

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 612-625.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00612
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Hong-Zhi4,5, YANG Xing-Lan4, LI Qiu-Yue4, WEI Zi-Han1,2,3
Published:2023-04-25
Online:2022-12-30
LIU Hong-Zhi, YANG Xing-Lan, LI Qiu-Yue, WEI Zi-Han. (2023). Preference of dimension-based difference in intertemporal choice: Eye-tracking evidence. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(4), 612-625.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.00612
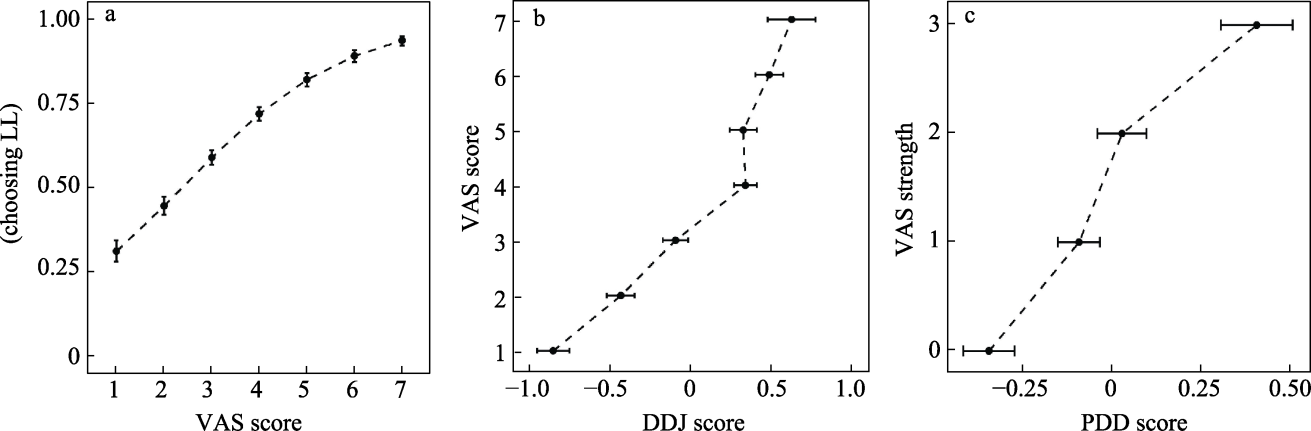
Figure 2. (a) Predictive effects of VAS scores on intertemporal choices, (b) the relationship between DDJ scores can VAS scores, and (c) the relationship between PDD scores and VAS strength in Experiment 1. Error lines represent 95% CI.
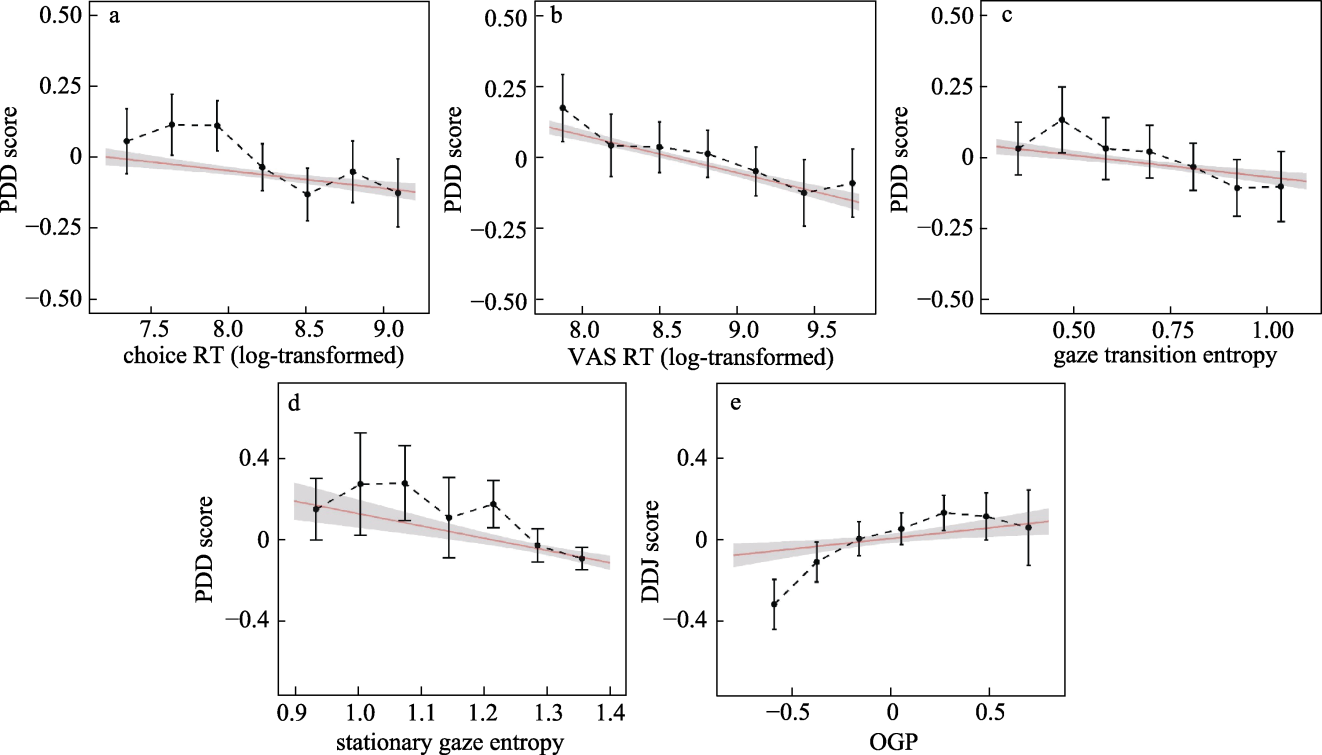
Figure 3. Relationship between (a) choice RT and PDD scores, (b) VAS RT and PDD scores, (c) gaze transition entropy and PDD scores, (d) stationary gaze entropy and PDD scores, and (e) OGP and DDJ scores in Experiment 1. The red lines represent the fitted line, and the error lines represent 95% CI.

Figure 4. (a) Predictive effects of VAS score on intertemporal choices, (b) the relationship between DDJ score can VAS score, and (c) the relationship between PDD score and VAS strength in Experiment 2. Error lines represent 95% CI.
