

CN 11-1911/B
主办:中国心理学会
中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (3): 450-466.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2026.0450 cstr: 32110.14.2026.0450
收稿日期:2025-02-18
发布日期:2025-12-26
出版日期:2026-03-25
通讯作者:
孙彦良, E-mail: yanliangsun@126.com基金资助:
LIANG Xingjie, CHEN Huifang, WANG Luyao, SUN Yanliang( )
)
Received:2025-02-18
Online:2025-12-26
Published:2026-03-25
摘要:
时间注意是指个体根据刺激发生的时间优先处理信息的能力, 对日常生活中的行为反应至关重要。然而, 节律性时间注意是否受意识状态调控尚不明确。本研究通过高频闪烁技术操纵视觉节律刺激被感知的意识状态水平, 将行为测量、分层漂移扩散模型(hierarchical drift-diffusion model, HDDM)分析与事件相关电位和时频分析技术相结合, 系统考察了意识状态对节律性时间注意的调节作用以及节律线索在亚秒与超秒时间尺度上的加工机制差异。实验1结果表明, 节律线索在有、无意识状态下均能引发时间注意效应, 但效应在无意识条件下显著减弱。HDDM分析进一步揭示, 有意识状态下节律线索能降低个体的决策边界, 提示其激活了决策层面的内源性加工, 而无意识状态下该效应不显著。实验2在此基础上发现, CNV成分与α震荡抑制均在有意识条件下更为显著, 进一步支持意识状态通过调节认知准备和注意维持机制增强时间注意效应。此外, 尽管节律线索时间间隔(ISI)不影响时间注意效应的强度, 但超秒间隔条件下整体反应更快, 支持时间认知分段综合模型的预测。综上, 节律性时间注意不仅依赖外在节奏驱动, 也可能涉及基于意识水平调节的内源性决策机制。
中图分类号:
梁星杰, 陈慧芳, 王璐瑶, 孙彦良. (2026). 意识状态调节节律性时间注意: 来自行为、分层漂移扩散模型与脑电指标的证据. 心理学报, 58(3), 450-466.
LIANG Xingjie, CHEN Huifang, WANG Luyao, SUN Yanliang. (2026). Modulation of rhythmic temporal attention by conscious awareness: Evidence from behavior, hierarchical drift-diffusion modeling, and EEG measures. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 58(3), 450-466.
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 0 |
