

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 629-638.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00629
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Jie1,2( ), WU Ke1,2, SHI Yupeng1,2(
), WU Ke1,2, SHI Yupeng1,2( ), AI Xiaoqing3
), AI Xiaoqing3
Received:2020-11-02
Published:2021-06-25
Online:2021-05-12
Supported by:CHEN Jie, WU Ke, SHI Yupeng, AI Xiaoqing. (2021). The relationship between dispositional self-construal and empathy for ingroup and outgroup members’ pain: evidence from ERPs. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(6), 629-638.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00629
| Stimulus type | Accuracy (%) | Reaction Time (MS) |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 88.33 ± 3.55 | 555.82 ± 13.96 |
| Outgroup | 88.89 ± 3.26 | 565.02 ± 9.74 |
| Non-pain | ||
| Intragroup | 93.15 ± 1.87 | 578.20 ± 8.20 |
| Outgroup | 93.15 ± 1.86 | 575.00 ± 8.12 |
Table 1 The reaction time and accuracy under different conditions (M ± SE)
| Stimulus type | Accuracy (%) | Reaction Time (MS) |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 88.33 ± 3.55 | 555.82 ± 13.96 |
| Outgroup | 88.89 ± 3.26 | 565.02 ± 9.74 |
| Non-pain | ||
| Intragroup | 93.15 ± 1.87 | 578.20 ± 8.20 |
| Outgroup | 93.15 ± 1.86 | 575.00 ± 8.12 |
| Stimulus type | Pain Intensity | Self-unpleasantness |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 3.18 ± 1.13 | 3.23 ± 1.23 |
| Outgroup | 3.15 ± 1.14 | 3.23 ± 1.32 |
| No Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 1.65 ± 0.62 | 1.55 ± 0.58 |
| Outgroup | 1.59 ± 0.55 | 1.51 ± 0.54 |
Table 2 Rating scores of pain intensity and self-unpleasantness (M ± SE)
| Stimulus type | Pain Intensity | Self-unpleasantness |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 3.18 ± 1.13 | 3.23 ± 1.23 |
| Outgroup | 3.15 ± 1.14 | 3.23 ± 1.32 |
| No Pain | ||
| Intragroup | 1.65 ± 0.62 | 1.55 ± 0.58 |
| Outgroup | 1.59 ± 0.55 | 1.51 ± 0.54 |
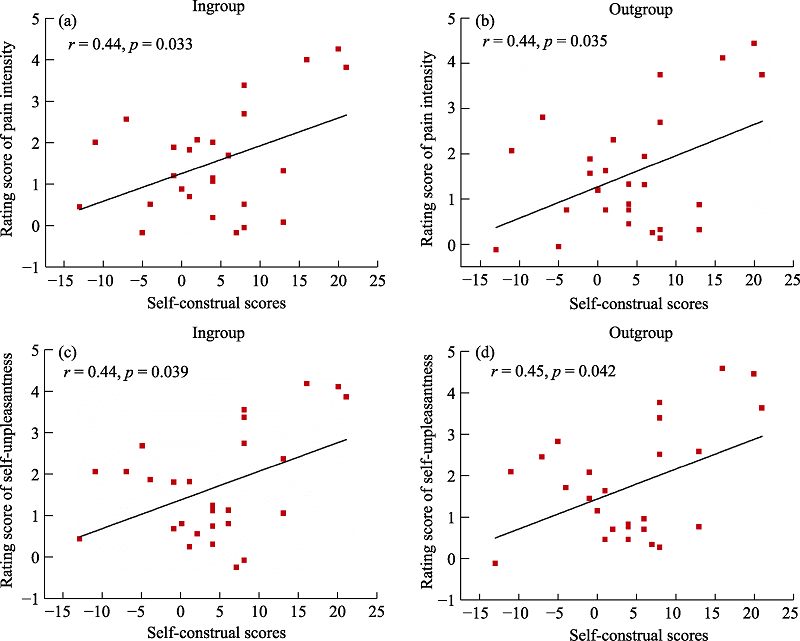
Figure 2. (a-b) scatter plot with correlation analysis between self-construal scores and rating score of pain intensity under ingroup and outgroup priming conditions; (c-d) scatter plot with correlation analysis between self-construal scores and rating score of unpleasantness under ingroup and outgroup priming conditions.
