

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (12): 1718-1733.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.01718
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiang1, JIA Lina2, WEI Shilin3,4, CHEN Juntao5, XIA Yaoyuan6, WANG Qin3,4,7, JIN Hua3,4,7( )
)
Published:2024-12-25
Online:2024-11-04
Contact:
JIN Hua
E-mail:jinhua@tjnu.edu.cn
LI Xiang, JIA Lina, WEI Shilin, CHEN Juntao, XIA Yaoyuan, WANG Qin, JIN Hua. (2024). Motor features of abstract verbs determine their representations in the motor system: An fMRI and EMG study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(12), 1718-1733.
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| Left precuneus, posterior cingulate gyrus | 3630 | ?3 | ?72 | 30 | 107.90 |
| Right precuneus | 12 | ?42 | 27 | 65.30 | |
| Left orbital superior frontal gyrus | 2966 | ?9 | 54 | ?3 | 39.97 |
| Left superior frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus | ?18 | 18 | 54 | 37.51 | |
| Left angular gyrus | 1570 | ?39 | ?63 | 36 | 73.17 |
| Right angular gyrus | 923 | 39 | ?66 | 39 | 35.53 |
| Right insula | 528 | 39 | 24 | ?3 | 31.21 |
| Right middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus | 448 | 63 | ?6 | ?15 | 28.47 |
| Left middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus | 347 | ?60 | ?24 | ?18 | 40.38 |
| Left fusiform gyrus | 135 | ?39 | ?90 | ?15 | 15.93 |
| Right cerebellum | 133 | 39 | ?66 | ?48 | 30.23 |
| Right supplementary motor area | 128 | 9 | 15 | 45 | 15.23 |
| Left triangular part of the inferior frontal gyrus | 72 | ?39 | 24 | 3 | 18.67 |
| Right cerebellum | 66 | 9 | ?57 | ?57 | 19.11 |
| Left postcentral gyrus, precentral gyrus | 59 | ?57 | ?6 | 45 | 17.05 |
Table 1 Peak activations of the F-test identifying brain regions activated for interaction of testing phase×word type
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| Left precuneus, posterior cingulate gyrus | 3630 | ?3 | ?72 | 30 | 107.90 |
| Right precuneus | 12 | ?42 | 27 | 65.30 | |
| Left orbital superior frontal gyrus | 2966 | ?9 | 54 | ?3 | 39.97 |
| Left superior frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus | ?18 | 18 | 54 | 37.51 | |
| Left angular gyrus | 1570 | ?39 | ?63 | 36 | 73.17 |
