

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 385-397.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00385
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Yijuan, HU Xinmu, MAI Xiaoqin( )
)
Received:2021-04-15
Published:2022-04-25
Online:2022-02-21
Contact:
MAI Xiaoqin
E-mail:maixq@ruc.edu.cn
HE Yijuan, HU Xinmu, MAI Xiaoqin. (2022). Influence of empathic concern on fairness-related decision making: Evidence from ERP. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 54(4), 385-397.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2022.00385
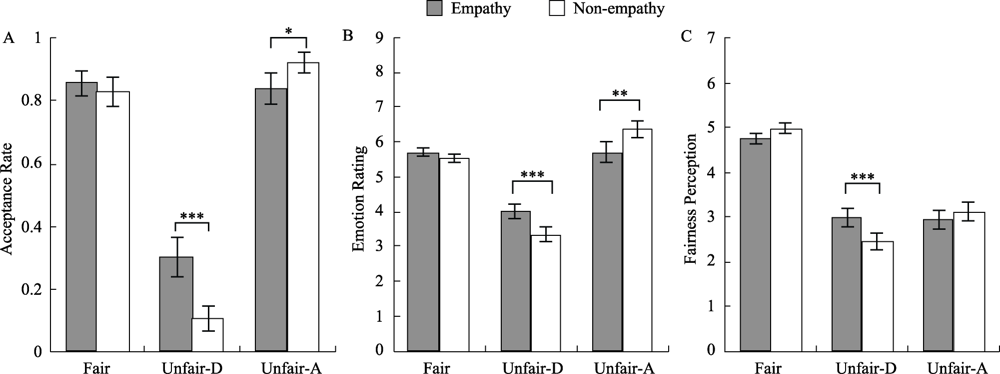
Figure 2. Histogram of interaction effect between empathy and fairness on ARs (A), emotion ratings (range from 1~9) (B) and fairness perception (range from 1~7) (C). Unfair-D means disadvantageous unfair. Unfair-A means advantageous unfair. Note. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
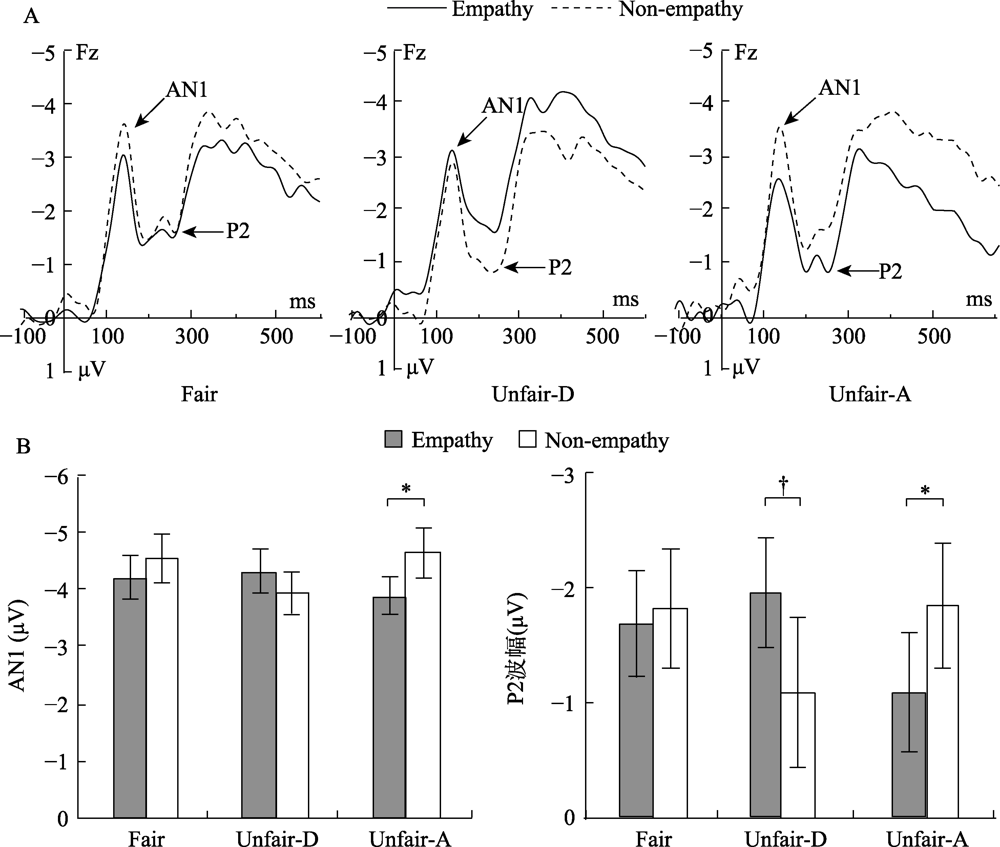
Figure 3. (A)The Grand-average ERP waveforms from Fz electrode sites for the 3 fairness conditions, respectively; (B) Histogram of interaction effect between empathy and fairness on AN1 and P2. Unfair-D means disadvantageous unfair. Unfair-A means advantageous unfair. Note. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM); † p < 0.1, * p < 0.01.
