criterion, translated into the 10 main languages of countries in which research on this condition has been conducted.ConclusionsUsing results from this cross-cultural collaboration, we outline important research directions for understanding and assessing internet gaming disorder. As this field moves forward, it is critical that researchers and clinicians around the world begin to apply a common methodology; this report is the first to achieve an international consensus related to the assessment of internet gaming disorder.
In pursuit of three theories: Authoritarianism, relative deprivation, and intergroup contact
DOI:10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033327
URL
PMID:26361053
[本文引用: 1]

Throughout my career, I have pursued three theories related to intergroup prejudice--each with a different mentor. Each theory and its supporting research help us to understand prejudice and ways to ameliorate the problem. This autobiographical review article summarizes some of the advances in these three areas during the past six decades. For authoritarianism, the article advocates removing political content from its measurement, linking it with threat and dismissive-avoidant attachment, and studying how authoritarians avoid intergroup contact. Increased work on relative deprivation made possible an extensive meta-analysis that shows the theory, when appropriately measured, has far broader effects than previously thought. Increased research attention to intergroup contact similarly made possible a meta-analysis that established the pervasive effectiveness of intergroup contact to reduce prejudice under a wide range of conditions. The article closes by demonstrating how the three theories relate to each other and contribute to our understanding of prejudice and its reduction.
Person theories and attention allocation: Preferences for stereotypic versus counterstereotypic information
DOI:10.1037/0022-3514.80.6.876 URL
Electronic gaming and psychosocial adjustment
DOI:10.1542/peds.2013-4021
URL
PMID:25092934
[本文引用: 1]

BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The rise of electronic games has driven both concerns and hopes regarding their potential to influence young people. Existing research identifies a series of isolated positive and negative effects, yet no research to date has examined the balance of these potential effects in a representative sample of children and adolescents. The objective of this study was to explore how time spent playing electronic games accounts for significant variation in positive and negative psychosocial adjustment using a representative cohort of children aged 10 to 15 years. METHODS: A large sample of children and adolescents aged 10 to 15 years completed assessments of psychosocial adjustment and reported typical daily hours spent playing electronic games. Relations between different levels of engagement and indicators of positive and negative psychosocial adjustment were examined, controlling for participant age and gender and weighted for population representativeness. RESULTS: Low levels (<1 hour daily) as well as high levels (>3 hours daily) of game engagement was linked to key indicators of psychosocial adjustment. Low engagement was associated with higher life satisfaction and prosocial behavior and lower externalizing and internalizing problems, whereas the opposite was found for high levels of play. No effects were observed for moderate play levels when compared with non-players. CONCLUSIONS: The links between different levels of electronic game engagement and psychosocial adjustment were small (<1.6% of variance) yet statistically significant. Games consistently but not robustly associated with children's adjustment in both positive and negative ways, findings that inform policy-making as well as future avenues for research in the area.
Relative deprivation: A theoretical and meta- analytic review
DOI:10.1177/1088868311430825 URL [本文引用: 1]
RETRACTED: Key factors of heuristic evaluation for game design: Towards massively multi-player online role-playing game
DOI:10.1016/j.ijhcs.2007.01.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
A review on the research in the dimension of entity theory versus incremental theory of implicit personality theories
Relationships of peer player proportion, maladaptive cognition, and online game addiction
Objective:We examined the relationships between proportion of players in individual peer relation network,maladaptive cognition and online game addiction.Methods:We used peer relation network structure questionnaire,maladaptive cognition questionnaire and online game addiction questionnaire to measure 1906 online game players.Results:1The proportion of players in individual peer relation network was significantly and positively correlated to maladaptive cognition and online game addiction.Maladaptive cognition was significantly positively correlated to online game addiction.2The proportion of players in individual peer relation network affected online game addiction via maladaptive cognition as a mediating effect.Conclusion:The larger the proportion of players in individual peer relation network,the higher degree of maladaptive cognition and online game addiction.The proportion of players in Maladaptive cognition may serve as a mediator between individual peer relation network and online game addiction.
同伴玩家比例、非适应性认知与网络游戏成瘾的关系
An analysis of the relative deprivation of college students and its influence on mental health
The relationship between Internet addiction and life events of college students: The mediating effect of escape motivation
Online game addiction: Effects and mechanisms of flow experience
This study examined the effects of flow experience on online game addiction and its mechanism and antecedents.A total of 491 male undergraduate students took part in the current study.The results showed that(1) Flow experience was significantly and positively related to online game addiction,control and challenge;online game addiction was significantly and positively related to control and challenge.(2) Flow experience played a full mediating role in challenge's effect on online game addiction,indicating that an indirect effect of challenge on online game addiction;flow experience had a partial mediating effect between control and online game addiction,revealing direct and indirect effects of the control on online game addiction.
网络游戏成瘾: 沉浸的影响及其作用机制
本研究以491名男大学生为被试,考察了沉浸对网络游戏成瘾的影响、沉浸的前因变量和相关作用机制。结果发现:(1)网络游戏中的沉浸与网络游戏成瘾呈显著正相关,与控制、挑战呈显著正相关;挑战和控制与网络游戏成瘾呈显著正相关。(2)挑战通过沉浸的完全中介作用对网络游戏成瘾产生影响,挑战对网络游戏成瘾没有直接效应;控制除了通过沉浸的部分中介作用对网络游戏成瘾产生影响,还对网络游戏成瘾有直接效应。
Different methods for testing moderated mediation models: Competitors or backups?
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00714
URL

