

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 714-728.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00714
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
TIAN Xinran1, HOU Wenxia1, OU Yuxiao1, YI Bing1, CHEN Wenfeng1( ), SHANG Junchen2(
), SHANG Junchen2( )
)
Received:2020-06-04
Published:2021-07-25
Online:2021-05-24
Contact:
CHEN Wenfeng,SHANG Junchen
E-mail:wchen@ruc.edu.cn;Junchen_20081@163.com
Supported by:TIAN Xinran, HOU Wenxia, OU Yuxiao, YI Bing, CHEN Wenfeng, SHANG Junchen. (2021). Average percept in ensemble perception is based on morphed average object: Evidence from average facial attractiveness. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(7), 714-728.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00714
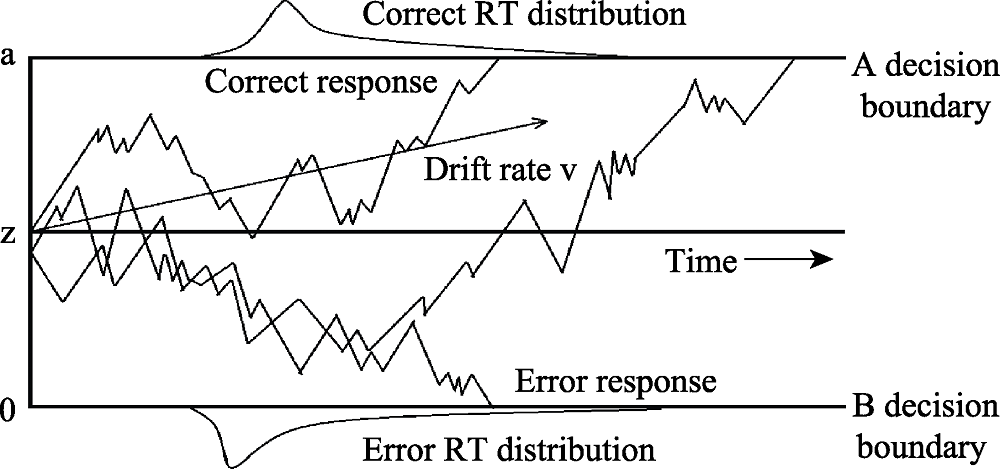
Figure 2. Diffusion Model (translated from Ratcliff & McKoon, 2008, Figure 2). A sample of three paths of the diffusion model is shown in figure. The information accumulates from the starting point (z) at an average rate (v) until the threshold of reaction A (a) or of reaction B (0) is reached. These paths vary from trial to trial due to random noise
