

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 603-612.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00603
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Hongbo1, XING Xiaoli1, WANG Huiying2,3( )
)
Received:2020-11-09
Published:2021-06-25
Online:2021-04-25
Contact:
WANG Huiying
E-mail:wanghuiyingwing@foxmail.com
Supported by:WANG Hongbo, XING Xiaoli, WANG Huiying. (2021). Propranolol rescued secondary trauma induced by immediate extinction. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(6), 603-612.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00603
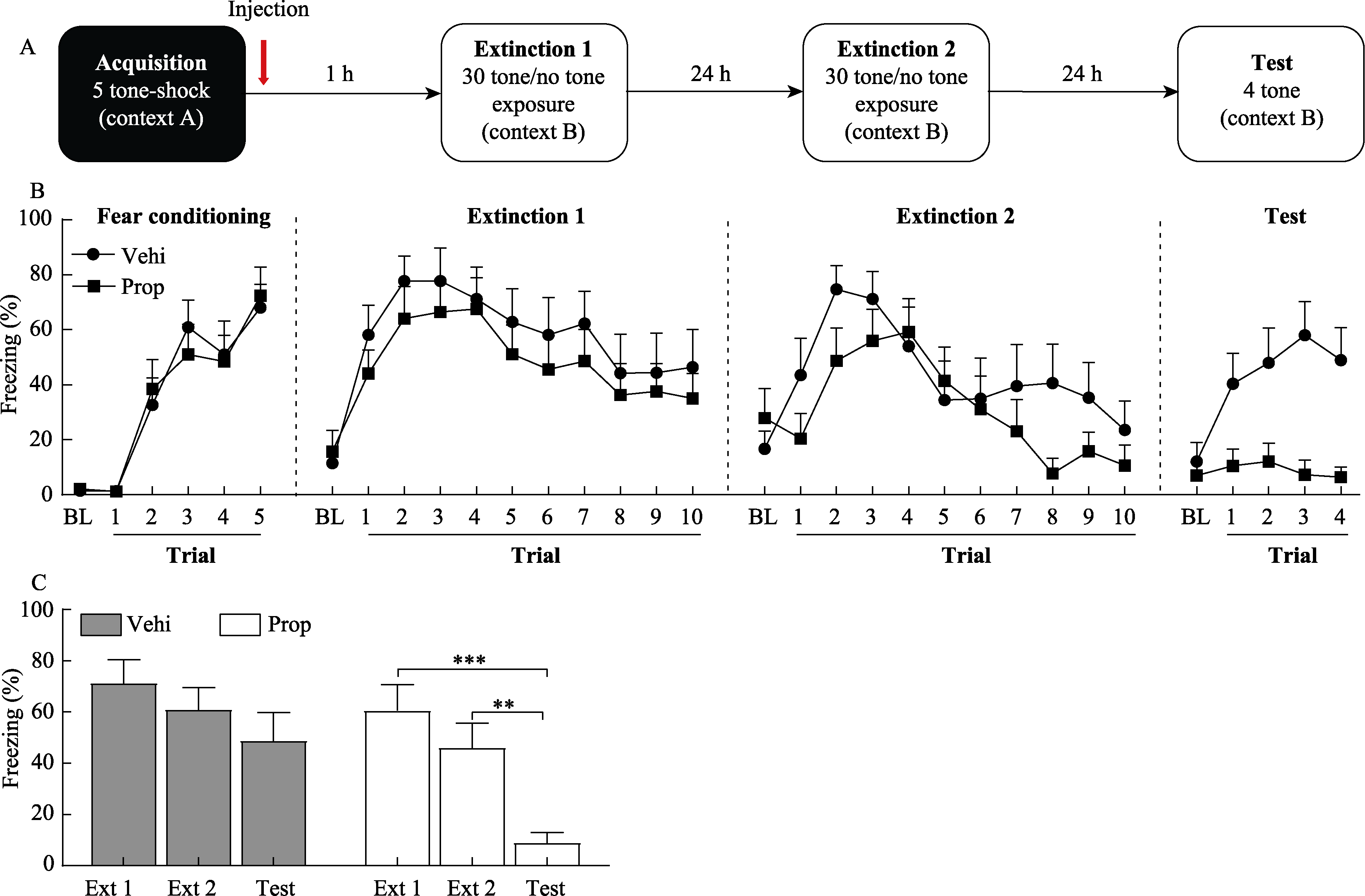
Figure 2. Propranolol rescued deficit in re-extinction which was induced by immediate extinction Note. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, the error bar is standard error (SE)

Figure 2. Propranolol rescued deficit in re-extinction which was induced by immediate extinction Note. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, the error bar is standard error (SE)
| [1] | Argolo F. C., Cavalcanti-Ribeiro P., Netto L. R., & Quarantini L. C. (2015). Prevention of posttraumatic stress disorder with propranolol: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 79(2), 89-93. |
| Argolo F. C., Cavalcanti-Ribeiro P., Netto L. R., & Quarantini L. C. (2015). Prevention of posttraumatic stress disorder with propranolol: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 79(2), 89-93. | |
| [2] | American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders(DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub. |
| American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders(DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub. | |
| [3] | Borodovitsyna O., Joshi N.,& Chandler D. (2018). Persistent stress- induced neuroplastic changes in the locus coeruleus/norepinephrine system. Neural Plasticity, 2018, 1892570. |
| Borodovitsyna O., Joshi N.,& Chandler D. (2018). Persistent stress- induced neuroplastic changes in the locus coeruleus/norepinephrine system. Neural Plasticity, 2018, 1892570. | |
| [4] | Cain C. K., Blouin A. M., & Barad M. (2004). Adrenergic transmission facilitates extinction of conditional fear in mice. Learning & Memory, 11(2), 179-187. |
| Cain C. K., Blouin A. M., & Barad M. (2004). Adrenergic transmission facilitates extinction of conditional fear in mice. Learning & Memory, 11(2), 179-187. | |
| [5] | Careaga M. B. L., Girardi C. E. N., & Suchecki D. (2016). Understanding posttraumatic stress disorder through fear conditioning, extinction and reconsolidation. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71,48-57. |
| Careaga M. B. L., Girardi C. E. N., & Suchecki D. (2016). Understanding posttraumatic stress disorder through fear conditioning, extinction and reconsolidation. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71,48-57. | |
| [6] | Chalkia A., Weermeijer J., van Oudenhove L., & Beckers T. (2019). Acute but not permanent effects of propranolol on fear memory expression in humans. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 51. |
| Chalkia A., Weermeijer J., van Oudenhove L., & Beckers T. (2019). Acute but not permanent effects of propranolol on fear memory expression in humans. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 13, 51. | |
| [7] | Chang, C. H., & Maren, S. (2009). Early extinction after fear conditioning yields a context-independent and short-term suppression of conditional freezing in rats. Learning & Memory, 16(1), 62-68. |
| Chang, C. H., & Maren, S. (2009). Early extinction after fear conditioning yields a context-independent and short-term suppression of conditional freezing in rats. Learning & Memory, 16(1), 62-68. | |
