需要(Need)是动机心理学与人格心理学的基本术语, 也是心理学体系中的一个核心概念, 指的是人体组织系统中的一种缺乏、不平衡的状态(彭聃龄, 2001, p321)。在这种状态作用下, 个体会产生行为的动力, 即动机, 进而驱使个体发起各种不同的行为, 以满足自己的需要, 解除这种缺乏、不平衡的状态。因此, 需要是心理学家用于理解和预测个体行为的最重要的变量之一。
对需要的研究, 早期有两种完全不同的研究范式:第一种是由Hull提出, 他认为人有一系列的生理需要(例如食物、水、性), 这些需要会产生一种驱力状态, 进而促进有机体的行动, 当需要获得满足的时候个体就会朝着健康的方向发展(Hull, 1943)。第二种研究范式由Murray提出, Murray更强调需要是指心理的而不是生理的, 他把需要看成是后天习得的一种力量, 这种力量会将个体的观点、统觉、智力、努力、行为组织起来, 然后促进个体在某个特定的方向上采取行动(Murray, 1938)。
Deci和Ryan (2000)则认为前人所提出的这两种研究范式, 并不能完全解释和定义心理需要, 因此他们提出了基本心理需要(Basic Psychological Needs)这一概念。首先和Hull的理论一样, Deci和Ryan把基本心理需要定义为先天的、内在的、有机体必须的, 而不是Murray所说的后天可获得的动机; 其次, 他们又把需要定义为心理的而不是生理的。在Deci和Ryan看来, 需要就像是心理的营养物一样, 对于心理的成长、整合和幸福感必不可少。他们假设人类有一种朝向活力、整合和健康的基本倾向; 当具备了必要的营养物时, 人们就会实现这种倾向, 而当营养物缺乏时就会导致消极的心理结果; 而基本心理需要就像是这样一种营养物。Deci和Ryan还指出, 基本心理需要必须能够通过观察来鉴别, 当基本心理需要满足的时候, 能够观察到个体表现出适宜的发展和幸福感, 而在需要受挫时, 能够观察到个体表现出不幸感(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。上述界定使得基本心理需要这一概念自诞生时起, 便独立于以往大多数研究者所提到的需要。
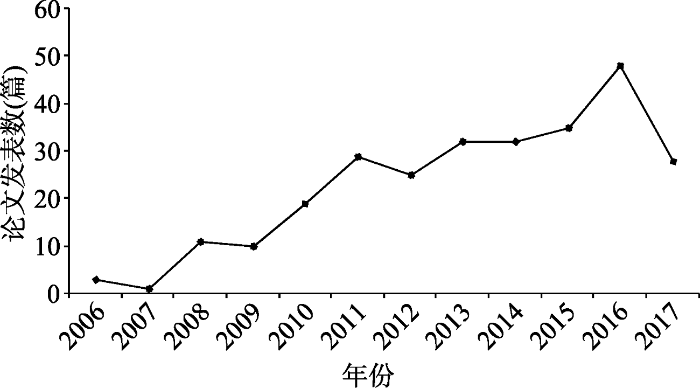
基本心理需要这个概念自提出以来, 便受到心理学界的重视, 越来越多的研究者开展了相关研究。本文作者在Web of Knowledge数据库中, 以“basic psychological needs”为检索词, 对2006年至2017年7月间已发表的基本心理需要的外文文献进行检索, 最后得到了200篇英文相关文献。进一步分析发现, 每年出版的文献数和每年的引文数都呈现逐年增长的趋势,在2016年则达到高峰, 详见图1。
图1
本文以国内外已有的研究文献为基础, 对Deci和Ryan所提出的基本心理需要的概念、理论、测量工具以及相关应用研究进行系统的梳理, 同时对于一些质疑和问题展开讨论, 并在此基础上提出未来研究中值得关注的若干问题。
1 基本心理需要
1.1 基本心理需要的概念
基本心理需要这一概念由Deci和Ryan提出。他们认为, 人类的基本心理需要就像是心理上的营养物一样, 对个体心理的健康成长、整合和幸福感必不可少、至关重要; 基本心理需要又分为三种, 分别是胜任需要(competence, 也译作能力需要)、关系需要(relatedness, 也译作关联需要)和自主需要(autonomy) (Deci & Ryan, 2000)。Deci和Ryan将胜任需要定义为个体感觉到的对于环境的掌控感, 并在此基础上发展出一种新的技能, 是个体先天所具有的一种对于环境的探索倾向。第二种是关系需要, 是指个体感受到的与他人良好的关系, 以及来自他人的支持; 当关系需要得到满足的时候, 人们会感受到一种安全的人际氛围。第三种基本心理需要是自主需要, 是指个体感觉到的对自己行为上的控制感和心理上的自由(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。当人们的自主需要得到满足时, 他们对于日常活动会有更高的主动性、参与度和创造力(Deci & Ryan, 2012)。值得注意的是, 自主需要不一定是指独立于他人期望的行为, 而是指个体在行动中能感觉到选择感, 哪怕这种行动是符合别人的期望的(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。比如说员工被安排在午饭时间完成一份工作, 如果员工赞成主管的安排, 那么他的自主需要得到了满足; 反之, 如果员工更愿意去吃午饭而不是工作, 则他会体验到自主需要的受挫(Trougakos, Hideg, Cheng, & Beal, 2014)。自主并不仅仅存在于个体身上, 在整个群体中, 人们同样也会为了自主而斗争(Deci & Ryan, 2012)。
Deci和Ryan (2000)认为, 这三种需要有两个重要的特点:第一, 这三种需要是天生的、与生俱来的, 而不是通过后天习得的, 这与大多数理论认为的需要是后天习得的观点有很大的差别。因此, 每一个人都有每一种需要, 并且这三种需要是同样重要的, 任何一种需要的受挫都会影响到个体心理上的成长、内化和幸福感。心理上的成长通常表现为个体内在动机的增强, 对于活动的好奇心和探索性增强; 内化是指个体行为的动机从外部动机到内部动机的转换; 而心理上的幸福感主要是指个体的生活满意度、精神和身体上的健康、活力等(Deci & Ryan, 1985a)。第二, 这三种需要都能够促进个体心理上的成长、内化和幸福感。他们还制定了成为基本心理需要的标准:必须要能够表达出个体朝向成长、内化和幸福感的自然倾向, 并且必须要有大量的证据证明它能够导致人们的这种倾向。在他们看来, 只有胜任、关系和自主这三种需要能够被称为人的基本心理需要, 也只有这三种需要能够同时促进个体心理上的成长、内化和幸福感, 其他的需要则不能。而大量的研究也证实了这一点(Gunnell, Crocker, Wilson, Mack, & Zumbo, 2013; van den Broeck, Ferris, Chang, & Rosen, 2016)。
基本心理需要来源于Deci和Ryan所提出的自我决定理论(Self-Determination Theory, SDT), 本身也是自我决定理论的核心概念与重要的理论分支。自我决定理论是一个研究人类动机和人格的宏观理论(Deci & Ryan, 1985b, 2000), 它假设人是积极的有机体, 并具有积极的自我整合、自我完善与不断学习的倾向, 但这种倾向的发生并非自然而然的, 而是通过外部环境的支持实现的。因此, 与以往的动机理论相比, 自我决定理论突出强调个体与社会环境之间有机互动的重要性。而社会环境通常会涉及到个体比较亲密的人, 如父母、老师、教练等等, 每一段亲近的人际关系同时又会嵌入在其他的大环境中, 形成与个体间的有机互动(Deci & Ryan, 2012)。
自我决定理论主要有5个分支, 分别是认知评价理论、有机整合理论、因果定向理论、基本心理需要理论、目标内容理论。基本心理需要在其中起到贯穿整个自我决定理论的核心作用, 比如认知评价理论认为, 胜任需要和自主需要的满足程度会受内部动机和外部动机强度的影响; 在有机整合理论和因果定向理论中, 自主动机和控制动机是根据自主需要的满足程度来区分的, 三种基本心理需要的满足也是外部动机内化的重要条件; 在目标内容理论中, 通过目标内容能否直接和有效地满足个体基本心理需要, 来区分外在目标和内在目标。
基本心理需要与马斯洛的需要层次理论相比, 虽有一定的相似之处, 比如前者的关系需要与后者的社交需要相类似, 但二个理论实则有着很大的不同:首先, 基本心理需要理论强调三种需要之间是一种平等的关系, 而需要层次理论则把需要从下到上分为5个等级, 只有当下层的需要得到满足后, 上层的需要才能得到满足(Maslow, 1943)。其次, 基本心理需要只包括心理上的需要, 而需要层次理论除了心理需要外, 还包括生理方面的需要(即生理需要和安全需要)。最后, 对于需要层次理论中的尊重需要和自我实现的需要, 在基本心理需要理论看来, 它们更像是胜任、关系、自主这三种需要满足后的结果, 而不是需要本身(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。
1.2 基本心理需要的测量
1.2.1 对基本心理需要满足的测量
为评估基本心理需要在一般领域的满足, Gagné (2003)在工作需要满足量表(Ilardi, Leone, Kasser, & Ryan, 1993)的基础上, 编制了一般需要满足量表(General Need Satisfaction Scale, GNSS)。该量表共有21个项目, 分为3个维度, 其中, 用来测量自主需要的有7个项目(比如:我感觉到我能够决定自己的生活方式), 测量关系需要的有6个项目(比如:我确实喜欢和我接触的这些人), 测量胜任需要的有8个项目(比如:我经常感觉缺乏能力)。自主、关系和胜任的内部一致性信度(α系数)分别为:0.69、0.86、0.71, 各个分量表之间的相关在0.62~0.65之间; 高分代表基本心理需要满足的程度较高(Gagné, 2003)。在Gagné的量表提出之后, 很多研究都使用该量表对于基本心理需要的满足进行了测量(Gagné, 2003; Niemiec, Ryan, & Deci, 2009), 而理论提出者本人也认为这是一个有效的、灵活的测量工具(Deci, personal communication, 2008)。
Johnston和Finney (2010)为了进一步检验GNSS的外部效度, 对该量表进行了验证和修订, 证实了这三种需要之间的辨别性。而在国内, 喻承甫等人(2012)也对一般需要满足量表进行多次的直译和回译, 显示该量表结构模型拟合较好。谢东杰、王利刚、白羽和高文斌(2012)为了检测西方的基本心理需要结构是否符合中国的情况, 以及GNSS在中国的适用性如何, 也对一般需要满足量表进行了检验与修订。经过三次探索性因素分析后, 谢东杰最后得到中文版的GNSS有15个条目, 包含4个因子, 分别为:自主需要满足、自主需要满足受阻、关系需要满足、关系需要满足受阻, 累计方差贡献率为63.95%, 中文版GNSS的Cronbach α系数为0.76。相比起原量表, 修订后的量表并不包含胜任需要这个维度, 修订者认为可能是因为原量表中的胜任需要维度不符合中国人的基本需要结构, 或者原量表中使用的题目不能很好地衡量中国人的胜任需要。
为了测量基本心理需要在网络上的满足程度, 有研究者在GNSS的基础上编制了网络基本心理需要量表(Basic Psychological Needs in the Online World, BPNOW) (Wang, Tao, Fan, & Gao, 2015)。该量表共有13个项目, 分为3个维度。其中, 用来测验自主需要的有5个项目, 测量关系需要的有5个项目, 测量胜任需要的有3个项目。自主、关系和胜任的Cronbach α系数分别为:0.75、0.73、0.72, 整个量表的Cronbach α系数为0.83。
1.2.2 对基本心理需要受挫的测量
Bartholomew, Ntoumanis, Ryan, Bosch和Thøgersen-Ntoumani (2011)编制了心理需要受挫量表(Psychological Need Thwarting Scale, PNTS), 主要是为了测量运动员在运动过程中心理需要的受挫程度。该量表采用7点评分的方式, 共有三个维度, 12个项目, 其中用来测验自主需要的有4个项目, 测量关系需要的有4个项目, 测量胜任需要的有4个项目, 这三个分量表有较高的内部一致性(0.77-0.82)。在Bartholomew等人的基础上, Gunnell等人(2013)对于PNTS进行了修订, 把原量表中的“在运动中”改为了“在身体活动中”, 建立了PNTS-PA量表, 用来检验在身体活动中基本心理需要受阻的情况。量表同样有三个维度, 每个维度下有4个题目, 效度和复合信度>0.67。
2 基本心理需要的满足与受挫
2.1 基本心理需要的满足
2.1.1 满足基本心理需要的条件
Deci和Ryan (2000)认为人天生就会被一些有趣的活动所吸引, 去训练自己的能力, 去追求与社会群体的关系, 去体验自主感; 当环境满足了三种基本心理需要的时候, 个体就会朝着积极、健康的方向发展。所以说, 环境是影响个体基本心理需要满足的主要因素, 而环境大致可分为微观环境和宏观环境。微观环境主要指人们的家庭环境、学习环境以及工作环境。已有研究证实, 家庭环境会影响个体基本心理需要的满足, 当家庭成员间的关系越和谐, 家庭系统越完善, 个体的基本心理需要满足程度就越高(Jang-hoe & AhnDoehee, 2015)。关于学习环境的研究发现, 如果教练或教师能给学生提供一种自主支持的氛围, 那么学生的基本心理需要满足程度就会更高, 进而能够促进学生有更好的表现(Balaguer et al., 2012; Yu, Li, & Zhang, 2015)。而在工作环境方面, 工作需求(例如工作压力)和工作资源(例如社会支持)会影响人们基本心理需要的满足程度:当工作需求越高时, 人们的基本心理需要满足程度越低, 而当工作资源越多时, 人们的基本心理需要满足程度越高(van den Broeck, Vansteenkiste, de Witte, & Lens, 2008)。
宏观环境主要是指一个社会的经济体系、政治体系以及文化价值观, 同样会影响个体基本心理需要的满足。首先, 一个社会的经济体系会影响个体基本心理需要的满足, 如果一个社会更加强调个人资本的拥有, 个人的劳动、想法、时间和产品都是可以用来交换和出售的, 人们则可以根据自己的兴趣来选择工作, 这在一定程度上会增加个体的自主性, 从而促进基本心理需要的满足。其次, 对于政治体系来说, 如果社会制度能够赋予人们自主选择的权利, 让个人对于管理他们的生活具有一定的话语权, 那么在这种制度下生活的个体, 基本心理需要的满足程度将会较高(Deci & Ryan, 2012)。最后, 关于文化价值观的研究表明, 对于不同的文化——集体主义文化和个人主义文化, 影响基本心理需要满足的并不是文化本身, 而是个体对于文化的内化程度(Chirkov, Ryan, Kim, & Kaplan, 2003)。也就是说, 如果人们对于自己的文化认同程度较高, 则有利于基本心理需要的满足, 反之, 则会导致基本心理需要的受挫。
2.1.2 满足基本心理需要的后果
幸福感(well-being)是指一个人对于自己生活的主观经验和评价, 个人基本心理需要满足的程度越高, 体验到的幸福感就会越高。基本心理需要与幸福感的正相关已被多个研究证实:首先对于学生群体来说, 基本心理需要的满足能显著提高学生的幸福感(Simões & Alarcão, 2014)。而除了现实中基本心理需要的满足外, 网络基本需要同样能够正向预测幸福感, 并且现实中基本心理需要的满足将网络基本心理需要的满足与幸福感联系在一起, 即:在现实生活中基本心理需要满足程度较高的学生, 更有可能从网络上获得基本心理需要的满足, 从而获得更高的幸福感(Wang et al., 2015)。其次, 对于运动员来说, 胜任、自主、关系需要在教练的自主支持和心理上的幸福感之间起到部分中介作用(López-Walle, Balaguer, Castillo, & Tristán, 2012)。如果教练在训练中能够提供充分自主支持, 那么运动员基本心理需要的满足程度就会较高, 他们也就会体验到更多的幸福感。最后, 基本心理需要对于幸福感的预测也具有跨文化的普遍性, 一项在比利时、中国、美国和秘鲁四个国家的跨文化研究表明:三种基本心理需要的满足能够预测幸福感, 并且不受个体差异以及对于需要的渴望程度的影响(Chen et al., 2015)。
除了与幸福感呈正相关外, 基本心理需要还与自杀、抑郁和问题行为等存在着负向相关。比如:对于年轻人来说, 当基本心理需要得到满足时, 他们更少地出现自杀意念和自杀行为(Britton, van Orden, Hirsch, & Williams, 2014)。除了自杀外, 对于抑郁的研究也同样证实了基本心理需要的重要性。相比起基本心理需要满足较低的个体, 那些满足较高的个体表现出更少的抑郁症状以及更少的冷漠行为(Ferrand, Martinent, & Charry, 2015)。仅仅对基本心理需要与其他变量之间作直接的相关研究似乎还不足以突出基本心理需要的重要性, 如果将基本心理需要作为另外两个变量之间的中介变量或调节变量则更能凸显其价值。Rowe, Walker, Britton和Hirsch (2013)的研究表明, 基本心理需要在负性生活事件和自杀行为之间起到调节作用, 也就是说, 当一个人经历负性生活事件之后, 如果能够通过一定的方式满足他的基本心理需要, 则可以有效地阻止自杀行为。在网络问题行为(POGU)方面, 学生基本心理需要的满足能够促进他们遵守学校的规定, 从而减少由于网络游戏所带来的问题行为; 基本心理需要在教师的自主支持和学生的网络问题行为之间起中介作用(Yu et al., 2015); 而压力性生活事件对于网络成瘾的影响同样受到基本心理需要的中介作用, 个体所体会到的压力性事件越多, 基本心理需要的满足程度就越低, 网络成瘾的可能性就越大(Li et al., 2016)。此外, 夏扉和叶宝娟(2014)的研究发现, 基本心理需要是压力性生活事件与青少年烟酒使用之间的中介变量, 应对方式是基本心理需要与青少年烟酒使用之间的中介变量; 因此,基本心理需要和应对方式一起, 在压力性生活事件与青少年烟酒使用之间起链式中介作用。综上, 基本心理需要是导致个体自杀、抑郁和问题行为的重要影响因素, 当个体的基本心理需要受挫时, 可能会导致一系列严重的后果。
