

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (7): 1231-1247.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1231
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
CEN Yushan1, XIA Lingxiang1( ), HUANG Runyu2, LV Jie1
), HUANG Runyu2, LV Jie1
Published:2025-07-25
Online:2025-04-24
Contact:
XIA Lingxiang, E-mail: CEN Yushan, XIA Lingxiang, HUANG Runyu, LV Jie. (2025). The two-factor structure of harm aversion and the mechanism underlying its function of resisting aggression. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(7), 1231-1247.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1231
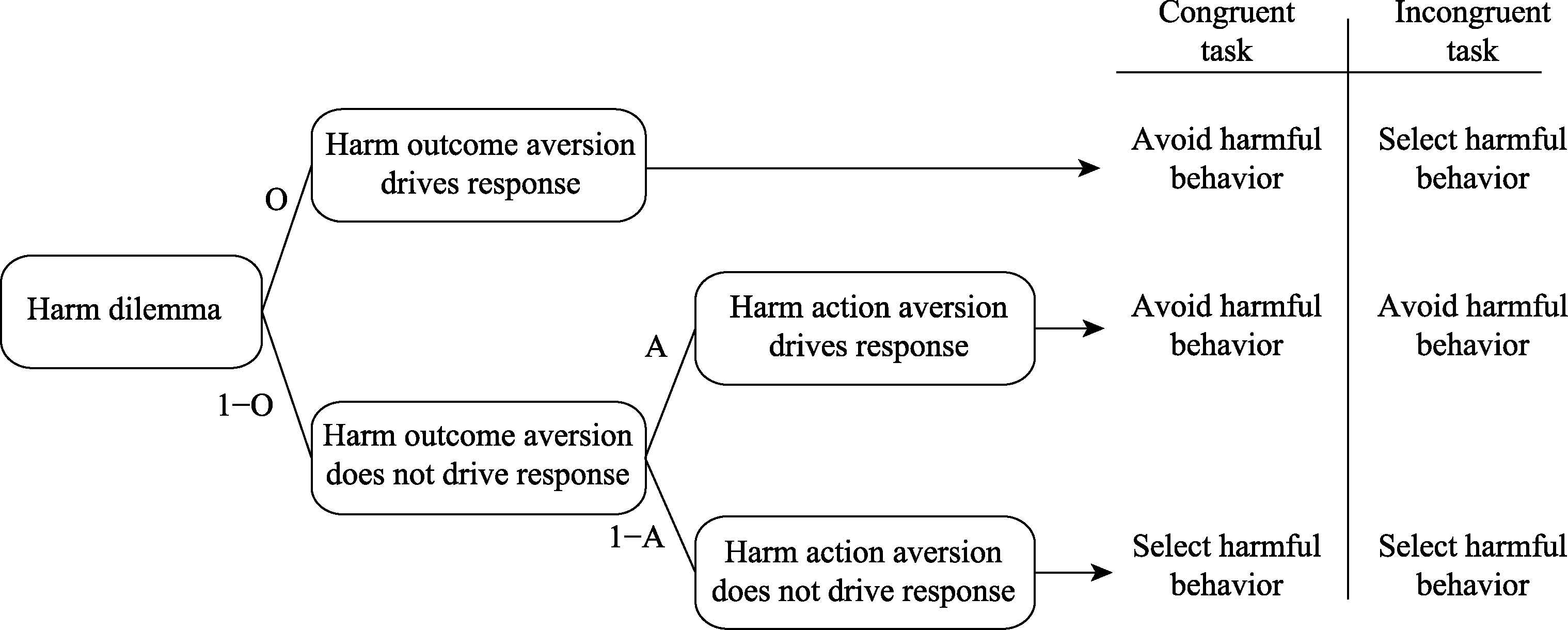
Figure 1. Processing Tree for Separating Harm Action Aversion and Harm Outcome Aversion. Note: A, Harm action aversion parameter; O, Harm outcome aversion parameter
| Criterion | Parameter A | Parameter O | Correlation Difference Test z | Correlation Difference Test p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harm Action Aversion Score | 0.16** | 0.23*** | ?0.90 | 0.370 |
| Harm Outcome Aversion Score | 0.08 | 0.23*** | ?2.02* | 0.044 |
| Empathy | 0.13* | 0.30*** | ?2.25* | 0.024 |
