

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (12): 2202-2219.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.2202
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Weiwei1,2,3( ), OU Minhua1, KANG Zhiqiang1, WEN Yuting1, LIN Xueqing1
), OU Minhua1, KANG Zhiqiang1, WEN Yuting1, LIN Xueqing1
Published:2025-12-25
Online:2025-09-28
Contact:
LI Weiwei
E-mail:weiweil2020@hunnu.edu.cn
LI Weiwei, OU Minhua, KANG Zhiqiang, WEN Yuting, LIN Xueqing. (2025). Equity or Efficiency? Impact of Completion Motivation on Prosocial Behavior Preferences. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(12), 2202-2219.
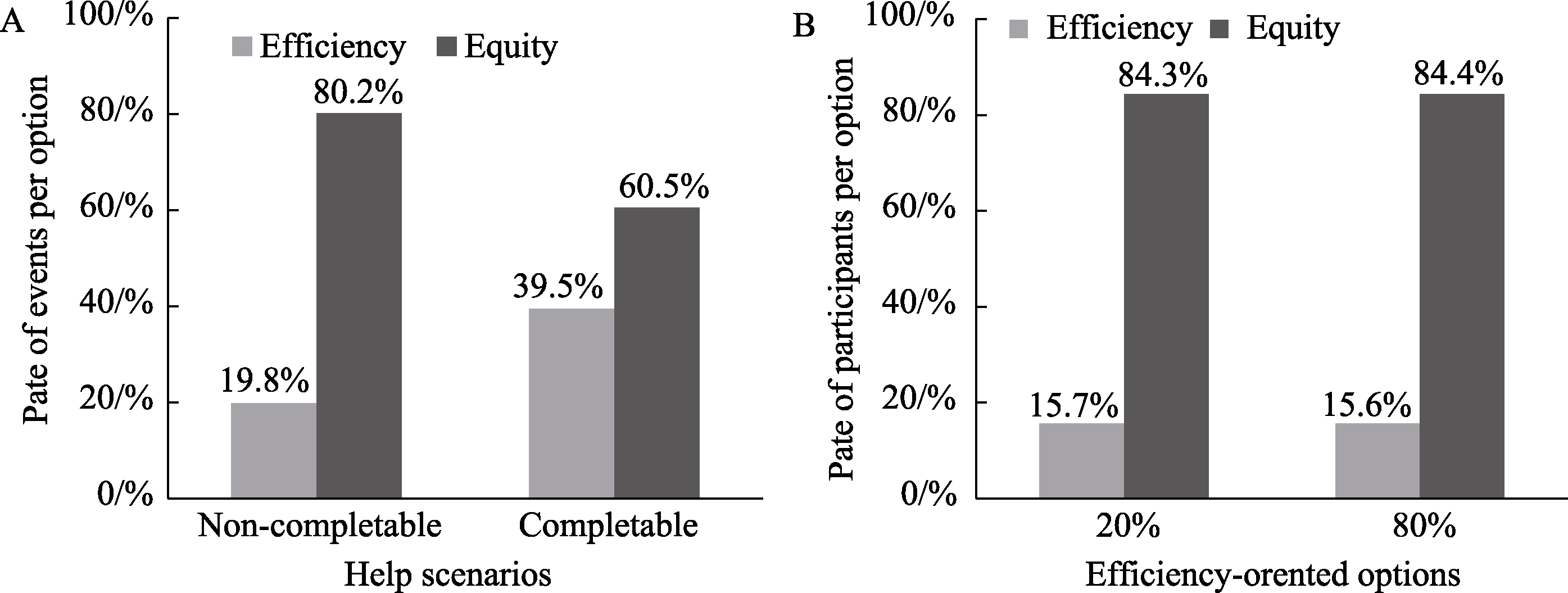
Figure 1 The influence of help scenarios and the efficiency of efficiency-oriented options on help preferences: (A) The influence of help scenarios on individual help preferences (Study 1); (B) The influence of efficiency on individual help preferences in the non-completable situation (Study 2).