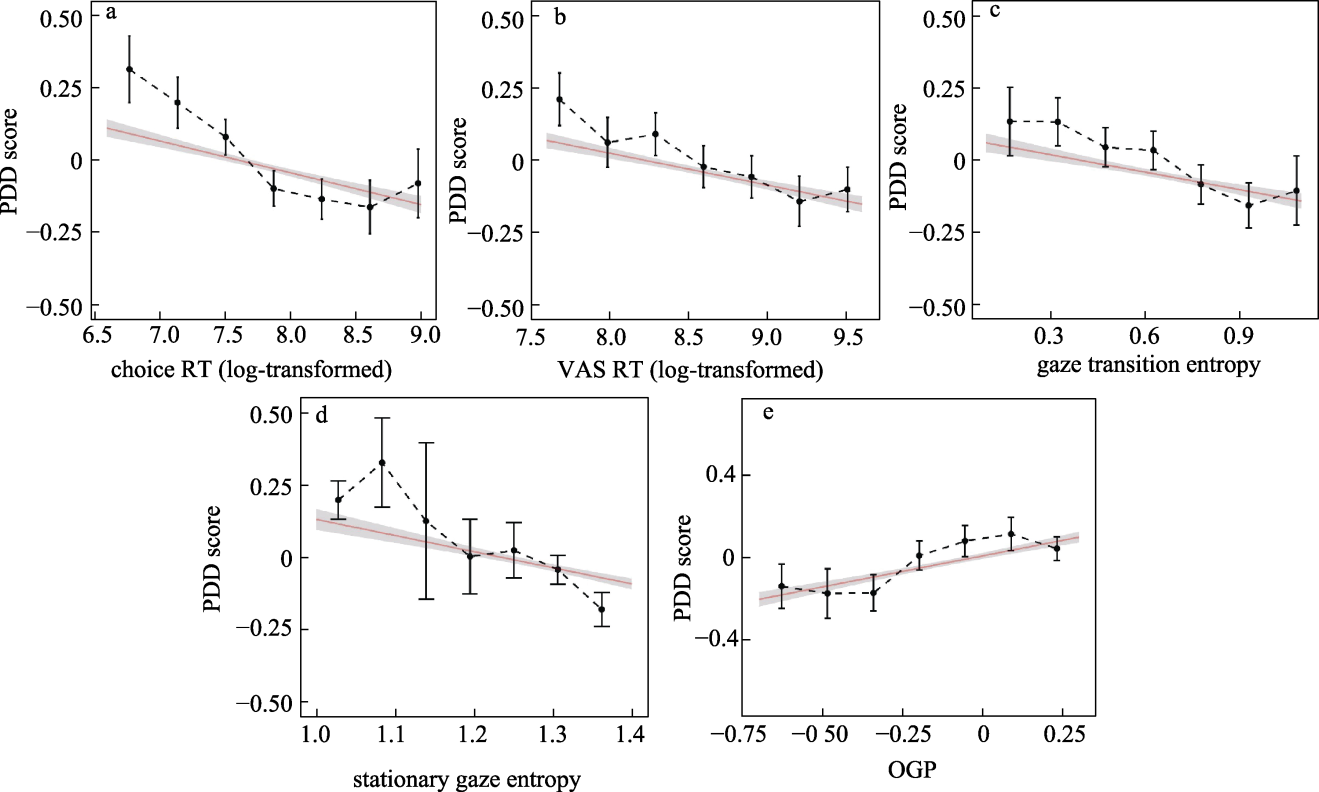
Figure 6. Relationship between (a) choice RT and PDD scores, (b) VAS RT and PDD scores, (c) gaze transition entropy and PDD scores, (d) stationary gaze entropy and PDD scores, and (e) OGP and DDJ scores in Experiment 2. The red lines represent the fitted line, and the error lines represent 95% CI.
| [1] |
Ainslie G.(1975). Specious reward: A behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychological Bulletin, 82(4), 463-496.
pmid: 1099599 |
| [2] |
Alós-Ferrer C., & Garagnani M.(2021). Choice consistency and strength of preference. Economics Letters, 198, 109672.
doi: 10.1016/j.econlet.2020.109672 URL |
| [3] |
Amasino D. R., Sullivan N. J., Kranton R. E., & Huettel S. A.(2019). Amount and time exert independent influences on intertemporal choice. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(4), 383-392.
doi: 10.1038/s41562-019-0537-2 pmid: 30971787 |
| [4] |
Arieli A., Ben-Ami Y., & Rubinstein A.(2011). Tracking decision makers under uncertainty. American Economic Journal: Microeconomics, 3, 68-76.
doi: 10.1257/mic.3.4.68 URL |
| [5] |
Ashby N. J. S., Yechiam E., & Ben-Eliezer D.(2018). The consistency of visual attention to losses and loss sensitivity across valuation and choice. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 147(12), 1791-1809.
doi: 10.1037/xge0000524 URL |
| [6] |