| Traditional Moral Judgment | 0.27*** | 0.22*** | 0.61 | 0.544 |
| Deontology Parameter | 0.29*** | 0.28*** | 0.22 | 0.830 |
| Utilitarianism Parameter | ?0.05 | ?0.01 | ?0.56 | 0.579 |
| Psychopathy | ?0.27*** | ?0.42*** | 2.07* | 0.038 |
| Physical Aggression | ?0.22*** | ?0.22*** | 0.05 | 0.958 |
| Verbal Aggression | ?0.09 | ?0.13* | 0.47 | 0.638 |
Table 1. Correlations between Parameter A, Parameter O, and Criteria
| Criterion | Parameter A | Parameter O | Correlation Difference Test z | Correlation Difference Test p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harm Action Aversion Score | 0.16** | 0.23*** | ?0.90 | 0.370 |
| Harm Outcome Aversion Score | 0.08 | 0.23*** | ?2.02* | 0.044 |
| Empathy | 0.13* | 0.30*** | ?2.25* | 0.024 |
| Traditional Moral Judgment | 0.27*** | 0.22*** | 0.61 | 0.544 |
| Deontology Parameter | 0.29*** | 0.28*** | 0.22 | 0.830 |
| Utilitarianism Parameter | ?0.05 | ?0.01 | ?0.56 | 0.579 |
| Psychopathy | ?0.27*** | ?0.42*** | 2.07* | 0.038 |
| Physical Aggression | ?0.22*** | ?0.22*** | 0.05 | 0.958 |
| Verbal Aggression | ?0.09 | ?0.13* | 0.47 | 0.638 |
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Parameter A | 0.57 | 0.16 | ? | ||||