Mediation and moderation models are frequently used in the research of psychology and many other social science disciplines. Mediation indicates that the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable is transmitted through a third variable, namely a mediator. For example, students' gratitude promoted their academic achievement medially by increasing everyday academic resilience. Moderation occurs when the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable varies according to the level of a third variable, which interacts with the independent variable. For instance, adolescents' perceptions of their teachers' authoritative teaching moderated the effect of antisocial disruption on peer acceptance. It is not uncommon for hypotheses about moderation and mediation relationships to occur in the same context where more than three variables are involved. When a mediation effect is moderated by a moderator, the effect is termed moderated mediation and the model is moderated mediation model. For example, everyday academic resilience acts as a mediator between gratitude and academic achievement, and this mediation process is moderated by stressful life events. There are several methods for testing moderated mediation models. The moderated mediation models being used for proposed testing methods are different. We are wondering whether different testing methods are competitors, or some of them are only backups. We discussed the different testing methods based on the most general type of model. The traditional testing method is the moderated causal steps approach, in which the regression coefficients are tested in sequence. Modern methods include the testing of the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method, and testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects. On the basis of the previous studies it can be summarized that the power of test with the moderated causal steps approach is the lowest among the three testing methods, whereas the testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects has the highest power of test. After comparing significant results of the three testing methods by reviewing the simplification, implication, information, and explanation, we concluded that the moderated causal steps approach should be recommended first; testing of the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method should be treated as a backup; testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects should be the final choice. We proposed a hierarchical procedure for testing moderated mediation models as follows: Step 1. Adopt the moderated causal steps approach to test the model. If the significant result is obtained from the test, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, go to Step 2. Step 2. Test the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method. If any product is significantly different from zero, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, go to Step 3. Step 3. Test the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects. If the difference is significant, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, the mediating effect is not moderated. As an illustration, the procedure was applied to an empirical study in which everyday academic resilience played the role of a mediator between gratitude and academic achievement, and this mediation process moderated by stressful life events. The relationship and difference between moderated mediation models and mediated moderation models were also discussed.
有调节的中介模型检验方法: 竞争还是替补?
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00714
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Mediation and moderation models are frequently used in the research of psychology and many other social science disciplines. Mediation indicates that the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable is transmitted through a third variable, namely a mediator. For example, students gratitude promoted their academic achievement medially by increasing everyday academic resilience. Moderation occurs when the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable varies according to the level of a third variable, which interacts with the independent variable. For instance, adolescents perceptions of their teachers authoritative teaching moderated the effect of antisocial disruption on peer acceptance. It is not uncommon for hypotheses about moderation and mediation relationships to occur in the same context where more than three variables are involved. When a mediation effect is moderated by a moderator, the effect is termed moderated mediation and the model is moderated mediation model. For example, everyday academic resilience acts as a mediator between gratitude and academic achievement, and this mediation process is moderated by stressful life events. There are several methods for testing moderated mediation models. The moderated mediation models being used for proposed testing methods are different. We are wondering whether different testing methods are competitors, or some of them are only backups. We discussed the different testing methods based on the most general type of model. The traditional testing method is the moderated causal steps approach, in which the regression coefficients are tested in sequence. Modern methods include the testing of the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method, and testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects. On the basis of the previous studies it can be summarized that the power of test with the moderated causal steps approach is the lowest among the three testing methods, whereas the testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects has the highest power of test. After comparing significant results of the three testing methods by reviewing the simplification, implication, information, and explanation, we concluded that the moderated causal steps approach should be recommended first; testing of the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method should be treated as a backup; testing of the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects should be the final choice. We proposed a hierarchical procedure for testing moderated mediation models as follows: Step 1. Adopt the moderated causal steps approach to test the model. If the significant result is obtained from the test, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, go to Step 2. Step 2. Test the products of coefficients by using Bootstrap method or MCMC method. If any product is significantly different from zero, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, go to Step 3. Step 3. Test the difference between the maximum and minimum of the mediation effects. If the difference is significant, the mediating effect is moderated. Otherwise, the mediating effect is not moderated. As an illustration, the procedure was applied to an empirical study in which everyday academic resilience played the role of a mediator between gratitude and academic achievement, and this mediation process moderated by stressful life events. The relationship and difference between moderated mediation models and mediated moderation models were also discussed.
The concept, measurement, influencing factors and effects of relative deprivation
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00438 URL
The neural mechanisms of impulsivity implicated in drug addiction and non-drug addiction
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00159
URL