| Right angular gyrus | 923 | 39 | ?66 | 39 | 35.53 |
| Right insula | 528 | 39 | 24 | ?3 | 31.21 |
| Right middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus | 448 | 63 | ?6 | ?15 | 28.47 |
| Left middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus | 347 | ?60 | ?24 | ?18 | 40.38 |
| Left fusiform gyrus | 135 | ?39 | ?90 | ?15 | 15.93 |
| Right cerebellum | 133 | 39 | ?66 | ?48 | 30.23 |
| Right supplementary motor area | 128 | 9 | 15 | 45 | 15.23 |
| Left triangular part of the inferior frontal gyrus | 72 | ?39 | 24 | 3 | 18.67 |
| Right cerebellum | 66 | 9 | ?57 | ?57 | 19.11 |
| Left postcentral gyrus, precentral gyrus | 59 | ?57 | ?6 | 45 | 17.05 |
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| post- > prelearning test | |||||
| Left precuneus | 1742 | ?9 | ?69 | 24 | 12.92 |
| Left posterior cingulate gyrus | ?3 | ?36 | 27 | 9.32 | |
| Right precuneus | 6 | ?66 | 24 | 7.75 | |
| Left angular gyrus | 688 | ?36 | ?63 | 36 | 8.74 |
| Left superior frontal gyrus | 187 | ?21 | 66 | 0 | 6.57 |
| Right middle occipital gyrus | 183 | 36 | ?72 | 33 | 5.68 |
| Left precentral gyrus | 130 | ?42 | 9 | 39 | 4.56 |
| pre- > postlearning test | |||||
| left superior temporal gyrus | 215 | ?57 | ?39 | 12 | 6.15 |
Table 2 Peak activations of pre- vs. postlearning test for learning novel words at the whole brain level
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| post- > prelearning test | |||||
| Left precuneus | 1742 | ?9 | ?69 | 24 | 12.92 |
| Left posterior cingulate gyrus | ?3 | ?36 | 27 | 9.32 | |
| Right precuneus | 6 | ?66 | 24 | 7.75 | |
| Left angular gyrus | 688 | ?36 | ?63 | 36 | 8.74 |
| Left superior frontal gyrus | 187 | ?21 | 66 | 0 | 6.57 |
| Right middle occipital gyrus | 183 | 36 | ?72 | 33 | 5.68 |
| Left precentral gyrus | 130 | ?42 | 9 | 39 | 4.56 |
| pre- > postlearning test | |||||
| left superior temporal gyrus | 215 | ?57 | ?39 | 12 | 6.15 |
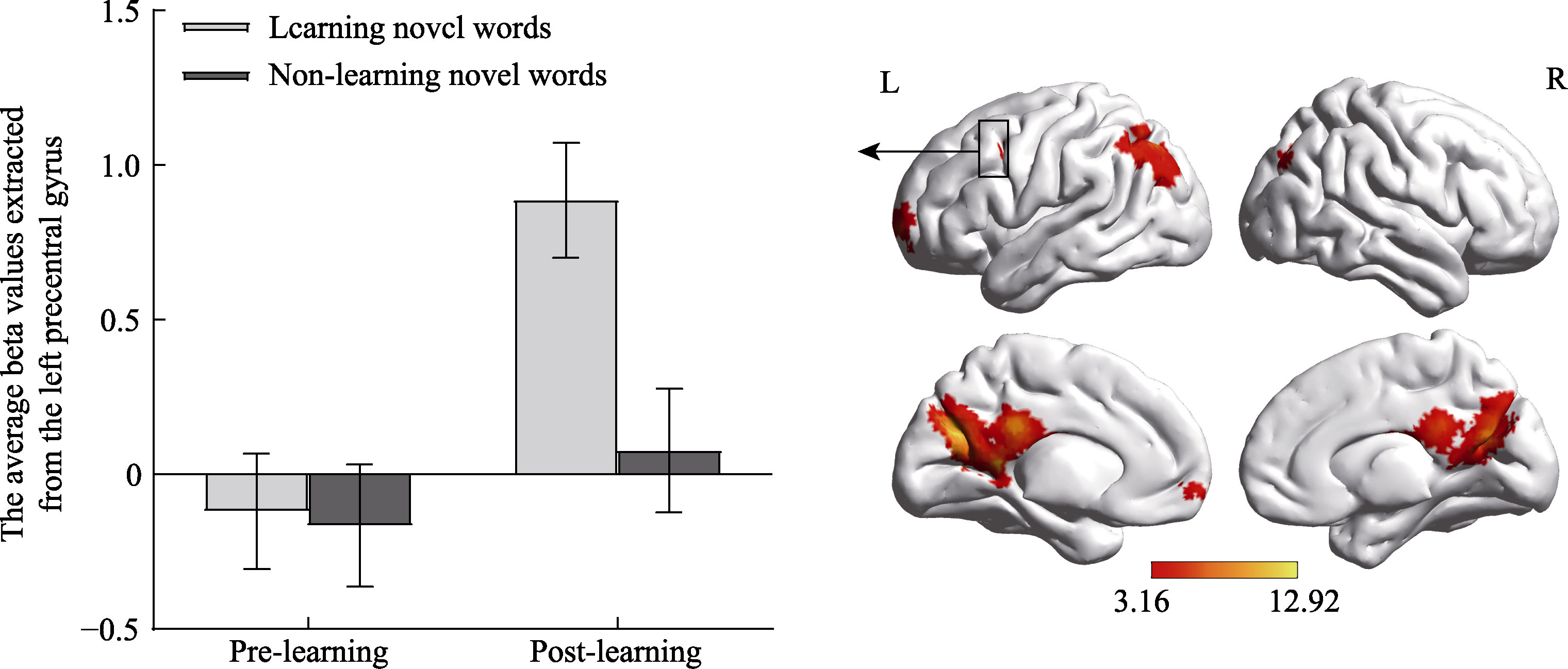
Figure 3. Significant activation of pre- vs. postlearning test for learning novel words at the whole brain level (right) and the average beta values extracted from the left precentral gyrus under each condition (left, error bars represent M ± SEM).