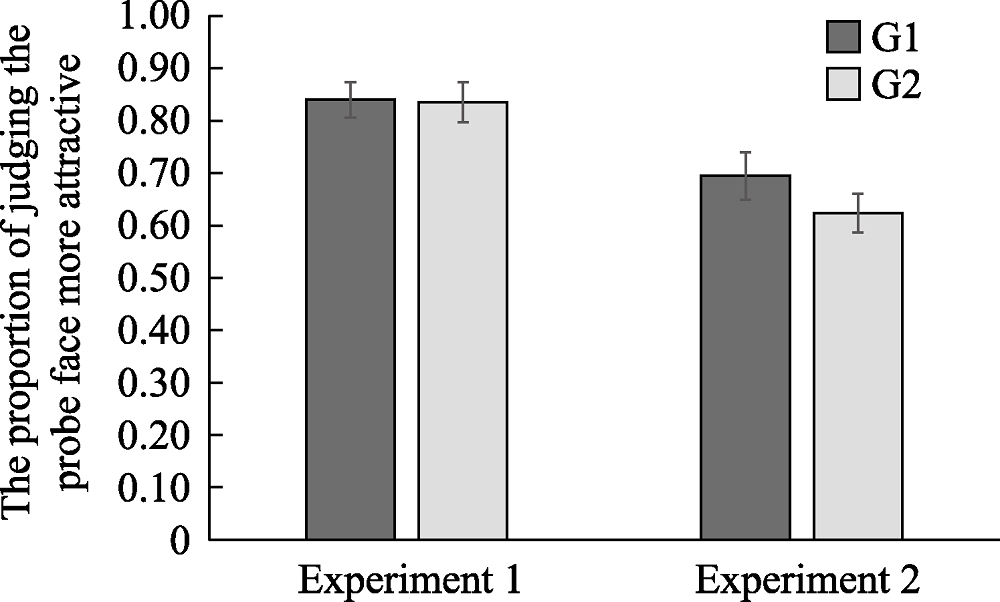
Figure 3. The participants judged the average faces to be more attractive under different conditions (Note: G1 is the set without the average faces and G2 is the set with the average faces)
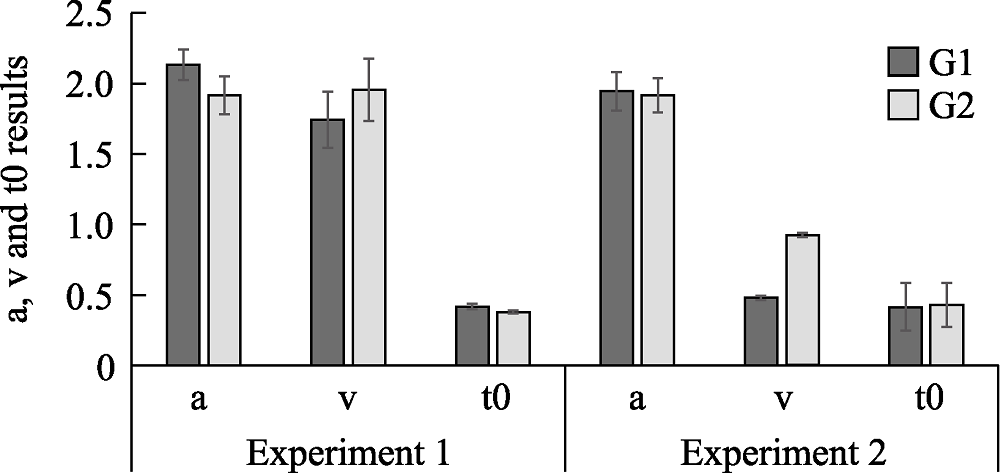
Figure 4. Experiment 1, Experiment 2 obtained the results of hierarchical diffusion model fitting (Note: G1 is the set without average faces and G2 is the set with average faces)
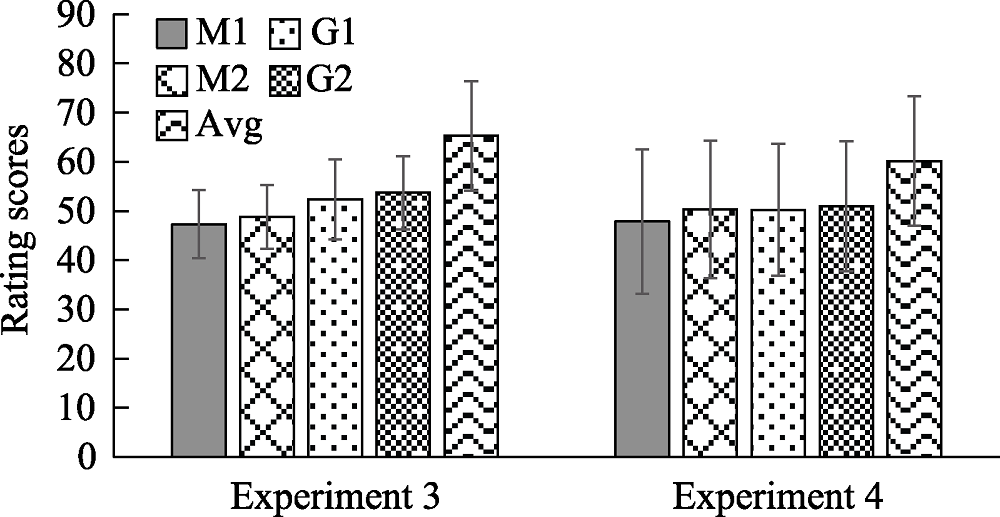
Figure 6. In Experiment 3,4, the results of attractiveness score (Note: M1 is the member mean of the set without the average face, M2 is the member mean of the set without the physical average face, G1 is the set without the average face, G2 is the set with the average face, AVG is the average face)
| [1] |
Abbas, Z.-A., & Duchaine, B. ( 2008). The role of holistic processing in judgments of facial attractiveness. Perception , 37 (8), 1187-1196.
