

CN 11-4766/R
主办:中国科学院心理研究所
出版:科学出版社


心理科学进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 296-310.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2021.00296 cstr: 32111.14.2021.00296
刘宇1, 胡传鹏2( ), 樊富珉1(
), 樊富珉1( ), 孙沛1, 徐杰3, 蔡玉清1, 刘雪莉4
), 孙沛1, 徐杰3, 蔡玉清1, 刘雪莉4
收稿日期:2019-12-17
出版日期:2021-02-15
发布日期:2020-12-29
基金资助:
LIU Yu1, HU Chuan-Peng2( ), FAN Fumin1(
), FAN Fumin1( ), SUN Pei1, XU Jie3, CAI Yuqing1, LIU Xueli4
), SUN Pei1, XU Jie3, CAI Yuqing1, LIU Xueli4
Received:2019-12-17
Online:2021-02-15
Published:2020-12-29
摘要:
物质成瘾是一种涉及生理、心理和环境等多因素的复杂现象, 但是当前基于生物还原论的解释对物质成瘾现象整体性的理解和康复研究造成了阻碍。网络理论聚焦于心理障碍变量之间相互作用形成的反馈环路, 从整体视角为研究物质成瘾提供了新的理论框架。将网络理论应用于物质成瘾的研究中将有利于:(1)理解症状之间的相互关系和影响; (2)理解症状网络的整体性和系统性动态变化过程; 以及(3)将多层次和多水平因素整合到统一的理论框架中。从网络理论视角来理解物质成瘾, 也将对未来的干预和治疗提供了理论支持。目前, 网络理论仍处于言语模型阶段, 未来需要进一步提出更具体、可验证的统计模型, 以完善对于物质成瘾机制的了解, 更加有效地推进物质成瘾的治疗与恢复。
中图分类号:
刘宇, 胡传鹏, 樊富珉, 孙沛, 徐杰, 蔡玉清, 刘雪莉. (2021). 基于网络理论的物质成瘾新视角. 心理科学进展 , 29(2), 296-310.
LIU Yu, HU Chuan-Peng, FAN Fumin, SUN Pei, XU Jie, CAI Yuqing, LIU Xueli. (2021). A New perspective of substance addiction based on network theory. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(2), 296-310.
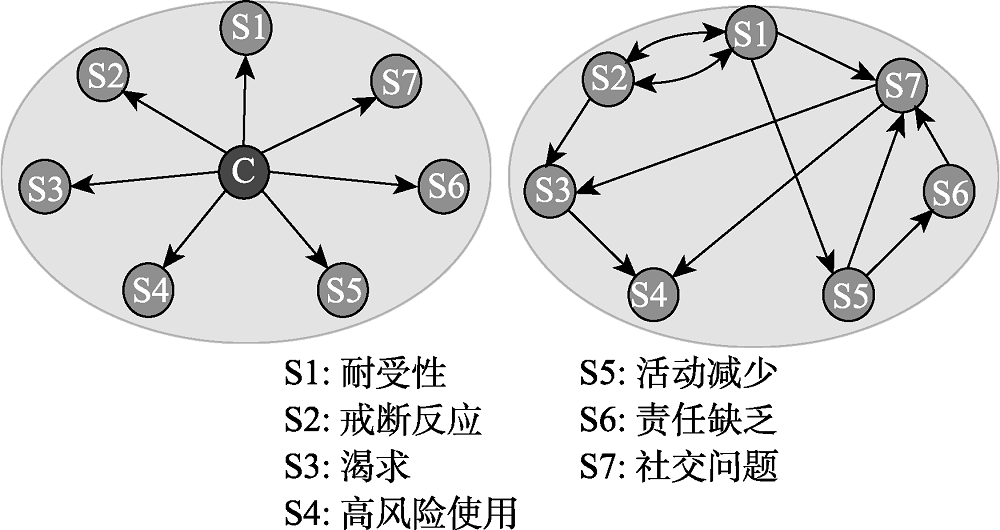
图1 基于生物还原论的潜变量模型与网络理论下的网络分析模型物质成瘾症状关系示意图。左侧为潜变量模型, 假定有一个共同的生理病因(中央的黑色C)导致了各种症状; 右侧为网络分析模型, 箭头表示各个节点之间的相互作用, 症状之间的密切联系形成了一个稳定的整体1(1本图作为示意图, 图中节点与连线关系来自文献查阅(Rhemtulla et al., 2016), 并非真实数据研究结果。以下图2与图3同样仅作为示意图, 而非基于实证数据。)。
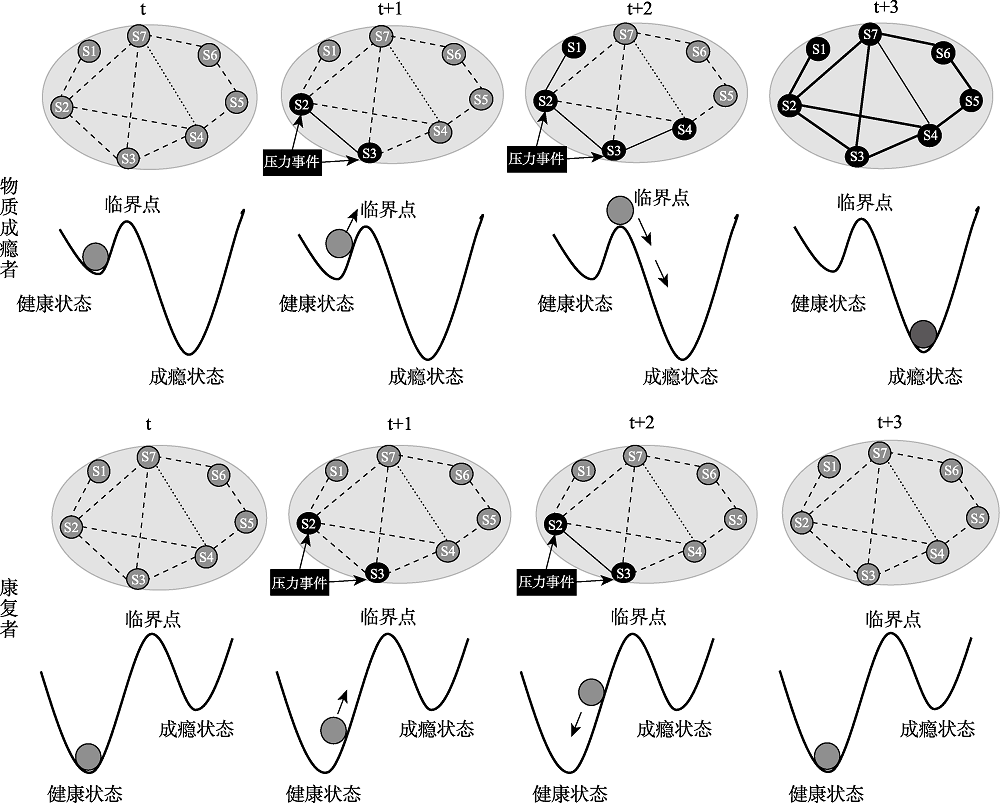
图2 物质成瘾者与康复者症状网络发展过程与对应的双稳态示意图。t时间点症状处于休眠状态, 成瘾者与康复者均表现为健康状态(节点均为浅灰色); 时间点t+1时出现压力事件, 两者均出现了症状S2和S3(黑色节点), 网络作为一个整体均向临界状态移动; 在时间点t+2, 由于网络联结状况差异, 康复者尚未到临界点, 而成瘾者则超过了临界点; 时间点t+3, 当外在压力事件消失后, 康复者回到了健康状态, 而物质成瘾者则因为t+2时越过临界点, 进入了成瘾状态。
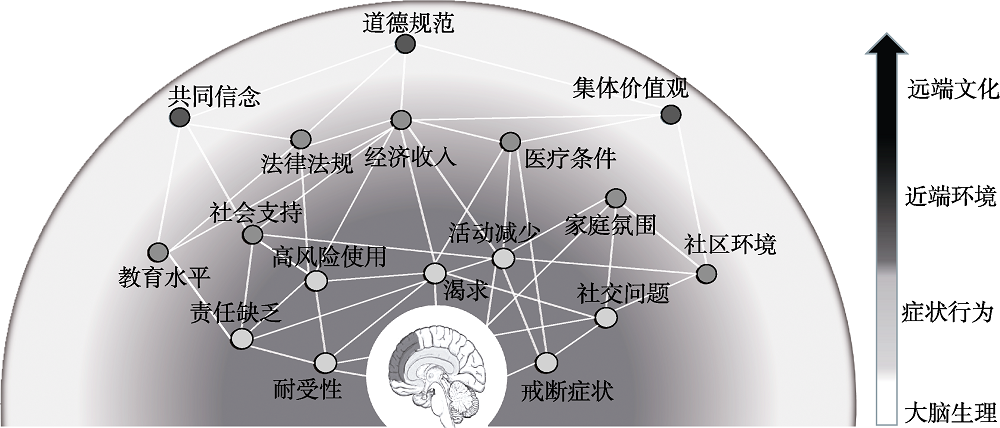