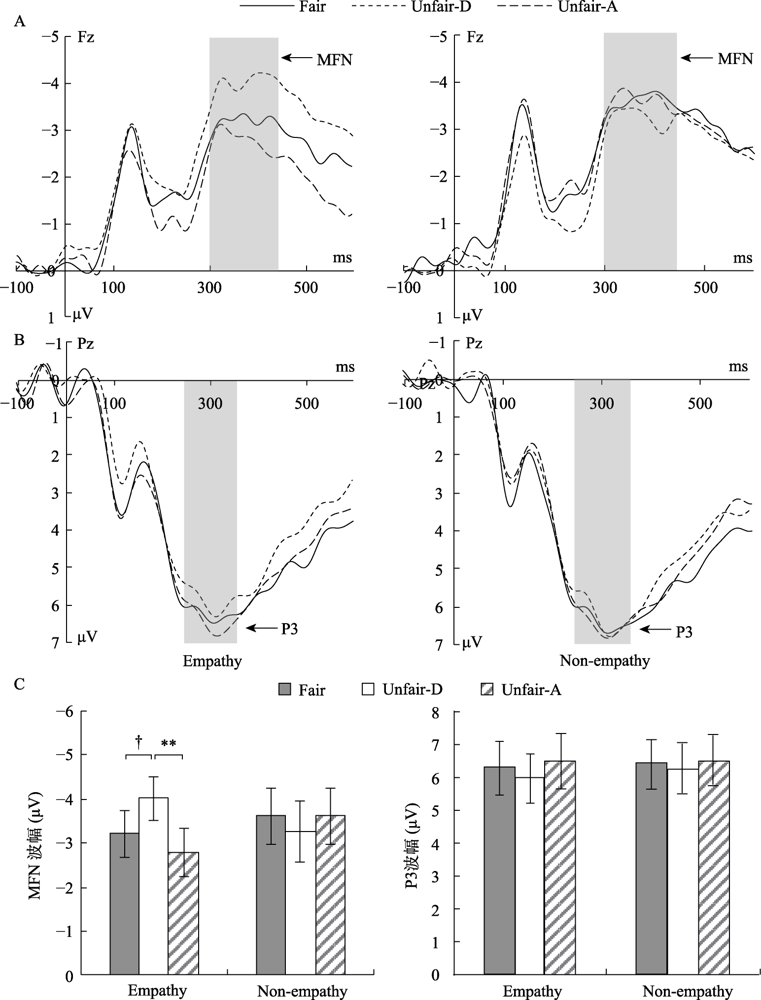
Figure 4. The Grand-average ERP waveforms from Fz(A) and Pz(B) sites for empathy and non-empathy condition, respectively; (C) Histogram of interaction effect between empathy and fairness on MFN and P3.Unfair-D means disadvantageous unfair. Unfair-A means advantageous unfair. Note. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM); † p < 0.1, ** p < 0.01.