| 2. Parameter O | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.09 | ? | |||
| 3. Moral Disengagement | 1.99 | 0.55 | ?0.17*** | ?0.32*** | ? | ||
| 4. Physical Aggression | 1.84 | 0.63 | ?0.16** | ?0.32*** | 0.60*** | ? | |
| 5. Verbal Aggression | 2.60 | 0.73 | ?0.05 | ?0.13** | 0.32*** | 0.48*** | ? |
Table 2 Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis (Experiments 2a)
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Parameter A | 0.57 | 0.16 | ? | ||||
| 2. Parameter O | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.09 | ? | |||
| 3. Moral Disengagement | 1.99 | 0.55 | ?0.17*** | ?0.32*** | ? | ||
| 4. Physical Aggression | 1.84 | 0.63 | ?0.16** | ?0.32*** | 0.60*** | ? | |
| 5. Verbal Aggression | 2.60 | 0.73 | ?0.05 | ?0.13** | 0.32*** | 0.48*** | ? |
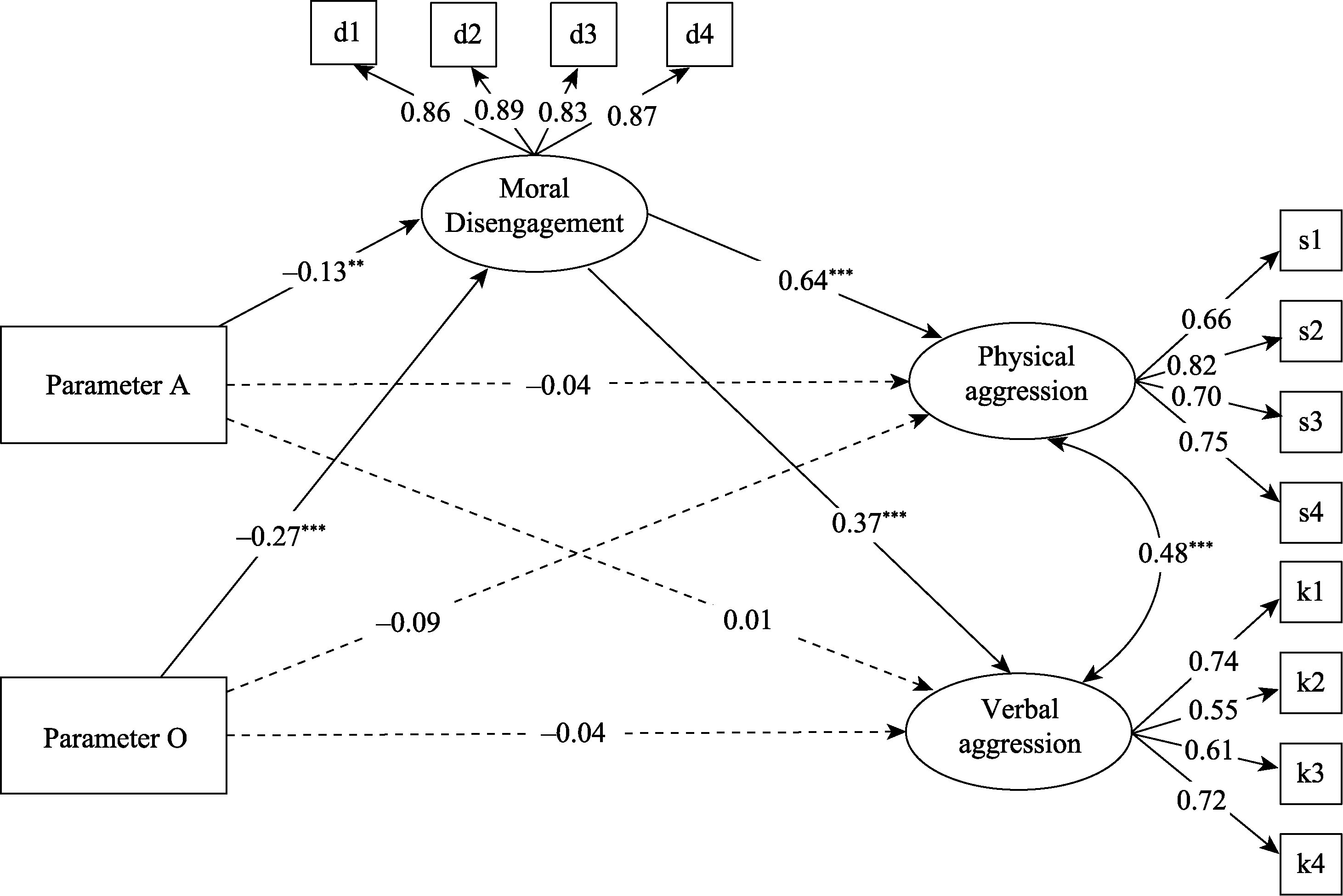
Figure 2. Structural Model of Parameter A/O, Moral Disengagement, and Physical/Verbal Aggression. Note. Path coefficients are standardized coefficients, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.. For visual clarity, paths for gender and age are hidden; dashed lines indicate non-significant paths.