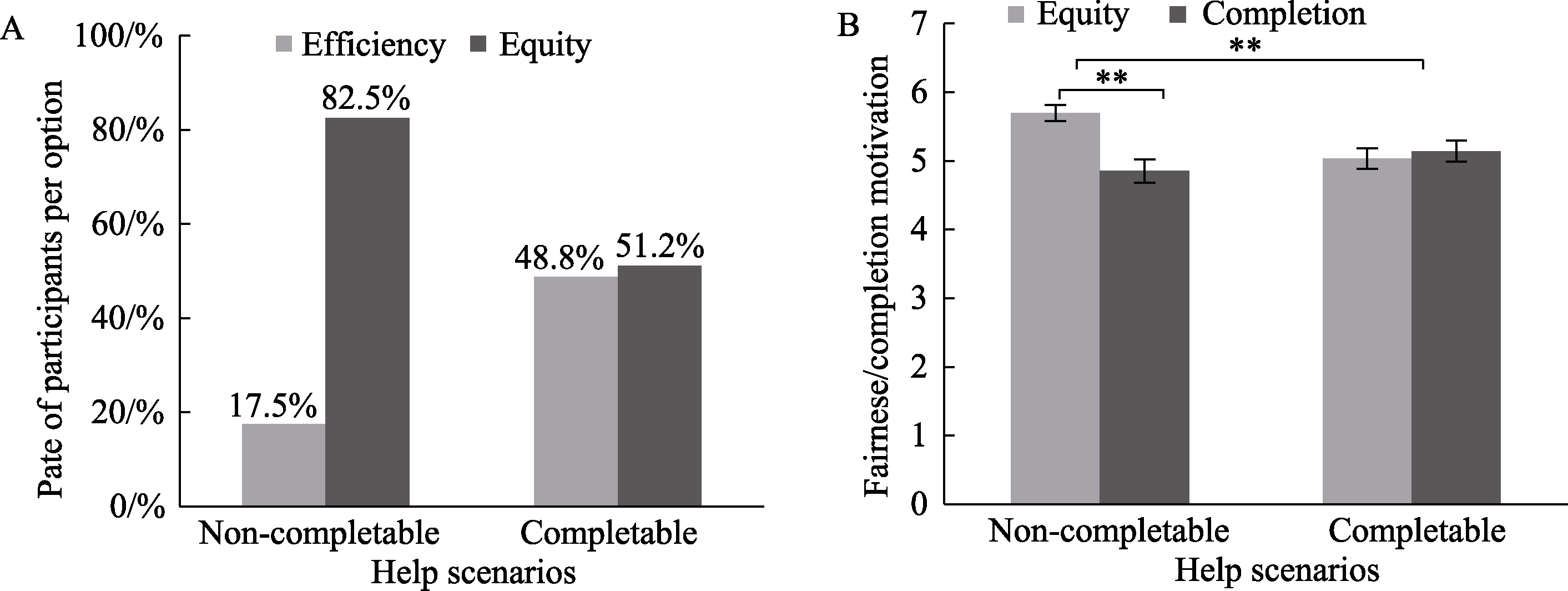
Figure 2 The influence of help scenarios on help preferences and motivation levels: (A) The influence of help scenarios on individual help preferences; (B) The influence of help scenarios on individual fairness motivation and completion motivation. ** p < 0.01
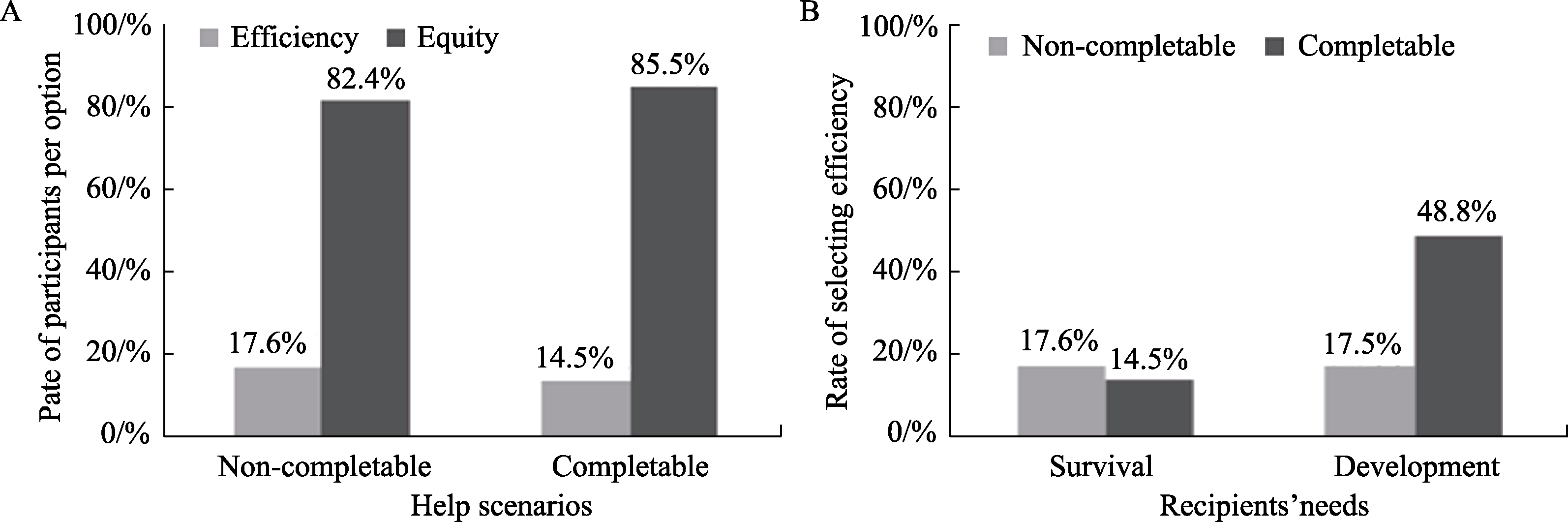
Figure 4 The influence of help scenarios and recipients' need on help preferences: (A) The influence of help completability on individual help preferences in the survival-related need situation; (B) The interaction effect of help scenarios and recipients' needs on individual help preferences.
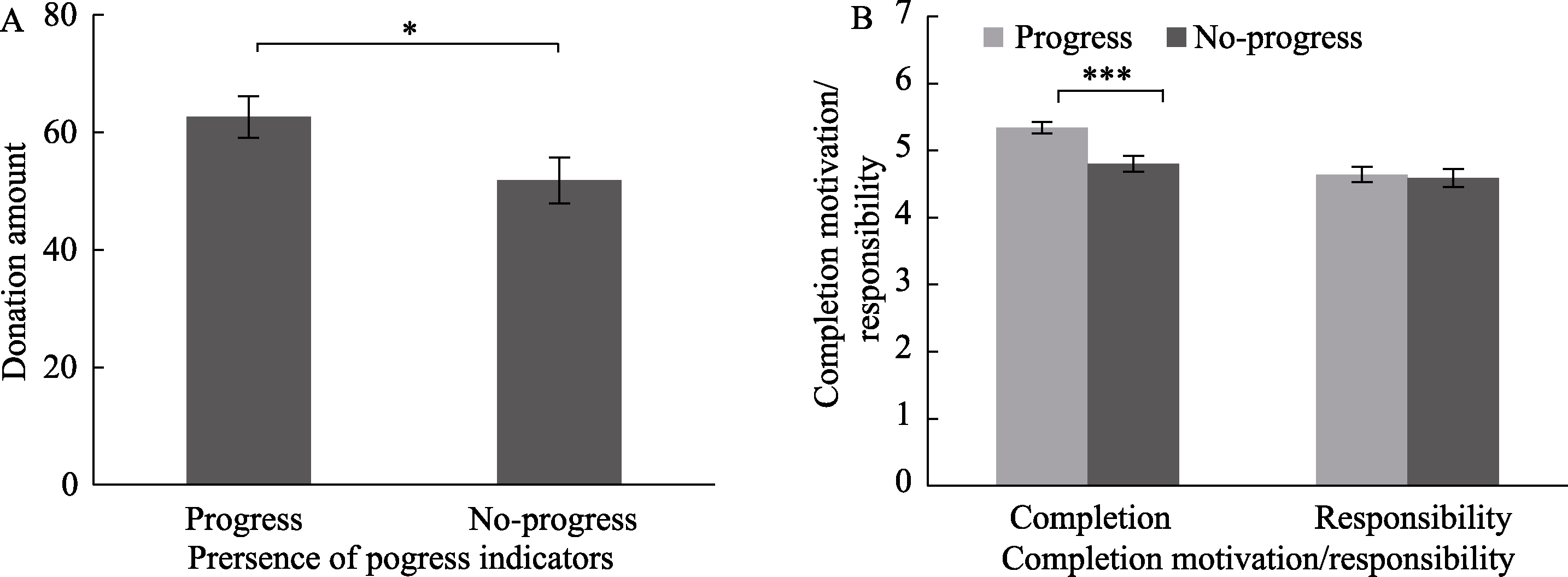
Figure 5. Effects of presence of progress indicators on donation amounts and completion motivation: (A) The effect of presence of progress indicators on individual donation amounts; (B) The effect of presence of progress indicators on individual completion motivation and sense of responsibility. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001
| [1] | Aknin L. B., Mayraz G., & Helliwell J. F. (2016). The emotional consequences of donation opportunities. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 12(2), 169-177. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2016.1163409 |
| [2] | Bergh R., & Reinstein D. (2021). Empathic and numerate giving: The joint effects of victim images and charity evaluations. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 12(3), 407-416. https://doi.org/10.1177/1948550619893968 |
| [3] |
Berman J. Z., Barasch A., Levine E. E., & Small D. A. (2018). Impediments to effective altruism: The role of subjective preferences in charitable giving. Psychological Science, 29(5), 834-844. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797617747648
doi: 10.1177/0956797617747648 URL pmid: 29659341 |
| [4] | Cai R., Wang Y. C., & Zhang T. (2025). Does metaverse stimulate tourism prosocial behavior? A mindfulness-driven model with a psychological ownership perspective. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 37(4), 1065-1096. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-08-2023-1130 |
| [5] |
Caviola L., Schubert S., & Greene J. D. (2021). The psychology of (in) effective altruism. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(7), 596-607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2021.03.015
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2021.03.015 URL pmid: 33962844 |
| [6] | Chen Y. G., Dai R. Y., Yao J. R., & Li Y. X. (2019). Donate time or money? The determinants of donation intention in online crowdfunding. Sustainability, 11(16), 4269. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164269 |
| [7] |
Colby H., DeWitt J., & Chapman G. B. (2015). Grouping promotes equality: The effect of recipient grouping on allocation of limited medical resources. Psychological Science, 26(7), 1084-1089. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615583978
doi: 10.1177/0956797615583978 URL pmid: 26078294 |
| [8] |
Conrad F. G., Couper M. P., Tourangeau R., & Peytchev A. (2010). The impact of progress indicators on task completion. Interacting with Computers, 22(5), 417-427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intcom.2010.03.001
URL pmid: 20676386 |
| [9] | Converse B. A., Tsang S., & Hennecke M. (2023). The value of mere completion. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 152(11), 3021-3036. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001434 |