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| post- > prelearning test | |||||
| none | |||||
| pre-> postlearning test | |||||
| Right middle temporal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus | 1690 | 60 | ?9 | ?15 | 6.23 |
| Left inferior parietal lobule | 1220 | ?60 | ?42 | 39 | 5.75 |
| Right medial superior frontal gyrus | 611 | 12 | 48 | 36 | 6.77 |
Table 3 Peak activations of pre- vs. postlearning test for non-learning novel words at the whole brain level
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| post- > prelearning test | |||||
| none | |||||
| pre-> postlearning test | |||||
| Right middle temporal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus | 1690 | 60 | ?9 | ?15 | 6.23 |
| Left inferior parietal lobule | 1220 | ?60 | ?42 | 39 | 5.75 |
| Right medial superior frontal gyrus | 611 | 12 | 48 | 36 | 6.77 |
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| high > low motor feature abstract verbs | |||||
| Left inferior occipital gyrus | 454 | ?33 | ?87 | ?9 | 7.01 |
| Right fusiform gyrus | 223 | 27 | ?87 | ?3 | 6.49 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 22 | 42 | ?15 | 42 | 4.17 |
| Left precentral gyrus | 12 | ?51 | ?6 | 45 | 4.09 |
| Left postcentral gyrus | 10 | ?42 | ?27 | 60 | 4.70 |
| low > high motor feature abstract verbs | |||||
| none | |||||
Table 4 Peak activations of hign vs. low motor feature abstract verbs at the whole brain level
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| high > low motor feature abstract verbs | |||||
| Left inferior occipital gyrus | 454 | ?33 | ?87 | ?9 | 7.01 |
| Right fusiform gyrus | 223 | 27 | ?87 | ?3 | 6.49 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 22 | 42 | ?15 | 42 | 4.17 |
| Left precentral gyrus | 12 | ?51 | ?6 | 45 | 4.09 |
| Left postcentral gyrus | 10 | ?42 | ?27 | 60 | 4.70 |
| low > high motor feature abstract verbs | |||||
| none | |||||
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| Left posterior cingulate gyrus | 22536 | ?3 | ?36 | 27 | 14.20 |
| Left precuneus, cuneus cortex | ?6 | ?45 | 6 | 12.06 | |
| Left inferior parietal lobule, angular gyrus | ?36 | ?69 | 42 | 11.49 | |
| Right middle occipital gyrus, angular gyrus | 36 | ?69 | 39 | 10.37 | |
| Left superior frontal gyrus, orbital superior frontal gyrus | ?12 | 72 | ?3 | 8.87 | |
| Left precentral gyrus | ?36 | 6 | 47 | 6.50 | |
| Right precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus | 154 | 60 | 3 | 21 | 3.88 |
Table 5 Peak activations of the parametric modulation analysis
| Region | Cluster size | MNI | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| Left posterior cingulate gyrus | 22536 | ?3 | ?36 | 27 | 14.20 |
| Left precuneus, cuneus cortex | ?6 | ?45 | 6 | 12.06 | |
| Left inferior parietal lobule, angular gyrus | ?36 | ?69 | 42 | 11.49 | |
| Right middle occipital gyrus, angular gyrus | 36 | ?69 | 39 | 10.37 | |
| Left superior frontal gyrus, orbital superior frontal gyrus | ?12 | 72 | ?3 | 8.87 | |
| Left precentral gyrus | ?36 | 6 | 47 | 6.50 | |
| Right precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus | 154 | 60 | 3 | 21 | 3.88 |
| [1] |
Barsalou, L. W. (2008). Grounded cognition. Annual Review of Psychology, 59, 617-645.