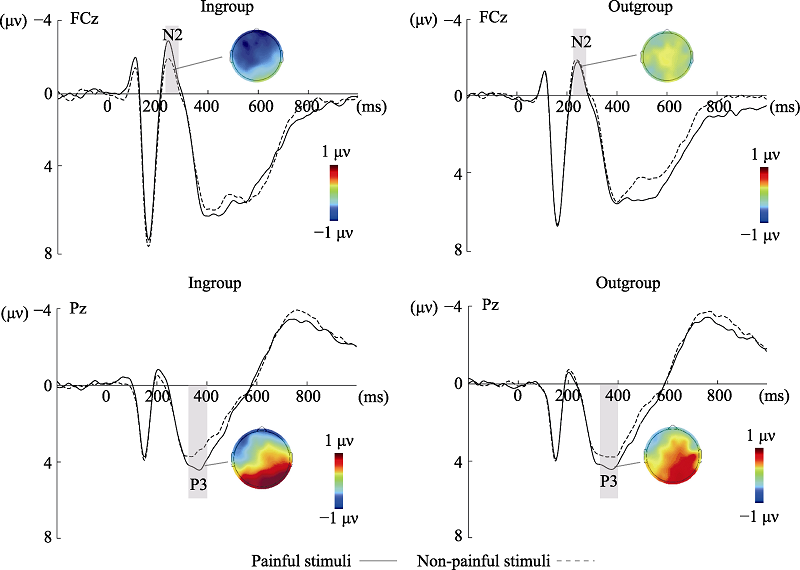
Figure 3. Averaged ERPs at FCz and Pz to painful (solid line) and non-painful (dotted line) stimuli and topographical maps of voltage amplitudes for painful minus non-painful stimuli difference at the N2 and P3 components.
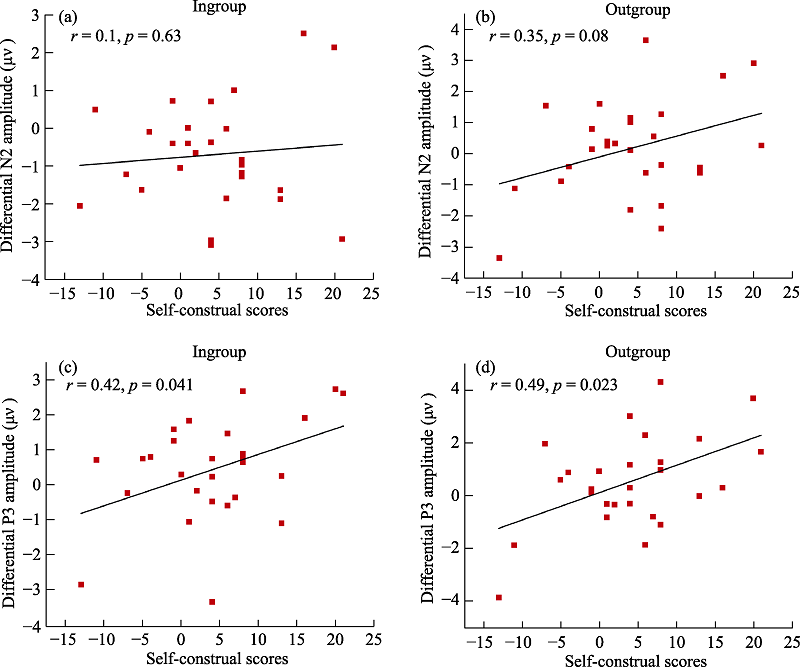
Figure 4. (a-b) scatter plot with correlation analysis between self-construal scores and differential N2 amplitude (painful minus non-painful stimuli); (c-d) scatter plot with correlation analysis between self-construal scores and differential P3 amplitude (painful minus non-painful stimuli).
