

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 1441-1452.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01441
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Guanghui, LI Yihan, DING Wen, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Liang( ), ZHANG Wenxin
), ZHANG Wenxin
Received:2022-07-18
Published:2023-09-25
Online:2023-06-09
Contact:
ZHANG Liang
E-mail:Zhangliang1@sdnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CHEN Guanghui, LI Yihan, DING Wen, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Wenxin. (2023). The association between transgressor’s remorse and victim’s forgiveness among young children: The activation effect of bystanders. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(9), 1441-1452.
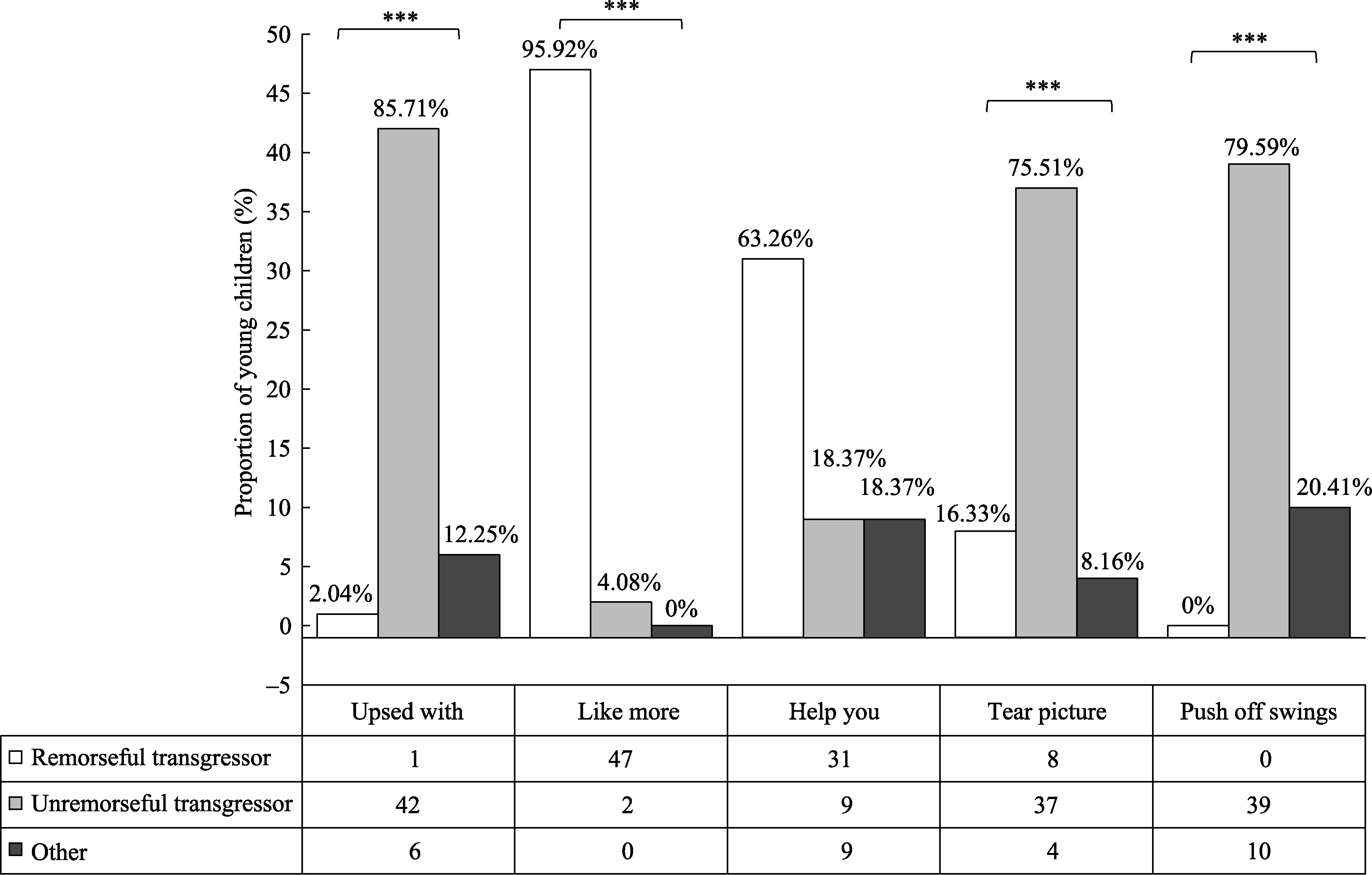
Figure 1. Proportion of young children in Study 1 who answered each test question in the hypothesized ways. Note. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
| [1] | Botto S. V., & Rochat P. (2018). Sensitivity to the evaluation of others emerges by 24 months. Developmental Psychology, 54(9), 1723−1734. |
| [2] | Botto S. V., & Rochat P. (2019). Evaluative audience perception (EAP): How children come to care about reputation. Child Development Perspectives, 13(3), 180−185. |
| [3] | Brooks J. H., & Reddon J. R. (2003). The two dimensional nature of remorse: An empirical inquiry into internal and external aspects. Journal of Offender Rehabilitation, 38(2), 1−15. |
| [4] | Cigala A., & Mori A. (2022). Perspective taking ability in psychologically maltreated children: A protective factor in peer social adjustment. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.816514 |
| [5] | Davis J. R., & Gold G. J. (2011). An examination of emotional empathy, attributions of stability, and the link between perceived remorse and forgiveness. Personality and Individual Differences, 50(3), 392−397. |
| [6] | Deem M. J., & Ramsey G. (2016). Guilt by association? Philosophical Psychology, 29(4), 570−585. |
| [7] | DiFonzo N., Alongi A., & Wiele P. (2020). Apology, restitution, and forgiveness after psychological contract breach. Journal of Business Ethics, 161(1), 53−69. |
| [8] | Domagała-Zyśk E. (2006). The significance of adolescents’ relationships with significant others and school failure. School Psychology International, 27(2), 232−247. |
| [9] | Draper K., Siegel C., White J., Solis C. M., & Mishna F. (2009). Preschoolers, parents, and teachers (PPT): A preventive intervention with an at risk population. International Journal of Group Psychotherapy, 59(2), 221−242. |
| [10] | Engelmann J. M., Herrmann E., & Tomasello M. (2012). Five-year olds, but not chimpanzees, attempt to manage their reputations. PLOS ONE, 7(10), Article e48433. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048433 |
| [11] | Engelmann J. M., Over H., Herrmann E., & Tomasello M. (2013). Young children care more about their reputation with ingroup members and potential reciprocators. Developmental Science, 16(6), 952−958. |
| [12] | Enright R. D. (1991). The moral development of forgiveness. In W. M. Kurtines & J. L. Gewirtz (Eds.), Handbook of moral behavior and development, Vol. 1. Theory; Vol. 2. Research; Vol. 3. Application (pp. 123−152). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. |
| [13] | Enright R. D., Gassin E. A., & Wu C. R. (1992). Forgiveness: A developmental view. Journal of Moral Education, 21(2), 99−114. |
| [14] | Fu G., Heyman G. D., Qian M., Guo T., & Lee K. (2015). Young children with a positive reputation to maintain are less likely to cheat. Developmental Science, 19(2), 275−283. |
