

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 651-666.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00651
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUE Tong1( ), HUANG Xiting1(
), HUANG Xiting1( ), YUE Caizhen2, XUE Liming1, FU Anguo3
), YUE Caizhen2, XUE Liming1, FU Anguo3
Received:2020-08-14
Published:2021-06-25
Online:2021-04-25
Contact:
YUE Tong,HUANG Xiting
E-mail:yue.suhong @163.com;xthuang@swu.edu.cn
Supported by:YUE Tong, HUANG Xiting, YUE Caizhen, XUE Liming, FU Anguo. (2021). Influence of an individual’s own gains and losses on the evaluation of friends’ gambling results: Evidence from ERPs. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(6), 651-666.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00651
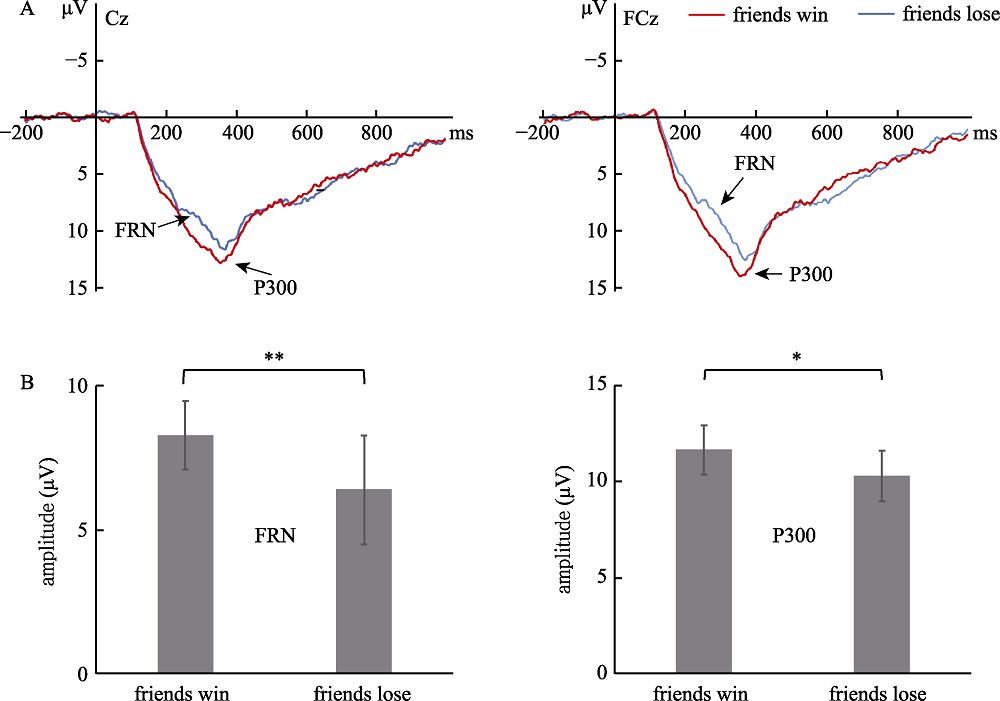
Figure 3. The results of the pre-experiment are as follows: (a) the average waveforms of FRN and P300 when Cz and FCz are watching the results of friends’ game, in which the red line is the waveforms when friends win money and the Blue Line is the waveforms when friends