

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (11): 2022-2042.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.2022
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Feng1,2,3, DING Huimin4,5, LI Sijia6, HAN Nuo7,8, DI Yazheng1,2, LIU Xiaoqian1,2, ZHAO Nan1,2, LI Linyan3,9, ZHU Tingshao1,2( )
)
Received:2024-08-15
Published:2025-11-25
Online:2025-09-25
Contact:
ZHU Tingshao, E-mail: tszhu@psych.ac.cn
Supported by:HUANG Feng, DING Huimin, LI Sijia, HAN Nuo, DI Yazheng, LIU Xiaoqian, ZHAO Nan, LI Linyan, ZHU Tingshao. (2025). Self-help AI psychological counseling system based on large language models and its effectiveness evaluation. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(11), 2022-2042.
| Evaluation Dimension | GPT-4o | Claude 3 Opus | Yi-Large | F | η2p | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | 2.36 (1.25) | 1.58 (0.91) | 1.53 (0.74) | 8.04** | 0.13 | ANOVA |
| Professionalism | 1.67 (1.01) | 1.56 (0.81) | 1.44 (0.74) | 0.60 | 0.01 | ANOVA |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | 2.53 (1.32) | 1.47 (0.74) | 2.36 (1.36) | 11.92*** | - | Welch ANOVA |
| Consistency & Coherence | 2.17 (1.11) | 2.14 (1.20) | 1.44 (0.74) | 7.47** | - | Welch ANOVA |
| Total Score | 8.72 (4.03) | 6.75 (3.02) | 6.78 (2.90) | 4.09* | 0.07 | ANOVA |
Table 1 Descriptive statistics and ANOVA results for candidate base models across evaluation dimensions
| Evaluation Dimension | GPT-4o | Claude 3 Opus | Yi-Large | F | η2p | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | 2.36 (1.25) | 1.58 (0.91) | 1.53 (0.74) | 8.04** | 0.13 | ANOVA |
| Professionalism | 1.67 (1.01) | 1.56 (0.81) | 1.44 (0.74) | 0.60 | 0.01 | ANOVA |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | 2.53 (1.32) | 1.47 (0.74) | 2.36 (1.36) | 11.92*** | - | Welch ANOVA |
| Consistency & Coherence | 2.17 (1.11) | 2.14 (1.20) | 1.44 (0.74) | 7.47** | - | Welch ANOVA |
| Total Score | 8.72 (4.03) | 6.75 (3.02) | 6.78 (2.90) | 4.09* | 0.07 | ANOVA |
| Evaluation Dimension | Model Comparison | Mean Difference | 95% CI | Post-hoc Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 0.78** | [0.23, 1.33] | Tukey HSD |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.83** | [0.28, 1.39] | Tukey HSD | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | ?0.06 | [?0.61, 0.50] | Tukey HSD | |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 1.06*** | [0.55, 1.56] | Games-Howell |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.17 | [?0.46, 0.80] | Games-Howell | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | ?0.89** | [?1.40, ?0.37] | Games-Howell | |
| Consistency & Coherence | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | ?0.03 | [?0.57, 0.52] | Games-Howell |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.72** | [0.28, 1.17] | Games-Howell | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | 0.69** | [0.23, 1.16] | Games-Howell | |
| Total Score | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 1.97* | [0.09, 3.85] | Tukey HSD |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 1.94* | [0.06, 3.82] | Tukey HSD | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | 0.03 | [?1.85, 1.91] | Tukey HSD |
Table 2 Tukey HSD post-hoc test results for pairwise comparisons between base models
| Evaluation Dimension | Model Comparison | Mean Difference | 95% CI | Post-hoc Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 0.78** | [0.23, 1.33] | Tukey HSD |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.83** | [0.28, 1.39] | Tukey HSD | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | ?0.06 | [?0.61, 0.50] | Tukey HSD | |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 1.06*** | [0.55, 1.56] | Games-Howell |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.17 | [?0.46, 0.80] | Games-Howell | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | ?0.89** | [?1.40, ?0.37] | Games-Howell | |