| [10] | Crowne D. P., & Marlowe D. (1960). A new scale of social desirability independent of psychopathology. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 24(4), 349-354. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0047358 |
| [11] | Cryder C. E., Loewenstein G., & Seltman H. (2013). Goal gradient in helping behavior. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49(6), 1078-1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2013.07.003 |
| [12] |
Dai H. C., & Zhang D. J. (2019). Prosocial goal pursuit in crowdfunding: Evidence from Kickstarter. Journal of Marketing Research, 56(3), 498-517. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022243718821697
doi: 10.1177/0022243718821697 URL |
| [13] | Darley J. M., & Batson C. D. (1973). "From Jerusalem to Jericho": A study of situational and dispositional variables in helping behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 27(1), 100-108. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0034449 |
| [14] | Daunizeau J., Sheskin M., & Baumard N. (2016). Switching away from utilitarianism: The limited role of utility calculations in moral judgment. Plos One, 11(8), e0160084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160084 |
| [15] | Dewitte S., & Schouwenburg H. C. (2002). Procrastination, temptations, and incentives: The struggle between the present and the future in procrastinators and the punctual. European Journal of Personality, 16(6), 469-489. https://doi.org/10.1002/per.461 |
| [16] | Dovidio J. F., Piliavin J. A., Schroeder D. A., & Penner L. (2006). The social psychology of prosocial behavior. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. |
| [17] | Edwards A. R., Thorpe R., Masser B. M., & Barlow F. K. (2024). “Yeah, this is my donation”: An application of psychological ownership in blood donation. Journal of Health Psychology, 30(5), 1028-1043. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591053241254581 |
| [18] | Fahrenwaldt A., Olsen J., Rahal R. M., & Fiedler S. (2025). Intuitive deontology? A systematic review and multivariate, multilevel meta-analysis of experimental studies on the psychological drivers of moral judgments. Psychological Bulletin, 151(4), 428-454. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000472 |
| [19] | Fisher M., & Mormann M. (2022). The off by 100% bias: The effects of percentage changes greater than 100% on magnitude judgments and consumer choice. Journal of Consumer Research, 49(4), 561-573. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucac006 |
| [20] | Frey B. S., Savage D. A. & Torgler B. (2010). Interaction of natural survival instincts and internalized social norms exploring the Titanic and Lusitania disasters. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(11), 4862-4865. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911303107 |
| [21] | Gainsburg I., Pauer S., Abboub N., Aloyo E. T., Mourrat J. C., & Cristia A. (2023). How effective altruism can help psychologists maximize their impact. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 18(1), 239-253. https://doi.org/10.1177/17456916221079596 |
| [22] |
Gawronski B., Armstrong J., Conway P., Friesdorf R., & Hütter M. (2017). Consequences, norms, and generalized inaction in moral dilemmas: The CNI model of moral decision-making. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 113(3), 343-367. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspa0000086
doi: 10.1037/pspa0000086 URL pmid: 28816493 |