lose money; (b) the mean and standard error of FRN and P300 amplitudes caused by watching friends win/lose (** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05)
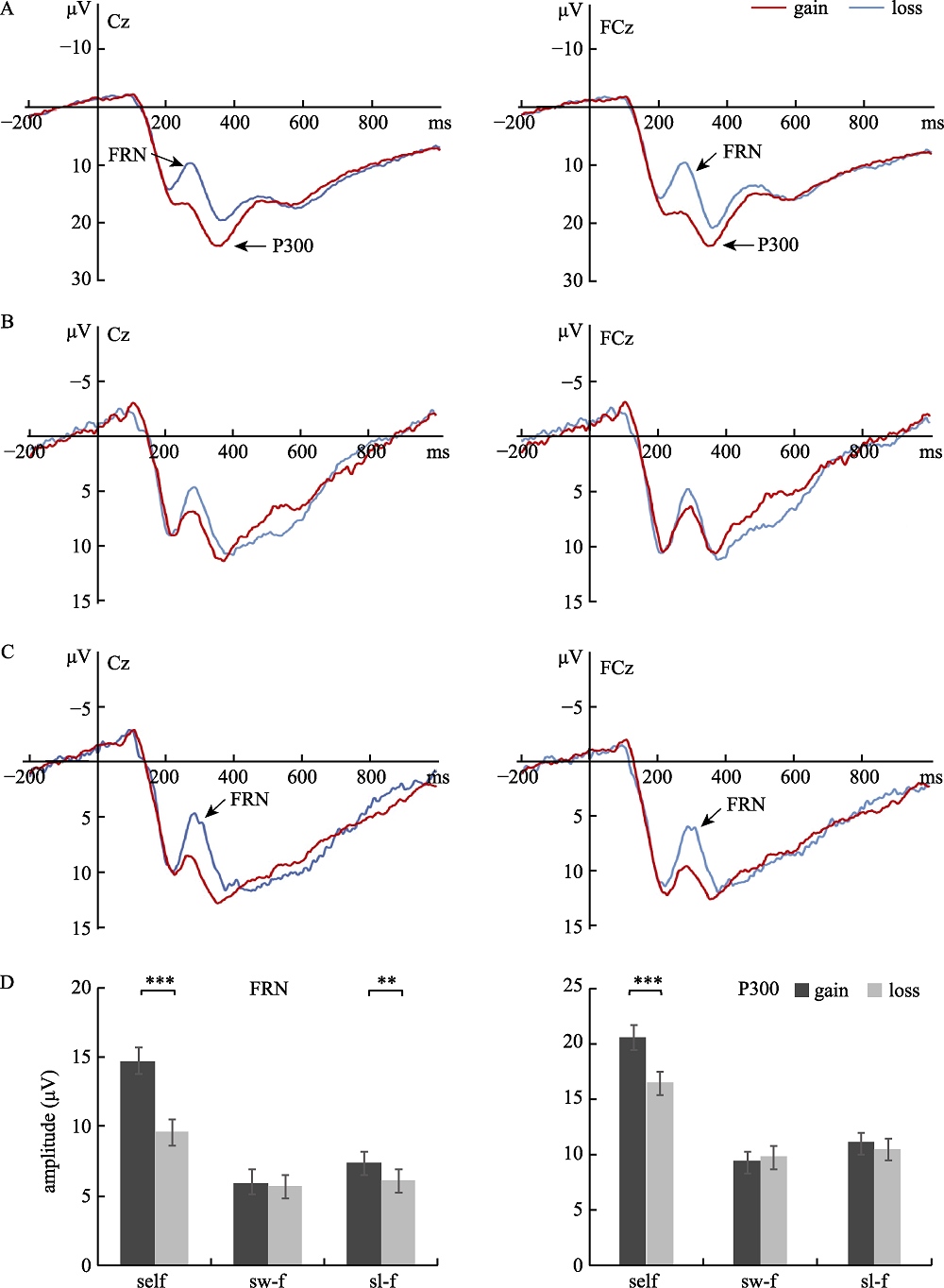
Figure 5. Results of study 1. (a) the average waveforms of FRN and P300 at CZ and FCZ when the participants themselves participated in the game, in which the red line was the waveforms when the friends gained, and the blue line was the waveforms when the friends lost; (b) the average waveforms of FRN and P300 were shown at CZ and FCZ points after the participants gained the benefit, and (c) the average waveforms of FRN and P300 were shown at CZ and FCZ points after the participants lost money (d) the comparison of the mean and standard error of the amplitudes of FRN and P300 under different operating conditions, “self” represented the operating conditions, “sw-f” represented the playing conditions of friends after winning, “sl-f” represented the condition of watching a friend’s game after a loss (** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05).