| Consistency & Coherence | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | ?0.03 | [?0.57, 0.52] | Games-Howell |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 0.72** | [0.28, 1.17] | Games-Howell | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | 0.69** | [0.23, 1.16] | Games-Howell | |
| Total Score | GPT-4o vs. Claude 3 Opus | 1.97* | [0.09, 3.85] | Tukey HSD |
| GPT-4o vs. Yi-Large | 1.94* | [0.06, 3.82] | Tukey HSD | |
| Claude 3 Opus vs. Yi-Large | 0.03 | [?1.85, 1.91] | Tukey HSD |
| Evaluation Dimension | Simple Instructions | Prompt Engineering | t | d | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | 2.36(1.05) | 4.17(0.97) | 7.68*** | 1.28 | [1.33, 2.28] |
| Professionalism | 1.67(0.89) | 2.56(1.08) | 3.04** | 0.51 | [0.30, 1.48] |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | 2.53(1.18) | 4.08(0.87) | 6.38*** | 1.06 | [1.06, 2.05] |
| Consistency & Coherence | 2.17(1.03) | 3.86(0.76) | 6.83*** | 1.14 | [1.19, 2.20] |
| Total Score | 8.72(3.63) | 14.67(3.20) | 6.35*** | 1.06 | [4.04, 7.85] |
Table 3 Comparison of GPT-4o performance before and after prompt engineering optimization
| Evaluation Dimension | Simple Instructions | Prompt Engineering | t | d | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | 2.36(1.05) | 4.17(0.97) | 7.68*** | 1.28 | [1.33, 2.28] |
| Professionalism | 1.67(0.89) | 2.56(1.08) | 3.04** | 0.51 | [0.30, 1.48] |
| Emotional Understanding & Empathy | 2.53(1.18) | 4.08(0.87) | 6.38*** | 1.06 | [1.06, 2.05] |
| Consistency & Coherence | 2.17(1.03) | 3.86(0.76) | 6.83*** | 1.14 | [1.19, 2.20] |
| Total Score | 8.72(3.63) | 14.67(3.20) | 6.35*** | 1.06 | [4.04, 7.85] |
| Time Point | Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1. Age | 24.06 | 4.05 | - | ||||
| (n = 202) | 2. Gender | 0.50 | 0.50 | ?0.03 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 5.41 | 4.52 | ?0.00 | 0.04 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 4.69 | 4.02 | ?0.08 | 0.00 | 0.76*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 6.52 | 4.34 | 0.02 | ?0.03 | 0.74*** | 0.82*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 6.76 | 2.67 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.66*** | 0.62*** | 0.67*** | |
| T2 | 1. Age | 23.81 | 3.67 | ? | ||||
| (n = 180) | 2. Gender | 0.50 | 0.50 | ?0.00 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 2.98 | 4.07 | ?0.05 | 0.01 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 2.48 | 3.20 | ?0.10 | ?0.03 | 0.71*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 5.45 | 3.98 | ?0.05 | ?0.07 | 0.69*** | 0.73*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 4.77 | 2.47 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.51*** | 0.57*** | 0.40*** | |
| T3 | 1. Age | 23.74 | 3.81 | ? | ||||
| (n = 153) | 2. Gender | 0.51 | 0.50 | ?0.01 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 5.19 | 3.59 | ?0.08 | 0.08 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 2.43 | 3.08 | ?0.15 | ?0.02 | 0.74*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 5.76 | 3.84 | 0.01 | ?0.07 | 0.74*** | 0.77*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 6.69 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.60*** | 0.56*** | 0.56*** |
Table 4 Descriptive statistics and correlation matrix for main variables at each measurement time point