Baayen R. H., Davidson D. J., & Bates D. M.(2008). Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. Journal of Memory and Language, 59(4), 390-412.
doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005 URL |
| [7] | Bates D., Maechler M., Bolker B., & Walker S.(2015). lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4. R Package Version 1.1-9 Retrieved from http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4. |
| [8] |
Brandstätter E., & Körner C.(2014). Attention in risky choice. Acta Psychologica, 152, 166-176.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2014.08.008 pmid: 25226548 |
| [9] | Brysbaert M., & Stevens M.(2018). Power analysis and effect size in mixed effects models: A tutorial. Journal of Cognition, 1(1), Article 9. |
| [10] |
Cheng J., & González-Vallejo C.(2016). Attribute-wise vs. alternative-wise mechanism in intertemporal choice: Testing the proportional difference, trade-off, and hyperbolic models. Decision, 3(3), 190-215.
doi: 10.1037/dec0000046 URL |
| [11] |
Cuve H. C., Castiello S., Shiferaw B., Ichijo E., Catmur C., & Bird G.(2021). Alexithymia explains atypical spatiotemporal dynamics of eye gaze in autism. Cognition, 212, 104710.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104710 URL |
| [12] |
Dai J., & Busemeyer J. R.(2014). A probabilistic, dynamic, and attribute-wise model of intertemporal choice. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 143(4), 1489-1514.