另外, 也有研究表明:基本心理需要对于精神上的健康、良好的关系起着积极的预测作用(Patrick, Knee, Canevello, & Lonsbary, 2007), 当个体的基本心理需要得到满足时, 个体的心理健康水平会更高, 也更容易与他人建立良好的关系, 同时, 也会体验到更多的生活意义感(Eakman, 2014)。
2.2 基本心理需要满足的受阻与补偿
当基本心理需要的满足受到阻碍时, 个体就会集中在自己的需要上, 而不会去关注周围的环境, 这样就可能会导致个体去遵循外在的规则, 进而使个体的行为变得不协调, 变得缺乏动机, 甚至会做出反社会的行为(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。Deci和Ryan将这个过程定义为需要的受挫。研究表明, 需要的受挫可能会导致躯体化疾病、焦虑、压抑、内部的矛盾等等(Vansteenkiste & Ryan, 2013)。Shields, Ryan和Cicchetti (2001)的研究表明, 那些受到虐待的孩子相比起正常的孩子会体会到更少的自主支持, 更少的积极情绪, 出现更多的行为问题和情绪问题。并且, 需要的受挫会影响孩子的学习, 同时也会产生暴食的症状(Verstuyf, Vansteenkiste, Soenens, Boone, & Mouratidis, 2013)。Ryan和Deci (2000)认为, 需要的满足和需要的受挫是两个独立的维度, 而不是一个维度的两端; 需要的满足更多的与积极的结果相关, 而需要的受挫更多的与消极的结果相关。
Deci和Ryan认为, 当基本心理需要受挫时, 个体会倾向于寻找补偿的活动或替代的满足。一般来说, 人们会发展出补偿性动机(Compensatory Motives)、非自主的控制风格(Regulatory Style)以及僵硬、刻板的行为模式(Behavior Patterns), 来帮助他们免受需要受阻的伤害; 尽管采用了这三种方式, 他们的需要依然没有得到满足(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。
当需要受阻时, 人们首先可能发展出需要的替代或补偿性动机; 补偿性动机虽然不能真正满足被剥夺的需要, 但是能够提供替代的满足(Deci & Ryan, 2000),比如说, 如果一个人在年轻时的关系需要被剥夺了, 那么在之后他可能就会为了得到别人的赞扬去追求金钱和地位, 这种对于金钱和地位的追求, 就是补偿性动机的一种。Kuzucu和Şimşek (2013)的研究也表明, 当基本心理需要受挫时, 会导致青少年的侵略性增加, 而侵略性同样也是一种需要的替代。尽管需要的受挫会让人们转向一些目标和行为来补偿, 但是这种补偿可能会导致一些比较严重的心理和生理问题, 并且会使需要持续受挫; 因为它使一个人集中在需要的补偿和对于外在目标(金钱、地位)的追求上, 而不是基本心理需要的满足上。
第二种补偿的方式就是发展出非自主的控制风格和不适宜的动机偏向, 即高的控制动机或无动机(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。有研究表明, 对于那些具有高个人控制和非个人倾向的罪犯, 当他们面临社会困境时, 倾向于责备他人来保护自己的面子。他们的这种行为并不会缓解当前的社会困境, 相反只会加重他们的紧张感, 使关系需要受挫, 进而也会使胜任和自主需要受挫; 尽管他们的行为看起来是保住了自己的面子, 但是这些行为既不会增加他们的社会能力, 也不会增加自主感, 因为他们将注意力过度地集中在自己身上, 而非基本心理需要的满足上(Hodgins & Liebeskind, 2003)。其他的研究则发现, 当基本心理需要受挫时会导致内部动机的降低, 而低的内部动机又会增加个体感受到的压力和疲劳感(Alcaraz, Torregrosa, & Viladrich, 2015; Li, Wang, Pyun, & Kee, 2013)。
第三种补偿的方式是发展出一种僵硬、刻板的行为模式, 通过这种行为模式来适应敌意的环境, 以及保护自己免受需要受阻所带来的伤害, 但是这种模式会让人们远离他们内在的经验, 而在新环境中坚持一种有消极结果的行为(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。例如, 暴饮暴食就是由于基本心理需要的受挫, 当个体的三种基本心理需要得不到满足时, 个体暴饮暴食的概率就会增加(Verstuyf et al., 2013)。同样, 对于自伤行为的研究也表明, 当人们的基本心理需要受挫时, 自伤行为会明显增加, 这种行为虽然可能会得到一些好处(减少内心的愧疚), 但会导致自我中心和自我规则的破坏, 并因此增加情绪上的紧张感(Emery, Heath, & Mills, 2016)。
3 对基本心理需要的质疑
3.1 为什么是这三种需要?
基本心理需要理论将胜任、关系和自主作为三种基本的需要。有研究者质疑, 为什么是这三种需要, 而不是其他的几种?或者说, 除了这三种需要之外, 是否还有其他的基本心理需要?比如Pyszczynski把安全感(Safety-Security)看成是基本心理需要的一种, 认为安全感比胜任、关系和自主需要更加重要(转引自Ryan & Deci, 2000)。Deci和Ryan则认为首先要将生理需要和心理需要进行区分, 对于个体的生存来说, 安全感是必不可少的, 就像食物和氧气一样。但是, 基本心理需要主要是针对心理上的健康和成长, 而安全感更偏向于一种生理的需要。这与马斯洛需要层次理论(Maslow, 1943)的分类相类似。因此, 安全感并不属于心理需要的一种, 并且, 如果孩子在小的时候得不到良好的照顾, 无法与父母建立良好的关系(需要受挫), 则会导致安全感的缺乏(Goldner & Berenshtein-Dagan, 2016),所以说安全感并不是基本心理需要本身, 而是作为一种需要的补偿, 也就是说, 代表着心理需要没有被满足(Ryan & Deci, 2000)。
第二种被认为可以作为基本心理需要的是意义感(Meaningfulness)。Andersen认为, 人们有一个基本的渴望, 就是能够理解他们自己的人生经验, 其中也包括他们生活中的不幸, 当人们体会到意义感的时候, 个体会感觉到一致, 而这种一致的体验对于个体的幸福感来说是非常重要的, 所以, 他们认为意义感也能够作为基本心理需要的一种(转引自Ryan & Deci, 2000)。但是, 在Deci和Ryan看来, 意义感本质上是一个内化和整合的过程, 包括个人的价值、规则和情感的同化; 意义感只是我们趋向完整的一个过程。当人们的自主和胜任需要得到满足的时候, 人们就会体验到意义感(Tims, Derks, & Bakker, 2016),而对于工作关系的研究也发现, 员工与上司良好的关系有利于增加员工的工作意义感(Monnot, 2016)。当人们想要表达意义感时, 他们的表达通常会集中在个体对于关系、胜任和自主需要的经验与体验上(Ryan & Deci, 2000), 因此意义感更像是基本心理需要满足的结果, 而不是需要本身。
第三种被认为可以作为基本心理需要的是自尊(Self-Esteem)。自尊这个概念由Maslow (1943)最先提出, Kernis, Grannemann和Barclay (1989)把自尊区分为安全的高自尊(Secure high self-esteem)和易碎的高自尊(Fragile high self-esteem)。安全的自尊是指一种固定的、比他人感觉好的感觉, 而易碎的自尊虽然也是一种对于自己的积极感觉, 但是这种感觉是与具体的结果相联系的, 那些具有易碎高自尊的人会不断地寻找证据来证明自己的价值。所以, 自尊是否也是基本心理需要中的一种呢?对此, 基本心理需要理论认为, 对于安全的高自尊, 就像意义感一样, 它是幸福感的一种指标, 一种成分, 是基本心理需要满足的结果, 是不需要刻意去追求的。而对于易碎的高自尊, 人们追求它的原因则是一种对于基本心理需要的补偿, 是一种强烈的动机, 而不是需要本身。之后的研究也表明, 胜任, 关系, 自主三种基本心理需要的满足与个体的自尊呈正向相关(Monteiro, Fernandes, & Novas, 2015)。因此, 在基本心理需要理论看来, 自尊并不是基本心理需要的一种。
3.2 这三种基本需要是矛盾的吗?
对于基本心理需要的另一个疑问在于:这三种需要之间是否是矛盾的?比如说, 一个人可能会为了追求同伴间的关系而放弃自己的自主性。但是在Deci和Ryan看来, 这三种需要并不矛盾, 而是相互补偿的, 也就是说, 当一个人的某一种需要得到了满足, 会进一步地促进另外两种需要也得到满足, 而当一个人的某种需要受到了阻碍, 也会进一步地导致其他两种需要受挫(Ryan & Deci, 2000)。因此, 可以根据基本心理需要来预测人们的行为, 比如安全的家庭氛围(关系需要得到满足)能预测孩子表现出更多的代表自己真实自我的行为(自主需要的满足) (Goldner & Berenshtein-Dagan, 2016)。而当孩子不能体验到父母无条件的爱(关系需要的受挫)时, 他们成长与发展的内部动机会减少(三种基本心理需要的受挫) (Assor, Roth, & Deci, 2000)。
3.3 需要会改变吗?
基本心理需要理论认为需要的满足对于个人的成长、整合和幸福感是非常重要的, 那么, 随着我们年龄的增长, 需要是否会改变呢?对于这一问题, 很多研究者也进行了验证, 结果发现, 对于儿童、青少年, 大学生, 以及成年人, 基本心理需要都能够预测个体的幸福感(Simões & Alarcão, 2014; Chen et al., 2015), 并且大量的研究表明, 对于不同的文化、年龄和社会阶层, 基本心理需要得到满足的人心理健康水平会更高(Chirkov et al., 2003)。而对于衰老与需要满足之间的关系的研究也表明, 随着年龄的增长, 虽然可获得的基本需要的满足在改变, 但是基本需要的重要性没有改变, 而这些需要的满足也同样能够预测老年人的意义感、生命感和幸福感(Ferrand et al., 2015)。因此, Deci和Ryan认为在人的一生中基本心理需要是不会改变的。
3.4 自主需要具有文化普适性吗?
在这三种需要中, 关系需要和胜任需要很快就被人们所接受, 但自主需要却受到了较多的质疑。尽管大量的研究证明了自主需要的重要性, 但依然有些观点认为自主需要并不重要, 甚至认为自主不是一种需要, 或者说自主仅仅只是西方意识形态的产物(Ryan & Deci, 2000)。
对于这些质疑, Deci和Ryan从三个方面进行了阐述和解释。首先, 他们认为, 自主是整合后的自我, 自主包含着自我决定, 而整合是自我决定的基础。如果一个行为规则能够被自我很好地整合, 那么这个行为就是个体完全同意的, 个体也会感觉到自由。而如果一个行为没有被整合, 即使它是自我的组成部分, 并且也会激励行动, 但它并不能代表自主(Ryan & Deci, 2000)。
其次, 考虑到东西方不同的文化差异(在西方文化中人们可能比较喜欢自主, 但是对于东方文化来说, 强调的是社会的和谐性和关联性, 并不重视自主性和独立性等典型的西方概念), Deci和Ryan对自主在不同文化中的普遍性问题进行了解释。他们指出, 我们需要了解需要某些东西和想要某些东西的区别。“想要”与个人的意愿有关, 而“需要”则代表着这些东西对于个人来说是不可或缺的。因此, 虽然在不同的文化中对于自主的渴望是有区别的, 但自主却是每个人都需要的, 是具有普遍性的(Ryan & Deci, 2000; Chen et al., 2015; Şimşek & Demir, 2014)。并且已有研究也表明, 在集体主义文化的学校中, 自主与幸福感有显著的相关(Ahmad, Vansteenkiste, & Soenens, 2013)。另外, 一些专门致力于检验基本心理需要跨文化普遍性的研究者也指出:对于自主是否具有跨文化普遍性的质疑, 主要源于质疑者对自主的理解和定义与Deci和Ryan的定义和理解不相同, 并且提供了大量的证据予以辅证(Vansteenkiste, Niemiec, & Soenens, 2010)。在不同的文化下, 自主的表达可能不一样, 对于美国文化, 人们可能通过表达自己的观点来体验到自主, 对于亚洲文化, 可能会通过赞成他们认可的人来体验到自主感。因此, 只要个体能够认同、内化他们的文化价值观, 他们就能体验到自主感, 进一步增加幸福感(Deci & Ryan, 2012)。
第三是把自主与自私进行了区分。很多研究者倾向于把自主与自私自利、权利以及得到自己想要的东西相联系。但事实并不是这样, 临床的观察表明, 这些自私自利的行为并不是受自我控制的, 而经常是冲动的、缺乏调节的; 并且, 有研究表明, 这些反社会行为是由于心理需要的受挫导致的(Hodge & Gucciardi, 2015)。所以说, 自主并不是自私, 并且恰恰相反, 自主需要的满足能够预测更少的自私行为(Sheldon & McGregor, 2000)。
4 小结与展望
目前对于基本心理需要的研究, 主要集中在与其他变量之间的关系以及基本心理需要的中介和调节作用上。已有研究表明, 基本心理需要与心理健康呈正向相关, 而与自杀、抑郁、问题行为等呈负向相关, 且对于精神上的健康、生活满意度起预测作用。尽管心理学界对于基本心理需要的研究取得了一些成果, 但是基本心理需要毕竟是一个较新的概念、理论, 还有很多问题需要进一步的研究和验证。未来的研究可以从以下几个方面入手:
4.1 验证基本心理需要的测量方式
目前大多数对于基本心理需要满足程度的测量, 都是以基本心理需要的总分来计算的。有研究指出, 胜任、关系和自主这三种需要都必不可少, 他们之间是不能相互替代的, 把三种需要的分数加起来计算是不合理的, 并且这种测量方法也与基本心理需要提出时将三种需要分开的初衷相违背(Deci & Ryan, 2000)。但是另一些研究者表明, 这三种需要之间存在着较高的相关, 以总分进行计算更加适合于进行因素分析(Gagné, 2003)。可见目前对于基本心理需要的计量方式存在着相互矛盾的看法。未来仍然需要更多的实证研究, 去探索到底哪一种计量方式更加切合基本心理需要理论, 哪种方式能够更加准确地测量出个体基本心理需要的满足程度。
4.2 增加基本心理需要受挫的研究
有研究表明, 基本心理需要的满足与积极的结果有较强的相关, 而与消极的结果相关不大(Colquitt, Long, Rodell, & Halvorsen-Ganepola, 2015)。在当前的研究中, 大多数都是关于基本心理需要的满足的, 相关的变量也都是偏向积极方面, 而对于基本心理需要受挫的研究还比较少, 并且测量的工具也比较少, 只涉及到了某些特定的领域(如运动)。而我们知道, 需要的受挫会影响人们的身心健康, 甚至会导致一些躯体化疾病、焦虑、压抑、内部的矛盾等等(Vansteenkiste & Ryan, 2013)。并且, 当个体的基本心理需要受挫时, 个体会通过一些措施(补偿性动机, 非自主的控制风格, 僵硬、刻板的行为模式)来帮助他们免受需要受阻的伤害(Deci & Ryan, 2000), 但是, 这些方式并不会促进需要的满足, 因此, 在未来的研究中, 开发或编制基本心理需要受挫量表, 增加对于基本心理需要受挫的研究, 以减少基本心理需要受挫所带来的伤害, 将是十分有意义的。
4.3 加强基本心理需要的纵向研究
目前大多数的研究都只探讨了基本心理需要与其他变量间的关系, 而如果要了解基本心理需要的预测作用, 有必要加强纵向研究。已有个别纵向研究表明基本心理需要的满足能够减少个体的问题行为(Yu et al., 2015)。未来还需要更多的纵向研究来验证基本心理需要的预测作用。这对于增强基本心理需要的解释力也有非常重要的作用。
4.4 研究促进基本心理需要满足的策略
Deci和Ryan认为三种基本心理需要与个体的成长、内化和幸福感有着密切的联系。基本心理需要的满足能增加人们的幸福感, 减少自杀、抑郁和问题行为, 且对于精神上的健康、良好的关系起着积极的预测作用(Simões & Alarcão, 2014; Ferrand et al., 2015; Patrick et al., 2007)。所以在社会环境中如何促进基本心理需要的满足, 对于个体的成长来说非常必要; 而个体所处的环境在一定程度上是可以进行干预的。但目前很少有学者致力于研究促进基本心理需要满足的干预方案, 比如:可以通过怎样的方案、策略, 干预个体的家庭环境、学校环境与社会环境, 来避免个体基本心理需要的受挫, 促进个体基本心理需要的满足?对这些问题的回答能进一步增加基本心理需要的实践应用价值, 还有待深入探讨。
参考文献
中文版基本心理需要满足量表的修订
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2012.05.026
URL
[本文引用: 1]