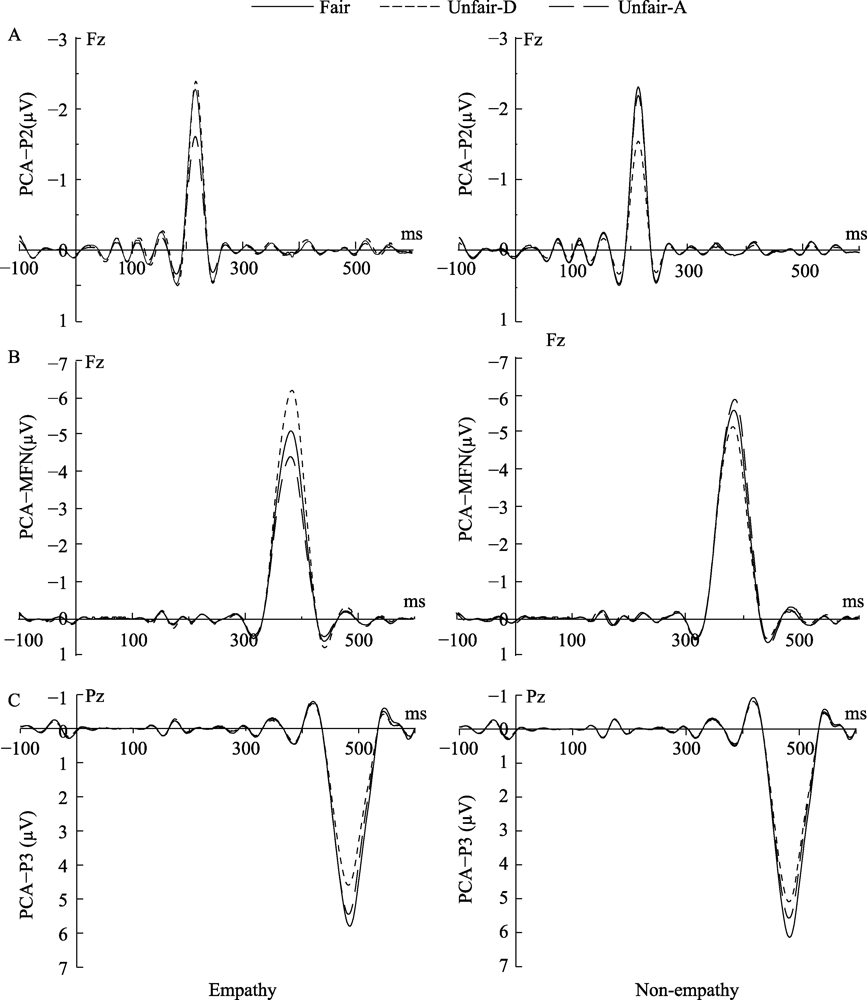
Figure 5. Grand-average waveforms of PCA-P2 (A) and PCA-MFN (B) at the Fz electrode site and PCA-P3 (C) at the Pz electrode site. Unfair-D means disadvantageous unfair. Unfair-A means advantageous unfair.
| [1] |
Annic, A., Bocquillon, P., Bourriez, J.-L., Derambure, P., & Dujardin, K. (2014). Effects of stimulus-driven and goal-directed attention on prepulse inhibition of the cortical responses to an auditory pulse. Clinical Neurophysiology, 125(8), 1576-1588. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.12.002
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.12.002 URL |
| [2] | Batson, C. D. (1991). The altruism question: Toward a social-psychological answer. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. |
| [3] |
Batson, C. D., & Ahmad, N. (2001). Empathy-induced altruism in a prisoner’s dilemma II: What if the target of empathy has defected? European Journal of Social Psychology, 31(1), 25-36. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.26
doi: 10.1002/ejsp.26 URL |
| [4] |
Batson, C. D., Chang, J., Orr, R., & Rowland, J. (2002). Empathy, attitudes, and action: Can feeling for a member of a stigmatized group motivate one to help the group? Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28(12), 1656-1666. doi: 10.1177/014616702237647
doi: 10.1177/014616702237647 URL |
| [5] |
Batson, C. D., Eklund, J. H., Chermok, V. L., Hoyt, J. L., & Ortiz, B. G. (2007). An additional antecedent of empathic concern: Valuing the welfare of the person in need. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93(1), 65-74. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.93.1.65
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.93.1.65 URL |
| [6] |
Batson, C. D., & Moran, T. (1999). Empathy-induced altruism in a prisoner’s dilemma. European Journal Of Social Psychology, 29(7), 909-924. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0992(199911)29:7<909::AID-EJSP965>3.0.CO;2-L
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0992(199911)29:7<909::AID-EJSP965>3.0.CO;2-L URL |
| [7] |
Batson, C. D., Polycarpou, M. P., Harmon-Jones, E., Imhoff, H. J., Mitchener, E. C., Bednar, L. L., ... Highberger, L. (1997). Empathy and attitudes: Can feeling for a member of a stigmatized group improve feelings toward the group? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72(1), 105-118. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.105
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.105 pmid: 9008376 |
| [8] |
Batson, C. D., & Shaw, L. L. (1991). Evidence for altruism: Toward a pluralism of prosocial motives. Psychological Inquiry, 2(2), 107-122. doi: 10.1207/s15327965pli0202_1
doi: 10.1207/s15327965pli0202_1 URL |
| [9] |
Bellebaum, C., Polezzi, D., & Daum, I. (2010). It is less than you expected: The feedback-related negativity reflects violations of reward magnitude expectations. Neuropsychologia, 48(11), 3343-3350. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.07.023
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.07.023 URL |
| [10] |
Bernhardt, B. C., & Singer, T. (2012). The neural basis of empathy. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 35, 1-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150536
doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150536 pmid: 22715878 |
| [11] |
Bieleke, M., Gollwitzer, P. M., Oettingen, G., & Fischbacher, U. (2017). Social value orientation moderates the effects of intuition versus reflection on responses to unfair ultimatum offers. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 30(2), 569-581. doi: 10.1002/bdm.1975
doi: 10.1002/bdm.1975 URL |
| [12] |
Boksem, M. A. S., & de Cremer, D. (2010). Fairness concerns predict medial frontal negativity amplitude in ultimatum bargaining. Social Neuroscience, 5(1), 118-128. doi: 10.1080/17470910903202666
doi: 10.1080/17470910903202666 URL |
| [13] |