| Group | n | M | SD | t | p | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent self group | ||||||
| Independent self sentences count | 18 | 6.17 | 1.54 | 7.86 | < 0.001 | 1.62 |
| Interdependent self sentences count | 3.22 | 2.06 | ||||
| Interpendent self group | ||||||
| Independent self sentences count | 22 | 3.45 | 1.11 | -4.94 | < 0.001 | 1.47 |
| Interependent self sentence count | 5.59 | 1.74 |
Table 1 Statistical analysis table of sentences description difference between independent self group and interdependent self group
| Group | n | M | SD | t | p | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent self group | ||||||
| Independent self sentences count | 18 | 6.17 | 1.54 | 7.86 | < 0.001 | 1.62 |
| Interdependent self sentences count | 3.22 | 2.06 | ||||
| Interpendent self group | ||||||
| Independent self sentences count | 22 | 3.45 | 1.11 | -4.94 | < 0.001 | 1.47 |
| Interependent self sentence count | 5.59 | 1.74 |
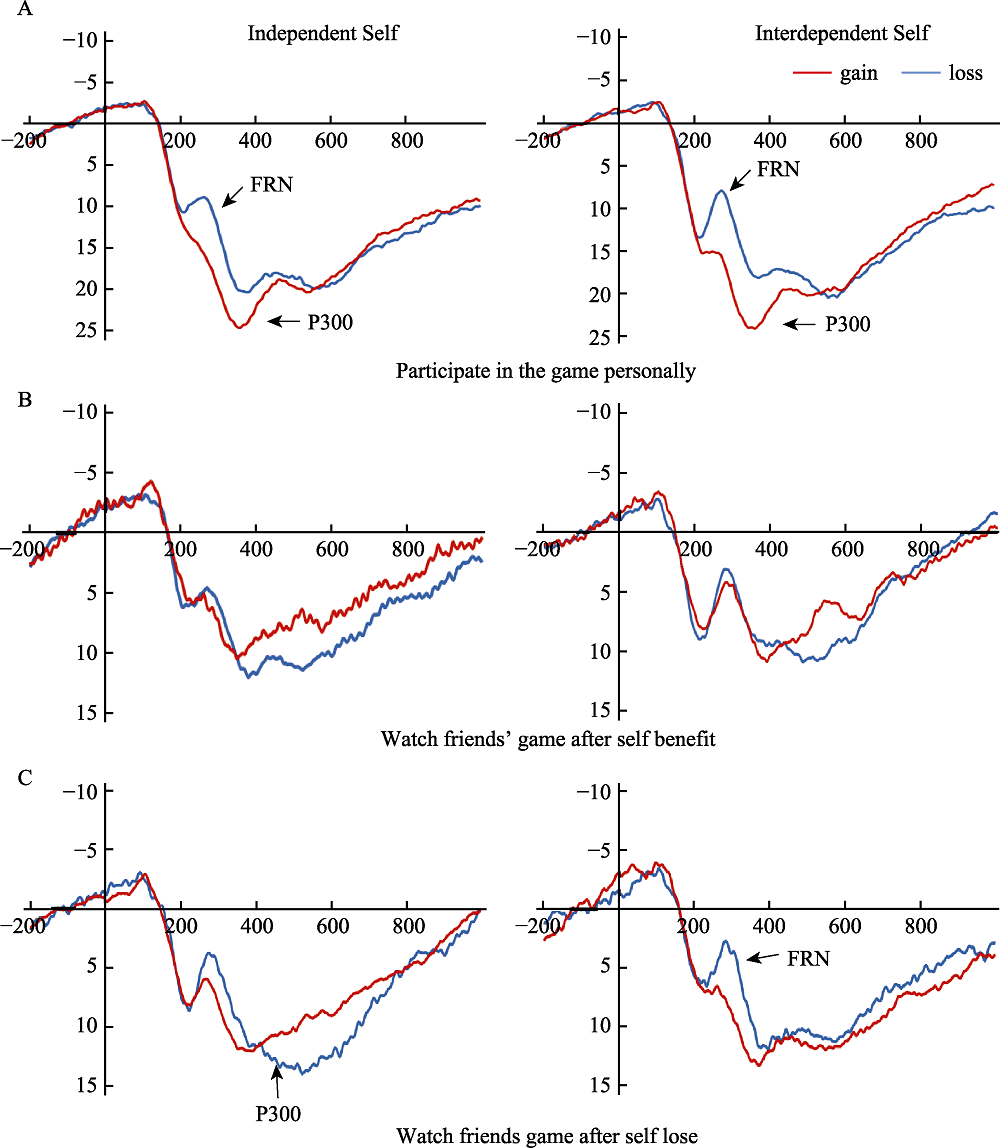
Figure 6. The results of Experiment 2 are as follows: (a) the average waveforms of the self-initiated group and the self-initiated group at the Cz point; (b) the average waveforms on the Cz points when the self-initiated group and the self-initiated group benefit from watching the friends’ game; (c) the average waveform at a Cz point when watching friends’ game after a loss for the independent self group and the interdependent self group.