| [8] | Chang, C. H., & Maren, S. (2011). Medial prefrontal cortex activation facilitates re-extinction of fear in rats. Learning & Memory, 18(4), 221-225. |
| Chang, C. H., & Maren, S. (2011). Medial prefrontal cortex activation facilitates re-extinction of fear in rats. Learning & Memory, 18(4), 221-225. | |
| [9] | Cho J. H., Deisseroth K., & Bolshakov V. Y. (2013). Synaptic encoding of fear extinction in mPFC-amygdala circuits. Neuron, 80(6), 1491-1507. |
| Cho J. H., Deisseroth K., & Bolshakov V. Y. (2013). Synaptic encoding of fear extinction in mPFC-amygdala circuits. Neuron, 80(6), 1491-1507. | |
| [10] | Dunsmoor J. E., Kroes M. C. W., Moscatelli C. M., Evans M. D., Davachi L., & Phelps E. A. (2018). Event segmentation protects emotional memories from competing experiences encoded close in time. Nature Human Behaviour, 2(4), 291-299. |
| Dunsmoor J. E., Kroes M. C. W., Moscatelli C. M., Evans M. D., Davachi L., & Phelps E. A. (2018). Event segmentation protects emotional memories from competing experiences encoded close in time. Nature Human Behaviour, 2(4), 291-299. | |
| [11] | Fan S. J., Jiang H., Yang L. -J., Liu X., Song J., & Pan F. (2011). Effects of adrenergic agents on stress-induced brain microstructural and immunochemical changes in adult male Wistar rats. Annals of Anatomy-Anatomischer Anzeiger, 193(5), 418-424. |
| Fan S. J., Jiang H., Yang L. -J., Liu X., Song J., & Pan F. (2011). Effects of adrenergic agents on stress-induced brain microstructural and immunochemical changes in adult male Wistar rats. Annals of Anatomy-Anatomischer Anzeiger, 193(5), 418-424. | |
| [12] | Fitzgerald P. J., Giustino T. F., Seemann J. R., & Maren S. (2015). Noradrenergic blockade stabilizes prefrontal activity and enables fear extinction under stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(28), E3729-3737. |
| Fitzgerald P. J., Giustino T. F., Seemann J. R., & Maren S. (2015). Noradrenergic blockade stabilizes prefrontal activity and enables fear extinction under stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(28), E3729-3737. | |
| [13] | Giustino T. F., Fitzgerald P. J., & Maren S. (2016). Revisiting propranolol and PTSD: Memory erasure or extinction enhancement? Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 130, 26-33. |
| Giustino T. F., Fitzgerald P. J., & Maren S. (2016). Revisiting propranolol and PTSD: Memory erasure or extinction enhancement? Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 130, 26-33. | |
| [14] | Giustino T. F., Fitzgerald P. J., Ressler R. L., & Maren S. (2019). Locus coeruleus toggles reciprocal prefrontal firing to reinstate fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(17), 8570-8575. |
| Giustino T. F., Fitzgerald P. J., Ressler R. L., & Maren S. (2019). Locus coeruleus toggles reciprocal prefrontal firing to reinstate fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(17), 8570-8575. | |
| [15] | Giustino, T. F., & Maren, S. (2018). Noradrenergic modulation of fear conditioning and extinction. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 12, 43. |
| Giustino, T. F., & Maren, S. (2018). Noradrenergic modulation of fear conditioning and extinction. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 12, 43. | |
| [16] | Giustino T. F., Ramanathan K. R., Totty M. S., Miles O. W., & Maren S. (2020). Locus coeruleus norepinephrine drives stress-induced increases in basolateral amygdala firing and impairs extinction learning. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(4), 907-916. |
| Giustino T. F., Ramanathan K. R., Totty M. S., Miles O. W., & Maren S. (2020). Locus coeruleus norepinephrine drives stress-induced increases in basolateral amygdala firing and impairs extinction learning. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(4), 907-916. | |