pmid: 17705682 |
| [2] |
Barsalou, L. W., Simmons, W. K., Barbey, A. K., & Wilson, C. D. (2003). Grounding conceptual knowledge in modality-specific systems. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(2), 84-91.
pmid: 12584027 |
| [3] | Binder, J. R., Desai, R. H., Graves, W. W., & Conant, L. L. (2009). Where is the semantic system? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cerebral Cortex, 19(12), 2767-2796. |
| [4] | Bird, H., Franklin, S., & Howard, D. (2001). Age of acquisition and imageability ratings for a large set of words, including verbs and function words. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 33(1), 73-79. |
| [5] |
Bonner, M. F., Peelle, J. E., Cook, P. A., & Grossman, M. (2013). Heteromodal conceptual processing in the angular gyrus. NeuroImage, 71, 175-186.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.006 pmid: 23333416 |
| [6] | Borghi, A. M., & Binkofski, F. (2014). Words as social tools: An embodied view on abstract concepts. Berlin, Germany: Springer. |
| [7] |
Borghi, A. M., Binkofski, F., Castelfranchi, C., Cimatti, F., Scorolli, C., & Tummolini, L. (2017). The challenge of abstract concepts. Psychological Bulletin, 143(3), 263-292.
doi: 10.1037/bul0000089 pmid: 28095000 |
| [8] | Bucur, M., & Papagno, C. (2021). An ALE meta-analytical review of the neural correlates of abstract and concrete words. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 15727. |
| [9] | Cai, Q., & Brysbaert, M. (2010). SUBTLEX-CH: Chinese word and character frequencies based on film subtitles. PloS ONE, 5(6), e10729. |
| [10] |
Clark, D., & Wagner, A. D. (2003). Assembling and encoding word representations: fMRI subsequent memory effects implicate a role for phonological control. Neuropsychologia, 41(3), 304-317.
pmid: 12457756 |
| [11] |
Courson, M., Macoir, J., & Tremblay, P. (2018). A facilitating role for the primary motor cortex in action sentence processing. Behavioural Brain Research, 336, 244-249.
doi: S0166-4328(17)31066-5 pmid: 28899820 |
| [12] |
Davis, M. H., Di Betta, A. M., Macdonald, M. J., & Gaskell, M. G. (2009). Learning and consolidation of novel spoken words. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(4), 803-820.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21059 pmid: 18578598 |
| [13] | Del Maschio, N., Fedeli, D., Garofalo, G., & Buccino, G. (2021). Evidence for the concreteness of abstract language: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Brain Sciences, 12(1), 32. |
| [14] | Desai, R. H., Reilly, M., & van Dam, W. (2018). The multifaceted abstract brain. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 373(1752), 20170122. |
| [15] |
Dreyer, F. R., & Pulvermüller, F. (2018). Abstract semantics in the motor system?-An event-related fMRI study on passive reading of semantic word categories carrying abstract emotional and mental meaning. Cortex, 100, 52-70.