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Parameter A | 0.51 | 0.16 | ? | |||
| 2. Parameter O | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.17 | ? | ||
| 3. Moral Disengagement | 2.00 | 0.58 | ?0.02 | ?0.21* | ? | |
| 4. Aggressive Behavior | 0.48 | 0.36 | ?0.01 | ?0.24* | 0.60*** | ? |
Table 3 Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis (Experiments 2b)
| Variable | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Parameter A | 0.51 | 0.16 | ? | |||
| 2. Parameter O | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.17 | ? | ||
| 3. Moral Disengagement | 2.00 | 0.58 | ?0.02 | ?0.21* | ? | |
| 4. Aggressive Behavior | 0.48 | 0.36 | ?0.01 | ?0.24* | 0.60*** | ? |
| Path | Effect Size | 95% CI | Effect Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLCI | ULCI | |||
| Total effect: Parameter O → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.23 | ?0.39 | ?0.06 | 100% |
| Mediation effect: Parameter O → Moral Disengagement → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.12 | ?0.26 | 0.03 | 50.00% |
| Direct effect: Parameter O → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.12 | ?0.21 | ?0.02 | 50.00% |
Table 4 Overall Test of Mediation Effect
| Path | Effect Size | 95% CI | Effect Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLCI | ULCI | |||
| Total effect: Parameter O → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.23 | ?0.39 | ?0.06 | 100% |
| Mediation effect: Parameter O → Moral Disengagement → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.12 | ?0.26 | 0.03 | 50.00% |
| Direct effect: Parameter O → Aggressive Behavior | ?0.12 | ?0.21 | ?0.02 | 50.00% |
| [1] | Almeida, G., Flanagan, B., & Hannikainen, I. (2024). Trait empathy predicts purposivist rule application: Nationally representative survey evidence. SSRN Electronic Journal. Advance online publication. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4710786 |
| [2] | Ariso, J. M. (2022). Is there an internal link between seeing a human and seeing one to whom moral consideration is due? In C. Eriksen, J. Hermann, N. O'Hara, & N. Pleasants (Eds.), Philosophical Perspectives on Moral Certainty (pp. 212-228). Routledge. |
| [3] | Armstrong, J., Friesdorf, R., & Conway, P. (2018). Clarifying gender differences in moral dilemma judgments: The complementary roles of harm aversion and action aversion. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 10(3), 353-363. |
| [4] |
Bandura, A. (1999). Moral disengagement in the perpetration of inhumanities. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 3(3), 193-209.
doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr0303_3 pmid: 15661671 |
| [5] | Bandura, A. (2002). Selective moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency. Journal of Moral Education, 31(2), 101-119. |
| [6] | Bjärehed, M., Thornberg, R., Wänström, L., & Gini, G. (2020). Mechanisms of moral disengagement and their associations with indirect bullying, direct bullying, and pro-aggressive bystander behavior. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 40(1), 28-55. |
| [7] |
Blair, R. J. R. (1995). A cognitive developmental approach to morality: Investigating the psychopath. Cognition, 57(1), 1-29.
doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(95)00676-p pmid: 7587017 |
| [8] |
Blair, R. J. R. (2007). The amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex in morality and psychopathy. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(9), 387-392.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.07.003 pmid: 17707682 |
| [9] |
Buss, A. H. (1966). Instrumentality of aggression, feedback, and frustration as determinants of physical aggression. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 3(2), 153-162.
doi: 10.1037/h0022826 pmid: 5903523 |
| [10] |
Buss, A. H., & Perry, M. (1992). The aggression questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63(3), 452-459.
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.63.3.452 pmid: 1403624 |
| [11] | Caprara, G. V., Fida, R., Vecchione, M., Tramontano, C., & Barbaranelli, C. (2009). Assessing civic moral disengagement: Dimensionality and construct validity. Personality and Individual Differences, 47(5), 504-509. |
| [12] | Carroll, A., McCarthy, M., Houghton, S., Sanders O'Connor, E., & Zadow, C. (2018). Reactive and proactive aggression as meaningful distinctions at the variable and person level in primary school-aged children. Aggressive Behavior, 44(5), 431-441. |
| [13] |
Cen, Y., Su, S., Dong, Y., & Xia, L. X. (2022). Longitudinal effect of self-control on reactive-proactive aggression: Mediating roles of hostile rumination and moral disengagement. Aggressive Behavior, 48(6), 583-594.
doi: 10.1002/ab.22046 pmid: 35853143 |
| [14] | Chowdhury, R., & Fernando, M. (2014). The relationships of empathy, moral identity and cynicism with consumers' ethical beliefs: The mediating role of moral disengagement. Journal of Business Ethics, 124(4), 677-694. |
| [15] | Cohen, J. (1969). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Academic Press |
| [16] | Contreras-Huerta, L. S., Lockwood, P. L., Bird, G., Apps, M., & Crockett, M. J. (2022). Prosocial behavior is associated with transdiagnostic markers of affective sensitivity in multiple domains. Emotion, 22(5), 820-835. |
| [17] | Conway, P., Dawtry, R. J., Lam, J., & Gheorghiu, A. I. (2024). Is it fair to kill one to save five? How just world beliefs shape sacrificial moral decision-making. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, Advance online publication. http://doi.org/10.1177/01461672241287815. |
| [18] |
Conway, P., & Gawronski, B. (2013). Deontological and utilitarian inclinations in moral decision making: A process dissociation approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 104(2), 216-235.