目的修订中文版基本心理需要满足量表(BNSG—S),并检验其信效度。方法采用分层取样的方法对全国5个单位的6366名青年职工进行问卷调查,回收有效问卷6071份。通过项目分析筛选项目,对数据进行探索性因素分析和验证性因素分析检验问卷的结构效度,用幸福感指数量表来检验效标效度,并检验问卷的信度。结果经过3次探索性因素分析,最后得到的中文版BNSG—S有15个条目,包含4个因子,分别为:自主需要满足、自主需要满足受阻、归属需要满足、归属需要满足受阻,累计方差贡献率为63.95%。验证性因素分析所得指标均符合心理测量学的要求(RMSEA=0.056,NFI=0.97,NNFI=0.96,CFI=0.97)。中文版BNSG—S总分与幸福感指数量表的相关系数为0.50(P〈0.01),各维度与幸福感指数量表也显著相关。中文版BNSG—S的Cronbachα系数为0.76,其中,各因子的Cronbachα系数分别为0.80,0.67,0.83,0.80。结论基本心理需要满足量表中文版具有较好的信效度,包括四个因子,可作为测量中国人基本心理需要满足的工具。
青少年感恩、基本心理需要与病理性网络使用的关系
采用青少年感恩量表、基本心理需要量表和病理性网络使用问卷对760名中学生进行调查,考察了中国文化背景下青少年感恩与病理性网络使用的关系,以及基本心理需要的能力需要、关系需要和自主需要的三大成分在其中的链式中介效应。结果表明:(1)青少年感恩与病理性网络使用显著负相关;(2)基本心理需要三大成分在感恩与病理性网络使用之间具有链式中介作用,即感恩既直接促进青少年自主需要的满足,也通过促进能力需要和关系需要的满足间接增进其自主需要的满足,进而减少病理性网络使用。
The relations of Arab Jordanian adolescents’ perceived maternal parenting to teacher-rated adjustment and problems: The intervening role of perceived need satisfaction
DOI:10.1037/a0027837
URL
PMID:22468568
[本文引用: 1]