| [1] |
Azevedo R. T., Macaluso E., Avenanti A., Santangelo V., Cazzato V., & Aglioti S. M. (2012). Their pain is not our pain: Brain and autonomic correlates of empathic resonance with the pain of same and different race individuals. Human Brain Mapping, 34(12), 3168-3181.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.v34.12 URL |
| [2] |
Chen J., Chang B., Li W., Shi Y., Shen H., Wang R., & Liu L. (2020). Dispositional self-construal modulates the empathy for others’ pain: An ERP study. Frontiers in Psychology, 11,508141.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.508141 URL |
| [3] |
Chen J., Yuan P., Cai Y., Liu C., & Li W. (2020). Dispositional self-construal modulates neural representation of self: An ERP study. Frontiers in Psychology, 11,895.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00895 pmid: 32528355 |
| [4] |
Cheng J., Jiao C., Luo Y., & Cui F. (2017). Music induced happy mood suppresses the neural responses to otherʼs pain: Evidences from an ERP study. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 13054.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13386-0 URL |
| [5] |
Cheng J., Luo Y., & Cui F. (2017). Empathy for pain influenced by cognitive load: Evidence from an ERP study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49(5), 622-630.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00622 URL |
| [6] |
Chiao J. Y., Harada T., Komeda H., Li Z., Mano Y., Saito D. N., .. Iidaka T. (2009). Neural basis of individualistic and collectivistic views of self. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2813-2820.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.20707 pmid: 19107754 |
| [7] |
Cosmides L., Tooby J., & Kurzban R. (2003). Perceptions of race. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(4), 173-179.
pmid: 12691766 |
| [8] |
Cross S. E., Hardin E. E., & Gercek-Swing B. (2011). The what, how, why, and where of self-construal. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 15(2), 142-179.
doi: 10.1177/1088868310373752 URL |
| [9] |
Cui F., Ma N., & Luo Y. (2016). Moral judgment modulates neural responses to the perception of other’s pain: An ERP study. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 20851.
doi: 10.1038/srep20851 URL |
| [10] |
Decety, J. (2009). Empathy, sympathy and the perception of pain. Pain, 145(3), 365-366.
doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.006 pmid: 19716658 |
| [11] | Decety, J., & Jackson, P. L. (2004). The functional architecture of human empathy. Behavioral & Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 3(2), 71-100. |
| [12] |
Decety J., Yang C., & Cheng Y. (2010). Physicians down-regulate their pain empathy response: An event-related brain potential study. Neuroimage, 50(4), 1676-1682.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.025 pmid: 20080194 |
| [13] |
Diedenhofen B., & Musch J. (2015). cocor: A comprehensive solution for the statistical comparison of correlations. Plos One, 10(4), e0121945.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121945 URL |
| [14] |
Fan Y., & Han S. (2008). Temporal dynamic of neural mechanisms involved in empathy for pain: An event-related brain potential study. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 160-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.07.023 URL |
| [15] |
Feng C., Li Z., Feng X., Wang L., Tian T., & Luo Y. (2016). Social hierarchy modulates neural responses of empathy for pain. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(3), 485-495.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv135 URL |
| [16] |
Han S., Fan Y., & Mao L. (2008). Gender difference in empathy for pain: An electrophysiological investigation. Brain Research, 1196,85-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.12.062 URL |
| [17] | Huang R., Liu M., Yao S., & John, R. Z. A. (2009). The self-construal scale: An examination of its reliability and validity among Chinese university students. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 17(3), 306-308. |
| [18] |
Ito T. A., Larsen J. T., Smith N. K., & Cacioppo J. T. (1998). Negative information weighs more heavily on the brain: The negativity bias in evaluative categorizations. Journal of personality and social psychology, 75(4), 887-900.
pmid: 9825526 |
| [19] |
Ito, T. A., & Urland, G. R. (2003). Race and gender on the brain: Electrocortical measures of attention to the race and gender of multiply categorizable individuals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85(4), 616-626.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.85.4.616 URL |
| [20] |
Jackson P. L., Brunet E., Meltzoff A. N., & Decety J. (2006). Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain. Neuropsychologia, 44(5), 752-761.