doi: 10.1037/a0031021 pmid: 23276267 |
| [19] |
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1996). Social information-processing mechanisms on reactive and proactive aggression. Child Development, 67(3), 993-1002.
pmid: 8706540 |
| [20] |
Crockett, M. J., Clark, L., Hauser, M. D., & Robbins, T. W. (2010). Serotonin selectively influences moral judgment and behavior through effects on harm aversion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(40), 17433-17438.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009396107 pmid: 20876101 |
| [21] | Crockett, M. J., Kurth-Nelson, Z., Siegel, J. Z., Dayan, P., & Dolan, R. J. (2014). Harm to others outweighs harm to self in moral decision making. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(48), 17320-17325. |
| [22] |
Crockett, M. J., Siegel, J. Z., Kurth-nelson, Z., Ousdal, O. T., Story, G. W., Frieband, C., ... Dolan, R. J. (2015). Dissociable effects of serotonin and dopamine on the valuation of harm in moral decision making. Current Biology, 25(14), 1852-1859.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.05.021 pmid: 26144968 |
| [23] |
Cushman, F. (2013). Action, outcome, and value: A dual-system framework for morality. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 17(3), 273-292.
doi: 10.1177/1088868313495594 pmid: 23861355 |
| [24] |
Cushman, F., Gray, K., Gaffey, A., & Mendes, W. B. (2012). Simulating murder: The aversion to harmful action. Emotion, 12(1), 2-7.
doi: 10.1037/a0025071 pmid: 21910540 |
| [25] |
Cushman, F., Sheketoff, R., Wharton, S., & Carey, S. (2013). The development of intent-based moral judgment. Cognition, 127(1), 6-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.11.008 pmid: 23318350 |
| [26] | Cushman, F., Young, L., & Greene, J. D. (2010). Our multi-system moral psychology:Towards a consensus view. In J. M. Doris (Ed.), Oxford handbook of moral psychology (pp. 1-20). Oxford University Press. |
| [27] |
Cushman, F., Young, L., & Hauser, M. (2006). The role of conscious reasoning and intuition in moral judgment: Testing three principles of harm. Psychological Science, 17(12), 1082-1089.
pmid: 17201791 |
| [28] | Davis, M. H. (1983). Measuring individual differences in empathy: Evidence for a multidimensional approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44(1), 113-126. |
| [29] | Deng, Q., Deng, J., Lai, H., Huang, Y., & Wang, M. (2017). The factor structure and psychometric properties of the Levenson self-report psychopathic scale. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 25(4), 659-666. |
| [30] | Diedenhofen, B., & Musch, J. (2015). Cocor: A comprehensive solution for the statistical comparison of correlations. Plos One, 10(4), Article e121945. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121945 |
| [31] | Dou, K., Chen, L. Y., Li, Y. Y., Lin, X. Q., Yuan, X. Q., & Li, J. B. (2024). The longitudinal associations between nonviolent/violent stressful life events, moral disengagement, and online aggression in Chinese young people through the lens of general aggression model. Psychology of Violence, 14(5), 364-372. |
| [32] | Falla, D., Ortega-Ruiz, R., & Romera, E. M. (2023). Minimizing responsibility in the aggressive dynamics of bullying and its impact on other strategies of moral disengagement: A longitudinal study. Current Psychology, 42(36), 32512-32523. |
| [33] |
Feldmanhall, O., Dalgleish, T., Evans, D., & Mobbs, D. (2015). Empathic concern drives costly altruism. Neuroimage, 105, 347-356.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.043 pmid: 25462694 |
| [34] | Fitouchi, L., Andre, J. B., & Baumard, N. (2022). Moral disciplining: The cognitive and evolutionary foundations of puritanical morality. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 46, Article e293. http://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X22002047 |
| [35] | Fung, A. L. (2021). Sex differences in the relationships between forms of peer victimization and reactive and proactive aggression in schoolchildren. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), Article 5443 http://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105443 |
| [36] | Gawronski, B., & Ng, N. L. (2025). Beyond trolleyology: The CNI model of moral-dilemma responses. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 29(1), 32-80. |
| [37] | Gibson, S., & Ninness, B. (2005). Robust maximum-likelihood estimation of multivariable dynamic systems. Automatica, 41(10), 1667-1682. |
| [38] | Gini, G., Thornberg, R., Bussey, K., Angelini, F., & Pozzoli, T. (2021). Longitudinal links of individual and collective morality with adolescents’ peer aggression. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 51(3), 524-539. |
| [39] |
Gray, K., Waytz, A., & Young, L. (2012). The moral dyad: A fundamental template unifying moral judgment. Psychological Inquiry, 23(2), 206-215.