Although the effects of important parenting dimensions, such as responsiveness and psychological control, are well documented among Western populations, research has only recently begun to systematically identify psychological processes that may account for the cross-cultural generalization of these effects. A first aim of this study was to examine whether perceived maternal responsiveness and psychological control would relate differentially to teacher ratings of adolescent adjustment in a vertical-collectivist society (i.e., Jordan). The most important aim of this study was to examine, on the basis of self-determination theory, whether these associations would be accounted for by perceived satisfaction of the basic psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Results in a large sample of Jordanian adolescents (N = 545) showed that perceived maternal psychological control and responsiveness yielded, respectively, a positive and negative association with teacher-rated problems, whereas psychological control was negatively related to teacher-rated adjustment. Further, these 2 parenting dimensions related to adjustment and problems via perceived satisfaction of the basic psychological needs for autonomy and competence (but not relatedness). The findings are discussed in light of the ongoing debate between universalistic and relativistic perspectives on parenting and adolescent adjustment.
How coaches’ motivations mediate between basic psychological needs and well-being/ill-being
DOI:10.1080/02701367.2015.1049691
URL
PMID:26230963
[本文引用: 1]

PURPOSE: The purpose of the present research was to test how behavioral regulations are mediated between basic psychological needs and psychological well-being and ill-being in a sample of team-sport coaches. Based on self-determination theory, we hypothesized a model where satisfaction and thwarting of the basic psychological needs predicted coaches' behavioral regulations, which in turn led them to experience well-being (i.e., subjective vitality, positive affect) or ill-being (i.e., perceived stress, negative affect). METHOD: Three-hundred and two coaches participated in the study (Mage=25.97 years; 82% male). For each instrument employed, the measurement model with the best psychometric properties was selected from a sequence of nested models sustained by previous research, including exploratory structural equation models and confirmatory factor analysis. These measurement models were included in 3 structural equation models to test for mediation: partial mediation, complete mediation, and absence of mediation. RESULTS: The results provided support for the partial mediation model. Coaches' motivation mediated the relationships from both relatedness need satisfaction and basic psychological needs thwarting for coaches' well-being. In contrast, relationships between basic psychological needs satisfaction and thwarting and ill-being were only predicted by direct effects. CONCLUSION: Our results highlight that 3 conditions seem necessary for coaches to experience psychological well-being in their teams: basic psychological needs satisfaction, especially relatedness; lack of basic psychological needs thwarting; and self-determined motivation.
Relations of the perceptions of parental conditional love to children’s affects and motivation
Coaches' interpersonal style, basic psychological needs and the well- and ill-being of young soccer players: A longitudinal analysis
DOI:10.1080/02640414.2012.731517
URL
PMID:23062028
[本文引用: 1]