| Time Point | Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1. Age | 24.06 | 4.05 | - | ||||
| (n = 202) | 2. Gender | 0.50 | 0.50 | ?0.03 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 5.41 | 4.52 | ?0.00 | 0.04 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 4.69 | 4.02 | ?0.08 | 0.00 | 0.76*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 6.52 | 4.34 | 0.02 | ?0.03 | 0.74*** | 0.82*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 6.76 | 2.67 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.66*** | 0.62*** | 0.67*** | |
| T2 | 1. Age | 23.81 | 3.67 | ? | ||||
| (n = 180) | 2. Gender | 0.50 | 0.50 | ?0.00 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 2.98 | 4.07 | ?0.05 | 0.01 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 2.48 | 3.20 | ?0.10 | ?0.03 | 0.71*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 5.45 | 3.98 | ?0.05 | ?0.07 | 0.69*** | 0.73*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 4.77 | 2.47 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.51*** | 0.57*** | 0.40*** | |
| T3 | 1. Age | 23.74 | 3.81 | ? | ||||
| (n = 153) | 2. Gender | 0.51 | 0.50 | ?0.01 | ? | |||
| 3. Depression | 5.19 | 3.59 | ?0.08 | 0.08 | ? | |||
| 4. Anxiety | 2.43 | 3.08 | ?0.15 | ?0.02 | 0.74*** | ? | ||
| 5. Stress | 5.76 | 3.84 | 0.01 | ?0.07 | 0.74*** | 0.77*** | ? | |
| 6. Loneliness | 6.69 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.60*** | 0.56*** | 0.56*** |
| Variable | (1) Depression Model | (2) Anxiety Model | (3) Stress Model | (4) Loneliness Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 5.86(1.77)*** | 7.09(1.42)*** | 7.28(1.71)*** | 5.97(0.89)*** |
| Control Variables | ||||
| Age | ?0.03(0.07) | ?0.10(0.06) | ?0.01(0.07) | 0.04(0.03) |
| Gender (Male) | 0.32(0.54) | ?0.19(0.43) | ?0.53(0.52) | 0.05(0.27) |
| Group Fixed Effects | ||||
| Group F | 0.20(0.83) | 0.37(0.68) | ?0.12(0.82) | ?0.51(0.45) |
| Group M | 0.29(0.83) | ?0.01(0.68) | ?0.61(0.82) | ?0.13(0.45) |
| Group R | 0.12(0.84) | ?0.07(0.68) | 0.08(0.82) | ?0.37(0.45) |
| Time Fixed Effects | ||||
| T2 | ?0.28(0.46) | 0.21(0.41) | ?0.27(0.50) | 0.40(0.34) |
| T3 | 0.12(0.48) | ?0.18(0.43) | ?0.45(0.53) | 0.23(0.35) |
| Group × Time | ||||
| Group F × T2 | ?2.66(0.63)*** | ?3.51(0.57)*** | ?0.59(0.69) | ?3.47(0.47)*** |
| Group M × T2 | ?3.25(0.63)*** | ?3.28(0.57)*** | ?0.46(0.69) | ?3.85(0.47)*** |
| Group R × T2 | ?2.48(0.63)*** | ?2.75(0.57)*** | ?2.07(0.69)** | ?1.83(0.47)*** |
| Group F × T3 | ?0.24(0.67) | ?2.84(0.60)*** | ?0.33(0.73) | ?0.49(0.49) |
| Group M × T3 | ?0.47(0.67) | ?2.55(0.61)*** | ?0.17(0.73) | ?0.51(0.50) |
| Group R × T3 | 0.41(0.66) | ?2.23(0.60)*** | ?0.30(0.73) | 0.14(0.49) |
| Model Fit Indices | ||||
| Marginal R2 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.27 |
| Conditional R2 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.64 |
Table 5 Linear mixed models
| Variable | (1) Depression Model | (2) Anxiety Model | (3) Stress Model | (4) Loneliness Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 5.86(1.77)*** | 7.09(1.42)*** | 7.28(1.71)*** | 5.97(0.89)*** |
| Control Variables | ||||
| Age | ?0.03(0.07) | ?0.10(0.06) | ?0.01(0.07) | 0.04(0.03) |
| Gender (Male) | 0.32(0.54) | ?0.19(0.43) | ?0.53(0.52) | 0.05(0.27) |
| Group Fixed Effects | ||||
| Group F | 0.20(0.83) | 0.37(0.68) | ?0.12(0.82) | ?0.51(0.45) |
| Group M | 0.29(0.83) | ?0.01(0.68) | ?0.61(0.82) | ?0.13(0.45) |
| Group R | 0.12(0.84) | ?0.07(0.68) | 0.08(0.82) | ?0.37(0.45) |
| Time Fixed Effects | ||||
| T2 | ?0.28(0.46) | 0.21(0.41) | ?0.27(0.50) | 0.40(0.34) |
| T3 | 0.12(0.48) | ?0.18(0.43) | ?0.45(0.53) | 0.23(0.35) |
| Group × Time | ||||