doi: 10.1080/1047840X.2012.686247 pmid: 22815620 |
| [40] |
Greene, J. D., Cushman, F. A., Stewart, L. E., Lowenberg, K., Nystrom, L. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2009). Pushing moral buttons: The interaction between personal force and intention in moral judgment. Cognition, 111(3), 364-371.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2009.02.001 pmid: 19375075 |
| [41] | Guo, Y., Li, R., & Xia, L. X. (2024). Effects of relative deprivation on change in displaced aggression and the underlying motivation mechanism: A three-wave cross-lagged analysis. British Journal of Psychology, 115(1), 1-19. |
| [42] | Hou, Y., Li, X., & Xia, L. X. (2024). Common mechanisms underlying the effect of angry rumination on reactive and proactive aggression: A moderated mediation model. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 39(5-6), 1035-1057. |
| [43] | Hoyle, R. H., & Panter, A. T. (1995). Writing about structural equation models. In R. H.Hoyle (Ed.), Structural equation modeling: Concepts, issues, and applications (pp. 158-176). Thousand Oaks: Sage publications. |
| [44] | Jacoby, L. L. (1991). A process dissociation framework: Separating automatic from intentional uses of memory. Journal of Memory and Language, 30(5), 513-541. |
| [45] |
Khemka, S., Tzovara, A., Gerster, S., Quednow, B. B., & Bach, D. R. (2017). Modeling startle eyeblink electromyogram to assess fear learning. Psychophysiology, 54(2), 204-214.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.12775 pmid: 27753123 |
| [46] |
Levenson, M. R., Kiehl, K. A., & Fitzpatrick, C. M. (1995). Assessing psychopathic attributes in a noninstitutionalized population. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68(1), 151-158.
doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.68.1.151 pmid: 7861311 |
| [47] | Leviston, Z., & Walker, I. (2020). Influence of moral disengagement on responses to climate change. Asian Journal of Social Psychology, 24(2), 144-155. |
| [48] |
Li, R., & Xia, L. (2021). The mediating effect of aggression motivation on the relationship between trait anger and reactive aggression: A longitudinal study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(7), 788-797.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00788 |
| [49] | Li, X., & Xia, L. (2024). A serial cascade effect of cybervictimization and hostile rumination on the within-person change of moral disengagement. Journal of Personality. 92(6), 1726-1743. |
| [50] | Li, Y. (2023). Cognitive and emotional factors in moral decision- making. Journal of Education, Humanities and Social Sciences, 22, 774-779. |
| [51] | Liao, J., Wang, J., Jia, S., Cai, Z., & Liu, H. (2024). Correlation of muscle strength, working memory, and activities of daily living in older adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 16, Article1453527. http://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1453527 |
| [52] | Little, R. J., & Rubin, D. B. (2002). Statistical analysis with missing data. New York, NY: Wiley. |
| [53] | Martinez, R. M., Chou, S. H., Fan, Y. T., Chen, Y. C., Goh, K. K., & Chen, C. (2024). Negative emotionality down-regulation affects moral choice but not moral judgement of harm: A pharmacological study. Scientific Reports, 14(1), Article 1200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-51345-8 |
| [54] | Miller, R., & Cushman, F. (2013). Aversive for me, wrong for you: First-person behavioral aversions underlie the moral condemnation of harm. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 7(10), 707-718. |
| [55] |
Miller, R. M., Hannikainen, I. A., & Cushman, F. A. (2014). Bad actions or bad outcomes? Differentiating affective contributions to the moral condemnation of harm. Emotion, 14(3), 573-587.