Boudreau, C., McCubbins, M. D., & Coulson, S. (2009). Knowing when to trust others: An ERP study of decision making after receiving information from unknown people. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4(1), 23-34. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsn034
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsn034 pmid: 19015085 |
| [14] |
Bouwer, F. L., Honing, H., & Slagter, H. A. (2020). Beat-based and memory-based temporal expectations in rhythm: Similar perceptual effects, different underlying mechanisms. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 32(7), 1221-1241. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01529
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01529 pmid: 31933432 |
| [15] |
Bradley, M. M., Codispoti, M., Cuthbert, B. N., & Lang, P. J. (2001). Emotion and motivation I: Defensive and appetitive reactions in picture processing. Emotion, 1(3), 276-298. doi: 10.1037//1528-3542.1.3.276
doi: 10.1037//1528-3542.1.3.276 pmid: 12934687 |
| [16] |
Camerer, C. F. (2003). Behavioural studies of strategic thinking in games. Trends In Cognitive Sciences, 7(5), 225-231. doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(03)00094-9
doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(03)00094-9 pmid: 12757825 |
| [17] |
Campanha, C., Minati, L., Fregni, F., & Boggio, P. S. (2011). Responding to unfair offers made by a friend: Neuroelectrical activity changes in the anterior medial prefrontal cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(43), 15569-15574. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.1253-11.2011
doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.1253-11.2011 URL |
| [18] |
Carretie, L., Hinojosa, J. A., Martin-Loeches, M., Mercado, F., & Tapia, M. (2004). Automatic attention to emotional stimuli: Neural correlates. Human Brain Mapping, 22(4), 290-299. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20037
doi: 10.1002/hbm.20037 URL |
| [19] |
Decety, J., & Lamm, C. (2006). Human empathy through the lens of social neuroscience. The Scientific World Journal, 6, 1146-1163. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2006.221
doi: 10.1100/tsw.2006.221 URL |
| [20] |
Decety, J., Yang, C.-Y., & Cheng, Y. (2010). Physicians down-regulate their pain empathy response: An event-related brain potential study. Neuroimage, 50(4), 1676-1682. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.025
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.025 pmid: 20080194 |
| [21] |
DeWall, C. N., MacDonald, G., Webster, G. D., Masten, C. L., Baumeister, R. F., Powell, C., ... Eisenberger, N. I. (2010). Acetaminophen reduces social pain: Behavioral and neural evidence. Psychological Science, 21(7), 931-937. doi: 10.1177/0956797610374741
doi: 10.1177/0956797610374741 URL |
| [22] |
Duzcu, H., Ozkurt, T. E., Mapelli, I., & Hohenberger, A. (2019). N1-P2: Neural markers of temporal expectation and response discrimination in interval timing. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis, 79(2), 193-204. doi: 10.21307/ane-2019-0017
doi: 10.21307/ane-2019-0017 URL |
| [23] |
Eisenberger, N. I. (2015). Social pain and the brain: Controversies, questions, and where to go from here. Annual Review Of Psychology, 66 (601-629). doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115146
doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115146 pmid: 25251482 |
| [24] |
Eisenberger, N. I., Lieberman, M. D., & Williams, K. D. (2003). Does rejection hurt? An fMRI study of social exclusion. Science, 302(5643), 290-292. doi: 10.1126/science.1089134
doi: 10.1126/science.1089134 pmid: 14551436 |
| [25] |
Fan, Y., & Han, S. (2008). Temporal dynamic of neural mechanisms involved in empathy for pain: An event-related brain potential study. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 160-173. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.07.023
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.07.023 URL |
| [26] |
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A.-G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149-1160. doi: 10.3758/brm.41.4.1149