图3 物质成瘾多水平因素网络框架整合示意图。脑代表的是物质成瘾的神经生物机制, 其与成瘾症状水平的节点相关(浅灰色), 而不同的成瘾症状涉及不同的生物性(圆心中的脑)和社会性(近端环境因素, 即示例中的深灰色节点)因素, 它们共同形成相互作用的网络反馈环路; 同时, 成瘾个体的神经生物学机制、成瘾行为以及近端的环境因素又处于更大的社会文化背景之下(远端文化因素, 即示例中的黑色节点)。
| [1] | 蔡玉清, 董书阳, 袁帅, 胡传鹏. (2020). 变量间的网络分析模型及其应用. 心理科学进展, 28(1), 178-190. |
| [2] | 刘肇瑞, 黄悦勤, 陈曦, 程辉, 罗晓敏. (2013). 北京市社区人群心境障碍、焦虑障碍及物质使用障碍的现况调查. 中国心理卫生杂志, 27(2), 102-110. |
| [3] | 孙步青, 叶遇高, 秦领军. (2001). 615例海洛因依赖者复吸原因调查与分析. 中国药物依赖性杂志, 10(3), 214-216. |
| [4] | 杨波, 秦启文. (2005). 成瘾的生物心理社会模型. 心理科学, 28(1), 32-35. |
| [5] |
Adam, D. (2013). Mental health: On the spectrum. Nature, 496(7446), 416-418.
doi: 10.1038/496416a URL pmid: 23619674 |
| [6] |
Afzali, M. H., Sunderland, M., Batterham, P. J., Carragher, N., Calear, A., & Slade, T. (2017). Network approach to the symptom-level association between alcohol use disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 52(3), 329-339.
doi: 10.1007/s00127-016-1331-3 URL pmid: 28013328 |
| [7] | American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric. |
| [8] |
Amodia, D. S., Cano, C., & Eliason, M. J. (2005). An integral approach to substance abuse. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 37(4), 363-371.
doi: 10.1080/02791072.2005.10399809 URL pmid: 16480163 |
| [9] |
An, Y., Hu, C.-P., Zhao, J., Chen, Y., & Wu, X. (2020). Changes in the network structure of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms among earthquake exposed adolescents in china: A two-year longitudinal study. Child Psychiatry & Human Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-020-00995-6
doi: 10.1007/s10578-020-01100-7 URL pmid: 33387164 |
| [10] | Barabasi, A. L. (2012). The network takeover. Nature Physics, 8(1), 14-16. |
| [11] |
Barton, S. (1994). Chaos, self-organization, and psychology. American Psychologist, 49(1), 5-14.
doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.49.1.5 URL |
| [12] |
Booth, R. E., Kwiatkowski, C. F., & Chitwood, D. D. (2000). Sex related HIV risk behaviors: Differential risks among injection drug users, crack smokers, and injection drug users who smoke crack. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 58(3), 219-226.
doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(99)00094-0 URL pmid: 10759032 |
| [13] |
Bornstein, R. (2019). Beyond trait reductionism: Implications of network structures for dimensional models of psychopathology. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 42, E4.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X18001243 URL |
| [14] | Borsboom, D. (2017). A network theory of mental disorders. World Psychiatry, 1 6(1), 5-13. |
| [15] |
Borsboom, D., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2013). Network analysis: An integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 91-121.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185608 URL pmid: 23537483 |
| [16] |
Borsboom, D., Cramer, A. O. J., & Kalis, A. (2019). Brain disorders? Not really: Why network structures block reductionism in psychopathology research. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 42, E2.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X17002266 URL |
| [17] |
Borsboom, D., Cramer, A. O. J., Schmittmann, V. D., Epskamp, S., & Waldorp, L. J. (2011). The small world of psychopathology. PloS One, 6(11), e27407. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027407
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028283 URL pmid: 22140568 |
| [18] |
Boyd, R. (1991). Realism, anti-foundationalism and the enthusiasm for natural kinds. Philosophical Studies, 61(1), 127-148.