| Group F × T2 | ?2.66(0.63)*** | ?3.51(0.57)*** | ?0.59(0.69) | ?3.47(0.47)*** |
| Group M × T2 | ?3.25(0.63)*** | ?3.28(0.57)*** | ?0.46(0.69) | ?3.85(0.47)*** |
| Group R × T2 | ?2.48(0.63)*** | ?2.75(0.57)*** | ?2.07(0.69)** | ?1.83(0.47)*** |
| Group F × T3 | ?0.24(0.67) | ?2.84(0.60)*** | ?0.33(0.73) | ?0.49(0.49) |
| Group M × T3 | ?0.47(0.67) | ?2.55(0.61)*** | ?0.17(0.73) | ?0.51(0.50) |
| Group R × T3 | 0.41(0.66) | ?2.23(0.60)*** | ?0.30(0.73) | 0.14(0.49) |
| Model Fit Indices | ||||
| Marginal R2 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.27 |
| Conditional R2 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.64 |
| Variable | Group | T1→T2 | Confidence Interval | T1→T3 | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | C | 0.28(0.46) | [?0.80, 1.35] | ?0.12(0.48) | [?1.25, 1.01] |
| F | 2.93(0.43)*** | [1.91, 3.95] | 0.11(0.46) | [?0.97, 1.20] | |
| M | 3.53(0.43)*** | [2.51, 4.54] | 0.35(0.46) | [?0.74, 1.44] | |
| R | 2.76(0.43)*** | [1.73, 3.78] | ?0.53(0.46) | [?1.61, 0.55] | |
| Anxiety | C | ?0.21(0.41) | [?1.18, 0.77] | 0.18(0.44) | [?0.85, 1.20] |
| F | 3.30(0.39)*** | [2.37, 4.23] | 3.02(0.42)*** | [2.03, 4.01] | |
| M | 3.07(0.39)*** | [2.15, 3.99] | 2.73(0.42)*** | [1.73, 3.72] | |
| R | 2.54(0.39)*** | [1.62, 3.47] | 2.40(0.42)*** | [1.42, 3.38] | |
| Stress | C | 0.27(0.50) | [?0.90, 1.45] | 0.45(0.52) | [?0.79, 1.68] |
| F | 0.86(0.48) | [?0.26, 1.98] | 0.78(0.51) | [?0.41, 1.96] | |
| M | 0.73(0.47) | [?0.38, 1.84] | 0.61(0.51) | [?0.59, 1.81] | |
| R | 2.35(0.48)*** | [1.23, 3.47] | 0.74(0.50) | [?0.44, 1.92] | |
| Loneliness | C | ?0.40(0.34) | [?1.20, 0.40] | ?0.23(0.36) | [?1.07, 0.60] |
| F | 3.07(0.32)*** | [2.31, 3.83] | 0.25(0.34) | [?0.55, 1.06] | |
| M | 3.45(0.32)*** | [2.69, 4.20] | 0.28(0.35) | [?0.54, 1.09] | |
| R | 1.43(0.32)*** | [0.67, 2.20] | ?0.38(0.34) | [?1.18, 0.43] |
Table 6 Simple effects analysis
| Variable | Group | T1→T2 | Confidence Interval | T1→T3 | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | C | 0.28(0.46) | [?0.80, 1.35] | ?0.12(0.48) | [?1.25, 1.01] |
| F | 2.93(0.43)*** | [1.91, 3.95] | 0.11(0.46) | [?0.97, 1.20] | |
| M | 3.53(0.43)*** | [2.51, 4.54] | 0.35(0.46) | [?0.74, 1.44] | |
| R | 2.76(0.43)*** | [1.73, 3.78] | ?0.53(0.46) | [?1.61, 0.55] | |
| Anxiety | C | ?0.21(0.41) | [?1.18, 0.77] | 0.18(0.44) | [?0.85, 1.20] |
| F | 3.30(0.39)*** | [2.37, 4.23] | 3.02(0.42)*** | [2.03, 4.01] | |
| M | 3.07(0.39)*** | [2.15, 3.99] | 2.73(0.42)*** | [1.73, 3.72] | |
| R | 2.54(0.39)*** | [1.62, 3.47] | 2.40(0.42)*** | [1.42, 3.38] | |
| Stress | C | 0.27(0.50) | [?0.90, 1.45] | 0.45(0.52) | [?0.79, 1.68] |
| F | 0.86(0.48) | [?0.26, 1.98] | 0.78(0.51) | [?0.41, 1.96] | |
| M | 0.73(0.47) | [?0.38, 1.84] | 0.61(0.51) | [?0.59, 1.81] | |
| R | 2.35(0.48)*** | [1.23, 3.47] | 0.74(0.50) | [?0.44, 1.92] | |
| Loneliness | C | ?0.40(0.34) | [?1.20, 0.40] | ?0.23(0.36) | [?1.07, 0.60] |
| F | 3.07(0.32)*** | [2.31, 3.83] | 0.25(0.34) | [?0.55, 1.06] | |
| M | 3.45(0.32)*** | [2.69, 4.20] | 0.28(0.35) | [?0.54, 1.09] | |
| R | 1.43(0.32)*** | [0.67, 2.20] | ?0.38(0.34) | [?1.18, 0.43] |
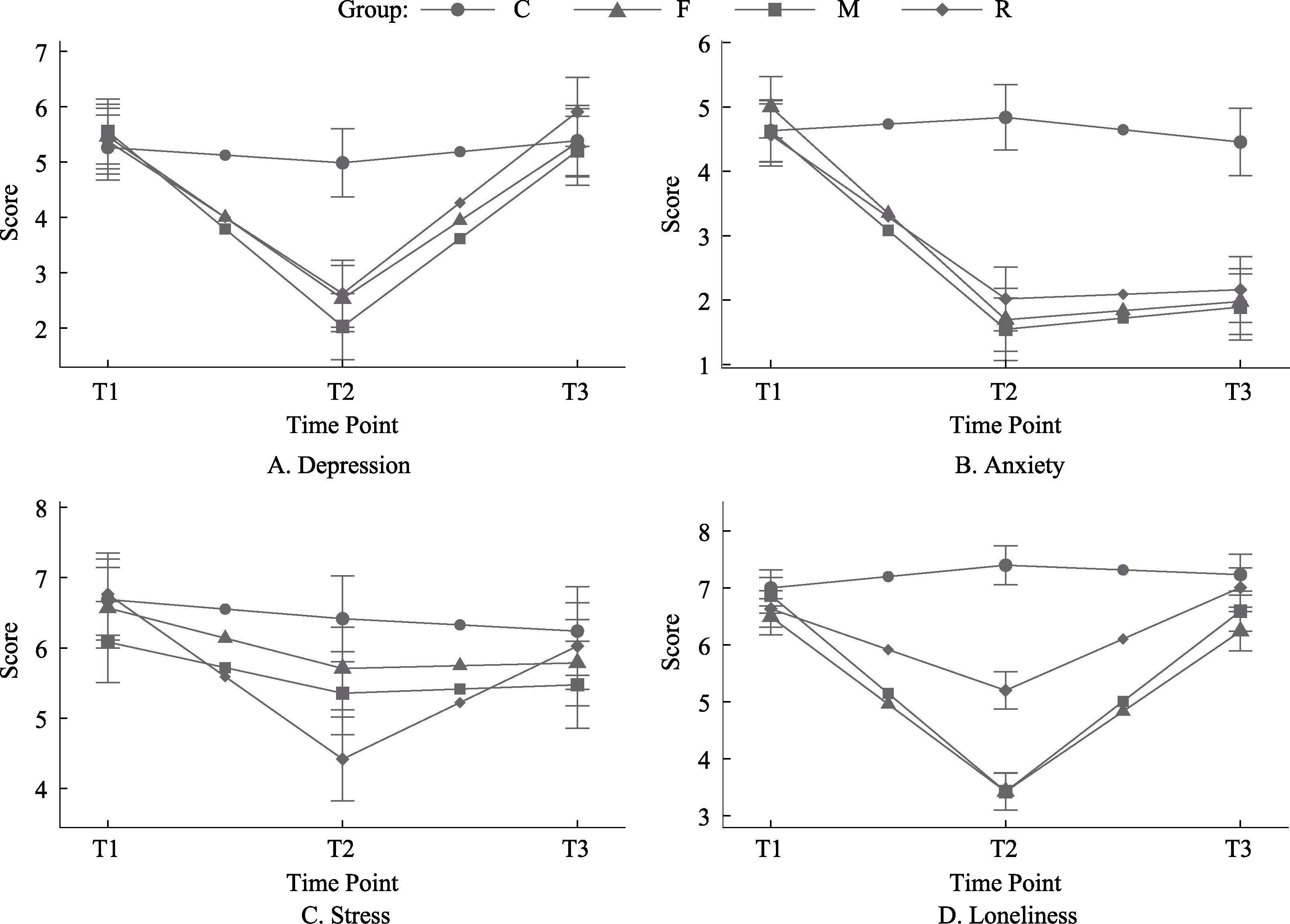
Figure 4. Trends in mental health indicators for each group across time points. Note. Data points represent estimated marginal means for each group at different time points, and error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. All models controlled for age and gender. Group C = control group; Group F = anthropomorphized female robot group; Group M = anthropomorphized male robot group; Group R = non-anthropomorphized robot group. T1 = pre-test; T2 = post-test; T3 = follow-up.