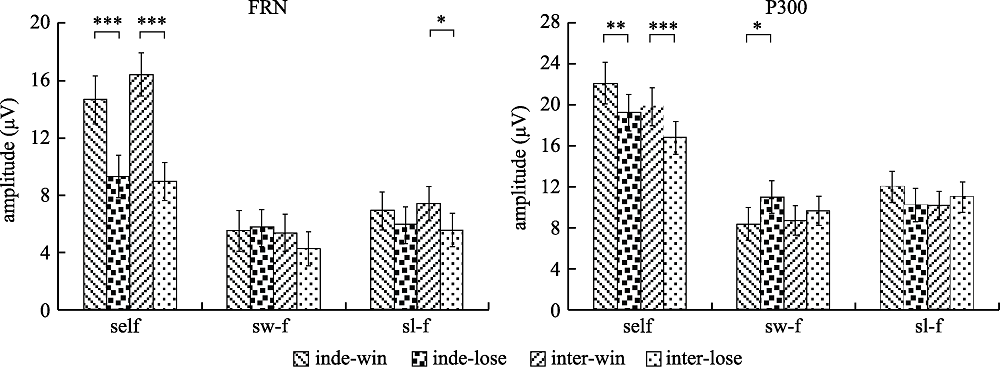
Figure 7. Comparison of mean and standard error of FRN and P300 amplitude under different operating conditions (*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05). “self” represents the condition of self-operation, “sw-f” represents the condition of watching a friend’s game after winning, “sl-f” represents the condition of watching a friend’s game after losing, and “inde-win” represents the condition of starting to win money for an independent group, “inde-lose” represents the conditions under which the independent group started losing money, “Inter-win” represents the conditions under which the interdependent group started winning money, and “Inter-lose” represents the conditions under which the interdependent group started losing money.
| [1] |
Aron, A., Aron, E. N., & Smollan, D. (1992). Inclusion of other in the self scale and the structure of interpersonal closeness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63(4), 596-612.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.63.4.596 URL |
| [2] |
Aron, A., McLaughlin-Volpe, T., Mashek, D., Lewandowski, G., Wright, S. C., & Aron, E. N. (2004). Including others in the self. European Review of Social Psychology, 15(1), 101-132.