This study entailed a longitudinal test of basic psychological needs theory, a sub-theory in the self-determination framework (Deci & Ryan, 2000), in young soccer players. We examined whether changes in soccer players' perceptions of the coaches' interpersonal style (autonomy supportive and controlling) predicted changes in the players' need satisfaction/need thwarting, and in turn, variability in their reported subjective vitality and burnout over the course of a season. Young male soccer players (M02=0212.5802±020.54 years) completed a questionnaire at two time points in the season [n(T1)02=02725; n(T2)02=02597]. Changes in the players' perceptions of an autonomy supportive environment significantly predicted changes in psychological need satisfaction (positively) and in psychological need thwarting (negatively). Changes in psychological need satisfaction positively predicted changes in subjective vitality and negatively related to cross-time variation in global burnout scores. In contrast, changes in the players' perceptions of a controlling coach-created environment were positively associated with changes in psychological need thwarting that corresponded to increases in player burnout. Finally, results provided support for the assumed mediational roles of psychological need satisfaction and need thwarting in the social environment to well- and ill-being relationships.
Self-determination theory and diminished functioning: The role of interpersonal control and psychological need thwarting
DOI:10.1177/0146167211413125 URL [本文引用: 1]
Basic psychological needs, suicidal ideation, and risk for suicidal behavior in young adults
DOI:10.1111/sltb.12074
URL
PMID:24494652
[本文引用: 1]

Associations between the satisfaction of basic psychological needs of autonomy, competence, and relatedness with current suicidal ideation and risk for suicidal behavior were examined. Two logistic regressions were conducted with a cross-sectional database of 440 university students to examine the association of need satisfaction with suicidal ideation and risk for suicidal behavior, while controlling for demographics and depressive symptoms. Suicidal ideation was reported by 15% of participants and 18% were found to be at risk for suicidal behavior. A one standard deviation increase in need satisfaction reduced the odds of suicidal ideation by 53%, OR (95% CI) = 0.47 (0.33–0.67), and the odds of being at risk for suicidal behavior by 50%, OR (95% CI) = 0.50 (0.37–0.69). Young adults whose basic psychological needs are met may be less likely to consider suicide and engage in suicidal behavior. Prospective research is needed to confirm these associations.
Basic psychological need satisfaction, need frustration, and need strength across four cultures
DOI:10.1007/s11031-014-9450-1
URL
[本文引用: 3]

The present study investigated whether satisfaction and frustration of the psychological needs for autonomy, relatedness, and competence, as identified within Basic Psychological Need Theory (BPNT; Deci and Ryan, Psychol Inquiry 11:227–268, 2000 ; Ryan and Deci, Psychol Inquiry 11:319–338, 2000 ), contributes to participants’ well-being and ill-being, regardless of their cultural background and interpersonal differences in need strength, as indexed by either need valuation (i.e., the stated importance of the need to the person) or need desire (i.e., the desire to get a need met). In Study 1, involving late adolescents from Belgium and China (total N 02=02685; Mean age02=021702years), autonomy and competence satisfaction had unique associations with well-being and individual differences in need valuation did not moderate these associations. Study 2 involved participants from four culturally diverse nations (Belgium, China, USA, and Peru; total N 02=021,051; Mean age02=022002years). Results provided evidence for the measurement equivalence of an adapted scale tapping into both need satisfaction and need frustration. Satisfaction of each of the three needs was found to contribute uniquely to the prediction of well-being, whereas frustration of each of the three needs contributed uniquely to the prediction of ill-being. Consistent with Study 1, the effects of need satisfaction and need frustration were found to be equivalent across the four countries and were not moderated by individual differences in the desire for need satisfaction. These findings underscore BPNT’s universality claim, which states that the satisfaction of basic needs for autonomy, relatedness, and competence represent essential nutrients for optimal functioning across cultures and across individual differences in need strength.
Differentiating autonomy from individualism and independence: A self-determination theory perspective on internalization of cultural orientations and well-being
DOI:10.1037/0022-3514.84.1.97
URL
PMID:12518973
[本文引用: 2]

On the basis of self-determination theory (R. M. Ryan & E. L. Deci, 2000) and cultural descriptions drawn from H. C. Triandis (1995), the authors hypothesized that (a) individuals from different cultures internalize different cultural practices; (b) despite these differences, the relative autonomy of individuals' motivation for those practices predicts well-being in all 4 cultures examined; and (c) horizontal practices are more readily internalized than vertical practices across all samples. Five hundred fifty-nine persons from South Korea, Russia, Turkey and the United States participated. Results supported the hypothesized relations between autonomy and well-being across cultures and gender. Results also suggested greater internalization of horizontal relative to vertical practices. Discussion focuses on the distinction between autonomy and individualism and the relative fit of cultural forms with basic psychological needs.
Adding the “in” to justice: A qualitative and quantitative investigation of the differential effects of justice rule adherence and violation
DOI:10.1037/a0038131
URL
PMID:25420056
[本文引用: 1]

Although justice scholars often assume that individuals react to injustice in a manner that is distinct from their reactions to justice, few studies have examined this assumption. Indeed, the most widely utilized measures in the literature assess only the adherence to rules of justice--not their violation. We conducted 2 studies to build and test theory about differential reactions to justice and injustice. An inductive study revealed that reactions to the adherence to justice rules reflected different constructs than reactions to the violations of justice rules. In a follow-up field study, we derived hypotheses for those patterns by drawing on the negativity bias and regulatory focus literatures. Specifically, justice rule violation was predicted to be more relevant to prevention-laden outcomes that represent a high level of vigilance and concerns about safety. Justice rule adherence was predicted to be more relevant to promotion-laden outcomes that represent concerns about becoming the ideal self. The field study supported many of those predictions while showing that a full-range justice measure (i.e., one that sampled both justice rule adherence and justice rule violation) explained more variance in outcomes than existing "truncated" justice measures.
Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior
The general causality orientations scale: Self-determination in personality
DOI:10.1016/0092-6566(85)90023-6
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper describes the development and validation of a general causality orientations scale. Causality orientations are conceptualized as relatively enduring aspects of people that characterize the source of initiation and regulation, and thus the degree of self-determination, of their behavior. Three orientations—autonomy, control, and impersonal—are measured by the three subscales of the instrument. Individuals are given a score on each orientation, thus allowing the use of the theoretically appropriate subscale (or, in some cases, a combination of subscales) to predict affects, cognitions, and behaviors. The scale was shown to have internal consistency and temporal stability. The orientations were shown to fit appropriately into a nomological network of constructs and to relate to various behaviors that were hypothesized to be theoretically relevant.
The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior
DOI:10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01 URL [本文引用: 17]
A prospective longitudinal study testing relationships between meaningful activities, basic psychological needs fulfillment, and meaning in life
DOI:10.3928/15394492-20140211-01
URL
PMID:24649934
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract The current study used a prospective longitudinal design to determine whether change in meaningful activity over an 11-month period could help explain change in meaning in life in a sample of 174 undergraduate and graduate students. The Engagement in Meaningful Activities Survey, Basic Psychological Needs Scales (i.e., autonomy, competence, relatedness), and the Meaning in Life Questionnaire were used as indicators of the constructs of meaningful activity, basic psychological needs fulfillment, and meaning and purpose in life. The findings were in support of the study hypotheses and indicated that change in meaningful activity explained both change in basic psychological needs fulfillment (i.e., autonomy, competence, relatedness) and change in meaning in life. Further, this study reports findings consistent with results from cross-sectional studies in support of the hypothesis that change in meaningful activity may influence change in meaning in life through two pathways: a direct path of influence from meaningful activity to meaning in life and an indirect path through change in basic psychological needs fulfillment. The current study contributes to a growing literature implicating subjective evaluations of day-to-day action (or meaningful activity) as a fruitful means for exploring relationships between occupation and well-being. Copyright 2014, SLACK Incorporated.
Basic psychological need satisfaction, emotion dysregulation, and non-suicidal self-injury engagement in young adults: An application of self-determination theory
DOI:10.1007/s10964-015-0405-y
URL
PMID:26685906
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract Non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) is a public health concern that affects young adults at alarming rates. The present study examines the role of satisfaction of self-determination theory's three basic needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness in young adults' NSSI engagement. University students who reported ever having engaged in NSSI (n0002=000240, 850002% female; Mage0002=000220.10, SD0002=00021.66) reported significantly lower levels of the satisfaction of all three needs, as well as more difficulties with all aspects of emotion regulation (non-acceptance of emotional responses, difficulty engaging in goal directed behavior, impulse control, lack of emotional awareness, limited access to regulation strategies, lack of emotional clarity), compared to students with no history of NSSI (n0002=000246, 910002% female; Mage0002=000219.79, SD0002=00021.37). Results of a logistic regression analysis revealed that need satisfaction added to the prediction of NSSI group membership after controlling for the effects of emotion regulation. Satisfaction of the need for competence and limited access to emotion regulation strategies accounted for significant variance in NSSI in the final model. The findings suggest that self-determination theory may be a useful framework under which to conceptualize NSSI and that the need for competence may be particularly salient for University students.
Satisfaction des besoins psychologiques fondamentaux, symptômes dépressifs et apathie chez des personnes âgées hospitalisées
DOI:10.1037/a0037419
URL
[本文引用: 3]