| [17] | Giustino T. F., Seemann J. R., Acca G. M., Goode T. D., Fitzgerald P. J., & Maren S. (2017). Beta-adrenoceptor blockade in the basolateral amygdala, but not the medial prefrontal cortex, rescues the immediate extinction deficit. Neuropsychopharmacology, 42(13), 2537-2544. |
| Giustino T. F., Seemann J. R., Acca G. M., Goode T. D., Fitzgerald P. J., & Maren S. (2017). Beta-adrenoceptor blockade in the basolateral amygdala, but not the medial prefrontal cortex, rescues the immediate extinction deficit. Neuropsychopharmacology, 42(13), 2537-2544. | |
| [18] | Gökçek-Saraç Ç., Wesierska M., & Jakubowska-Doğru E. (2015). Comparison of spatial learning in the partially baited radial-arm maze task between commonly used rat strains: Wistar, Spargue-Dawley, Long-Evans, and outcrossed Wistar/Sprague-Dawley. Learning & Behavior, 43(1), 83-94. |
| Gökçek-Saraç Ç., Wesierska M., & Jakubowska-Doğru E. (2015). Comparison of spatial learning in the partially baited radial-arm maze task between commonly used rat strains: Wistar, Spargue-Dawley, Long-Evans, and outcrossed Wistar/Sprague-Dawley. Learning & Behavior, 43(1), 83-94. | |
| [19] | Hölscher, C . (2002). Different strains of rats show different sensitivity to block of long-term potentiation by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. European Journal of Pharmacology, 457(2-3), 99-106. |
| Hölscher, C . (2002). Different strains of rats show different sensitivity to block of long-term potentiation by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. European Journal of Pharmacology, 457(2-3), 99-106. | |
| [20] | Huff N. C., Hernandez J. A., Blanding N. Q., & LaBar K. S. (2009). Delayed extinction attenuates conditioned fear renewal and spontaneous recovery in humans. Behavioral Neuroscience, 123(4), 834-843. |
| Huff N. C., Hernandez J. A., Blanding N. Q., & LaBar K. S. (2009). Delayed extinction attenuates conditioned fear renewal and spontaneous recovery in humans. Behavioral Neuroscience, 123(4), 834-843. | |
| [21] | Khan V., Sharma S., Bhandari U., Ali S. M., & Haque S. E. (2018). Raspberry ketone protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sciences, 194, 205-212. |
| Khan V., Sharma S., Bhandari U., Ali S. M., & Haque S. E. (2018). Raspberry ketone protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sciences, 194, 205-212. | |
| [22] | Kyriazi P., Headley D. B., & Pare D. (2018). Multi-dimensional coding by basolateral amygdala neurons. Neuron, 99(6), 1315-1328. e1315. |
| Kyriazi P., Headley D. B., & Pare D. (2018). Multi-dimensional coding by basolateral amygdala neurons. Neuron, 99(6), 1315-1328. e1315. | |
| [23] | Maren, S . (2014). Nature and causes of the immediate extinction deficit: A brief review. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 113, 19-24. |
| Maren, S . (2014). Nature and causes of the immediate extinction deficit: A brief review. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 113, 19-24. | |
| [24] | Maren, S., & Chang, C. H. (2006). Recent fear is resistant to extinction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103 (47), 18020-18025. |
| Maren, S., & Chang, C. H. (2006). Recent fear is resistant to extinction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103 (47), 18020-18025. | |
| [25] | McCall J. G., Al-Hasani R., Siuda E. R., Hong D. Y., Norris A. J., Ford C. P., & Bruchas M. R. (2015). CRH engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron, 87(3), 605-620. |
| McCall J. G., Al-Hasani R., Siuda E. R., Hong D. Y., Norris A. J., Ford C. P., & Bruchas M. R. (2015). CRH engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron, 87(3), 605-620. | |
| [26] | McGaugh, J. L. (2000). Memory - a century of consolidation. Science, 287(5451), 248-251. |