doi: 10.1080/10463280440000008 URL |
| [3] |
Bai, L. Y., Yuan, B., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Lan, J., & Wang, Y. W. (2014). Interpersonal cooperation and conflict influenced outcome evaluation in social decision-making. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(11), 1760-1771.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.01760 URL |
| [4] |
Baker, T. E., & Holroyd, C. B. (2011). Dissociated roles of the anterior cingulate cortex in reward and conflict processing as revealed by the feedback error-related negativity and N200. Biological Psychology, 87(1), 25-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.01.010 URL |
| [5] |
Boksem, M. A. S., Kostermans, E., & de Cremer, D. (2011). Failing where others have succeeded: Medial frontal negativity tracks failure in a social context. Psychophysiology, 48(7), 973-979.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.2011.48.issue-7 URL |
| [6] |
Chiao, J. Y., Harada, T., Komeda, H., Li, Z., & Iidaka, T. (2009). Neural basis of individualistic and collectivistic views of self. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2813-2820.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.20707 pmid: 19107754 |
| [7] |
Chiao, J. Y., Harada, T., Komeda, H., Li, Z., Mano, Y., & Saito, D., … Iidaka, T. (2010). Dynamic cultural influences on neural representations of the self. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(1), 1-11.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21192 pmid: 19199421 |
| [8] |
Crawford, M. T. (2007). The renegotiation of social identitiesin response to a threat to self-evaluation maintenance. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 43(1), 39-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2005.12.011 URL |
| [9] |
Crocker, J., &Park, L. E. (2004). The costly pursuit of self-esteem. Psychological Bulletin, 130(3), 392-414.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.130.3.392 URL |
| [10] |
Delgado, M. R., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, C., Noll, D. C., & Fiez, J. A. (2000). Tracking the hemodynamic responses to reward and punishment in the striatum. Journal of Neurophysiology, 84(6), 3072-3077.
doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.6.3072 URL |
| [11] |
Eastwick, P. W., &Finkel, E. J. (2008). Sex differences in mate preferences revisited: Do people know what they initially desire in a romantic partner? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 94(2), 245-264.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.94.2.245 pmid: 18211175 |
| [12] |
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. -G., & Buchner, A. (2007) G Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 175-191.
doi: 10.3758/BF03193146 URL |
| [13] | Fei, X. T., & Liu, H. X. (1985). Rural China. Beijing: Life, Read and New Knowledge Sanlian Bookstore. |
| [14] |
Fukushima, H., & Hirak, K. (2006). Perceiving an opponent's loss: Gender-related differences in the medial-frontal negativity. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 1(2), 149-157.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsl020 pmid: 18985125 |
| [15] | Gergen, K. J. (2009). Relational being: Beyond self and community. Oxford University Press. |
| [16] |
Glazer, J. E., Kelley, N. J., Pornpattananangkul, N., Mittal, V. A., & Nusslock, R. (2018). Beyond the FRN: Broadening the time-course of EEG and ERP components implicated in reward processing. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 132, 184-202.
doi: S0167-8760(17)30473-7 pmid: 29454641 |
| [17] |
Gray, H. M., Ambady, N., Lowenthal, W. T., & Deldin, P. (2004). P300 as an index of attention to self-relevant stimuli. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 40(2), 216-224.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-1031(03)00092-1 URL |
| [18] | Greve, F.(2009-05-23). America’s poor are its most generous donars. The Seattle Times. (Retrieved June 18, 2014 from http://seattletimes.com/html/nationworld/2009253657_char ity23.html) |
| [19] |
Gu, R. L., Wu, T. T., Jiang, Y., & Luo, Y. -J. (2011). Woulda, coulda, shoulda: The evaluation and the impact of the alternative outcome. Psychophysiology, 48(10), 1354-1360.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.2011.48.issue-10 URL |
| [20] |
Hajcak, G., Holroyd, C. B., Moser, J. S., & Simons, R. F. (2005). Brain potentials associated with expected and unexpected good and bad outcomes. Psychophysiology, 42(2), 161-170.
pmid: 15787853 |
| [21] |
Holroyd, C. B., Hajcak, G., & Larsen, J. T. (2006). The good, the bad and the neutral: Electrophysiological responses to feedback stimuli. Brain Research, 1105(1), 93-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.015 URL |
| [22] | Kitayama, S., & Park, J. (2012). Culture and the self: Implications for consumer behavior. In A. A. Ruvio & R. W. Belk (Eds.), The Routledge companion to identity and consumption: 5-20. London; New York: Routledge. |
| [23] |
Koban, L., Pourtois, G., Vocat, R., & Vuilleumier, P. (2010). When your errors make me lose or win: Event-related potentials to observed errors of cooperators and competitors. Social Neuroscience, 5(4), 360-374.