| [15] | Grocke P., Rossano F., & Tomasello M. (2019). Preschoolers consider (absent) others when choosing a distribution procedure. PLOS ONE, 14(8), Article e0221186. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221186 |
| [16] | Günsoy C., Cross S. E., Uskul A. K., Adams G., & Gercek-Swing B. (2015). Avoid or fight back? Cultural differences in responses to conflict and the role of collectivism, honor, and enemy perception. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 46(8), 1081−1102. |
| [17] | Hair Jr J. F., Hult G. T. M., Ringle C. M., & Sarstedt M. (2017). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) (2th ed. pp. 56−60). Sage publications. |
| [18] | Hook J. N., Worthington E. L., Jr., & Utsey S. O. (2009). Collectivism, forgiveness, and social harmony. The Counseling Psychologist, 37(6), 821−847. |
| [19] | Izuma K., Saito D.N., Sadato N. (2010). The roles of the medial prefrontal cortex and striatum in reputation processing. Social Neuroscience, 5(2), 133−47. |
| [20] | Keltner D., & Anderson C. (2000). Saving face for darwin. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9(6), 187−192. |
| [21] | Leary M. R., Landel J. L., & Patton K. M. (1996). The motivated expression of embarrassment following a self presentational predicament. Journal of Personality, 64(3), 619−636. |
| [22] | Li J., Wang W., Yu J., & Zhu L. (2016). Young children’s development of fairness preference. Frontiers in Psychology, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01274 |
| [23] | Louie J. Y., Wang S., Fung J., & Lau A. (2014). Children’s emotional expressivity and teacher perceptions of social competence. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 39(6), 497−507. |
| [24] | Ma F., Zeng D., Xu F., Compton B. J., & Heyman G. D. (2020). Delay of gratification as reputation management. Psychological Science, 31(9), 1174−1182. |
| [25] | Markus H. R., & Kitayama S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98(2), 224−253. |
| [26] | Martínez-Lozano V., Sánchez-Medina J. A., & Goudena P. P. (2011). A cross-cultural study of observed conflicts between young children. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 42(6), 895−907. |
| [27] | McCullough M. E., Pedersen E. J., Tabak B. A., & Carter E. C. (2014). Conciliatory gestures promote forgiveness and reduce anger in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(30), 11211−11216. |
| [28] | Mills T. M. (1953). Power relations in three-person groups. American Sociological Review, 18(4), 351−357. |
| [29] | Nader-Grosbois N., Houssa M., & Mazzone S. (2013). How could theory of mind contribute to the differentiation of social adjustment profiles of children with externalizing behavior disorders and children with intellectual disabilities? Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(9), 2642−2660. |
| [30] | Ohtsubo Y., Matsunaga M., Himichi T., Suzuki K., Shibata E., Hori R., … Ohira H. (2019). Costly group apology communicates a group’s sincere “intention”. Social Neuroscience, 15(2), 244−254. |
| [31] | Ohtsubo Y., Matsunaga M., Tanaka H., Suzuki K., Kobayashi F., Shibata E., … Ohira H. (2018). Costly apologies communicate conciliatory intention: An fMRI study on forgiveness in response to costly apologies. Evolution and Human Behavior, 39(2), 249−256. |
| [32] | Oostenbroek J., & Vaish A. (2018). The emergence of forgiveness in young children. Child Development, 90(6), 1969−1986. |
| [33] |
Richland L. E., Chan T.-K., Morrison R. G., & Au T. K.-F. (2010). Young children’s analogical reasoning across cultures: Similarities and differences. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 105(1-2), 146−153.
doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2009.09.003 URL |
| [34] | Rochat P., Dias M. D. G., Guo Liping, Broesch T., Passos-Ferreira C., Winning A., & Berg B. (2009). Fairness in distributive justice by 3- and 5-year-olds across seven cultures. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 40(3), 416−442. |
| [35] | Shah J. (2003). Automatic for the people: How representations of significant others implicitly affect goal pursuit. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 661−681. |
| [36] | Shinohara A., Kanakogi Y., Okumura Y., & Kobayashi T. (2022). Children manage their reputation by caring about gossip. Social Development, 31(2), 455−465. |
| [37] | Tamis-LeMonda C. S., Way N., Hughes D., Yoshikawa H., Kalman R. K., & Niwa E. Y. (2008). Parents’ goals for children: The dynamic coexistence of individualism and collectivism in cultures and individuals. Social Development, 17(1), 183−209. |
| [38] | Tang Y., Harris P. L., Pons F., Zou H., Zhang W., & Xu Q. (2018). The understanding of emotion among young Chinese children. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 42(5), 512−517. |
| [39] | Vaish A., Carpenter M., & Tomasello M. (2011). Young children’s responses to guilt displays. Developmental Psychology, 47(5), 1248−1262. |
| [40] | Vaish A., & Oostenbroek J. (2021). Preferential forgiveness: The impact of group membership and remorse on preschoolers’ forgiveness. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 151(5), 1132−1140. |
| [41] | Vaish A., & Savell S. (2022). Young children value recipients who display gratitude. Developmental Psychology, 58(4), 680−692. |
| [42] | Van Hoorn J., Van Dijk E., Güroğlu B., & Crone E. A. (2016). Neural correlates of prosocial peer influence on public goods game donations during adolescence. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(6), 923−933. |
| [43] | Vlachou M., Andreou E., Botsoglou K., & Didaskalou E. (2011). Bully/victim problems among preschool children: A review of current research evidence. Educational Psychology Review, 23(3), 329−358. |
| [44] | Wang X. N., Hao Y., & Su Y. J. (2019). Effect of competition and collaboration on preschoolers’ resource distribution: The role of theory of mind and inhibitory control. Psychological Development and Education, 35(4), 385−392. |
| [45] | Weiner B. (1986). An attributional theory of motivation and emotion. New York: Springer. |
| [46] | Wu Z., Chen X., Gros-Louis J., & Su Y. (2018). “She is looking at me! Shall I share?” How Chinese and American preschoolers respond to eye gaze during sharing. Social Development, 27(2), 447−460. |
| [47] | Yau J., Smetana J. G., & Metzger A. (2009). Young Chinese children’s authority concepts. Social Development, 18(1), 210−229. |
| [48] | Zajonc R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149(3681), 269−274. |
| [49] | Zhang Q. P., Liu J. L., Huang H., Li J., & Kou Y. (2012). Adolescents’ prosocial intention in conflict situations: The effect of anticipated significant others’ viewpoint. Psychological Development and Education, 28(4), 368−375. |
| [50] | Zhang T., Sun H., & Fu A. Q. (2012). Forgiveness in collectivism culture and its enlightenment to forgiveness intervention. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(2), 265−273. |
| [51] | Zhang W. X., Li. X., Chen G. H., & Cao Y. M. (2021). The relationship between positive parenting and adolescent prosocial behavior: The mediating role of empathy and the moderating role of the oxytocin receptor gene. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(9), 976−991. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||