doi: 10.1007/BF00385837 URL |
| [19] |
Bringmann, L. F., Elmer, T., Epskamp, S., Krause, R. W., Schoch, D., Wichers, M., ... Snippe, E. (2019). What do centrality measures measure in psychological networks? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 128(8), 892-903.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000446 URL pmid: 31318245 |
| [20] |
Chambers, R. A., Bickel, W. K., & Potenza, M. N. (2007). A scale-free systems theory of motivation and addiction. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 31(7), 1017-1045.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.04.005 URL pmid: 17574673 |
| [21] |
Connolly, C. G., Bell, R. P., Foxe, J. J., & Garavan, H. (2013). Dissociated grey matter changes with prolonged addiction and extended abstinence in cocaine users. PloS One. 8(3), e59645. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059645
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060529 URL pmid: 23555989 |
| [22] |
Contreras, A., Nieto, I., Valiente, C., Espinosa, R., & Vazquez, C. (2019). The study of psychopathology from the network analysis perspective: A systematic review. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 88(2), 71-83.
doi: 10.1159/000497425 URL pmid: 30889609 |
| [23] |
Cramer, A. O., van Borkulo, C. D., Giltay, E. J., van der Maas, H. L., Kendler, K. S., Scheffer, M., & Borsboom, D. (2016). Major depression as a complex dynamic system. PLoS One, 11(12), e0167490. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167490
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169091 URL pmid: 28036384 |
| [24] |
Cramer, A. O., Waldorp, L. J., van der Maas, H. L., & Borsboom, D. (2010). Comorbidity: A network perspective. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 33(2-3), 137-193.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X09991567 URL pmid: 20584369 |
| [25] |
Czoty, P. W., Gage H. D, & Nader, M. A. (2010). Differences in D2 dopamine receptor availability and reaction to novelty in socially housed male monkeys during abstinence from cocaine. Psychopharmacology, 208, 585-592.
doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1756-4 URL pmid: 20066401 |
| [26] |
de Ron, J., Fried, E. I., & Epskamp, S. (2019). Psychological networks in clinical populations: Investigating the consequences of Berkson's bias. Psychological Medicine, 1-9.
URL pmid: 33436120 |
| [27] |
Devinsky, O., Morrell, M. J., & Vogt, B. A. (1995). Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain, 118(1), 279-306.
doi: 10.1093/brain/118.1.279 URL |
| [28] |
Field, M., Heather, N., & Wiers, R. W. (2019). Indeed, not really a brain disorder: Implications for reductionist accounts of addiction. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 42, E9.
doi: 10.1017/S0140525X18001024 URL |
| [29] |
Fisher, H. E., Brown, L. L., Aron, A., Strong, G., & Mashek, D. (2010). Reward, addiction, and emotion regulation systems associated with rejection in love. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(1), 51-60.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00784.2009 URL pmid: 20445032 |
| [30] |
Forbes, M. K., Wright, A. G. C., Markon, K. E., & Krueger, R. F. (2019). The network approach to psychopathology: Promise versus reality. World Psychiatry, 18(3), 272-273.
doi: 10.1002/wps.20659 URL pmid: 31496101 |
| [31] |
Forbush, K. T., Siew, C. S. Q., & Vitevitch, M. S. (2016). Application of network analysis to identify interactive systems of eating disorder psychopathology. Psychological Medicine, 46(12), 2667-2677.
doi: 10.1017/S003329171600012X URL pmid: 27387196 |
| [32] |
Fried, E. I., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2017). Moving forward: Challenges and directions for psychopathological network theory and methodology. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 12(6), 999-1020.
doi: 10.1177/1745691617705892 URL pmid: 28873325 |
| [33] |
Fried, E. I., van Borkulo, C. D., Epskamp, S., Schoevers, R. A., Tuerlinckx, F., & Borsboom, D. (2016). Measuring depression over time.. Or not? Lack of unidimensionality and longitudinal measurement invariance in four common rating scales of depression. Psychological Assessment, 28(11), 1354-1367.