doi: 10.1080/17470911003651547 URL |
| [24] |
Komissarouk, S., & Nadler, A. (2014). “I” seek autonomy, “we” rely on each other: Self-construal and regulatory focus as determinants of autonomy-and dependency-oriented help-seeking behavior. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40(6), 726-738.
doi: 10.1177/0146167214524444 URL |
| [25] |
Leng, Y., & Zhou, X. (2010). Modulation of the brain activity in outcome evaluation by interpersonal relationship: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia, 48(2), 448-455.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.10.002 pmid: 19822163 |
| [26] |
Luck, S. J., & Gaspelin, N. (2017). How to get statistically significant effects in any ERP experiment (and why you shouldn’t). Psychophysiology, 54(1), 146-157.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.12639 URL |
| [27] |
Macrae, C. N., Heatherton, T. F., Banfield, J. F., & Kelley, W. M. (2004). Medial prefrontal activity predicts memory for self. Cerebral Cortex, 14(6), 647-654.
pmid: 15084488 |
| [28] |
Ma, Q. G., Shen, Q., Xu, Q., Li, D. D., Shu, L. C., & Weber, B. (2011). Empathic responses to others' gains and losses: An electrophysiological investigation. Neuroimage, 54(3), 2472-2480.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.045 URL |
| [29] | Markus, H. R., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implication for cognition, emotion and motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 98, 224-253. |
| [30] | Markus, H. R., Kitayama, S., & Heiman, R. J. (1996). Culture and “basic” psychological principles. New York: Guiford. |
| [31] |
Marco-Pallares, J., Cucurell, D., Cunillera, T., García, R., Andrés- Pueyo, A., Münte, T. F., & Rodríguez-Fornells, A. (2008). Human oscillatory activity associated to reward processing in a gambling task. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 241-248.
pmid: 17804025 |
| [32] |
Marco-Pallarés, J., Krämer, U. M., Strehl, S., Schröder, A., & Münte, T. F. (2010). When decisions of others matter to me: An electrophysiological analysis. BMC Neuroscience, 11(1), 86.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-86 URL |
| [33] |
Masaki, H., Takeuchi, S., Gehring, W. J., Takasawa, N., & Yamazaki, K. (2006). Affective motivational influences on feedback-related ERPs in a gambling task. Brain Research, 1105, 110-121.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.022 URL |
| [34] | Meyer, M. L., Masten, C. L., Ma, Y., Wang, C., Shi, Z., Eisenberger, N. I., & Han, S. (2013). Empathy for the social suffering of friends and strangers recruits distinct patterns of brain activation. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, nss019. |
| [35] |
Nieuwenhuis, S., Aston-Jones, G., & Cohen, J. D. (2005). Decision making, the P3, and the locus coeruleus--norepinephrine system. Psychological Bulletin, 131(4), 510-532.
pmid: 16060800 |
| [36] |
Ng, S. H., Han, S., Mao, L., & Lai, J. C. L. (2010). Dynamic bicultural brains: FMRI study of their flexible neural representation of self and significant others in response to culture primes. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 13(2), 83-91.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-839X.2010.01303.x URL |
| [37] |
Oliveira, F. T. P., McDonald, J. J., & Goodman, D. (2007). Performance monitoring in the anterior cingulate is not all error related: Expectancy deviation and the representation of action-outcome associations. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(12), 1994-2004.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.12.1994 URL |
| [38] |
Polezzi, D., Sartori, G., Rumiati, R., Vidotto, G., & Daum, I. (2010). Brain correlates of risky decision-making. Neuroimage, 49(2), 1886-1894.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.068 pmid: 19761850 |
| [39] |
Preis, M. A., & Kroener‐Herwig, B. (2012). Empathy for pain: The effects of prior experience and sex. European Journal of Pain, 16(9), 1311-1319.
doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00119.x pmid: 22949180 |
| [40] | Qi, Y. Y., Wu, H. Y., Raiha, S., & Liu, X. (2018). Social value orientation modulates context-based social comparison preference in the outcome evaluation: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia, 112, 135-144. |
| [41] | Schreuders, E., Klapwijk, E. T., Will, G. J., & Guroglu, B. (2018). Friend versus foe: Neural correlates of prosocial decisions for liked and disliked peers. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 18(1), 127-142. |
| [42] | Singelis, T. M. (1994). The measurement of independent and interdependent self-construals. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 20(5), 580-591. |
| [43] |
Sui, J., & Han, S. (2007). Self-construal priming modulates neural substrates of self-awareness. Psychological Science, 18(10), 861-866.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01992.x URL |
| [44] | Toppe, C. M., Kirsch, A. D., & Michel, J. (2001). Giving & Volunteering in the United States: Findings from a National Survey.Washington, DC: Independent Sector. |
| [45] |
van Veen, V., & Carter, C. S. (2002). The anterior cingulate as a conflict monitor: FMRI and ERP studies. Physiology & Behavior, 77(4-5), 477-482.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00930-7 URL |
| [46] |
Varnum, M. E., Shi, Z., Chen, A., Qiu, J., & Han, S. (2014). When “Your” reward is the same as “My” reward: Self-construal priming shifts neural responses to own vs. friends' rewards. NeuroImage, 87, 164-169.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.042 URL |
| [47] |
Vohs, K. D., Mead, N. L., & Goode, M. R. (2006). The psychological consequences of money. Science, 314(5802), 1154-1156.
doi: 10.1126/science.1132491 URL |
| [48] |
Walsh, M. M., & Anderson, J. R. (2012). Learning from experience: Event-related potential correlates of reward processing, neural adaptation, and behavioral choice. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(8), 1870-1884.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.05.008 URL |
| [49] | Wang, Y. H., Yuan, Q. H., & Xu, Q. M. (2008). A preliminary study on self-constructionals scales (SCS) of Chinese-version. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 16(6), 602-604. |
| [50] | Wang, Y. W., Kuhlman, D. M., Roberts, K., Yuan, B., Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., & Simons, R. F. (2017). Social value orientation modulates the FRN and P300 in the chicken game. Biological Psychology, 127, 89-98. |
| [51] |
Wang, Y. W., Yuan, B., Lin, C. D., Zheng, Y. W., Zhang, Z., & Du, C. L. (2011). The influence of interpersonal relationship on outcome evaluation in competitive situations: An ERP study. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 41(11), 1112-1120
doi: 10.1360/052011-377 URL |
| [52] | Yang, G. S., & Lin, Y. Z. (2002). Discrepancy patterns in and around family: Confirmation of self-reference effects. In Search of excellence for Chinese indigenous psychological research. Taipei: Psychology Department of Taiwan University, China. |
| [53] |
Yang, S., Huang, X. T., Chen, Y. G., Fu, Y, L., & Liu, M. C. (2014). Effect of interpersonal distance on neural basis of self- and other representation: Evidence from the oFRN component. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46(5), 666-676.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2014.00666 URL |
| [54] |
Yeung, N., & Sanfey, A. G. (2004). Independent coding of reward magnitude and valence in the human brain. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(28), 6258-6264.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4537-03.2004 URL |
| [55] | Yu, R., Luo, Y., Ye, Z., & Zhou, X. (2007). Does the FRN in brain potentials reflect motivational/affective consequence of outcome evaluation? Progress in Natural Science, 17, 136-143. |
| [56] | Zhang, H. Y., Zhang, M. M., Lu, J. C., Zhao, L. L., Zhao, D. F., Xiao, C., … Luo, W. B. (2020). Interpersonal relationships modulate outcome evaluation in a social comparison context: The pain and pleasure of intimacy. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 20(1), 115-127. |
| [57] |