| McGaugh, J. L. (2000). Memory - a century of consolidation. Science, 287(5451), 248-251. | |
| [27] | Merz C. J., Hamacher-Dang T. C., & Wolf O. T. (2016). Immediate extinction promotes the return of fear. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 131, 109-116. |
| Merz C. J., Hamacher-Dang T. C., & Wolf O. T. (2016). Immediate extinction promotes the return of fear. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 131, 109-116. | |
| [28] | Muravieva, E. V., & Alberini, C. M. (2010). Limited efficacy of propranolol on the reconsolidation of fear memories. Learning & Memory, 17(6), 306-313. |
| Muravieva, E. V., & Alberini, C. M. (2010). Limited efficacy of propranolol on the reconsolidation of fear memories. Learning & Memory, 17(6), 306-313. | |
| [29] | Przybyslawski J., Roullet P., & Sara S. J. (1999). Attenuation of emotional and nonemotional memories after their reactivation: Role of beta adrenergic receptors. Journal of Neuroscience, 19(15), 6623-6628. |
| Przybyslawski J., Roullet P., & Sara S. J. (1999). Attenuation of emotional and nonemotional memories after their reactivation: Role of beta adrenergic receptors. Journal of Neuroscience, 19(15), 6623-6628. | |
| [30] | Robinson, M. J. F., & Franklin, K. B. J. (2010). Reconsolidation of a morphine place preference: Impact of the strength and age of memory on disruption by propranolol and midazolam. Behavioural Brain Research, 213(2), 201-207. |
| Robinson, M. J. F., & Franklin, K. B. J. (2010). Reconsolidation of a morphine place preference: Impact of the strength and age of memory on disruption by propranolol and midazolam. Behavioural Brain Research, 213(2), 201-207. | |
| [31] | Rodriguez-Romaguera J., Sotres-Bayon F., Mueller D., & Quirk G. J. (2009). Systemic propranolol acts centrally to reduce conditioned fear in rats without impairing extinction. Biological Psychiatry, 65(10), 887-892. |
| Rodriguez-Romaguera J., Sotres-Bayon F., Mueller D., & Quirk G. J. (2009). Systemic propranolol acts centrally to reduce conditioned fear in rats without impairing extinction. Biological Psychiatry, 65(10), 887-892. | |
| [32] | Rothbaum B. O., Kearns M. C., Reiser E., Davis J. S., Kerley K. A., Rothbaum A. O., … Ressler K. J. (2014). Early intervention following trauma may mitigate genetic risk for PTSD in civilians: A pilot prospective emergency department study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 75(12), 1380-1387. |
| Rothbaum B. O., Kearns M. C., Reiser E., Davis J. S., Kerley K. A., Rothbaum A. O., … Ressler K. J. (2014). Early intervention following trauma may mitigate genetic risk for PTSD in civilians: A pilot prospective emergency department study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 75(12), 1380-1387. | |
| [33] | Sah, P. (2017). Fear, anxiety, and the amygdala. Neuron, 96(1), 1-2. |
| Sah, P. (2017). Fear, anxiety, and the amygdala. Neuron, 96(1), 1-2. | |
| [34] | Sharp, B. M. (2017). Basolateral amygdala and stress-induced hyperexcitability affect motivated behaviors and addiction. Translational Psychiatry, 7(8), e1194. |
| Sharp, B. M. (2017). Basolateral amygdala and stress-induced hyperexcitability affect motivated behaviors and addiction. Translational Psychiatry, 7(8), e1194. | |
| [35] | Siddiqui S. A., Singh S., Ranjan V., Ugale R., Saha S., & Prakash A. (2017). Enhanced histone acetylation in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex is associated with fear extinction. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 37(7), 1287-1301. |
| Siddiqui S. A., Singh S., Ranjan V., Ugale R., Saha S., & Prakash A. (2017). Enhanced histone acetylation in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex is associated with fear extinction. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 37(7), 1287-1301. | |