| [1] | Alazraki, L., Ghachem, A., Polydorou, N., Khosmood, F., & Edalat, A. (2021, December 13-15). An empathetic AI coach for self- attachment therapy. 2021 IEEE Third International Conference on Cognitive Machine Intelligence (CogMI 2021), Atlanta, GA, United States. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9750315 |
| [2] | Baldazzi, T., Bellomarini, L., Ceri, S., Colombo, A., Gentili, A., & Sallinger, E. (2023). Fine-tuning large enterprise language models via ontological reasoning. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.10723 |
| [3] | Bao, H. -W. -S. (2024). BruceR: Broadly useful convenient and efficient R functions. https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.bruceR |
| [4] | Barish, G., Marlotte, L., Drayton, M., Mogil, C., & Lester, P. (2023, August 3-5). Automatically enriching content for a behavioral health learning management system: A first look. The 9th World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (EECSS 2023), London, United Kingdom. https://doi.org/10.11159/cist23.125 |
| [5] | Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of statistical software, 67(1), 1-48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01 |
| [6] | Beck, A., LeBlanc, J. C., Morissette, K., Hamel, C., Skidmore, B., Colquhoun, H., … Stevens, A. (2021). Screening for depression in children and adolescents: A protocol for a systematic review update. Systematic Reviews, 10(1), 24. |
| [7] | Binz, M., & Schulz, E. (2022). Using cognitive psychology to understand GPT-3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 120(6), Article e2218523120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2218523120 |
| [8] |
Breit, M., Scherrer, V., Tucker-Drob, E. M., & Preckel, F. (2024). The stability of cognitive abilities: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal studies. Psychological Bulletin, 150(4), 399-439. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000425
doi: 10.1037/bul0000425 URL pmid: 38330347 |
| [9] | Bruckner, T., Scheffler, R., Shen, G., Yoon, J., Chisholm, D., Morris, J., Fulton, B. D., Poz, M. D. D., & Saxena, S. (2011). The mental health workforce gap in low- and middle-income countries: A needs-based approach. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 89(1), 184-194. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.10.082784 |
| [10] |
Cacioppo, S., Grippo, A. J., London, S., Goossens, L., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2015). Loneliness: Clinical import and interventions. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(2), 238-249. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691615570616
doi: 10.1177/1745691615570616 URL pmid: 25866548 |
| [11] |
Castonguay, L. G., Eubanks, C. F., Goldfried, M. R., Muran, J. C., & Lutz, W. (2015). Research on psychotherapy integration: Building on the past, looking to the future. Psychotherapy Research, 25(3), 365-382. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2015.1014010
doi: 10.1080/10503307.2015.1014010 URL pmid: 25800531 |
| [12] |
Cavanagh, J. F., & Allen, J. J. B. (2008). Multiple aspects of the stress response under social evaluative threat: An electrophysiological investigation. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 33(1), 41-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.09.007
URL pmid: 17964737 |
| [13] | Cerf, V. G. (2023). Large language models. Communications of the ACM, 66(8), Article 7. https://doi.org/10.1145/3606337 |
| [14] | Chan, C., & Li, F. (2023). Developing a natural language-based AI-chatbot for social work training: An illustrative case study. China Journal of Social Work, 16(2), 121-136. https://doi.org/10.1080/17525098.2023.2176901 |
| [15] | Chen, Y., Xing, X., Lin, J., Zheng, H., Wang, Z., Liu, Q., & Xu, X. (2023, December 6-10). SoulChat: Improving LLMs’ empathy, listening, and comfort abilities through fine-tuning with multi-turn empathy conversations. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, Sentosa, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.findings-emnlp.83 |
| [16] | Chiang, W. -L., Zheng, L., Sheng, Y., Angelopoulos, A. N., Li, T., Li, D., … Stoica, I. (2024). Chatbot arena: An open platform for evaluating LLMs by human preference. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.04132 |
| [17] | Craske, M. G., Hermans, D., & Vervliet, B. (2018). State-of-the-art and future directions for extinction as a translational model for fear and anxiety. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1742), Article 20170025. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2017.0025 |
| [18] |
Craske, M. G., Meuret, A. E., Ritz, T., Treanor, M., Dour, H., & Rosenfield, D. (2019). Positive affect treatment for depression and anxiety: a randomized clinical trial for a core feature of anhedonia. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 87(5), 457-471. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000396
doi: 10.1037/ccp0000396 URL pmid: 30998048 |
| [19] |
Cuijpers, P., van Straten, A., Andersson, G., & van Oppen, P. (2008). Psychotherapy for depression in adults: A meta-analysis of comparative outcome studies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76(6), 909-922. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013075
doi: 10.1037/a0013075 URL pmid: 19045960 |
| [20] | De Oliveira, C., Saka, M., Bone, L., & Jacobs, R. (2023). The role of mental health on workplace productivity: A critical review of the literature. Applied Health Economics and Health Policy, 21(2), 167-193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-022-00761-w |
| [21] |
Dickerson, S. S., Gruenewald, T. L., & Kemeny, M. E. (2004). When the social self is threatened: Shame, physiology, and health. Journal of Personality, 72(6), 1191-1216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2004.00295.x
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2004.00295.x URL pmid: 15509281 |
| [22] | Firth, J., Torous, J., Nicholas, J., Carney, R., Pratap, A., Rosenbaum, S., & Sarris, J. (2017). The efficacy of smartphone-based mental health interventions for depressive symptoms: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World Psychiatry, 16(3), 287-298. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20472 |
| [23] |
Folkman, S., Lazarus, R. S., Dunkel-Schetter, C., DeLongis, A., & Gruen, R. J. (1986). Dynamics of a stressful encounter: Cognitive appraisal, coping, and encounter outcomes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50(5), 992-1003. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.50.5.992
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.50.5.992 URL pmid: 3712234 |
| [24] | Fox, J., & Weisberg, S. (2019). An R companion to applied regression (3rd ed.). Sage. https://www.john-fox.ca/Companion/ |
| [25] | Giles, D. C. (2002). Parasocial interaction: A review of the literature and a model for future research. Media Psychology, 4(3), 279-305. https://doi.org/10.1207/S1532785XMEP0403_04 |