doi: 10.3758/brm.41.4.1149 URL |
| [27] |
Fehr, E., & Gachter, S. (2002). Altruistic punishment in humans. Nature, 415(6868), 137-140. doi: 10.1038/415137a
doi: 10.1038/415137a URL |
| [28] |
Fehr, E., & Schmidt, K. M. (1999). A theory of fairness, competition, and cooperation. Quarterly Journal Of Economics, 114(3), 817-868. doi: 10.1162/003355399556151
doi: 10.1162/003355399556151 URL |
| [29] |
FeldmanHall, O., Dalgleish, T., Evans, D., & Mobbs, D. (2015). Empathic concern drives costly altruism. Neuroimage, 105, 347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.043
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.043 pmid: 25462694 |
| [30] |
Foti, D., Weinberg, A., Dien, J., & Hajcak, G. (2011). Event-related potential activity in the basal ganglia differentiates rewards from nonrewards: Response to commentary. Human Brain Mapping, 32(12), 2267-2269. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21357
doi: 10.1002/hbm.21357 pmid: 21761509 |
| [31] |
Gratton, G., Coles, M. G. H., & Donchin, E. (1983). A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalography And Clinical Neurophysiology, 55(4), 468-484. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90135-9
doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90135-9 pmid: 6187540 |
| [32] |
Güth, W., Schmittberger, R., & Schwarze, B. (1982). An experimental- analysis of ultimatum bargaining. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 3(4), 367-388. doi: 10.1016/0167-2681(82)90011-7
doi: 10.1016/0167-2681(82)90011-7 URL |
| [33] |
Hewig, J., Kretschmer, N., Trippe, R. H., Hecht, H., Coles, M. G. H., Holroyd, C. B., & Miltner, W. H. R. (2011). Why humans deviate from rational choice. Psychophysiology, 48(4), 507-514. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01081.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01081 URL |
| [34] |
Horat, S. K., Herrmann, F. R., Favre, G., Terzis, J., Debatisse, D., Merlo, M. C. G., & Missonnier, P. (2016). Assessment of mental workload: A new electrophysiological method based on intra-block averaging of ERP amplitudes. Neuropsychologia, 82, 11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.12.013
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.12.013 URL |
| [35] |
Hu, X. M., & Mai, X. Q. (2021). Social value orientation modulates fairness processing during social decision-making: Evidence from behavior and brain potentials. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. 16(7), 670-682. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsab032
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsab032 URL |
| [36] | Hu, Z. J., & Dai, H. Q. (2011). The comparison for assessing methods of the effect size and statistical power of ANOVA. Psychological Exploration, 31(3), 254-259. |
| [37] |
Kross, E., Berman, M. G., Mischel, W., Smith, E. E., & Wager, T. D. (2011). Social rejection shares somatosensory representations with physical pain. Proceedings Of the National Academy Of Sciences Of the United States Of America, 108(15), 6270-6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102693108
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102693108 URL |
| [38] |
Kubota, J. T., & Ito, T. A. (2007). Multiple cues in social perception: The time course of processing race and facial expression. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 43(5), 738-752. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2006.10.023
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2006.10.023 URL |
| [39] |
Leliveld, M. C., van Dijk, E., & van Beest, I. (2012). Punishing and compensating others at your own expense: The role of empathic concern on reactions to distributive injustice. European Journal of Social Psychology, 42(2), 135-140. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.872
doi: 10.1002/ejsp.872 URL |
| [40] |