| [36] | Sierra-Mercado D., Padilla-Coreano N., & Quirk G. J. (2011). Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(2), 529-538. |
| Sierra-Mercado D., Padilla-Coreano N., & Quirk G. J. (2011). Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(2), 529-538. | |
| [37] | Singewald, N., & Holmes, A. (2019). Rodent models of impaired fear extinction. Psychopharmacology, 236(1), 21-32. |
| Singewald, N., & Holmes, A. (2019). Rodent models of impaired fear extinction. Psychopharmacology, 236(1), 21-32. | |
| [38] | Singh S., Siddiqui S. A., Tripathy S., Kumar S., Saha S., Ugale R., … Prakash A. (2018). Decreased level of histone acetylation in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex following immediate extinction may result in deficit of extinction memory. Brain Research Bulletin, 140, 355-364. |
| Singh S., Siddiqui S. A., Tripathy S., Kumar S., Saha S., Ugale R., … Prakash A. (2018). Decreased level of histone acetylation in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex following immediate extinction may result in deficit of extinction memory. Brain Research Bulletin, 140, 355-364. | |
| [39] | Stafford J. M., Maughan D. K., Ilioi E. C., & Lattal K. M. (2013). Exposure to a fearful context during periods of memory plasticity impairs extinction via hyperactivation of frontal-amygdalar circuits. Learning & Memory, 20(3), 156-163. |
| Stafford J. M., Maughan D. K., Ilioi E. C., & Lattal K. M. (2013). Exposure to a fearful context during periods of memory plasticity impairs extinction via hyperactivation of frontal-amygdalar circuits. Learning & Memory, 20(3), 156-163. | |
| [40] | Taherian F., Vafaei A. A., Vaezi G. H., Eskandarian S., Kashef A., & Rashidy-Pour A. (2014). Propranolol-induced impairment of contextual fear memory reconsolidation in rats: A similar effect on weak and strong recent and remote memories. Basic & Clinical Neuroscience, 5(3), 231-239. |
| Taherian F., Vafaei A. A., Vaezi G. H., Eskandarian S., Kashef A., & Rashidy-Pour A. (2014). Propranolol-induced impairment of contextual fear memory reconsolidation in rats: A similar effect on weak and strong recent and remote memories. Basic & Clinical Neuroscience, 5(3), 231-239. | |
| [41] | Totty M. S., Payne M. R., & Maren S. (2019). Event boundaries do not cause the immediate extinction deficit after Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 9459. |
| Totty M. S., Payne M. R., & Maren S. (2019). Event boundaries do not cause the immediate extinction deficit after Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 9459. | |
| [42] | van Marle, H. J. F. V., Hermans E. J., Qin S., & Fernández G. (2009). From specificity to sensitivity: How acute stress affects amygdala processing of biologically salient stimuli. Biological Psychiatry, 66(7), 649-655. |
| van Marle, H. J. F. V., Hermans E. J., Qin S., & Fernández G. (2009). From specificity to sensitivity: How acute stress affects amygdala processing of biologically salient stimuli. Biological Psychiatry, 66(7), 649-655. | |
| [43] | Vervliet B., Craske M. G., & Hermans D. (2013). Fear extinction and relapse: State of the art. Annu Rev Clin Psychol, 9, 215-248. |
| Vervliet B., Craske M. G., & Hermans D. (2013). Fear extinction and relapse: State of the art. Annu Rev Clin Psychol, 9, 215-248. | |
| [44] | Wicking M., Steiger F., Nees F., Diener S. J., Grimm O., Ruttorf M., … Flor H. (2016). Deficient fear extinction memory in posttraumatic stress disorder. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 136, 116-126. |
| Wicking M., Steiger F., Nees F., Diener S. J., Grimm O., Ruttorf M., … Flor H. (2016). Deficient fear extinction memory in posttraumatic stress disorder. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 136, 116-126. | |