Zhou, Z., Yu, R., & Zhou, X. (2010). To do or not to do? Action enlarges the FRN and P300 effects in outcome evaluation. Neuropsychologia, 48(12), 3606-3613.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.08.010 URL |
| [58] | Zhu, X. R., Wang, L. L., Yang, S. Y., Gu, R. L., Wu, H. Y., & Luo, Y. L. (2016). The motivational hierarchy between the personal self and close others in the Chinese brain: An ERP study. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1-7. |
| [59] | Zhu, X. R., Xu, M., Wang, H. B., Gu, R. L., & Jin, Z. (2020). The influence of self-construals on the ERP response to the rewards for self and friend. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 147. |
| [60] | Zhu, X. R., Zhang, H. J., Wu, L. L., Yang, S. Y., Wu, H. Y., & Luo, W. B., … Luo, Y. -J. (2018). The influence of self-construals on the erp response to the rewards for self and mother. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 18, 366-374. |
| [1] | LI Jianhua, XIE Jiajia, ZHUANG Jin-Ying. An effect of menstrual cycle phase on episodic memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 466-480. |
| [2] | CHEN Jie, WU Ke, SHI Yupeng, AI Xiaoqing. The relationship between dispositional self-construal and empathy for ingroup and outgroup members’ pain: evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(6): 629-638. |
| [3] | DENG Xiaohong, LI Ting, XUE Chao, J. Peter ROSENFELD, LU Yang, WANG Ying, ZHAN Xiaofei, YAN Gejun, OUYANG Dan. The Complex Trial Protocol based on self-referential encoding: Discriminating the guilty from the knowledgeable innocent [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(10): 1105-1119. |
| [4] | Zhenzhong ZHU,Fu LIU,Chen Haipeng (Allan). Warmth or competence? The influence of advertising appeal and self-construal on consumer-brand identification and purchase intention [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(3): 357-370. |
| [5] | ZHU Zhenzhong, LI Xiaojun, LIU Fu, Haipeng CHEN. How visual novelty affects consumer purchase intention: The moderating effects of self-construal and product type [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(11): 1352-1364. |
| [6] | REN Xi,WANG Yan,HU Xiang,YANG Juan. Social support buffers acute psychological stress in individuals with high interdependent self-construal [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(4): 497-506. |
| [7] | WANG Pei, CHEN Qingwei, TANG Xiaochen, LUO Junlong, TAN Chenhao, GAO Fan. The situational primacy of Chinese individual self, relational self, collective self: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1072-1079. |
| [8] | WANG Yiwen, FU Chao, REN Xiangfeng, LIN Yuzhong, GUO Fengbo. Narcissistic personality modulates outcome evaluation in the trust game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1080-1088. |
| [9] | FU Yilei, LUO Yuejia, CUI Fang. Consistency of choice modulates outcome evaluation: Evidence from ERP studies [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1089-1099. |
| [10] | WANG Haizhong, FAN Xiaowen, OUYANG Jianying. Consumer self-construal, need of uniqueness and preference of brand logo shape [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1113-1124. |
| [11] | ZHOU AiBao;LIU PeiRu;ZHANG YanChi;YIN YuLong. Friend-reference Effect in Older Adults [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(9): 1143-1151. |
| [12] | WANG Yiwen, ZHANG Zhen, YUAN Sheng, GUO Fengbo, HE Shaoying, JING Yiming. The Decision-making and Outcome Evaluation during a Repeated Trust Game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(8): 1028-1038. |
| [13] | GAO Xuemei, WENG Lei, ZHOU Qun, ZHAO Cai, LI Fang. Dose Violent Offenders Have Lower Capacity of Empathy for Pain: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(4): 478-487. |
| [14] | YANG Shuai;HUANG Xiting;CHEN Youguo;FU Yuling;LIU Mengchao. Effect of Interpersonal Distance on Neural Basis of Self- and Other Representation: Evidence from the oFRN Component [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(5): 666-676. |
| [15] | ZHONG Yiping;FAN Wei;CAI Ronghua;TAN Qianbao;XIAO Lihui;ZHAN Youlong;LUO Xi;QIN Minhui. The Influence of Positive Emotion on the Degree Effect in Self-referential Processes: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(3): 341-352 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||