Leng, Y., & Zhou, X. (2010). Modulation of the brain activity in outcome evaluation by interpersonal relationship: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia, 48(2), 448-455. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.10.002
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.10.002 pmid: 19822163 |
| [41] |
Light, S. N., Moran, Z. D., Swander, L., Le, V., Cage, B., Burghy, C., ... Davidson, R. J. (2015). Electromyographically assessed empathic concern and empathic happiness predict increased prosocial behavior in adults. Biological Psychology, 104, 116-129. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.11.015
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.11.015 URL |
| [42] |
Liu, X., Hu, X. M., Shi, K., & Mai, X. Q. (2018). Empathy modulates the evaluation processing of altruistic outcomes. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 407. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00407
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00407 URL |
| [43] |
Liu, X., Hu, X. M., Shi, K., & Mai, X. Q. (2020). Your losses are mine: The influence of empathic concern on evaluative processing of others’ outcomes. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 20(3), 481-492. doi: 10.3758/s13415-020-00779-4
doi: 10.3758/s13415-020-00779-4 |
| [44] |
Luck, S. J., & Hillyard, S. A. (1994). Spatial-filtering during visual- search: Evidence from human electrophysiology. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 20(5), 1000-1014. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.20.5.1000
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.20.5.1000 URL |
| [45] | Matarazzo, O., Pizzini, B., Greco, C., & Carpentieri, M. (2016, October). Effects of a chance task outcome on the offers in the ultimatum game: The mediation role of emotions. In 2016 7th Ieee International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (pp. 295-300). |
| [46] |
McAuliffe, W. H. B., Forster, D. E., Philippe, J., & McCullough, M. E. (2018). Digital altruists: Resolving key questions about the empathy-altruism hypothesis in an internet sample. Emotion, 18(4), 493-506. doi: 10.1037/emo0000375
doi: 10.1037/emo0000375 pmid: 29154584 |
| [47] |
Moser, A., Gaertig, C., & Ruz, M. (2014). Social information and personal interests modulate neural activity during economic decision- making. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 31. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00031
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00031 pmid: 24567708 |
| [48] |
Pfattheicher, S., Sassenrath, C., & Keller, J. (2019). Compassion magnifies third-party punishment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 117(1), 124-141. doi: 10.1037/pspi0000165
doi: 10.1037/pspi0000165 pmid: 30945902 |
| [49] |
Pillutla, M. M., & Murnighan, J. K. (1996). Unfairness, anger, and spite: Emotional rejections of ultimatum offers. Organizational Behavior And Human Decision Processes, 68(3), 208-224. doi: 10.1006/obhd.1996.0100
doi: 10.1006/obhd.1996.0100 URL |
| [50] |
Polezzi, D., Daum, I., Rubaltelli, E., Lotto, L., Civai, C., Sartori, G., & Rumiati, R. (2008). Mentalizing in economic decision-making. Behavioural Brain Research, 190(2), 218-223. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.03.003
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.03.003 pmid: 18406476 |
| [51] | Qi, Y. Y., Wu, H. Y., & Liu, X. (2017). The influences of social value orientation on prosocial behaviors: The evidences from behavioral and neuroimaging studies. Chinese Science Bulletin, 62(11), 1136-1144. |
| [52] |
Sanfey, A. G., Rilling, J. K., Aronson, J. A., Nystrom, L. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2003). The neural basis of economic decision-making in the ultimatum game. Science, 300(5626), 1755-1758. doi: 10.1126/science.1082976
doi: 10.1126/science.1082976 pmid: 12805551 |
| [53] |
Spape, M., Harjunen, V., Ahmed, I., Jacucci, G., & Ravaja, N. (2019). The semiotics of the message and the messenger: How nonverbal communication affects fairness perception. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 19(5), 1259-1272. doi: 10.3758/s13415-019-00738-8