08 la lumière de la théorie de l'autodétermination (TAD; Deci & Ryan, 1985; Ryan & Deci, 2002),...
The role of autonomy support and autonomy orientation in prosocial behavior engagement
DOI:10.1023/A:1025007614869
URL
[本文引用: 4]

Two studies examined individual and environmental forces that affect engagement in prosocial behavior. Self-determination theory was used to derive a model in which autonomy orientation and autonomy support predicted satisfaction of three core psychological needs, which in turn led to engagement in prosocial activities. In Study 1, college students reported their engagement in various prosocial activities, and completed measures of autonomy orientation, parental autonomy support, and general need satisfaction. In Study 2, volunteer workers completed measures of autonomy orientation, work autonomy support and need satisfaction at work. The number of volunteered hours indicated the amount of prosocial engagement. Results across the studies showed that autonomy orientation was strongly related to engagement in prosocial behavior, while autonomy support was modestly related. Need satisfaction partially mediated the effect of autonomy orientation, and fully mediated the effect of autonomy support. Interestingly, autonomy support predicted lower volunteer turnover. Implications for how prosocial behavior can be motivated are discussed.
Adolescents' true-self behavior and adjustment: The role of family security and satisfaction of basic psychological needs
DOI:10.13110/merrpalmquar1982.62.1.0048
URL
[本文引用: 2]

The Self During AdolescenceThe self is a complex construct that is frequently described as a...
Psychological need satisfaction and thwarting: A test of basic psychological needs theory in physical activity contexts
DOI:10.1016/j.psychsport.2013.03.007
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Objectives: To test Basic Psychological Needs Theory (BPNT; Deci & Ryan, 2002) to determine if psychological need thwarting experienced when physically active contributes to the understanding of wellbeing and ill-being.Design/method: Participants (N = 155, 67.70% female, M-age = 37.46 years; SDage = 19.89 years) completed assessments of psychological need satisfaction and thwarting, subjective vitality and positive/negative affect during separate testing sessions separated by 6 months.Results: Scores from the modified version of the Psychological Need Thwarting Scale (PNTS-PA; Bartholomew, Ntoumanis, Ryan, & Thogersen-Ntoumani, 2011) demonstrated discriminant evidence of validity, evidence of internal structure and minimal error variance. Changes in psychological need satisfaction positively predicted positive affect (R-2 =.16, p .05) or subjective vitality (Delta R-2 =.04, p >.05) beyond contributions made by psychological need satisfaction.Conclusions: Overall, these results extend the potential utility of the PNTS-PA as an instrument for use with BPNT beyond sport and support Deci and Ryan's (2002) contentions regarding the critical role of psychological need thwarting. (C) 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Antisocial and prosocial behavior in sport: The role of motivational climate, basic psychological needs, and moral disengagement
DOI:10.1123/jsep.2014-0225
URL
PMID:26265339
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract The purpose of this investigation was to examine whether the relationships between contextual factors and basic psychological needs were related to antisocial and prosocial behavior in sport. A two-study project employing Bayesian path analysis was conducted with competitive athletes (Study 1, n = 291; Study 2, n = 272). Coach and teammate autonomy-supportive climates had meaningful direct relations with need satisfaction and prosocial behavior. Coach and teammate controlling climates had meaningful direct relations with antisocial behavior. Need satisfaction was both directly and indirectly related with both prosocial and antisocial behavior, whereas moral disengagement was directly and indirectly related with antisocial behavior. Overall, these findings reflected substantial evidence from the literature on self-determination theory that autonomy-supportive motivational climates are important environmental influences for need satisfaction, and are important correlates of prosocial behavior in sport, whereas controlling coach and teammate climates, along with moral disengagement, were important correlates of antisocial behavior in sport.
Apology versus defense: Antecedents and consequences
DOI:10.1016/S0022-1031(03)00024-6
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Participants imagined themselves in face-threatening predicaments in two studies that examined the reproach and evaluation phases of predicament management. In Study 1, participants gave accounts of their behavior after receiving hypothetical reproaches that were mild/moderate or severe. Results showed that reproach severity influenced perpetrator accounts in opposite ways for females and males. Male perpetrators became more defensive under severe reproach, whereas females became less defensive. Expectations for a future relationship were more negative under severe reproach, and this was more pronounced when the victim was an acquaintance rather than a friend. Individuals high in Self-Determination were less defensive under mild/moderate reproach, but not under severe reproach. In Study 2, participants gave evaluations after receiving hypothetical accounts that varied in responsibility-taking. Results showed that greater responsibility-taking led to more positive victim evaluations and better expected future relationships. The advantage of responsibility-taking was especially pronounced when the perpetrator was a friend, suggesting that friends are forgiven more than acquaintances when they take responsibility and apologize, but not if they fail to do so. Results are interpreted in terms of reciprocal facework and thresholds for face threat.
Principles of behavior: An introduction to behavior theory
Employee and supervisor ratings of motivation: Main effects and discrepancies associated with job satisfaction and adjustment in a factory setting
DOI:10.1111/j.1559-1816.1993.tb01066.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Research and theory on employee job satisfaction and well-being has increasingly concentrated on both intrinsic and extrinsic motivational factors. According to self-determination theory (Deci & Ryan, 1985). autonomy, relatedness, and competence are three intrinsic psychological needs that, if fulfilled in the workplace, will lead to greater satisfaction, performance, and general well-being. This study examines employee and supervisor perceptions of the employee's autonomy, competence, and relatedness in the workplace, as well as the degree and direction of discrepancies between employee and supervisor reports. Both employee and supervisor ratings of intrinsic motivational factors were significantly related to work satisfaction, psychological health, and self-esteem, after controlling for the extrinsic factors of pay and job status. Results of discrepancy analyses were somewhat supportive of overrating being associated with greater well-being and job satisfaction. Discussion of the results ties this study to relevant research from a self-determination perspective and to the growing literature on discrepancies and self-perception.
The relationship among family environment, basic psychological needs, and school engagement of upper elementary school students in Korea
Measuring basic needs satisfaction: Evaluating previous research and conducting new psychometric evaluations of the basic needs satisfaction in general scale
DOI:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.04.003
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Self-Determination Theory specifies the existence of three basic psychological needs: autonomy, competence, and relatedness. The current set of studies (a) provides a narrative review of past research on the Basic Needs Satisfaction in General Scale, (b) examines its dimensionality which has been assumed but not empirically studied, and (c) gathers external validity evidence. Confirmatory factor analysis was used to test the existence of a one- and a three-factor solution; neither model fit the data. After patterns of misfit were examined across three independent samples, a reduced, 16-item three-factor model with a negative-worded method effect was championed. External validity evidence, collected by examining the differential relationships between the three needs and measures of well-being and worry, supported the distinctiveness of the three needs. Although the results are promising, future research is needed to examine the generalizability of the psychometric properties of the modified scale.
Stability and level of self-esteem as predictors of anger arousal and hostility
DOI:10.1037//0022-3514.56.6.1013
URL
PMID:2746456
[本文引用: 1]