| [26] | Golden, A., & Aboujaoude, E. (2024). Describing the framework for AI tool assessment in mental health and applying it to a generative AI obsessive-compulsive disorder platform: Tutorial. JMIR formative research, 8(1), Article e62963. https://doi.org/10.2196/62963 |
| [27] | Gong, Y., Xie, X., Xu, R., & Luo, Y. (2010). Psychometric properties of the Chinese versions of DASS-21 in Chinese college students. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(4), 443-446. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2010.04.020 |
| [28] | Green, P., & MacLeod, C. J. (2016). SIMR: An R package for power analysis of generalized linear mixed models by simulation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7(4), 493-498. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12504 |
| [29] |
Hardy, G., Woods, D., & Wall, T. (2003). The impact of psychological distress on absence from work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(2), 306-314. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.2.306
URL pmid: 12731714 |
| [30] | Hassanein, K., & Head, M. (2007). Manipulating perceived social presence through the web interface and its impact on attitude towards online shopping. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 65(8), 689-708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2006.11.018 |
| [31] |
Hofmann, W., Schmeichel, B. J., & Baddeley, A. D. (2012). Executive functions and self-regulation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(3), 174-180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2012.01.006
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2012.01.006 URL pmid: 22336729 |
| [32] | Hofstede, G., Neuijen, B., Ohayv, D. D., & Sanders, G. (1990). Measuring organizational cultures: A qualitative and quantitative study across twenty cases. Administrative Science Quarterly, 35(2), 286-316. https://doi.org/10.2307/2393392 |
| [33] | Horton, D., & Wohl, R. R. (1956). Mass communication and para-social interaction. Psychiatry (New York), 19(3), 215-229. https://doi.org/10.1080/00332747.1956.11023049 |
| [34] | Huang, F., Ding, H., Liu, Z., Wu, P., Zhu, M., Li, A., & Zhu, T. (2020). How fear and collectivism influence public's preventive intention towards COVID-19 infection: A study based on big data from the social media. BMC Public Health, 20(1), Article 1707. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09674-6 |
| [35] | Huang, F., Li, S., Ding, H., Han, N., & Zhu, T. (2022). Does more moral equal less corruption? The different mediation of moral foundations between economic growth and corruption in China. Current Psychology, 42(30), 26125-26137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03735-2 |
| [36] | Huang, F., Sun, X., Mei, A., Wang, Y., Ding, H., & Zhu, T. (2025). LLM plus machine learning outperform expert rating to predict life satisfaction from self-statement text. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 12(3), 1092-1099. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcss.2024.3475413 |
| [37] | Hughes, M. E., Waite, L. J., Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2004). A short scale for measuring loneliness in large surveys: Results from two population-based studies. Social Psychology Quarterly, 26(6), 655-672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027504268574 |
| [38] | Hwang, K. -K. (1987). Face and Favor: The Chinese Power Game. American Journal of Sociology, 92(4), 944-974. https://doi.org/10.1086/228588 |
| [39] |
Ji, L. -J., Peng, K., & Nisbett, R. E. (2000). Culture, control, and perception of relationships in the environment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(5), 943-955. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.78.5.943
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.78.5.943 URL pmid: 10821200 |
| [40] | Ji, S., Zhang, T., Yang, K., Ananiadou, S., & Cambria, E. (2023). Rethinking large language models in mental health applications. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.11267 |
| [41] | Jiang, Q., Zhang, Y., & Pian, W. (2022). Chatbot as an emergency exist: Mediated empathy for resilience via human-AI interaction during the COVID-19 pandemic. Information Processing & Management, 59(6), Article 103074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2022.103074 |
| [42] | Jiang, Q., Zhao, F., Xie, X., Wang, X., Nie, J., Lei, L., & Wang, P. (2022). Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Cyberbullying Among Chinese Adolescents: A Mediation Model of Loneliness and Depression [Article]. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 37(1), 1105-1124. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260520917517 |
| [43] | Kalyan, K. S. (2023). A survey of GPT-3 family large language models including ChatGPT and GPT-4. Natural Language Processing Journal, 6, 100048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlp.2023.100048 |
| [44] | Karani, A., Deshpande, R., Jayswal, M., & Panda, R. (2021). Work-life balance and psychological distress: A structural equation modeling approach. Human Systems Management, 41(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3233/HSM-201145 |
| [45] |
Karyotaki, E., Efthimiou, O., Miguel, C., Maas genannt Bermpohl, F., Furukawa, T. A., Cuijpers, P., & for Depression Collaboration, I. P. D. M. -A. (2021). Internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy for depression: A systematic review and individual patient data network meta-analysis. Jama Psychiatry, 78(4), 361-371. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4364
doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4364 URL pmid: 33471111 |
| [46] | Kojima, T., Gu, S., Reid, M., Matsuo, Y., & Iwasawa, Y. (2022, December 9). Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, United States. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/hash/8bb0d291acd4acf06ef112099c16f326-Abstract-Conference.html |
| [47] | Konya-Baumbach, E., Biller, M., & von Janda, S. (2022). Someone out there? A study on the social presence of anthropomorphized chatbots. Computers in Human Behavior, 139(1), Article 107513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107513 |
| [48] | Lee, J., Daeho, L., & Lee, J. -G. (2024). Influence of rapport and social presence with an AI psychotherapy chatbot on users’ self-disclosure. International Journal of Human-computer Interaction, 40(7), 1620-1631. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2146227 |
| [49] | Liu, X., Jiao, G., Zhou, F., Kendrick, K., Yao, D., Xiang, S., … Becker, B. (2024). A neural signature for the subjective experience of threat anticipation under uncertainty. Nature Communications, 15(1), Article 1544. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.20.558716 |
| [50] |
Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the beck depression and anxiety inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33(3), 335-343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-U
doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-u URL pmid: 7726811 |