doi: S0010-9452(17)30369-6 pmid: 29455946 |
| [16] | Fernandino, L., Tong, J. Q., Conant, L. L., Humphries, C. J., & Binder, J. R. (2022). Decoding the information structure underlying the neural representation of concepts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(6), e2108091119. |
| [17] |
Foroni, F., & Semin, G. R. (2009). Language that puts you in touch with your bodily feelings: The multimodal responsiveness of affective expressions. Psychological Science, 20(8), 974-980.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02400.x pmid: 19594858 |
| [18] | Fukuda, T. Y., Echeimberg, J. O., Pompéu, J. E., Lucareli, P. R. G., Garbelotti, S., Gimenes, R. O., & Apolinário, A. (2010). Root mean square value of the electromyographic signal in the isometric torque of the quadriceps, hamstrings and brachial biceps muscles in female subjects. The Journal of Applied Research, 10(1), 32-39. |
| [19] | Gallese, V., & Lakoff, G. (2005). The brain's concepts: The role of the sensory-motor system in conceptual knowledge. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 22(3-4), 455-479. |
| [20] | Gálvez-García, G., Aldunate, N., Bascour-Sandoval, C., Martínez-Molina, A., Peña, J., & Barramuño, M. (2020). Muscle activation in semantic processing: An electromyography approach. Biological Psychology, 152, 107881. |
| [21] | Glenberg, A. M., & Kaschak, M. P. (2002). Grounding language in action. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(3), 558-565. |
| [22] | Granito, C., Scorolli, C., & Borghi, A. M. (2015). Naming a lego world. The role of language in the acquisition of abstract concepts. PloS ONE, 10(1), e0114615. |
| [23] | Günther, F., Dudschig, C., & Kaup, B. (2018). Symbol grounding without direct experience: Do words inherit sensorimotor activation from purely linguistic context?. Cognitive Science, 42 (Suppl 2), 336-374. |
| [24] |
Harpaintner, M., Sim, E. J., Trumpp, N. M., Ulrich, M., & Kiefer, M. (2020). The grounding of abstract concepts in the motor and visual system: An fMRI study. Cortex, 124, 1-22.
doi: S0010-9452(19)30368-5 pmid: 31821905 |
| [25] |
Hauk, O., Johnsrude, I., & Pulvermüller, F. (2004). Somatotopic representation of action words in human motor and premotor cortex. Neuron, 41(2), 301-307.
doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00838-9 pmid: 14741110 |
| [26] |
Innocenti, A., De Stefani, E., Sestito, M., & Gentilucci, M. (2014). Understanding of action-related and abstract verbs in comparison: A behavioral and TMS study. Cognitive Processing, 15(1), 85-92.
doi: 10.1007/s10339-013-0583-z pmid: 24113915 |
| [27] | Jin, H., & Li, X. (2022). The embodied representation of abstract verbs: The effect of motor features. Journal of Psychological Science, 45, 614-619. |
| [28] | Kaschak, M. P., & Madden, J. (2021). Embodiment in the lab:Theory, measurement, and reproducibility. In Robinson, M. D., & Thomas, L. E, (Eds.), Handbook of embodied psychology: Thinking, feeling, and acting (pp: 619-635). Switzerland: Springer. |
| [29] | Kemmerer, D. (2015). Are the motor features of verb meanings represented in the precentral motor cortices? Yes, but within the context of a flexible, multilevel architecture for conceptual knowledge. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(4), 1068-1075. |
| [30] | Khatin-Zadeh, O., Farsani, D., Hu, J., Eskandari, Z., Zhu, Y., & Banaruee, H. (2023). A review of studies supporting metaphorical embodiment. Behavioral Sciences, 13(7), 585. |
| [31] | Kiefer, M., & Harpaintner, M. (2020). Varieties of abstract concepts and their grounding in perception or action. Open Psychology, 2(1), 119-137. |
| [32] | Kiefer, M., Pielke, L., & Trumpp, N. M. (2022). Differential temporo-spatial pattern of electrical brain activity during the processing of abstract concepts related to mental states and verbal associations. NeuroImage, 252, 119036. |
| [33] |
Kiefer, M., & Pulvermüller, F. (2012). Conceptual representations in mind and brain: Theoretical developments, current evidence and future directions. Cortex, 48(7), 805-825.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2011.04.006 pmid: 21621764 |
| [34] |