doi: 10.1037/a0035976 URL |
| [13] |
Dai J., Pleskac T. J., & Pachur T.(2018). Dynamic cognitive models of intertemporal choice. Cognitive Psychology, 104, 29-56.
doi: S0010-0285(17)30211-6 pmid: 29587183 |
| [14] |
de Martino B., Fleming S. M., Garrett N., & Dolan R. J.(2013). Confidence in value-based choice. Nature Neuroscience, 16(1), 105-110.
doi: 10.1038/nn.3279 pmid: 23222911 |
| [15] |
Diederich A.(2003). MDFT account of decision making under time pressure. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 10(1), 157-166.
doi: 10.3758/BF03196480 URL |
| [16] |
di Stasi L. L., Diaz-Piedra C., Rieiro H., Sanchez Carrion J. M., Martin Berrido M., Olivares G., & Catena A.(2016). Gaze entropy reflects surgical task load. Surgical Endoscopy, 30(11), 5034-5043.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4851-8 URL |
| [17] |
Ericson K. M. M., White J. M., Laibson D., & Cohen J. D.(2015). Money earlier or later? Simple heuristics explain intertemporal choices better than delay discounting does. Psychological Science, 26(6), 826-833.
doi: 10.1177/0956797615572232 pmid: 25911124 |
| [18] |
Fisher G.(2021). Intertemporal choices are causally influenced by fluctuations in visual attention. Management Science, 67(8), 4961-4981.
doi: 10.1287/mnsc.2020.3732 URL |
| [19] |
Franco-Watkins A. M., Mattson R. E., & Jackson M. D.(2016). Now or later? Attentional processing and intertemporal choice. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 29(2-3), 206-217.
doi: 10.1002/bdm.1895 URL |
| [20] |
Frederick S., Loewenstein G., & O'donoghue T.(2002). Time discounting and time preference: A critical review. Journal of Economic Literature, 40(2), 351-401.
doi: 10.1257/jel.40.2.351 URL |
| [21] |
Gluth S., Kern N., Kortmann M., & Vitali C. L.(2020). Value-based attention but not divisive normalization influences decisions with multiple alternatives. Nature Human Behaviour, 4(6), 634-645.
doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-0822-0 pmid: 32015490 |
| [22] |
Jiang C. M., Liu H. Z., Cai X. H., & Li S.(2016). A process test of priority models of intertemporal choice. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(1), 59-72.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00059 URL |
| [23] |
Jiang Y., Jiang C., Hu T., & Sun H.(2022). Effects of emotion on intertemporal decision-making: Explanation from the single dimension priority model. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 54(2), 122-140.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00122 URL |
| [24] |
Judd C. M., Westfall J., & Kenny D. A.(2012). Treating stimuli as a random factor in social psychology: A new and comprehensive solution to a pervasive but largely ignored problem. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 103(1), 54-69.
doi: 10.1037/a0028347 pmid: 22612667 |
| [25] | Kahneman D., & Frederick S.(2002). Representativeness revisited:Attribute substitution in intuitive judgment. In T.Gilovich, D.Griffin, & D.Kahneman(Eds.), Heuristics and biases: The psychology of intuitive judgment (pp. 49-81). Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [26] | Konovalov A., & Krajbich I.(2019). Revealed strength of preference: Inference from response times. Judgment and Decision Making, 14(4), 381-394. |
| [27] |
Krajbich I., Armel C., & Rangel A.(2010). Visual fixations and the computation and comparison of value in simple choice. Nature Neuroscience, 13(10), 1292-1298.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2635 pmid: 20835253 |
| [28] |
Krajbich I., Lu D., Camerer C., & Rangel A.(2012). The attentional drift-diffusion model extends to simple purchasing decisions. Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 193.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00193 pmid: 22707945 |
| [29] |
Krajbich I., & Rangel A.(2011). Multialternative drift-diffusion model predicts the relationship between visual fixations and choice in value-based decisions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(33), 13852-13857.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101328108 URL |
| [30] | Krejtz K., Szmidt T., Duchowski A. T., & Krejtz I.(2014). Entropy-based statistical analysis of eye movement transitions. Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, 159-166. |
| [31] | Kuznetsova A., Brockhoff P. B., & Christensen R. H. B.(2017). lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. Journal of Statistical Software, 82(13), 1-26. |
| [32] |
Laibson D.(1997). Golden eggs and hyperbolic discounting. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 112(2), 443-478.