doi: 10.1068/p5984 URL |
| [2] |
Alvarez, G.A. ( 2011). Representing multiple objects as an ensemble enhances visual cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 15 (3), 122-131.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.01.003 pmid: 21292539 |
| [3] |
Alvarez, G.A., & Oliva, A. ( 2008). The representation of simple ensemble visual features outside the focus of attention. Psychological Science , 19 (4), 392-398.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02098.x pmid: 18399893 |
| [4] |
Anderson, N.H. ( 1965). Averaging versus adding as a stimulus-combination rule in impression formation. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 70 (4), 394-400.
pmid: 5826027 |
| [5] |
Anderson, N. H., Lindner, R., & Lopes, L. L. ( 1973). Integration theory applied to judgments of group attractiveness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 26 (3), 400-408.
pmid: 4710110 |
| [6] |
Ariely, D. ( 2001). Seeing sets: Representation by statistical properties. Psychological Science , 12 (2), 157-162.
pmid: 11340926 |
| [7] |
Bauer, B. ( 2009). Does Stevens’s power law for brightness extend to perceptual brightness averaging? Psychological Record , 59 (2), 171-185.
doi: 10.1007/BF03395657 URL |
| [8] |
Bauer, B. ( 2017). Perceptual averaging of line length: Effects of concurrent digit memory load. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics , 79 (8),2510-2522.
doi: 10.3758/s13414-017-1388-4 URL |
| [9] |
Brady, T.F., & Alvarez, G. A. ( 2015). No evidence for a fixed object limit in working memory: Spatial ensemble representations inflate estimates of working memory capacity for complex objects. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition , 41 (3), 921-929.
doi: 10.1037/xlm0000075 URL |
| [10] |
Carragher, D. J., Lawrence, B. J., Thomas, N. A., & Nicholls, M. E. R. ( 2018). Visuospatial asymmetries do not modulate the cheerleader effect. Scientific Reports , 8 (1), 2548.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20784-5 pmid: 29416057 |
| [11] |
de Fockert, J. W., & Marchant, A. P. ( 2008). Attention modulates set representation by statistical properties. Perception & Psychophysics , 70 (5), 789-794.
doi: 10.3758/PP.70.5.789 URL |
| [12] |
Haberman, J., Brady, T. F., & Alvarez, G. A. ( 2015). Individual differences in ensemble perception reveal multiple, independent levels of ensemble representation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 144 (2), 432-446.
doi: 10.1037/xge0000053 URL |
| [13] |
Haberman, J., & Whitney, D. ( 2007). Rapid extraction of mean emotion and gender from sets of faces. Current Biology , 17 (17), R751-R753.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.039 URL |
| [14] | Haberman, J., & Whitney, D. ( 2009). Seeing the mean: Ensemble coding for sets of faces. Journal of Experimental Psychology , 35 (3), 718-734. |
| [15] | Haberman, J., & Whitney, D. ( 2012) Ensemble perception: Summarizing the scene and broadening the limits of visual processing. In J. Wolfe & L. Robertson (Eds.), Oxford series in visual cognition. From perception to consciousness: Searching with Anne Treisman (pp. 339-349). Oxford University Press . |
| [16] |
Hochstein, S., & Ahissar, M. ( 2002). View from the top: Hierarchies and reverse hierarchies in the visual system. Neuron , 36 (5), 791-804.
pmid: 12467584 |
| [17] |
Hochstein, S., Pavlovskaya, M., Bonneh, Y. S., & Soroker, N. ( 2015). Global statistics are not neglected. Journal of Vision , 15 (4), 7.
doi: 10.1167/15.4.7 pmid: 26288033 |
| [18] | Huang, L. ( 2015). Statistical properties demand as much attention as object features. Plos One , 10 (8), e0131191. |
| [19] | Ji, L., Chen, W., Loeys, T., & Pourtois, G. ( 2018). Ensemble representation for multiple facial expressions: Evidence for a capacity limited perceptual process. Journal of Vision , 18 (3), 1-19 |
| [20] |
Komori, M., Kawamura, S., & Ishihara, S. ( 2009). Averageness or symmetry: Which is more important for facial attractiveness? Acta Psychologica , 131 (2), 136-142.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2009.03.008 URL |
| [21] |
Langlois, J.H., & Roggman, L. A. ( 1990). Attractive faces are only average. Psychological Science , 1 (2), 115-121.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1990.tb00079.x URL |
| [22] | Li, H., Ji, L., Tong, K., Ren, N., Chen, W., Liu, C. H., & Fu, X. ( 2016). Processing of individual items during ensemble coding of facial expressions. Frontiers in Psychology , 7 , 1332 |
| [23] | Luo, A. X., & Zhou, G. ( 2018). Ensemble perception of facial attractiveness. Journal of Vision , 18 (8), 1-19. |
| [24] |
Maule, J., & Franklin, A. ( 2015). Effects of ensemble complexity and perceptual similarity on rapid averaging of hue. Journal of Vision , 15 (4), 6.