Klepp, A., Weissler, H., Niccolai, V., Terhalle, A., Geisler, H., Schnitzler, A., & Biermann-Ruben, K. (2014). Neuromagnetic hand and foot motor sources recruited during action verb processing. Brain and Language, 128(1), 41-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2013.12.001 pmid: 24412808 |
| [35] | Li, M. Y., Xu, Y. W., Luo, X. Q., Zeng, J. H., & Han, Z. Z. (2020). Linguistic experience acquisition for novel stimuli selectively activates the neural network of the visual word form area. NeuroImage, 215, 116838. |
| [36] | Li, X., Luo, D., Wang, C., Xia, Y. Y., & Jin, H. (2022). Motor features of abstract verbs determine their representations in the motor system. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 957426. |
| [37] | Morey, R. D., Kaschak, M. P., Díez-Álamo, A. M., Glenberg, A. M., Zwaan, R. A., Lakens, D.,... Ziv-Crispel, N. (2021). A pre-registered, multi-lab non-replication of the action-sentence compatibility effect (ACE). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. 29(2), 613-626. |
| [38] | Moseley, R., Carota, F., Hauk, O., Mohr, B., & Pulvermüller, F. (2012). A role for the motor system in binding abstract emotional meaning. Cerebral Cortex, 22(7), 1634-1647. |
| [39] |
Newman, S. D., & Twieg, D. (2001). Differences in auditory processing of words and pseudowords: An fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 14(1), 39-47.
pmid: 11500989 |
| [40] |
Ostarek, M., & Huettig, F. (2019). Six challenges for embodiment research. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 28(6), 593-599.
doi: 10.1177/0963721419866441 |
| [41] | Öttl, B., Dudschig, C., & Kaup, B. (2017). Forming associations between language and sensorimotor traces during novel word learning. Language and Cognition, 9(1), 156-171. |
| [42] |
Popp, M., Trumpp, N. M., Sim, E. J., & Kiefer, M. (2019). Brain activation during conceptual processing of action and sound verbs. Advances in Cognitive Psychology, 15(4), 236-255.
doi: 10.5709/acp-0272-4 pmid: 32494311 |
| [43] | Qu, F. B., Yin, R., Zhong, Y., Ye, H. S. (2012). Motor perception in language comprehension: Perspective from embodied cognition. Advances in Psychological Science, 20(6), 834-842. |
| [44] |
Raposo, A., Moss, H. E., Stamatakis, E. A., & Tyler, L. K. (2009). Modulation of motor and premotor cortices by actions, action words and action sentences. Neuropsychologia, 47(2), 388-396.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.09.017 pmid: 18930749 |
| [45] |
Repetto, C., Colombo, B., Cipresso, P., & Riva, G. (2013). The effects of rTMS over the primary motor cortex: The link between action and language. Neuropsychologia, 51(1), 8-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.11.001 pmid: 23142706 |
| [46] | Repetto, C., Mathias, B., Weichselbaum, O., & Macedonia, M. (2021). Visual recognition of words learned with gestures induces motor resonance in the forearm muscles. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 17278. |
| [47] |
Rodríguez-Ferreiro, J., Gennari, S. P., Davies, R., & Cuetos, F. (2011). Neural correlates of abstract verb processing. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(1), 106-118.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2010.21414 pmid: 20044889 |
| [48] | San Miguel Abella, R. A., & González-Nosti, M. (2019). Motor content norms for 4, 565 verbs in Spanish. Behavior Research Methods, 52(2), 447-454. |
| [49] | Sui, X., & Zhang, X. L. (2012). Review about the research of recognition of Chinese 2-character words. Journal of Liaoning Normal University (Social Science Edition), 35(6), 768-771. |
| [50] | Tan, L. H., & Perfetti, C. A. (1999). Phonological activation in visual identification of Chinese two-character words. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory & Cognition, 25(2), 382-393. |
| [51] |
Tomasino, B., & Gremese, M. (2016). The cognitive side of M1. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 298.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00298 pmid: 27378891 |
| [52] |
Tomasino, B., Nobile, M., Re, M., Bellina, M., Garzitto, M., Arrigoni, F.,... Brambilla, P. (2018). The mental simulation of state/psychological verbs in the adolescent brain: An fMRI study. Brain and Cognition, 123, 34-46.