| Model_v | v | 138.6 |
| Model_t | t | 325.8 |
表1 实验1中随意识状态和线索呈现方式变化的模型参数和ΔDIC
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 0 |
| Model_v | v | 138.6 |
| Model_t | t | 325.8 |
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 7.7 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 34.4 |
表2 实验1中随ISI变化的模型参数和ΔDIC
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 7.7 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 34.4 |
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 0.4 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 80.9 |
表3 实验2中随意识状态和线索呈现方式变化的模型参数和ΔDIC
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 0.4 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 80.9 |
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 40.5 |
| Model_v | v | 74 |
| Model_t | t | 0 |
表4 实验2中随ISI变化的模型参数和ΔDIC
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 40.5 |
| Model_v | v | 74 |
| Model_t | t | 0 |
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 62.2 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 135.3 |
表5 实验2中随意识状态和ISI变化的模型参数和ΔDIC
| 模型 | 随条件变化的参数 | ΔDIC |
|---|---|---|
| Model_a | a | 62.2 |
| Model_v | v | 0 |
| Model_t | t | 135.3 |
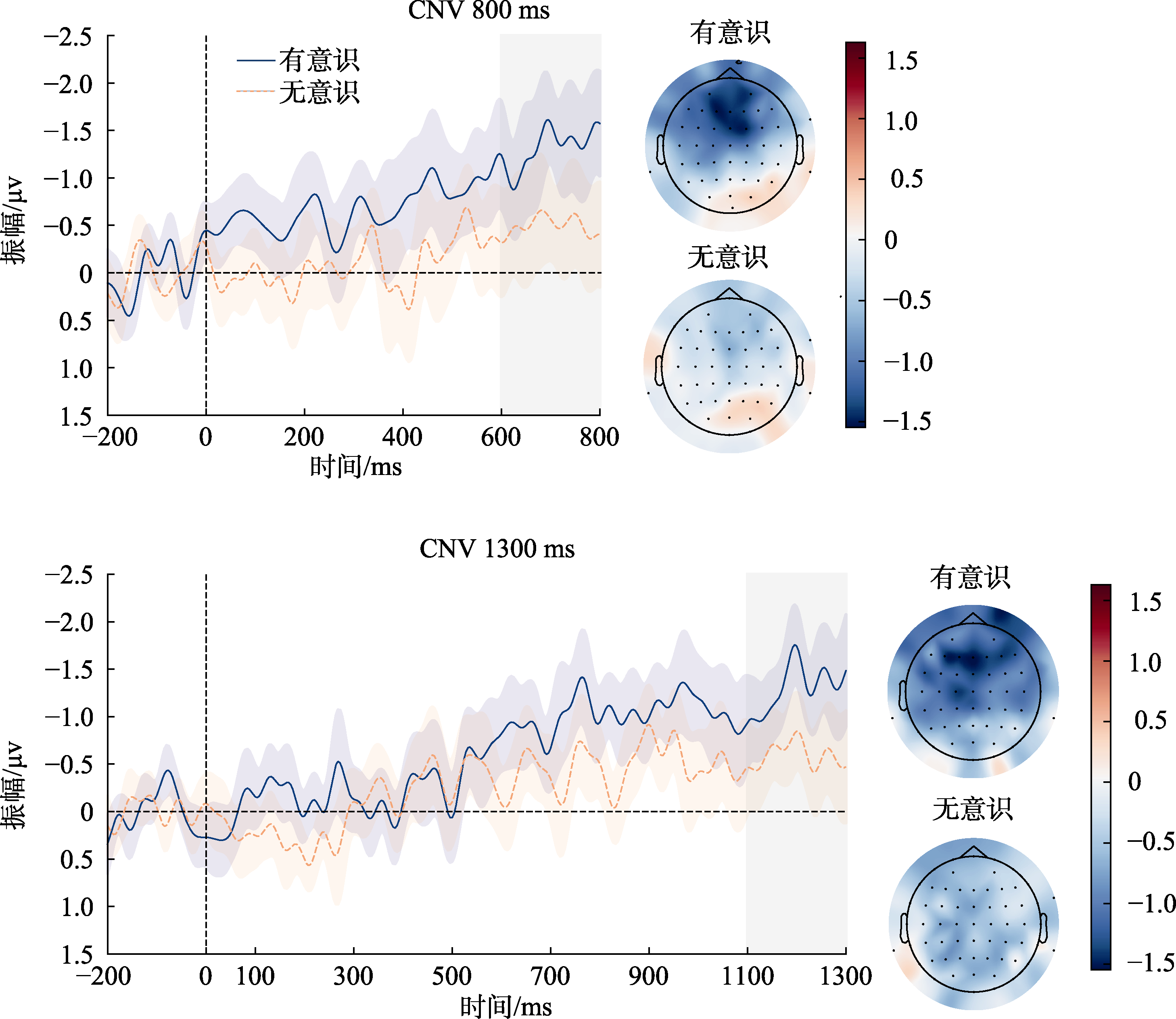
图11 实验2不同条件下CNV差值波形图及地形图 注: 图中蓝色实线代表有意识状态下的CNV差值(节律−随机), 橙色虚线代表无意识状态下的CNV差值; 蓝色、橙色阴影是误差线, 代表被试内95%的置信区间; 灰色阴影区域代表分析CNV的时间窗口; 右侧为不同意识状态和ISI条件下的CNV差值地形图(数据取自时间窗口内的差值均值)。