doi: 10.3758/s13415-019-00738-8 |
| [54] |
van der Veen, F. M., & Sahibdin, P. P. (2011). Dissociation between medial frontal negativity and cardiac responses in the ultimatum game: Effects of offer size and fairness. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 11(4), 516-525. doi: 10.3758/s13415-011-0050-1
doi: 10.3758/s13415-011-0050-1 |
| [55] |
Wang, Y. W., Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., Huang, L., Guo, F. B., & Yuan, S. (2014). Group membership modulates the recipient’s fairness consideration in ultimatum game. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(12), 1850-1859.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01850 URL |
| [56] |
Wu, Y., Leliveld, M. C., & Zhou, X. (2011). Social distance modulates recipient's fairness consideration in the dictator game: An ERP study. Biological Psychology, 88(2-3), 253-262. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.08.009
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.08.009 |
| [57] |
Wu, Y., & Zhou, X. (2009). The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation. Brain Research, 1286, 114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.032
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.032 URL |
| [58] |
Wu, Y., & Zhou, X. L. (2012). The Context-Dependency of Fairness Processing: Evidence from ERP Study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 44(6), 797-806.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2012.00797 URL |
| [59] |
Yeung, N., & Sanfey, A. G. (2004). Independent coding of reward magnitude and valence in the human brain. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(28), 6258-6264. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.4537-03.2004
doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.4537-03.2004 pmid: 15254080 |
| [60] |
Yu, R., Hu, P., & Zhang, P. (2015). Social distance and anonymity modulate fairness consideration: An ERP study. Scientific Reports, 5. doi: 10.1038/srep13452
doi: 10.1038/srep13452 URL |
| [61] |
Zhang, G., Li, X., & Cong, F. (2020). Objective extraction of evoked event-related oscillation from time-frequency representation of event- related potentials. Neural Plasticity, 2020, 8841354. doi: 10.1155/2020/8841354
doi: 10.1155/2020/8841354 URL |
| [1] | CHENG Jiaping; LUO Yuejia; CUI Fang. Empathy for pain influenced by cognitive load: Evidence from an ERP study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(5): 622-630. |
| [2] | MENG Yingfang, LIN Wuji, LIN Jingyuan, CAI Chaoqun. The phonological or semantic activation of non-target language in an immediate cross-language switching paradigm [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(2): 121-129. |
| [3] | WANG Yiwen, ZHANG Zhen, YUAN Sheng, GUO Fengbo, HE Shaoying, JING Yiming. The Decision-making and Outcome Evaluation during a Repeated Trust Game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(8): 1028-1038. |
| [4] | GAO Xuemei, WENG Lei, ZHOU Qun, ZHAO Cai, LI Fang. Dose Violent Offenders Have Lower Capacity of Empathy for Pain: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(4): 478-487. |
| [5] | DENG Lin;LUO Pinchao;WANG Junfang;FANG Juncong;ZHENG Xiaochun;LI Yue;ZHENG Xifu. The Enhancement of Self-orientation on Counterempathy [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(8): 1103-1111. |
| [6] | ZHONG Yiping;FAN Wei;CAI Ronghua;TAN Qianbao;XIAO Lihui;ZHAN Youlong;LUO Xi;QIN Minhui. The Influence of Positive Emotion on the Degree Effect in Self-referential Processes: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(3): 341-352 . |
| [7] | WANG Yiwen; ZHANG Zhen; ZHANG Wei; HUANG Liang; GUO Fengbo; Yuan Sheng. Group Membership Modulates The Recipient’s Fairness Consideration in Ultimatum Game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(12): 1850-1859. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||