pmid: 16140345 |
| [21] |
Jiang C., Varnum M. E. W., Hou Y., & Han S. (2014). Distinct effects of self-construal priming on empathic neural responses in Chinese and Westerners. Social Neuroscience, 9(2), 130-138.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2013.867899 pmid: 24341541 |
| [22] |
Kitayama S., Yanagisawa K., Ito A., Ueda R., Uchida Y., & Abe N. (2017). Reduced orbitofrontal cortical volume is associated with interdependent self-construal. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(30), 7969-7974.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704831114 pmid: 28701382 |
| [23] | Li S. (2011). The neural mechanism of the own-group bias and the effect of group size . (Unpublished master’s thesis) Southwest University, China. |
| [24] |
Li W., & Han S. (2010). Perspective taking modulates event-related potentials to perceived pain. Neuroscience Letters, 469(3), 328-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.12.021 URL |
| [25] |
Lin Z., & Han S. (2009). Self-construal priming modulates the scope of visual attention. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62(4), 802-813.
doi: 10.1080/17470210802271650 URL |
| [26] |
Markus,H. R., & Kitayama S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98(2), 224-253.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.98.2.224 URL |
| [27] |
Mathur V. A., Harada T., Lipke T., & Chiao J. Y. (2010). Neural basis of extraordinary empathy and altruistic motivation. Neuroimage, 51(4), 1468-1475.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.025 pmid: 20302945 |
| [28] |
Polich J. (2007). Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(10), 2128-2148.
pmid: 17573239 |
| [29] | Sessa P., Meconi F., Castelli L., & Dell’Acqua R. (2014). Taking one’s time in feeling other-race pain: An event-related potential investigation on the time-course of cross-racial empathy. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 9(4), 454-463. |
| [30] |
Sheng F., Du N., & Han S. (2016). Degraded perceptual and affective processing of racial out-groups: An electrophysiological approach. Social Neuroscience, 12(4), 479-487.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2016.1182944 URL |
| [31] |
Sheng F., & Han S. (2012). Manipulations of cognitive strategies and intergroup relationships reduce the racial bias in empathic neural responses. Neuroimage, 61(4), 786-797.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.028 pmid: 22542636 |
| [32] | Singelis, T. M. (1994). The measurement of independent and interdependent self-construals. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 20(5), 580-591. |
| [33] |
Singer T., Seymour B., O’Doherty J. P., Stephan K. E., Dolan R. J., & Frith C. D. (2006). Empathic neural responses are modulated by the perceived fairness of others. Nature, 439(7075), 466-469.
pmid: 16421576 |
| [34] |
Song J., Guo F., Zhang Z., Yuan S., Jin H., & Wang Y. (2016). Interpersonal distance influences on pain empathy: Friends priming effect. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(7), 833-844.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00833 URL |
| [35] |
Sui J., &Han S. (2007). Self-construal priming modulates neural substrates of self-awareness. Psychological Science, 18(10), 861-866.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01992.x URL |
| [36] | Sui J., Hong Y., Liu C. H., Humphreys G. W., & Han S. (2013). Dynamic cultural modulation of neural responses to oneʼs own and friendʼs faces. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 8(3), 326-332. |
| [37] |
Suzuki Y., Galli L., Ikeda A., Itakura S., & Kitazaki M. (2015). Measuring empathy for human and robot hand pain using electroencephalography. Scientific Reports, 5,15924.
doi: 10.1038/srep15924 URL |
| [38] | Wang C. (2014). Influences of self-construal priming on pain processing and empathy for pain (Unpublished doctor’s thesis). , Peking University, China. |
| [39] |
Wang C., Ma Y., & Han S. (2014). Self-construal priming modulates pain perception: Event-related potential evidence. Cognitive Neuroscience, 5(1), 3-9.