doi: 10.1162/003355397555253 URL |
| [33] |
Leland J. W.(2002). Similarity judgments and anomalies in intertemporal choice. Economic Inquiry, 40(4), 574-581.
doi: 10.1093/ei/40.4.574 URL |
| [34] |
Li S.(2004). A behavioral choice model when computational ability matters. Applied Intelligence, 20, 147-163.
doi: 10.1023/B:APIN.0000013337.01711.c7 URL |
| [35] | Li S.(2016). An equate-to-differentiate way of decision-making. Shanghai, China: East China Normal University Press. |
| [36] |
Liu H. Z., Jiang C. M., Rao L. L., & Li S.(2015). Discounting or priority: Which rule dominates the intertemporal choice process? Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(4), 522-532.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00522 URL |
| [37] |
Liu H. Z., Lyu X. K., Wei Z. H., Mo W. L., Luo J. R., & Su X. Y.(2021). Exploiting the dynamics of eye gaze to bias intertemporal choice. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 34(3), 419-431.
doi: 10.1002/bdm.2219 URL |
| [38] |
Liu H. Z., Wei Z. H., & Li P.(2021). Influence of the manner of information presentation on risky choice. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 650206.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.650206 URL |
| [39] |
Liu H. Z., Zhou Y. B., Wei Z. H., & Jiang C. M.(2020). The power of last fixation: Biasing simple choices by gaze-contingent manipulation. Acta Psychologica, 208, 103106.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2020.103106 URL |
| [40] |
Loewenstein G., & Prelec D.(1992). Anomalies in intertemporal choice: Evidence and an interpretation. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 107(2), 573-597.
doi: 10.2307/2118482 URL |
| [41] |
Moran R., Teodorescu A. R., & Usher M.(2015). Post choice information integration as a causal determinant of confidence: Novel data and a computational account. Cognitive Psychology, 78, 99-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2015.01.002 pmid: 25868113 |
| [42] |
Read D.(2001). Is time-discounting hyperbolic or subadditive? Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 23(1), 5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011198414683 URL |
| [43] |
Read D., & Scholten M.(2012). Tradeoffs between sequences: Weighing accumulated outcomes against outcome-adjusted delays. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 38 (6), 1675-1688.
doi: 10.1037/a0028216 URL |
| [44] |
Reeck C., Wall D., & Johnson E. J.(2017). Search predicts and changes patience in intertemporal choice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(45), 11890-11895.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707040114 URL |
| [45] | Rodriguez C. A., Turner B. M., & McClure S. M.(2014). Intertemporal choice as discounted value accumulation. PLoS One, 9(2), e90138. |
| [46] |
Samuelson P. A.(1937). A note on measurement of utility. The Review of Economic Studies, 4(2), 155-161.
doi: 10.2307/2967612 URL |
| [47] |
Scholten M., & Read D.(2006). Discounting by intervals: A generalized model of intertemporal choice. Management Science, 52(9), 1424-1436.
doi: 10.1287/mnsc.1060.0534 URL |
| [48] |
Scholten M., & Read D.(2010). The psychology of intertemporal tradeoffs. Psychological Review, 117(3), 925-944.
doi: 10.1037/a0019619 pmid: 20658858 |
| [49] |
Shannon C. E.(1948). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27(3), 379-423.
doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x URL |
| [50] |
Shiferaw B., Downey L., & Crewther D.(2019). A review of gaze entropy as a measure of visual scanning efficiency. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 96, 353-366.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.007 URL |
| [51] |
Shiferaw B. A., Downey L. A., Westlake J., Stevens B., Rajaratnam S. M. W., Berlowitz D. J.,... Howard M. E.(2018). Stationary gaze entropy predicts lane departure events in sleep-deprived drivers. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2220.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20588-7 pmid: 29396509 |
| [52] |
Stewart N., Hermens F., & Matthews W. J.(2015). Eye movements in risky choice. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 29(2-3), 116-136.