doi: 10.1037/a0035361 pmid: 24512250 |
| [56] | Nocera, T. R., Dahlen, E. R., Poor, A., Strowd, J., Dortch, A., & Van Overloop, E. C. (2022). Moral disengagement mechanisms predict cyber aggression among emerging adults. Cyberpsychology-Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 16(1), 1-18. |
| [57] | Ogunfowora, B. T., Nguyen, V. Q., Steel, P., & Hwang, C. C. (2022). A meta-analytic investigation of the antecedents, theoretical correlates, and consequences of moral disengagement at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 107(5), 746-775. |
| [58] | Ouvrein, G., De Backer, C. J. S., & Vandebosch, H. (2018). Online celebrity aggression: A combination of low empathy and high moral disengagement? The relationship between empathy and moral disengagement and adolescents' online celebrity aggression. Computers in Human Behavior, 89, 61-69. |
| [59] | Patil, I. (2015). Trait psychopathy and utilitarian moral judgement: The mediating role of action aversion. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 27(3), 349-366. |
| [60] | Pavailler, N., Gevers, W., & Burle, B. (in press). Temporal metacognition: Direct readout or mental construct? The case of introspective reaction time. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001708 |
| [61] | Pearson, K., & Filon, L. N. G. (1898). Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution.—IV. On the probable errors of frequency constants and on the influence of random selection on variation and correlation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series a, Containing Papers of a Mathematical or Physical Character, 191, 229-311. |
| [62] | Perera, P., Canic, E., & Ludvig, E. A. (2016). Cruel to be kind but not cruel for cash: Harm aversion in the dictator game. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(3), 893-898. |
| [63] | Quan, F., Yang, R., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Gong, X., Chen, Y., ... Xia, L. (2019). The relationship between hostile attribution bias and aggression and the mediating effect of anger rumination. Personality and Individual Differences, 139, 228-234. |
| [64] |
Reynolds, C. J., & Conway, P. (2018). Not just bad actions: Affective concern for bad outcomes contributes to moral condemnation of harm in moral dilemmas. Emotion, 18(7), 1009-1023.
doi: 10.1037/emo0000413 pmid: 29389202 |
| [65] | Richard, F. D., Bond, C. F., & Stokes-Zoota, J. J. (2003). One hundred years of social psychology quantitatively described. Review of General Psychology, 7(4), 331-363. |
| [66] | Rong, X., Sun, B., Huang, X., Cai, M., & Li, W. (2010). Reliabilities and validities of Chinese version of interpersonal reactivity index. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(2), 158-160. |
| [67] | Sarlo, M., Lotto, L., Rumiati, R., & Palomba, D. (2014). If it makes you feel bad, don't do it! Egoistic rather than altruistic empathy modulates neural and behavioral responses in moral dilemmas. Physiology and Behavior, 130, 127-134. |
| [68] | Shen, Y., Yuan, L., Xiong, X., & Xin, T. (2023). Empathy and cyberbystander behavior: The role of moral disengagement. Current Psychology 42(21), 18070-18079. |
| [69] | Sonnentag, T. L., Wadian, T. W., & Wolfson, M. J. (2024). The role of moral identity in the salience of the prescriptive and proscriptive systems of moral self-regulation. Ethics & Behavior, 34(6), 425-437. |
| [70] | Su, S., & Xia, L. X. (2024). Neurostructural correlates of harm action/outcome aversion: The role of empathy. Neuroimage, Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120972. |
| [71] |
Teng, Z., Nie, Q., Guo, C., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., & Bushman, B. J. (2019). A longitudinal study of link between exposure to violent video games and aggression in Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of moral disengagement. Developmental Psychology, 55(1), 184-195.