| [51] | Lozano, A., Fleming, S. L., Chiang, C. -C., & Shah, N. (2023, January 3-7). Clinfo.ai: An open source retrieval augmented large language model system for answering medical questions using scientific literature. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2024, Kohala Coast, HI, United States. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789811286421_0002 |
| [52] | Lu, J., Xu, X., Huang, Y., Li, T., Ma, C., Xu, G.,... Zhang, N. (2021). Prevalence of depressive disorders and treatment in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 8(11), 981-990. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00251-0 |
| [53] | Luo, Y., Yang, Z., Meng, F., Li, Y., Zhou, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). An empirical study of catastrophic forgetting in large language models during continual fine-tuning. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2308.08747 |
| [54] | Ma, Z., Mei, Y., & Su, Z. (2024, November 11-15). Understanding the benefits and challenges of using large language model-based conversational agents for mental well-being support. AMIA 2023 Annual Symposium, New Orleans, LA, United States. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38222348 |
| [55] | Ma, Z., Sansom, J., Peng, R., & Chai, J. (2023). Towards a holistic landscape of situated theory of mind in large language models. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.19619 |
| [56] | Martinengo, L., Lum, E., & Car, J. (2022). Evaluation of chatbot-delivered interventions for self-management of depression: Content analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 319(1), 598-607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2022.09.028 |
| [57] | McCarthy, J., Minsky, M. L., Rochester, N., & Shannon, C. E. (2006). A proposal for the dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence, august 31, 1955. AI Magazine, 27(4), 12-14. https://doi.org/10.1609/aimag.v27i4.1904 |
| [58] | Mitra, C., Huang, B., Darrell, T., & Herzig, R. (2024, June 17-21). Compositional chain-of-thought prompting for large multimodal models. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, United States. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.17076 |
| [59] | Morris, M. W., & Peng, K. (1994). Culture and cause: American and Chinese attributions for social and physical events. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(6), 949-971. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.67.6.949 |
| [60] | Munnukka, J., Talvitie-Lamberg, K., & Maity, D. (2022). Anthropomorphism and social presence in human-virtual service assistant interactions: The role of dialog length and attitudes. Computers in Human Behavior, 135(1), Article 107343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107343 |
| [61] | National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. (2019). Healthy China Action (2019—2030). https://www.nhc.gov.cn/guihuaxxs/c100133/201907/2a6ed52f1c264203b5351bdbbadd2da8.shtml |
| [62] | Noor, N., Hill, S., & Troshani, I. (2021). Artificial intelligence service agents: Role of parasocial relationship. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 62(5), 1009-1023. https://doi.org/10.1080/08874417.2021.1962213 |
| [63] | Norcross, J. C., & Goldfried, M. R. (2019). Handbook of psychotherapy integration (Third ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/med-psych/9780190690465.001.0001 |
| [64] | Noukhovitch, M., Lavoie, S., Strub, F., & Courville, A. C. (2023, December 10-16). Language model alignment with elastic reset. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2023, New Orleans, LA, United States. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/ paper/2023/hash/0a980183c520446f6b8afb6fa2a2c70e-Abstract-Conference.html |
| [65] | OpenAI, Achiam, J., Adler, S., Agarwal, S., Ahmad, L., Akkaya, I.,... Zoph, B. (2024). GPT-4 technical report. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.08774 |
| [66] |
Păsărelu, C. R., Andersson, G., Bergman Nordgren, L., & Dobrean, A. (2017). Internet-delivered transdiagnostic and tailored cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 46(1), 1-28. https://doi.org/10.1080/16506073.2016.1231219
URL pmid: 27712544 |
| [67] | Patel, V., Xiao, S., Chen, H., Hanna, F., Jotheeswaran, A., Luo, D., … Saxena, S. (2016). The magnitude of and health system responses to the mental health treatment gap in adults in India and China. The Lancet, 388(10063), 3074-3084. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00160-4 |
| [68] | Peng, K., Nisbett, R. E., & Wong, N. Y. C. (1997). Validity problems comparing values across cultures and possible solutions. Psychological Methods, 2(4), 329-344. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.2.4.329 |
| [69] | Perlman, D., & Peplau, L. A. (1981). Toward a social psychology of loneliness. Personal Relationships, 3, 31-56. |
| [70] |
Polinghorne, D. E., & Vernon, R. (2000). The psychotherapy relationship: Theory, research, and practice. Psychotherapy Research, 10(4), 494-497. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2000.104.9620561
doi: 10.1080/10503307.2000.104.9620561 URL pmid: 21756120 |
| [71] | R, Core Team. (2025). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. https://cran.rstudio.com/manuals.html |
| [72] | Rafferty, A., & Minbashian, A. (2018). Cognitive beliefs and positive emotions about change: Relationships with employee change readiness and change-supportive behaviors. Human Relations, 72(10), 1623-1650. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018726718809154 |
| [73] | Sajja, R., Sermet, Y., Cwiertny, D., & Demir, I. (2023). Platform-independent and curriculum-oriented intelligent assistant for higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), Article 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00412-7 |
| [74] | Saxena, S., Thornicroft, G., Knapp, M., & Whiteford, H. (2007). Resources for mental health: Scarcity, inequity, and inefficiency. The Lancet, 370(9590), 878-889. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61239-2 |
| [75] | Sezgin, E., Chekeni, F., Lee, J., & Keim, S. (2023). Clinical accuracy of large language models and Google search responses to postpartum depression questions: Cross-sectional study. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 25(1), Article e49240. https://doi.org/10.2196/49240 |
| [76] | Singla, D. R., Raviola, G., & Patel, V. (2018). Scaling up psychological treatments for common mental disorders: A call to action. World Psychiatry, 17(2), 226-227. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20532 |
| [77] |
Snippe, E., Elmer, T., Ceulemans, E., Smit, A., Lutz, W., & Helmich, M. (2024). The temporal order of emotional, cognitive, and behavioral gains in daily life during treatment of depression. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 92(8), 466-478. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000890
doi: 10.1037/ccp0000890 URL pmid: 38780574 |
| [78] | Stever, G. S. (2017). Parasocial theory: Concepts and measures. In The International Encyclopedia of Media Effects (pp. 1-12). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118783764.wbieme0069 |