Mounting evidence has demonstrated that impulsivity could be a potential biomarker that plays a crucial role in the development of addictive behaviors, thus impulsivity is considered a possible treatment target for early intervention of addiction. Nevertheless, it remains unclear how the mechanisms underlying the trajectories of impulsivity are involved in drug addiction and non-drug addiction. This project aims to identify the neural mechanisms of impulsivity in both nicotine dependence and internet gaming disorder by combining a direct comparison of drug and non-drug addictive behaviors with longitudinal studies and a cognitive-behavioral intervention study, using neurocognitive tasks and neuroimaging techniques. Firstly, nicotine-dependent individuals and internet gaming addicts would be tested on a series of behavioral tasks of impulsivity as well as in fronto-striatal brain systems using both structured and functional magnetic resonance imaging(f MRI) with a 3T Philips Trio MRI. Then we will move on to investigate the predictive role of impulsivity for nicotine dependence and internet gaming disorder through a 2 to 3 year follow-up study with a large sample of non-addicted adolescents consisting of two groups with either high- or lowlevels of impulsivity. Thirdly, a study of 6 to 12 month cognitive behavioral intervention would be conducted on nicotine-dependent individuals and internet gaming addicts to explore the possible effects of reducing impulsivity level on the exacerbation of addictive behaviors. And this study will also evaluate the effects of continuous behavioral training on brain functions in fronto-striatal brain systems through f MRI tests. Totally, these studies should be helpful for shedding light on the possible efficacy of impulsivity as a potential biomarker and treatment target for addictive disorders.
冲动性对不同成瘾行为发展的调控及其神经机制
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00159
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Mounting evidence has demonstrated that impulsivity could be a potential biomarker that plays a crucial role in the development of addictive behaviors, thus impulsivity is considered a possible treatment target for early intervention of addiction. Nevertheless, it remains unclear how the mechanisms underlying the trajectories of impulsivity are involved in drug addiction and non-drug addiction. This project aims to identify the neural mechanisms of impulsivity in both nicotine dependence and internet gaming disorder by combining a direct comparison of drug and non-drug addictive behaviors with longitudinal studies and a cognitive-behavioral intervention study, using neurocognitive tasks and neuroimaging techniques. Firstly, nicotine-dependent individuals and internet gaming addicts would be tested on a series of behavioral tasks of impulsivity as well as in fronto-striatal brain systems using both structured and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) with a 3T Philips Trio MRI. Then we will move on to investigate the predictive role of impulsivity for nicotine dependence and internet gaming disorder through a 2 to 3 year follow-up study with a large sample of non-addicted adolescents consisting of two groups with either high- or low- levels of impulsivity. Thirdly, a study of 6 to 12 month cognitive behavioral intervention would be conducted on nicotine-dependent individuals and internet gaming addicts to explore the possible effects of reducing impulsivity level on the exacerbation of addictive behaviors. And this study will also evaluate the effects of continuous behavioral training on brain functions in fronto-striatal brain systems through fMRI tests. Totally, these studies should be helpful for shedding light on the possible efficacy of impulsivity as a potential biomarker and treatment target for addictive disorders.
How to improve adolescent stress responses: Insights from integrating implicit theories of personality and biopsychosocial models
DOI:10.1177/0956797616649604
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract This research integrated implicit theories of personality and the biopsychosocial model of challenge and threat, hypothesizing that adolescents would be more likely to conclude that they can meet the demands of an evaluative social situation when they were taught that people have the potential to change their socially relevant traits. In Study 1 (N = 60), high school students were assigned to an incremental-theory-of-personality or a control condition and then given a social-stress task. Relative to control participants, incremental-theory participants exhibited improved stress appraisals, more adaptive neuroendocrine and cardiovascular responses, and better performance outcomes. In Study 2 (N = 205), we used a daily-diary intervention to test high school students' stress reactivity outside the laboratory. Threat appraisals (Days 5-9 after intervention) and neuroendocrine responses (Days 8 and 9 after intervention only) were unrelated to the intensity of daily stressors when adolescents received the incremental-theory intervention. Students who received the intervention also had better grades over freshman year than those who did not. These findings offer new avenues for improving theories of adolescent stress and coping. The Author(s) 2016.
The formation and endorsement of customer’s stereotypes in service contacts: From the perspective of implicit personality theory
服务接触中顾客刻板印象的形成与支持: 内隐人格理论视角
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5097.2014.02.031
URL
[本文引用: 1]