| [23] | Ghoshal S. (2005). Bad management theories are destroying good management practices. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 4(1), 75-91. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2005.16132558 |
| [24] | Gillon R. (1985). Philosophical medical ethic rights. British Medical Journal, 290(6485), 1890-1891. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.290.6485.1890 |
| [25] | Gino F., & Pierce L. (2009). The abundance effect: Unethical behavior in the presence of wealth. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 109(2), 142-155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2009.03.003 |
| [26] | Gordon‐Hecker T., Schneider I. K., Shalvi S., & Bereby‐Meyer Y. (2020). Leaving with something: When do people experience an equity-efficiency conflict? Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 34(2), 213-227. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdm.2205 |
| [27] | Gu Y. J., Botti S., & Faro D. (2018). Seeking and avoiding choice closure to enhance outcome satisfaction. Journal of Consumer Research, 45(4), 792-809. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucy025 |
| [28] | Haley K. J., & Fessler D. M. (2005). Nobody's watching? Subtle cues affect generosity in an anonymous economic game. Evolution and Human Behavior, 26(3), 245-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2005.01.002 |
| [29] | Huang L., Lei W., Xu F., Liu H., Yu L., Shi F., & Wang L. (2020). Maxims nudge equitable or efficient choices in a trade-off game. Plos One, 15(6), e0235443. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235443 |
| [30] |
Hsu M., Anen C., & Quartz S. R. (2008). The right and the good: Distributive justice and neural encoding of equity and efficiency. Science, 320(5879), 1092-1095. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1153651
doi: 10.1126/science.1153651 URL pmid: 18467558 |
| [31] | Jaeger B., & Vugt M. V. (2022). Psychological barriers to effective altruism: An evolutionary perspective. Current Opinion in Psychology, 44, 130-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.008 |
| [32] | Jensen J. D., King A. J., & Carcioppolo N. (2013). Driving toward a goal and the goal-gradient hypothesis: The impact of goal proximity on compliance rate, donation size, and fatigue. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 43(9), 1881-1895. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12152 |
| [33] | Jhang J. H., & Lynch J. G. (2015). Pardon the interruption: Goal proximity, perceived spare time, and impatience. Journal of Consumer Research, 41(5), 1267-1283. https://doi.org/10.1086/679308 |
| [34] | Kahneman D., Knetsch J. L., & Thaler R. H. (1986). Fairness and the assumptions of economics. Journal of Business, 59(4), 285-300. https://doi.org/10.1086/296367 |
| [35] | Karlan D., & Wood D. H. (2017). The effect of effectiveness: Donor response to aid effectiveness in a direct mail fundraising experiment. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 66, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2016.05.005 |
| [36] | Karni E., Salmon T., & Sopher B. (2007). Individual sense of fairness: An experimental study. Experimental Economics, 11(2), 174-189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10683-007-9165-1 |
| [37] | Kivetz R., Urminsky O., & Zheng Y. (2006). The goal-gradient hypothesis resurrected: Purchase acceleration, illusionary goal progress, and customer retention. Journal of Marketing Research, 43(1), 39-58. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkr.43.1.39 |