doi: S0278-2626(17)30437-2 pmid: 29505944 |
| [53] |
Villani, C., Lugli, L., Liuzza, M. T., & Borghi, A. M. (2019). Varieties of abstract concepts and their multiple dimensions. Language and Cognition, 11(3), 403-430.
doi: 10.1017/langcog.2019.23 |
| [54] | Wang, J., Conder, J. A., Blitzer, D. N., & Shinkareva, S. V. (2010). Neural representation of abstract and concrete concepts: A meta- analysis of neuroimaging studies. Human Brain Mapping, 31(10), 1459-1468. |
| [55] | Wang, J. Y., Ye, H. S., & Su, D. Q. (2018). The correlativity of action and sematic processing: Perspect of embodied metaphor. Psychological Exploration, 38(1), 15-19. |
| [56] | Wenderoth, N., Debaere, F., Sunaert, S., & Swinnen, S. P. (2005). The role of anterior cingulate cortex and precuneus in the coordination of motor behaviour. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 22(1), 235-246. |
| [57] | Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339-351. |
| [58] | Yu, X., Law, S. P., Han, Z. Z., Zhu, C. Z., & Bi, Y. C. (2011). Dissociative neural correlates of semantic processing of nouns and verbs in Chinese-A language with minimal inflectional morphology. NeuroImage, 58(3), 912922. |
| [59] |
Zhang, K., & Du, X. M. (2024). Creative thinking from the perspective of embodied cognition. Advances in Psychological Science, 32(7), 1126-1137.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2024.01126 |
| [60] | Zheng, X. L., Xu, R., Hou, W. S., Wu, X. Y., & Ma, L. (2009). Effect of handgrip force on the activation level of forearm muscles. Chinese Journal of Ergonomics, 15(4), 14-17. |
| [61] | Zwaan, R. A. (2021). Two challenges to "embodied cognition" research and how to overcome them. Journal of Cognition, 4(1), 14. |
| [1] | JIN Hua, JIA Lina, YIN Xiaojuan, YAN Shizhen, WEI Shilin, CHEN Juntao. The neural basis of the continued influence effect of misinformation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(4): 343-354. |
| [2] | GAO Zhihua,LU Zhongyi. Why “no” implies “negative emotion”? Emotional representation in negation processing [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(2): 177-187. |
| [3] | LI Xiaodan; DU Jianzheng; YE Haosheng. Bidirectionality metaphorical effect of Chinese ritual culture: Contractive postures make people humble [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(6): 746-756. |
| [4] | YE Haosheng. The significances of mirror neurons [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(4): 444-456. |
| [5] | YANG Huilan, HE Xiayou, ZHAO Xueru, ZHANG Wei. Multiple Metaphorical Representations of Power: Evidence from Size and Color [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(7): 939-949. |
| [6] | YE Haosheng. Theoretical Analysis of the Meaning of Embodiment [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2014, 46(7): 1032-1042. |
| [7] | Liu Mingzhe,Dong Dekang,Li Xiang,Sun Bo,Tsinghua University,Zhang Shao Ying Division Of Biomedical Engineering Departmemt Of Electrical Engineering 100084 Beijing, P. R. of China National Shooting Field. DIGITAL EMG DISPLAY INSTRUMENT AND APPLICATION IN SPORT AREA [J]. , 1992, 24(01): 98-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||