doi: 10.1037/dev0000624 pmid: 30335433 |
| [72] | Thornberg, R., Pozzoli, T., & Gini, G. (2022). Defending or remaining passive as a bystander of school bullying in Sweden: The role of moral disengagement and anti-bullying class norms. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 37(19-20), NP18666-NP18689. |
| [73] | Vaughan, E. P., Speck, J. S., Frick, P. J., Walker, T. M., Robertson, E. L., Ray, J. V., ... Cauffman, E. (2023). Proactive and reactive aggression: Developmental trajectories and longitudinal associations with callous-unemotional traits, impulsivity, and internalizing emotions. Development and Psychopathology, Advance online publication. http://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579423000317 |
| [74] | Vollberg, M. C., & Cikara, M. (2024). Affective prediction errors in persistence and escalation of aggression. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 153(6), 1551-1567. |
| [75] | Wagenmakers, E. J., Love, J., Marsman, M., Jamil, T., Ly, A., Verhagen, J., ... Morey, R. D. (2018). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II: Example applications with JASP. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(1), 58-76. |
| [76] | Wagenmakers, E. J., Marsman, M., Jamil, T., Ly, A., Verhagen, J., Love, J., ... Morey, R. D. (2018). Bayesian inference for psychology. Part I: Theoretical advantages and practical ramifications. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(1), 35-57. |
| [77] |
Wagenmakers, E. J., Wetzels, R., Borsboom, D., & van der Maas, H. L. (2011). Why psychologists must change the way they analyze their data: The case of psi: Comment on Bem (2011). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100(3), 426-432.
doi: 10.1037/a0022790 pmid: 21280965 |
| [78] | Wang, X., Lei, L., Yang, J., Gao, L., & Zhao, F. (2017). Moral disengagement as mediator and moderator of the relation between empathy and aggression among Chinese male juvenile delinquents. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 48(2), 316-326. |
| [79] | Wang, X., Wang, W., Qiao, Y., Gao, L., Yang, J., & Wang, P. (2022). Parental phubbing and adolescents' cyberbullying perpetration: A moderated mediation model of moral disengagement and online disinhibition. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 37(7-8), NP5344- NP5366. |
| [80] | Wang, X., Yang, J., & Gao, L. (2013). The Chinese version of civic moral disengament scale. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 11(6), 838-842. |
| [81] |
Wiech, K., Kahane, G., Shackel, N., Farias, M., Savulescu, J., & Tracey, I. (2013). Cold or calculating? Reduced activity in the subgenual cingulate cortex reflects decreased emotional aversion to harming in counterintuitive utilitarian judgment. Cognition, 126(3), 364-372.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.11.002 pmid: 23280149 |
| [82] | Wu, Y., & Wen, Z. (2011a). The statistical analysis procedure involving null hypothesis significance testing. Journal of Psychological Science, 34(1), 230-234. |
| [83] | Wu, Y., & Wen, Z. (2011b). Item parceling strategies in structural equation modeling. Advances in Psychological Science, 19(12), 1859-1867. |
| [84] | Xia, Y., Wehrli, J., Abivardi, A., Hostiuc, M., Kleim, B., & Bach, D. R. (2024). Attenuating human fear memory retention with minocycline: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Translational Psychiatry, 14(28), 1-8. |
| [85] | Yu, H., Siegel, J. Z., Clithero, J. A., & Crockett, M. J. (2021). How peer influence shapes value computation in moral decision-making. Cognition, 211, Article 104641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104641 |
| [86] |
Yu, H., Siegel, J. Z., & Crockett, M. J. (2019). Modeling morality in 3-D: Decision-making, judgment, and inference. Topics in Cognitive Science, 11(2), 409-432.
doi: 10.1111/tops.12382 pmid: 31042018 |
| [87] | Zapata, J., & Deroy, O. (2023). Ordinary citizens are more severe towards verbal than nonverbal hate-motivated incidents with identical consequences. Scientific Reports, 13(1), Article 7126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-33892-8 |
| [88] |
Zhao, H., & Seibert, S. E. (2006). The big five personality dimensions and entrepreneurial status: A meta-analytical review. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(2), 259-271.
pmid: 16551182 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||