| [38] | Kouchaki M., Smith-Crowe K., Brief A. P., & Sousa C. (2013). Seeing green: Mere exposure to money triggers a business decision frame and unethical outcomes. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 121(1), 53-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2012.12.002 |
| [39] | Kreps T. A., & Monin B. (2011). “Doing well by doing good”? Ambivalent moral framing in organizations. Research in Organizational Behavior, 31, 99-123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2011.09.008 |
| [40] | Kupor D. M., Reich T., & Shiv B. (2014). Can't finish what you started? The effect of climactic interruption on behavior. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 25(1), 113-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcps.2014.05.006 |
| [41] | Kuppuswamy V., & Bayus B. L. (2017). Does my contribution to your crowdfunding project matter? Journal of Business Venturing, 32(1), 72-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2016.10.004 |
| [42] | Li M., & Chapman G. B. (2009). “100% of anything looks good”: The appeal of one hundred percent. Psychological Science, 16(1), 156-162. https://doi.org/10.3758/PBR.16.1.156 |
| [43] | Li M., & Chapman G. B. (2013). A big fish or a small pond? Framing effects in percentages. Organizational Behavior Human Decision Processes, 122(2), 190-199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2013.07.003 |
| [44] | Li Y., & Pandelaere M. (2024). The purity premium effect: The asymmetrical value change around pure products. Psychology Marketing, 41(2), 328-343. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21937 |
| [45] | Liang B. C. (2021). The goal is attainable: The effects of goal gradient and sub-goals on escalation of commitment in a new product evaluation. Innovation & Management Review, 18(3), 258-275. https://doi.org/10.1108/Inmr-05-2020-0064 |
| [46] |
Lin J., Xu Y. B., Yang Y., Zhang Q. P., & Kou Y. (2024). Network analysis and core dimensions of adolescent prosocial behavior. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(9), 1252-1265. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.01252
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.01252 URL |
| [47] | MacAskill W. (2015). Doing good better: Effective altruism and a radical new way to make a difference. Guardian Faber Publishing. |
| [48] | Markowitz E. M., Slovic P., Västfjäll D., & Hodges S. D. (2023). Compassion fade and the challenge of environmental conservation. Judgment and Decision Making, 8(4), 397-406. https://doi.org/10.1017/s193029750000526x |
| [49] | Merchant A., Ford J. B., & Sargeant A. (2010). Charitable organizations' storytelling influence on donors' emotions and intentions. Journal of Business Research, 63(7), 754-762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2009.05.013 |
| [50] | Metzger L. A., & Günther I. (2019). Is it what you say or how you say it? The impact of aid effectiveness information and its framing on donation behavior. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 83, 101461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2019.101461 |
| [51] | Morvinski C. (2022). The effect of unavailable donation opportunities on donation choice. Marketing Letters, 33(1), 45-60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-021-09613-4 |
| [52] | Moskowitz G. B. (2002). Preconscious effects of temporary goals on attention. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 38(4), 397-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1031(02)00001-x |
| [53] |