文章以服务接触中的员工行为为刺激,探讨了顾客所持有的内隐人格理论(实体论/渐变论)在其对服务组织刻板印象的形成与支持中所扮演的角色。通过对254个样本采用2×2被试间实验设计的方式,结合方差分析等方法进行了假设检验。研究结果发现:实体论者较渐变论者更容易在服务接触中通过观察员工行为形成对服务组织的刻板印象,而且实体论者认为这些零散的员工行为足以作为依据对组织做出判断;此外,这种刻板印象一旦形成,无论后续的服务表现如何,实体论者对服务组织的看法都很难改变。研究结论为服务企业特别是新成立的服务企业提供了一个新的质量管理和顾客行为分析视角。
Who is to blame? The relationship between ingroup identification and relative deprivation is moderated by ingroup attributions
DOI:10.1027/1864-9335/a000153 URL [本文引用: 2]
The relationship between online game experience and online game addiction among adolescents: A cross-lagged regression analysis
The motivational process model of adolescent online gamers’ playing intention
Relative deprivation and psychopathology of Chinese college students
DOI:10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.013
URL
PMID:23714373
[本文引用: 2]

Previous researchers have studied the relationship between mental disorder and major demographic variables, but the study on the relationship between relative poverty or relative deprivation, a subjectively perceived status in comparison with people around, and psychopathology is rare. Data for this study were obtained from a survey research conducted on a university campus in Beijing China, between 2007 and 2011, with a total of 5925 college students who participated in the surveys over the past five years. According to the Strain Theory of suicide we hypothesized that the stronger the relative deprivation, the higher the level of depression for the students and the higher the degree of suicidal ideation the students would experience. Findings indicated that relative deprivation is significantly correlated with suicidal ideation, positively related with depression and negatively related to social support. It is proposed that reduction of psychological strains might be an effective procedure to reduce college students' psychopathology and increase their positive psychological feelings such as self-perceived social support.
Basic psychological needs and adolescents’ online game addiction tendencies: A moderated mediation model
基本心理需要与青少年网络游戏成瘾倾向: 一个有调节的中介模型
DOI:10.16518/j.cnki.emae.2016.11.009
URL
[本文引用: 6]

探讨网络游戏成瘾的形成机制,识别出容易形成网络游戏成瘾的个体,对网络游戏成瘾的科学预防和有效控制具有积极的作用。为了考察非适应性认知在基本心理需要与青少年的网络游戏成瘾倾向间的中介作用,以及该过程是否受到行为抑制/激活系统的调节,本文采用整群取样法,选取广东省5所学校初一到高二的1990名中学生为被试,匿名填写基本心理需要问卷、非适应性认知量表、行为抑制/激活系统问卷和网络游戏成瘾问卷。研究结果表明,在控制了性别和年龄后,基本心理需要对网络游戏成瘾倾向具有正向预测作用;非适应性认知中介了基本心理需要与网络游戏成瘾倾向的关系;基本心理需要与非适应性认知的关系以及非适应性认知与网络游戏成瘾倾向的关系,受到行为激活系统中驱力的调节。
Statistical remedies for common method biases
The problem of common method biases has being given more and more attention in the field of psychology, but there is little research about it in China, and the effects of common method bias are not well controlled. Generally, there are two ways of controlling common method biases, procedural remedies and statistical remedies. In this paper, statistical remedies for common method biases are provided, such as factor analysis, partial correlation, latent method factor, structural equation model, and their advantages and disadvantages are analyzed separately. Finally, suggestions of how to choose these remedies are given.
共同方法偏差的统计检验与控制方法
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3710.2004.06.018
URL
[本文引用: 1]

共同方法偏差是心理学研究中一个越来越被关注的课题,但国内心理学界对其的介绍、研究还比较少,导致研究中对共同方法偏差的控制还有所欠缺。共同方法偏差的控制方法分为程序控制和统计控制,该文介绍了共同方法偏差的多种统计控制法,如因素分析法、偏相关法、潜在的误差变量控制法、结构方程模型法等,分析了其各自的优缺点,并提出了如何选择采用这些方法的建议。