doi: 10.1037/pas0000275 URL pmid: 26821198 |
| [34] | Geng, L., Xiang, P., Yang, J., Shen, H., & Sang, Z. (2016). Association between hair cortisol concentration and perceived stress in female methamphetamine addicts. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 9 1, 82-86. |
| [35] |
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: Neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(10), 1642-1652.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.10.1642 URL |
| [36] |
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(11), 652-669.
doi: 10.1038/nrn3119 URL pmid: 22011681 |
| [37] | Gossop, M., Green, L., Phillips, G., & Bradley, B. (1989). Lapse, relapse and survival among opiate addicts after treatment: A prospective follow-up study. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 154(3), 348-353. |
| [38] |
Gossop, M., Marsden, J., Stewart, D., & Rolfe, A. (2000). Reductions in acquisitive crime and drug use after treatment of addiction problems: 1-year follow-up outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 58(1-2), 165-172.
doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(99)00077-0 URL pmid: 10669068 |
| [39] |
Gossop, M., Stewart, D., Browne, N., & Marsden, J. (2002). Factors associated with abstinence, lapse or relapse to heroin use after residential treatment: Protective effect of coping responses. Addiction, 97(10), 1259-1267.
doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00227.x URL pmid: 12359030 |
| [40] | Griffiths, M. (2005). A ‘components’ model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. Journal of Substance Use, 10(4), 191-197. |
| [41] |
Hallquist, M. N., Wright, A. G. C., & Molenaar, P. C. M. (2019). Problems with centrality measures in psychopathology symptom networks: Why network psychometrics cannot escape psychometric theory. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 1-25.
doi: 10.1080/00273171.2020.1822148 URL pmid: 32996335 |
| [42] | Haslbeck, J. M. B., Ryan, O., Robinaugh, D., Waldorp, L., & Borsboom, D. (2019). Modeling Psychopathology: From data models to formal theories. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/jgm7f |
| [43] |
Heyman, G. M. (2013). Quitting drugs: Quantitative and qualitative features. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 29-59.
URL pmid: 23330937 |
| [44] |
Insel, T. R., & Cuthbert, B. N. (2015). Brain disorders? Precisely. Science, 348(6234), 499-500.
doi: 10.1126/science.aab2358 URL pmid: 25931539 |
| [45] |
Isvoranu, A. M., Borsboom, D., van Os, J., & Guloksuz, S. (2016). A network approach to environmental impact in psychotic disorder: Brief theoretical framework. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42(4), 870-873.
doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw049 URL |
| [46] |
Isvoranu, A. M., Guloksuz, S., Epskamp, S., van Os, J., Borsboom, D., & GROUP, Investigators. (2020). Toward incorporating genetic risk scores into symptom networks of psychosis. Psychological Medicine, 50(4), 636-643.
doi: 10.1017/S003329171900045X URL pmid: 30867074 |
| [47] |
Jayawickreme, N., Mootoo, C., Fountain, C., Rasmussen, A., Jayawickreme, E., & Bertuccio, R. F. (2017). Post-conflict struggles as networks of problems: A network analysis of trauma, daily stressors and psychological distress among Sri Lankan war survivors. Social Science & Medicine, 190, 119-132.
URL pmid: 28858697 |
| [48] |
Kalisch, R., Cramer, A. O., Binder, H., Fritz, J., Leertouwer, I., Lunansky, G., ... van Harmelen, A.-L. (2019). Deconstructing and reconstructing resilience: A dynamic network approach. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14(5), 765-777.
URL pmid: 31365841 |
| [49] |
Kalivas, P. W., & Stewart, J. (1991). Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Research Reviews, 16(3), 223-244.
doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(91)90007-u URL pmid: 1665095 |
| [50] | Kauffman, S. A. (1990). The sciences of complexity and "origins of order". PSA: Proceedings of the Biennial Meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association, 1990(2), 299-322. |
| [51] | Kendler, K. S. (2005). Toward a philosophical structure for psychiatry. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(3), 433-440. |
| [52] |
Kendler, K. S. (2012). Levels of explanation in psychiatric and substance use disorders: Implications for the development of an etiologically based nosology. Molecular Psychiatry, 17(1), 11-21.
doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.70 URL pmid: 21670729 |
| [53] |
Kendler, K. S., Zachar, P., & Craver, C. (2011). What kinds of things are psychiatric disorders? Psychological Medicine, 41(6), 1143-1150.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291710001844 URL pmid: 20860872 |
| [54] | Kievit, R. A., Romeijn, J. W., Waldorp, L. J., Wicherts, J. M., Scholte, H. S., & Borsboom, D. (2011). Mind the gap: A psychometric approach to the reduction problem. Psychological Inquiry, 22(2), 67-87. |
| [55] |
Kirshenbaum, A. P., Olsen, D. M., & Bickel, W. K. (2009). A quantitative review of the ubiquitous relapse curve. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 36(1), 8-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2008.04.001 URL pmid: 18571890 |
| [56] |
Koob, G. F. (1992). Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 13, 177-184.
doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90060-j URL pmid: 1604710 |
| [57] |
Kotov, R., Krueger, R. F., Watson, D., Achenbach, T. M., Althoff, R. R., Bagby, R. M., ... Zimmerman, M. (2017). The hierarchical taxonomy of psychopathology (HiTOP): A dimensional alternative to traditional nosologies. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 126(4), 454-477.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000258 URL pmid: 28333488 |
| [58] |
Kramers, H. A. (1940). Brownian motion in a field of force and the diffusion model of chemical reactions. Physica, 7(4), 284-304.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-8914(40)90098-2 URL |
| [59] |
Leshner, A. I. (1997). Addiction is a brain disease, and it matters. Science, 278(5335), 45-47.
URL pmid: 9311924 |
| [60] |
Levy, N. (2013). Addiction is not a brain disease (and it matters). Frontiers in Psychiatry, 4, 24.
URL pmid: 23596425 |
| [61] | Levy, N. (2017). Hijacking addiction. Philosophy, Psychiatry, & Psychology, 24(1), 97-99. |
| [62] |
Lewis, M. (2017). Addiction and the brain: Development, not disease. Neuroethics, 10(1), 7-18.
URL pmid: 28725282 |
| [63] |
Lewis, M. (2018). Brain change in addiction as learning, not disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 379(16), 1551-1560.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1602872 URL |
| [64] |
Lewis, M. D., & Todd, R. M. (2007). The self-regulating brain: Cortical-subcortical feedback and the development of intelligent action. Cognitive Development, 22(4), 406-430.
doi: 10.1016/j.cogdev.2007.08.004 URL |
| [65] |
Lunansky, G., van Borkulo, C., & Borsboom, D. (2019). Personality, resilience, and psychopathology: A model for the interaction between slow and fast network processes in the context of mental health. European Journal of Personality. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.2263
doi: 10.1002/per.2046 URL pmid: 27688595 |
| [66] |
Maguire, E. A., Gadian, D. G., Johnsrude, I. S., Good, C. D., Ashburner, J., Frackowiak, R. S., & Frith, C. D. (2000). Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(8), 4398-4403.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.070039597 URL pmid: 10716738 |
| [67] |
Majer, J. M., Payne, J. C., & Jason, L. A. (2015). Recovery resources and psychiatric severity among persons with substance use disorders. Community Mental Health Journal, 51(4), 437-444.
doi: 10.1007/s10597-014-9762-3 URL pmid: 25069418 |
| [68] |
Marsman, M., Borsboom, D., Kruis, J., Epskamp, S., van Bork, R., Waldorp, L. J., van der Maas, H. L. J., & Maris, G. K. J. (2017). An introduction to network psychometrics: Relating Ising network models to item response theory models. Multivariate Behavioral Research, (53((1), 15-35.
URL pmid: 29111774 |
| [69] |
Mattick, R. P., Breen, C., Kimber, J., & Davoli, M. (2009). Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (3), CD002209. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002209. pub2
doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011118.pub2 URL pmid: 25803793 |
| [70] | McNally, R. J., Robinaugh, D. J., Wu, G. W. Y., Wang, L., Deserno, M. K., & Borsboom, D. (2015). Mental disorders as causal systems: A network approach to posttraumatic stress disorder. Clinical Psychological Science, 3(6), 836-849. |
| [71] | Müller, C. P. (2019). Making a case for constructive reductionism. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 42, E16. |
| [72] |
Nathan, P. E., Conrad, M., & Skinstad, A. H. (2016). History of the Concept of Addiction. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 12, 29-51.