Penner L. A., Dovidio J. F., Piliavin J. A., & Schroeder D. A. (2005). Prosocial behavior: Multilevel perspectives. Annual Review of Psychology, 56, 365-392. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070141
URL pmid: 15709940 |
| [54] | Persson E., & Tinghög G. (2023). The effect of fast and slow decision-making on equity-efficiency tradeoffs and moral repugnance. Royal Society Open Science, 10(9), 230558. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.230558 |
| [55] | Pierce J. L., Kostova T., & Dirks K. T. (2003). The state of psychological ownership: Integrating and extending a century of research. Review of General Psychology, 7(1), 84-107. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.7.1.84 |
| [56] | Roberts A. R., Imas A., & Fishbach A. (2024). Can’t wait to pay: The desire for goal closure increases impatience for costs. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 126(6), 1019-1035. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspa0000367 |
| [57] | Ruan B. W., Polman E., & Tanner R. J. (2024). The one-away effect: The pursuit of mere completion. Journal of Consumer Research, 50(5), 945-961. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucad030 |
| [58] | Schroeder, D. A., & Graziano W. G. (Eds.). (2015). The Oxford handbook of prosocial behavior. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780195399813.001.0001 |
| [59] | Schweitzer M. E., Ordóñez L., & Douma B. (2004). Goal setting as a motivator of unethical behavior. Academy of Management Journal, 47(3), 422-432. https://doi.org/10.2307/20159591 |
| [60] |
Sharps D. L., & Schroeder J. (2019). The preference for distributed helping. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 117(5), 954-977. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000179
doi: 10.1037/pspi0000179 URL pmid: 30883144 |
| [61] | Shi R., Qi W. G., Ding Y., Liu C., & Shen W. (2020). Under what circumstances is helping an impulse? Emergency and prosocial traits affect intuitive prosocial behavior. Personality and Individual Differences, 159, 109828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.109828 |
| [62] | Shine A., Simonyan Y., & Johnson S. (2022, November). Consumer choices around corporate giving: Should companies prioritise aid to the most effective causes? Paper presented at Society of Judgement and Decision Making, San Diego, CA. |
| [63] | Tobler P. N., Kalis A., & Kalenscher T. (2008). The role of moral utility in decision making: An interdisciplinary framework. Cognitive, Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 8(4), 390-401. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.8.4.390 |
| [64] |
Ubel P. A., Baron J., Nash B., & Asch D. A. (2000). Are preferences for equity over efficiency in health care allocation "all or nothing"? Medical Care, 38(4), 366-373. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-200004000-00003
URL pmid: 10752968 |
| [65] |
Ubel P. A., DeKay M. L., Baron J., & Asch D. A. (1996). Cost-effectiveness analysis in a setting of budget constraints — Is it equitable? New England Journal of Medicine, 334(18), 1174-1177. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199605023341807
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199605023341807 URL pmid: 8602185 |
| [66] | Van Staveren I. (2007). Beyond utilitarianism and deontology: Ethics in economics. Review of Political Economy, 19(1), 21-35. https://doi.org/10.1080/09538250601080776 |