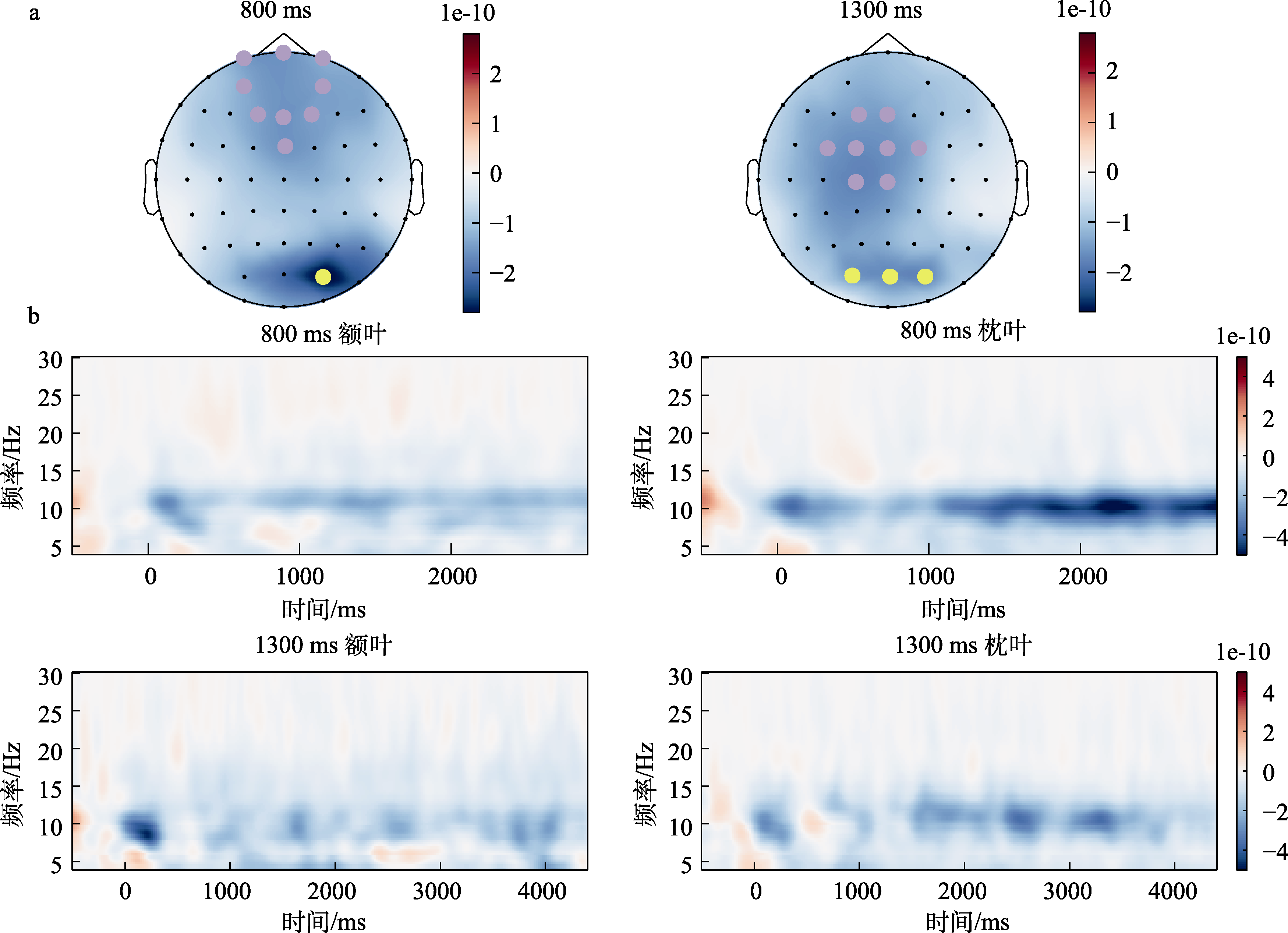
图13 实验2编码阶段的α频段地形图以及时频图 注: a图为α频段意识状态差值(有意识−无意识)地形图, 左图为800 ms ISI条件, 右图为1300 ms ISI条件。图a中的紫色圆点为b图时频分析中所挑选的额叶电极, 黄色圆点则为所挑选的枕叶电极。b图为不同时间间隔和脑区下的意识状态差值(有意识−无意识)时频图。
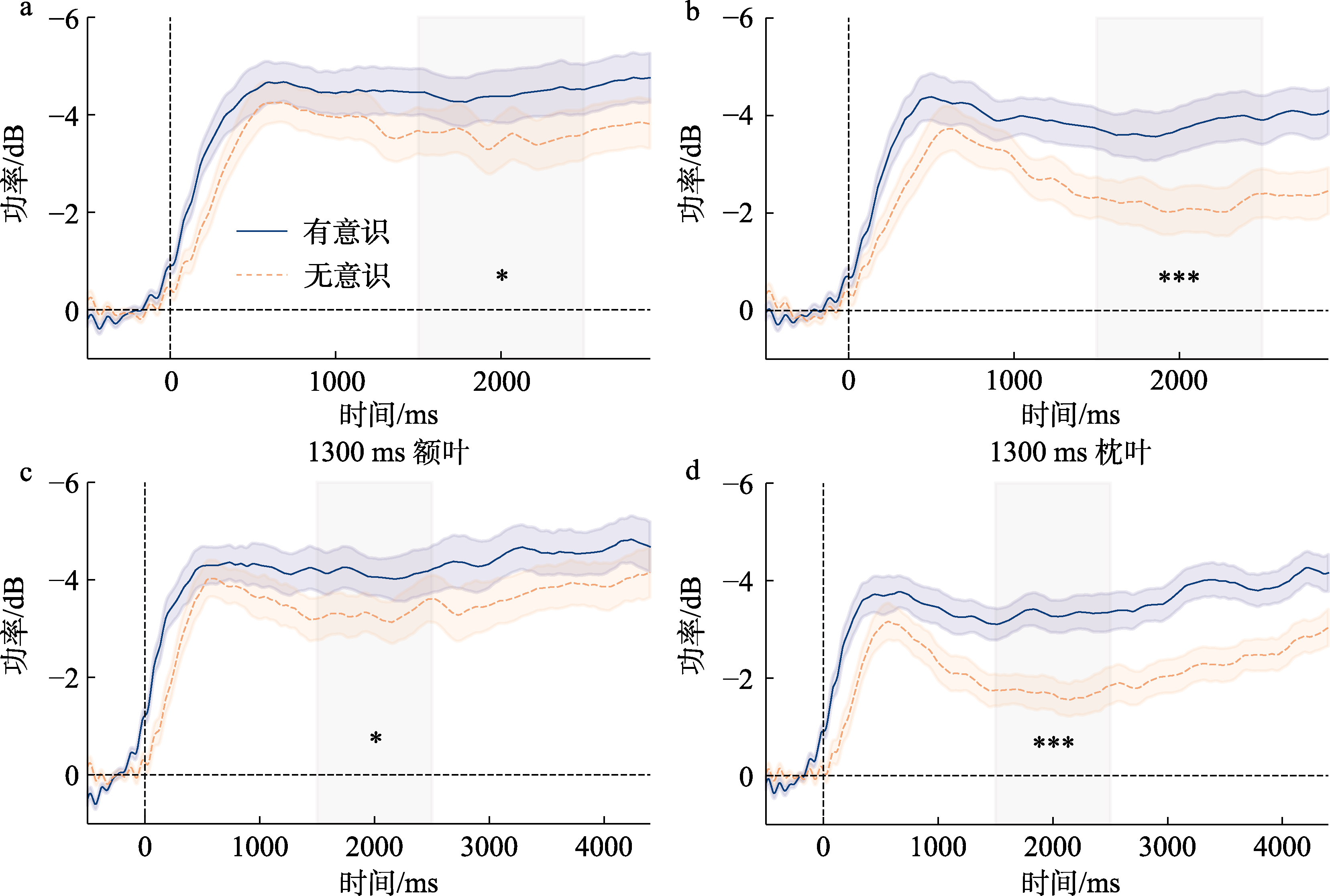
图14 实验2编码阶段的α频段功率图 注: 图中蓝色实线代表有意识状态下的α频段功率, 橙色虚线代表无意识状态下的α频段功率; 蓝色、橙色阴影是误差线, 代表被试内95%的置信区间; 灰色阴影区域代表分析的时间窗口(1500~2500 ms)。*表示p < 0.05, ***表示p > 0.001。
| [1] | Baars B. J. (2005). Global workspace theory of consciousness: Toward a cognitive neuroscience of human experience. Progress in Brain Research, 150, 45-53. |
| [2] |
Bauer F., Cheadle S. W., Parton A., Müller H. J., & Usher M. (2009). Gamma flicker triggers attentional selection without awareness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(5), 1666-1671.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810496106 pmid: 19124766 |
| [3] |
Bouwer F. L., Honing H., & Slagter H. A. (2020). Beat-based and memory-based temporal expectations in rhythm: Similar perceptual effects, different underlying mechanisms. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(7), 1221-1241.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01529 pmid: 31933432 |
| [4] |
Breska A., & Deouell L. Y. (2014). Automatic bias of temporal expectations following temporally regular input independently of high-level temporal expectation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(7), 1555-1571.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00564 pmid: 24392898 |
| [5] |
Breska A., & Deouell L. Y. (2016). When synchronizing to rhythms is not a good thing: Modulations of preparatory and post-target neural activity when shifting attention away from on-beat times of a distracting rhythm. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 36(27), 7154-7166.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4619-15.2016 URL |
| [6] |
Breska A., & Deouell L. Y. (2017). Neural mechanisms of rhythm-based temporal prediction: Delta phase-locking reflects temporal predictability but not rhythmic entrainment. PLoS Biology, 15(2), e2001665. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2001665
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001665 URL |
| [7] |
Breska A., & Ivry R. B. (2020). Context-specific control over the neural dynamics of temporal attention by the human cerebellum. Science Advances, 6(49), eabb1141. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb1141
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb1141 URL |
| [8] |
Correa A., & Nobre A. C. (2008). Neural modulation by regularity and passage of time. Journal of Neurophysiology, 100(3), 1649-1655.