| [79] | Sun, M., Zhou, H., Li, Y., Wang, J., Yang, W., Gong, Y., … Zhou, L. (2024). Professional characteristics, numbers, distribution and training of China's mental health workforce from 2000 to 2020: A scoping review. The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, 45(1), Article 100992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100992 |
| [80] | Toader, D., Boca, G., Toader, R., Macelaru, M., Toader, C., Ighian, D., & Rădulescu, A. (2019). The effect of social presence and chatbot errors on trust. Sustainability, 12(1), Article 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010256 |
| [81] | Tukachinsky, R., Walter, N., & Saucier, C. J. (2020). Antecedents and effects of parasocial relationships: A meta-analysis. Journal of Communication, 70(6), 868-894. https://doi.org/10.1093/joc/jqaa034 |
| [82] | Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., & Polosukhin, I. (2017, December 4-9). Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, United States. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017 |
| [83] | Wampold, B. E. (2015). How important are the common factors in psychotherapy? An update. World Psychiatry, 14(3), 270-277. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20238 |
| [84] | Webb, T., Holyoak, K. J., & Lu, H. (2023). Emergent analogical reasoning in large language models. Nature Human Behaviour, 7(9), 1526-1541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01659-w |
| [85] | Wei, J., Wang, X., Schuurmans, D., Bosma, M., Ichter, B., Xia, F., … Zhou, D. (2022, November 28-December 9). Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans, LA, United States. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022 |
| [86] | Wu, T., Terry, M., & Cai, C. J. (2022, April 30-May 5). AI chains: Transparent and controllable human-AI interaction by chaining large language model prompts. Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, United States. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491102.3517582 |
| [87] | Xue, X., Zhang, D., Sun, C., Shi, Y., Wang, R., Tan, T., … Hu, M. (2024). Xiaoqing: A Q & A model for glaucoma based on LLMs. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 174(1), Article 108399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108399 |
| [88] | You, Y., Tsai, C. -H., Li, Y., Ma, F., Heron, C., & Gui, X. (2023). Beyond self-diagnosis: How a chatbot-based symptom checker should respond. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 30(4), Article 64. https://doi.org/10.1145/3589959 |
| [89] | Yu, S., Kowitt, S., Fisher, E., & Li, G. (2018). Mental health in China: Stigma, family obligations, and the potential of peer support. Community Mental Health Journal, 54(1), 757-764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-017-0182-z |
| [90] |
Zhang, Y., Huang, F., Mo, L., Liu, X., & Zhu, T. (2025). Suicidal ideation data augmentation and recognition technology based on large language models. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(6), 987-1000. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.0987
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.0987 URL |
| [1] | JIAO Liying, LI Chang-Jin, CHEN Zhen, XU Hengbin, XU Yan. When AI “possesses” personality: Roles of good and evil personalities influence moral judgment in large language models [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(6): 929-946. |
| [2] | GAO Chenghai, DANG Baobao, WANG Bingjie, WU Michael Shengtao. The linguistic strength and weakness of artificial intelligence: A comparison between Large Language Model (s) and real students in the Chinese context [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(6): 947-966. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yanbo, HUANG Feng, MO Liuling, LIU Xiaoqian, ZHU Tingshao. Suicidal ideation data augmentation and recognition technology based on large language models [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(6): 987-1000. |
| [4] | FAN Yunge, MA Zijuan, LIN Weishi, ZHANG Rui, WANG Dongfang, FAN Fang. The concept and dimensional characteristics of spiritual support for older adults in contemporary China [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(12): 2131-2148. |
| [5] | WU Michael Shengtao, PENG Kaiping. Human advantages and psychological transformations in the era of artificial intelligence [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(11): 1879-1884. |
| [6] | LI Bin, RUI Jianxi, YU Weinan, LI Aimei, YE Maolin. When design meets AI: The impact of AI design products on consumers’ response patterns [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(11): 1914-1932. |
| [7] | WEI Xinni, YU Feng, PENG Kaiping. Perceived unsustainability decreases acceptance of artificial intelligence [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(11): 1973-1987. |
| [8] | YUAN Hang, LUO Siyang. Representation similarity analysis − A new perspective to study sociocultural change: Taking the mental health of elderly people as an example* [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(7): 938-953. |
| [9] | HUANG Shunsen, LAI Xiaoxiong, ZHANG Cai, ZHAO Xinmei, DAI Xinran, QI Mengdi, WANG Huanlei, WANG Wenrong, WANG Yun. Relationship between adolescents’ smartphone stress and mental health: Based on the multiverse-style analysis and intensive longitudinal method [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(6): 745-758. |
| [10] | WANG Chen, CHEN Weicong, HUANG Liang, HOU Suyu, WANG Yiwen. Robots abide by ethical principles promote human-robot trust? The reverse effect of decision types and the human-robot projection hypothesis [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(2): 194-209. |
| [11] | DU Xiayu, LAI Lizu, SHI Congrong, GUO Zihan, HAN Jing, ZHANG Tao, REN Zhihong. Internet-based cognitive bias modification of interpretation in health anxiety: A randomized controlled trial [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(10): 1351-1366. |
| [12] | HU Yiqiu, ZENG Zihao, PENG Liyi, WANG Hongcai, LIU Shuangjin, YANG Qin, FANG Xiaoyi. The effects of the parent-child relationship and parental educational involvement on adolescent depression, self-injury, and suicidal ideation: The roles of defeat and meaning in life [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(1): 129-141. |
| [13] | GE Xiaoyu, HOU Yubo. Confucian ideal personality traits (Junzi personality) and mental health: The serial mediating roles of self-control and authenticity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(4): 374-386. |
| [14] | JIANG Guangrong, LI Danyang, REN Zhihong, YAN Yupeng, WU Xinchun, ZHU Xu, YU Lixia, XIA Mian, LI Fenglan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin. The status quo and characteristics of Chinese mental health literacy [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(2): 182-198. |
| [15] | REN Zhihong, ZHAO Chunxiao, TIAN Fan, YAN Yupeng, LI Danyang, ZHAO Ziyi, TAN Mengling, JIANG Guangrong. Meta-analysis of the effect of mental health literacy intervention in Chinese people [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||