URL pmid: 26565120 |
| [73] |
Nestler, E. J. (2001). Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(2), 119-128.
URL pmid: 11252991 |
| [74] |
Niaura, R. (2000). Cognitive social learning and related perspectives on drug craving. Addiction, 95(8s2), 155-163.
doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.95.8s2.4.x URL |
| [75] |
Noori, H. R., Cosa, L. A., & Spanagel, R. (2016). Largely overlapping neuronal substrates of reactivity to drug, gambling, food and sexual cues: A comprehensive meta- analysis. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 26(9), 1419-1430.
URL pmid: 27397863 |
| [76] |
O'Brien, C. (2011). Addiction and dependence in DSM-V. Addiction, 106(5), 866-867.
doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03144.x URL pmid: 21477226 |
| [77] | Office of China National Narcotics Control Commission. (2020). Drug Situation in China 2019. Retrieved July 20, 2020, from http://www.nncc626.com/2020-06/25/c_1210675877.htm |
| [78] | Redei, E. E., Andrus, B. M., Kwasny, M. J., Seok, J., Cai, X., Ho, J., & Mohr, D. C. (2014). Blood transcriptomic biomarkers in adult primary care patients with major depressive disorder undergoing cognitive behavioral therapy. Translational Psychiatry, 4(9), e442. |
| [79] | Reuter, P., & MacCoun, R. (2002). Heroin maintenance: Is a U.S. experiment needed? In: D. Musto (Eds). One Hundred Years of Heroin (pp. 159-180). Westport, CT: Greenwood. |
| [80] | Klatzky, R. L. (1998). Allocentric and egocentric spatial representations: Definitions, distinctions, and interconnections. In C. Freksa, C. Habel, & K. F. Wender (Eds.), Lecture notes in artificial intelligence: Vol. 1404: Spatial cognition: An interdisciplinary approach to representing and processing spatial knowledge (pp. 1-17). Springer-Verlag. |
| [81] |
Rhemtulla, M., Fried, E. I., Aggen, S. H., Tuerlinckx, F., Kendler, K. S., & Borsboom, D. (2016). Network analysis of substance abuse and dependence symptoms. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 161, 230-237.
doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.02.005 URL pmid: 26898186 |
| [82] | Robinaugh, D., Haslbeck, J. M. B., Waldorp, L., Kossakowski, J. J., Fried, E. I., Millner, A., … Borsboom, D. (2019). Advancing the network theory of mental disorders: A computational model of panic disorder. Retrieved October 26, 2020, from https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/km37w |
| [83] |
Robinaugh, D., Hoekstra, R., Toner, E., & Borsboom, D. (2020). The network approach to psychopathology: A review of the literature 2008-2018 and an agenda for future research. Psychological Medicine, 50(3), 353-366.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291719003404 URL pmid: 31875792 |
| [84] |
Robinson, T. E., & Berridge, K. C. (1993). The neural basis of drug craving: An incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Research Reviews, 18(3), 247-291.
URL pmid: 8401595 |
| [85] | Robinson, T. E., & Berridge, K. C. (2000). The psychology and neurobiology of addiction: An incentive-sensitization view. Addiction, 95(8s2), 91-117. |
| [86] |
Salamone, J. D. (1996). The behavioral neurochemistry of motivation: Methodological and conceptual issues in studies of the dynamic activity of nucleus accumbens dopamine. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 64(2), 137-149.
doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(95)00125-5 URL pmid: 8699874 |
| [87] |
Scheffer, M., Bascompte, J., Brock, W. A., Brovkin, V., Carpenter, S. R., Dakos, V., ... Sugihara, G. (2009). Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature, 461(7260), 53-59.
doi: 10.1038/nature08227 URL pmid: 19727193 |
| [88] |
Schwabe, L., Dickinson, A., & Wolf, O. T. (2011). Stress, habits, and drug addiction: A psychoneuroendocrinological perspective. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 19(1), 53-63.