doi: 10.1167/15.4.6 pmid: 26114595 |
| [25] |
Myczek, K., & Simons, D. J. ( 2008). Better than average: Alternatives to statistical summary representations for rapid judgments of average size. Perception & Psychophysics , 70 (5), 772-788.
doi: 10.3758/PP.70.5.772 URL |
| [26] |
Neumann, M. F., Schweinberger, S. R., & Burton, A. M. ( 2013). Viewers extract mean and individual identity from sets of famous faces. Cognition , 128 (1), 56-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2013.03.006 pmid: 23587844 |
| [27] |
O’Toole, A. J., Price, T., Vetter, T., Bartlett, J. C., & Blanz, V. ( 1999). 3D shape and 2D surface textures of human faces: The role of “averages” in attractiveness and age. Image and Vision Computing , 18 (1), 9-19.
doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(99)00012-8 URL |
| [28] |
Parkes, L., Lund, J., Angelucci, A., Solomon, J. A., & Morgan, M. ( 2001). Compulsory averaging of crowded orientation signals in human vision. Nature Neuroscience , 4 (7), 739-744.
pmid: 11426231 |
| [29] |
Ratcliff, R. ( 1978). A theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review , 85 (2), 59-108.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.85.2.59 URL |
| [30] |
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. ( 2008). The diffusion decision model: Theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation , 20 (4), 873-922.
pmid: 18085991 |
| [31] |
Rhodes, G., Yoshikawa, S., Clark, A., Lee, K., McKay, R., & Akamatsu, S. ( 2001). Attractiveness of facial averageness and symmetry in non-western cultures: In search of biologically based standards of beauty. Perception , 30 (5), 611-625.
pmid: 11430245 |
| [32] |
Vandekerckhove, J., Tuerlinckx, F., & Lee, M. D. ( 2011). Hierarchical diffusion models for two-choice response times. Psychological Methods , 16 (1), 44-62.
doi: 10.1037/a0021765 pmid: 21299302 |
| [33] |
van Osch, Y., Blanken, I., Meijs, M. H. J., & van Wolferen, J. ( 2015). A group’s physical attractiveness is greater than the average attractiveness of its members: the group attractiveness effect. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 41 (4), 559-574.
doi: 10.1177/0146167215572799 URL |
| [34] | Vehtari, A., Gelman, A., Simpson, D., Carpenter, B., & Bürkner, P.-C. ( 2021). Rank-normalization, folding, and localization: An improved $\widehat{R}$ for assessing convergence of MCMC. Bayesian Analysis, Advance publication (2019) . doi: 10.1214/20-BA1221 |
| [35] |
Voss, A., Nagler, M., & Lerche, V. ( 2013). Diffusion models in experimental psychology: A practical introduction. Experimental Psychology , 60 (6), 385-402.
doi: 10.1027/1618-3169/a000218 URL |
| [36] |
Walker, D., & Vul, E., ( 2014). Hierarchical encoding makes individuals in a group seem more attractive. Psychological Science , 25 (1), 230-235.
doi: 10.1177/0956797613497969 pmid: 24163333 |
| [37] | Wang, Y, & Luo, Y. J. ( 2005). Standardization and assessment of college students’ facial expression of emotion. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology , 13 (4), 396-398. |
| [38] |
Whitney, D., & Leib, A. Y. ( 2018). Ensemble perception. Annual Review of Psychology , 69 (1), 105-129.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010416-044232 URL |
| [39] |
Willis, R. H. ( 1960). Stimulus pooling and social perception. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 60 (3), 365-373.
doi: 10.1037/h0048912 URL |
| [40] |
Ying, H., Burns, E., Choo, A. M., & Xu, H.( 2020). Temporal and spatial ensemble statistics are formed by distinct mechanisms. Cognition , 195 , 104128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104128 URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||