| [45] | Woods, A. M., & Bouton, M. E. (2008). Immediate extinction causes a less durable loss of performance than delayed extinction following either fear or appetitive conditioning. Learning & Memory, 15(12), 909-920. |
| Woods, A. M., & Bouton, M. E. (2008). Immediate extinction causes a less durable loss of performance than delayed extinction following either fear or appetitive conditioning. Learning & Memory, 15(12), 909-920. | |
| [46] | Wright L. A., Sijbrandij M., Sinnerton R., Lewis C., Roberts N. P., & Bisson J. I. (2019). Pharmacological prevention and early treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Translational Psychiatry, 9(1), 334. |
| Wright L. A., Sijbrandij M., Sinnerton R., Lewis C., Roberts N. P., & Bisson J. I. (2019). Pharmacological prevention and early treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder and acute stress disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Translational Psychiatry, 9(1), 334. |
| [1] | LI Junjiao, CHEN Wei, HU Yanjian, CAOYANG Jingwen, ZHENG Xifu. Effects of prediction error and acute stress on retrieval-extinction of fear memories of different strengths [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(6): 587-602. |
| [2] | HU Jingchu,ZHANG Weixin,CHEN Xiaoting,WANG Wenqing,WANG Zijie,ZHUANG Chuqun,FENG Biao,ZHENG Xifu. Cue specificity of reconsolidation update mechanism in remote fear memories [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(3): 316-323. |
| [3] | Wei CHEN, Junjiao LI, Jingwen CAOYANG, Yong YANG, Yanjian Hu, Xifu ZHENG. Effects of prediction error on post-retrieval extinction of fear to compound stimuli [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(7): 739-749. |
| [4] | XU Liang, XIE Xiaoyuan, YAN Pei, LI Junjiao, ZHENG Xifu. Sex differences in fear generalization [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(2): 197-205. |
| [5] | ZHUANG Chuqun, WANG Wenqing, HU Jingchu, ZHANG Weixin, WANG Penggui, ZHENG Xifu. The effect of compound stimulus to conditioned fear extinction in retrieval-extinction paradigm [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(3): 329-335. |
| [6] | LIAO Suqun, ZHENG Xifu. Inhibition of cognitive reappraisal on the negative valence facilitates extinction in conditioned fear [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(4): 352-361. |
| [7] | AN Xianli, CHEN Siguang. Inhibitory effects of reappraisal on conditioned fear acquisition and expression: Long-term influences measured by a spontaneous recovery test [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(10): 1239-1247. |
| [8] | DU Juan, ZENG Xiangxing, ZHENG Xifu, ZHUANG Chuqun. The Impact of Unconditioned Stimulus Devaluation on Conditional Fear Extinction [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(3): 344-352. |
| [9] | SUN Nan;ZhENG Xifu. Conditioned Acquisition and Extinction Modulates in Men and Women: Event-related Potential Research [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(4): 507-515. |
| [10] | ZHANG Qin;XU Xiaohong;LIU Xingyi;DONG Fangni;YANG Yanling;ZHANG Guangxia. The Effects of Long-term Exposure to Bisphenol-A on Fear Memory of Adult Mice [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(4): 500-506. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yuhe;JIN Yan;ZHENG Xifu;YAN Ke;ZHOU Shangyun. The Impact of State Anxiety on Fear Acquisition and Extinction [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(3): 396-404. |
| [12] | SUN Nan,WEI Yi-Ming,LI Qian,ZHENG Xi-Fu. Sex Differences in Extinction Return of Conditioned Fear Memory [J]. , 2012, 44(3): 314-321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||