doi: 10.1002/bdm.1854 URL |
| [53] |
Su Y., Rao L. L., Sun H. Y., Du X. L., Li X., & Li S.(2013). Is making a risky choice based on a weighting and adding process? An eye-tracking investigation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 39 (6), 1765-1780.
doi: 10.1037/a0032861 URL |
| [54] |
Sui X. Y., Liu H. Z., & Rao L. L.(2020). The timing of gaze-contingent decision prompts influences risky choice. Cognition, 195, 104077.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104077 URL |
| [55] |
Sullivan N. J., & Huettel S. A.(2021). Healthful choices depend on the latency and rate of information accumulation. Nature Human Behaviour, 5(12), 1698-1706.
doi: 10.1038/s41562-021-01154-0 pmid: 34226708 |
| [56] |
Tversky A., & Shafir E.(1992). Choice under conflict: The dynamics of deferred decision. Psychological Science, 3(6), 358-361.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1992.tb00047.x URL |
| [57] |
Wei Z. H., & Li X. (2015). Decision process tracing: Evidence from eye-movement data. Advances in Psychological Science, 23(12), 2029-2041.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2015.02029 URL |
| [1] | SHEN Si-Chu, Khishignyam BAZARVAANI, DING Yang, MA Jia-Tao, YANG Shu-Wen, KUANG Yi, XU Ming-Xing, John E. TAPLIN, LI Shu. Changes in the intertemporal choices of people in or close to Chinese culture can predict their self-rated survival achievement in the fight against COVID-19: A cross-national study in 18 Asian, African, European, American, and Oceanian countries [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(3): 435-454. |
| [2] | SONG Xiyan, CHENG Yahua, XIE Zhouxiutian, GONG Nanyan, LIU Lei. The influence of anger on delay discounting: The mediating role of certainty and control [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(5): 456-468. |
| [3] | ZHOU Lei, LI Ai-Mei, ZHANG Lei, LI Shu, LIANG Zhu-Yuan. Similarity in processes of risky choice and intertemporal choice: The case of certainty effect and immediacy effect [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(3): 337-352. |
| [4] | WANG Peng, WANG Xiaotian, GAO Juan, LI Xialan, XU Jing. Adaptive time management: The effects of death awareness on time perception and intertemporal choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(12): 1341-1350. |
| [5] | XU Lan,CHEN Quan,CUI Nan,LU Kaili. Enjoy the present or wait for the future? Effects of individuals’ view of time on intertemporal choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(1): 96-105. |
| [6] | LI Aimei, WANG Haixia, SUN Hailong, XIONG Guanxing, YANG Shaoli . The nudge effect of “foresight for the future of our children”: Pregnancy and environmental intertemporal choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(8): 858-867. |
| [7] | JIANG Cheng-Ming, LIU Hong-Zhi, CAI Xiao-Hong, LI Shu. A process test of priority models of intertemporal choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(1): 59-72. |
| [8] | LIU Hong-Zhi, JIANG Cheng-Ming, RAO Li-Lin, LI Shu. Discounting or Priority: Which Rule Dominates the Intertemporal Choice Process? [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(4): 522-532. |
| [9] | LI Aimei, PENG Yuan, XIONG Guanxing. Are Pregnant Women More Foresighted? #br# The Effect of Pregnancy on Intertemporal Choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(11): 1360-1370. |
| [10] | CHEN Haixian;HE Guibing. The Effect of Psychological Distance on Intertemporal Choice and Risky Choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(5): 677-690. |
| [11] | SUO Tao;ZHANG Feng;ZHAO Guoxiang;LI Hong. The Influence of Time Perception Difference on Intertemporal Choice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(2): 165-173. |
| [12] | MA Wen-Juan,SUO Tao,LI Ya-Dan,LUO Li-Zhu,FENG Ting-Yong,LI Hong. Dissecting the Win-Loss Framing Effect of Intertemporal Choice: Researches from Intertemporal Choice of Money-Gain & Loss [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2012, 44(8): 1038-1046. |
| [13] | CHEN Hai-Xian, HE Gui-Bing. The Effect of Construal Level on Intertemporal Choice and Risky Choice [J]. , 2011, 43(04): 442-452. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||