doi: 10.1152/jn.90656.2008 pmid: 18632896 |
| [9] |
Coull J. T., & Nobre A. C. (1998). Where and when to pay attention: The neural systems for directing attention to spatial locations and to time intervals as revealed by both PET and fMRI. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(18), 7426-7435.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-18-07426.1998 URL |
| [10] |
Coull J., & Nobre A. (2008). Dissociating explicit timing from temporal expectation with fMRI. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 18(2), 137-144.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.07.011 pmid: 18692573 |
| [11] |
Denison R. N., Heeger D. J., & Carrasco M. (2017). Attention flexibly trades off across points in time. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 24(4), 1142-1151.
doi: 10.3758/s13423-016-1216-1 URL |
| [12] |
Faul F., Erdfelder E., Buchner A., & Lang A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149-1160.
doi: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149 pmid: 19897823 |
| [13] | Gooch C. M., Wiener M., Hamilton A. C., & Coslett H. B. (2011). Temporal discrimination of sub- and suprasecond time intervals: A voxel-based lesion mapping analysis. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2011.00059 |
| [14] | Gramfort A., Luessi M., Larson E., Engemann D. A., Strohmeier D., Brodbeck C., … Hämäläinen M. (2013). MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 267. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00267 |
| [15] | Huang X., Li B., & Zhang Z. (2003). The research of the range-synthetic model of temporal cognition. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 29(2), 5-9. |
| [黄希庭, 李伯约, 张志杰. (2003). 时间认知分段综合模型的探讨. 西南师范大学学报(人文社会科学版), 29(2), 5-9.] | |
| [16] |
Jiang Y., Zhou K., & He S. (2007). Human visual cortex responds to invisible chromatic flicker. Nature Neuroscience, 10(5), 657-662.
pmid: 17396122 |
| [17] |
Jones M. R., & Boltz M. (1989). Dynamic attending and responses to time. Psychological Review, 96(3), 459-491.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.96.3.459 pmid: 2756068 |
| [18] |
Kingstone A. (1992). Combining expectancies. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology A: Human Experimental Psychology, 44(1), 69-104.
doi: 10.1080/14640749208401284 URL |
| [19] | Koch G., Oliveri M., & Caltagirone C. (2009). Neural networks engaged in milliseconds and seconds time processing: Evidence from transcranial magnetic stimulation and patients with cortical or subcortical dysfunction. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 364(1525), 1907-1918. |
| [20] |
Lange K. (2009). Brain correlates of early auditory processing are attenuated by expectations for time and pitch. Brain and Cognition, 69(1), 127-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2008.06.004 pmid: 18644669 |
| [21] |
Laquitaine M., Polosan M., Kahane P., Chabardes S., Yelnik J., Fernandez-Vidal S., … Bastin J. (2024). Optimal level of human intracranial theta activity for behavioral switching in the subthalamo-medio-prefrontal circuit. Nature Communications, 15(1), 7827. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52290-w
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52290-w URL |
| [22] |
Lewis P. A., & Miall R. C. (2003). Brain activation patterns during measurement of sub- and supra-second intervals. Neuropsychologia, 41(12), 1583-1592.
pmid: 12887983 |
| [23] | Mankowska N. D., Marcinkowska A. B., Waskow M., Sharma R. I., Kot J., & Winklewski P. J. (2021). Critical flicker fusion frequency: A narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania), 57(10), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101096 |
| [24] |
Miller J. E., Carlson L. A., & McAuley J. D. (2013). When what you hear influences when you see: Listening to an auditory rhythm influences the temporal allocation of visual attention. Psychological Science, 24(1), 11-18.
doi: 10.1177/0956797612446707 pmid: 23160202 |
| [25] |
Miniussi C., Wilding E. L., Coull J. T., & Nobre A. C. (1999). Orienting attention in time. Modulation of brain potentials. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 122(Pt 8), 1507-1518.