| [67] | Wang S. S. (2024). Streaming for good: Streamer‐viewer interaction, beneficiary focus, and donation progress. Journal of Philanthropy and Marketing, 29(2), e1849. https://doi.org/10.1002/nvsm.1849 |
| [68] | Wang T. H., Shen S. J., Cheng Z. P., & Xie X. F. (2024). From surviving to thriving: How preferences shift in helping resource allocation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 30(4), 571-585. https://doi.org/10.1037/xap0000516 |
| [69] | Wang Y. L., & Xie X. F. (2020). Halfway to my request is not halfway to my heart: Underestimating appreciation for partial help. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 47(10), 1466-1479. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167220975276 |
| [70] | Weng H. Y., Fox A. S., Hessenthaler H. C., Stodola D. E., & Davidson R. J. (2015). The role of compassion in altruistic helping and punishment behavior. Plos One, 10(12), e0143794. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143794 |
| [71] | Xie D. J., Meng P., & Su Y. J. (2019). “Favoring my playmate seems fair”: Inhibitory control and theory of mind in preschoolers’ self-disadvantaging behaviors. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 184, 158-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2019.03.004 |
| [72] | Yu J. X., Wang Y., Yu J. L., & Zeng J. M. (2021). Racial ingroup bias and efficiency consideration influence distributive decisions: A dynamic analysis of time domain and time frequency. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 630811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.630811 |
| [73] | Zhang S. M., & Feng T. Y. (2020). Modeling procrastination: Asymmetric decisions to act between the present and the future. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 149(2), 311-322. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000643 |
| [74] | Zhu M., Yang Y., & Hsee C. K. (2018). The mere urgency effect. Journal of Consumer Research, 45(3), 673-690. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucy008 |
| [1] | WANG Zuo-Jun, YE Yan, CHENG Xue-Yan, XU Sihua. ‘Renqing’ or equity? The influence of favor acceptance on inequity aversion [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(8): 1452-1467. |
| [2] | YANG Zijian, ZHAO Xiaolin, GUO Kaige, LUO Jiahao, DU Tengfei, ZHANG Yajie, HU Yueqin, YANG Juan. Variability in cortisol awakening response related to sleep efficiency and its relationship with trait anxiety and psychological resilience [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2025, 57(1): 84-99. |
| [3] | DING Ying, ZHONG Jiaqi. The effect of social crowding on individual preference for self-improvement products [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(2): 216-228. |
| [4] | YIN Rong; ZHANG Feifei; WANG Yuanyuan; ZANG Rixia. Protest encounters setback: Effects of emotional reactions on participation intention in context of frustrate collective action [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(4): 482-499. |
| [5] | LIU Wen, ZHU Lin, ZHANG Xue, ZHANG Yu, LIU Ying. Equity Sensitivity of 2~3 Years Old Children in Distribution Condition [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(11): 1341-1348. |
| [6] | Ling-Wenquan,Yang-Huijun,Fang-Liluo. Perceived Organizational Support(POS) of the Employees [J]. , 2006, 38(02): 281-287. |
| [7] | Jin Zhicheng, Sui Jie(Department of Psychology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024). A STUDY ON THE COGNITIVE PROCESSING MECHANISM OF STUDENTS WITH LEARNING DIFFICULTIES [J]. , 1999, 31(01): 47-52. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||