doi: 10.1080/17588928.2013.797388 URL |
| [40] | Wang C., Wu B., Liu Y., Wu X., & Han S. (2015). Challenging emotional prejudice by changing self-concept: Priming independent self-construal reduces racial in-group bias in neural responses to otherʼs pain. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 10(9), 1195-1201. |
| [41] |
Xu X., Zuo X., Wang X., & Han S. (2009). Do you feel my pain? Racial group membership modulates empathic neural responses. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(26), 8525-8529.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2418-09.2009 URL |
| [42] |
Zhu Y., Zhang L., Fan J., & Han S. (2007). Neural basis of cultural influence on self-representation. Neuroimage, 34(3), 1310-1316.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.047 URL |
| [1] | LI Jianhua, XIE Jiajia, ZHUANG Jin-Ying. An effect of menstrual cycle phase on episodic memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(5): 466-480. |
| [2] | YUE Tong, HUANG Xiting, YUE Caizhen, XUE Liming, FU Anguo. Influence of an individual’s own gains and losses on the evaluation of friends’ gambling results: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(6): 651-666. |
| [3] | DENG Xiaohong, LI Ting, XUE Chao, J. Peter ROSENFELD, LU Yang, WANG Ying, ZHAN Xiaofei, YAN Gejun, OUYANG Dan. The Complex Trial Protocol based on self-referential encoding: Discriminating the guilty from the knowledgeable innocent [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(10): 1105-1119. |
| [4] | LUO Yu, NIAN Jingqing, BAO Wei, ZHANG Jingjing, ZHAO Shouying, PAN Yun, XU Shuang, ZHANG Yu. Acute psychological stress impairs attention disengagement toward threat-related stimuli [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(1): 26-37. |
| [5] | LI Shouxin, CHE Xiaowei, LI Yanjiao, WANG Li, CHEN Kaisheng. The effects of capacity load and resolution load on visual selective attention during visual working memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(5): 527-542. |
| [6] | FU Chao, ZHANG Zhen, HE Jinzhou, HUANG Silin, QIU Jianyin, WANG Yiwen. Brain dynamics of decision-making in the generalized trust game: Evidence from ERPs and EEG time-frequency analysis [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(3): 317-326. |
| [7] | TIAN Lumei, YUAN Jingchi, LI Yongmei. Effects of peer presence and self-esteem on adolescent risk-taking behavior: Evidence from an ERP study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(1): 47-57. |
| [8] | WANG Yiwen, FU Chao, REN Xiangfeng, LIN Yuzhong, GUO Fengbo. Narcissistic personality modulates outcome evaluation in the trust game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1080-1088. |
| [9] | FU Yilei, LUO Yuejia, CUI Fang. Consistency of choice modulates outcome evaluation: Evidence from ERP studies [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(8): 1089-1099. |
| [10] | CHENG Jiaping; LUO Yuejia; CUI Fang. Empathy for pain influenced by cognitive load: Evidence from an ERP study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(5): 622-630. |
| [11] | FAN Wei, ZHONG Yiping, YANG Zilu, LI Jin, OUYANG Yi. The degree of self-reference effect of extroversion individuals [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(8): 1002-1012. |
| [12] | HU Yanmei, ZHANG Ming. Electrophysiological evidence for memory-based attentional capture and memory-based attentional rejection effects [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(1): 12-21. |
| [13] | WANG Yiwen, ZHANG Zhen, YUAN Sheng, GUO Fengbo, HE Shaoying, JING Yiming. The Decision-making and Outcome Evaluation during a Repeated Trust Game [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(8): 1028-1038. |
| [14] | GAO Xuemei, WENG Lei, ZHOU Qun, ZHAO Cai, LI Fang. Dose Violent Offenders Have Lower Capacity of Empathy for Pain: Evidence from ERPs [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(4): 478-487. |
| [15] | YANG Yaping, XU Qiang, ZHANG Lin, DENG Peizhuang, LIANG Ningjian. Scenes Differing in Spatial Frequencies Affect Facial Expression Processing: Evidence from ERP [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(12): 1433-1444. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||