We examined stability of self-esteem and level of self-esteem as predictors of dispositional tendencies to experience anger and hostility. We reasoned that individuals with unstable high self-esteem would report especially high tendencies to experience anger and hostility, and that individuals with stable high self-esteem would report particularly low tendencies. We expected individuals with stable and unstable low self-esteem to fall between these two extremes. These predictions were derived from an analysis of anger and hostility that emphasized the instigating role of threats to self-esteem. Stability of self-esteem was assessed through multiple assessments of global self-esteem in naturalistic settings. Results revealed the predicted pattern for the tendency to experience anger and a "motor" component of hostility. The importance of considering both stability and level of self-esteem in analyses of anger and hostility is discussed.
Self-determined choices and consequences: The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfactions and aggression in late adolescents
DOI:10.1080/00221309.2013.771607
URL
PMID:24837531
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract This research examined the mediatory role of life purpose and career indecision in the relationship between the satisfaction of basic psychological needs and aggression. Data were collected from high school students (n = 466) and results showed that life purpose and career indecision fully mediated the relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and aggression. These findings suggested that unsatisfied basic psychological needs foster late adolescents' aggression by promoting less clear life purposes and career indecision.
Burnout and its relations with basic psychological needs and motivation among athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.psychsport.2013.04.009
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Self-determination theory was generally supported in explaining athlete burnout.
Stressful life events and adolescent Internet addiction: The mediating role of psychological needs satisfaction and the moderating role of coping style
DOI:10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.070 URL [本文引用: 1]
Autonomy support, basic psychological needs and well-being in Mexican athletes
DOI:10.5209/rev_SJOP.2012.v15.n3.39414
URL
PMID:23156932
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract Based on Basic Needs Theory, one of the mini-theories of Self-determination Theory (Ryan & Deci, 2002), the present study had two objectives: (a) to test a model in the Mexican sport context based on the following sequence: perceived coach autonomy support, basic psychological needs satisfaction, and psychological well-being, and b) to analyze the mediational effect of the satisfaction of perceived coach autonomy support on indicators of psychological well-being (satisfaction with life and subjective vitality). Six hundred and sixty-nine young Mexican athletes (Boys = 339; Girls = 330; M(age) = 13.95) filled out a questionnaire assessing the study variables. Structural equations analyses revealed that perceived coach autonomy support predicted satisfaction of the basic psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Furthermore, basic need satisfaction predicted subjective vitality and satisfaction with life. Autonomy, competence and relatedness partially mediated the path from perceived coach autonomy support to psychological well-being in young Mexican athletes.
A theory of human motivation
DOI:10.1037/h0054346
URL
[本文引用: 3]

In a previous paper (13) various propositions were presented which would have to be included in any theory of human motivation that could lay claim to being definitive. These conclusions may be briefly summarized as follows: 1. The integrated wholeness of the organism must be one of the foundation
Relational-interdependent self-construal with supervisor (RISCS): Scale development and conditional model of meaningfulness at work
DOI:10.1037/mgr0000043
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract The experience of meaning and meaningfulness at work is associated with important individual and organizational outcomes. Relationships, particularly with higher status role partners, are a pathway through which employees construct meaningful experience. Relationship with one's supervisor is often cited as 1 of the most important job characteristics with regard to individual attitudes and performance. In Study 1 a brief measure of Relational-Interdependent Self-Construal With Supervisor (RISCS) is produced. Utilizing RISCS, Study 2 draws on social identity theory (Tajfel and Turner, 1986) to construct a conditional model involving communication with one's supervisor, RISCS, general social status, and meaningfulness at work. Results show that communication with one's supervisor serves as a form of social support in that it has a direct positive effect on relational identification and meaningfulness. Relational identification also acts as a mediator of the relationship between communication and reported meaningfulness. The first and second stage mediation effect is moderated by general social status, such that the mediating effect of relational identification is only present when subordinate general social status is low. In combination, these results suggest that employees of lower general social status utilize relational identification with a higher work status individual (i.e., supervisor) to experience a higher level of meaningfulness at work. These results explicate previous equivocal findings on social support, and, offer practical implications for supervisor training.
Relationships between basic psychological needs, body dissatisfaction and self-esteem in dance practitioners
ABSTRACT Aim. The aim of this study was to analyze the relationships between age, body mass index (BMI), dancing time, and the joint influence of basic psychological needs with regard to body dissatisfaction and self-esteem. Methods. A total of 135 dance students participated in this study, all females and between 9 and 15 years old (M=11.62; SD=1.67). The basic instruments administered were the basic psychological needs in exercise scale (BPNES), the body dissatisfaction evaluation scale for teenagers (Escala de Evaluacion de Insatisfacion Corporal para Adolescente-EEICA), and Rosenberg's self-esteem scale. The results of this study were analyzed using the statistical software SPSS, version 16.0. Analyses included descriptive and inferential statistics, tests for univariate normality (i.e., skewness and kurtosis), Pearson's "r" correlations and a linear regression analysis. Results. Results revealed that basic psychological needs did not significantly affect body dissatisfaction levels (F=0.18; P=0.909; R-adj(2)=0.02). Although overall participants' scores on the body dissatisfaction scale (EEICA) were not high, 9 students (6.7%) reported feeling dissatisfied with their bodies. Higher scores indicate greater levels of body dissatisfaction, with an internal consistency (Cronbach's a) of 0.77 to 0.81 for the Rosenberg's self-esteem scale. Conclusion. Findings from this study suggest that teenagers with high levels of self-determination engage in dance exercise more regularly and have more positive relationships with people. It is also important to note that the BPNES instrument may be used with a high degree of confidence in future research aiming to assess basic psychological needs in the context of dance.
The path taken: Consequences of attaining intrinsic and extrinsic aspirations in post-college life
DOI:10.1016/j.jrp.2008.09.001
URL
PMID:2736104
[本文引用: 1]

Life goals, or aspirations, organize and direct behavior over extended periods of time. The current study, guided by self-determination theory, examined the consequences of pursuing and attaining aspirations over a 1-year period in a post-college sample. Results indicated that placing importance on either intrinsic or extrinsic aspirations related positively to attainment of those goals. Yet, whereas attainment of intrinsic aspirations related positively to psychological health, attainment of extrinsic aspirations did not; indeed, attainment of extrinsic aspirations related positively to indicators of ill-being. Also as predicted, the association between change in attainment of intrinsic aspirations and change in psychological health was mediated by change in the satisfaction of the basic psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Discussion focuses on the idea that not all goal attainment is beneficial; rather, attainment of aspirations with different contents relates differentially to psychological health.
The role of need fulfillment in relationship functioning and well-being: A self-determination theory perspective
DOI:10.1037/0022-3514.92.3.434
URL
PMID:17352602
[本文引用: 2]

Self-determination theory posits 3 basic psychological needs: autonomy (feeling uncoerced in one's actions), competence (feeling capable), and relatedness (feeling connected to others). Optimal well-being results when these needs are satisfied, though this research has traditionally focused on individual well-being outcomes (e.g., E. L. Deci & R. M. Ryan, 2000). Three studies examined the role of need fulfillment in relationship functioning and well-being. Study 1 found that fulfillment of each need individually predicted both individual and relationship well-being, with relatedness being the strongest unique predictor of relationship outcomes. Study 2 found that both partners' need fulfillment uniquely predicted one's own relationship functioning and well-being. Finally, in Study 3, the authors used a diary recording procedure and tested a model in which the association between need fulfillment and relationship quality was mediated by relationship motivation. Those who experienced greater need fulfillment enjoyed better postdisagreement relationship quality primarily because of their tendency to have more intrinsic or autonomous reasons for being in their relationship.
The relationship between negative life events and suicidal behavior: Moderating role of basic psychological needs
DOI:10.1027/0227-5910/a000173 URL [本文引用: 1]
The darker and brighter sides of human existence: Basic psychological needs as a unifying concept
DOI:10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_03
URL
[本文引用: 9]

Self-determination theory (SDT) maintains that an understanding of human motivation requires a consideration of innate psychological needs for competence, autonomy and relatedness. We discuss the SDT concept of needs as it relates to previous need theories, emphasizing that needs specify the necessary conditions for psychological growth, integrity and well-being. This concept of needs leads to the hypotheses that different regulatory processes underlying goal pursuits are differentially associated that effective functioning and well-being and also that different goal contents have different relations to the quality of behavior and mental health, specifically because different regulatory: processes and different goal contents are associated with differing degrees of need satisfaction. Social contexts and individual differences that support satisfaction of the basic needs facilitate natural growth processes including intrinsically motivated behavior and integration of extrinsic motivations, whereas those that forestall autonomy, competence, or relatedness are associated with poorer motivation, performance, and well-being. We also discuss the relation of the psychological needs to cultural values, evolutionary processes, and other contemporary motivation theories.
Extrinsic value orientation and “the tragedy of the commons”
DOI:10.1111/1467-6494.00101
URL
PMID:10820691
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract Two studies examined the effect of Extrinsic Value Orientation (Kasser & Ryan, 1993, 1996) upon harvesting strategies and personal profit within commons dilemmas, in which individual and group interests can be at odds. At an individual or within-group level of analysis, extrinsically oriented persons (who value money, fame, and popularity) harvested more than intrinsically oriented persons (who value self-acceptance, intimacy, and community). However, a counteracting group-level effect was found such that groups with a greater number of extrinsic members harvested less on average than did groups with more intrinsic members, because their commons did not last as long. As a result, even excessive harvesters within extrinsic groups did no better than did self-restrained harvesters within intrinsic groups. Supplementary analyses indicate that extrinsic values are associated with acquisitiveness regarding resources, more so than apprehension regarding others' acquisitiveness.
Narrative representations of caregivers and emotion dysregulation as predictors of maltreated children’s rejection by peers
DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.37.3.321
URL
PMID:11370909
[本文引用: 1]

This study examined whether maltreated children were more likely than nonmaltreated children to develop poor-quality representations of caregivers and whether these representations predicted children's rejection by peers. A narrative task assessing representations of mothers and fathers was administered to 76 maltreated and 45 nonmaltreated boys and girls (8-12 years old). Maltreated children's representations were more negative/constricted and less positive/coherent than those of nonmaltreated children. Maladaptive representations were associated with emotion dysregulation, aggression, and peer rejection, whereas positive/coherent representations were related to prosocial behavior and peer preference. Representations mediated maltreatment's effects on peer rejection in part by undermining emotion regulation. Findings suggest that representations of caregivers serve an important regulatory function in the peer relationships of at-risk children.
Promoting well-being in school-based mentoring through basic psychological needs support: Does it really count?
DOI:10.1007/s10902-013-9428-9
URL
[本文引用: 3]