doi: 10.1093/brain/122.8.1507 URL |
| [26] |
Myers C. E., Interian A., & Moustafa A. A. (2022). A practical introduction to using the drift diffusion model of decision-making in cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and health sciences. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1039172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1039172
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1039172 URL |
| [27] | Nobre, A. C. (2010). How can temporal expectations bias perception and action. In A. C. Nobre, & J. T. Coull (Eds.), Attention and time (pp. 371-392). Oxford. |
| [28] |
Nobre A. C., & van Ede F. (2018). Anticipated moments: Temporal structure in attention. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 19(1), 34-48.
doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.141 pmid: 29213134 |
| [29] |
Nobre A., Correa A., & Coull J. (2007). The hazards of time. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 17(4), 465-470.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.07.006 pmid: 17709239 |
| [30] |
Nozaradan S., Peretz I., Missal M., & Mouraux A. (2011). Tagging the neuronal entrainment to beat and meter. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(28), 10234-10240.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0411-11.2011 URL |
| [31] |
Peirce J. W. (2007). PsychoPy-Psychophysics software in Python. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 162(1-2), 8-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.11.017 URL |
| [32] |
Pomper U. (2023). No evidence for tactile entrainment of attention. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1168428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1168428
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1168428 URL |
| [33] |
Pouthas V., George N., Poline J. B., Pfeuty M., Vandemoorteele P. F., Hugueville L., … Renault B. (2005). Neural network involved in time perception: An fMRI study comparing long and short interval estimation. Human Brain Mapping, 25(4), 433-441.
pmid: 15852471 |
| [34] |
Praamstra P., Kourtis D., Kwok H. F., & Oostenveld R. (2006). Neurophysiology of implicit timing in serial choice reaction-time performance. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(20), 5448-5455.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0440-06.2006 URL |
| [35] |
Rammsayer T., & Ulrich R. (2011). Elaborative rehearsal of nontemporal information interferes with temporal processing of durations in the range of seconds but not milliseconds. Acta Psychologica, 137(1), 127-133.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2011.03.010 pmid: 21474111 |
| [36] |
Rohenkohl G., & Nobre A. C. (2011). α oscillations related to anticipatory attention follow temporal expectations. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(40), 14076-14084.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3387-11.2011 URL |
| [37] |
Rozier C., Seidel Malkinson T., Hasboun D., Baulac M., Adam C., Lehongre K., … Naccache L. (2020). Conscious and unconscious expectancy effects: A behavioral, scalp and intracranial electroencephalography study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 131(2), 385-400.
doi: S1388-2457(19)31288-X pmid: 31865140 |
| [38] |
Shady S., MacLeod D. I., & Fisher H. S. (2004). Adaptation from invisible flicker. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(14), 5170-5173.
pmid: 15051882 |
| [39] |
Sun Y., Wang K., Liang X., Zhou P., & Sun Y. (2024). Unconscious temporal attention induced by invisible temporal association cues. Consciousness and Cognition, 126, 103786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2024.103786
doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2024.103786 URL |
| [40] |
Tal I., Large E. W., Rabinovitch E., Wei Y., Schroeder C. E., Poeppel D., & Zion Golumbic E. (2017). Neural entrainment to the beat: The "missing-pulse" phenomenon. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(26), 6331-6341.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2500-16.2017 URL |
| [41] |
Tian S., Cheng Y. A., & Luo H. (2025). Rhythm facilitates auditory working memory via beta-band encoding and theta-band maintenance. Neuroscience Bulletin, 41(2), 195-210.
doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01289-w |
| [42] |
Walter W. G., Cooper R., Aldridge V. J., McCallum W. C., & Winter A. L. (1964). Contingent negative variation: An electric sign of sensori-motor association and expectancy in the human brain. Nature, 203, 380-384.
doi: 10.1038/203380a0 |
| [43] | Wiecki T. V., Sofer I., & Frank M. J. (2013). HDDM: Hierarchical bayesian estimation of the drift-diffusion model in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2013.00014 |
| [44] |
Wiener M., Turkeltaub P. E., & Coslett H. B. (2010). Implicit timing activates the left inferior parietal cortex. Neuropsychologia, 48(13), 3967-3971.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.09.014 pmid: 20863842 |
| [45] |
Xu Z., Ren Y., Misaki Y., Wu Q., & Lu S. (2021). Effect of tempo on temporal expectation driven by rhythms in dual-task performance. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 755490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.755490
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.755490 URL |
| [1] | 崔茜,张庆林,邱江,刘强,杜秀敏,阮小林. P300和CNV在GKT的延时反应范式中测谎效果的分离[J]. 心理学报, 2009, 41(04): 316-328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||