URL pmid: 21341923 |
| [89] | Skewes, M. C., & Gonzalez, V. M. (2013). The biopsychosocial model of addiction. Principles of Addiction, 1, 61-70. |
| [90] |
Spanagel, R., & Kiefer, F. (2008). Drugs for relapse prevention of alcoholism: Ten years of progress. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 29(3), 109-115.
doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2007.12.005 URL pmid: 18262663 |
| [91] | St Quinton, T., & Stain, H. J. (2020). A network approach to depressive disorders. Journal of Rational Emotive & Cognitive Behavior Therapy, 38, 1-13. |
| [92] | Sussman, S., Lisha, N., & Griffiths, M. (2011). Prevalence of the addictions: A problem of the majority or the minority? Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, 34(1), 3-56. |
| [93] |
Tulloch, H., Pipe, A., Els, C., Aitken, D., Clyde, M., Corran, B., & Reid, R. D. (2014). Flexible and extended dosing of nicotine replacement therapy or varenicline in comparison to fixed dose nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation: Rationale, methods and participant characteristics of the FLEX trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials, 38(2), 304-313.
doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2014.05.011 URL pmid: 24861558 |
| [94] | United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. (2017). World Drug Report 2017. Retrieved July 12, 2020, from https://www.unodc.org/wdr2017/field/Booklet_1_EXSUM.pdf |
| [95] |
Volkow, N. D., & Fowler, J. S. (2000). Addiction, a disease of compulsion and drive: Involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 10, 318-325.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.3.318 URL pmid: 10731226 |
| [96] |
Volkow, N. D., Koob, G. F., & McLellan, A. T. (2016). Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. New England Journal of Medicine, 374(4), 363-371.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1511480 URL |
| [97] |
Westerink, B. H. (1995). Brain microdialysis and its application for the study of animal behaviour. Behavioural Brain Research, 70(2), 103-124.
doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(95)80001-8 URL pmid: 8561902 |
| [98] | White, W. L. (2007). A recovery revolution in Philadelphia. Counselor, 8(5), 34-38. |
| [99] |
Wigman, J. T. W., van Os, J., Borsboom, D., Wardenaar, K. J., Epskamp, S., Klippel, A., ... Wichers, M. (2015). Exploring the underlying structure of mental disorders: Cross-diagnostic differences and similarities from a network perspective using both a top-down and a bottom-up approach. Psychological Medicine, 45(11), 2375-2387.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291715000331 URL pmid: 25804221 |
| [100] |
Wilson, M. (1993). DSM-III and the transformation of American psychiatry: A history. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 150(3), 399-410.
doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.3.399 URL pmid: 8434655 |
| [101] |
Wise, R. A. (2002). Brain reward circuitry: Insights from unsensed incentives. Neuron, 36(2), 229-240.
URL pmid: 12383779 |
| [102] | Witkiewitz, K., & Marlatt, G. A. (2004). Relapse prevention for alcohol and drug problems: That was Zen, this is Tao. American Psychologist, 59(4), 224-235. |
| [1] | 方琪, 栾琨. 多团队成员身份及其作用机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2022, 30(5): 1143-1157. |
| [2] | 陈琛, 王力, 曹成琦, 李根. 心理病理学网络理论、方法与挑战[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(10): 1724-1739. |
| [3] | 杨玲, 刘文鑫, 张炀, 张建勋, 牛禄霖. 物质成瘾领域延迟折扣研究中的外部效度问题[J]. 心理科学进展, 2021, 29(1): 140-149. |
| [4] | 陈乐乐, 黄蓉, 贾世伟. 反馈相关负波与成瘾[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(6): 959-968. |
| [5] | 苏波波, 郑美红. 物质相关线索对成瘾者反应抑制的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2019, 27(11): 1863-1874. |
| [6] | 王志燕, 崔彩莲. 个体冲动性对物质滥用与成瘾的影响及脑机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2017, 25(12): 2063-2074. |
| [7] | 杨玲;苏波波;张建勋;柳斌;卫晓芸;赵鑫. 物质成瘾人群金钱奖赏加工的异常机制及可恢复性[J]. 心理科学进展, 2015, 23(9): 1617-1626. |
| [8] | 曾红;叶浩生;杨文登. 镜像神经在药物心理渴求中的作用及机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(4): 581-588. |
| [9] | 孟景;沈林;Todd Jackson;陈红. 疼痛对心理的影响及其机制[J]. 心理科学进展, 2011, 19(10): 1493-1501. |
| [10] | 佟云霞. 临床心理学的认知研究及信息加工观点[J]. 心理科学进展, 1995, 3(1): 40-45. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||