The main goal of this research was to assess whether satisfying basic psychological needs (BPN) in a Portuguese school-based mentoring (SBM) program improved the mentored students’ well-being. One uncommon feature of this program was that the mentors were also teachers of the mentees. A two-wave experimental study design was implemented to compare the mentored ( n 02=02157) and non-mentored students ( n 02=02160). Surveys were completed twice, with a 6-month interval between time points 1 and 2. The results indicate that SBM that was associated with increased support for BPN was the most effective condition for promoting academic well-being, particularly in terms of improving the mentored students’ perceptions of their school environment. However, no significant differences between the mentored and non-mentored students were detected regarding personal well-being (e.g., psychological well-being) and social well-being (e.g., peer support). These findings suggest that the balanced support of BPN was important in this particular SBM program. This support and enduring mentoring relationships can facilitate the general improvement of the mentored students’ well-being.
A cross-cultural investigation into the relationships among parental support for basic psychological needs, sense of uniqueness, and happiness
DOI:10.1080/00223980.2013.805115
URL
PMID:24946386
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract A significant number of empirical studies have reported that parental support for basic psychological needs is a robust correlate of adolescent happiness. Yet, less is known about the mechanisms responsible for this link. The present study proposed a model suggesting that personal sense of uniqueness explains why satisfaction of basic psychological needs in parent-child relationships is related to happiness. This mediational model was tested among late adolescents in Turkey and the United States. Analyses relying on structural equation modeling and bootstrapping supported the model in both cultures. Implications of the findings for theory and cross-cultural research are discussed. Directions for future research that could improve our understanding of the dynamic interplay between basic needs, sense of uniqueness and well-being are provided.
Job crafting and its relationships with person-job fit and meaningfulness: A three-wave study
DOI:10.1016/j.jvb.2015.11.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Although scholars imply that job crafting contributes to person–job fit and meaningful work, to date, no study examined the relationships between these variables. The present three-wave weekbook study was designed to gain more knowledge about the influence of job crafting on person–job fit and meaningfulness. We collected data among a heterogeneous group of employees (N02=02114) during three consecutive weeks (N02=02430 occasions). At the end of their working week, employees reported their job crafting behaviors, their person–job fit (demands–abilities fit and needs–supplies fit), and the meaningfulness of their work that week. Results indicated that individuals who crafted their job by increasing their job resources (e.g., support, autonomy) and challenging job demands (e.g., participate in new projects), and by decreasing their hindering job demands (e.g., less emotional job demands) reported higher levels of person–job fit the next week. In turn, demands–abilities fit related to more meaningfulness in the final week. No support was found for alternative causal models. These findings suggest that by crafting their job demands and job resources, individuals can proactively optimize their person–job fit and as a consequence experience their work as meaningful.
Lunch breaks unpacked: The role of autonomy as a moderator of recovery during lunch
DOI:10.5465/amj.2011.1072
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Work recovery research has focused mainly on how after-work break activities help employees replenish their resources and reduce fatigue. Given that employees spend a considerable amount of time at work, understanding how they can replenish their resources during the workday is critical. Drawing on ego depletion (Muraven & Baumeister, 2000) and self-determination theory (Deci & Ryan, 1985), we employed multi-source experience sampling methods to test the effects of a critical boundary condition, employee lunch break autonomy, on the relation between lunch break activities and end-of-workday fatigue. Although specific energy-relevant activities had a main effect on end-of-workday fatigue, each of these was moderated by the degree of autonomous choice associated with the break. Specifically, for activities that supported the psychological needs of relatedness and competence (i.e., social and work activities, respectively), as lunch break autonomy increased, effects switched from increasing fatigue to reducing fatigue. To the extent that lunch break activities involved relaxation, however, lunch break autonomy was only important when levels of relaxation were low. We conclude that lunch break autonomy plays a complex and pivotal role in conferring the potential energetic benefits of lunch break activities. Contributions to theory and practice are discussed.
A review of self-determination theory’s basic psychological needs at work
DOI:10.1177/0149206316632058
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Self-determination theory (SDT) conceptualizes basic psychological needs for autonomy, competence and relatedness as innate and essential for ongoing psychological growth, internalization, and well-being. We broadly review the literature on basic psychological need satisfaction at work, with three more specific aims: to test SDT requirement that each basic psychological need should uniquely predict psychological growth, internalization, and well-being; to test whether use of an overall need satisfaction measure is appropriate; and to test whether the scale used to assess basic psychological needs influenced our results. To this end, we conducted a meta-analytic review of 99 studies with 119 distinct samples examining the antecedents and consequences of basic need satisfaction. We conclude with recommendations for addressing issues arising from our review and also identify points for future research, including the study of need frustration and culture, integrating the basic needs with other motivation theories, and a caution regarding the measures and methods used.
Explaining the relationships between job characteristics, burnout, and engagement: The role of basic psychological need satisfaction
DOI:10.1080/02678370802393672
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Within the Job Demands-Resources model, the presence of job demands (e.g., work pressure) and the absence of job resources (e.g., social support) relate to burnout through a psychological energetic process, whereas the presence of job resources associates with work engagement through a motivational process. Although various mechanisms have been suggested to understand these processes, empirical evidence for these mechanisms is scarce within the JD-R framework. This study examines the role of basic need satisfaction, as defined within Self-Determination Theory, in the relationships between job demands, job resources, and employees exhaustion and vigour, the main components of burnout and engagement, respectively. Structural equation modelling in a heterogeneous sample of 745 employees of the Dutch-speaking part of Belgium confirmed that satisfaction of basic psychological needs partially explained the relationships from job demands to exhaustion and from job resources to vigour. It fully accounted for the relationship between job resources and exhaustion. We conclude that the current study adds to the research pointing at need satisfaction as a promising underlying mechanism for employees thriving at work.
The development of the five mini-theories of self- determination theory: An historical overview, emerging trends, and future directions
DOI:10.1108/ama URL [本文引用: 1]
On psychological growth and vulnerability: Basic psychological need satisfaction and need frustration as a unifying principle
DOI:10.1037/a0032359
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Humans have a potential for growth, integration, and well-being, while also being vulnerable to defensiveness, aggression, and ill-being. Self-determination theory (R. M. Ryan & E. L. Deci, 2000, Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development and well-being, American Psychologist, Vol. 55, pp. 68-78) argues that satisfaction of the basic psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness both fosters immediate well-being and strengthens inner resources contributing to subsequent resilience, whereas need frustration evokes ill-being and increased vulnerabilities for defensiveness and psychopathology. We briefly review recent research indicating how contextual need support and the experience of need satisfaction promote well-being and different growth manifestations (e.g., intrinsic motivation, internalization), as well as a rapidly growing body of work relating need thwarting and need frustration to ill-being, pursuit of need substitutes, and various forms of maladaptive functioning. Finally, we discuss research on differences in autonomous self-regulation and mindfulness, which serve as factors of resilience.
Daily ups and downs in women’s binge eating symptoms: The role of basic psychological needs, general self -control, and emotional eating
DOI:10.1521/jscp.2013.32.3.335 URL [本文引用: 2]
Does psychological need satisfaction perceived online enhance well-being?
DOI:10.1002/pchj.98
URL
PMID:26354155
[本文引用: 2]

Abstract The Internet has been building a new context, in which adolescents and young people complete their academic tasks, do their work, engage in social interaction, and even conduct anonymous identity experimentation. Therefore, it becomes very significant to assess psychological need satisfaction online, and to relate it to well-being. This study investigated the influence on well-being of psychological need satisfaction perceived online and the regulatory role in this relationship of psychological need satisfaction perceived in daily life. A total of 1,727 students from junior and senior high schools and universities in China were surveyed using the Basic Psychological Needs in General scale, the Basic Psychological Needs in the Online World scale, and the Index of Well-Being, Index of General Affect scale. The mean age of the adolescent sample was 17.47 years (ranging from 12.50 to 25.42 years). The results indicated that both need satisfaction perceived online and that perceived in daily life positively predicted psychological well-being, and psychological need satisfaction in daily life qualified the association between psychological need satisfaction perceived online and well-being. In particular, students who perceived higher psychological need satisfaction in daily life were found to benefit from psychological need satisfaction perceived online, but students with low psychological need satisfaction perceived in daily life did not. We suggest that people who perceive lower basic need satisfaction in daily life are more likely to use the Internet for socioaffective regulation and to consider cyberspace as a new world. Thus, need satisfaction perceived online may not transform into "real" happiness. 2015 The Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Predicting adolescent problematic online game use from teacher autonomy support, basic psychological needs satisfaction, and school engagement: A 2-year longitudinal study
DOI:10.1089/cyber.2014.0385
URL
PMID:25803769
[本文引用: 3]

Abstract Problematic online game use (POGU) has become a serious global public health concern among adolescents. However, its influencing factors and mediating mechanisms remain largely unknown. This study provides the first longitudinal design to test stage-environment fit theory empirically in POGU. A total of 356 Chinese students reported on teacher autonomy support, basic psychological needs satisfaction, school engagement, and POGU in the autumn of their 7th-9th grade years. Path analyses supported the proposed pathway: 7th grade teacher autonomy support increased 8th grade basic psychological needs satisfaction, which in turn increased 9th grade school engagement, which ultimately decreased 9th grade POGU. Furthermore, 7th grade teacher autonomy support directly increased 9th grade school engagement, which in turn decreased 9th grade POGU. These findings suggest that teacher autonomy support is an important protective predictor of adolescent POGU, and basic psychological needs satisfaction and school engagement are the primary mediators in this association.